1. Introduction
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs), as the most widely used positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) solution [
1], exhibit some inherent limitations [
2]. The most critical limitation of GNSS signals is the relatively high orbital altitude (greater than 19,000 km) [
3], which induces substantial signal path loss, resulting in low minimal received power (−155dBW–−163dBW) [
4]. This inherent limitation leads to significantly degraded positioning performance or complete service outages in blocked environments such as urban canyons, dense foliage, tunnels, and indoor spaces [
5]. Signal of opportunity-based (SOP-based) positioning has emerged as a promising alternative due to its non-cooperative texture, flexibility, and ubiquitous coverage. Recent studies have explored diverse signal sources, including amplitude modulation/frequency modulation radio broadcasts [
6], Wi-Fi [
7], fifth-generation cellular networks for mobile phones [
8], digital television transmissions [
9], and low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite signals [
10]. Notably, LEO satellite signals have garnered extensive research attention due to their unique advantages: the presence of large constellations offering global coverage [
11], rapidly evolving geometry [
12], enhanced ground-received power [
13], and pronounced Doppler frequency shifts [
14]. Previous studies have achieved positioning accuracy ranging from meters to hundreds of meters by leveraging SOPs from single or multiple LEO satellite constellations [
15,
16,
17,
18].
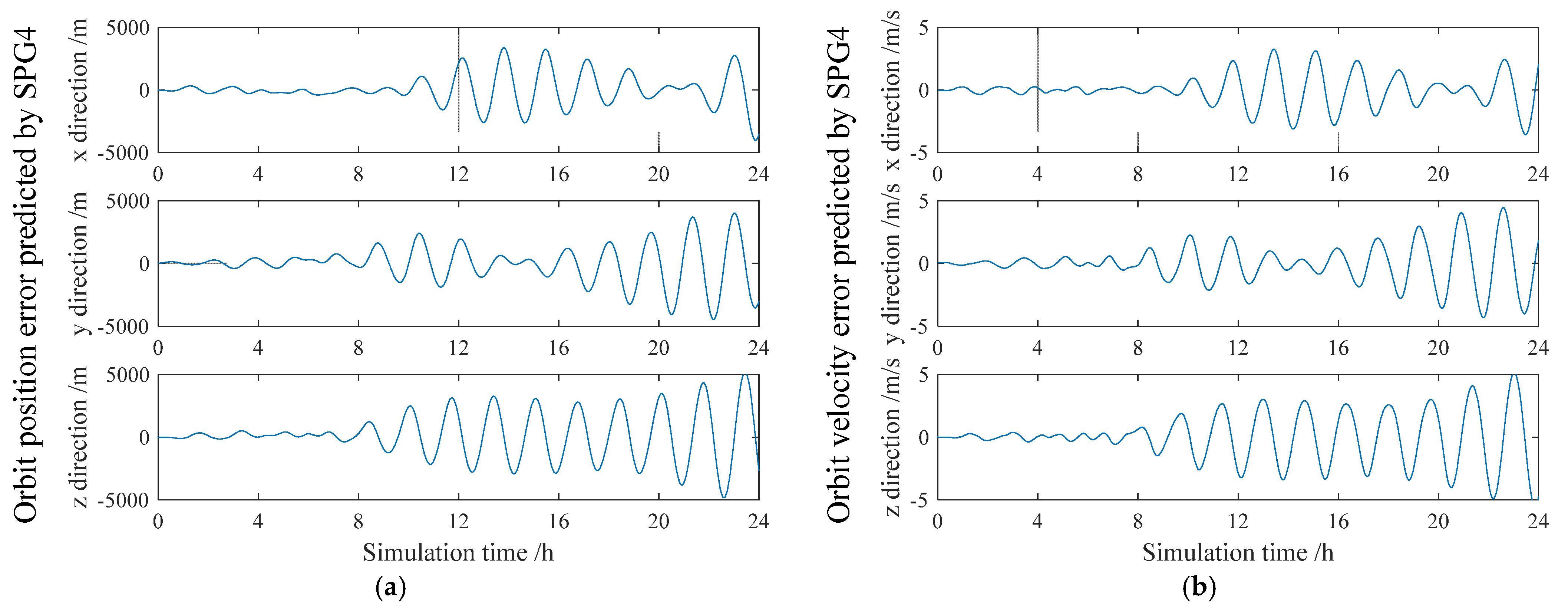
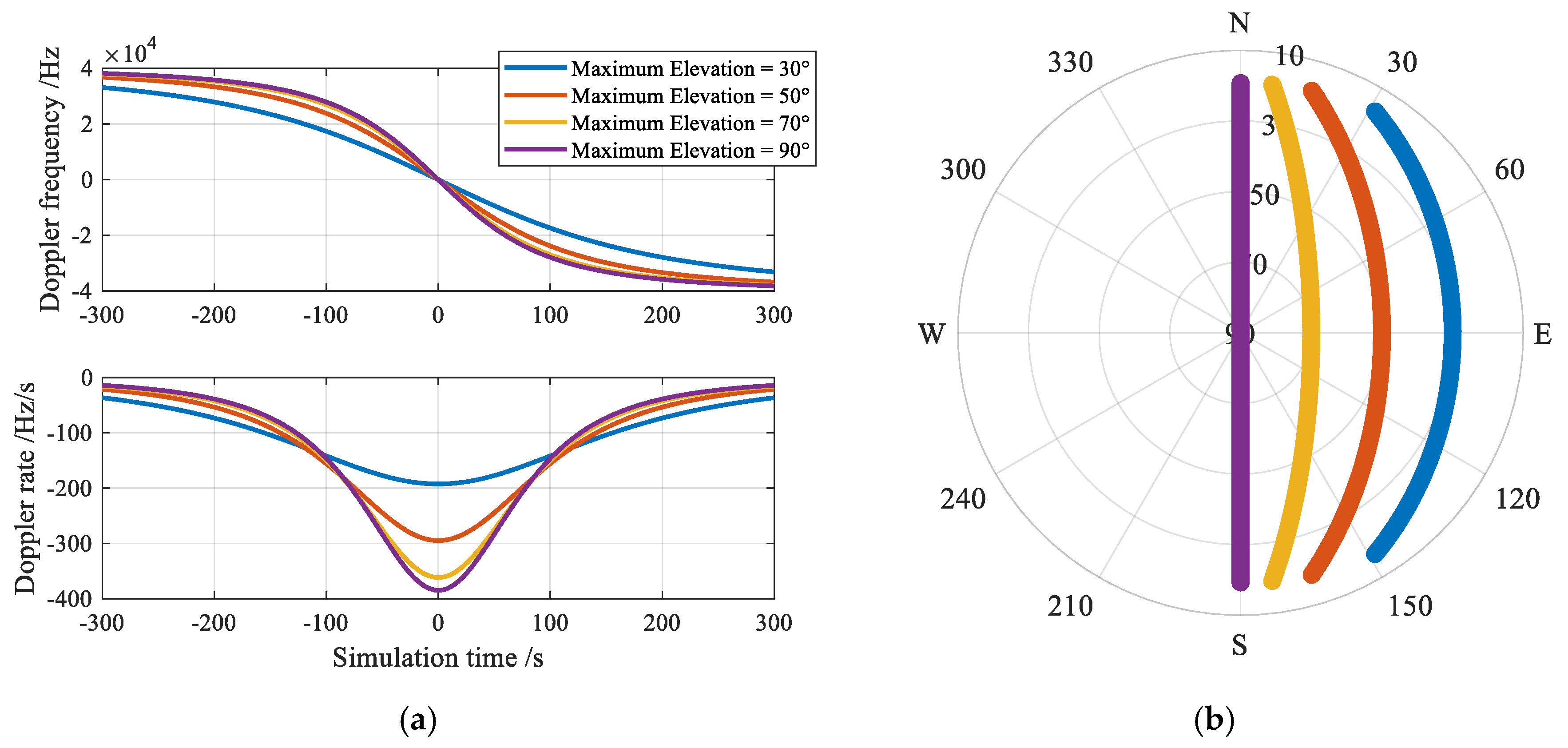
LEO SOP positioning utilizes satellite position and velocity information derived from ephemeris extrapolation as spatiotemporal references, combined with Doppler frequency and timestamp measurements extracted from LEO signals to achieve positioning. However, LEO-SOP-based positioning also suffers from inherent limitations. At the satellite level, the error of Two-Line Element (TLE)-based orbit extrapolation models grows over time [
19]. The geometric configuration of satellites, characterized by their elevation and azimuth angles, directly influences the Geometric Dilution of Precision (GDOP). A lower GDOP value, resulting from favorable satellite distributions, enhances positioning accuracy by reducing the sensitivity of results to observational errors. Conversely, an unfavorable configuration (e.g., satellites clustered in a narrow angular range) elevates GDOP, amplifying error propagation. At the epoch level, the LEO SOP positioning depends on capturing numerous epochs. The introduction of numerous similar epochs from the same satellite may lead to a near-singular observation matrix, resulting in severe degradation of positioning accuracy. At the signal level, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and Doppler frequency exhibit severe fluctuations [
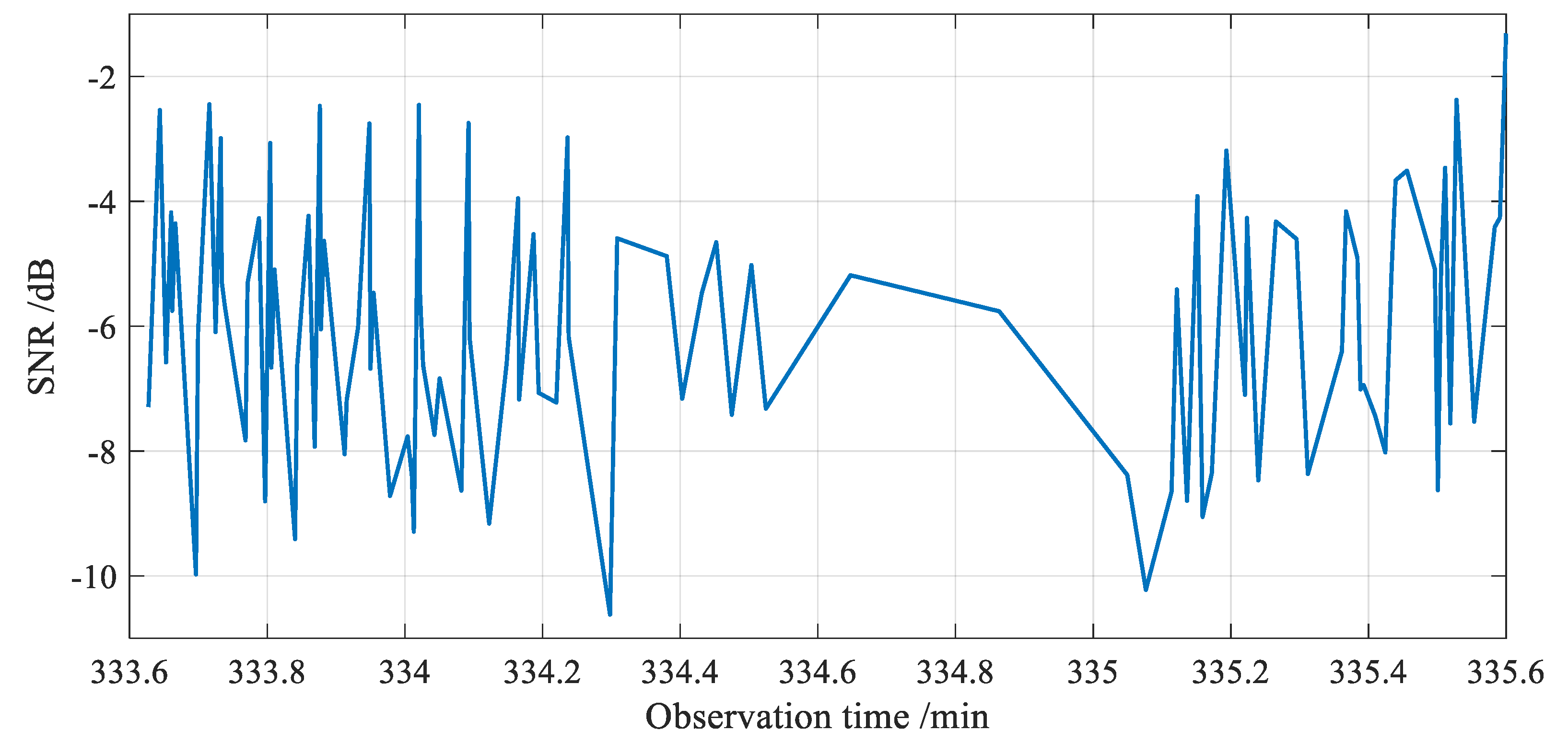
20]. These inherent drawbacks in multiple levels of LEO SOPs limit positioning accuracy.
