A Deep Learning-Based Method for Detection of Multiple Maneuvering Targets and Parameter Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We utilized the ACCF method to process the DFM and RM of multi-target signals. This method effectively eliminates RM, reduces the order of DFM, and mitigates interference caused by cross-terms in multi-target scenarios.
- (2)
- By integrating ACCF with FrFT, the proposed method first reduces higher-order DFM induced by complex motion characteristics using ACCF. Subsequently, FrFT is applied to achieve long-duration energy accumulation, enhancing the method’s capacity for the detection of weak targets and enabling the estimation of higher-order parameters such as jerk.
- (3)
- To further address the spectral superposition problem in the FrFT domain for multiple targets, we designed a CNN, which enhances the framework by learning intricate signal features to ensure accurate estimation of high-order parameters, significantly improving detection rates and accuracy.
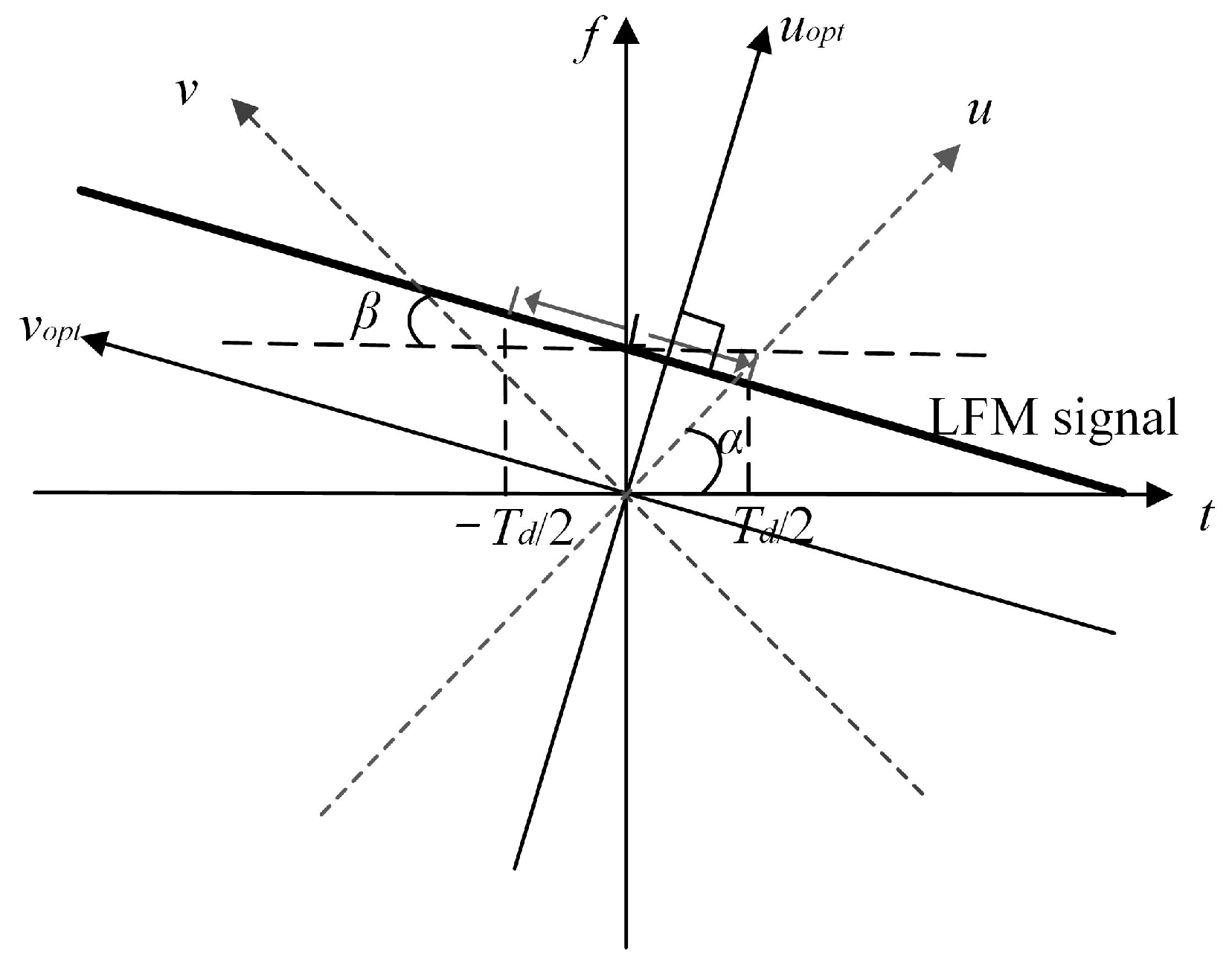
2. Methodology
3. Network Structure for High-Resolution Parameter Estimation
3.1. Input Layer
3.2. Upsampling Module
