Abstract
Hyperspectral image change detection (HSI-CD) provides substantial value in environmental monitoring, urban planning and other fields. In recent years, deep-learning based HSI-CD methods have made remarkable progress due to their powerful nonlinear feature learning capabilities, yet they face several challenges: mixed-pixel phenomenon affecting pixel-level detection accuracy; heterogeneous spatial scales of change targets where coarse-grained features fail to preserve fine-grained details; and dependence on high-quality labels. To address these challenges, this paper introduces WSCDNet, a weakly supervised HSI-CD network employing coarse-to-fine feature learning, with key innovations including: (1) A dual-branch detection framework integrating binary and multiclass change detection at the sub-pixel level that enhances collaborative optimization through a cross-feature coupling module; (2) introduction of multi-granularity aggregation and difference feature enhancement module for detecting easily confused regions, which effectively improves the model’s detection accuracy; and (3) proposal of a weakly supervised learning strategy, reducing model sensitivity to noisy pseudo-labels through decision-level consistency measurement and sample filtering mechanisms. Experimental results demonstrate that WSCDNet effectively enhances the accuracy and robustness of HSI-CD tasks, exhibiting superior performance under complex scenarios and weakly supervised conditions.
1. Introduction
Remote sensing image change detection (RSCD) is a technical approach that identifies dynamic changes in landcover types by analyzing and comparing multi-temporal remote sensing images acquired over the same geographical area [1,2,3,4]. Being a fundamental application in remote sensing earth observation, RSCD enables continuous monitoring of scene changes and has therefore been applied in multiple fields such as environmental monitoring, urban expansion assessment, and disaster response analysis [5,6,7,8,9]. Among various remote sensing data types, hyperspectral images (HSIs) contain hundreds of contiguous bands, enabling the acquisition of nearly continuous spectral signatures of ground objects. This significantly enhances the ability to identify subtle spectral differences between objects, making it possible to accurately detect and interpret subtle changes that are difficult to capture with traditional remote sensing techniques through spectral curve characteristic analysis.
Hyperspectral image change detection (HSI-CD) mainly consists of two levels: binary change detection (BCD) and multiclass change detection (MCD). BCD aims to identify areas as either changed or unchanged, while MCD further analyzes how different land cover types have changed from one type to another. Despite significant advances in deep learning algorithms for HSI-CD in recent years, existing research has largely focused on BCD problems. In practice, the prevalent mixed-pixel phenomenon in hyperspectral imagery [10] makes it challenging to accurately characterize complex land cover transformation patterns using conventional pixel-level features alone. Therefore, incorporating sub-pixel level feature representations becomes essential to enhance the reliability and discriminative capability of pixel-level multi-change decision making.
In addition to the mixed-pixel phenomenon, HSI-CD faces challenges in fine-grained feature extraction. Change detection algorithms require not only the effective characterization of spectral differences between image pixels but also the full utilization of contextual information from pixel neighborhoods to enhance detection accuracy and minimize both false alarms and missed detections [11,12]. However, current deep learning methods primarily rely on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for feature extraction. While multiple convolution operations can capture semantic information with larger receptive fields, the extracted features remain at coarse-grained semantic levels, leading to the progressive loss of fine-grained spatial details. This problem particularly hinders accurate detection of both small and easily confused regions [13].
Finally, while deep learning-based change detection methods can achieve superior detection performance through data-driven nonlinear transformations and adaptive learning of high-level feature representations, their data-driven nature makes them heavily dependent on the accuracy of training sample labels. In practical applications, obtaining large-scale, accurate labeled samples for change detection tasks is challenging, which creates a bottleneck in deploying deep learning methods. To address the label scarcity issue, existing studies often employ unsupervised mechanisms to generate weakly labeled samples for feature learning [14,15,16]. However, these weakly labeled samples typically contain noisy labels, which affects the process of model training. This is particularly problematic in an MCD task, where different types of changes exhibit varying degrees of label noise. Therefore, designing appropriate network architectures and learning strategies to effectively mitigate the unreliability of pseudo-labels remains a key challenge in improving the robustness of change detection models.
To address these challenges, we propose a Weakly Supervised Network for Coarse-to-Fine Change Detection (WSCDNet) in hyperspectral images. This method integrates sub-pixel level features and multi-granularity feature learning of HSIs, employs dual detection branches and achieves collaborative optimization through feature coupling. Meanwhile, WSCDNet introduces a noise-aware weakly supervised learning strategy to handle inaccurate pseudo-labels. The main contributions of this work are as follows:
- We propose a dual-branch learning framework that integrates binary and multiclass change detection, extracting sub-pixel level features through a spectral unmixing branch (SUB), while optimizing feature interaction between branches via a Cross-Feature Coupling Module (CFCM).
- To address heterogeneous spatial scales of change targets, WSCDNet introduces a Multi-Granularity Aggregation Module (MAM) that effectively integrates fine-grained spatial features with highly discriminative semantic features for detecting easily confused areas, while a Difference Feature Enhancement Module (DFEM) amplifies change features, significantly improving detection capabilities in challenging regions.
- To address limited labeled hyperspectral data, WSCDNet generates pseudo-labels by combining SUB-extracted abundance features with hierarchical partitioning. It mitigates label unreliability through dual-branch consistency loss, measuring probability distribution agreement, and employs a sample filtering mechanism to prevent overfitting to incorrect labels.
2. Related Works
2.1. Hyperspectral Change Detection
The core task of hyperspectral image change detection is to model and identify change features from bi-temporal images, which mainly includes two key steps: feature extraction and classification. Existing research can be categorized into algebraic methods, transformation methods, post-classification comparison methods, and deep learning methods. Algebraic methods quantify change features by designing algebraic operations between multi-temporal hyperspectral images, such as image differencing, image ratioing and absolute distance, and then distinguish background and changed regions based on statistical characteristics. The most representative work is the Change Vector Analysis (CVA) [17], which uses the Euclidean distance between bi-temporal spectral vectors as a measure of change magnitude. Transformation methods focus on feature space projection, enhancing the separability of change features by projecting the original high-dimensional spectral data into a new feature space. This mainly includes Principal Component Analysis [18] and Independent Component Analysis [19]. Post-classification comparison methods first perform independent classification on bi-temporal images and then identify changed regions through analysis of classification result differences [20,21]. The advantage of this approach lies in its ability to directly utilize mature classification algorithms; however, its performance heavily depends on the accuracy of single-temporal classification. In recent years, deep learning methods have achieved significant progress in change detection due to their powerful feature learning capabilities. These methods adaptively learn high-order features required for change detection tasks. For example, the Homogeneous Image Difference Representation Learning Network (HI-DRL) uses pre-clustering to generate self-supervised information for training fully connected neural networks [14]. The Deep Slow Feature Analysis Network (DSFANet) transforms multi-temporal hyperspectral images and combines slow feature analysis to suppress invariant components [15]. A self-supervised contrastive learning pre-training model uses high-confidence pseudo-labeled samples to train downstream change detection networks [16]. A Global Multi-head Interactive Self-attention Change Detection Network (GlobalMind) captures the interactive relationships between the global features of HSIs through multi-head self-attention mechanisms [22]. Despite the rapid development of deep learning methods, most works still face two main challenges: First, the majority of approaches only focus on BCD tasks and ignore the mixed pixel phenomenon in hyperspectral image acquisition. Consequently, these pixel-level classification methods fail to extract change features at the sub-pixel level, making them difficult to apply directly to multiclass change detection tasks. Second, these deep learning-based change detection models typically generate weakly labeled pseudo-labels in an automated way to guide model training, making detection accuracy highly susceptible to the quality of these pseudo-labels.
