A Refined Multipath Correction Model for High-Precision GNSS Deformation Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. GNSS Single-Difference Residuals
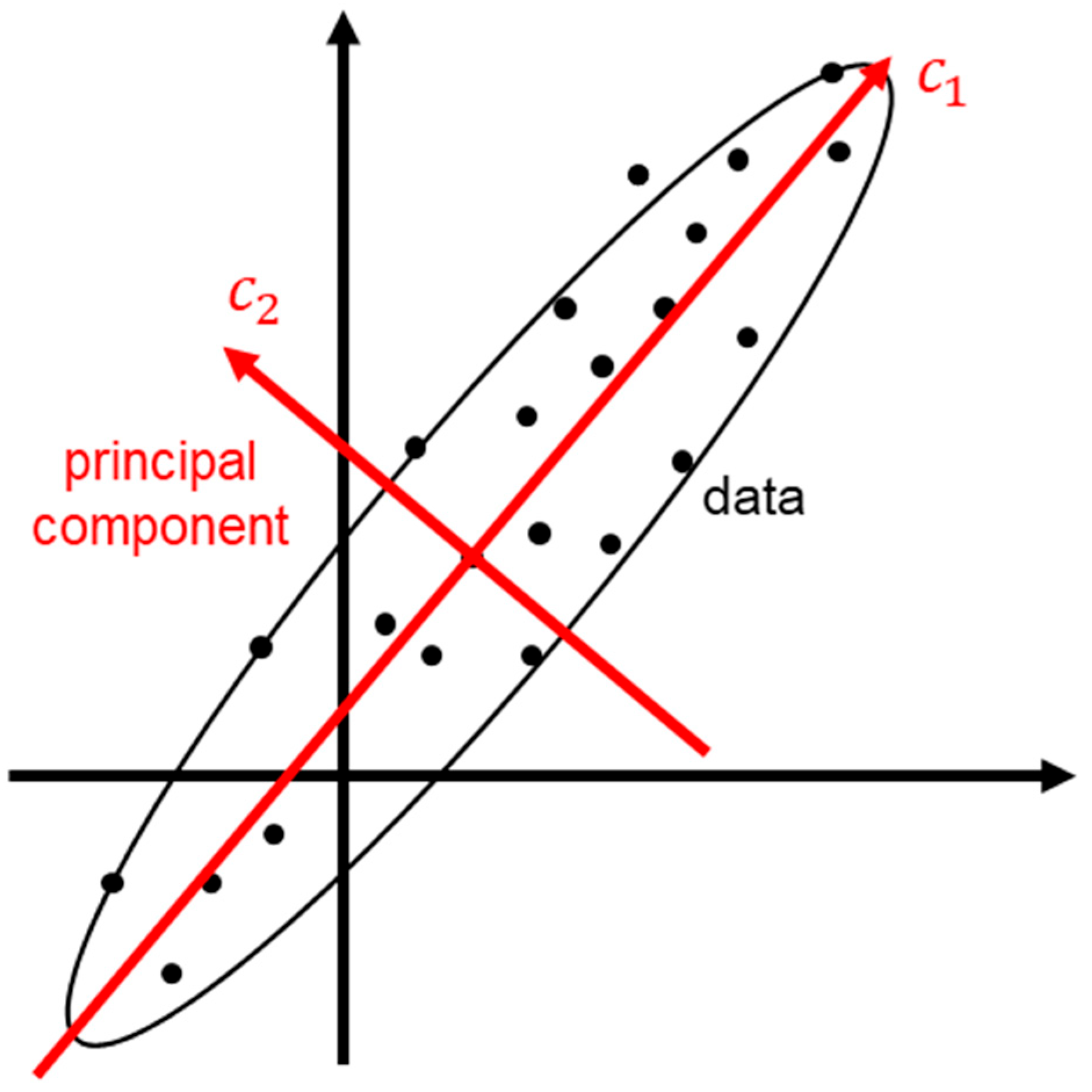
2.2. Method for Separating Multipath Errors from Residuals
2.3. Hemispherical Model Based on Trend Surface Analysis
2.4. Data and Strategies
- Residual Calculation: Derive double-difference residuals by resolving ambiguities using a double-difference observation model and corresponding processing strategies, then convert these to single-difference residuals through a zero-mean baseline adjustment (Section 2.1).
- Multipath Extraction: Apply PCA to the multi-day single-difference residuals to extract the multipath error signal (Section 2.2).
- Sky Grid Partitioning: Divide the station’s sky into grids based on specified intervals and assign the extracted multipath errors to their corresponding grid cells.
- Trend Surface Fitting: Within each grid cell, perform trend surface fitting on the multipath error values (as described in Section 2.3) to build the T-MHM model. Conduct statistical validation of the fitted model; if a fit is not statistically valid, use the mean error in that cell instead.
- Calculating Correction: Determine the satellite elevation and azimuth angles to locate the appropriate grid cell, then compute multipath corrections using either the stored polynomial coefficients or the mean error value.
- Final Positioning: Apply the computed multipath corrections to GNSS observations and perform least-squares estimation to obtain the final positioning results.
