Estimation of Ultrahigh Resolution PM2.5 in Urban Areas by Using 30 m Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 AOD Retrievals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Region and Data Description
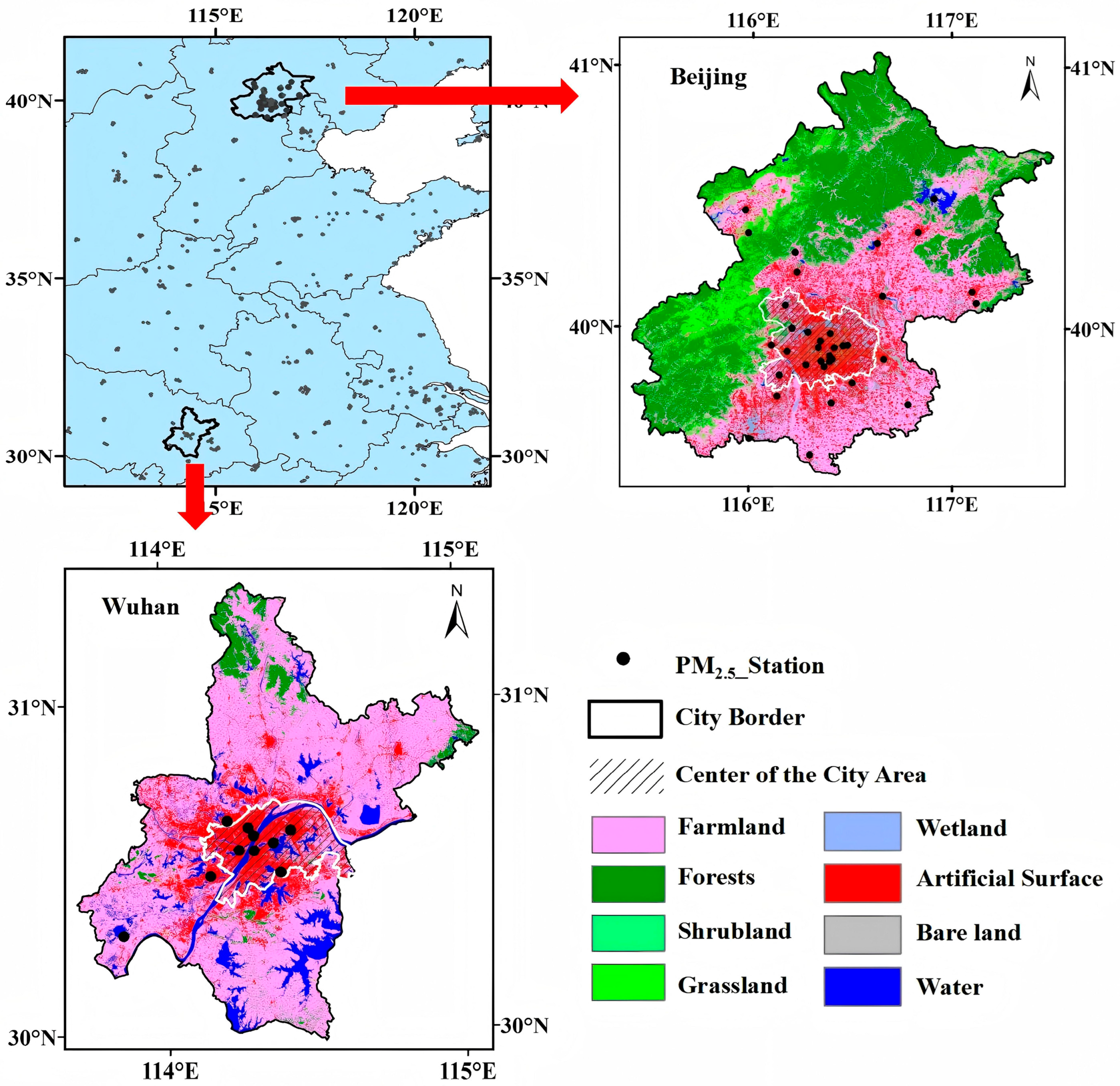
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data Sources
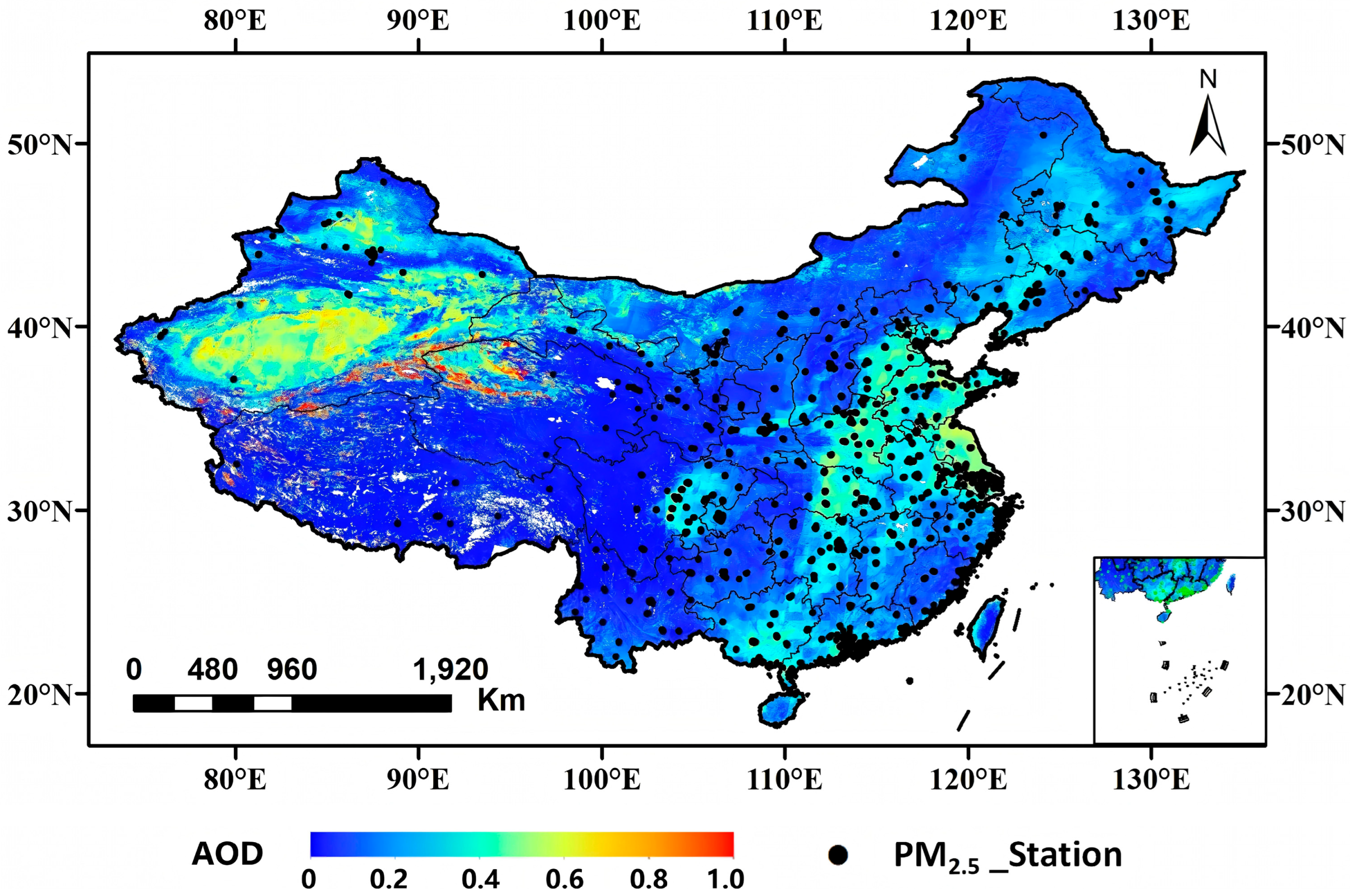
2.2.1. Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 AOD Data
2.2.2. Ground-Measured PM2.5 Data
2.2.3. Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
2.2.4. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
2.2.5. Land Use and Cover Change (LUCC) Data
2.2.6. Meteorological Reanalysis Data
3. Methodology
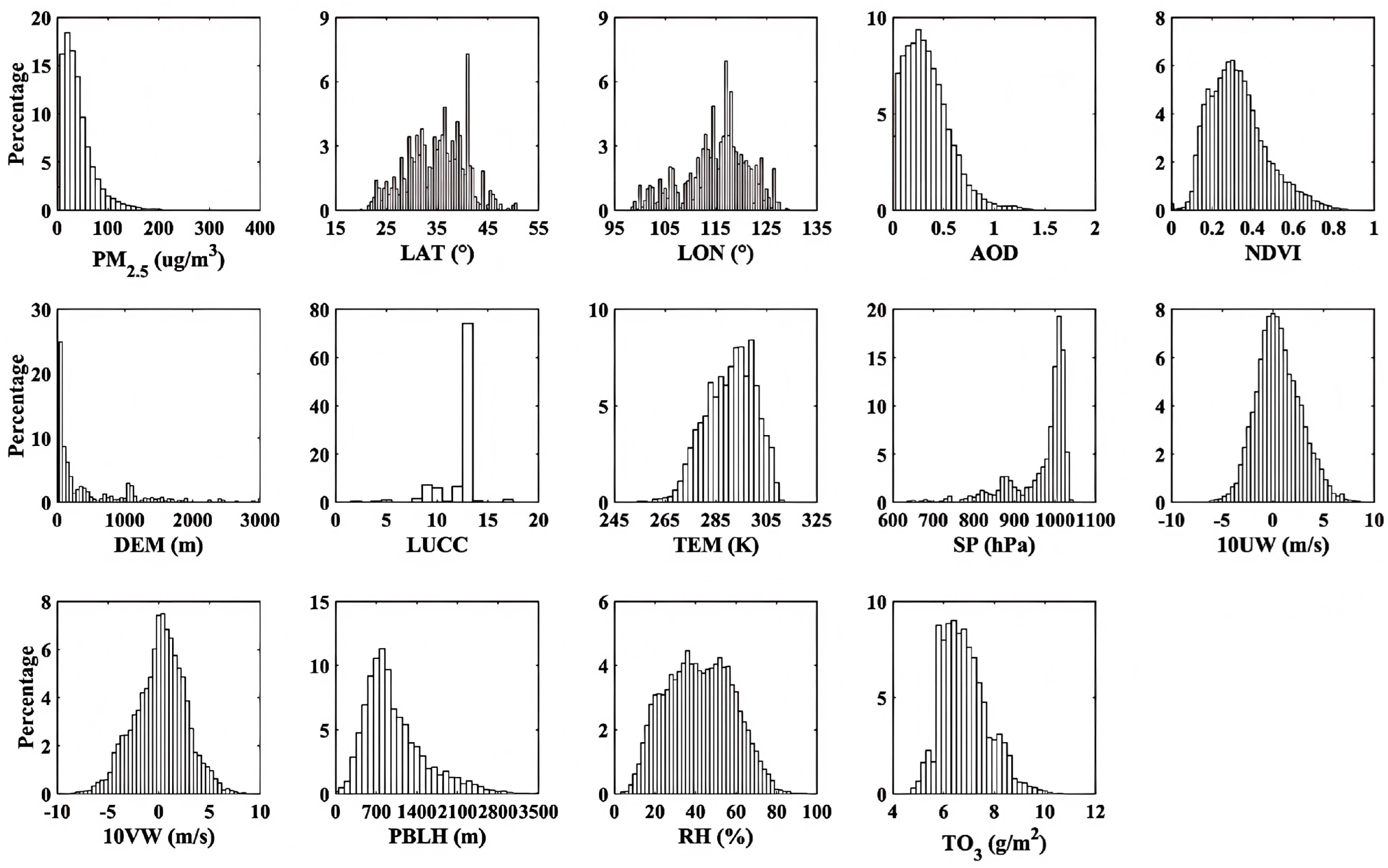
3.1. Selection of Model Parameters
3.2. Model Construction
3.3. Analysis of Model Parameters
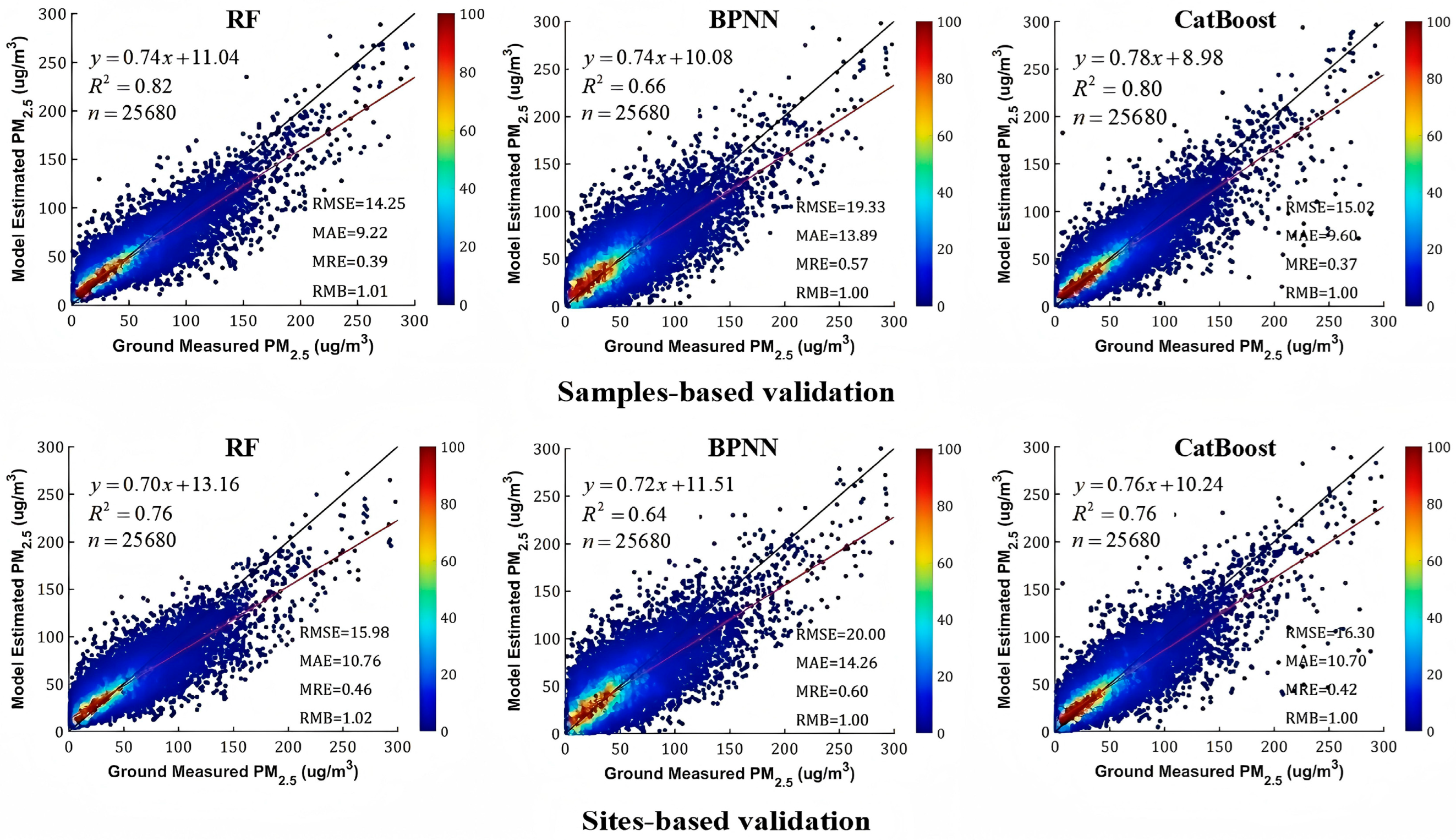
3.4. Model Validation and Evaluation
4. Results
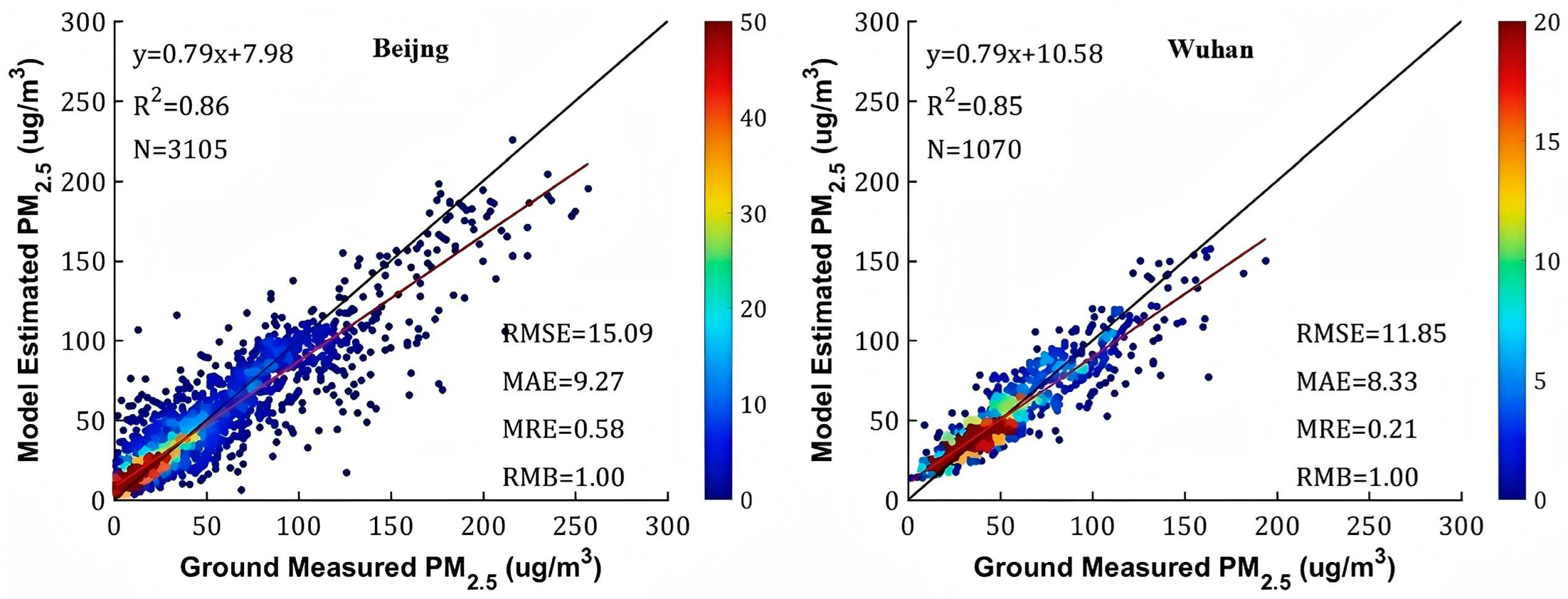
4.1. Overall Accuracy Evaluation
4.2. Accuracy Assessment in Beijing and Wuhan
5. Discussion
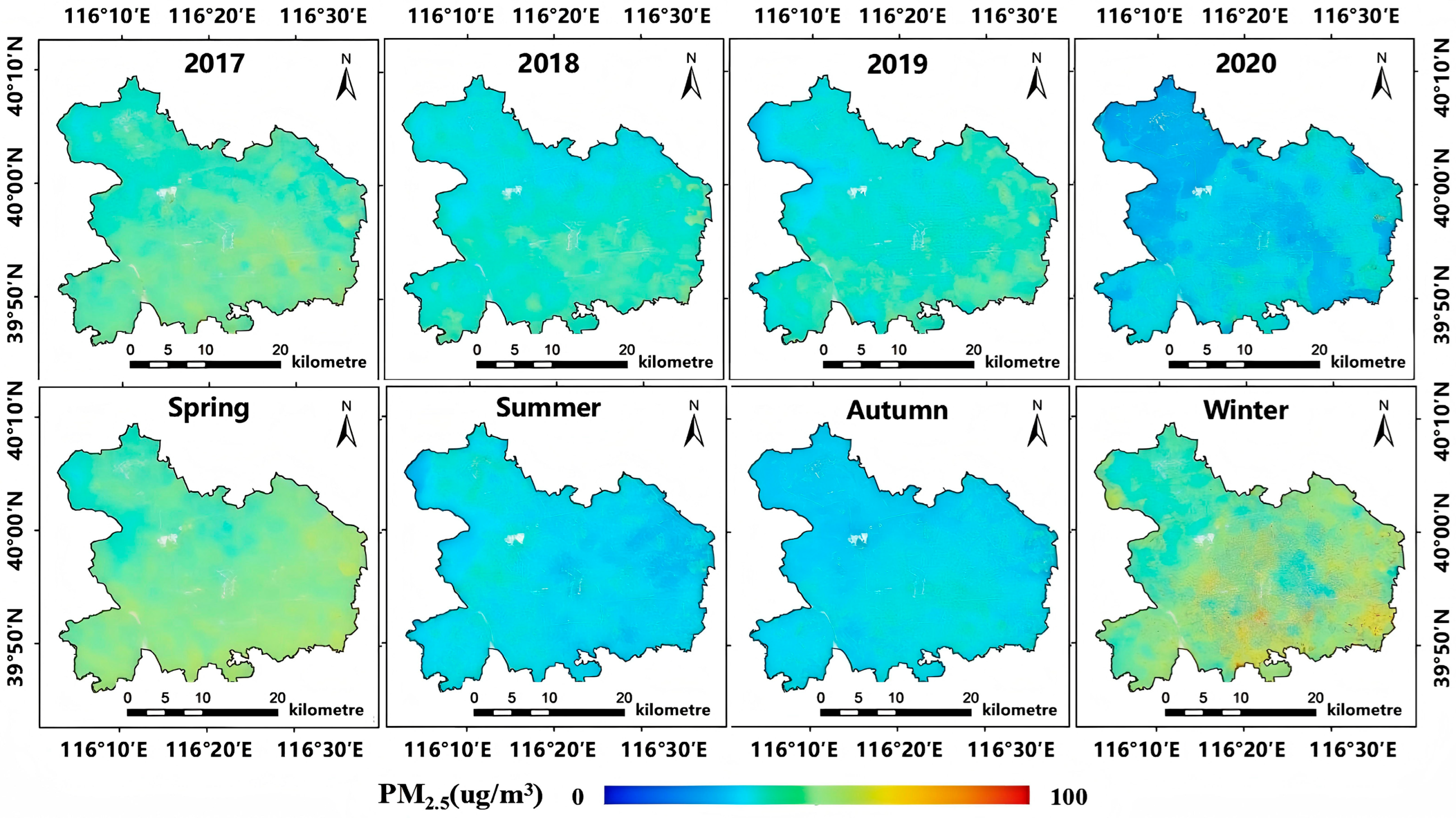
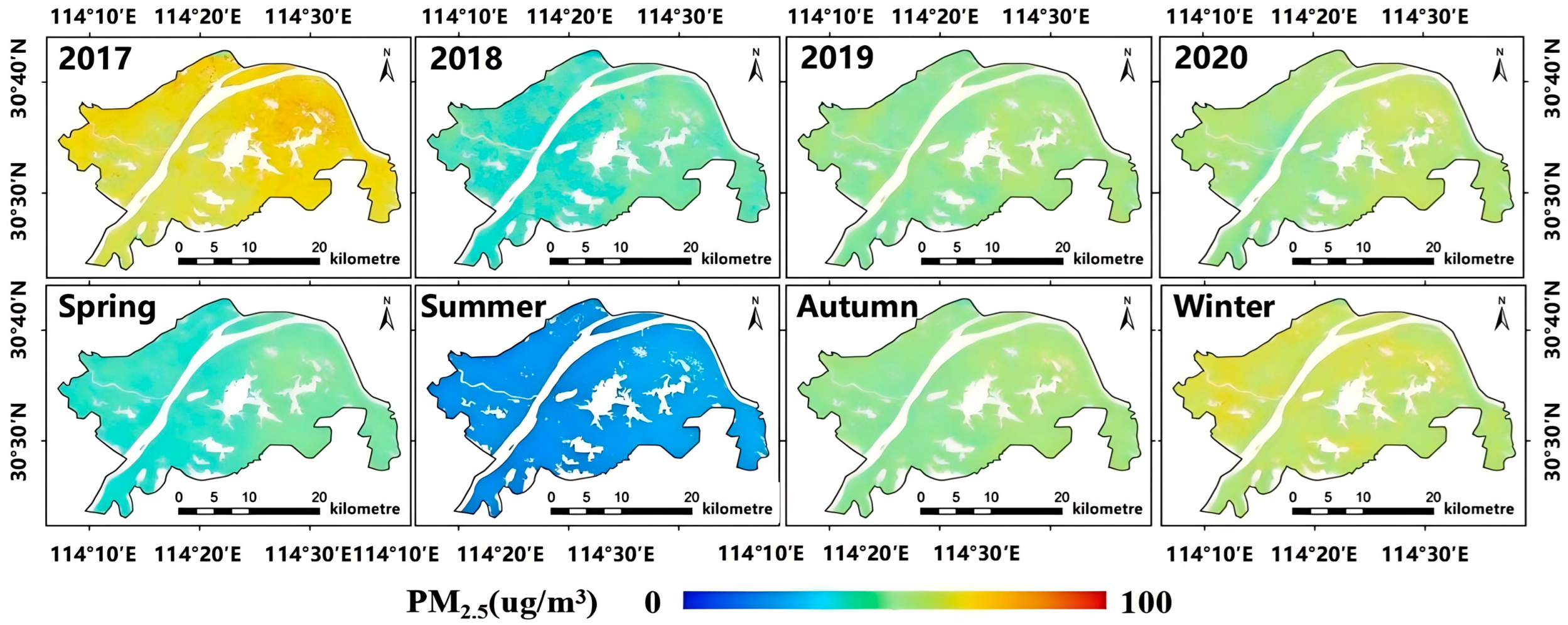
5.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Analysis of PM2.5
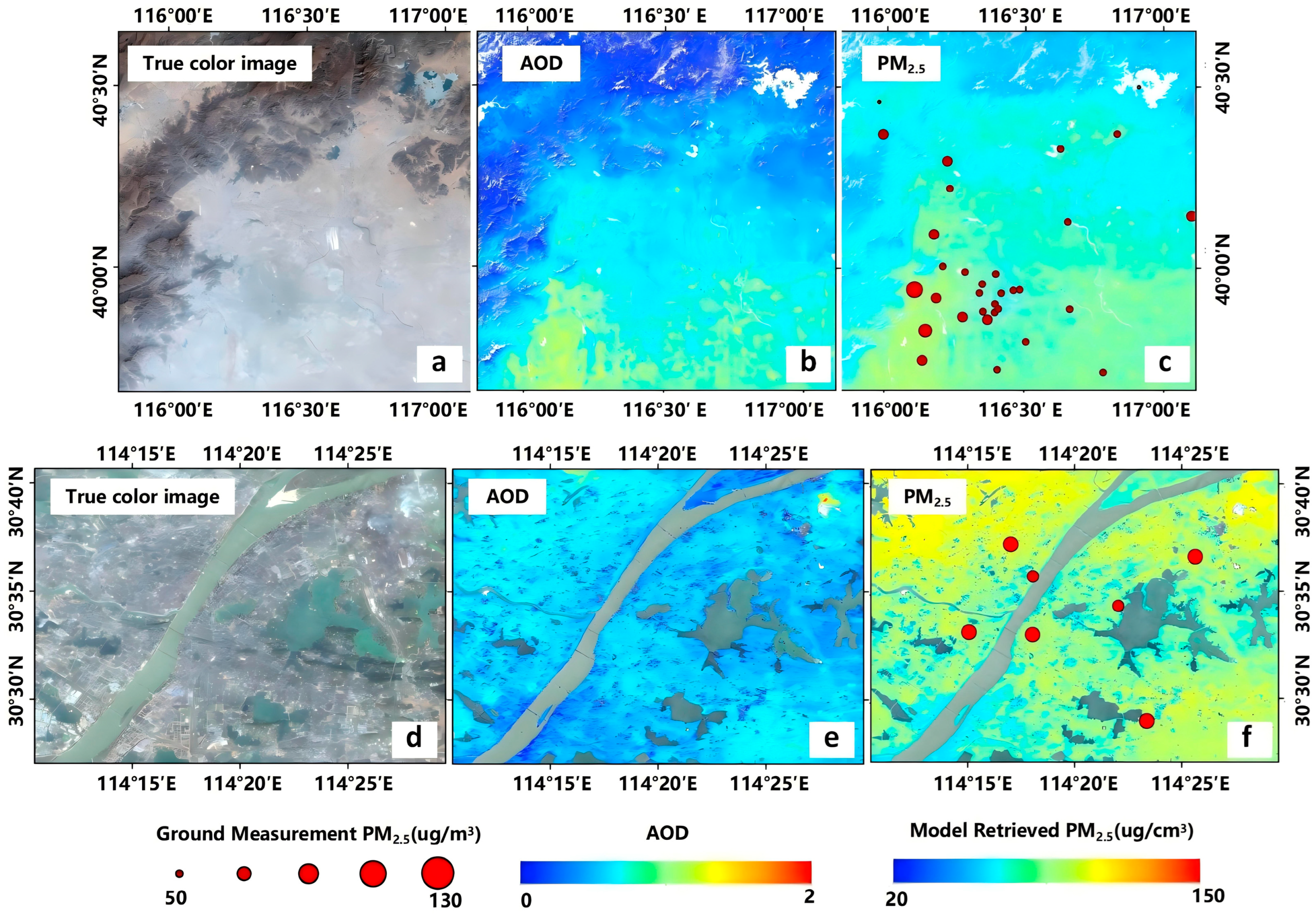
5.2. Monitoring of Point Source Pollution for PM2.5
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Characteristic Parameters (units) | Minimum | Maximum | Median | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (ug/m3) | 1.00 | 373.00 | 33.00 | 41.33 | 33.36 |
| LAT (°) | 20.00 | 50.43 | 35.48 | 34.90 | 5.74 |
| LON (°) | 98.58 | 129.49 | 116.13 | 115.06 | 6.30 |
| AOD (N/A) | 0.01 | 1.65 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.23 |
| NDVI (N/A) | 0.01 | 0.89 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.14 |
| DEM (m) | −1.00 | 3815.00 | 83.00 | 369.63 | 581.74 |
| LUCC (N/A) | 2.00 | 17.00 | 13.00 | 12.25 | 1.90 |
| TEM (K) | 250.30 | 312.40 | 291.70 | 290.76 | 9.64 |
| SP (hPa) | 60.90 | 104.30 | 100.00 | 96.75 | 7.20 |
| 10UW (m/s) | −10.24 | 10.47 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 2.21 |
| 10VW (m/s) | −10.29 | 9.57 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 2.54 |
| PBLH (m) | 12.00 | 4248.00 | 876.00 | 1010.12 | 534.68 |
| RH (%) | 3.14 | 94.52 | 41.69 | 41.91 | 16.23 |
| TO3 (g/m2) | 4.70 | 11.80 | 6.80 | 6.87 | 0.94 |
| Year/Season | Ground Measured PM2.5 (ug/m3) | Model Retrieved PM2.5 (ug/m3) | Error (ug/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 46.27 | 45.21 | 1.06 |