2.2. Feature Extraction of Hyperspectral Images
In recent research, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) have become a research hotspot in Hyperspectral Image Change Detection (HSI-CD) due to their strong feature extraction capabilities. Saha et al. [23] used pre-trained CNNs to obtain deep features from remote sensing images for change feature extraction. Seydi et al. [24] combined convolution kernels of different dimensions to optimize the feature extraction process. Wang et al. [25] proposed GETNET, which achieves change detection by extracting fused features from HSI abundance tensors in combination with 2-D CNN. However, the features extracted by these CNN-based methods mainly reflect coarse-grained deep discriminative semantic information of scenes. While these coarse-grained features can effectively identify areas with large-scale significant changes, they show obvious limitations when dealing with confusing areas such as change boundaries and small target changes, making it difficult to accurately capture fine-grained spatial detail information. Hu et al. [26] aggregated multi-level features through feature concatenation to extract change feature maps at different scales. Luo et al. [27] utilized a U-Net structure to extract multi-scale difference information from the encoding–decoding process of hyperspectral images to enhance change features. Although these methods have achieved good change detection results, there is still room for more effective and robust change feature extraction methods.
3. Methods
3.1. Overview of Network Structure
This paper introduces a Weakly Supervised Network for Coarse-to-Fine Change Detection (WSCDNet) in hyperspectral images, as illustrated in Figure 1. The framework is primarily composed of a spectral unmixing branch integrated with a dual-branch detection architecture. First, bi-temporal hyperspectral remote sensing images are processed by taking individual pixels as centers, generating bi-temporal hyperspectral image patches with a neighborhood size of q. In the spectral unmixing branch, the image patches are transformed into physically meaningful abundance tensors through an abundance encoder . Using the abundance encoder that is pre-trained through the spectral reconstruction process, WSCDNet employs a hierarchical partitioning algorithm to analyze the bi-temporal abundance differences of HSIs, generating initial binary and multiclass change pseudo-labels. These pseudo-labels provide weak supervision signals for training the whole network.
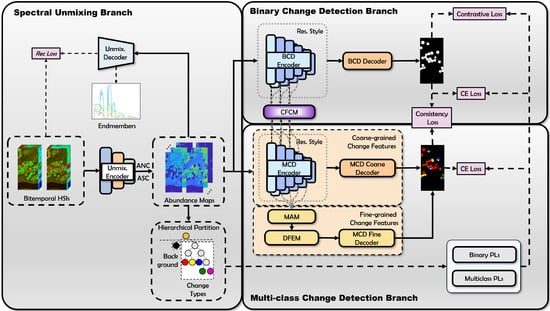
Figure 1.
Framework of the weakly supervised network for coarse-to-fine change detection in hyperspectral images.
Both detection branches are based on Siamese residual networks for change feature extraction. Specifically, the multiclass change detection branch independently utilizes a fine-grained detection mechanism for easily confused regions. It achieves multi-granularity feature extraction through a Multi-Granularity Aggregation Module (MAM), which fuses local detailed features and high-level semantic features of change targets, and enhances change feature representation using a Difference Feature Enhancement Module (DFEM). During the stage of collaborative training, feature interaction between the dual branches is achieved through a Cross-Feature Coupling Module (CFCM), effectively sharing discriminative signals from the BCD branch and distinctive features from the MCD branch. Meanwhile, a consistency loss is introduced to measure the consistency of prediction probability distribution between dual branches and is incorporated into the collaborative loss, enabling weakly supervised noisy learning through a sample filtering strategy. Therefore, WSCDNet enhances the model’s ability to express change features for targets at different scales through multi-granularity feature extraction and enhancement, and improves model performance through a dual collaborative mechanism of feature-decision coupling and weakly supervised learning strategies.
3.2. Spectral Unmixing Branch
Due to limitations in spatial resolution, each pixel in large-scale hyperspectral remote sensing images typically presents as a mixed pixel. Pixel-level change detection methods assume that each pixel contains only one type of ground cover, which is not suitable for detecting complex ground object changes in multi-temporal hyperspectral images. Therefore, the spectral unmixing branch (SUB) extracts sub-pixel level features from HSIs to achieve accurate feature representations. As shown in Figure 1, the unmixing process is based on the Linear spectral Mixture Module (LMM) and uses deep neural networks to achieve automated abundance encoding and spectral reconstruction processes for HSIs. The LMM model is formulated as follows
where the matrix represents the pixels in the hyperspectral image, N denotes the total number of pixels, and B represents the number of spectral bands. The endmember matrix contains the pure spectral signatures, with P representing the number of endmembers. The abundance matrix describes the proportions of each endmember in each pixel, while represents the noise matrix accounting for measurement errors in the hyperspectral image. Under the Linear Mixture Model (LMM) assumptions, the abundance values must satisfy two fundamental constraints. The first is the Abundance Nonnegative Constraint (ANC), which requires all abundance values to be non-negative, ensuring physical meaningfulness. The second is the Abundance Sum-to-one Constraint (ASC), which stipulates that the sum of abundance values for each pixel must equal one, reflecting the complete composition of the pixel. The assumptions can be denoted as and . To model this process using neural networks, the abundance encoder is employed to transform the high-dimensional HSIs from B dimensions into the abundance representation of P dimensions. The detailed architecture of this abundance encoder is illustrated in Figure 2a, and the abundance estimation process can be mathematically formulated as follows:
where represents the batch normalization layer and denotes an improved version of the function. The function is defined mathematically as , where controls the slope in the negative portion of the function. To satisfy both the ANC and ASC constraints, a Softmax function is applied to constrain the abundance tensor, implemented as follows:
where r represents the channel dimension. The decoder then reconstructs the spectral signals based on the estimated abundance tensor through a linear transformation. The reconstruction process is expressed as:
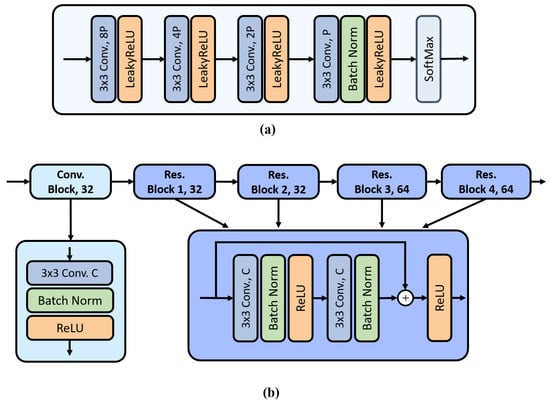
Figure 2.