3. Results
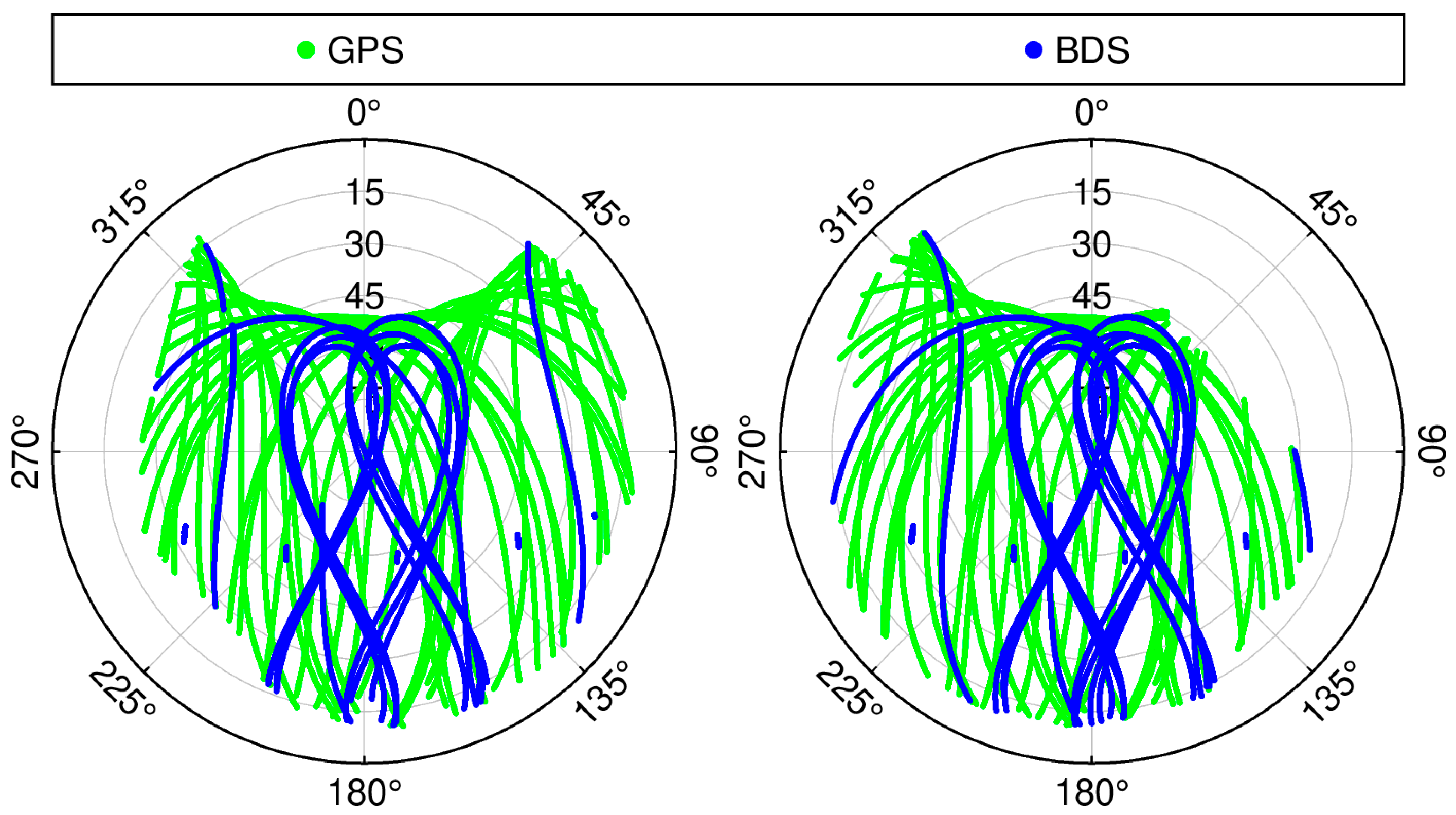
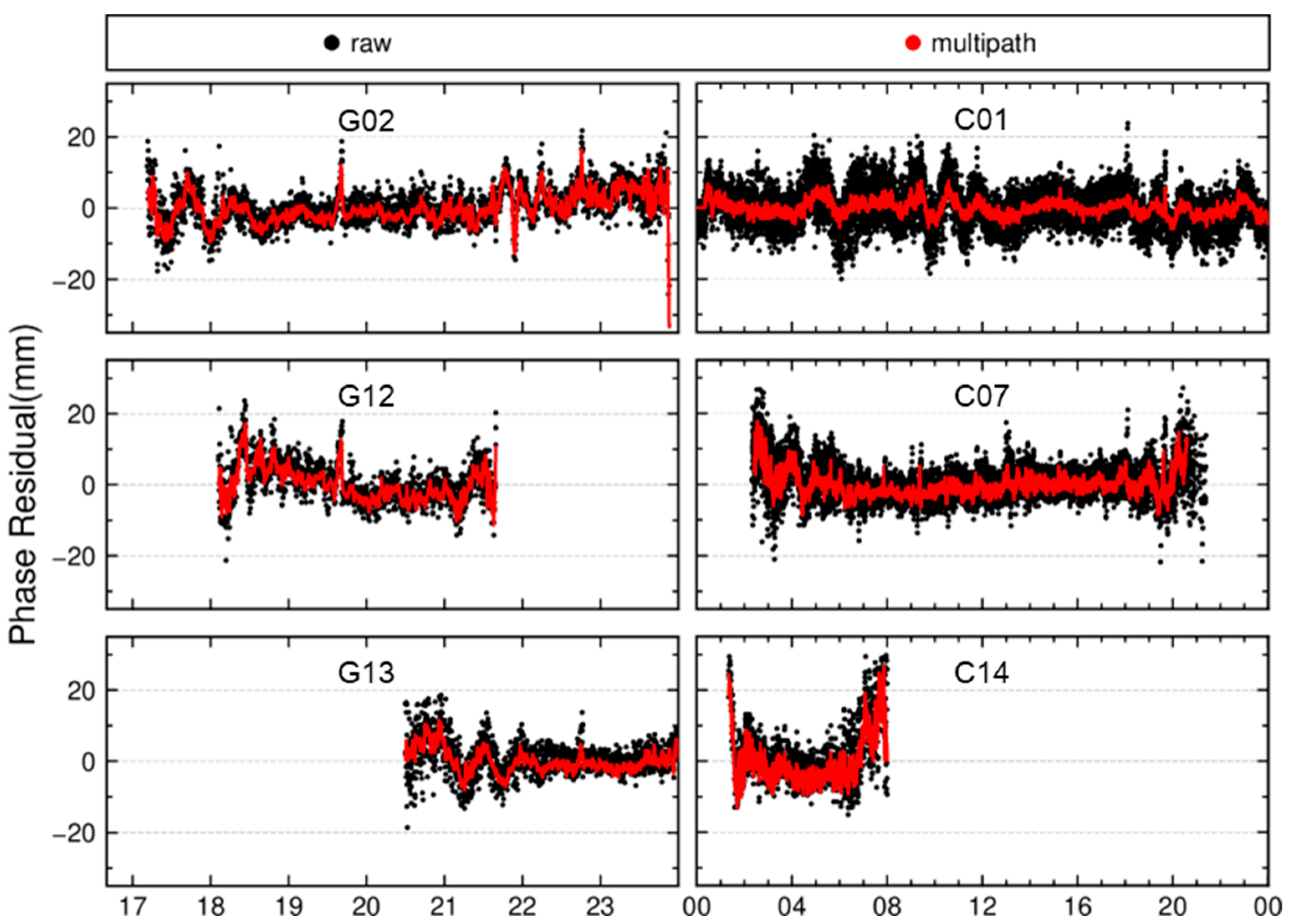
3.1. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Repeatability of Satellite Residuals
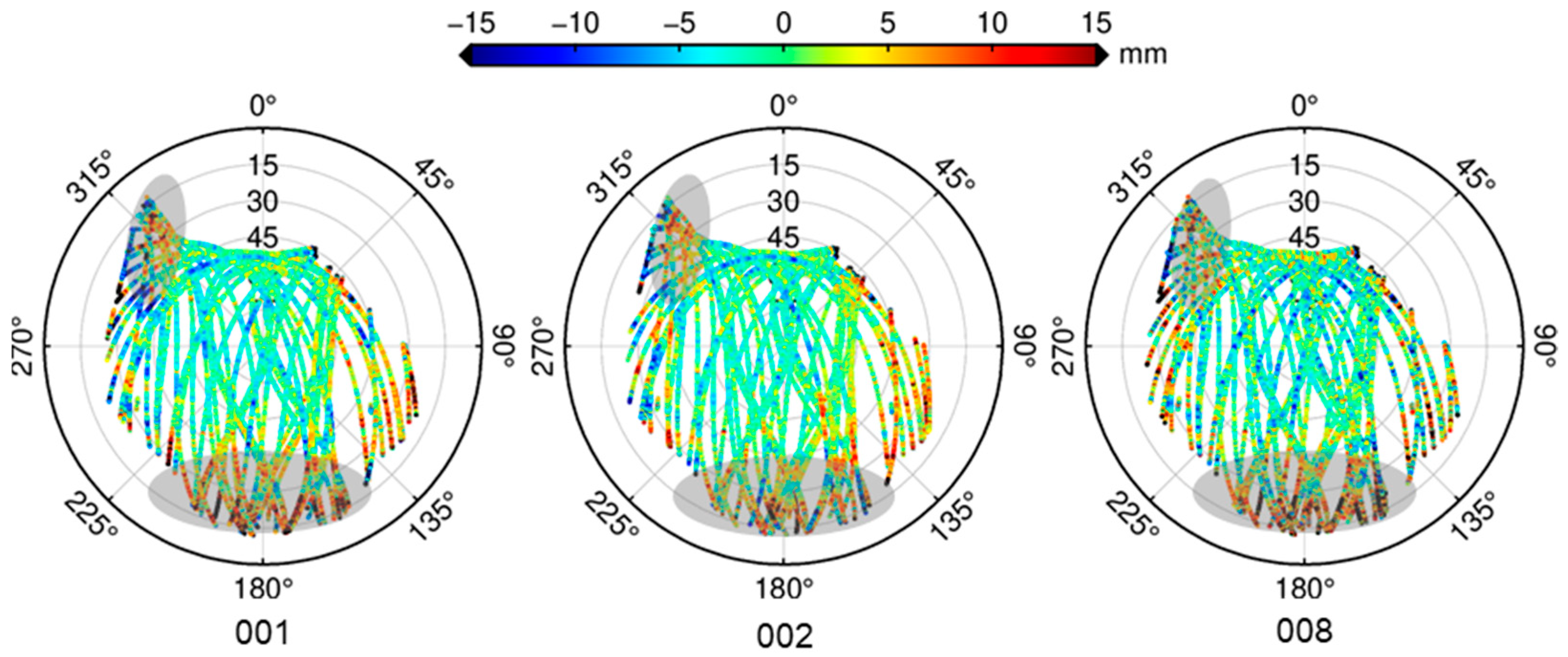
- GEO satellites (e.g., C01) orbit synchronously with Earth’s rotation, resulting in minimal positional variation over the station. As shown in the C01 time series (Figure 4), the GEO satellite is visible throughout the day from the station. One would expect its multipath errors to be relatively stable over time due to its static geometry. However, the residuals exhibit significant temporal trends and cross-day inconsistencies, suggesting the presence of additional unmodeled error sources.
