Artificial Surface Water Construction Aggregated Water Loss Through Evaporation in the North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
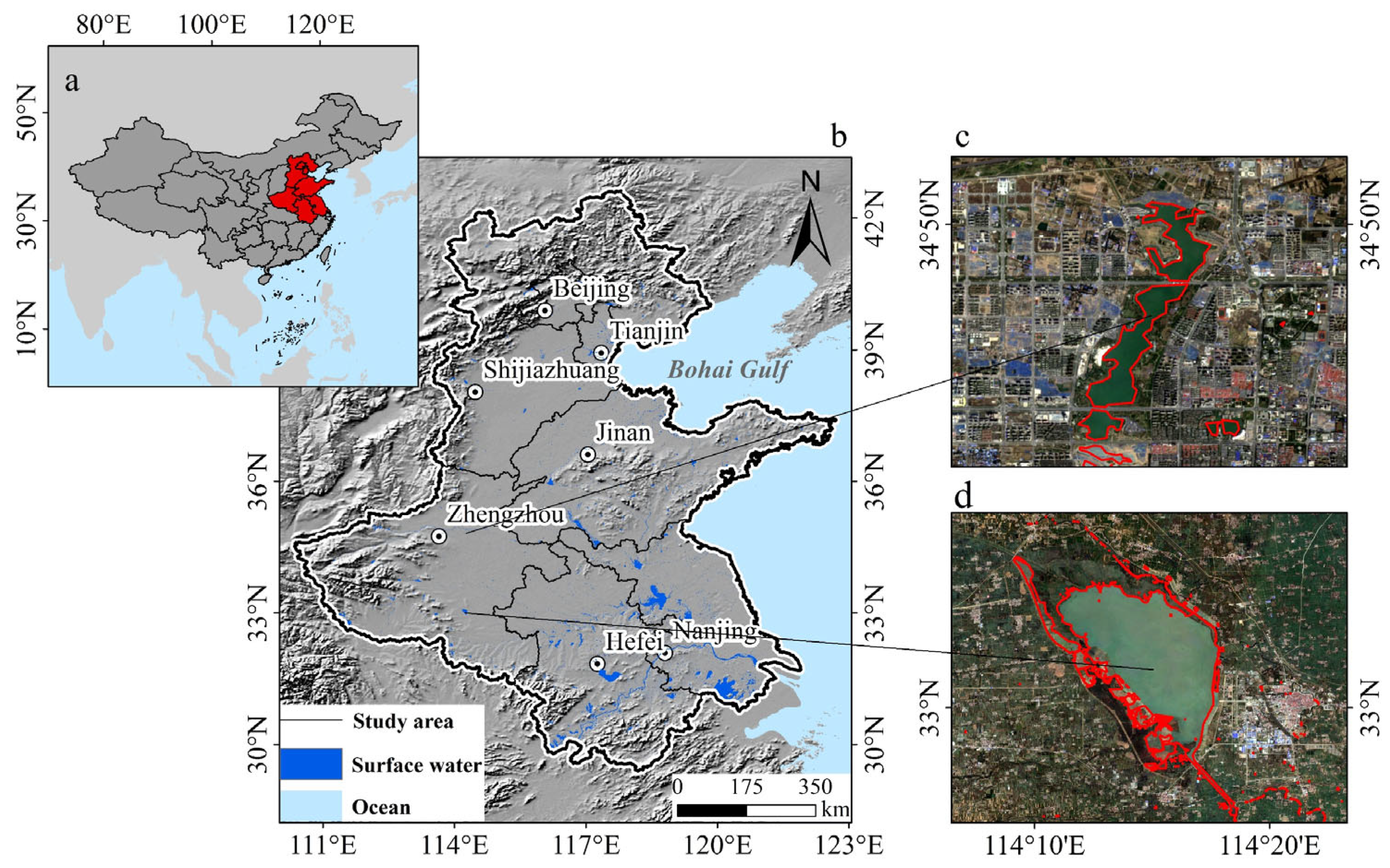
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
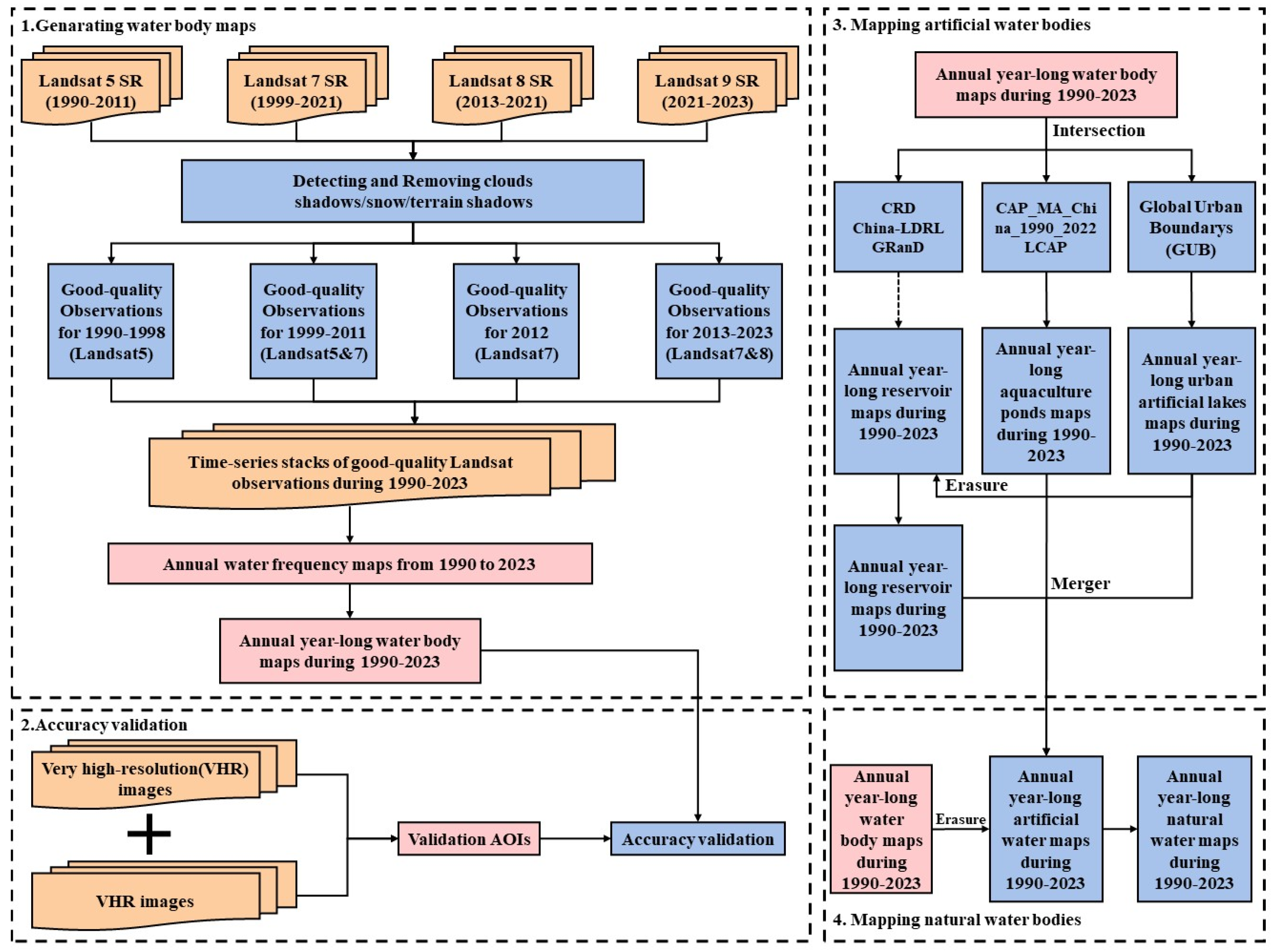
2.2.1. Landsat Data
2.2.2. Auxiliary Data for Identifying Different Kinds of Artificial Surface Water
2.2.3. Data on Water Evaporation and Evapotranspiration
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Identification of Different Kinds of Surface Water Bodies
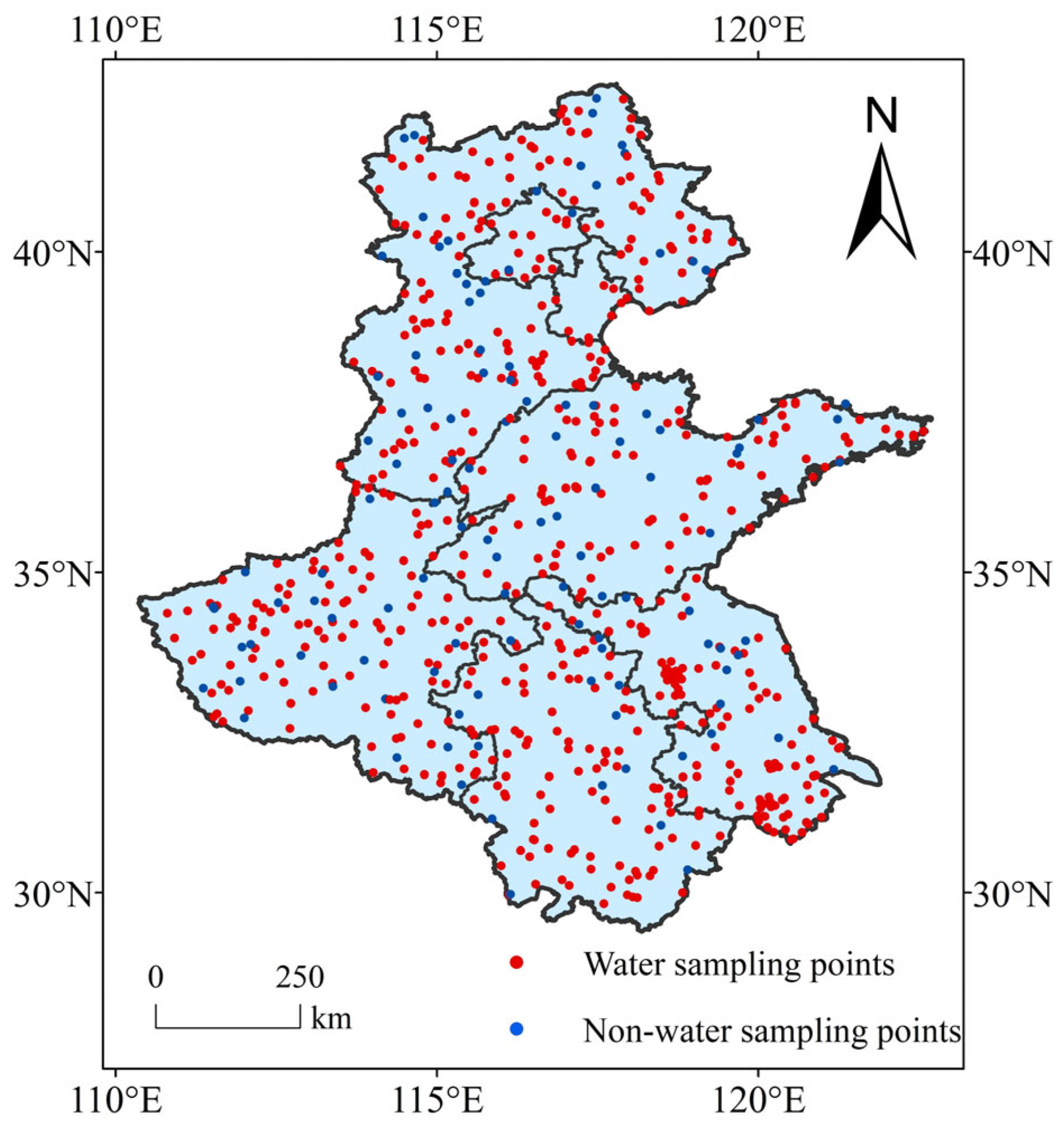
2.3.2. Accuracy Assessment
2.3.3. Change Analyses of Different Types of Artificial Surface Water Bodies
2.3.4. Calculation of Water Evaporation Volume
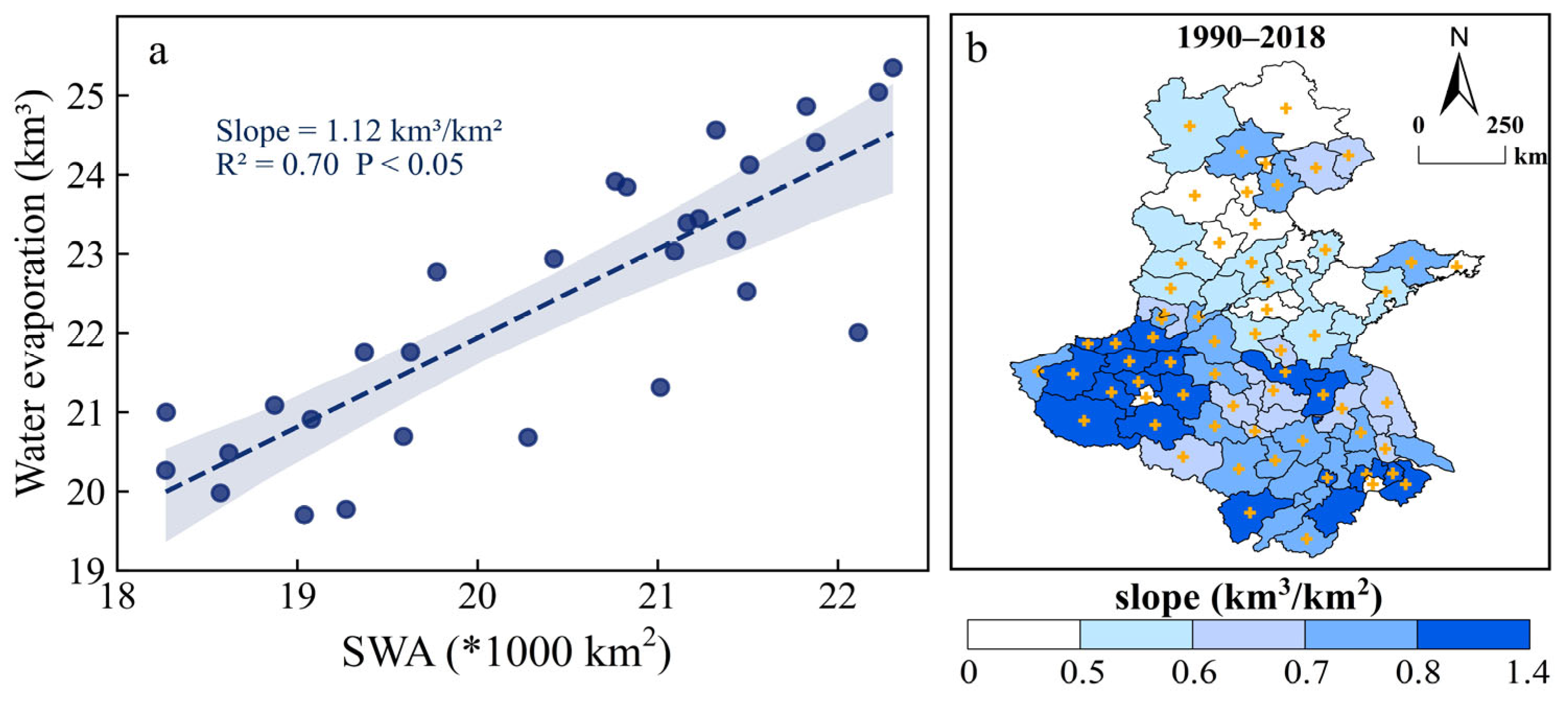
2.3.5. Effects of SWA Changes on Water Security
3. Results
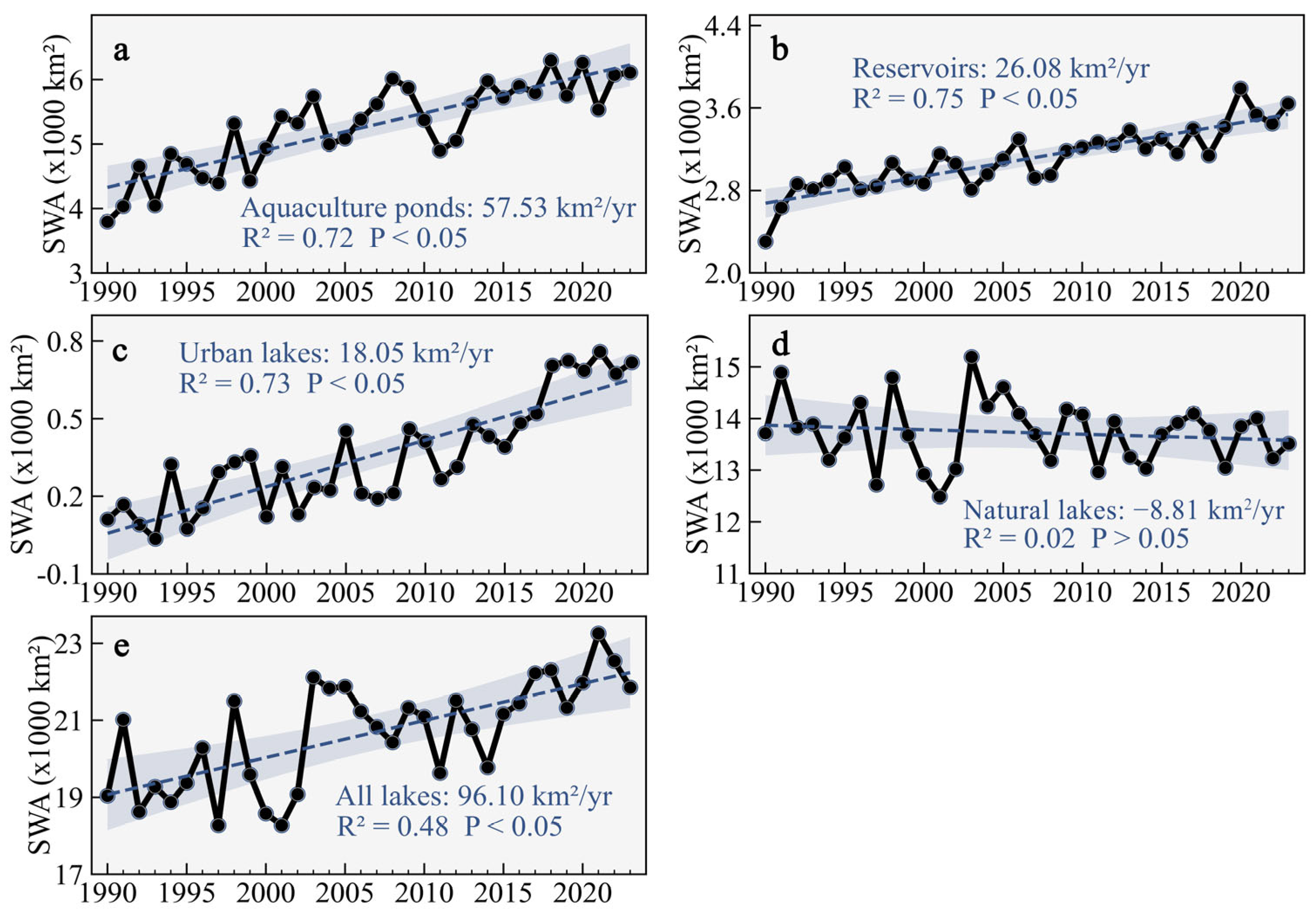
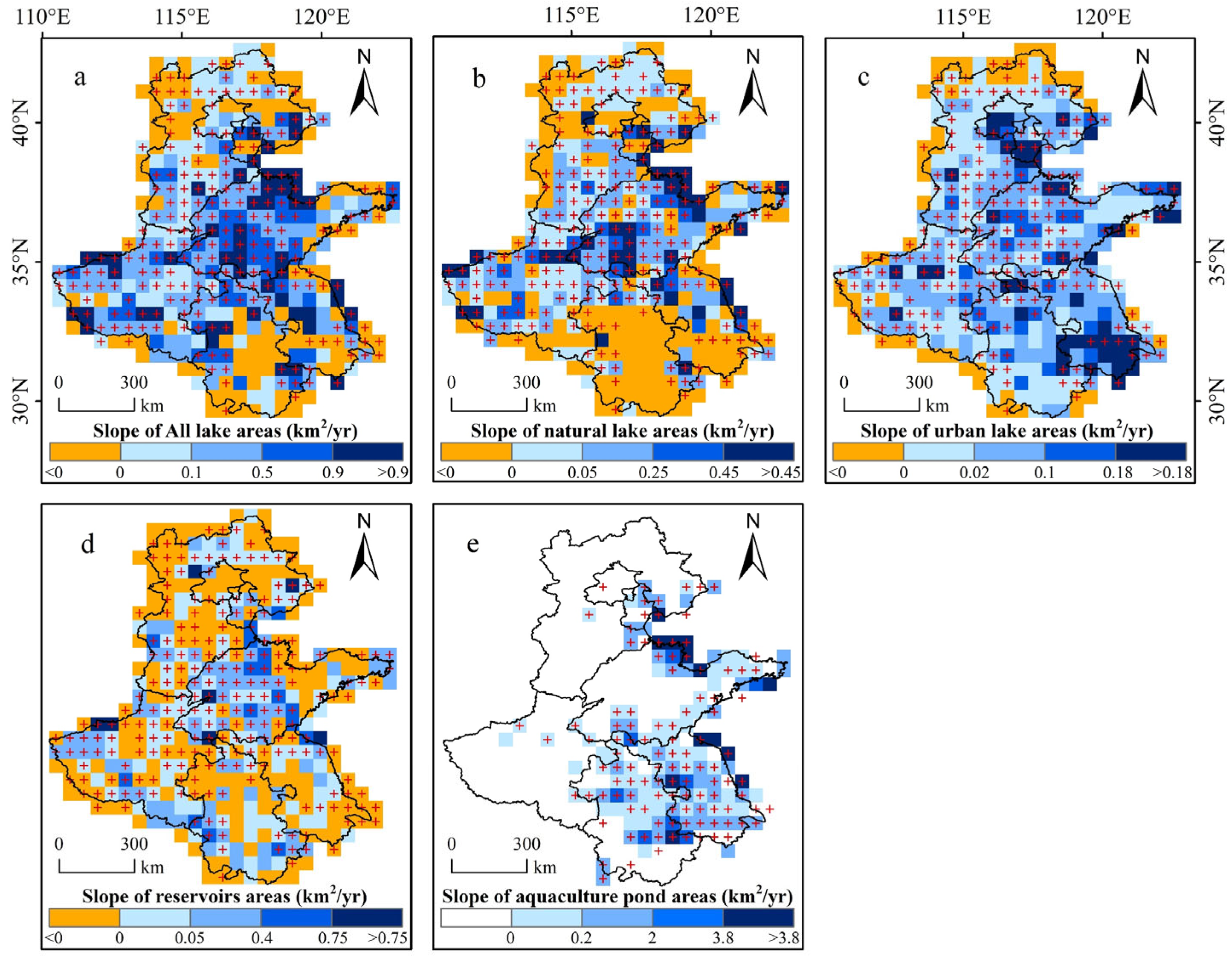
3.1. Changes in Different Types of Artificial Surface Water Bodies
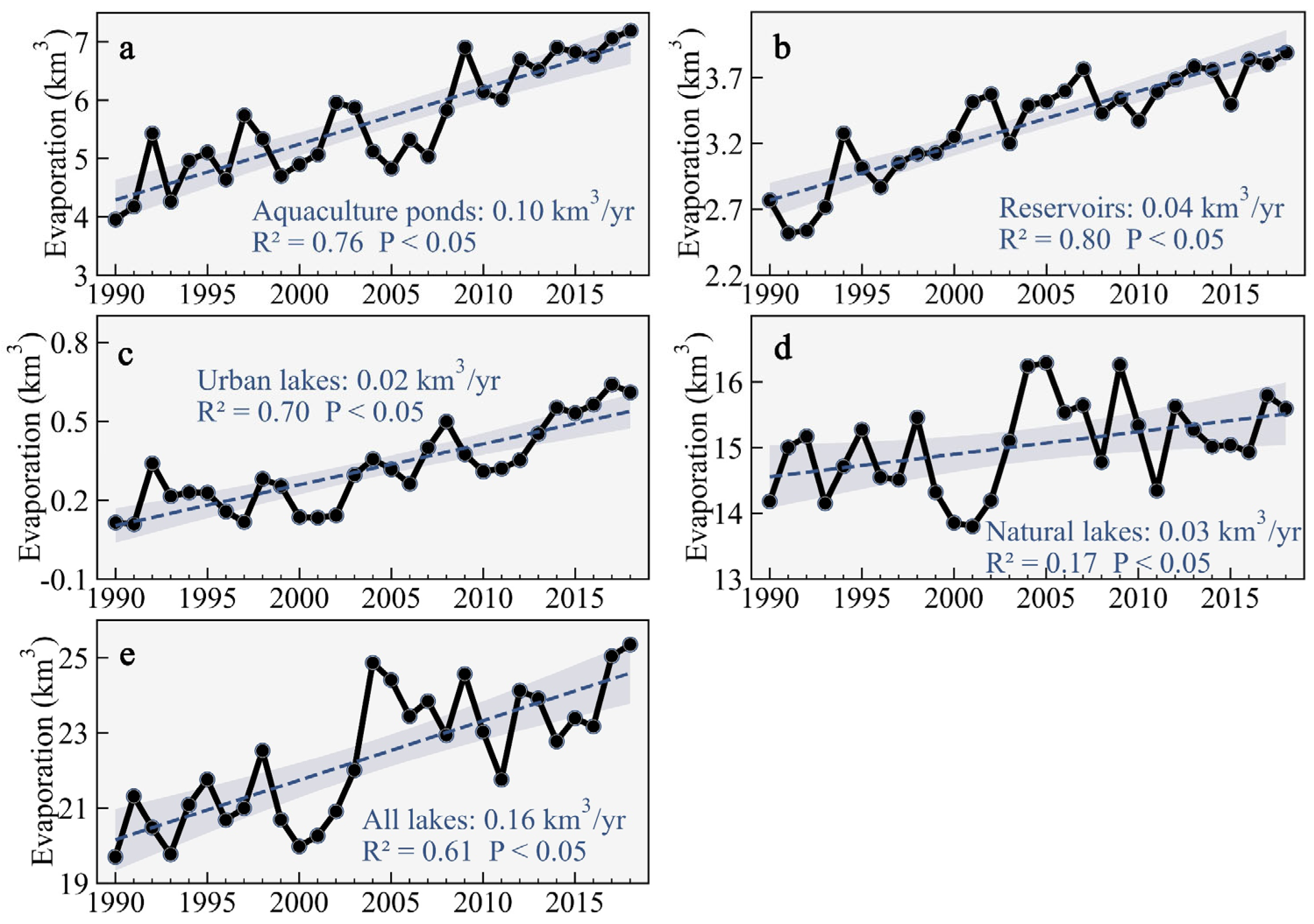
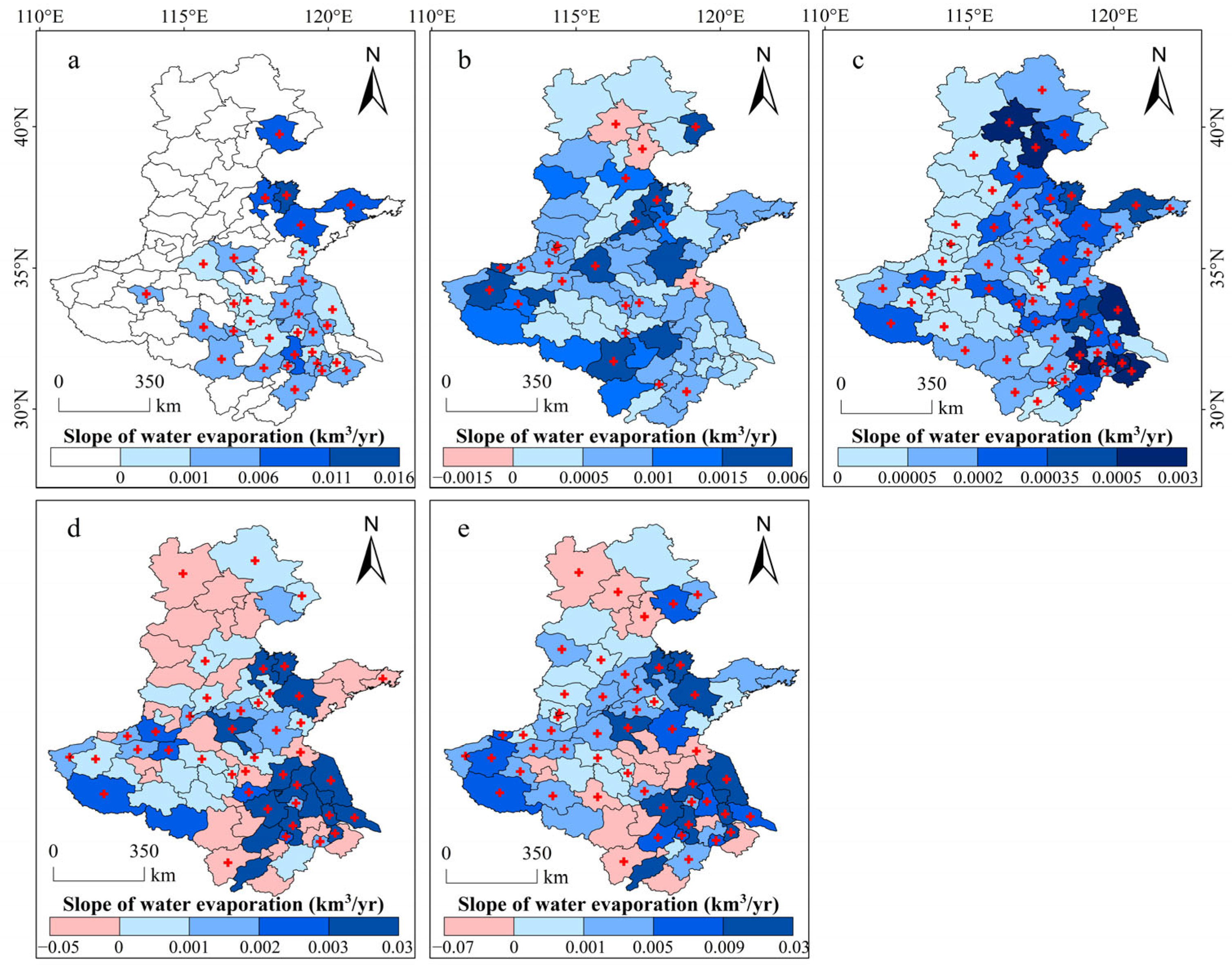
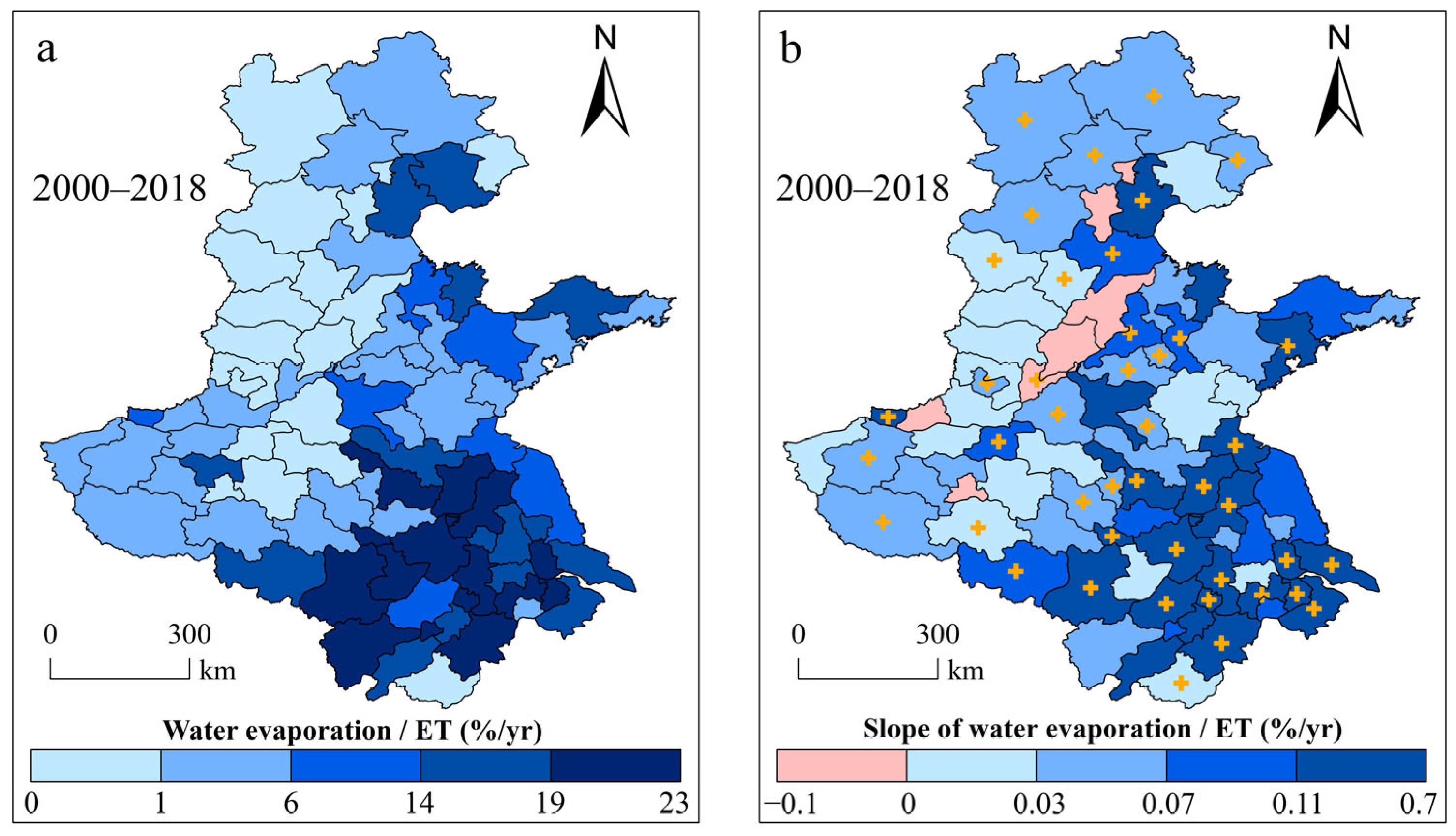
3.2. Changes in Water Evaporation Volumes
3.3. Effects of Water Evaporation Changes on ET
4. Discussion
4.1. Emerging Artificial Surface Water Bodies and Their Risks to Water Security
4.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.3. Uncertainty Analyses and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Q.X.; Ma, L.; Green, T.R.; Yu, Q.; Wang, T.D.; Ahuja, L.R. Water Resources and Water Use Efficiency in the North China Plain: Current Status and Agronomic Management Options. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1102–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.-G.; Hu, S.; Lin, Z.-H.; Liu, S.-X.; Xia, J. Impacts of Climate Change on Agricultural Water Resources and Adaptation on the North China Plain. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2017, 8, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Hanjra, M.A.; Mu, J. Water Management and Crop Production for Food Security in China: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Zhang, W.; Martinsen, G.; He, X.; Stisen, S. Estimating Net Irrigation across the North China Plain through Dual Modeling of Evapotranspiration. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Zou, Z.; Xiao, X. Rapid Surface Water Expansion Due to Increasing Artificial Reservoirs and Aquaculture Ponds in North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, W. Water Sustainability for China and Beyond. Science 2012, 337, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Bai, P.; Liu, C. Estimation of Reservoir Evaporation Losses for China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Duan, Q.; Yeh, P.J.-F.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Moradkhani, H.; Gong, W.; Lei, X.; Liao, W.; Xu, L. Sub-Regional Groundwater Storage Recovery in North China Plain after the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Long, D.; Scanlon, B.R.; Burek, P.; Zhang, C.; Han, Z.; Butler, J.J., Jr.; Pan, Y.; Lei, X.; Wada, Y. Human Intervention Will Stabilize Groundwater Storage across the North China Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, L.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Land Subsidence Caused by Groundwater Depletion in the North China Plain During the Past Six Decades. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, F.; Lemckert, C.; Zhang, H. Impacts of Climate Change on Temperature and Evaporation from a Large Reservoir in Australia. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Levine, X.J. Water Vapor and the Dynamics of Climate Changes. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Zou, Z.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Menarguez, M.A.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Ye, H. Gainers and Losers of Surface and Terrestrial Water Resources in China During 1989–2016. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Qi, Y. Estimation of Evaporation of Different Cover Types Using a Stable Isotope Method: Pan, Bare Soil, and Crop Fields in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Du, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, C.; Jian, H.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Bian, D.; Cui, Y. Sub-Surface Plastic Mulching Reduced Evaporation During the Fallow Season and Increased Spring Maize Yield in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 143, 126708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, N. Remote Sensing Estimation of Water Clarity for Various Lakes in China. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Detecting, Extracting, and Monitoring Surface Water from Space Using Optical Sensors: A Review. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, M.; Burggraaff, O.; Gurlin, D.; Saranathan, A.M.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Giardino, C.; Braga, F.; Bresciani, M.; Pellegrino, A.; Pinardi, M.; et al. On the Generalization Ability of Probabilistic Neural Networks for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Absorption Properties across Optically Complex Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 328, 114820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Y.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Du, S. Time-Series China Urban Land Use Mapping (2016–2022): An Approach for Achieving Spatial-Consistency and Semantic-Transition Rationality in Temporal Domain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 312, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Feng, M.; Wang, C.; Li, X. A high-Resolution Inland Surface Water Body Dataset for the Tundra and Boreal Forests of North America. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 3349–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellman, B.; Sullivan, J.A.; Kuhn, C.; Kettner, A.J.; Doyle, C.S.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Erickson, T.A.; Slayback, D.A. Satellite Imaging Reveals Increased Proportion of Population Exposed to Floods. Nature 2021, 596, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-Resolution Mapping of Global Surface Water and Its Long-Term Changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Long, D.; Wang, Y.; Woolway, R.I. Global Dominance of Seasonality in Shaping Lake-Surface-Extent Dynamics. Nature 2025, 642, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasechko, S.; Seybold, H.; Perrone, D.; Fan, Y.; Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.G.; Fallatah, O.; Kirchner, J.W. Rapid Groundwater Decline and Some Cases of Recovery in Aquifers Globally. Nature 2024, 625, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Duan, Q.