Architecture of (a) abundance encoder and (b) residual network.
The decoder consists of Fully Connected Layers (FC) without bias terms and activation functions. Its parameters are interpreted as the endmember matrix . In this method, the endmember matrix is initialized using the classical Vertex Component Analysis (VCA) algorithm [28], which extracts endmembers from the stacked bi-temporal HSIs . The reconstruction loss is calculated using Mean Square Error (MSE):
where represents the total number of samples.
3.3. Noisy Pseudo-Label Generation
The spectral unmixing branch can effectively estimate physically meaningful abundance values in hyperspectral images through an autoencoder mechanism, which can then be used to generate pseudo-labels to guide network training. Specifically, WSCDNet employs a pre-trained spectral unmixing model to obtain abundance estimates from bi-temporal hyperspectral images and then analyzes the abundance difference tensor using a hierarchical partitioning method to distinguish different types of ground object changes. As shown in Figure 1, this hierarchical partitioning adopts a top-down binary tree structure, starting with binary clustering and gradually subdividing into multiple cluster groups based on , with each cluster group representing a specific type of change. Compared to direct multiclass clustering, hierarchical partitioning decomposes the complex multiclass problem into a sequence of simpler binary decisions, substantially reducing decision complexity. In particular, when change categories exhibit overlapping feature distributions, the hierarchical partitioning strategy focuses first on the most distinguishable separations and progressively refines the classification. This step-wise decision-making process reduces category confusion, ultimately leading to improved change detection performance.
The specific implementation process is as follows: Assuming the total number of change types is , the binary tree contains nodes. The root node contains all pixels to be classified; leaf nodes represent cluster groups labeled as background or a specific change category; each child node contains a subset of pixels split from its parent node, while the parent node contains all pixels from its two child nodes. The leaf node partitioning is an iterative process. Let denote the number of leaf nodes to be partitioned in the current round. Based on the abundance difference tensor , each leaf node is preliminarily divided into two sub-cluster groups. For the leaf node containing samples, each sample’s feature representation is , where and . The Degree of Distinction (DD) between two potential cluster groups is defined as:
where represents the Silhouette Coefficient, which is calculated as follows:
where represents the average dissimilarity between the u sample and other samples within its potential cluster group, while is the minimum average dissimilarity between and all samples in the other potential sub-node of the leaf node. Here, Euclidean distance is used to measure dissimilarity. The Silhouette coefficient ranges from -1 to 1, with an ideal value of 1, indicating that the u sample has been correctly clustered. Therefore, we select the leaf node with the Silhouette coefficient closest to 1 as the parent node, and its potential child nodes become new leaf nodes for the next round of partitioning. This process is repeated until the number of leaf nodes representing change types reaches the preset number of change categories. Samples in each output leaf node are assigned to either background or a specific change category, thereby generating both binary change detection mask and multiclass change detection mask . Any valid unsupervised clustering or threshold segmentation method can be used for each partitioning process in the hierarchical division, and K-Means is selected in the practice of this work for simplicity and efficiency.
However, consistent with other methods that automatically generate pseudo-labels, the pseudo-labels generated through hierarchical partitioning are essentially weak supervision information with inherent imprecision. This imprecision primarily stems from two aspects: First, while mean square error can effectively guide the spectral reconstruction process of input images and preserve spectral detail information before and after unmixing, it is sensitive to amplitude changes in endmember spectra and tends to emphasize signals from strongly reflective endmembers. Second, the widespread presence of various noise interferences in hyperspectral images (including Gaussian white noise, sparse noise, and stripe noise) disrupts the abundance estimation process. Consequently, the generated pseudo-labels inevitably possess noisy labels. To address this, we will introduce a noise-aware learning strategy in the subsequent end-to-end network training process to enhance the model’s robustness against label noise.
3.4. Binary Change Detection Branch
The binary change detection branch designed in WSCDNet employs a Siamese residual network for binary change feature encoding. The abundance tensors obtained from bi-temporal hyperspectral image patches through the unmixing branch are input into two parallel channels of the Siamese residual network. Based on a parameter-sharing mechanism, both channels use identical convolutional filters for feature extraction, ensuring consistent activation responses for features at corresponding positions in the bi-temporal images. Given the input abundance tensors , the encoding process of the Siamese residual network can be expressed as:
The specific network structure is illustrated in Figure 2b. To maintain the integrity of temporal information and richness of feature representation, we fuse the features from both channels through feature concatenation . Subsequently, a binary classifier is constructed using a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Softmax function to predict labels for the input image patches:
where represents the Softmax function. The loss function for the binary change detection branch comprises two components: binary cross-entropy loss and contrastive loss. The binary cross-entropy loss is defined as:
where N represents the number of samples, and represents the binary change pseudo-label for the i-th sample. In change detection tasks, while traditional binary cross-entropy loss can guide the model to establish discriminative decision boundaries between unchanged and changed features, it overlooks the compactness of inter-class features and struggles to optimize feature space distribution patterns. Inspired by contrastive learning, we introduce a contrastive loss:
where represents the set of unchanged samples, T is the temperature coefficient, represents the encoded feature vector of the i-th sample, and represents the positive sample set for sample i. In this paper, all unchanged samples are considered as positive samples, which helps to compact the feature space distribution of unchanged samples. Therefore, the total loss function for the binary change detection branch is defined as:
where is a balancing factor applied to the contrastive loss. This combined loss function enables the model to simultaneously learn discriminative features and maintain feature space compactness.