- IGSO satellites (e.g., C07) follow a figure-eight ground track, covering a larger area than GEO satellites. For a station at mid-latitudes (such as in China), the IGSO satellites is visible during most of the day and repeats its ground track approximately every sidereal day. As expected, the C07 residuals exhibit strong repeatability on consecutive days (Figure 4), similarly to the GPS case.
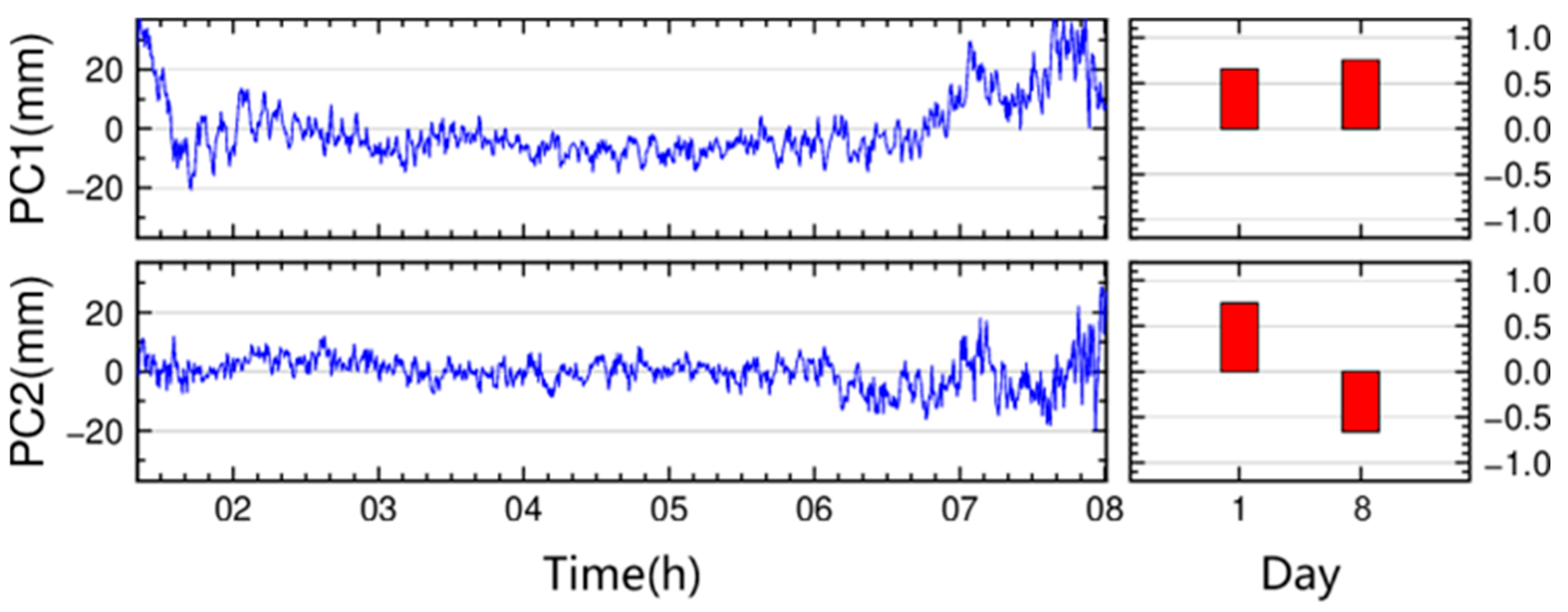
- MEO satellites (e.g., C14) have a longer revisit period of about seven sidereal days. The C14 residuals in Figure 4 illustrate that residual patterns on Day 001 vs. Day 002 (adjacent days) differ significantly in both shape and time coverage (because the satellite’s pass times differ), whereas Day 001 vs. Day 008 (seven days apart) show much higher correlation and more similar trends. This is consistent with the ~7-day repeat cycle for BDS MEO orbits.