To mitigate the aforementioned inherent limitations of LEO opportunistic signals, significant research efforts have been made. In 2023, an Orbit Error Compensation and Weighting (OECW) method was proposed to compensate for Doppler frequency errors caused by orbital inaccuracies at each epoch, achieving a 70% improvement in horizontal positioning accuracy [
21]. In 2024, a closed-loop machine learning model for LEO satellite orbit prediction was proposed, effectively reducing predicted orbital errors [
22]. Compared to orbits predicted using the Simplified General Perturbations Version 4 (SGP4) model, the proposed model-based prediction improved LEO SOP positioning accuracy by 84.6%. In 2023, a comprehensive analysis was conducted on the influence of baseline in LEO SOP differential Doppler positioning [
23]. The study achieved a 3D positioning accuracy of 122.1 m for long-baseline scenarios and 1.9 m for zero-baseline cases. At the satellite level, extensive research has been conducted on multi-constellation fusion to optimize the limited geometric configurations inherent in single-constellation systems. In 2024, a research team from Curtin University achieved positioning accuracy of approximately 10 m by performing Doppler-based joint positioning using SOPs from the Starlink, OneWeb, and Iridium constellations [
24]. In 2024, a study employing a differential architecture analyzed and compensated for LEO satellite ephemeris errors [
25]. In the integrated positioning experiment combining LEO opportunistic signals with an Inertial Navigation System (INS), the system achieved an average Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 11.74 m and a final positioning error of 12.01 m. At the signal level, some research achievements have been made to address the limitations of LEO SOPs, including the short availability of signal duration, irregular acquisition times, and large SNR fluctuations. In 2020, a research team from Tsinghua University developed an algorithm utilizing implicit pilot signals in Iridium SOP to enhance Doppler frequency estimation accuracy, achieving a 70% improvement in Doppler estimation accuracy [
26]. That same year, a novel Quadratic Square Accumulating Instantaneous Doppler Estimation (QSA-IDE) algorithm was proposed to improve Doppler estimation accuracy under weak signal conditions [
27]. Experimental results demonstrated that this algorithm achieved a 2D average positioning error of 163 m, representing a 17 m improvement over conventional methods. In 2022, the same research team further refined their approach by proposing a “phase-time” algorithm that leveraged entire Iridium signal frames rather than just pilot segments for Doppler estimation [
28]. Through 800 positioning experiments, this enhanced algorithm was shown to improve positioning accuracy by 31.57–42.81% compared to traditional methods. However, existing studies remain confined to single-factor optimization (satellite/epoch/signal level) and lack joint modeling capability for fusing-level error coupling mechanisms. More fundamentally, conventional methods cannot perceive single-epoch-level signal degradation in real time, leading to severely compromised positioning robustness in complex dynamic scenarios. This paper aims to resolve this core challenge.
This study systematically analyzes multi-level factors affecting LEO SOP positioning accuracy and proposes an innovative Agent-Weighted Recursive Least Squares (RLS) Positioning Framework (AWR-PF). The proposed framework employs an agent to evaluate the credibility of multi-level characteristics and decides epoch weights for real-time RLS iteration. Leveraging the inherent temporal dependency of RLS algorithms, our approach incorporates previously overlooked critical dimensions—epoch arrival sequence and inter-epoch dependencies. Unlike conventional “snapshot” processing, our framework treats positioning as a continuous decision-making process where each epoch generates a positioning state and the agent’s weighting actions directly influence future positioning states.
Our agent learns to predict how current epoch weighting affects future positioning accuracy based on historical epochs. This epoch weighting problem involves complex environmental conditions and strong inter-epoch decision dependencies. Since Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) excels at handling sequential decision-making under uncertainty [
29], we adopt DRL to address this challenge. To enable DRL-based training, we formulate the positioning problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) with multi-dimensional states and discrete actions, effectively transforming it into a model suitable for deep reinforcement learning. As illustrated in
Table 1, this MDP model trains an agent to optimize LEO SOP positioning performance through sequential decision-making.
As an advanced DRL method, Double Deep Q-Network (DDQN) effectively mitigates overestimation bias by decoupling action selection from value estimation [
30]. This method enables dynamic and precise epoch weight allocation, making it particularly suitable for multi-factor, noise-corrupted weighting scenarios in LEO SOP positioning.
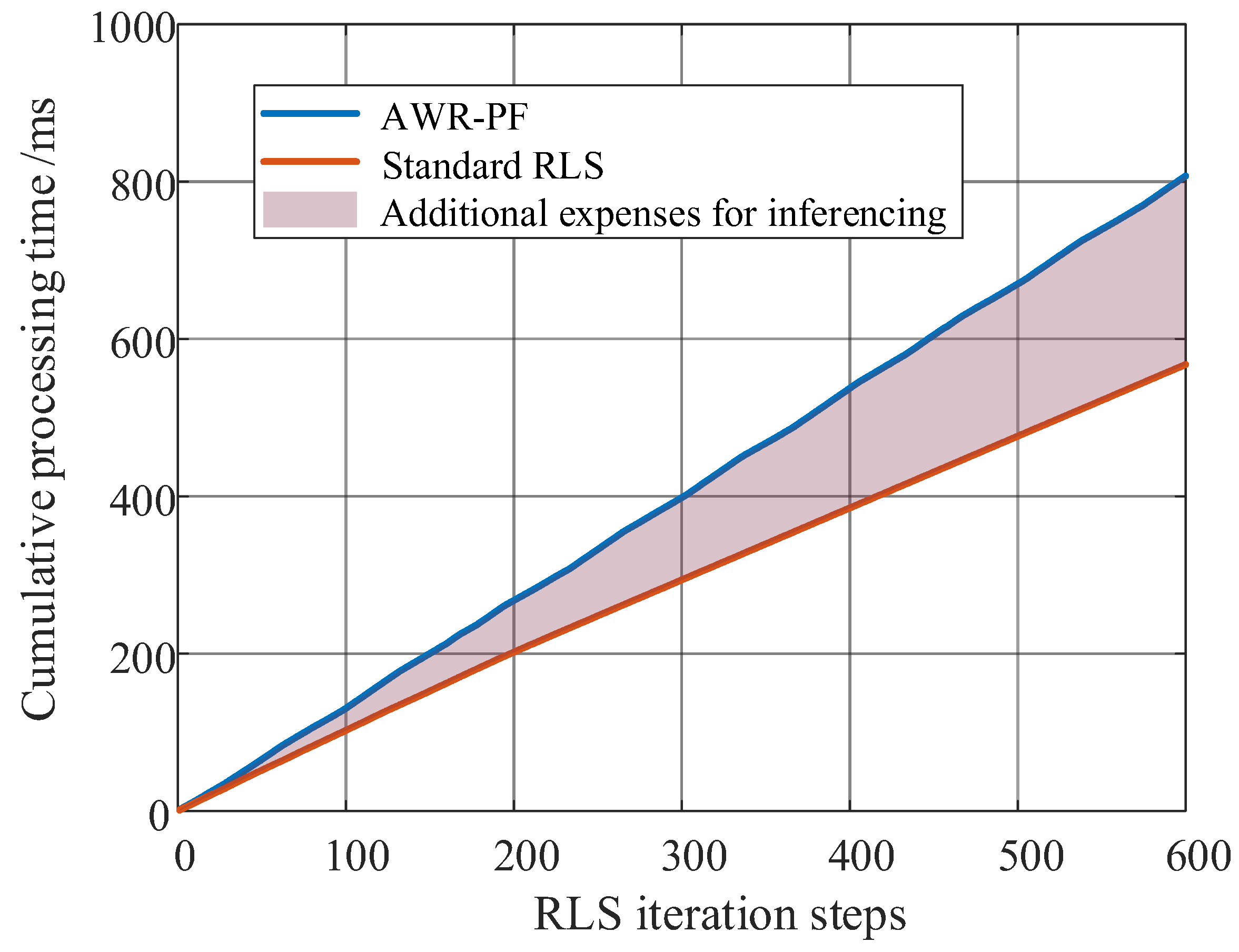
Building upon the DDQN, we developed the DDQN-based Epoch Weighting (DDQN-EW) algorithm by (1) employing a lightweight neural network to extract positioning-relevant features across satellite, epoch, signal, and positioning layers; (2) designing collaborative interaction between the agent and RLS for weight-based decision-making; and (3) formulating a reward mechanism sensitive to positioning error convergence dynamics. This specialized architecture enables intelligent epoch-wise weighting while maintaining computational efficiency for real-time navigation applications.