3.5. Multiclass Change Detection Branch
Feature extraction is a crucial step in HSI-CD. However, the physical scale of changed regions in satellite remote sensing images often varies significantly across different scenes. Although deep learning-based hyperspectral change detection methods have made significant progress, the progressive spatial downsampling operations of feature maps inevitably lead to the loss of fine-grained spatial detail information. This often results in problems such as blurred edges of change targets and missed detection of small objects.
Research has shown that hierarchical features in neural networks possess different properties: shallow-layer features typically contain rich spatial detail information and local structural features, while deep-layer features demonstrate strong semantic discriminative capabilities. Based on this understanding and fully considering the spatial characteristics of hyperspectral remote sensing images, this paper introduces a multi-granularity detection mechanism in the multiclass change detection branch. Specifically, for non-confusing regions with significant feature differences, change detection is performed using coarse-grained features with high semantic discrimination extracted from deeper network layers. For potentially confusing regions that may contain multiple types of changes, the approach fuses and enhances fine-grained spatial information preserved in shallow layers with high-semantic discriminative coarse-grained information from deep layers to perform fine-grained detection, thereby improving overall change detection performance. The fine-grained detection mechanism is based on the multi-stage feature extraction process of the Siamese residual network and achieves effective feature fusion and enhancement through two key modules: First, the Multi-Granularity Aggregation Module (MAM) adaptively fuses feature representations from different hierarchical levels to achieve complementary enhancement between shallow spatial detail information and deep semantic features. Second, the Difference Feature Enhancement Module (DFEM) is introduced to highlight feature expressions in changed regions and enhance the model’s sensitivity to change information. The specific process of the multiclass change detection branch is as follows.
Given bi-temporal hyperspectral image patches , and their corresponding abundance tensors obtained through the unmixing branch, the multiclass change feature encoder structure mirrors that of the binary change detection branch, with the feature extraction process expressed as:
For non-confusing region detection, WSCDNet performs concatenation operations on the obtained coarse-grained features , and constructs a coarse-grained detector through MLP and Softmax functions to predict final labels for non-confusing region image patches:
For confusing region detection, WSCDNet fuses multi-stage feature representations through the MAM, as illustrated in Figure 3. Unlike the bottom-up computation process of feature extraction, MAM implements a top-down feature fusion mechanism. Through layer-by-layer feature fusion, it facilitates the effective transmission of high semantic discriminative information to shallow spatial detail features, expressed as:
where represents channel concatenation operations, and implements feature upsampling using deconvolution. To effectively extract and enhance change features, the DFEM module models relationships between arbitrary positions within sequences through a self-attention mechanism based on the Transformer architecture, thereby effectively capturing long-range dependent features, as shown in Figure 4.
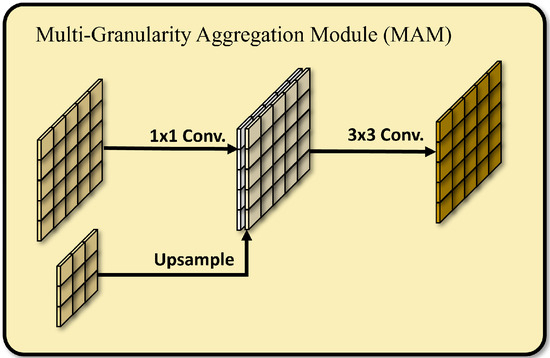
Figure 3.
Multi-granularity aggregation module.
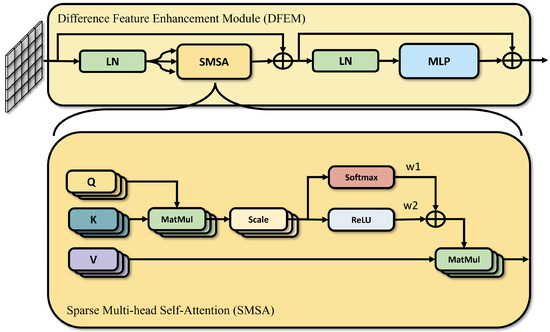
Figure 4.
Difference feature enhancement module.
However, in change detection scenarios, significant and correlated change features often exhibit spatial sparsity, meaning changes tend to concentrate in specific spatial regions. This characteristic makes traditional self-attention mechanisms computationally redundant when modeling global relationships across all positions, and indiscriminate feature interactions may introduce noise that interferes with the model’s ability to perceive actual change regions. To address these issues, this paper introduces Sparse Multi-head Self-Attention (SMSA) as a core component in DFEM. SMSA adaptively learns attention distributions between individual elements within feature maps, enhancing change features by preserving significant feature interaction relationships while suppressing redundant connections between irrelevant regions. The process proceeds as follows: First, DFEM generates multi-stage difference features based on bi-temporal multi-granularity aggregation features . Then, feature enhancement is constructed through residual connections and Layer Normalization (LN):
The SMSA process is expressed as:
where are feature representations obtained through layer normalization and three independent linear transformations from the input. Here, represents the scaling factor, while and are trainable weight coefficients used to dynamically balance between dense and sparse attention modeling. Finally, the enhanced multi-stage features are encoded through feature concatenation and grouped convolution operations, represented as . A fine-grained detector is constructed using MLP and Softmax functions to output prediction results for confusing region image patches. Therefore, the prediction probability of the multiclass change detection branch is represented as , which is optimized using Cross Entropy (CE) loss:
where represents the pseudo-labels for multiclass changes, and represents the number of multiple change categories. In this method, non-confusing regions are defined as areas where the corresponding pseudo-labels of bi-temporal HSI patches contain no more than one type of change class, while the remaining regions are classified as confusing regions. This distinction helps the model apply appropriate detection strategies based on the complexity of changes in different regions. This differentiation is crucial because the neural network performs change detection in a sliding-window manner across all regions. Certain regions with no more than one change class exhibit simple, repetitive spatial feature representations, where reliable detection can be achieved primarily through coarse-grained encoding. However, regions with more than one change class may display complex spatial patterns where coarse-grained detection fails to capture fine-grained features, leading to inadequate detection of small changed targets and edge detection scenarios. Thus, fine-grained detection is required for these challenging areas, thereby enhancing overall detection accuracy.