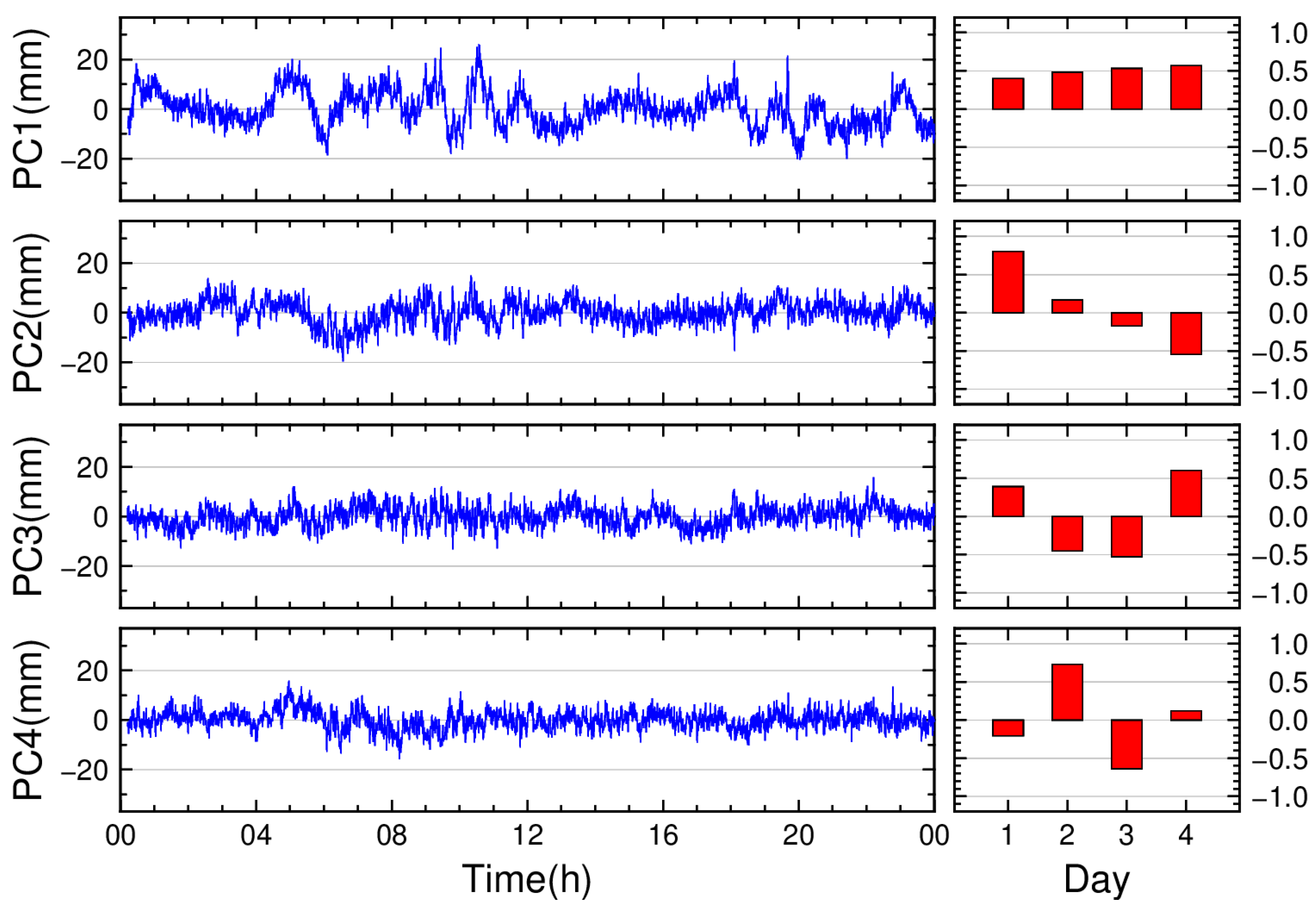
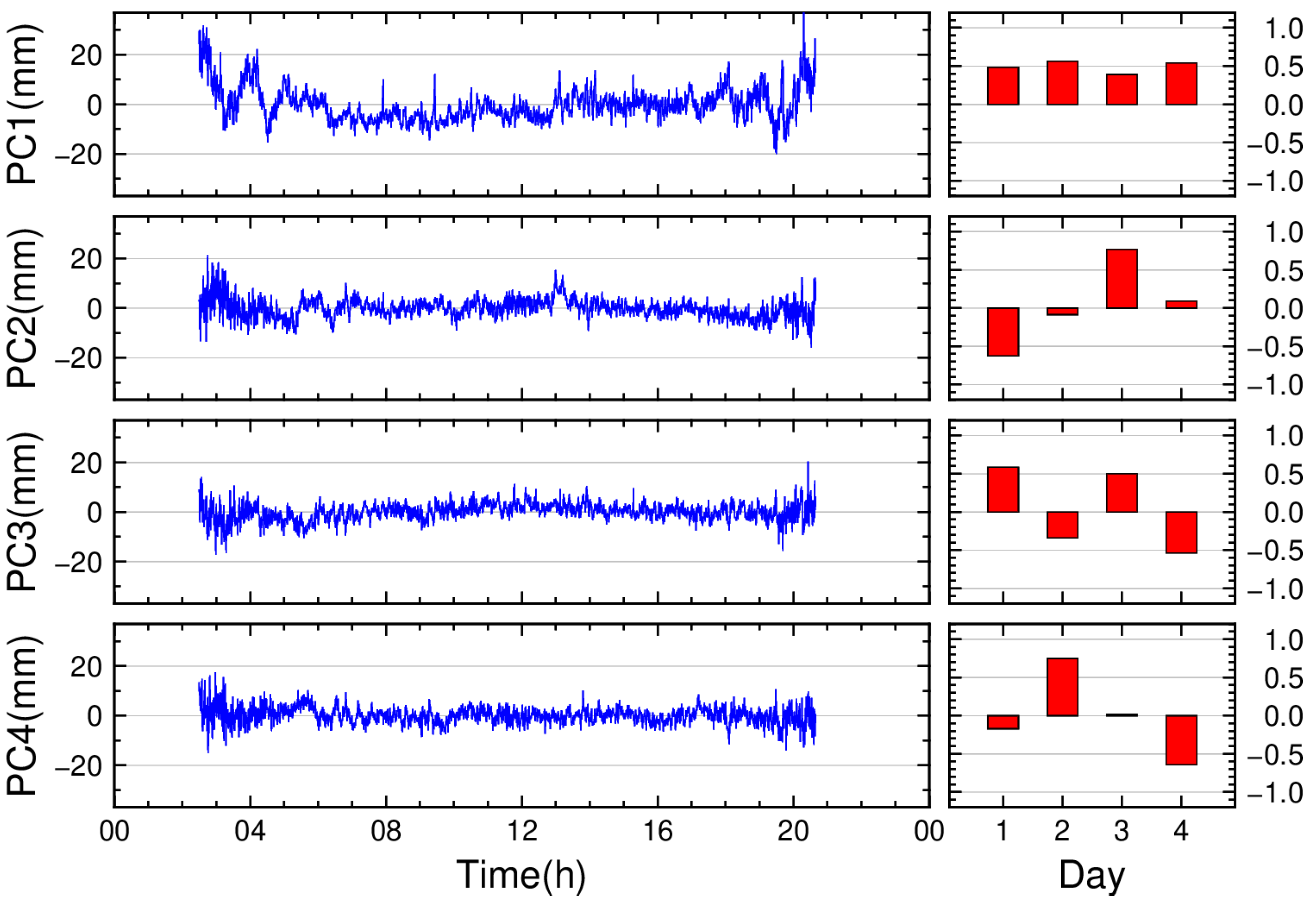
3.2. Identification of Multipath Errors in Residual Signals
- BDS GEO satellites: The daily coefficients of PC1 exhibit minor variations across days (maximum difference: 0.16), with a multi-day average of 0.50.