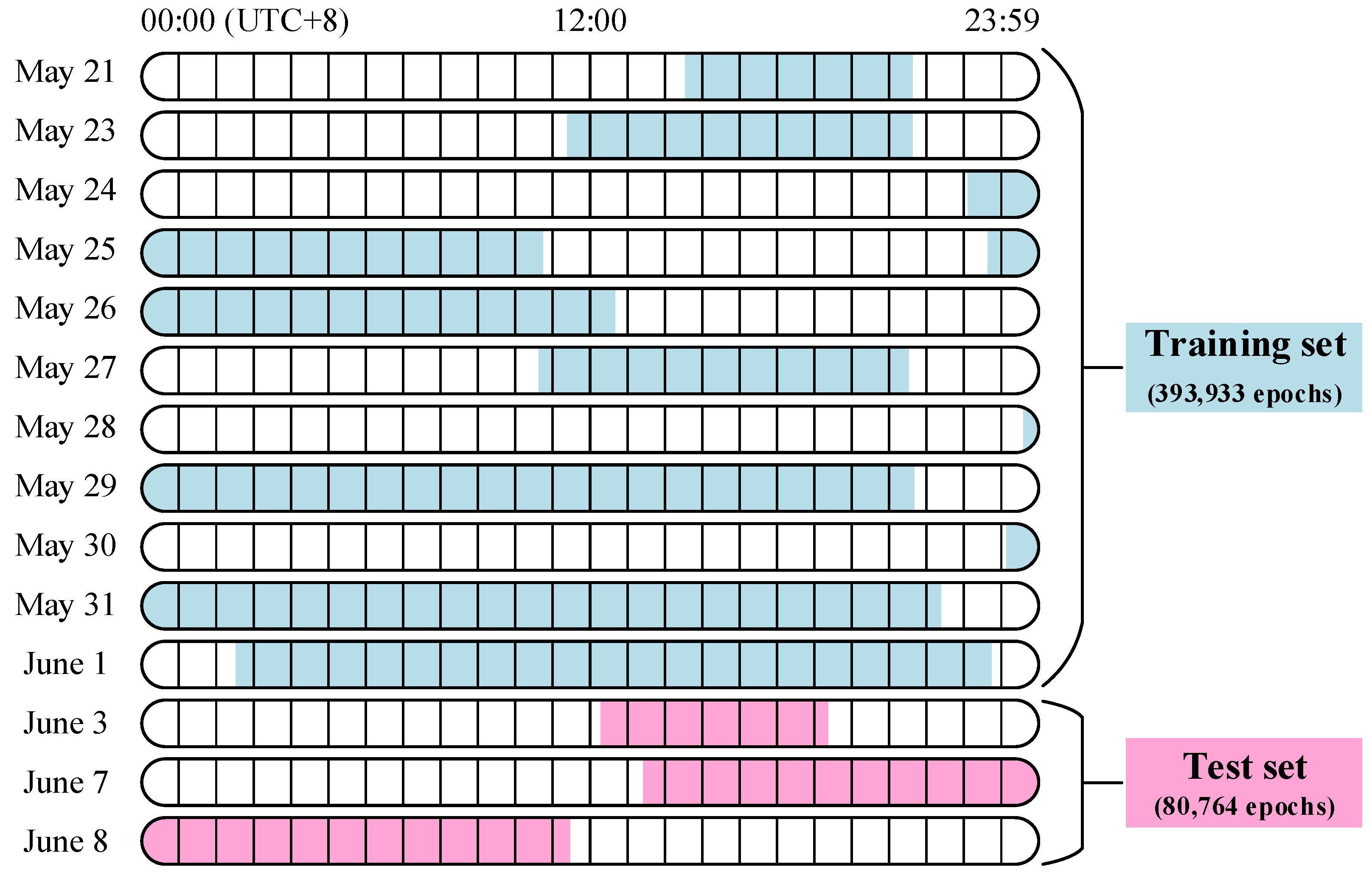
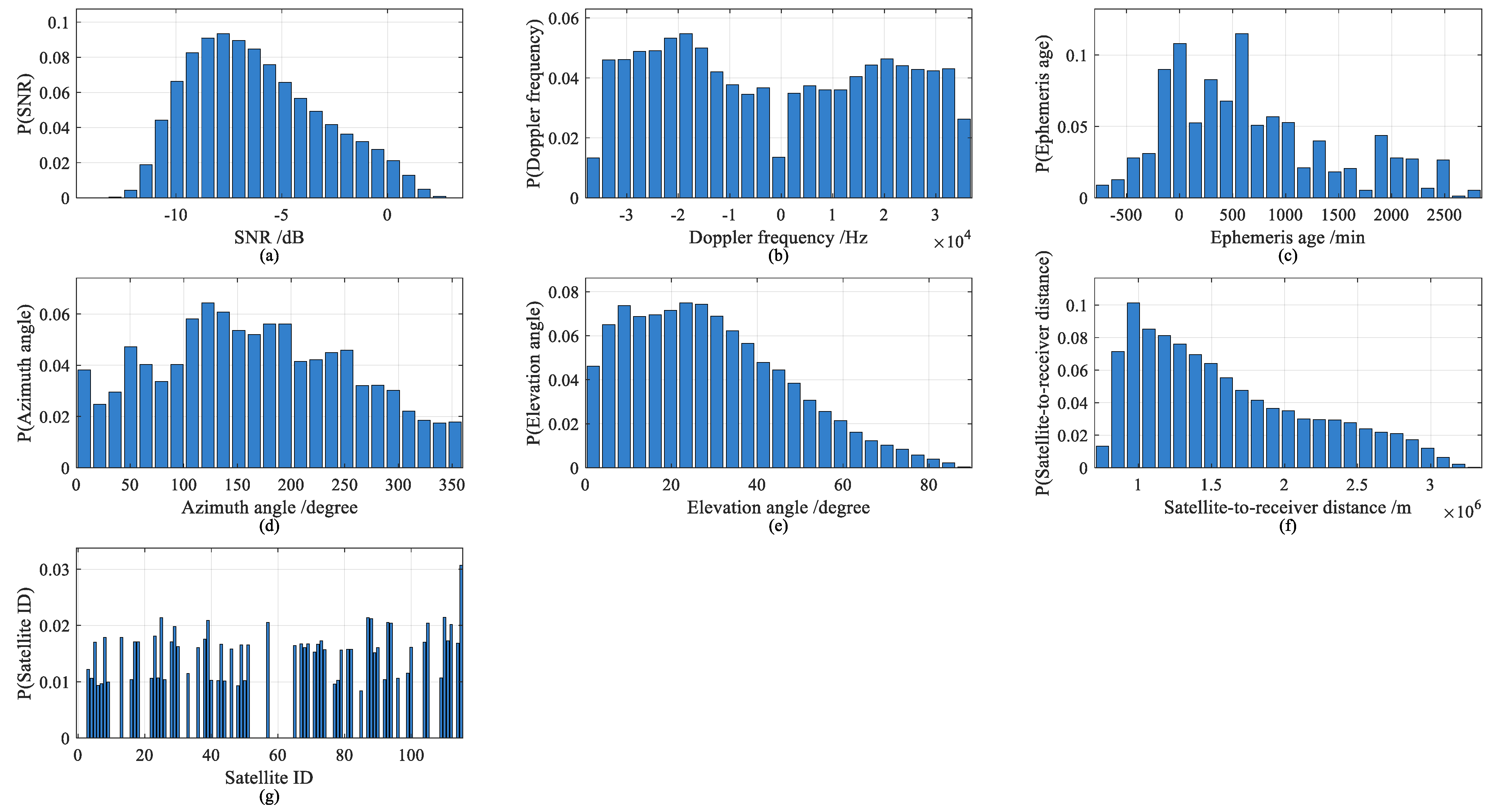
We trained the agent using the DDQN-EW algorithm on a training set comprising 393,933 real Iridium epochs extracted from 107 h of continuous observation. The agent learns to perform real-time epoch weighting by integrating multiple epoch characteristics. Unlike traditional static epoch weighting and screening algorithms, the proposed approach learns policy directly from extensive empirical data to autonomously generate optimal weighting policy through DRL. During evaluation, the agent generates dynamic weights through real-time analysis of epoch characteristics (SNR/Doppler/elevation angle, etc.), which serve as adaptive factors in RLS positioning, thereby establishing a closed-loop optimization framework. Due to the agent’s comprehensive consideration of multi-level characteristics and temporal dependency-aware decision-making, the proposed AWR-PF demonstrates superior positioning accuracy throughout the entire recursive process compared to both standard RLS and randomly weighted RLS in experimental trials. The main contributions of this study are threefold:
Systematic analysis of multi-level characteristics affecting LEO SOP positioning accuracy based on numerous independent trials.
Proposal of a novel Agent-Weighted RLS Positioning Framework (AWR-PF), a pioneering application of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms in LEO SOP positioning. By employing an agent trained on extensive real-world Iridium signal and comprehensively incorporating multiple positioning accuracy-influencing factors, our framework achieves superior positioning performance.
Definition of an innovative MDP model with precisely formulated states, actions, and rewards, effectively transforming practical opportunistic signal positioning problems into a model suitable for DRL algorithm training, thereby establishing a paradigm for intelligent algorithm applications in future LEO opportunistic signal positioning systems.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 characterizes the Iridium signal epoch features that influence positioning accuracy.
Section 3 presents the proposed Agent-Weighted RLS Positioning Framework.
Section 4 presents the proposed MDP model and details the agent training process using the DDQN-EW algorithm.
Section 5 analyzes the training and evaluation results.
Section 6 presents some valuable discussions. Finally,
Section 7 concludes the paper.
