Limitations of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Observations in Capturing the Diurnal Variability of Tropospheric NO2: A Case Study Using TROPOMI, GOME-2C, and Pandora Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Data
2.2.1. TROPOMI Tropospheric NO2 Data
2.2.2. GOME-2C Tropospheric NO2 Data
2.2.3. Ground-Based Pandora Data
2.3. Methods
3. Results
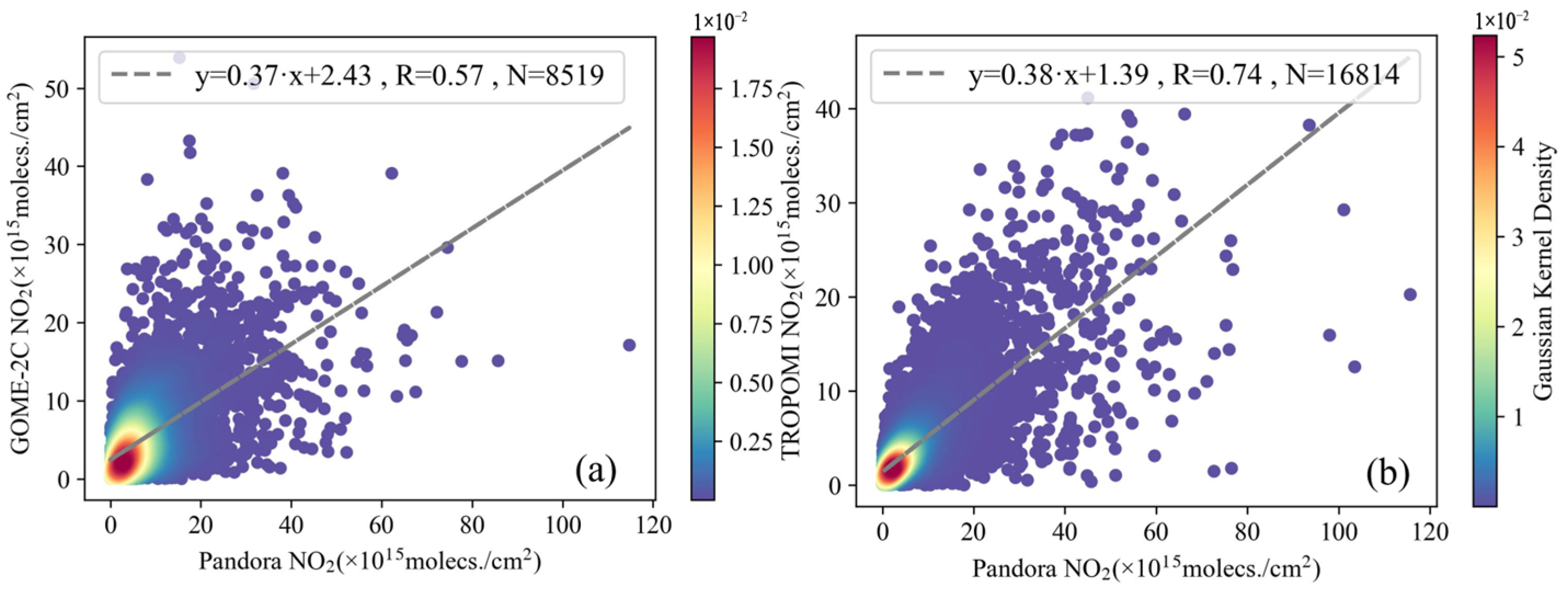
3.1. Validations Between Satellite Products and Pandora Datasets
3.1.1. Satellite Products Assessment
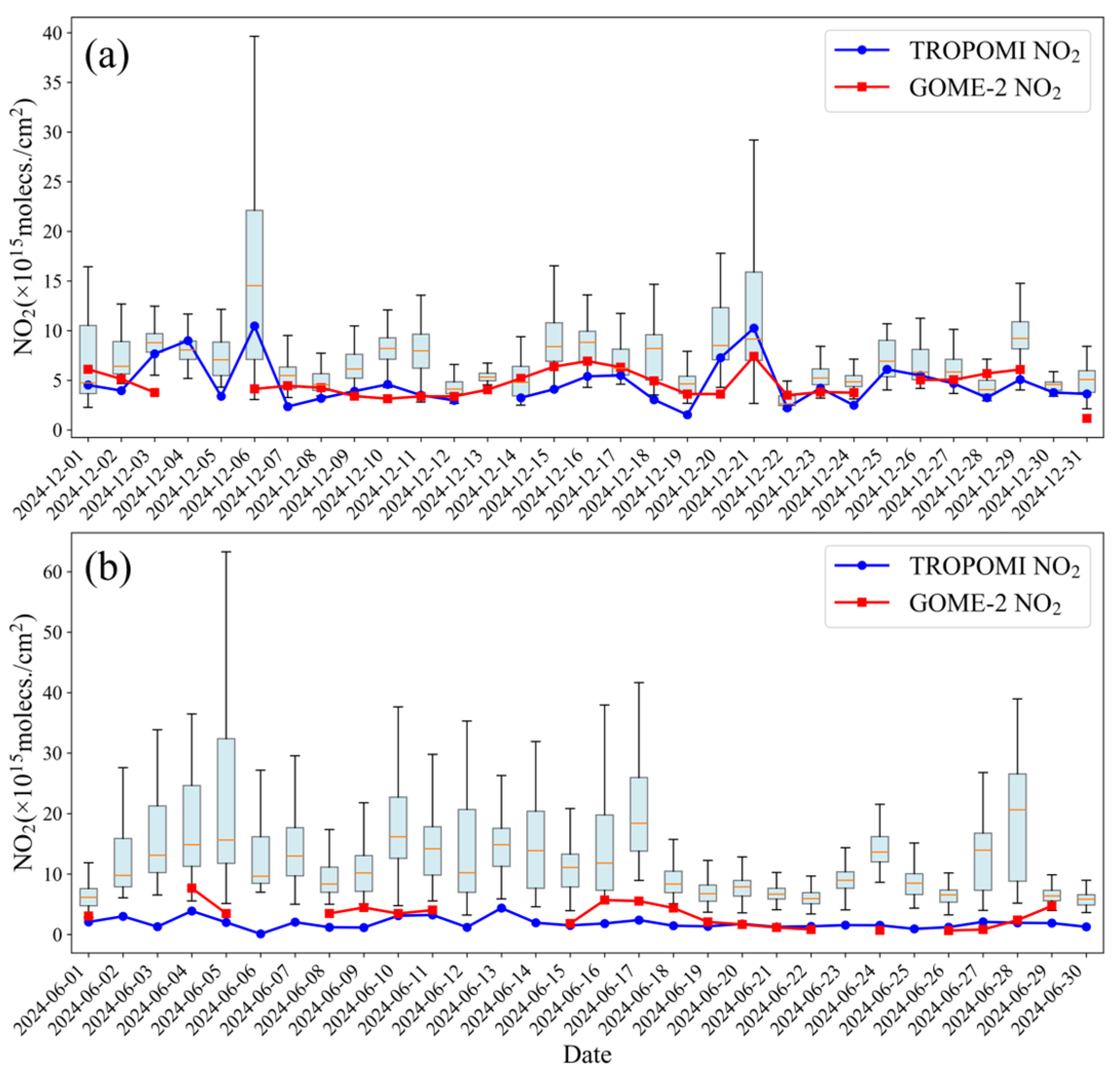
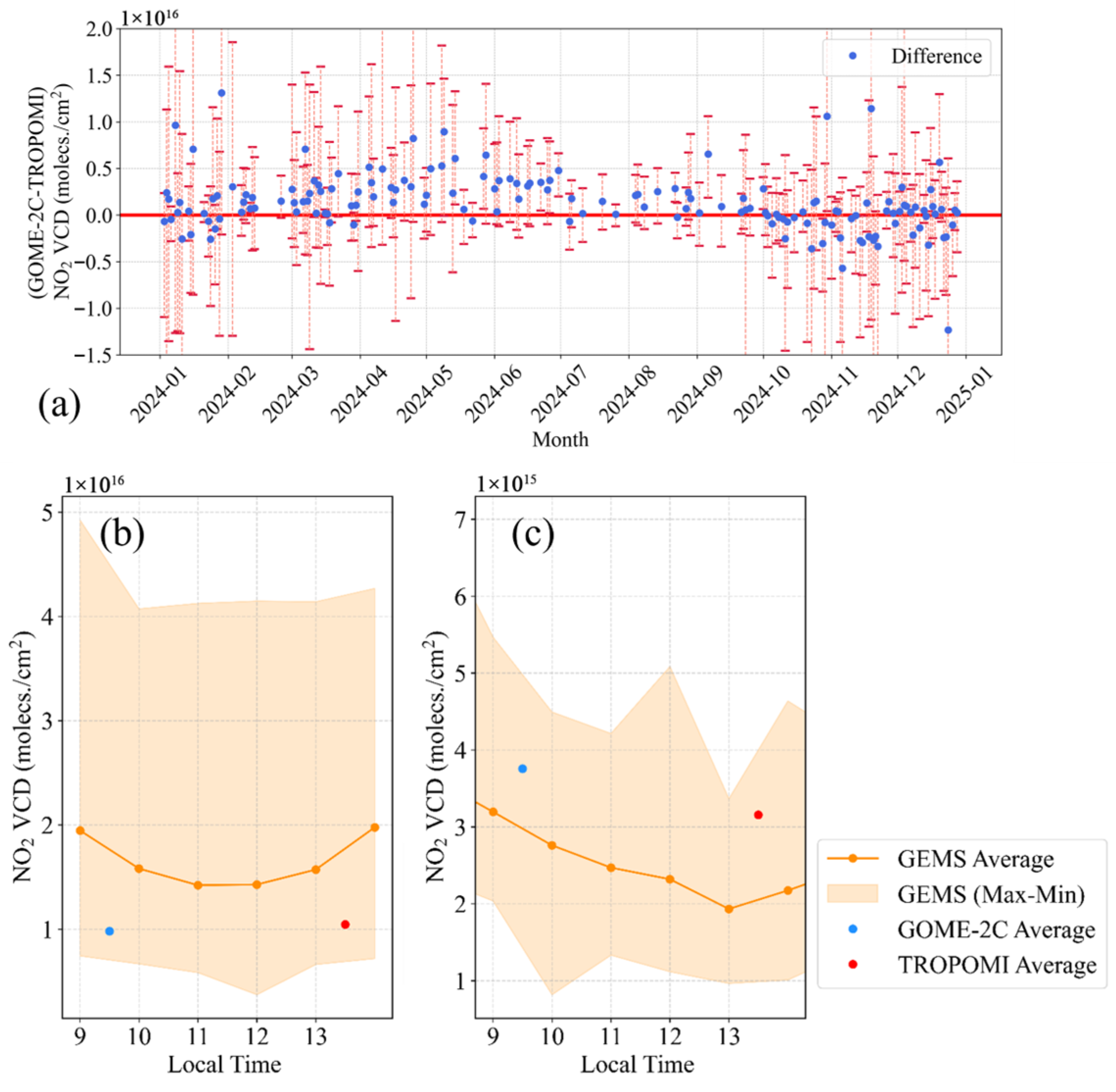
3.1.2. Daily Averaged Variations
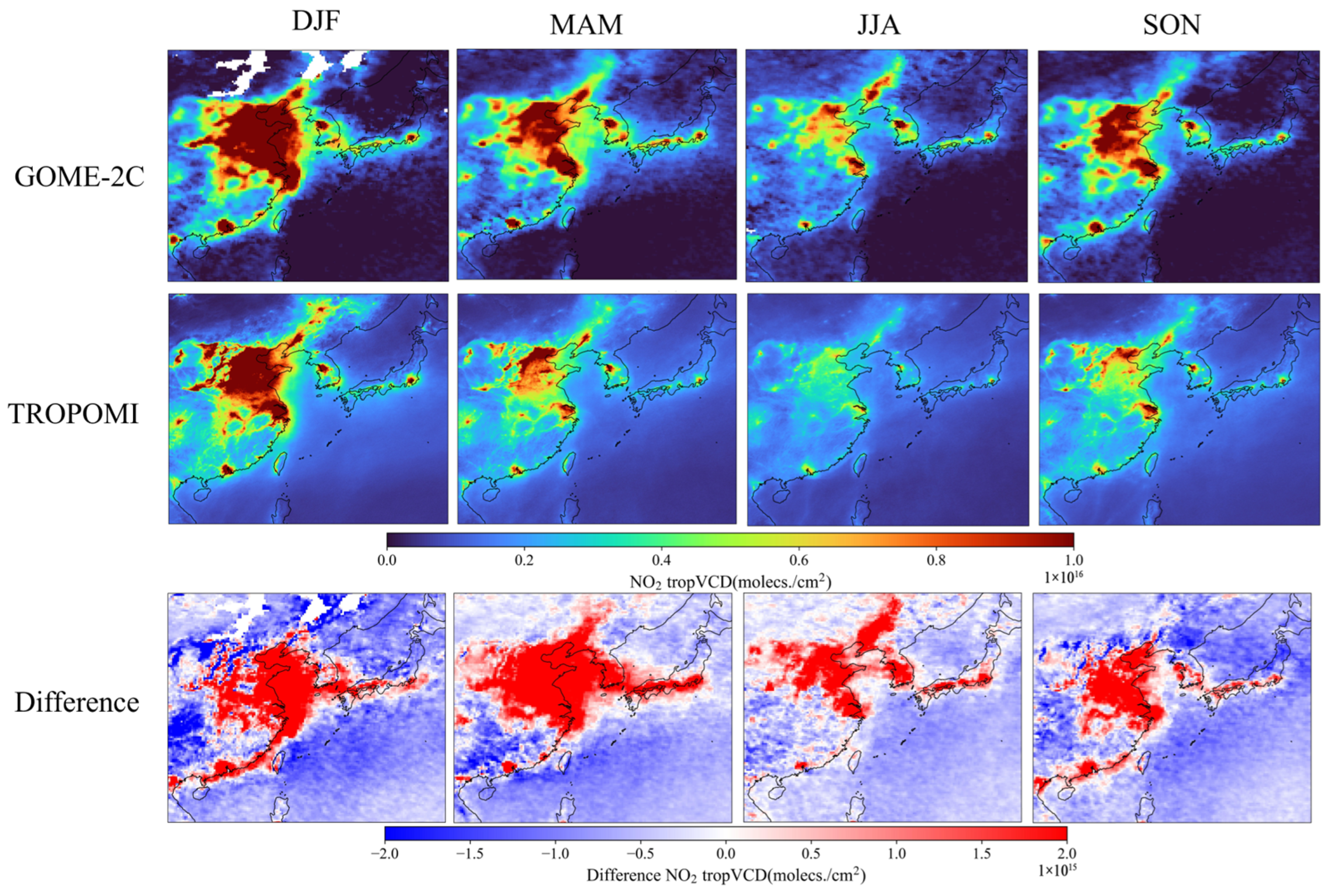
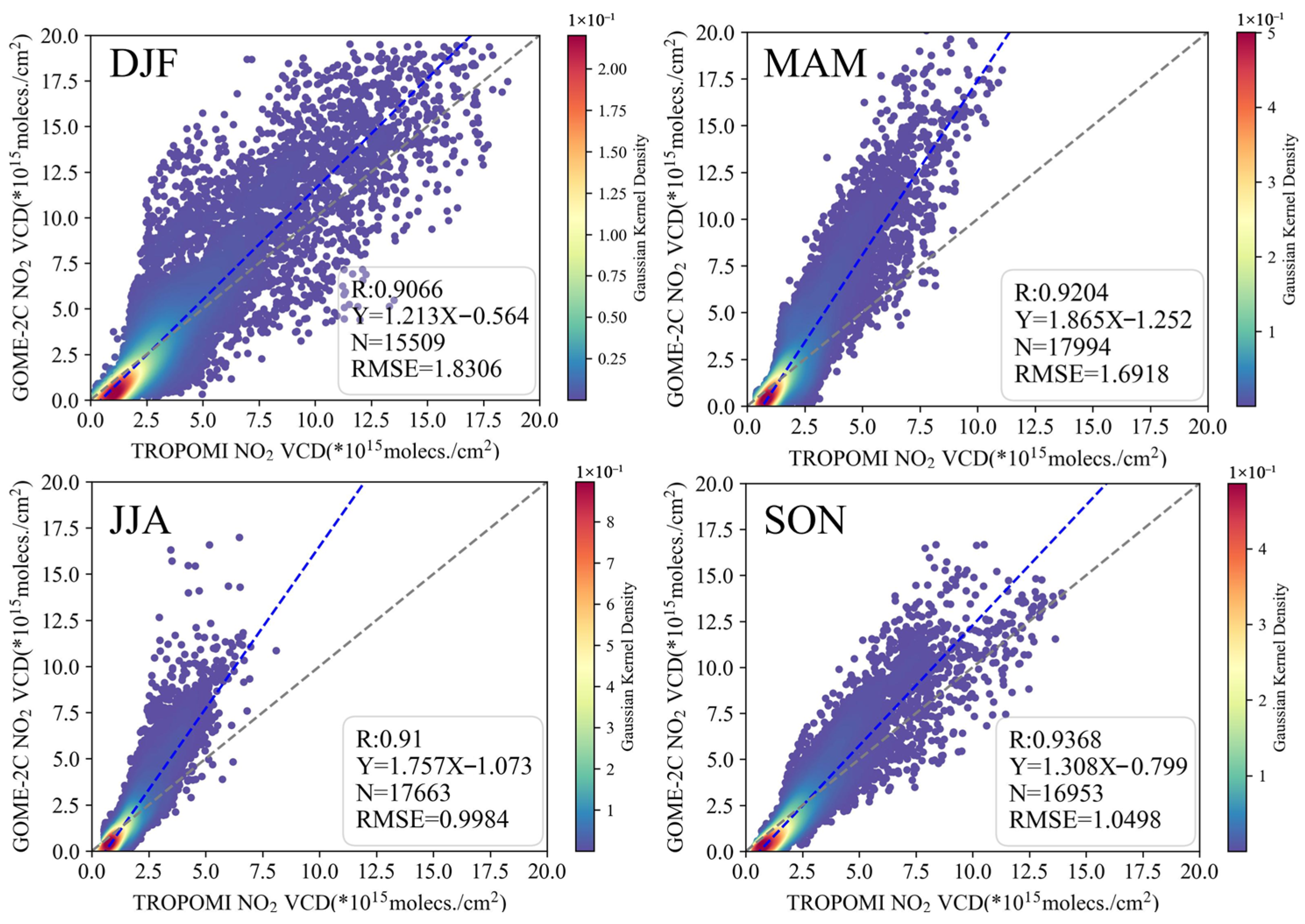
3.2. Evaluations in Typical Regions
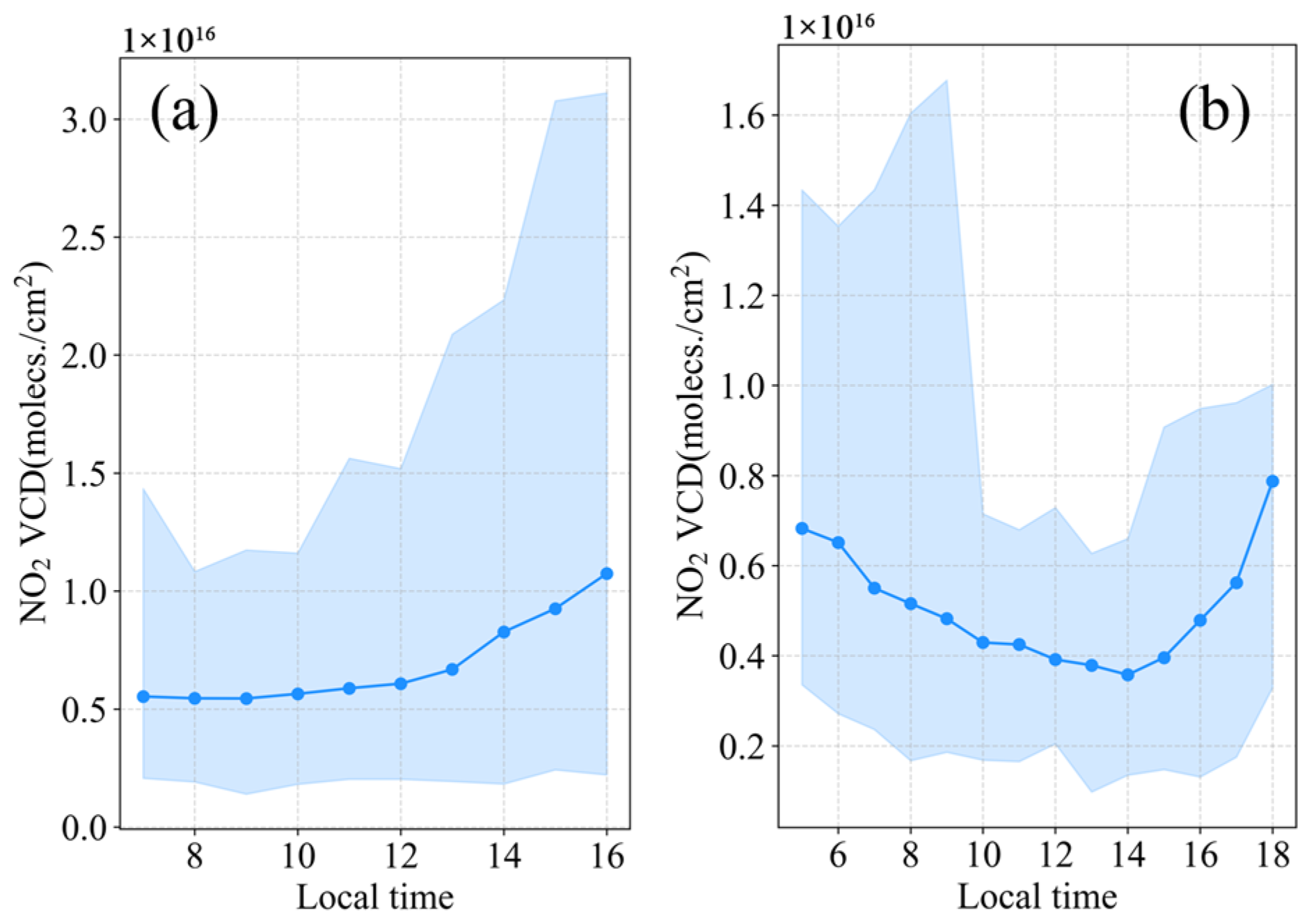
3.2.1. East Asia
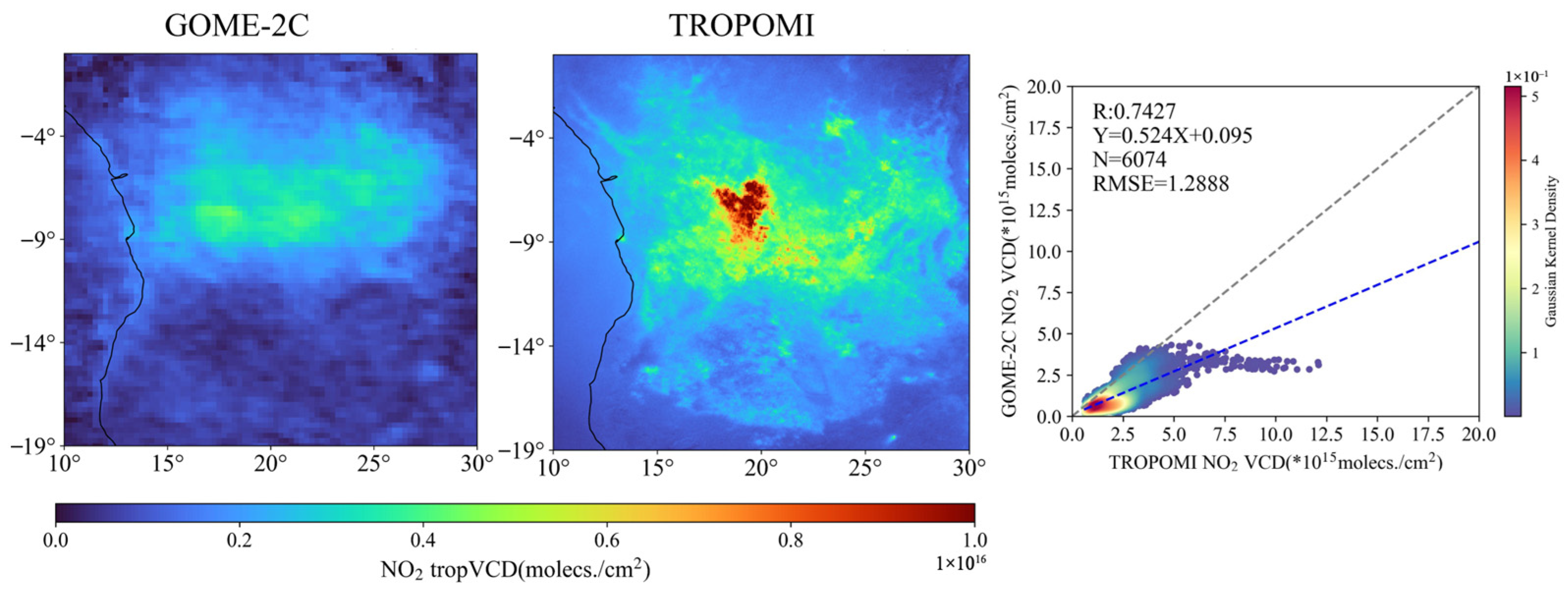
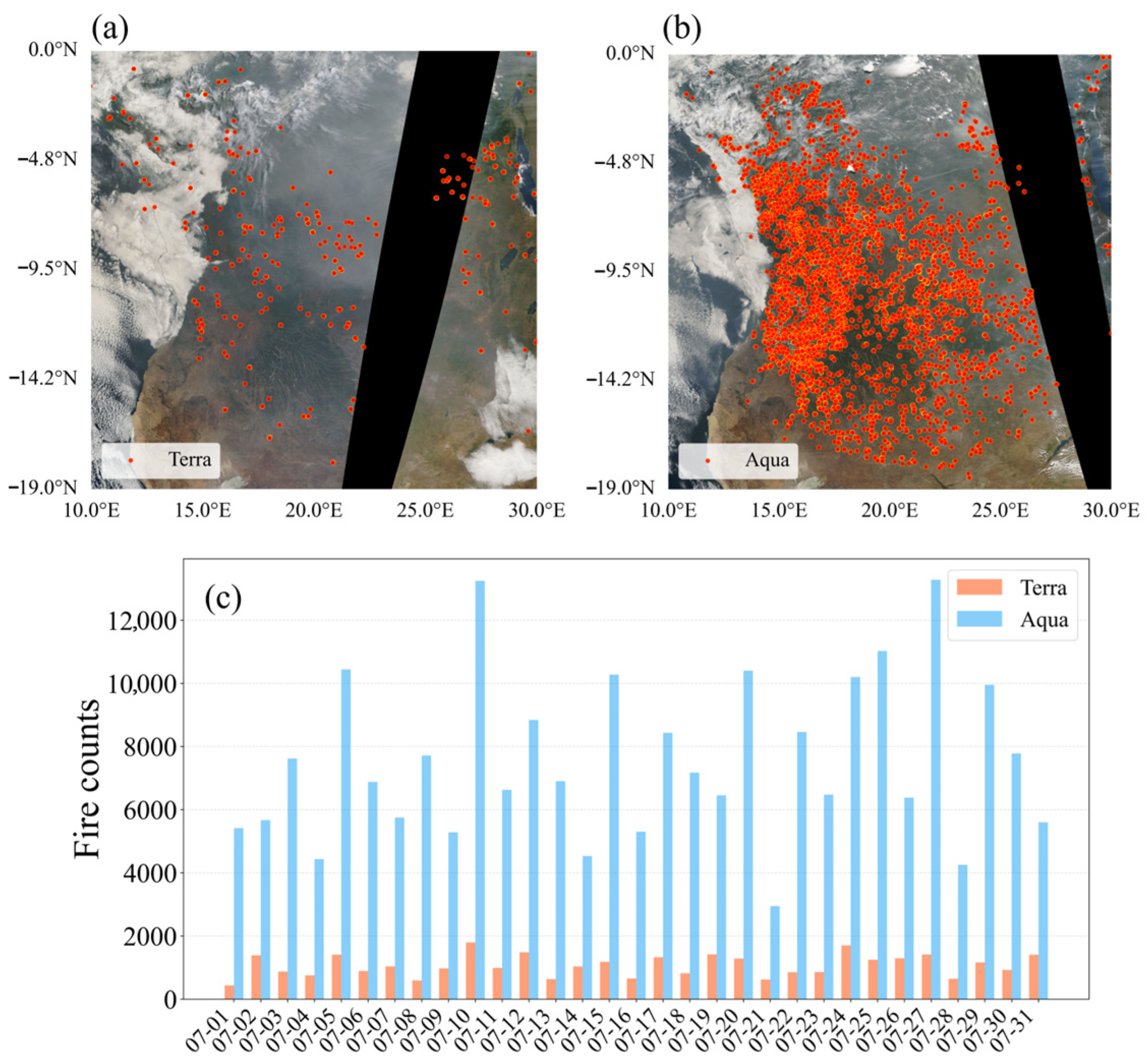
3.2.2. Central Africa
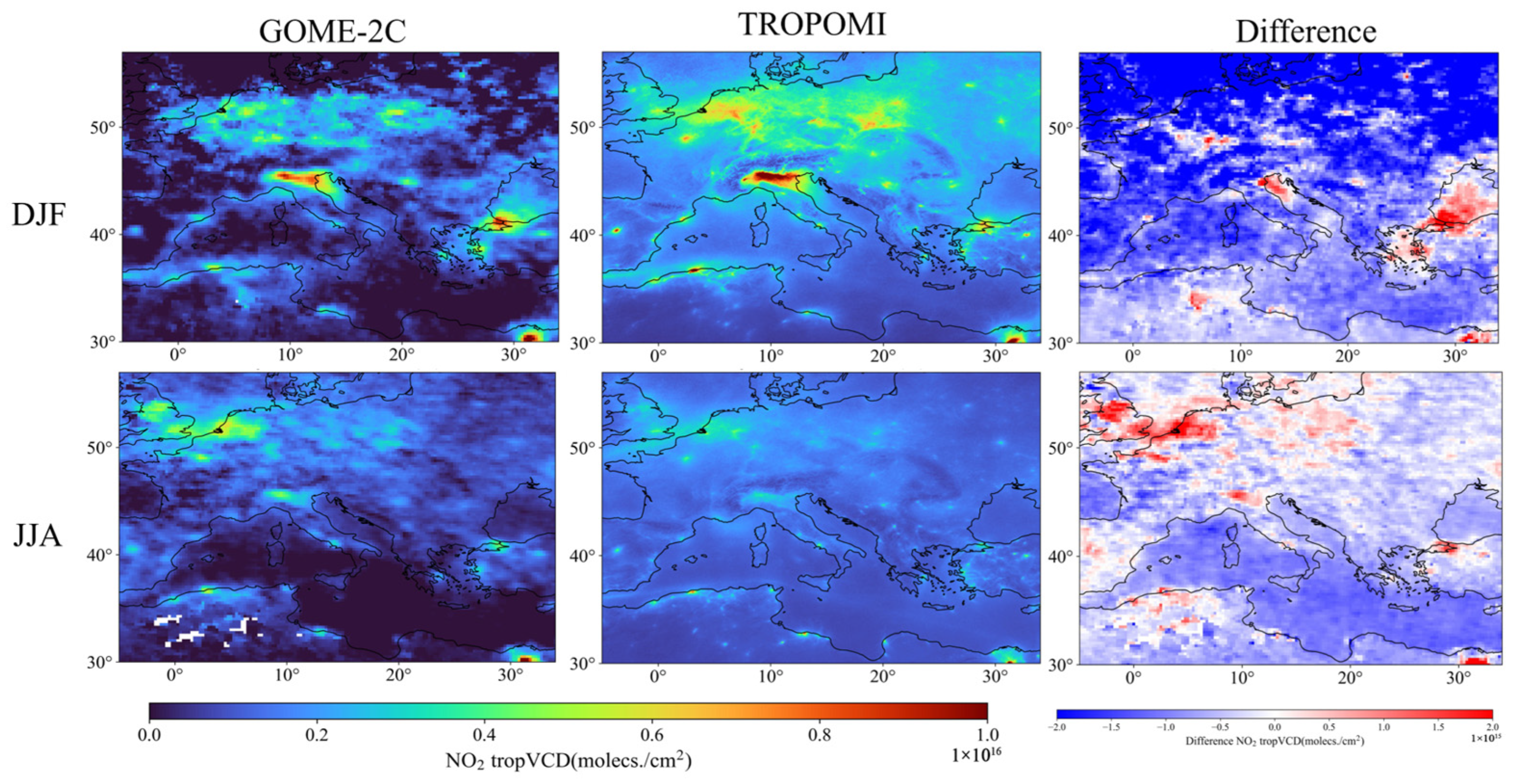
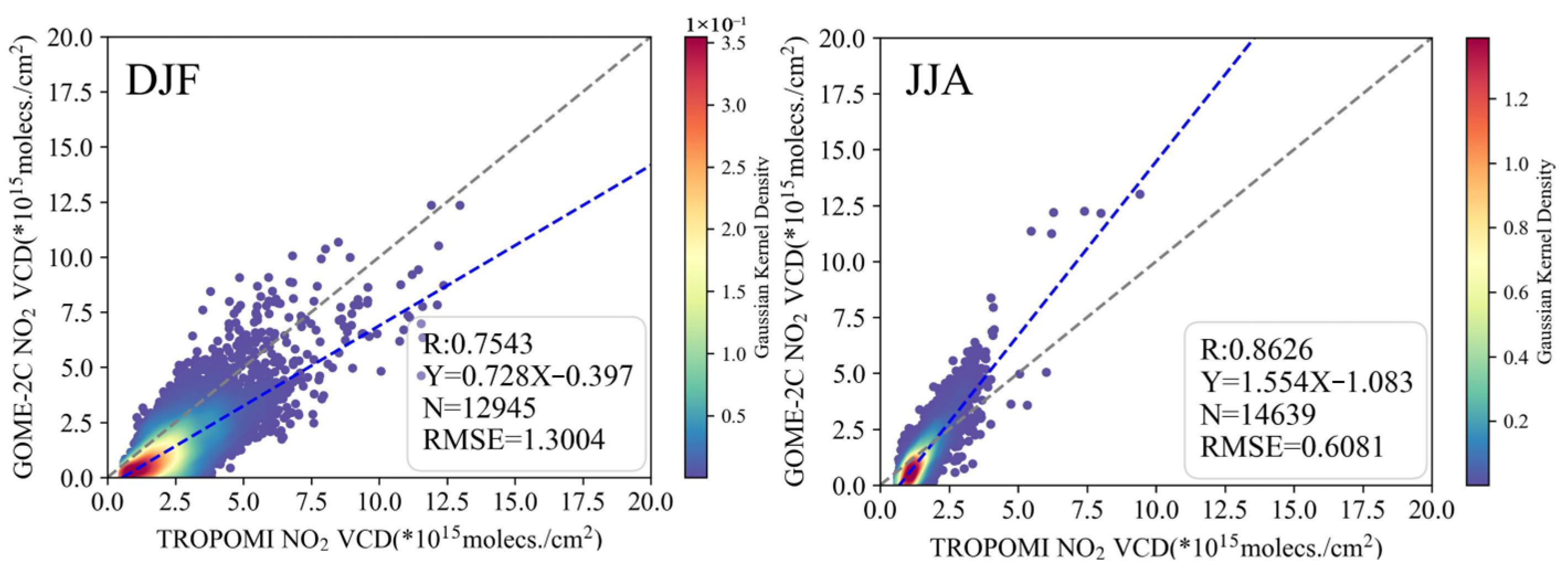
3.2.3. Europe
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Notholt, J.; Palm, M.; Liu, C. Spaceborne Tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Observations from 2005–2020 over the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), China: Variabilities, Implications, and Drivers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 4167–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Holloway, T. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Ozone Sensitivity over China Observed from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument: OZONE SENSITIVITY OVER CHINA. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7229–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geffen, J.; Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.; Sneep, M.; Ter Linden, M.; Zara, M.; Veefkind, J.P. S5P TROPOMI NO2 Slant Column Retrieval: Method, Stability, Uncertainties and Comparisons with OMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1315–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, B.; Xing, C.; Tan, W.; Zhou, H.; Si, F.; et al. First Observation of Tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide from the Environmental Trace Gases Monitoring Instrument Onboard the GaoFen-5 Satellite. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Valks, P.; Lutz, R.; Heue, K.-P.; Hedelt, P.; Loyola, D.; Lee, H.; Kim, J. Tropospheric NO2 Retrieval Algorithm for Geostationary Satellite Instruments: Applications to GEMS. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P. Variability of Nitrogen Oxide Emission Fluxes and Lifetimes Estimated from Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 2745–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Swartz, W.H.; Marchenko, S.V.; Bucsela, E.J.; Chan, K.L.; Wenig, M.; Zara, M. The Version 3 OMI NO2 Standard Product. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3133–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-S.; Kim, D.; Hong, H.; Kim, D.-R.; Yu, J.-A.; Lee, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.; Hong, J.; Jo, H.-Y.; et al. Evaluation of Correlated Pandora Column NO2 and in Situ Surface NO2 Measurements during GMAP Campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 10703–10720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, O.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Y.; Chen, T.; Dong, J.; et al. Evaluation of the First Year of Pandora NO2 Measurements over Beijing and Application to Satellite Validation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Wiegner, M.; van Geffen, J.; De Smedt, I.; Alberti, C.; Cheng, Z.; Ye, S.; Wenig, M. MAX-DOAS Measurements of Tropospheric NO2 and HCHO in Munich and the Comparison to OMI and TROPOMI Satellite Observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4499–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, J.P.; Weber, M.; Buchwitz, M.; Rozanov, V.; Ladstätter-Weißenmayer, A.; Richter, A.; DeBeek, R.; Hoogen, R.; Bramstedt, K.; Eichmann, K.-U.; et al. The Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment (GOME): Mission Concept and First Scientific Results. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P.; Buchwitz, M.; Frerick, J.; Noël, S.; Rozanov, V.V.; Chance, K.V.; Goede, A.P.H. SCIAMACHY: Mission Objectives and Measurement Modes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Burrows, J.; Fietkau, S.; Medeke, T.; Notholt, J.; Oetjen, H.; Sierk, B.; Warneke, T.; Wittrock, F.; Dix, B.; et al. A Scientific NO2 Product from SCIAMACHY: First Results and Validation. Atmos. Chem. Valid. ENVISAT (ACVE-2) 2004, 562, 41.1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Valks, P.; Pinardi, G.; De Smedt, I.; Yu, H.; Beirle, S.; Richter, A. An Improved Total and Tropospheric NO2 Column Retrieval for GOME-2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 1029–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callies, J.; Corpaccioli, E.; Eisinger, M.; Hahne, A.; Lefebvre, A. GOME-2–Metop’s Second-Generation Sensor for Operational Ozone Monitoring. ESA Bull. 2000, 102, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Levelt, P.F.; Van Den Oord, G.H.J.; Dobber, M.R.; Malkki, A.; Visser, H.; De Vries, J.; Stammes, P.; Lundell, J.O.V.; Saari, H. The Ozone Monitoring Instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, I.; Virta, H.; Eskes, H.; Hovila, J.; Douros, J. Comparison of TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 Precursor NO2 Observations with Ground-Based Measurements in Helsinki. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; De Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; De Haan, J.F.