| Summer | 32.89 | 32.65 | 0.24 |
| Autumn | 30.30 | 32.26 | −1.96 |
| Winter | 43.43 | 44.66 | −1.23 |
| 2017 | 45.36 | 43.14 | 2.22 |
| 2018 | 38.03 | 39.00 | −0.97 |
| 2019 | 38.34 | 36.94 | 1.40 |
| 2020 | 26.76 | 27.82 | −1.06 |
| Year/Season | Ground Measurements PM2.5 (ug/m3) | Model Retrieved PM2.5 (ug/m3) | Error (ug/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 43.92 | 43.15 | 0.77 |
| Summer | 29.34 | 31.93 | −2.59 |
| Autumn | 48.59 | 50.16 | −1.57 |
| Winter | 82.91 | 84.89 | −1.98 |
| 2017 | 62.86 | 65.05 | −2.19 |
| 2018 | 41.60 | 43.17 | −1.57 |
| 2019 | 48.79 | 50.34 | −1.55 |
| 2020 | 48.13 | 50.65 | −2.52 |
References
- Tian, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, Z. How Important Is Satellite-Retrieved Aerosol Optical Depth in Deriving Surface PM2.5 Using Machine Learning? Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, P.; Trier, A.; Reyes, J. Prediction of PM2.5 concentrations several hours in advance using neural networks in Santiago, Chile. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangasinghe, M.A.; Singhal, N.; Dirks, K.N.; Salmond, J.A.; Samarasinghe, S. Complex time series analysis of PM10 and PM2.5 for a coastal site using artificial neural network modelling and k-means clustering. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.J.; Hou, J.X.; Jin, L.Y.; Wang, J.J. Artificial neural networks forecasting of PM2.5 pollution using air mass trajectory based geographic model and wavelet transformation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: 2. A neural network approach. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-P.; Wu, Y.-R.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, X.-W. Estimation of PM2.5 over eastern China from MODIS aerosol optical depth using the back propagation neural network. Huanjing Kexue Xuebao/Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 34, 817–825. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.L.; Zhao, S.L.; Jiao, L.M.; Taylor, M.; Zhang, B.E.; Xu, G.; Hou, H.B. Estimation of PM2.5 Concentrations in China Using a Spatial Back Propagation Neural Network. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kow, P.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhou, Y.L.; Kao, I.F.; Issermann, M.; Chang, L.C.; Chang, F.J. Seamless integration of convolutional and back-propagation neural networks for regional multi-step-ahead PM2.5 forecasting. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.P.; Jiang, H.Y.; Wang, J.Z.; Zhou, J.L. A hybrid model for PM2.5 forecasting based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and a general regression neural network. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lian, X.; Wei, L.; Che, J.; Shen, X.; Yang, L.; Qiu, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Ren, X.; et al. PM2.5 forecasting using SVR with PSOGSA algorithm based on CEEMD, GRNN and GCA considering meteorological factors. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 183, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, T.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Estimating Regional Ground-Level PM2.5 Directly From Satellite Top-Of-Atmosphere Reflectance Using Deep Belief Networks. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13875–13886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yue, J.P.; Chen, C.; Xiang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Shi, M.X. A Deep Belief Network Combined with Modified Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm for PM2.5 Concentration Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W. Satellite Aerosol Retrieval Using Scene Simulation and Deep Belief Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Guo, G.; Chen, F.J.; Chen, Y.H. Meteorological pattern analysis assisted daily PM2.5 grades prediction using SVM optimized by PSO algorithm. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chang, F.-J.; Chang, L.-C.; Kao, I.-F.; Wang, Y.-S.; Kang, C.-C. Multi-output support vector machine for regional multi-step-ahead PM2. 5 forecasting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogollón-Sotelo, C.; Casallas, A.; Vidal, S.; Celis, N.; Ferro, C.; Belalcazar, L. A support vector machine model to forecast ground-level PM2. 5 in a highly populated city with a complex terrain. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Belle, J.H.; Meng, X.; Wildani, A.; Waller, L.A.; Strickland, M.J.; Liu, Y. Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations in the Conterminous United States Using the Random Forest Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6936–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, S.; Li, T. Estimating the daily PM2.5 concentration in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region using a random forest model with a 0.01° × 0.01° spatial resolution. Environ. Int. 2019, 134, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokamp, C.; Jandarov, R.; Hossain, M.; Ryan, P. Predicting Daily Urban Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations Using a Random Forest Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4173–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Xiao, Q.; Meng, X.; Geng, G.; Wang, Y.; Lyapustin, A.; Gu, D.; Liu, Y. Predicting monthly high-resolution PM2.5 concentrations with random forest model in the North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R.; Lei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Yue, X.; et al. Global estimates of daily ambient fine particulate matter concentrations and unequal spatiotemporal distribution of population exposure: A machine learning modelling study. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e209–e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-km-resolution high-quality PM2.5 data records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal variations and policy implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southerland, V.A.; Brauer, M.; Mohegh, A.; Hammer, M.S.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Apte, J.S.; Anenberg, S.C. Global urban temporal trends in fine particulate matter (PM2·5) and attributable health burdens: Estimates from global datasets. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e139–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wu, H.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y. Influence of spatial resolution of PM2.5 concentrations and population on health impact assessment from 2010 to 2020 in China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 326, 121505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. 10-year spatial and temporal trends of PM2.5 concentrations in the southeastern US estimated using high-resolution satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6301–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, L.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model for ground-level PM2.5 estimation from satellite-derived 500 m resolution AOD. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Zhao, M.; Xiu, G.; Yu, J. Simultaneous monitoring and compositions analysis of PM1 and PM2.5 in Shanghai: Implications for characterization of haze pollution and source apportionment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Bai, K.; Wei, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, Y.; Cohen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Z.; et al. Satellite remote sensing of atmospheric particulate matter mass concentration: Advances, challenges, and perspectives. Fundam. Res. 2021, 1, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, J.; Dubovik, O.; Schwartz, J.; Sun, L.