3. The Agent-Weighted RLS Positioning Framework
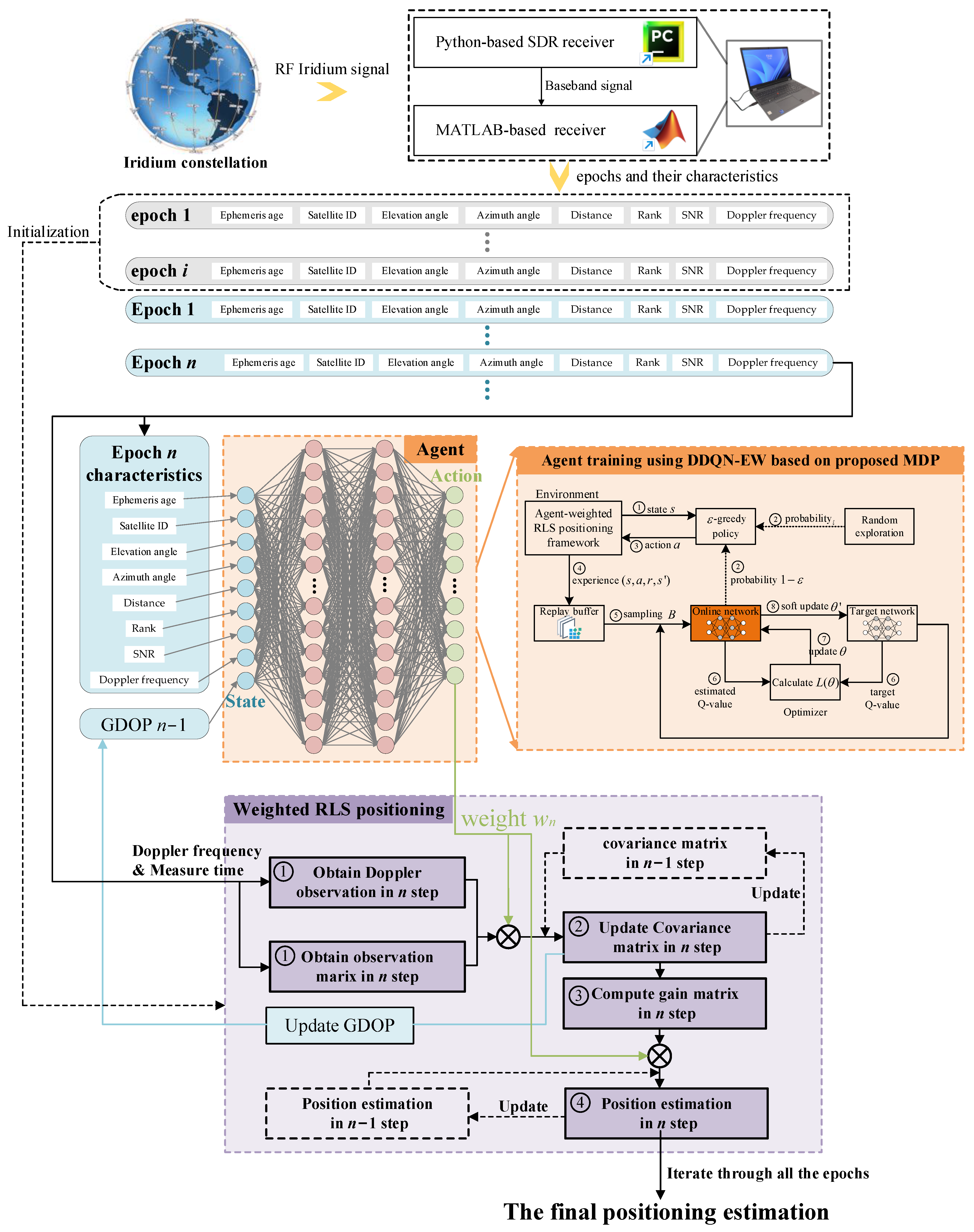
This paper proposes an Agent-Weighted RLS Positioning Framework (AWR-PF) for LEO SOP positioning to achieve real-time epoch dynamic weight decision-making and establish temporal dependencies between epochs. The innovation lies in designing a neural network-based agent that comprehensively evaluates each epoch in real-time based on multiple characteristics (ephemeris age, elevation angle, azimuth angle, satellite-to-receiver distance, SNR, Doppler frequency, and epoch rank within its satellite). The agent additionally incorporates current observation matrix GDOP information. The evaluation result is expressed as a dynamically generated weight, which participates in RLS iteration to enhance positioning accuracy.
To train the agent, we formulated an MDP model including state, environment, action, reward, and state transition process. This MDP model integrates all Iridium epoch characteristics and iteratively updates based on selected action. Using the DDQN-EW algorithm, we trained the agent on an extensive real-world dataset comprising 107 h of continuous observations, ensuring full 24 h coverage and representative sampling of all characteristic Iridium signal conditions. The trained agent effectively learns epoch credibility evaluation across dynamic scenarios, enabling comprehensive and robust positioning accuracy optimization.
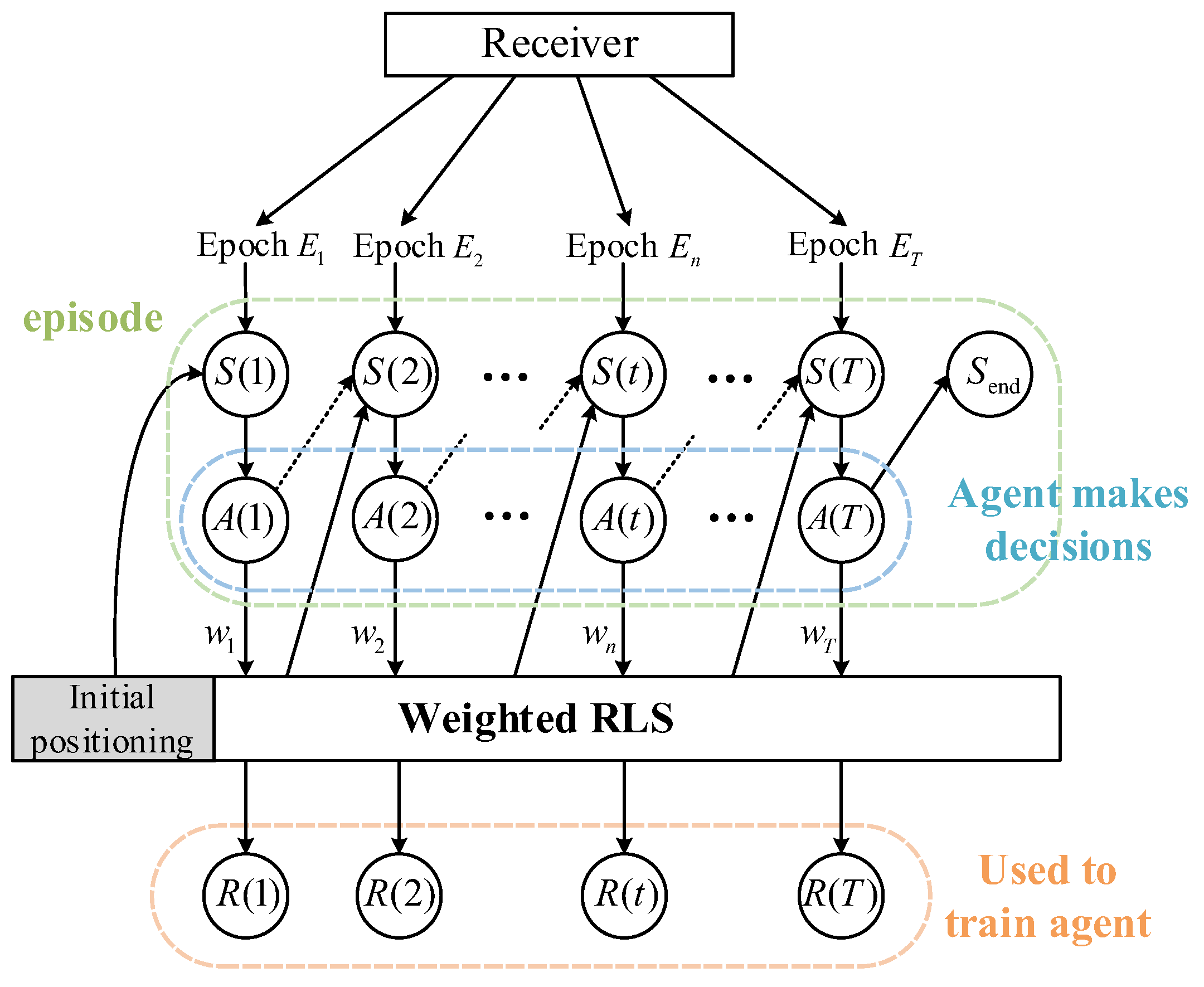
As demonstrated in
Figure 5, the framework initially computes the preliminary position estimation, observation matrix, and covariance matrix using epochs accumulated during an initialization period. Then it performs epoch-wise recursive estimation, where an agent dynamically weights each
n-th epoch based on its multi-dimensional features and current matrix conditions, and subsequently updates the position estimate and observation matrix through weighted RLS (Algorithm 1) until all epochs are processed to obtain the final position estimation.
| Algorithm 1 Agent-Weighted RLS Positioning Framework |
| Input: Initial position, LEO satellite epochs. |
| Output: Recursive position estimation. |
| 1 | //Initialize via LSM (LSM denotes least squares method): |
| 2 | Construct observation equation . //Equations (11) and (12) |
| 3 | Compute initial position estimation . //Equation (13) |
| 4 | . //Equation (14) |
| 5 | //Iterations: |
| 6 | for each new epoch do |
| 7 | Obtain the weight through the agent. |
| 8 | Obtain new observation and observation matrix . |
| 9 | //Update covariance matrix and GDOP. |
| 10 | . |
| 11 | . |
| 12 | //Compute gain matrix of this epoch. |
| 13 | . |
| 14 | //Update position estimation. |
| 15 | . |
| 16 | end for |
| 17 | return the final position estimation. |
Before applying the RLS for position estimation, an initial position estimate is required. This is to ensure that the recursion starts with a reasonable initial state, allowing it to recursively update the target position as new observations become available. In this article, a small number of observations are first processed using the least squares method (LSM) to obtain an initial positioning result. Subsequently, as epochs are captured, the RLS algorithm is applied to perform recursive estimation of the observations. Using the epochs from the first
time to establish the observation equation, assuming there are
LEO satellites during this period and the
-th satellite has
Doppler observation epochs, the observation equation can be written as:
where
denotes the approximate value of the rate of change of the pseudorange after Taylor expansion;
,
, and
are the partial derivatives of the pseudorange rate with respect to the three-dimensional position coordinates; and
denotes the joint Gaussian: white noise with covariance matrix
. For simplicity, Equation (11) can be written as:
where
represents the initial observation vector,
is the initial coefficient matrix, and
is the initial state vector. Using the minimum variance unbiased estimator (MVUE) for the linear equation, the estimation of
can be obtained as:
Simultaneously, the covariance matrix of the initial state is given by:
In this way, the initial state estimate and the initial covariance matrix are obtained, providing the foundation for subsequent recursive calculations.