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES Mission for Global Observations of the Atmospheric Composition for Climate, Air Quality and Ozone Layer Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Si, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, M.; Su, W.; Zhang, W.; Chan, K.L.; Liu, X.; et al. Preflight Evaluation of the Performance of the Chinese Environmental Trace Gas Monitoring Instrument (EMI) by Spectral Analyses of Nitrogen Dioxide. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3323–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Xu, N.; Chen, L.; Wu, R.; Liu, J.; Si, F. An Investigation on Inter-Calibrating EMI/GF-5 With TROPOMI/S5p in Ultraviolet–Visible Spectra. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5540916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Ahn, M.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, R.J.; Lee, H.; Song, C.H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Yoo, J.-M.; et al. New Era of Air Quality Monitoring from Space: Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E1–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoogman, P.; Liu, X.; Suleiman, R.M.; Pennington, W.F.; Flittner, D.E.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Hilton, B.B.; Nicks, D.K.; Newchurch, M.J.; Carr, J.L.; et al. Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO). J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 186, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Dirksen, R.J.; Van Der A, R.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Stammes, P.; Huijnen, V.; Kleipool, Q.L.; Sneep, M.; Claas, J.; et al. An Improved Tropospheric NO2 Column Retrieval Algorithm for the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1905–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Valks, P.; Pinardi, G.; Xu, J.; Argyrouli, A.; Lutz, R.; Tilstra, L.G.; Huijnen, V.; Hendrick, F.; Van Roozendael, M. An Improved Air Mass Factor Calculation for Nitrogen Dioxide Measurements from the Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment-2 (GOME-2). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 755–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geffen, J.; Eskes, H.; Compernolle, S.; Pinardi, G.; Verhoelst, T.; Lambert, J.-C.; Sneep, M.; Ter Linden, M.; Ludewig, A.; Boersma, K.F.; et al. Sentinel-5P TROPOMI NO2 Retrieval: Impact of Version v2.2 Improvements and Comparisons with OMI and Ground-Based Data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 2037–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Tao, M.; Kerr, G.H.; Ma, S.; Tong, D.Q.; Fiore, A.M.; Dickens, A.F.; Adelman, Z.E.; Anenberg, S.C. Evaluating the Spatial Patterns of U.S. Urban NOx Emissions Using TROPOMI NO2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 300, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zheng, B.; Liu, Y. Tracking Daily NOx Emissions from an Urban Agglomeration Based on TROPOMI NO2 and a Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2025, 25, 5959–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Brook, J.R.; He, K. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Variations in Surface NO2 for Beijing Reconstructed from Surface Data and Satellite Retrievals. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Valks, P.; Beirle, S.; Loyola, D.G. Nitrogen Dioxide Decline and Rebound Observed by GOME-2 and TROPOMI during COVID-19 Pandemic. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1737–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilboll, A.; Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P. Long-Term Changes of Tropospheric NO2 over Megacities Derived from Multiple Satellite Instruments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4145–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Lu, K.; Li, R. Global Estimates of Ambient NO2 Concentrations and Long-Term Health Effects during 2000–2019. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, X.; Gu, D.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Long-Term Spatiotemporal Trends in Ambient NO2 Concentrations and Attributable Health Burdens in China From 2005 to 2020. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2023GH000798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Wei, S.; Loo, B.P.Y.; Lai, P.C.; Lam, Y.F.; Wan, L.; Li, Y. Global Association between Satellite-Derived Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) and Lockdown Policies under the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Requia, W.J.; Sakhvidi, M.J.Z.; Lin, K.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Cao, P.; Yang, L.; et al. Associations of Long-Term Exposure to Nitrogen Oxides with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.H.; Jacob, D.J.; Dang, R.; Oak, Y.J.; Lin, H.; Kim, J.; Zhai, S.; Colombi, N.K.; Pendergrass, D.C.; Beaudry, E.; et al. Interpreting Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS) Geostationary Satellite Observations of the Diurnal Variation in Nitrogen Dioxide (NO 2 ) over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 7027–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Hong, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, J.; Van Roozendael, M.; Fayt, C.; Ahn, M.-H.; Jacob, D.J.; Seo, S.; et al. Tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide Levels Vary Diurnally in Asian Cities. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qin, K.; Cohen, J.B.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Ling, X.; Xue, Y. Combing GOME-2B and OMI Satellite Data to Estimate Near-Surface NO2 of Mainland China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10269–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Kim, J.; Zhang, T.; Yu, F.