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Gong, W.; Di, Z.; Lei, X.; Liao, W.; Huang, Z. The Effectiveness of the South-to-North Water Diversion Middle Route Project on Water Delivery and Groundwater Recovery in North China Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global Lake Responses to Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Study on Agricultural Cultivation Development Layout Based on the Matching Characteristic of Water and Land Resources in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Cao, G.; Kristensen, M.; Refsgaard, J.; Rasmussen, M.; He, X.; Liu, J.; Shu, Y.; Zheng, C. Integrated Hydrological Modeling of the North China Plain and Implications for Sustainable Water Management. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3759–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Liu, C. Improving Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Crops in the North China Plain—Measurements and Modelling. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 48, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Yu, Q.; Wu, D.; Xia, J. Climate, Agricultural Production and Hydrological Balance in the North China Plain. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Metternicht, G.; Hostert, P.; Fensholt, R.; Chowdhury, R.R. Remote Sensing and Geospatial Technologies in Support of a Normative Land System Science: Status and Prospects. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 38, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; Fosnight, E.A.; Shaw, J.; Masek, J.G.; Roy, D.P. The Global Landsat Archive: Status, Consolidation, and Direction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Roy, D.P.; Radeloff, V.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Anderson, M.C.; Johnson, D.M.; Healey, S.; Zhu, Z.; Scambos, T.A.; Pahlevan, N.; et al. Fifty Years of Landsat Science and Impacts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Fan, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Zhan, P.; Luo, S.; Yuan, C.; et al. A Comprehensive Geospatial Database of Nearly 100000 Reservoirs in China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4017–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J.; Wu, J.; Li, B. Improved Maps of Surface Water Bodies, Large Dams, Reservoirs, and Lakes in China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 3757–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, B.; Liermann, C.R.; Revenga, C.; Vörösmarty, C.; Fekete, B.; Crouzet, P.; Döll, P.; Endejan, M.; Frenken, K.; Magome, J. High-Resolution Mapping of the World’s Reservoirs and Dams for Sustainable River-Flow Management. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, T.; Wu, G. Quadrennial Series Dataset of Coastal Aquaculture Distribution of China Based on Landsat Images (1990–2022). J. Glob. Chang. Data Discov. 2023, 7, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, C.; Su, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Global Mapping of the Landside Clustering of Aquaculture Ponds from Dense Time-Series 10 m Sentinel-2 Images on Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Mapping Global Urban Boundaries from the Global Artificial Impervious Area (GAIA) Data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Gao, H. Evaporative Water Loss of 1.42 Million Global Lakes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the Volume and Age of Water Stored in Global Lakes Using a Geo-Statistical Approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Gao, H. Estimating Reservoir Evaporation Losses for the United States: Fusing Remote Sensing and Modeling Approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Eamus, D.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.H.; Yu, Q. Use of Satellite Leaf Area Index Estimating Evapotranspiration and Gross Assimilation for Australian Ecosystems. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, M.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J. Annual Improved Maps to Understand the Complete Evolution of 9 Thousand Lakes on the Tibetan Plateau in 1991–2023. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 217, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. Divergent Trends of Open-Surface Water Body Area in the Contiguous United States from 1984 to 2016. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 2018, 115, 3810–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, Z.; Xiao, X. Exacerbating Water Shortage Induced by Continuous Expansion of Surface Artificial Water Bodies in the Yellow River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 633, 130979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Dong, J.; Gao, Z.; Liu, B.; Xiao, X. Is Satellite-Observed Surface Water Expansion a Good Signal to China’s Largest Granary? Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.E. Evaporation of Water with Emphasis on Applications and Measurements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, S.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Quan, J. A global Assessment of Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Increase Due to Surface Water Area Change. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and Environment. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1965, 19, 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Skrzypek, G.; Mydłowski, A.; Dogramaci, S.; Hedley, P.; Gibson, J.J.; Grierson, P.F. Estimation of Evaporative Loss Based on the Stable Isotope Composition of Water Using Hydrocalculator. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ke, L.; Pan, H.; Zhan, S.; Liu, K.; Ma, R. Long-Term Surface Water Changes and Driving Cause in Xiong’an, China: From Dense Landsat Time Series Images and Synthetic Analysis. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Zou, Z.; Xiao, X. Rebound of Surface and Terrestrial Water Resources in Mongolian Plateau Following Sustained Depletion. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevermann, H.; Aminzadeh, M.; Madani, K.; Shokri, N. Quantifying Water Evaporation from Large Reservoirs: Implications for Water Management in Water-Stressed Regions. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Ryan, M.C.; Li, C.; Sun, B. Understanding the Role of Groundwater in a Remote Transboundary Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water 2017, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Xi, Y.; Xiao, X.; Doughty, R.B.; Liu, M.; Jia, M. Rapid Expansion of Coastal Aquaculture Ponds in China from Landsat Observations During 1984–2016. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 82, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Aquaculture pond fertilization. CABI Rev. 2018, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Investigation of Push-Flow Aeration on Improving Water Quality in Urban Lakes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R. Global Water Resources and the Role of Groundwater in a Resilient Water Future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Xia, J. Hydrological Cycle and Water Resources in a Changing World: A Review. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Gleeson, T. Regional Strategies for the Accelerating Global Problem of Groundwater Depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Du, J.; Wang, T. Detecting Seasonal and Long-Term Vertical Displacement in the North China Plain Using GRACE and GPS. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Long-Term and Seasonal Variation in Groundwater Storage in the North China Plain Based on GRACE. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Di, D.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Q. Utilizing Grace-Based Groundwater Drought Index for Drought Characterization and Teleconnection Factors Analysis in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G.; Shum, C.; Yang, K.; Piao, S.; Sheng, Y.; Yi, S.; Li, J. Regional Differences of Lake Evolution across China During 1960s–2015 and Its Natural and Anthropogenic Causes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, N.; Dong, J. Examining Earliest Identifiable Timing of Crops Using All Available Sentinel 1/2 Imagery and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 161, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Du, B.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Jia, M.; Zeng, Y.; Song, K.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y. National Wetland Mapping in China: A New Product Resulting from Object-Based and Hierarchical Classification of Landsat 8 Oli images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mao, D.; Xiao, X.; Song, K.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Wang, Z. Interannual Changes of Coastal Aquaculture Ponds in China at 10-M Spatial Resolution During 2016–2021. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Druce, D.; Kittel, C.M.M.; Tøttrup, C.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Impacts of Water Resources Management on Land Water Storage in the North China Plain: Insights from Multi-Mission Earth Observations. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 1990 | ||||
| Classification | Ground References | Total | User accuracy | |
| Water | Non-water | |||