- BDS IGSO satellites: The daily coefficients of PC1 show a maximum difference of 0.17 between days, averaging 0.50.
- BDS MEO satellites: The two-day coefficient difference for PC1 is 0.09, with an average of 0.7.
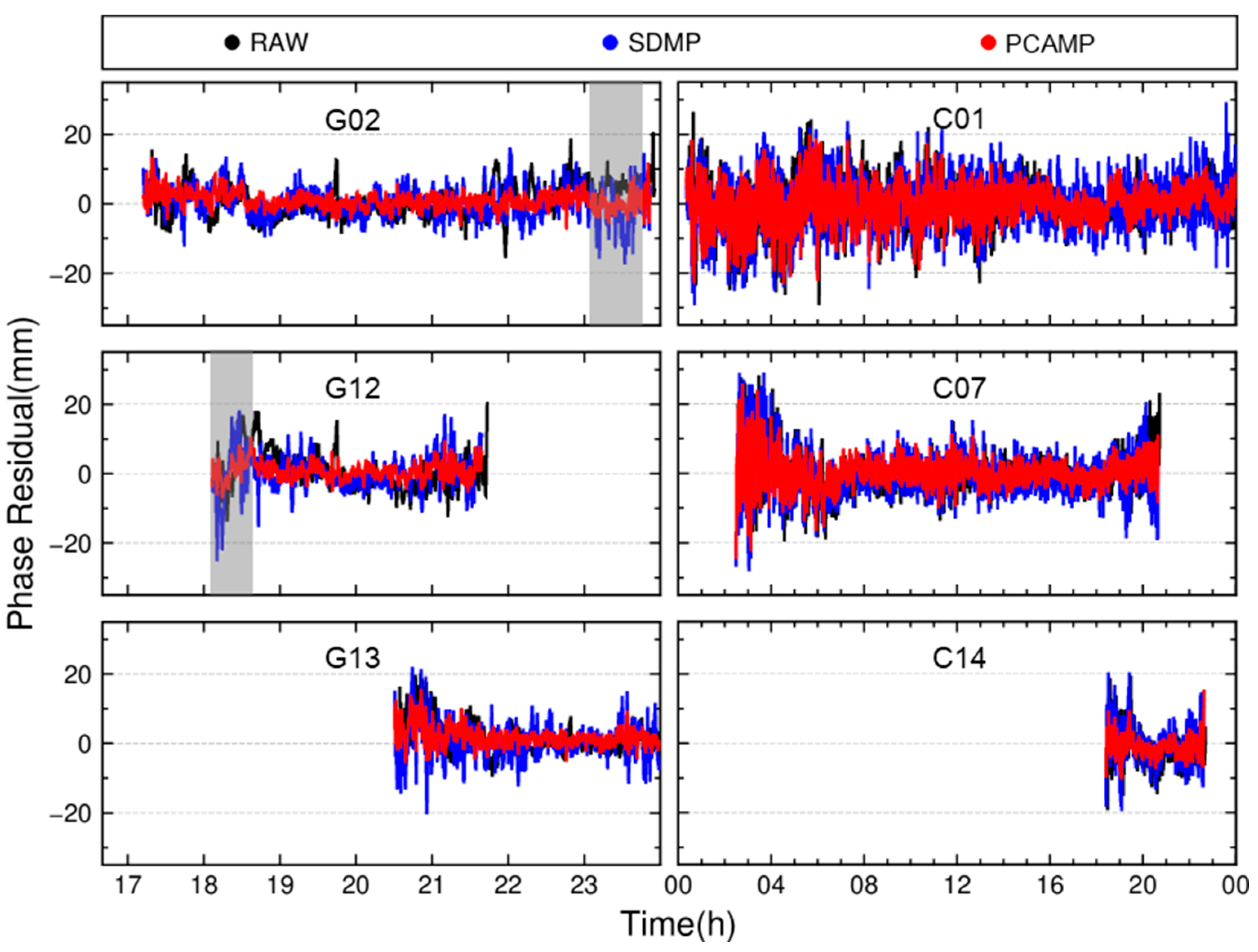
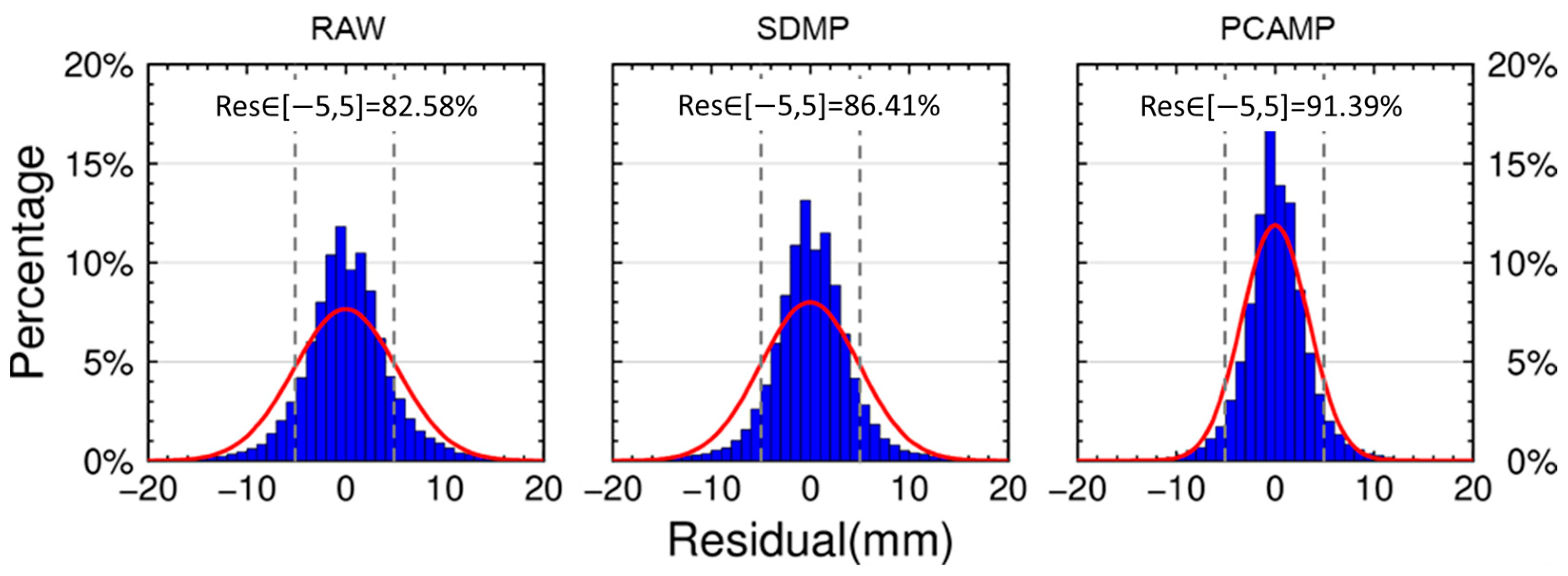
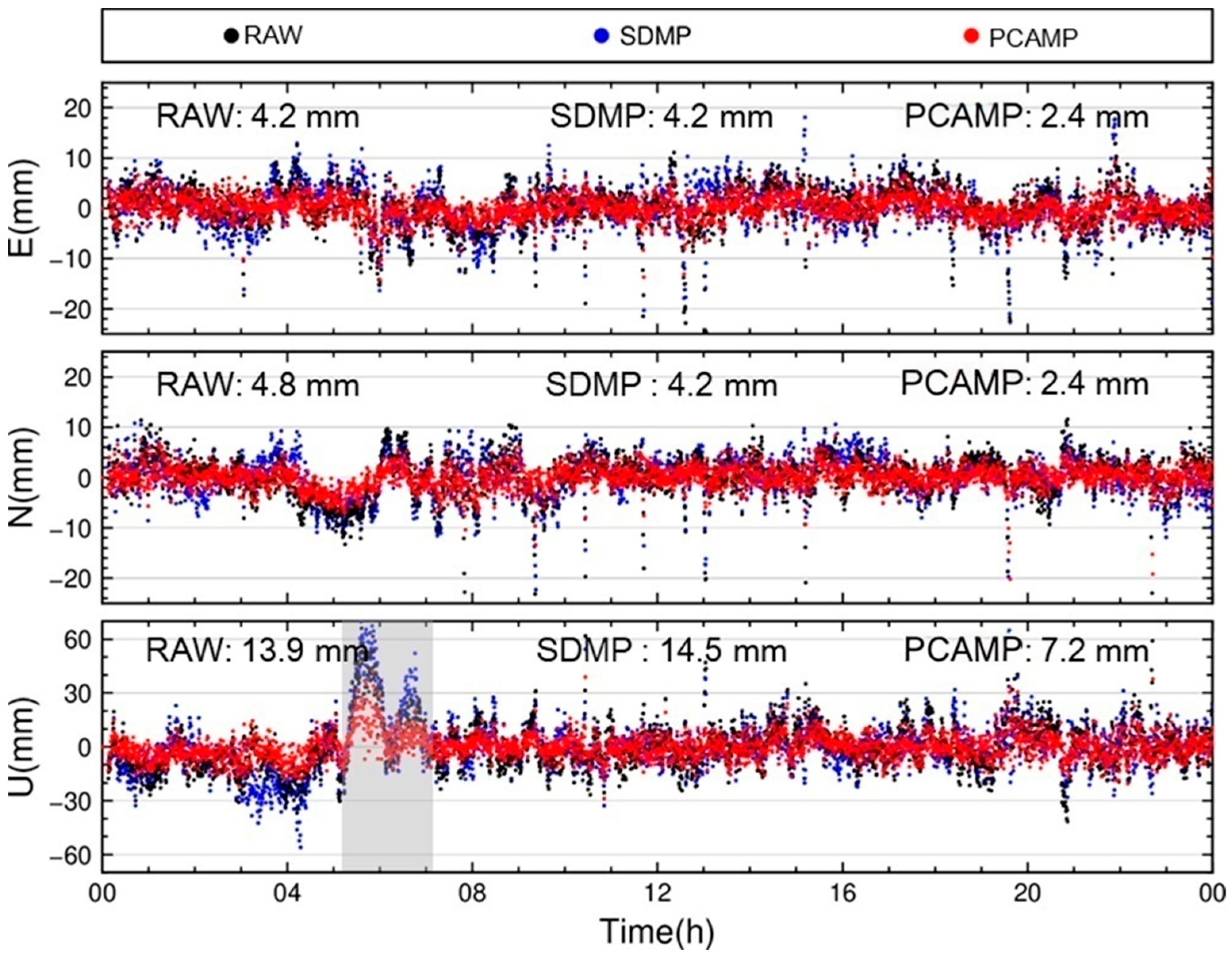
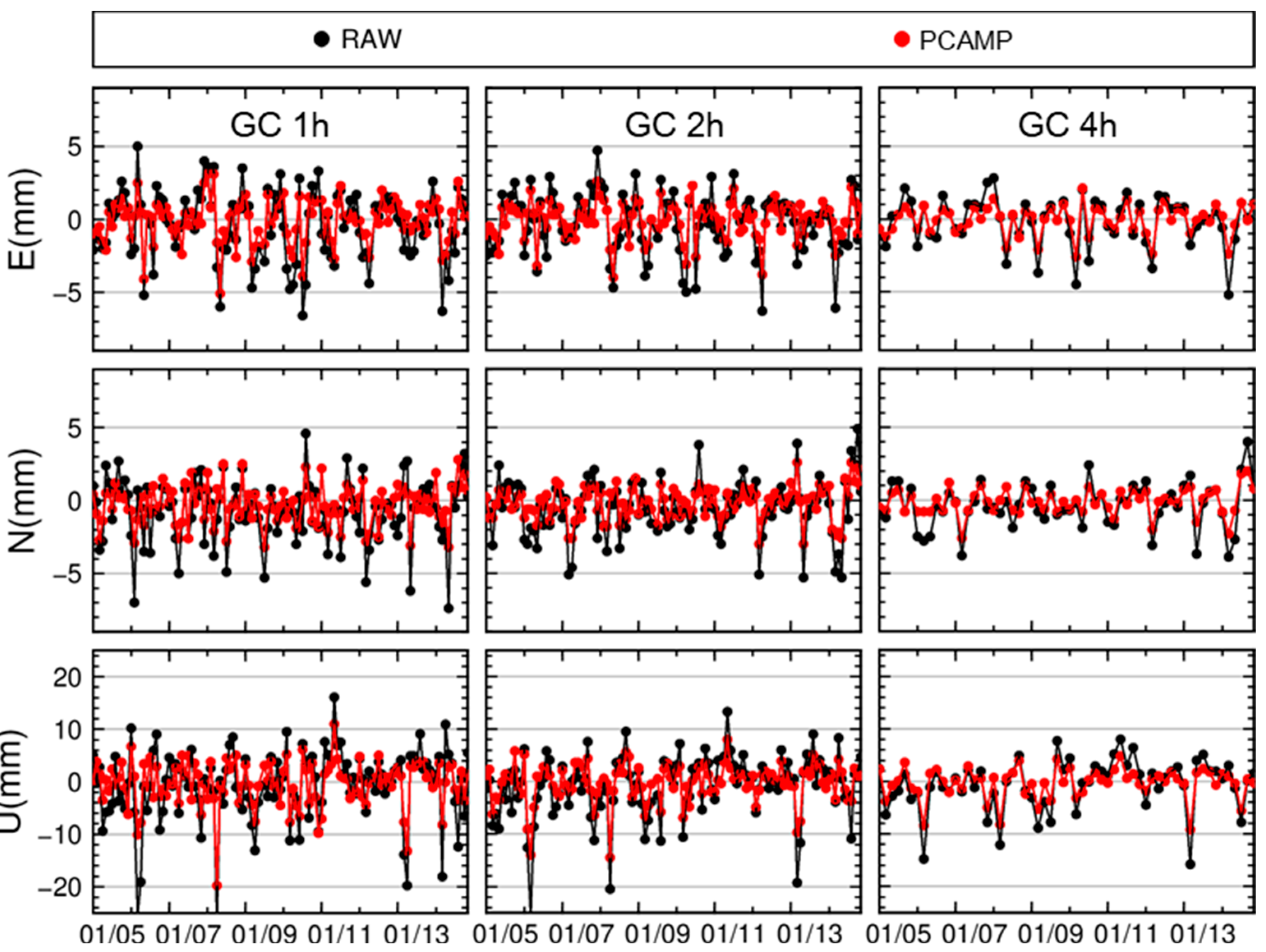
3.3. Model Correction and Positioning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MHM | Multipath Hemispherical Maps |
| T-MHM | MHM by incorporating trend-surface analysis |
| PC | Principal Component |
References
- Groves, P.D.; Jiang, Z. Height Aiding, C/N-0 Weighting and Consistency Checking for GNSS NLOS and Multipath Mitigation in Urban Areas. J. Navig. 2013, 66, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Song, J.; Ni, S. Overview of Multipath Mitigation Technology in Global Navigation Satellite System. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 1071539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, F.K.; Hartinger, H.; Troyer, L. GPS Signal Diffraction Modelling: The Stochastic SIGMA-δ Model. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Mayer, M.; Heck, B. Improving the Stochastic Model of GNSS Observations by Means of SNR-Based Weighting. In Observing Our Changing Earth; Sideris, M.G., Ed.; Springer-Verlag Berlin: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 133, pp. 725–734. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri-Simkooei, A.R.; Jazaeri, S.; Zangeneh-Nejad, F.; Asgari, J. Role of Stochastic Model on GPS Integer Ambiguity Resolution Success Rate. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, A.; Meng, X.; Zhao, D.; Hancock, C. GNSS Carrier-Phase Multipath Modeling and Correction: A Review and Prospect of Data Processing Methods. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, R.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W.; An, X.; He, Q.; Chen, Q. A Refined SNR Based Stochastic Model to Reduce Site-Dependent Effects. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilich, A.; Larson, K.M.; Axelrad, P. Modeling GPS Phase Multipath with SNR: Case Study from the Salar de Uyuni, Boliva. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid. Earth 2008, 113, B04401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, C.J.; Mitchell, C.N. Isolating the Multipath Component in GNSS Signal-to-Noise Data and Locating Reflecting Objects. Radio. Sci. 2011, 46, RS6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Han, S.; Rizos, C. Multipath Mitigation of Continuous GPS Measurements Using an Adaptive Filter. GPS Solut. 2000, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Ding, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. EMD Filter Method and Its Application in GPS Multipath-All Databases. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2006, 35, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Liang, S. Research on Multipath Correction of Observation Range Based on EEMD-MHM Model. Hydrogr. Surv. Charting 2022, 42, 54–58,64. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Feng, W.; Huang, D.; Li, J. Improved Global Navigation Satellite System–Multipath Reflectometry (GNSS-MR) Tide Variation Monitoring Using Variational Mode Decomposition Enhancement. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Ding, X.L.; Zheng, D.W.; Chen, W.; Huang, D.F. Adaptive Wavelet Transform Based on Cross-Validation Method and Its Application to GPS Multipath Mitigation. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Research on GPS Multipath Effect Correction Technology in Urban Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Genrich, J.; Bock, Y. Rapid Resolution of Crustal Motion at Short Ranges with the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid. Earth 1992, 97, 3261–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Ding, X.; Yuan, L.; Xu, Y.; Kwok, K.; Chen, Y. Sidereal Filtering Based on Single Differences for Mitigating GPS Multipath Effects on Short Baselines. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, C.; Ziebart, M. Effectiveness of Observation-Domain Sidereal Filtering for GPS Precise Point Positioning. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, D.C.; Larson, K.M. Finding the Repeat Times of the GPS Constellation. GPS Solut. 2007, 11, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Bilich, A.; Larson, K.M.; Axelrad, P. Modified Sidereal Filtering: Implications for High-Rate GPS Positioning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L22608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, D.; Li, H.; Han, L.; Chen, W. Comparison of Three Methods for Estimating GPS Multipath Repeat Time. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, Z. Characteristics of the BDS-3 Multipath Effect and Mitigation Methods Using Precise Point Positioning. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Dong, D.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Duan, X. An Improved Joint Modeling Method for Multipath Mitigation of GPS, BDS-3, and Galileo Overlapping Frequency Signals in Typical Environments. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.E.; Parkinson, B.W. Mitigating Multipath Error in GPS Based Attitude Determination. In Proceedings of the Guidance and Control 1991; Proceedings of the Annual Rocky Mountain Guidance and Control Conference, Keystone, CO, USA, 2–6 February 1991; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Zeng, Z.; Song, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, M.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, J. Mitigation of Multipath Effect in GNSS Short Baseline Positioning by the Multipath Hemispherical Map. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T.; Luo, X.; Knoepfler, A.; Mayer, M. Generating Statistically Robust Multipath Stacking Maps Using Congruent Cells. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Chen, W.; Dong, D.; Song, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, C. Reduction of Kinematic Short Baseline Multipath Effects Based on Multipath Hemispherical Map. Sensors 2016, 16, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Mitigation of Multipath Effects in Multi-GNSS and Multi-Frequency Precise Point Positioning with Multipath Hemispherical Maps. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Dong, D.; Wang, M.; Cai, M.; Yu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, M. Multipath Mitigation Based on Trend Surface Analysis Applied to Dual-Antenna Receiver with Common Clock. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Chen, W.; Dong, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Y.; Yu, C. Multipath Mitigation in GNSS Precise Point Positioning Based on Trend-Surface Analysis and Multipath Hemispherical Map. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; He, X.; Yuan, H.; Yang, H.; Zeng, J.; Jia, D. An Improved Multipath Mitigation Method Using Central Hemispherical Cell in Precise Point Positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 2721–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Tan, L.; Liu, K.; Chen, M.; Zeng, X. Assessing the Performance of Multipath Mitigation for Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning Ambiguity Resolution. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, C.; Tong, R.