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lao, X.Q. Estimation of Ground-Level NO2 and Its Spatiotemporal Variations in China Using GEMS Measurements and a Nested Machine Learning Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 9645–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, J.E.; Andela, N.; Tsigaridis, K.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Ossohou, M.; Bauer, S.E. Reductions in NO2 Burden over North Equatorial Africa from Decline in Biomass Burning in Spite of Growing Fossil Fuel Use, 2005 to 2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2002579118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Eskes, H.J.; Pinder, R.W.; Wang, J.; Van Der A, R.J. Intercomparison of SCIAMACHY and OMI Tropospheric NO2 Columns: Observing the Diurnal Evolution of Chemistry and Emissions from Space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 2007JD008816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Valks, P.; Pinardi, G.; Xu, J.; Chan, K.L.; Argyrouli, A.; Lutz, R.; Beirle, S.; Khorsandi, E.; Baier, F.; et al. An Improved TROPOMI Tropospheric NO2 Research Product over Europe. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 7297–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Xing, C.; Tan, W.; Liu, C. Relating Satellite NO2 Tropospheric Columns to Near-Surface Concentrations: Implications from Ground-Based MAX-DOAS NO2 Vertical Profile Observations. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Fiore, A.M.; Karambelas, A.; Miller, P.J.; Valin, L.C.; Judd, L.M.; Tzortziou, M.; Whitehill, A.; Teora, A.; Tian, Y.; et al. Insights Into Summertime Surface Ozone Formation From Diurnal Variations in Formaldehyde and Nitrogen Dioxide Along a Transect Through New York City. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2025, 130, e2024JD040922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.P.; Martínez-Alonso, S.; Jo, D.S.; Ortega, I.; Emmons, L.K.; Orlando, J.J.; Worden, H.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; et al. Quantifying the Diurnal Variation in Atmospheric NO2 from Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS) Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 8943–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, J.A. A Random Forest Partition Model for Predicting NO2 Concentrations from Traffic Flow and Meteorological Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, E.; Holloway, T. Evaluating Current Satellite Capability to Observe Diurnal Change in Nitrogen Oxides in Preparation for Geostationary Satellite Missions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 034038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Remer, L.A.; Eck, T.F. Quantitative Evaluation and Intercomparison of Morning and Afternoon Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Aerosol Measurements from Terra and Aqua. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 2004JD004987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Richter, A.; Bösch, T.; Zilker, B.; Latsch, M.; Behrens, L.K.; Okafor, C.M.; Bösch, H.; Burrows, J.P.; Merlaud, A.; et al. Validation of GEMS Tropospheric NO2 Columns and Their Diurnal Variation with Ground-Based DOAS Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 6315–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Choi, H.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Shin, M.; Song, C.-K.; Kim, S. Estimation of Surface-Level NO2 and O3 Concentrations Using TROPOMI Data and Machine Learning over East Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Pinardi, G.; Lambert, J.-C.; Eskes, H.J.; Eichmann, K.-U.; Fjæraa, A.M.; Granville, J.; Niemeijer, S.; Cede, A.; et al. Ground-Based Validation of the Copernius Sentinel-5P TROPOMI NO2 Measurements with the NDACC ZSL-DOAS, MAX-DOAS and Pandonia Global Networks. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, K. Non-Negligible Impacts of Clean Air Regulations on the Reduction of Tropospheric NO2 over East China during the COVID-19 Pandemic Observed by OMI and TROPOMI. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smedt, I.; Pinardi, G.; Vigouroux, C.; Compernolle, S.; Bais, A.; Benavent, N.; Boersma, F.; Chan, K.-L.; Donner, S.; Eichmann, K.-U.; et al. Comparative Assessment of TROPOMI and OMI Formaldehyde Observations and Validation against MAX-DOAS Network Column Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 12561–12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikwambana, L.; Mhangara, P.; Mbatha, N. Trend Analysis and First Time Observations of Sulphur Dioxide and Nitrogen Dioxide in South Africa Using TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 P Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 91, 102130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency. S5P Mission Performance Centre Formaldehyde [L2__HCHO___] Readme. Available online: https://sentiwiki.copernicus.eu/__attachments/1673595/S5P-MPC-BIRA-PRF-HCHO%20-%20Sentinel-5P%20Formaldehyde%20Level%202%20Readme%202023%20-%202.7.pdf?inst-v=43bfeaf2-06ce-48ec-adc6-68038c8e270d (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- European Space Agency. S5P Mission Performance Centre Nitrogen Dioxide [L2__NO2___] Readme. Available online: https://sentiwiki.copernicus.eu/__attachments/1673595/S5P-MPC-KNMI-PRF-NO2%20-%20Sentinel-5P%20Nitrogen%20Dioxide%20Level%202%20Product%20Readme%20File%202023%20-%202.5.pdf?inst-v=036311ce-c427-48a7-bdf2-a9ec5ad4ff29 (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Valks, P.; Pinardi, G.; Richter, A.; Lambert, J.