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Zhu, T. First close insight into global daily gapless 1 km PM2.5 pollution, variability, and health impact. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z. Investigation of air quality over the largest city in central China using high resolution satellite derived aerosol optical depth data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.H.; Zhu, Z.M.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z.R.; Sun, K.; Wang, L.C.; Huang, Y.S.; Mao, F.Y.; Shen, H.F.; Li, Z.W.; et al. Estimation of ultrahigh resolution PM2.5 concentrations in urban areas using 160 m Gaofen-1 AOD retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, S.; Xing, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Dong, L.; Zeng, X. Fusing Retrievals of High Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth from Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Observations over Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Pang, S.; Xi, X.; Cribb, M.; Sun, L. Global aerosol retrieval over land from Landsat imagery integrating Transformer and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 315, 114404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Deng, R.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hua, Z. Estimation of Ultrahigh Resolution PM2.5 Mass Concentrations Based on Mie Scattering Theory by Using Landsat8 OLI Images over Pearl River Delta. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lv, Z.; Deng, Q.; Liu, J.; Ezzati, M.; Baumgartner, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Ultra-high-resolution mapping of ambient fine particulate matter to estimate human exposure in Beijing. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Lee, H.F.; Deng, R.R.; Yim, S.H.L. An analysis of roadside particulate matter pollution and population exposure over the Pearl River Delta region of China under clear-sky condition using new ultra-high-resolution PM2.5 satellite-retrieval algorithms. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 034042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T. Ultrahigh-resolution PM2.5 estimation from top-of-atmosphere reflectance with machine learning: Theories, methods, and applications. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhai, S.