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J. Multipath Mitigation in Single-Frequency Multi-GNSS Tightly Combined Positioning via a Modified Multipath Hemispherical Map Method. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Dong, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, B. Multipath Mitigation in GNSS Precise Point Positioning Using Multipath Hierarchy for Changing Environments. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Gao, C.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, Z.; Shang, R. An Improved Multipath Mitigation Method and Its Application in Real-Time Bridge Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ye, S.; Xu, C.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, P.; Chen, H. Undifferenced Zenith Tropospheric Modeling and Its Application in Fast Ambiguity Recovery for Long-Range Network RTK Reference Stations. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ye, S.; Xia, F.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. A Multipath Mitigation Method in Long-Range RTK for Deformation Monitoring. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, P.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Cai, M.; Chen, Y.; Dong, D.; Jiang, W. Enhancing Multi-GNSS Positioning Performances in Harsh Environments via a Refined Joint Troposphere-Multipath Hemispherical Map. GPS Solut. 2025, 29, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tong, R.; Tao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. A Deep Learning-Enhanced Observation-Domain Multipath Mitigation Study of BDS-3. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 7049–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Liu, C.; Tao, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. ConvGRU-MHM: A CNN GRU-Enhanced MHM for Mitigating GNSS Multipath. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yao, Y.; Xu, C.; Hu, M. Method for Establishing the Multipath Adaptive Mitigation Model Considering Deformation Displacement of Monitoring Stations. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Guo, Z.; Yao, Y.; Hu, M.; Pan, P. A Multipath Mitigation Method for Significant Environmental Changes in Deformation Monitoring. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Möller, G.; Soja, B. Machine Learning-Based Multipath Modeling in Spatial Domain Applied to GNSS Short Baseline Processing. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhong, S.; Xi, K.; Shen, H. A Multipath Hemispherical Map with Strict Quality Control for Multipath Mitigation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Fang, P.; Bock, Y.; Webb, F.; Prawirodirdjo, L.; Kedar, S.; Jamason, P. Spatiotemporal Filtering Using Principal Component Analysis and Karhunen-Loeve Expansion Approaches for Regional GPS Network Analysis. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid. Earth 2006, 111, B03405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hua, X.; Yu, K.; Xuan, W.; Lu, T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Accuracy Enhancement of GPS Time Series Using Principal Component Analysis and Block Spatial Filtering. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowinski, S.; Bock, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, P.; Genrich, J. Southern California Permanent GPS Geodetic Array: Spatial Filtering of Daily Positions for Estimating Coseismic and Postseismic Displacements Induced by the 1992 Landers Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid. Earth 1997, 102, 18057–18070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, G.; Wang, J. A New Spatial Filtering Algorithm for Noisy and Missing GNSS Position Time Series Using Weighted Expectation Maximization Principal Component Analysis: A Case Study for Regional GNSS Network in Xinjiang Province. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Tan, L.; Liu, K.; Li, P.; Chen, M.; Zeng, X. Multipath Mitigation for Improving GPS Narrow-Lane Uncalibrated Phase Delay Estimation and Speeding up PPP Ambiguity Resolution. Measurement 2023, 206, 112243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alber, C.; Ware, R.; Rocken, C.; Braun, J. Obtaining Single Path Phase Delays from GPS Double Differences. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2661–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.; Steigenberger, P.; Gendt, G.; Ge, M.; Rothacher, M. Generation of a Consistent Absolute Phase-Center Correction Model for GPS Receiver and Satellite Antennas. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The Least-Squares Ambiguity Decorrelation Adjustment: A Method for Fast GPS Integer Ambiguity Estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D. Research on BDS Medium/long-range Quickly Ambiguity Resolution and Regional Error Correction. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]





| Parameters | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Observations | GPS L1/L2 BDS B1I/B2I |
| Ephemeris | GNSS broadcast ephemeris |
| Sampling interval | 10 s |
| PCO/PCV | Model correction (igs14_2196.atx) [51] |
| Tropospheric delay | GPT2w+ Saastamoinen |
| Tropospheric delay projection function | GMF |
| Ionospheric delay | Double difference elimination |
| Ambiguity fixing | LAMBDA [52] |
| G02 | G12 | G13 | C01 | C07 | C14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 71.0% | 73.0% | 57.2% | 48.3% | 53.5% | 77.8% |
| PC2 | 13.6% | 15.0% | 18.5% | 21.6% | 18.1% | 22.2% |
| PC3 | 9.3% | 6.5% | 15.2% | 15.8% | 14.7% | / |
| PC4 | 6.0% | 5.4% | 9.0% | 14.3% | 13.7% | / |
| Strategy | Content |
|---|---|
| RAW | No multipath correction |
| SDMP | Use Day 005 post-fit residuals as multipath errors estimates to correct Day 006 observations |
| PCAMP | Identify multipath errors via PCA from Days 001–004 residuals and correct Day 006 observations using the T-MHM model |
| GPS | BDS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEO | IGSO | MEO | ||
| RAW | 5.5 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 5.0 |
| SDMP | 4.8 | 6.0 | 5.8 | 4.3 |
| PCAMP | 2.8 | 5.5 | 4.3 | 2.9 |
| E | N | U | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAW | PCAMP | Improvement | RAW | PCAMP | Improvement | RAW | PCAMP | Improvement | |
| 1 h | 2.1 | 1.3 | 38.1 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 42.9 | 5.8 | 3.5 | 39.7 |
| 2 h | 1.8 | 1.1 | 38.9 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 38.9 | 4.8 | 3 | 37.5 |
| 4 h | 1.6 | 0.9 | 43.8 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 40 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 41.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Lu, R.; Zhou, X.; Su, M.; Zhang, M. A Refined Multipath Correction Model for High-Precision GNSS Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152694
Chen Y, Lu R, Zhou X, Su M, Zhang M. A Refined Multipath Correction Model for High-Precision GNSS Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152694
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yan, Ran Lu, Xingyu Zhou, Mingkun Su, and Mingyuan Zhang. 2025. "A Refined Multipath Correction Model for High-Precision GNSS Deformation Monitoring" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152694
APA StyleChen, Y., Lu, R., Zhou, X., Su, M., & Zhang, M. (2025). A Refined Multipath Correction Model for High-Precision GNSS Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152694