-C.; Hao, N.; Loyola, D.; Van Roozendael, M.; Emmadi, S. Operational Total and Tropospheric NO2 Column Retrieval for GOME-2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1491–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Valks, P.; Heue, K.-P.; Lutz, R.; Hedelt, P.; Loyola, D.; Pinardi, G.; Van Roozendael, M.; Hendrick, F.; Wagner, T.; et al. Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment-2 (GOME-2) Daily and Monthly Level-3 Products of Atmospheric Trace Gas Columns. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 1831–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.; Cede, A.; Spinei, E.; Mount, G.; Tzortziou, M.; Abuhassan, N. NO2 Column Amounts from Ground-based Pandora and MFDOAS Spectrometers Using the Direct-sun DOAS Technique: Intercomparisons and Application to OMI Validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 2009JD011848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Naja, M.; Rajwar, M.C.; Irie, H.; Lerot, C.; Kumar, M.; Lal, S. Long-Term Observations of NO2, SO2, HCHO, and CHOCHO over the Himalayan Foothills: Insights from MAX-DOAS, TROPOMI, and GOME-2. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 336, 120746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Beirle, S.; Lampel, J.; Koukouli, M.; De Smedt, I.; Theys, N.; Li, A.; Wu, D.; Xie, P.; Liu, C.; et al. Validation of OMI, GOME-2A and GOME-2B Tropospheric NO2, SO2 and HCHO Products Using MAX-DOAS Observations from 2011 to 2014 in Wuxi, China: Investigation of the Effects of Priori Profiles and Aerosols on the Satellite Products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5007–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-C.; Nakayama, T.; Matsumi, Y.; Kawasaki, M.; Imasu, R.; Morino, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishidoya, S.; Sato, K.; Ohashi, M. Observation of Column-Averaged Molar Mixing Ratios of Carbon Dioxide in Tokyo. Atmos. Environ. X 2019, 2, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloulakou, A.; Mavroidis, I.; Gavriil, I. Compliance with the Annual NO2 Air Quality Standard in Athens. Required NOx Levels and Expected Health Implications. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.M.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Janz, S.J.; Kowalewski, M.G.; Pierce, R.B.; Szykman, J.J.; Valin, L.C.; Swap, R.; Cede, A.; Mueller, M.; et al. Evaluating the Impact of Spatial Resolution on Tropospheric NO2 Column Comparisons within Urban Areas Using High-Resolution Airborne Data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 6091–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Jiang, F.; Feng, S.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, Z.; Lyu, X. Impact of Weather and Emission Changes on NO2 Concentrations in China during 2014–2019. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der A, R.J.; Eskes, H.