3.6. Cross-Feature Coupling Module
In the change detection task, the binary and multiclass change detection branches target objectives at different levels. The BCD branch focuses on discriminative features that distinguish between changed and unchanged regions, while the MCD branch aims to capture more refined category-discriminative features. In practice, there exists potential for feature interaction between these two branches. The strong discriminative supervision signals provided by the BCD branch can offer reliable prior information for classification in MCD branch. Meanwhile, the refined category features learned by the MCD branch can reciprocally enhance the feature representation capability of the BCD branch. Based on this understanding, WSCDNet implements a Cross-Feature Coupling Module (CFCM) between the dual detection branches to achieve collaborative optimization of both binary and multiclass change detection branches. Subsequent ablation experiments demonstrate that this feature complementarity helps improve the model’s overall performance. CFCM shares complementary basic feature representations from the shallow layers of both branch networks in a coupled form. Its specific implementation is shown in Figure 5, denoted as
where represents learnable weight matrices that enable dynamic feature fusion, satisfying the conditions , and . This coupling mechanism allows for effective information exchange and mutual enhancement between the two detection branches.

Figure 5.
Cross-feature coupling module.
3.7. Weakly Supervised Collaborative Learning with Noisy Labels
The powerful feature representation and nonlinear problem modeling capabilities of deep learning are typically data-driven. However, any method that automatically generates pseudo-labels to replace real labels (in this case, using the hierarchical partitioning method) inevitably introduces label noise, affecting the performance of change detection models. To enhance the model’s robustness against noisy labels, we introduce a consistency loss in WSCDNet between the dual branches to measure the consistency of probability distributions at the decision layer. Combined with collaborative loss, this approach implements a sample filtering mechanism to achieve weakly supervised learning with noisy labels.
The dual-branch structure of WSCDNet has an inherent hierarchical relationship at the decision level while providing different training perspectives for the same input data during training. Previous research has shown that when models from different perspectives make predictions on the same input, they tend to achieve high consistency on correctly labeled samples while showing prediction divergence on noisy-labeled samples [29,30]. Based on this understanding, we impose a consistency loss between the dual-branch networks to measure their decision consistency, defined as:
where KL represents the Kullback–Leibler Divergence, measuring the difference between two probability distributions:
Here, represents the prediction probability from the binary branch, while is the result of converting multiclass prediction probability distribution to binary probability distribution:
where . Therefore, the total of WSCDNet can be denoted as:
where is the balancing factor applied to the consistency loss. Meanwhile, the training process of deep neural networks tends to first learn simple patterns before gradually fitting (potentially noisy) complex samples. Based on this characteristic, sample loss values have been proven to be a reliable indicator for identifying potential noisy labels. According to the small-loss criterion, samples with lower loss values are considered more reliable and can be treated as clean samples [31,32]. Therefore, Equation (24) serves as the basis for determining whether a sample should be included in the training process:
where denote whether the i-th sample is selected into the training process and represents the rank of the loss value of the i-th sample in ascending order. However, this direct sample selection approach is not entirely suitable for HSI-CD tasks, because unchanged regions occupy a large proportion of hyperspectral images. Samples selected purely based on the small-loss criterion often over-select simple image patches from non-confusing regions while neglecting critical confusing region samples, which can limit the model’s adaptability to complex scenarios. Therefore, combining WSCDNet’s inherent independent detection mechanisms for non-confusing and confusing regions, our sample filtering mechanism executes the filtering process independently in both regions, expressed as:
where is the region type indicator ( for non-confusing regions, for confusing regions), and and represent the total number of samples in non-confusing and confusing regions respectively. In the collaborative training phase, WSCDNet incorporates the aforementioned consistency loss into the collaborative loss as a basis for identifying noisy labels:
Based on collaborative loss and the small-loss criterion, the number of samples from both non-confusing and confusing regions participating in parameter updates gradually decreases during network training. The retention ratio is defined as , where t represents the current epoch, K controls the epoch at which minimum retention rate is reached, and is the minimum retention rate. This sample filtering mechanism helps ensure that errors from noisy labels do not continuously accumulate during network training, thereby improving the model’s robustness and generalization ability in noisy label environments. The algorithm is summarized in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: WSCDNet for Coarse-to-Fine CD |
 |
4. Experimental Validation and Analysis
4.1. Datasets
WSCDNet was validated on three hyperspectral image datasets: two real multi-temporal datasets collected by the EO-1 satellite’s Hyperion sensor (Hermiston and Yancheng datasets) and one simulated dataset (Urban dataset), as shown in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. The Hermiston [33] dataset consists of bi-temporal HSIs captured by the sensor in 2004 and 2007, with a spatial size of and containing 242 spectral channels. The Yancheng dataset [34,35] comprises two images from 2006 and 2007, with a spatial size of and containing 132 spectral channels. Both real datasets include ground truth labels for both binary change and multiclass change scenarios, with multiple changes encompassing five different change categories. The Urban dataset [36] was constructed through simulation, with its base image captured by the Hydice sensor in 1995, featuring a spatial size of and containing 162 spectral channels. To construct the change detection dataset, several typical ground object blocks were selected from the base image, and artificial change regions were created through spatial position permutation. Gaussian white noise with a signal-to-noise ratio of 20 dB was added to simulate spectral deviations in actual imaging processes. The Urban dataset includes ground truth labels for both binary and multiclass change scenarios, with multiclass changes comprising 7 categories.

Figure 6.
Hermiston dataset and its ground truth map. (a) Shot in 2004 (b) Shot in 2007. (c) Ground truth.
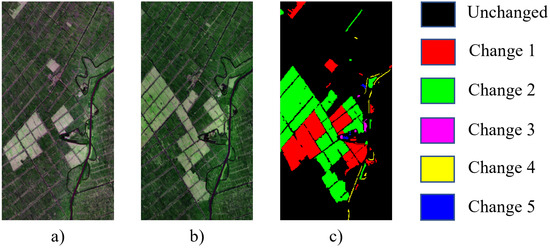
Figure 7.
Yancheng dataset and its ground truth map. (a) Shot in 2006. (b) Shot in 2007. (c) Ground truth.
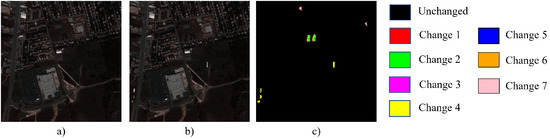
Figure 8.
Urban dataset and its ground truth map. (a) Shot in 1995. (b) Simulated temporal 2. (c) Ground truth.