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Yin, F.; Ma, Y. Estimating high-resolution PM2.5 concentration in the Sichuan Basin using a random forest model with data-driven spatial autocorrelation terms. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jin, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, N.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Shi, Y. Long-Term Investigation of Aerosol Optical and Radiative Characteristics in a Typical Megacity of Central China During Winter Haze Periods. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 12093–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, S.; Xing, J.; He, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. High resolution aerosol optical depth retrieval over urban areas from Landsat-8 OLI images. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.Y.; Chen, X.D.; Xie, S.; Gao, Y. Fine Land-Cover Mapping in China Using Landsat Datacube and an Operational SPECLib-Based Approach. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, S.; Xing, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, X.; Qin, Y. Joint features random forest (JFRF) model for mapping hourly surface PM2.5 over China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 273, 118969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, C.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Guo, H.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Shi, Z. Estimation of PM2.5 Concentration across China Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and Machine Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Li, Q.; Kilaru, V.; Sarnat, J.A. Mapping annual mean ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical thickness over the contiguous United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Puttaswamy, S.J.; et al. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the Southeastern United States using MAIAC AOD retrievals and a two-stage model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, X. A CatBoost approach with wavelet decomposition to improve satellite-derived high-resolution PM2.5 estimates in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 249, 118212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.D.; Pérez, A.; Lozano, J.A. Sensitivity Analysis of k-Fold Cross Validation in Prediction Error Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Knowland, K.E.; Keller, C.A.; Liu, Y. Combining Machine Learning and Numerical Simulation for High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentration Forecast. Env. Sci Technol. 