After obtaining the initial state estimate, each time an epoch is captured, it is added to the equation for an iterative calculation. Suppose that at the (
n − 1)-th iteration, the state estimate is
and the error covariance matrix is
. When a new
n-th epoch is added, the agent determines the weight of the epoch based on the epoch characteristics and GDOP, which can be written as:
where
denotes the ephemeris age,
denotes the identification of the Iridium satellite,
denotes the elevation angle,
denotes the azimuth angle,
denotes the satellite-to-receiver distance,
denotes the epoch rank in the satellite, and
denotes the estimated Doppler frequency. The new observation value of the epoch is
and the new observation coefficient matrix is
, expressed as:
To obtain the near real-time position estimation, the RLS is employed, which allows for recursive updates of the parameter matrix and state estimate based on existing values, after adding new observations. First, the covariance matrix is updated recursively. When a new observation is added at the
n-th step, the new covariance matrix, based on the covariance matrix from the (
n − 1)-th step and the weight
obtained by the agent, can be written as:
where
denotes the identity matrix. Then the gain matrix for the
n-th step is determined, which is used to balance the influence of the new observation on the state update and can be expressed as:
Finally, the weighted recursive update for the state estimate at the
n-th step can be obtained as:
By iteratively using Equations (17)–(19), the state estimate at each step can be recursively obtained, which corresponds to the 3D position solution of the receiver at each step.
4. Agent Training with Markov Decision Process (MDP)
In the AWR-PF proposed in
Section 3, the time-varying epoch observation characteristics (SNR, Doppler frequency, azimuth angle, etc.) and the temporal dependencies of epoch-weighting decisions collectively constitute a complex sequential decision-making problem. The MDP model provides a mathematical foundation for the agent to comprehend the AWR-PF and formulate decisions by modeling the state evolution mechanisms, action influence pathways, and long-term reward quantification mechanisms. The model’s definitions of state space, action space, state transitions, and reward function directly determine the upper bound of the agent’s decision-making performance.
To efficiently solve for optimal policies in such high-dimensional continuous state spaces, we employ DDQN—a DRL algorithm that decouples action selection from value estimation to mitigate Q-value overestimation. This approach establishes a novel paradigm for addressing the dynamic epoch-weighting optimization challenges in LEO SOP positioning. The DDQN-based training framework enables the agent to learn a robust weighting policy while maintaining generalization performance in complex positioning scenarios.
4.1. Design of the MDP Model
In the AWR-PF, we formulate the agent’s observable state space by integrating multi-dimensional information extracted from four layers: satellite, epoch, signal, and positioning. The action space is systematically constrained within a scientifically determined weighting range to ensure operational validity. A dynamic reward mechanism is designed to precisely quantify positioning error variations, while the state transition process is meticulously designed to reflect system dynamics. This integrated approach yields a mathematically rigorous MDP model that enables comprehensive epoch validity assessment for optimal weighting decisions. The proposed model establishes a theoretical foundation for intelligent epoch-weight optimization in advanced LEO SOP positioning systems.
4.1.1. Definitions of Each Element in the MDP Model
Consider a continuous sequence of epochs from the actual collected epoch set as the weighting targets for a complete iterative positioning process, where . The first epochs are used for initial positioning, while the weights of the subsequent epochs are determined by the agent.
Next, we define that at each timestep , the agent observes the environmental state and makes weighting decisions, completing one interaction with the environment (i.e., AWR-PF). After timesteps, the final positioning result is obtained, where . We define the agent’s interaction with the environment over these timesteps as an episode.
At any timestep , the agent’s decision-making process for the weight of epoch can be represented by the MDP model as a tuple . The following will introduce each element of the tuple in detail.
At timestep , the state observed by the agent from the environment is represented as , with a state space dimension of 9 (comprising 9 components). denotes the next state transitioned to after the agent observes and takes action , expressed as .
The satellite state
observed by the agent at timestep
is defined as:
where
denotes the ephemeris age (corresponding to
in Equation (15)) derived from the observed ephemeris data,
denotes the azimuth angle (corresponding to
in Equation (15)) of the satellite associated with epoch
,
denotes the elevation angle (corresponding to
in Equation (15)) of the same satellite, and
denotes the satellite-to-receiver distance (corresponding to
in Equation (15)). These components collectively characterize the satellite state for the agent’s positioning decisions.
The epoch state
observed by the agent at timestep
is defined as:
where
denotes the satellite identifier (corresponding to
in Equation (15)) associated with epoch
, and
denotes the cumulative observation count (corresponding to
in Equation (15)) of the corresponding satellite from the initial timestep up to the current timestep
. This provides essential epoch identification and historical tracking information for the agent.
The signal state
observed by the agent at timestep
is defined as:
where
denotes the SNR (corresponding to
in Equation (15)) of the observed epoch
, and
denotes the Doppler frequency (corresponding to
in Equation (15)) of the corresponding signal. These measurements provide critical signal quality metrics for the agent’s weighting decisions.
Additionally, denotes the latest GDOP value (corresponding to in Equation (15)) obtained by the agent at timestep through the weighted RLS algorithm, which serves as the agent’s observation of the current positioning system state.
At timestep , the weight action (corresponding to in Equation (15)) is determined by the agent after observing state through epoch , with a discrete action space defined as containing 20 possible weight values. The agent evaluates each component of the current state to assess epoch quality, quantizes this evaluation into a discrete weight value, and subsequently applies the selected weight to the weighted RLS algorithm to perform an iterative positioning update incorporating the current epoch’s information.
The reward function
is designed to evaluate the agent’s weighting decision
during the state transition from
to
, which can be formulated as:
where
denotes the positioning error obtained by comparing the AWR-PF output with the true position at timestep
, and
denotes the initial positioning error. The minimum offset term
is utilized to prevent the problem of an infinitely large reward due to
becoming exactly zero or near zero. The reward coefficients
and
serve distinct purposes:
focuses on absolute error reduction to encourage a rapid initial error decrease, while
emphasizes relative error reduction (percentage change) to promote stable convergence during later positioning stages, collectively guiding the agent’s learning toward both immediate and long-term positioning accuracy improvements during training.
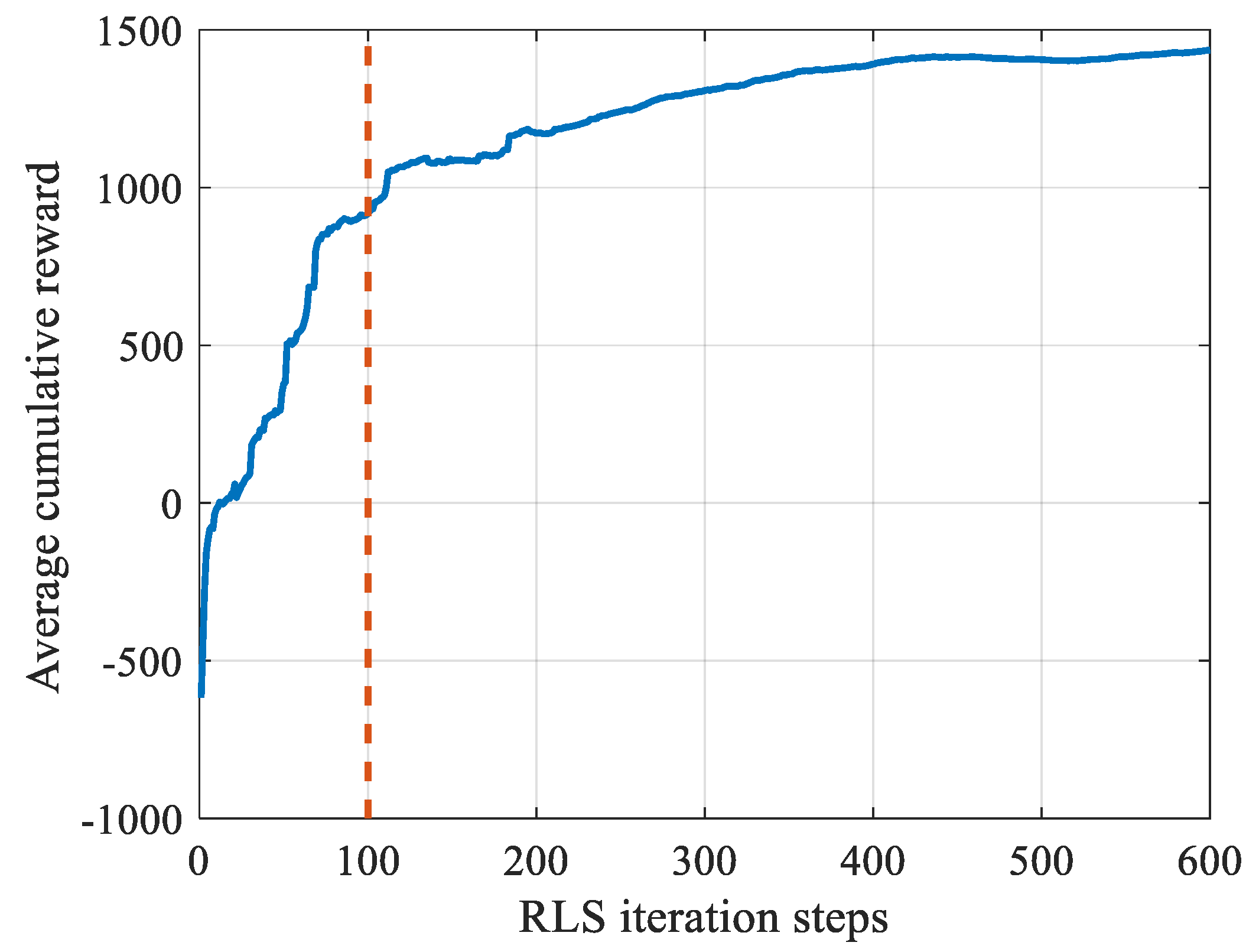
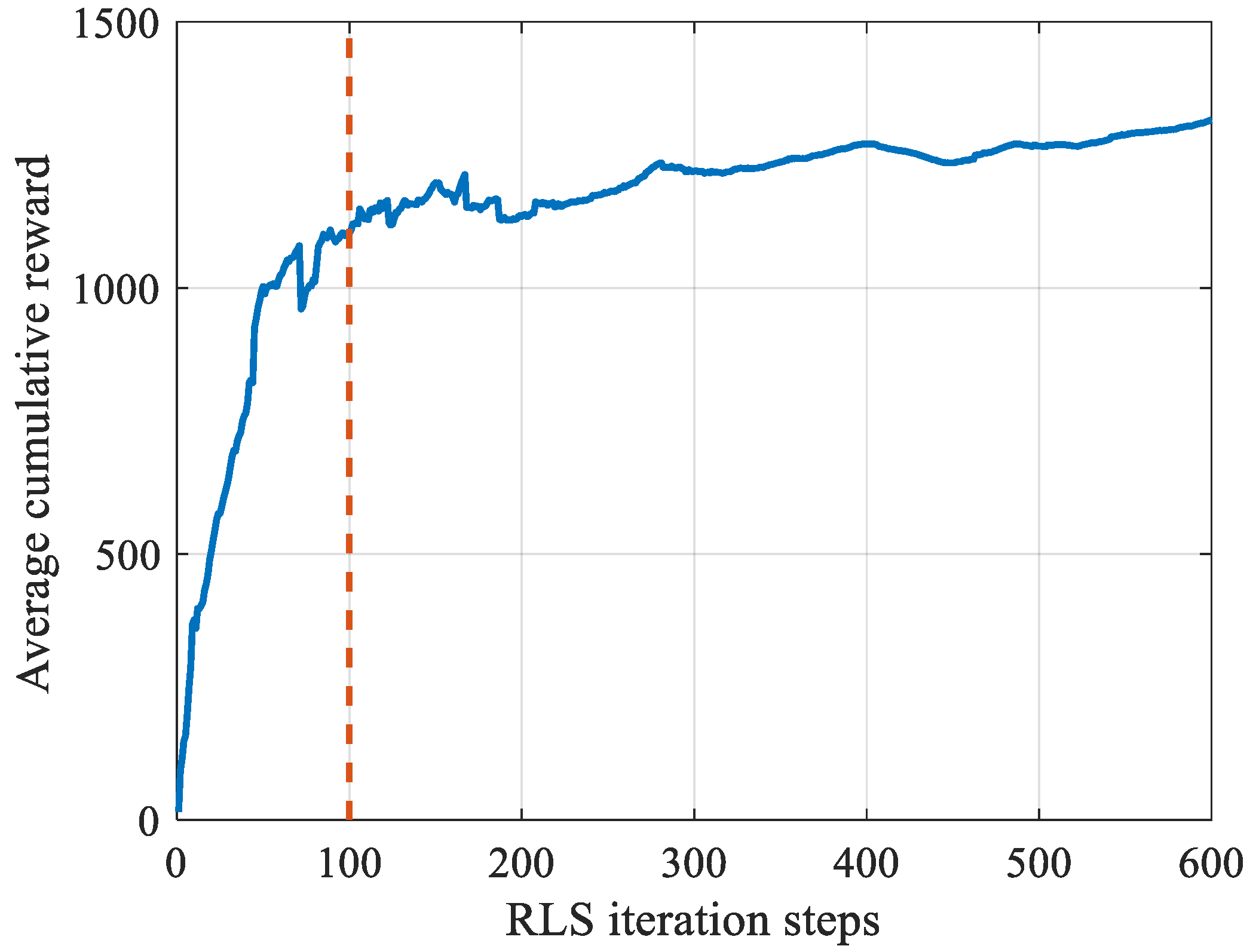
Our research aims to determine optimal epoch weights to minimize positioning errors. The optimization objective is defined as maximizing the expected discounted cumulative reward:
where
denotes the parameters of the agent’s neural network, and
denotes the discount factor that balances the importance between immediate and long-term rewards. This formulation effectively models the trade-off between rapid error reduction in early iterations and sustained accuracy improvement throughout the positioning process.
4.1.2. Analysis of the MDP Model Based on the Dynamic Bayesian Network
To further analyze this MDP model,
Figure 6 illustrates the corresponding dynamic Bayesian network (DBN) model that visually captures the temporal dependency relationships between states, actions, and rewards during the positioning process. This figure explicitly shows how the agent’s weighting decisions
at each timestep influence both the immediate reward
and the state transition
, while maintaining the Markov property where each state depends on its immediate predecessor. The DBN structure particularly highlights the sequential nature of the proposed AWR-PF, where epoch-specific observations progressively refine the positioning solution through the agent’s learned weighting policy.