4.2. Setup
WSCDNet was compared with eleven classic and advanced label-free binary change detection methods. These include the subspace-based change detection methods LSCD and ASCD [37], the PCA-based dimensionality reduction method PCAkMeans [18], and methods based on Multiple Morphological Profiles (MMPs) such as MaxTree and MinTree [38]. The comparison also included the tensor network-based change detection method SSTN [39] and several deep learning-based change detection methods: DSFANet [15], PCANet [40], DeepCVA [23], KPCA-MNet [41], and HI-DRL [14]. In the context of multiclass change detection tasks, WSCDNet was evaluated against six methods. These included three advanced multiclass change detection algorithms: DeepCVA, KPCA-MNet, and the spectral unmixing-based change detection method SNTS [42]. Additionally, three advanced binary change detection algorithms—DSFANet, MaxTree, and MinTree—were included in the comparison by applying K-Means clustering to their extracted change features to enable multiclass change detection. A series of ablation experiments was conducted to demonstrate the effects of four core components (MAM, DFEM, CFCM and Noisy Learning Strategy) in WSCDNet. Additionally, WSCDNet with the direct multiclass clustering method (K-Means) for pseudo-label generation is also conducted to show the superiority of our hierarchical clustering approach.
The default hyperparameter settings for WSCDNet are as follows. For all datasets, the neighborhood size q is set to 5, and the total maximum number of iterations is 100. This includes 20 epochs of pre-training for the spectral unmixing branch, 10 epochs of pre-training for both change detection branches (during which the spectral unmixing branch is frozen), and 60 epochs maximum for collaborative training. The balancing coefficients for reconstruction loss, contrastive loss, and consistency loss are set to = 0.1, = 0.0001, , respectively. The negative slope coefficient in LeakyReLU is set to 0.01. In the spectral unmixing branch, the number of endmembers P is set to 6, 4, and 7 for the Hermiston, Yancheng, and Urban datasets, respectively. In the CFCM, is initialized to and is . For the sample filtering mechanism, the epoch to reach minimum retention rate K is set to 20, with a minimum retention rate of 0.2. The batch size is set to 128, and network parameters are updated using the Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of 0.001 and a weight decay coefficient of 1e-4 to suppress model overfitting. The learning rate is reduced to 1/10 of its current value after the 20th and 40th epochs during collaborative training. For the generated noisy pseudo-labels, 20% of samples are randomly selected for training, with minority classes being oversampled. In the two real datasets, the total number of changed samples is maintained equal to the number of unchanged samples, while in the simulated dataset, the number of changed samples is increased to 10 times the original sample count. The remaining unselected samples are used for validation. In WSCDNet’s noisy learning process, we also conducted parameter analysis experiments focusing on the hyperparameter settings, specifically the balance factor applied to consistency loss and the minimum retention rate parameter for sample filtering.
The performance evaluation employs overall accuracy (OA) and Kappa coefficient (KAPPA) for quantitative assessment of change detection accuracy across different algorithms. Furthermore, visualization results of both binary and multiclass change detection maps from different algorithms are provided to facilitate qualitative analysis. All algorithms were run on a workstation equipped with an Intel Xeon E3 CPU, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080Ti GPU, and 64GB RAM. The implementation of these algorithms varied across different programming frameworks: LSCD and ASCD were implemented using Scikit-Learn; PCAkMeans, MaxTree, MinTree, and PCANet were implemented in MATLAB R2020b; DSFANet was implemented using the TensorFlow framework; while the remaining algorithms and WSCDNet were implemented using the PyTorch 2.4.0 framework.
4.3. Results
The binary change detection results of WSCDNet and different comparison methods are shown in Table 1, with the best performance metrics highlighted in bold. As demonstrated in the table, WSCDNet generally outperforms other methods, which is also reflected in the visualization results shown in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11. Among the comparison algorithms, LSCD, PCANet, MaxTree, and MinTree incorrectly identified many unchanged areas as changed, leading to false alarms. Meanwhile, ASCD missed a significant number of changed areas.

Table 1.
Binary change detection results of WSCDNet and comparative methods.
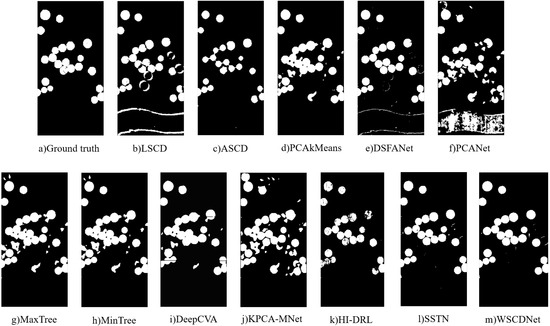
Figure 9.
Binary change detection performance of different methods on the Hermiston dataset.

Figure 10.
Binary change detection performance of different methods on the Yancheng dataset.

Figure 11.
Binary change detection performance of different methods on the Urban dataset.
Specifically, for the Hermiston dataset, DSFANet, DeepCVA, HI-DRL, SSTN, and WSCDNet achieved superior results, all with OA values above 97%. In contrast, LSCD, ASCD, PCAkMeans, PCANet, MaxTree, and MinTree showed OA values below 97%. PCANet’s relatively average performance can be attributed to its lack of spectral feature extraction, while LSCD and ASCD’s subspace distance measurements are susceptible to noise interference. MaxTree and MinTree rely on a limited set of handcrafted attribute features, which cannot fully capture the complex changes in multi-temporal hyperspectral images. Among the better-performing methods, DSFANet incorporates prior information into deep networks, HI-DRL enhances discrimination between background and changed regions by integrating clustering in the optimization process, and KPCA-MNet employs KPCA layers to extract spatial-spectral features. However, WSCDNet achieves the best detection results by leveraging sub-pixel level features of hyperspectral images, incorporating multi-granularity perception capabilities, and implementing noisy learning strategies. Visually, its results most closely align with ground truth. Similar conclusions can be drawn for the Yancheng and Urban datasets from Table 1 and Figure 10 and Figure 11.