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Van Noije, T.P.C.; Van Roozendael, M.; De Smedt, I.; Peters, D.H.M.U.; Meijer, E.W. Trends, Seasonal Variability and Dominant NOx Source Derived from a Ten Year Record of NO2 Measured from Space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 2007JD009021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.Y.; Ding, G.A.; Xu, X.B.; Xu, X.D.; Yu, H.Q.; Wang, S.F. Vertical Distributions of SO2 and NO2 in the Lower Atmosphere in Beijing Urban Areas, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-B.; Yuan, B.; Parrish, D.D.; Chen, D.; Song, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Shao, M. Long-Term Trend of Ozone in Southern China Reveals Future Mitigation Strategy for Air Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 269, 118869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremanloo, M.; Choi, Y.; Singh, D. Deep Learning Bias Correction of GEMS Tropospheric NO2: A Comparative Validation of NO2 from GEMS and TROPOMI Using Pandora Observations. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyrichidou, I.; Koukouli, M.E.; Balis, D.S.; Katragkou, E.; Melas, D.; Poupkou, A.; Kioutsioukis, I.; Van Der A, R.; Boersma, F.K.; Van Roozendael, M.; et al. Satellite Observations and Model Simulations of Tropospheric NO2 Columns over South-Eastern Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6119–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Fan, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J.; Chen, L. Limitations of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Observations in Capturing the Diurnal Variability of Tropospheric NO2: A Case Study Using TROPOMI, GOME-2C, and Pandora Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162846
Li Y, Yu C, Fan J, Fan M, Zhang Y, Tao J, Chen L. Limitations of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Observations in Capturing the Diurnal Variability of Tropospheric NO2: A Case Study Using TROPOMI, GOME-2C, and Pandora Data. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162846
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yichen, Chao Yu, Jing Fan, Meng Fan, Ying Zhang, Jinhua Tao, and Liangfu Chen. 2025. "Limitations of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Observations in Capturing the Diurnal Variability of Tropospheric NO2: A Case Study Using TROPOMI, GOME-2C, and Pandora Data" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162846
APA StyleLi, Y., Yu, C., Fan, J., Fan, M., Zhang, Y., Tao, J., & Chen, L. (2025). Limitations of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Observations in Capturing the Diurnal Variability of Tropospheric NO2: A Case Study Using TROPOMI, GOME-2C, and Pandora Data. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162846