The MDP’s state transition mechanism can be comprehensively illustrated through the example of . The agent initially constructs the complete state by integrating: (1) , which includes SNR and Doppler frequency from the first epoch; (2) , containing the satellite identifier and cumulative observation count; (3) , comprising ephemeris age, azimuth/elevation angles, and satellite–receiver distance; and (4) , obtained from the covariance matrix.
Upon receiving , the agent generates weighting decision , which is applied in the weighted RLS positioning. The resulting position estimate yields positioning error through comparison with the true position, enabling reward computation , which combines both absolute (-weighted) and relative (-weighted) error improvements from the initial error . Then the agent utilizes to optimize its parameters. The subsequent state (equivalent to ) is then assembled from the second epoch’s corresponding measurements, maintaining the temporal progression of the positioning process.
This transition logic iterates sequentially until terminal conditions are met. At the final timestep , after determining and computing , the system enters termination state —a null state indicating episode completion when all epoch weights have been decided. The complete cycle demonstrates how the MDP model achieves progressive positioning optimization through intelligent epoch weighting.
4.2. DRL-Based Solution
To address the sequential decision-making challenge in epoch weighting, we have established the MDP model as detailed in
Section 3. Given the complexity of the multi-level state space
and the discrete nature of action space
while pursuing long-term cumulative reward maximization, we employ DRL for optimal policy derivation.
While conventional value-based deep reinforcement learning approaches like the Deep Q-Network (DQN) [
29] offer theoretically sound solutions for Markov decision processes, they exhibit significant limitations when applied to the complex state–action spaces characteristic of our epoch weighting problem. The algorithm’s well-documented propensity for Q-value overestimation [
30] originates from its fundamental architecture—specifically, the use of a single network to perform dual functions: both selecting the optimal action and evaluating its value. To mitigate the Q-value overestimation issue inherent in the DQN algorithm and enhance both the stability of the learning process and the performance of the final policy, we adopt the DDQN algorithm.
The key improvement of DDQN lies in its decoupling of action selection and value estimation in the target Q-value computation, achieved through the use of an online network and a target network. Specifically, the online network (with parameters ), which undergoes continuous updates and is responsible for action exploration and selection based on current knowledge, determines the optimal action: , where denotes the current state, denotes the currently determined selected action, denotes the next state, and denotes the set of admissible actions available at state . The value of the selected action is then evaluated by the target network (with parameters ), which periodically synchronizes its parameters from the online network to provide a relatively stable benchmark for value estimation: . This decoupling mechanism effectively mitigates the Q-value overestimation problem.
While DDQN is conventionally applied in video game domains—where raw pixel frames serve as sequential input states processed through convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for feature extraction and direct-action generation (e.g., movement controls), with rewards derived from game scores to enable end-to-end learning—their direct adaptation to satellite navigation presents fundamental challenges. In LEO SOP applications, raw signal waveform images are unintelligible to agents without engineered state representations. Direct positioning output would cause exponential action space expansion, while undefined reward mechanisms for navigation problems require careful design.
To address these limitations, we innovatively customize DDQN:
Structured State Representation: Extracting positioning-relevant features from satellite, epoch, signal, and positioning layers using lightweight neural networks, enabling efficient interpretation of mathematical relationships.
Collaborative Decision Framework: Integrating the agent with RLS within the AWR-PF, where the agent evaluates epoch credibility and outputs weight for RLS-based positioning, dramatically reducing decision complexity.
Differential Reward Mechanism: Incorporating both absolute and proportional positioning error changes—rather than instantaneous error alone—to account for convergence dynamics during iterative positioning.
These adaptations transform DDQN from a gaming solution into a viable satellite positioning optimizer: the DDQN-based Epoch Weighting (DDQN-EW) algorithm. Subsequently, we will detail DDQN-EW’s implementation.
4.2.1. Network Architecture
Given that the state in our proposed MDP model comprises nine key environmental parameters (including a four-dimensional satellite state: ephemeris age, azimuth angle, elevation angle, and satellite-ground distance; two-dimensional epoch state: satellite identifier and cumulative observation count; two-dimensional signal state: SNR and Doppler frequency; and one-dimensional positioning state: GDOP), we represent it as a nine-dimensional feature vector.
We employ a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) as the approximator for the Q-value function, with identical architectures for both the online network and target network. Below, we define the structure of this MLP.
First, the input layer consists of nine neurons, matching the dimensionality of the state vector. Next, the network includes two hidden layers: the first is a fully connected (FC) layer with neurons, activated by the rectified linear unit (ReLU), and the second is another FC layer with neurons, also using ReLU activation. Finally, the output layer is an FC layer with 20 neurons, each corresponding to a discrete action, and if no activation function is applied, it allows direct Q-value estimation.
In evaluation mode, the agent selects the action associated with the highest Q-value in the output layer. In training mode, the agent adopts the
policy (see
Section 4.2.3 for details) to determine actions.
4.2.2. Optimization Objective
The optimization objective of the online network is to minimize the discrepancy between its predicted Q-value
and the target Q-values computed by the target network:
where
denotes the terminal state indicator (1 if
is terminal state, 0 otherwise). We employ the mean squared error (MSE) as the loss function:
The online network parameters are updated using the adaptive moment estimation (Adam) optimizer, which computes gradients based on . The learning rate (denoted as ) stands as the most critical hyperparameter in the Adam optimizer. This fundamental parameter governs the step size for updating neural network parameters during the optimization process, while the optimizer itself determines the parameter updates based on both and . The way the optimizer updates the network parameters is , where denotes the gradient of with respect to .
4.2.3. Efficient Training Mechanism
To break the temporal correlation between data samples and improve sample utilization, we incorporate experience replay. Each interaction between the agent and the environment generates an experience tuple
, which is stored in a fixed-size replay buffer
. Here,
denotes the immediate reward following the state transition from
to
via action
. The buffer operates as a first-in-first-out (FIFO) queue with a maximum capacity of
. During training iterations, a mini-batch of
experience tuples is uniformly sampled at random from the replay buffer:
which is then used to compute the loss function and update the online network.
To provide stable learning targets, we maintain a separate target network
. Unlike the online network
, the target network’s parameters
are not updated via gradient descent but instead through a soft update mechanism: after each update of the online network parameters
, the target network parameters are adjusted as follows:
where
is the update rate, controlling the speed at which the target network parameters converge toward those of the online network.
To balance exploration of new actions and exploitation of current knowledge during training, we employ the
policy as the behavior strategy for action selection. With probability
, an action is chosen uniformly at random from the action space
; with probability
, the agent selects the current optimal action corresponding to the highest Q-value output by the online network. The exploration rate
decays over time according to:
where
is the minimum exploration rate,
is the decay rate, and
is initialized to 1. This ensures that the policy prioritizes exploration in early training stages and gradually shifts toward exploitation as learning progresses.