From the perspective of multiclass change detection, WSCDNet achieved high accuracy, as shown in Table 2, along with superior visualization results as illustrated in Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14. Among the comparison algorithms, binary change detection methods such as DSFANet, MaxTree, and MinTree performed less effectively than DeepCVA, KPCA-MNet, SNTS, and WSCDNet, primarily because they only consider the division between changed areas and background regions without extracting features for multiple types of changes. SNTS achieved results closest to WSCDNet across all three datasets due to its consideration of sub-pixel level features. However, WSCDNet outperformed all methods by not only incorporating sub-pixel level features but also implementing multi-granularity perception capabilities for MCD tasks and integrating noisy learning strategies, thereby achieving the best overall results. The high OA values demonstrate WSCDNet’s ability to correctly classify most regions, while the high KAPPA values indicate strong inter-category consistency. This is further validated by the visualization of MCD results, where specific regions are magnified for better comparison of different methods, as shown in Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14. Within these magnified local regions, it is evident that the compared methods suffer from various limitations. For example, DeepCVA, KPCA-MNet and DSFANet generate a large number of false alarms and fail to preserve the true structure of the change areas. MaxTree, MinTree, and SNTS, while performing reasonably well for major change classes, still struggle with boundary ambiguity and misclassification in small-scale regions. In contrast, WSCDNet demonstrates clear advantages in fine-grained change detection. In most regions, it accurately delineates the boundaries between different change classes, effectively suppresses noise, and preserves the detailed spatial structure of complex change regions. This fine-grained discrimination enables WSCDNet to achieve results that are much closer to the ground truth, particularly in challenging and confusing areas, highlighting its superiority in multiclass change detection tasks. However, we could not help noticing that there are some challenges in the detection of minority classes in the Yancheng dataset. The main difficulty lies in the fact that WSCDNet is trained using pseudo-labels that rely on the spectral unmixing process, and the extreme class imbalance in the Yancheng dataset can cause a biased unmixing procedure. This, in turn, affects the detection of these minority class samples. Nevertheless, for the multiclass samples that are not relatively rare, WSCDNet demonstrates significantly better detection performance in confusing regions compared to other algorithms, which still proves its superiority in performing change detection tasks.

Table 2.
Multiclass change detection results of WSCDNet and comparative methods.
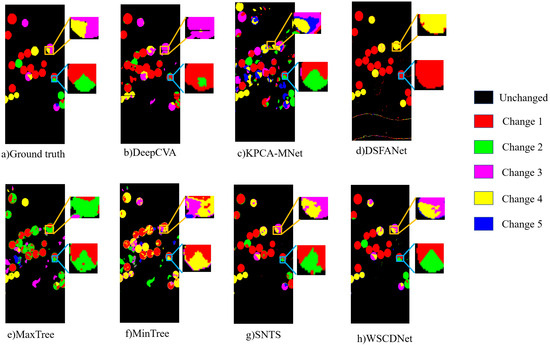
Figure 12.
Multiclass change detection performance of different methods on the Hermiston dataset.
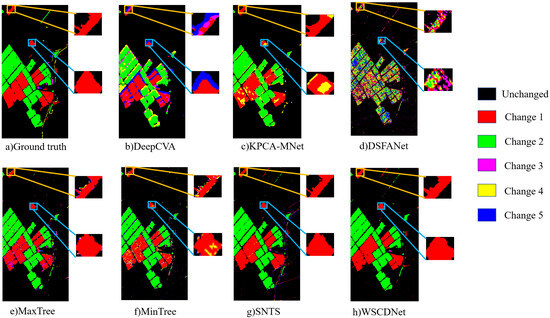
Figure 13.
Multiclass change detection performance of different methods on the Yancheng dataset.
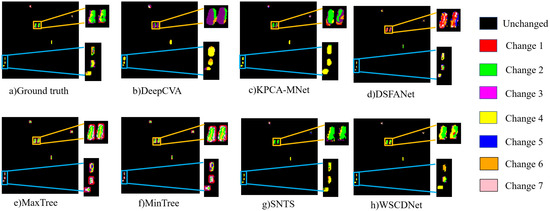
Figure 14.
Multiclass change detection performance of different methods on the Urban dataset.
The ablation experiments on the MAM module for multi-granularity feature extraction, the DFEM module, CFCM and weakly supervised noisy learning strategy are shown in Table 3. As can be seen from the table, the baseline model in Experiment A has already achieved decent basic performance. Building upon this, adding any single component leads to performance improvements, among which Experiment B shows the most significant improvement after introducing the MAM module, with notable increases in various metrics for both binary and multiclass change detection. This is attributed to MAM’s ability to enable WSCDNet to extract multi-granularity features, which is crucial for change detection tasks. In addition, we compared both binary and multiclass change detection performance using pseudo-labels generated by a direct multiclass clustering approach (K-Means) and our proposed hierarchical partitioning method. The results, shown in Table 3, indicate that the hierarchical partitioning strategy consistently outperforms the direct multiclass clustering setting. This demonstrates its effectiveness in reducing label noise and confusion during pseudo-label generation, thereby improving the overall detection performance.

Table 3.
Ablation study of key components in WSCDNet.
Regarding the hyperparameter settings in WSCDNet’s noisy learning process, parameter analysis experiments were conducted, as shown in Table 4. From experiments G-I in the table, when fixing at 0.001, as the minimum retention rate parameter decreases from 0.3 to 0.1, the model’s performance peaks at = 0.2. A larger would reduce the number of samples retained during model training, causing some valuable training samples to be excluded along with noisy samples. Conversely, a smaller represents a more conservative sample filtering mechanism, which is more likely to introduce noisy labels that affect model performance. Meanwhile, experiments I-K verify the impact of the balance factor applied to consistency loss on model training. In fact, a larger would increase the proportion of consistency loss in the total loss, causing the model to focus excessively on classification consistency while neglecting classification boundaries. On the other hand, too small would weaken the prediction consistency constraint of the dual-branch network, leading to decreased model performance. Therefore, WSCDNet selected as the balance factor for consistency loss and as the parameter for minimum retention rate. Convergence curves are drawn in Figure 15 across different datasets. They exhibit rapid convergence with minimal fluctuations and a stable pattern, highlighting the feasibility and stability of our change detection method.

Table 4.
Parameter analysis on the balance factor and minimum retention rate .
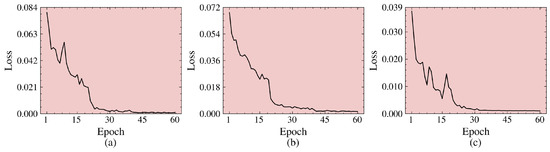
Figure 15.
Convergence curve of WSCDNet on (a) the Hermiston, (b) the Yancheng, and (c) the Urban datasets.
5. Conclusions
The proposed WSCDNet is a weakly supervised change detection framework for hyperspectral remote sensing images based on multi-granularity learning. It adopts a dual-branch detection approach, mining sub-pixel level representations of hyperspectral images through spectral unmixing, and achieves collaborative optimization of binary and multiclass change detection through a cross-feature coupling mechanism to enhance the model’s detection ability. Additionally, in the multiclass detection branch, a multi-granularity feature aggregation and change feature enhancement mechanism is introduced, effectively integrating multi-level feature information and enhancing change feature representation, thereby strengthening detection accuracy in confusing regions. Finally, WSCDNet designs a robust learning strategy based on consistency loss, reducing the model’s sensitivity to noisy labels through consistency measurement at the decision level and dynamic sample filtering mechanism. Experiments demonstrate that WSCDNet achieves superior detection performance under complex scenarios and weakly supervised conditions.