2022, 56, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, B.N.; Bi, J.; Wang, W.; Huff, A.; Kondragunta, S.; Liu, Y. Application of geostationary satellite and high-resolution meteorology data in estimating hourly PM2.5 levels during the Camp Fire episode in California. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Chang, X.; Xu, D. High-resolution estimation of PM2.5 concentrations across China using multiple machine learning approaches and model fusion. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Shi, W.; Zhang, L. Investigating the performance of satellite-based models in estimating the surface PM2.5 over China. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, S.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, H.; Liao, J.; Chen, Q.; et al. Temporal heterogeneity in the performance of machine learning models for PM2.5 concentration estimation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 189, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschuh, J.; Erbertseder, T.; Baier, F. Systematic Evaluation of Four Satellite AOD Datasets for Estimating PM2.5 Using a Random Forest Approach. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | Name | Abbr | Source | Spatial Resolution | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Measurements | Fine Particulate matter | PM2.5 | CNEMC | Point | ug/m3 |
| Longitude | LAT | CNEMC | Point | degree | |
| Latitude | LON | CNEMC | Point | degree | |
| Satellite Observations | Aerosol Optical Depth | AOD | L8-AOD, S2-AOD | 30 m | - N/A |
| Normalized Vegetation Index | NDVI | Landsat-8, Sentinel-2 | 30 m | - | |
| Digital Elevation Model | DEM | SRTM | 90 m | m | |
| Land Use Cover | LUCC | GLC_FCS30-2020 | 30 m | - | |
| Meteorological Data | 2 m Temperature | TEM | ERA-5 | 0.25° | K |
| Surface Pressure | SP | ERA-5 | 0.25° | hPa | |
| 10 m Eastward Wind Speed | 10UW | ERA-5 | 0.25° | m/s | |
| 10 m Northward Wind Speed | 10VW | ERA-5 | 0.25° | m/s | |
| Planetary Boundary Layer Height | PBLH | ERA-5 | 0.25° | m | |
| Relative Humidity | RH | ERA-5 | 0.25° | % | |
| Total Ozone Concentration | TO3 | ERA-5 | 0.25° | g/m2 |
| PM2.5 | LAT | LON | AOD | NDVI | DEM | LUCC | TEM | SP | 10 UW | 10 VW | PBLH | RH | TO3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 1.00 | −0.11 | −0.01 | 0.42 | −0.18 | −0.12 | 0.09 | −0.15 | 0.13 | −0.09 | 0.10 | −0.28 | 0.23 | −0.06 |
| LAT | / | 1.00 | 0.46 | −0.03 | −0.30 | −0.02 | 0.12 | −0.25 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.14 | −0.42 | 0.60 |