4.2.4. Once Training Process
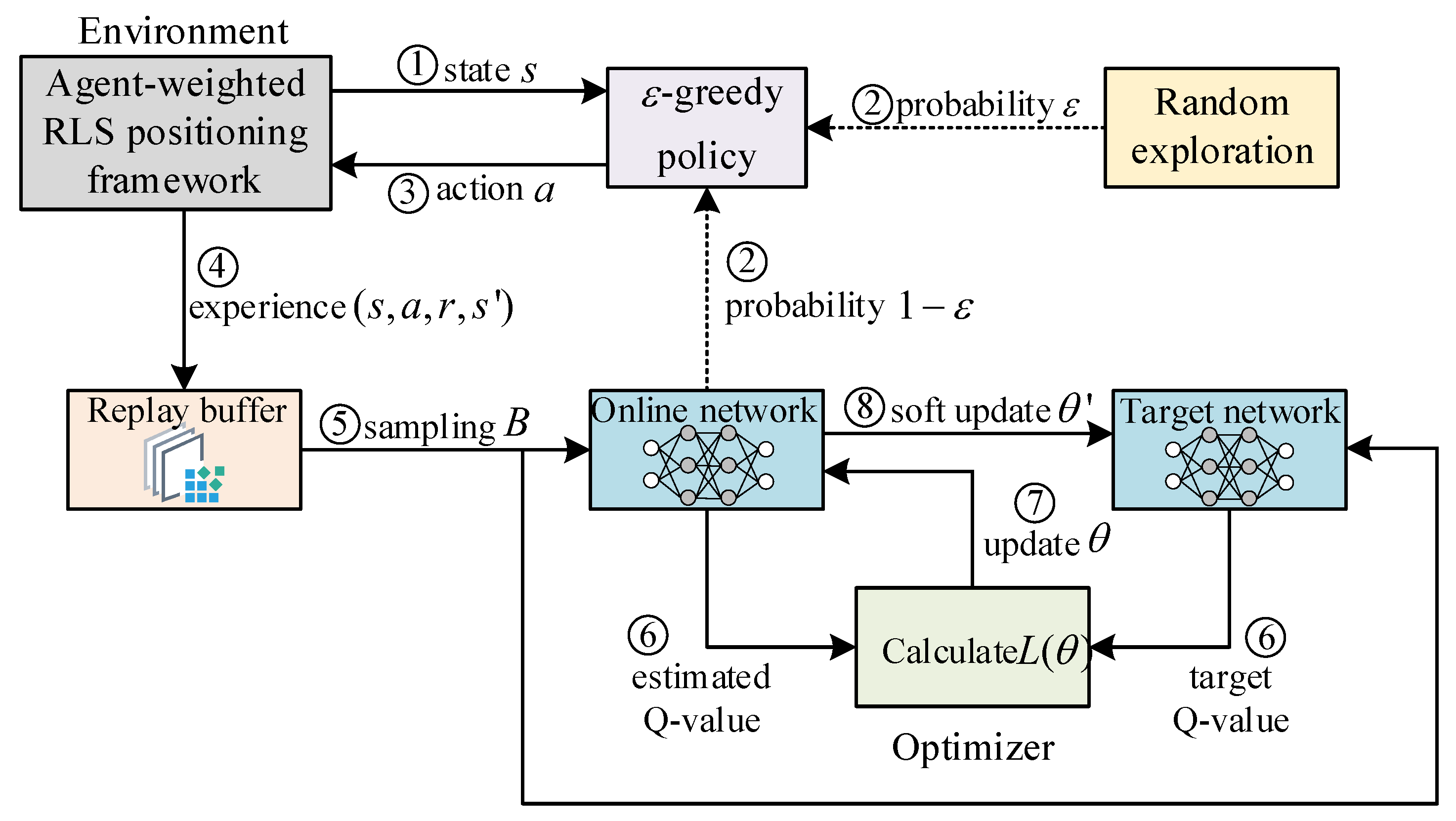
The single training process of the DDQN-EW agent is illustrated in
Figure 7. The process begins with the agent observing the current state
from the AWR-PF. An action
is then selected according to the
policy. Upon executing action
, the weight for the current epoch is determined, and the weighted RLS algorithm performs a single iterative positioning update using this weight combined with epoch-specific information. The positioning result is compared with the true position to compute the immediate reward
. The next state
is then observed, and the terminal flag
is determined based on
. The experience tuple
generated from this interaction is stored in the replay buffer
.
During training, a mini-batch is sampled uniformly from the replay buffer . The online network and target network are then used to compute the estimated Q-values and target Q-values, respectively. The optimizer calculates the loss based on these values and performs backpropagation to update the online network parameters . Finally, the target network parameters are softly updated to complete one training iteration.
This iterative process ensures stable and efficient learning through the policy, soft update, and experience replay mechanism.
4.2.5. Overall Training and Evaluation Process
The collected epoch set
is partitioned into subsets of length
, yielding
epoch subsets. For each subset, the first
epochs are used for initial positioning, while the remaining epochs form an episode of length
for training the agent (see Algorithm 2). This structured approach maximizes sample utilization efficiency and learning frequency while ensuring stable and uniform training progression. By optimizing both the injection and utilization processes of the experience replay buffer, it enables the learning process to closely follow the pace of agent–environment interactions.
| Algorithm 2 Training Iteration of the DDQN-EW Algorithm |
| Input: Online network , target network , replay buffer , exploration rate . |
| Output: The updated parameters and . |
| 1 | for timestep do |
| 2 | for episode do |
| 3 | Agent observes state from AWR-PF. |
| 4 | If then |
| 5 | . |
| 6 | end if |
| 7 | . |
| 8 | If then |
| 9 | , . |
| 10 | end if |
| 11 | With probability , agent randomly select an action from , |
| 12 | otherwise . |
| 13 | . |
| 14 | Obtain reward from AWR-PF. |
| 15 | Store tuple in . |
| 16 | Sample random mini-batch form . |
| 17 | Calculate estimated Q-value: . |
| 18 | Calculate . |
| 19 | Update online network: . |
| 20 | Update target network: . |
| 21 | end for |
| 22 | end for |
Upon completion of agent training, we evaluate its generalization capability using a separately collected epoch set
. Following the same protocol as the training phase, we partition
into
independent evaluation episodes. The trained agent then executes a pure exploitation policy (see Algorithm 3) to perform epoch-specific weighting and positioning throughout these episodes.
| Algorithm 3 Evaluation Process of the Trained Agent |
| Input: Trained online network . |
| 1 | for timestep do |
| 2 | for episode do |
| 3 | Agent observes state from AWR-PF. |
| 4 | . |
| 5 | end for |
| 6 | end for |
6. Discussion
6.1. A Comparative Discussion with the Results of Other Methods
At present, in the field of LEO SOP positioning, the research on epoch weighting and screening is relatively scarce, mainly focusing on satellite screening based on geometric configuration and weighting based on orbital error. It is not difficult to find that the existing LEO SOP weighting methods all have essential differences from the method proposed in this paper, which are specifically reflected in the following two points:
Current research can only screen satellites, while this paper delves into the weighting of each epoch of satellites.
The current research only optimizes based on one or two aspects of parameters, while this paper comprehensively considers nine parameters at four levels.
Furthermore, the use of different constellations and the opacity of engineering details makes it extremely difficult to reproduce algorithms in the same field under strictly con-trolled variables. Based on the above discussion, it is difficult for this paper to make an effective comparison with existing algorithms.