Although WSCDNet has achieved good results in hyperspectral change detection tasks, there are still limitations worth exploring in two aspects: First, from the perspective of feature sharing in dual-branch collaborative learning, WSCDNet adopts a single-weight feature interaction strategy but does not independently consider spatial and channel dimensions. Future work could introduce attention-based feature fusion mechanisms to promote collaborative training of dual branches. Second, in the noisy training strategy, the retention ratio of the sample filtering mechanism is a fixed setting. While this method filters noisy samples, it fails to effectively correct them. Future work could incorporate confidence estimation techniques and introduce dynamic label correction mechanisms to improve model robustness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and Z.C.; methodology, Y.Z. and Z.C.; software, Y.Z.; validation, Y.Z. and Z.C.; formal analysis, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.C.; visualization, Y.Z. and Z.C.; supervision, Z.C.; project administration, Z.C.; funding acquisition, Z.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by DHU Distinguished Young Professor Program Under Grant 25D211201.
Data Availability Statement
All three datasets are publicly available.
Acknowledgments
The authors of this paper would like to thank the researchers who kindly shared their datasets.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chengle, Z.; Qian, S.; Jun, L.; Xinchang, Z. Spectral-frequency domain attribute pattern fusion for hyperspectral image change detection. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2024, 28, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sicong, L.; Kecheng, D.; Yongjie, Z.; Jin, C.; Peijun, D.; Xiaohua, T. Remote sensing change detection technology in the Era of artificial intelligence: Inheritance, development and challenges. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2023, 27, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Lyu, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Q.; Xiang, S. Change detection methods for remote sensing in the last decade: A comprehensive review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Marinelli, D.; Bruzzone, L.; Bovolo, F. A review of change detection in multitemporal hyperspectral images: Current techniques, applications, and challenges. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Huazhong, R.; Desheng, C. The research of building earthquake damage object-oriented change detection based on ensemble classifier with remote sensing image. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 4950–4953. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Raza, A.; Syed, N.R.; Acharki, S.; Ray, R.L.; Hussain, S.; Dehghanisanij, H.; Zubair, M.; Elbeltagi, A. Land use/land cover change detection and NDVI estimation in Pakistan’s Southern Punjab Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah-Hosseini, R.; Homayouni, S.; Safari, A. Environmental monitoring based on automatic change detection from remotely sensed data: Kernel-based approach. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 095992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L. Building damage assessment for rapid disaster response with a deep object-based semantic change detection framework: From natural disasters to man-made disasters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Lorenzo, B. Scribble-Guided Structural Regression Fusion for Multimodal Remote Sensing Change Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 5002005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Xu, R.; Gao, L.; Han, Z.; Sun, X. Development of deep learning-based hyperspectral remote sensing image unmixing. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2024, 28, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Jin, Y. BGSNet: A boundary-guided Siamese multitask network for semantic change detection from high-resolution remote sensing images. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2025, 225, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Liu, S.; Li, M. SMGNet: A Semantic Map-Guided Multi-Task Neural Network for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Change Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 6009605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Proceedings, Part I 13. Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Gong, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Ban, Y. Unsupervised difference representation learning for detecting multiple types of changes in multitemporal remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 2277–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Ru, L.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L. Unsupervised deep slow feature analysis for change detection in multi-temporal remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9976–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Liu, L.; Tan, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Tu, B. A hyperspectral image change detection framework with self-supervised contrastive learning pretrained model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 7724–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. A theoretical framework for unsupervised change detection based on change vector analysis in the polar domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 45, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T. Unsupervised change detection in satellite images using principal component analysis and k-means clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, S.; Bruzzone, L. ICA and kernel ICA for change detection in multispectral remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 2, pp. II–980. [Google Scholar]
- Bovolo, F.; Marchesi, S.; Bruzzone, L. A framework for automatic and unsupervised detection of multiple changes in multitemporal images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 2196–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Du, B.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L. A post-classification change detection method based on iterative slow feature analysis and Bayesian soft fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L. GlobalMind: Global multi-head interactive self-attention network for hyperspectral change detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 211, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. Unsupervised deep change vector analysis for multiple-change detection in VHR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3677–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydi, S.T.; Hasanlou, M.; Amani, M. A new end-to-end multi-dimensional CNN framework for land cover/land use change detection in multi-source remote sensing datasets. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Du, Q.; Li, X. GETNET: A general end-to-end 2-D CNN framework for hyperspectral image change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wu, C.; Du, B. EMS-Net: Efficient multi-temporal self-attention for hyperspectral change detection. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 6664–6667. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Zhou, T.; Liu, J.; Guo, T.; Gong, X.; Ren, J. Multiscale diff-changed feature fusion network for hyperspectral image change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5502713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.M.; Dias, J.M. Vertex component analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, V.; Niyogi, P.; Belkin, M. A co-regularization approach to semi-supervised learning with multiple views. In Proceedings of the ICML Workshop on Learning with Multiple Views, Citeseer, Bonn, Germany, 7–11 August 2005; Volume 2005, pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Han, H.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Disc: Learning from noisy labels via dynamic instance-specific selection and correction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 24070–24079. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Lee, F.; Chen, Q. TCC-net: A two-stage training method with contradictory loss and co-teaching based on meta-learning for learning with noisy labels. Inf. Sci. 2023, 639, 119008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Cai, W.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Li, W. A review of research on co-training. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2023, 35, e6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Kondmann, L.; Song, Q.; Zhu, X.X. Change detection in hyperdimensional images using untrained models. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11029–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Du, Q.; Tong, X.; Samat, A.; Bruzzone, L. Unsupervised change detection in multispectral remote sensing images via spectral-spatial band expansion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3578–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Du, Q.; Tong, X.; Samat, A.; Pan, H.; Ma, X. Band selection-based dimensionality reduction for change detection in multi-temporal hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wu, C.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Binary change guided hyperspectral multiclass change detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. A subspace-based change detection method for hyperspectral images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Tao, R.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral change detection based on multiple morphological profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5507312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Chen, Z. Hyperspectral image change detection by self-supervised tensor network. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Virtual, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 2527–2530. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Dong, J.; Li, B.; Xu, Q. Automatic change detection in synthetic aperture radar images based on PCANet. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Unsupervised change detection in multitemporal VHR images based on deep kernel PCA convolutional mapping network. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 12084–12098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Z. Self-supervised change detection with nonlocal tensor train and subpixel signature guidance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5529617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).