| Water | 4859 | 602 | 5375 | 90.1% |
| Non-water | 645 | 23,994 | 24,639 | 97.38% |
| Total | 5508 | 24,596 | 30,100 | Accuracy = 95.9% |
| Producer accuracy | 88.28% | 97.55% | Kappa = 0.860 | |
| 2000 | ||||
| Classification | Ground References | Total | User accuracy | |
| Water | Non-water | |||
| Water | 4472 | 645 | 5117 | 84.39% |
| Non-water | 301 | 24,725 | 25,026 | 98.8% |
| Total | 4773 | 25,370 | 30,143 | Accuracy = 96.8% |
| Producer accuracy | 93.69% | 97.45% | Kappa = 0.886 | |
| 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Ground References | Total | User accuracy | |
| Water | Non-water | |||
| Water | 4343 | 473 | 4816 | 90.18% |
| Non-water | 387 | 23,908 | 24,295 | 98.41% |
| Total | 4730 | 24,381 | 29,111 | Accuracy = 97.1% |
| Producer accuracy | 91.82% | 98.06% | Kappa = 0.892 | |
| 2020 | ||||
| Classification | Ground References | Total | User accuracy | |
| Water | Non-water | |||
| Water | 4601 | 387 | 4988 | 92.24% |
| Non-water | 817 | 24,295 | 25,112 | 96.75% |
| Total | 5418 | 24,682 | 30,100 | Accuracy = 96% |
| Producer accuracy | 84.92% | 98.43% | Kappa = 0.915 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tian, S.; Cui, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, X.; Han, B. Artificial Surface Water Construction Aggregated Water Loss Through Evaporation in the North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152698
Wang Z, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Tian S, Cui Y, Tian H, Liu X, Han B. Artificial Surface Water Construction Aggregated Water Loss Through Evaporation in the North China Plain. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152698
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ziang, Yan Zhou, Wenge Zhang, Shimin Tian, Yaoping Cui, Haifeng Tian, Xiaoyan Liu, and Bing Han. 2025. "Artificial Surface Water Construction Aggregated Water Loss Through Evaporation in the North China Plain" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152698
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhou, Y., Zhang, W., Tian, S., Cui, Y., Tian, H., Liu, X., & Han, B. (2025). Artificial Surface Water Construction Aggregated Water Loss Through Evaporation in the North China Plain. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152698