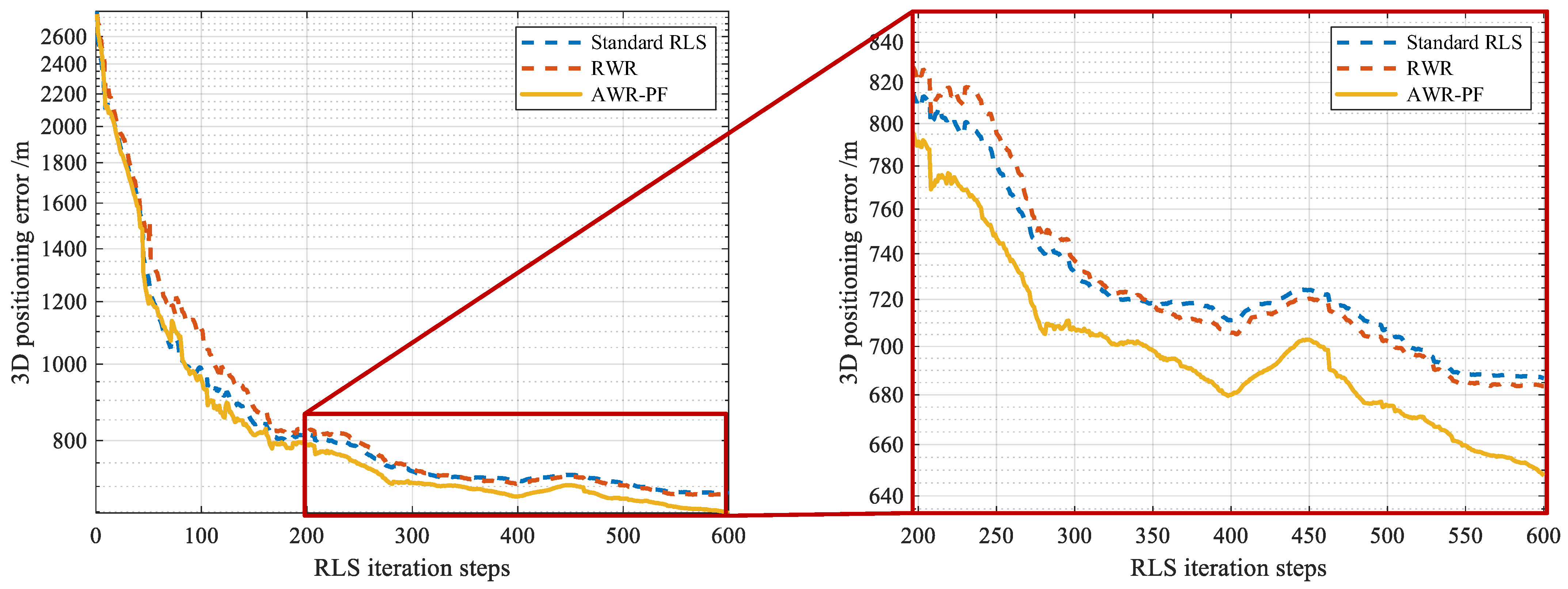
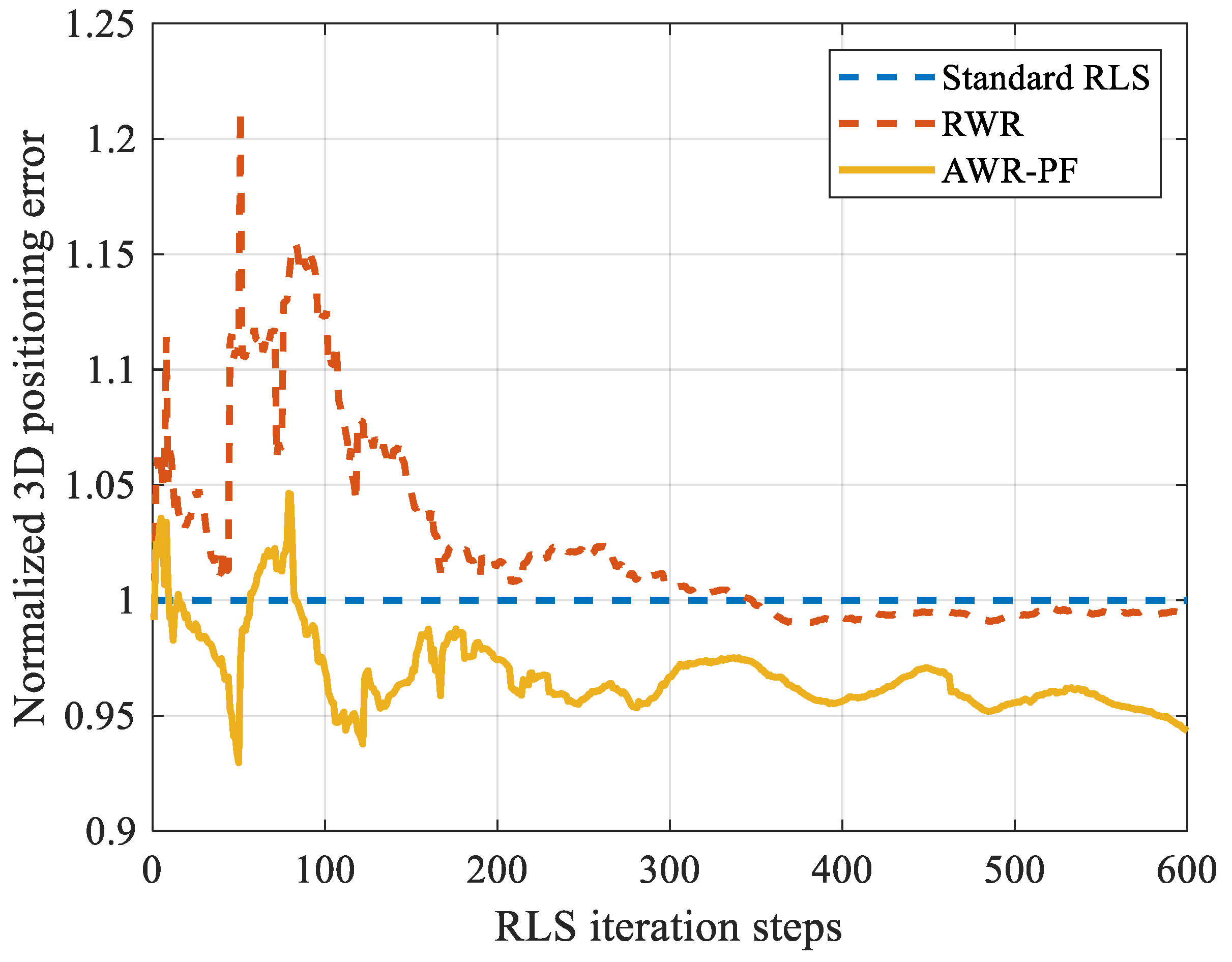
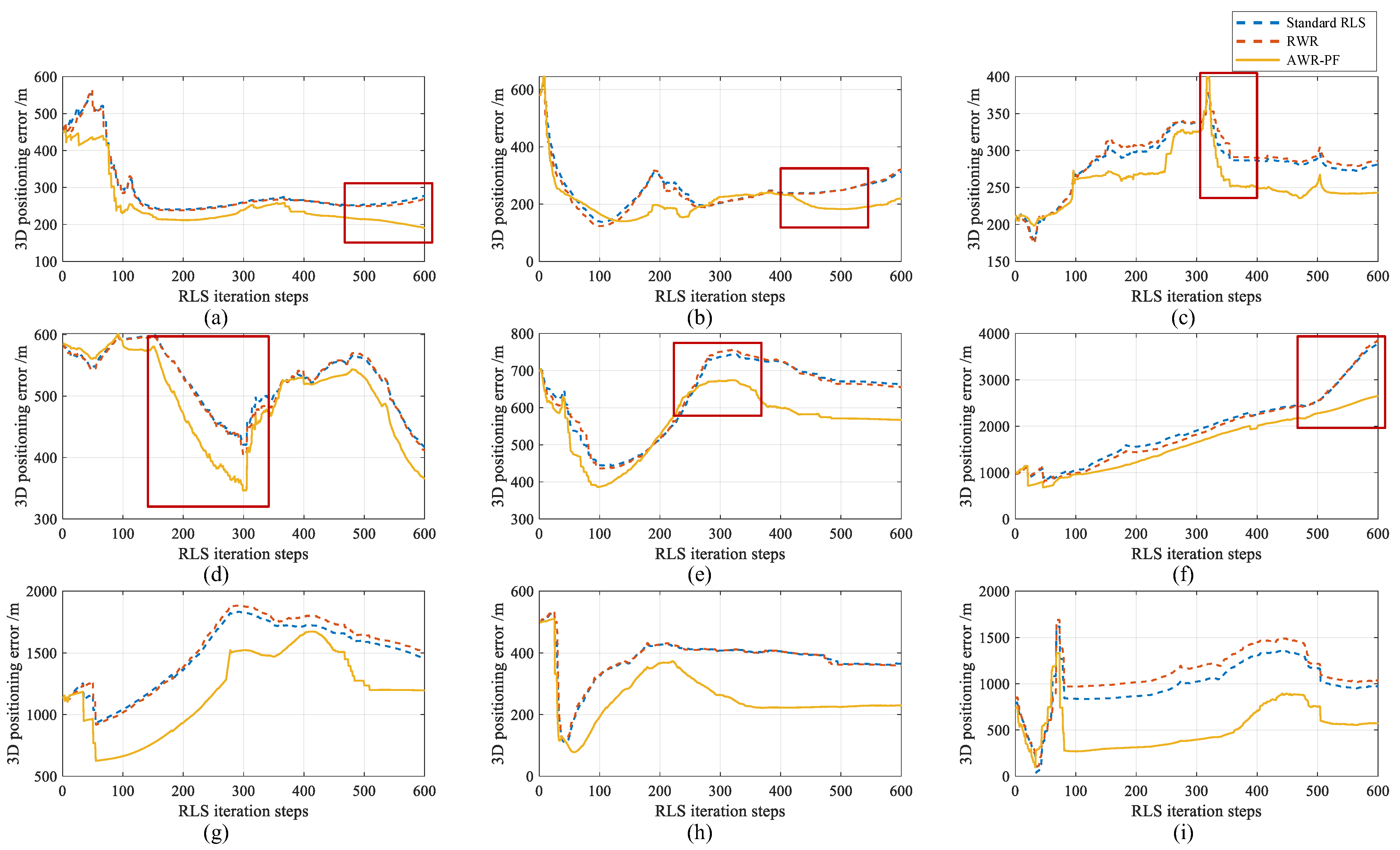
In this work, the test set covers almost all time periods of the 24 h of the day, with an observation duration of 27 h and a total of 80,764 epochs. Among the 97 independent LEO SOP locations examined during the observation period, the AWR-PF outperformed RLR and standard RLS on average. This indicates that the improvement in positioning accuracy by the AWR-PF is not an accidental phenomenon but a fact verified through a large number of experiments.
All the positioning comparisons in the paper have undergone strict variable control. That is, the only difference among the three methods lies in the weighting strategies for epoch elements (weighted by the agent, randomly weighted, and with a constant weight of 1). The results obtained from this comparison demonstrate that the weighting strategy of the agent optimizes the positioning results rather than due to other factors. This also supports the core innovation point of this article: an agent capable of weighting the fusion of multiple characteristics of epoch elements.
6.2. Future Work
Future research may explore migrating the agent from LEO SOP to MEO or GEO SOP scenarios, necessitating adaptation to altered observation characteristics. In MEO and GEO environments, geometric configuration changes will substantially reduce Doppler frequency fluctuations while moderating SNR variations. Consequently, the agent must undergo retraining using MEO/GEO-specific signals. Through this process, the agent will recalibrate its network parameters by enhancing Doppler frequency sensitivity while desensitizing to SNR changes, thereby maintaining effective collaboration with RLS within the AWR-PF. This adaptive retraining ensures optimal performance across distinct orbital regimes despite fundamental differences in signal dynamics.
The reward function in this study relies on positioning error, which poses implementation challenges in GNSS-denied environments, where true position is typically unavailable. This limitation necessitates developing truth-position-independent reward mechanisms for practical deployment. Notably, GDOP offers a significant advantage: Calculated solely from satellite geometry without requiring true position, it quantifies positioning solution sensitivity to measurement errors. This characteristic establishes GDOP as an effective indirect quality metric for epoch assessment. Empirical evidence further indicates that SNR and elevation angle critically influence epoch quality, with both being directly measurable from non-cooperative SOP. Consequently, future research should focus on designing reward mechanisms based on GDOP, SNR, and elevation angle—for instance, assigning higher rewards to epochs exhibiting lower GDOP, higher SNR, and larger elevation angles.
To enhance the agent’s versatility, future work could involve multi-constellation training across diverse locations and receivers. Our trained agent currently supports real-time positioning using Iridium signals with RLS at any time near the training location via corresponding receivers. However, significant changes in location (beyond 500 km), receiver hardware, or satellite constellations (e.g., switching to Starlink or OneWeb) necessitate agent retraining. Three primary factors challenge generalization: Location shifts (>500 km) alter ionospheric/tropospheric conditions, receiver variations introduce antenna gain/phase response discrepancies, and constellation differences fundamentally change geometric configurations. Achieving universal positioning—any location, any receiver, any constellation—requires more extensive and diverse training data. This expansion would simultaneously pose greater demands on MDP design and DRL algorithm performance to maintain robustness across such heterogeneous operational environments. Future implementations must address these scalability challenges to realize truly adaptable navigation agents.