| LON | 0.06 | / | 1.00 | 0.16 | −0.05 | −0.71 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.72 | 0.03 | 0.01 | −0.10 | 0.04 | 0.37 |
| AOD | / | / | / | 1.00 | −0.05 | −0.28 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.29 | −0.17 | 0.12 | −0.12 | 0.34 | −0.03 |
| NDVI | / | / | / | / | 1.00 | −0.04 | −0.42 | 0.50 | 0.01 | −0.13 | 0.06 | −0.03 | 0.31 | −0.40 |
| DEM | / | / | / | / | / | 1.00 | −0.20 | −0.24 | −0.98 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.17 | −0.17 | −0.16 |
| LUCC | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1.00 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | −0.05 | 0.12 |
| TEM | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1.00 | 0.16 | −0.14 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.20 | −0.28 |
| SP | / | / | / | / | 0.25 | / | / | / | 1.00 | −0.14 | −0.06 | −0.20 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| 10UW | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.28 | −0.30 | 0.29 |
| 10VW | / | / | 0.04 | / | / | / | 0.20 | / | / | / | 1.00 | −0.26 | 0.20 | −0.03 |
| PBLH | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1.00 | −0.52 | 0.24 |
| RH | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1.00 | −0.47 |
| TO3 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.; Li, S.; Niu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, S. Estimation of Ultrahigh Resolution PM2.5 in Urban Areas by Using 30 m Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 AOD Retrievals. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152609
Lin H, Li S, Niu J, Yang J, Wang Q, Li W, Liu S. Estimation of Ultrahigh Resolution PM2.5 in Urban Areas by Using 30 m Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 AOD Retrievals. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152609
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Hao, Siwei Li, Jiqiang Niu, Jie Yang, Qingxin Wang, Wenqiao Li, and Shengpeng Liu. 2025. "Estimation of Ultrahigh Resolution PM2.5 in Urban Areas by Using 30 m Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 AOD Retrievals" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152609
APA StyleLin, H., Li, S., Niu, J., Yang, J., Wang, Q., Li, W., & Liu, S. (2025). Estimation of Ultrahigh Resolution PM2.5 in Urban Areas by Using 30 m Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 AOD Retrievals. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2609. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152609