3.3. High-Resolution Module
3.4. Optimization Function
3.5. Computational Complexity
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Network Parameter Setting
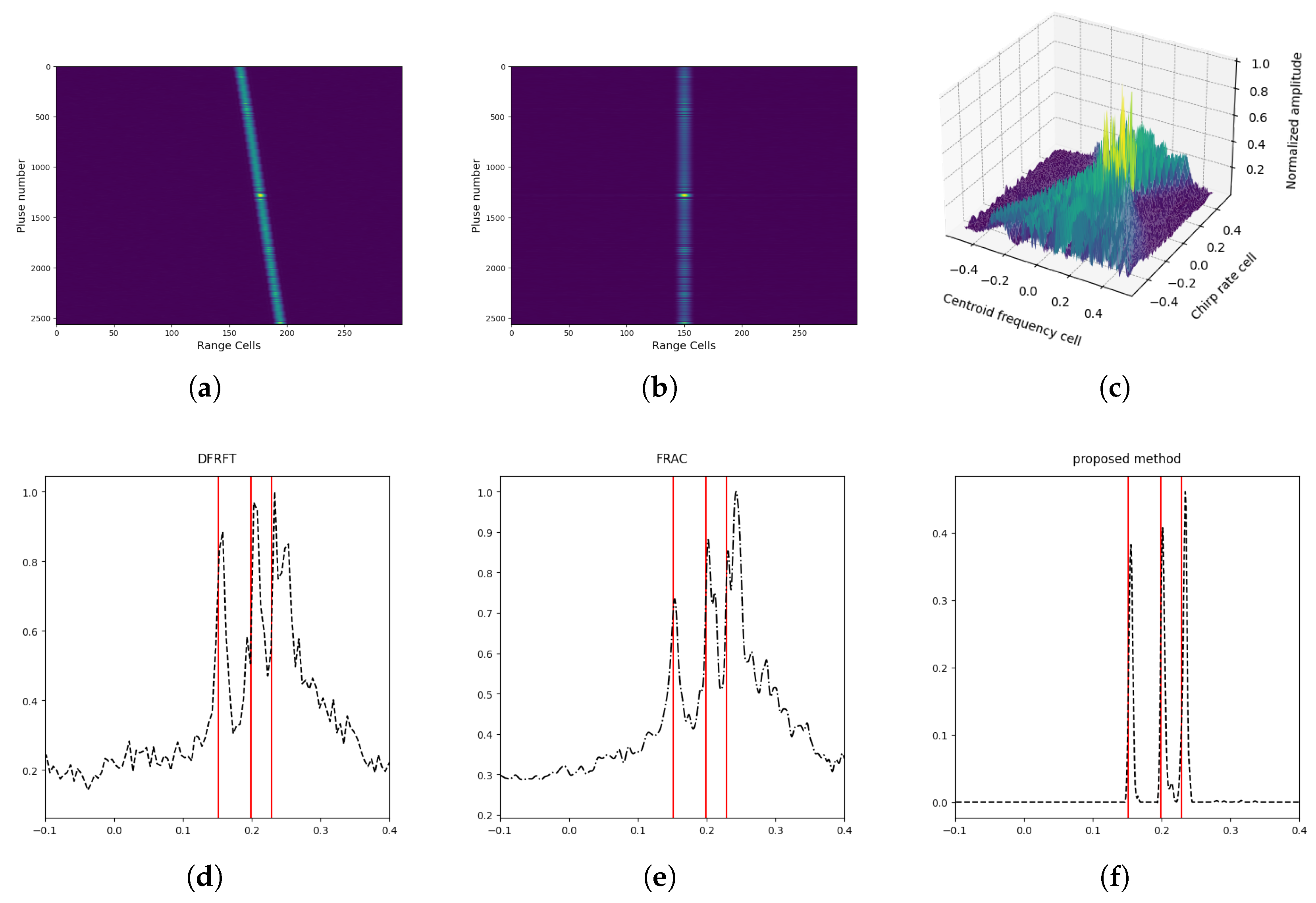
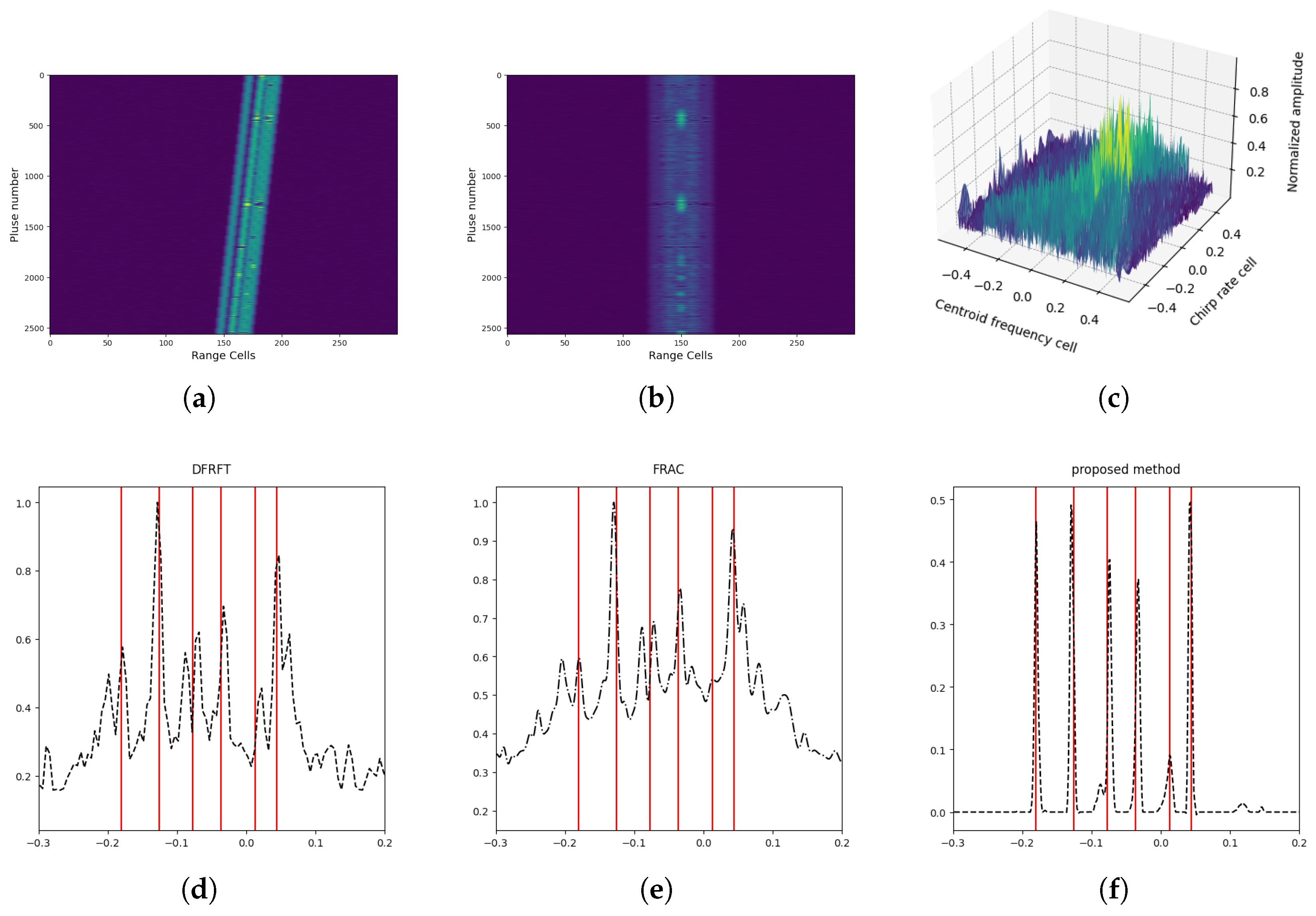
4.2. Capacity for the Coherent Integration of Multiple Targets
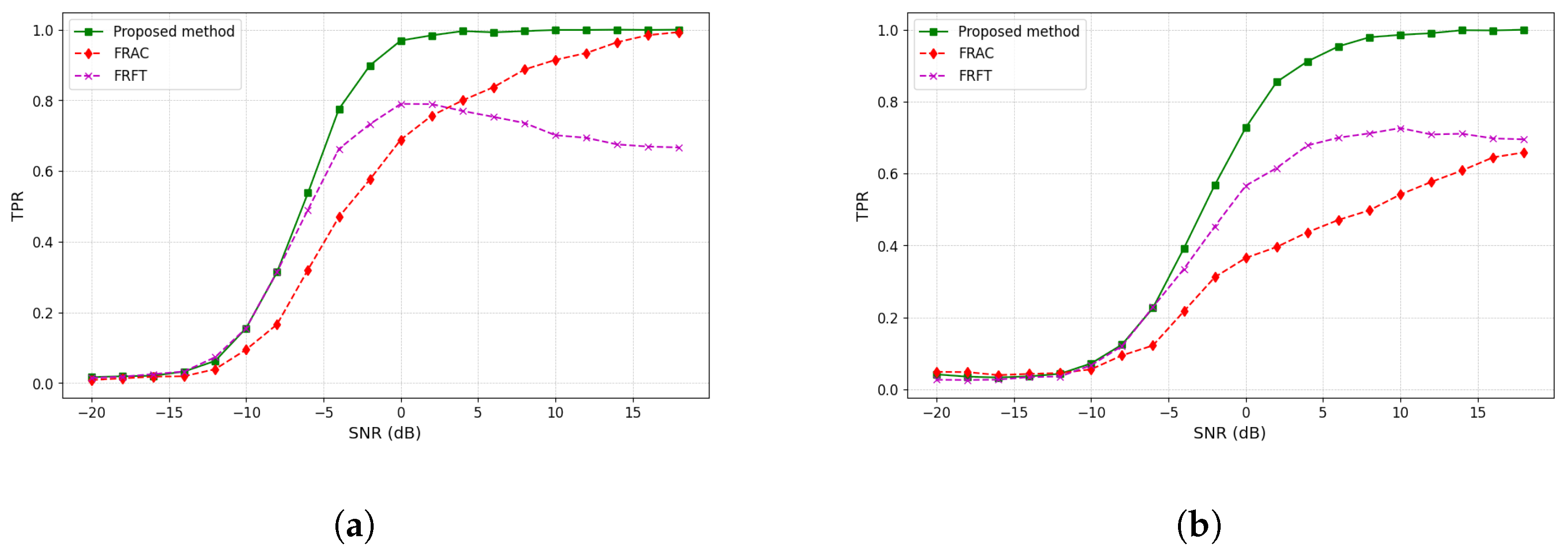
4.3. Capacity for the Detection of Multiple Targets
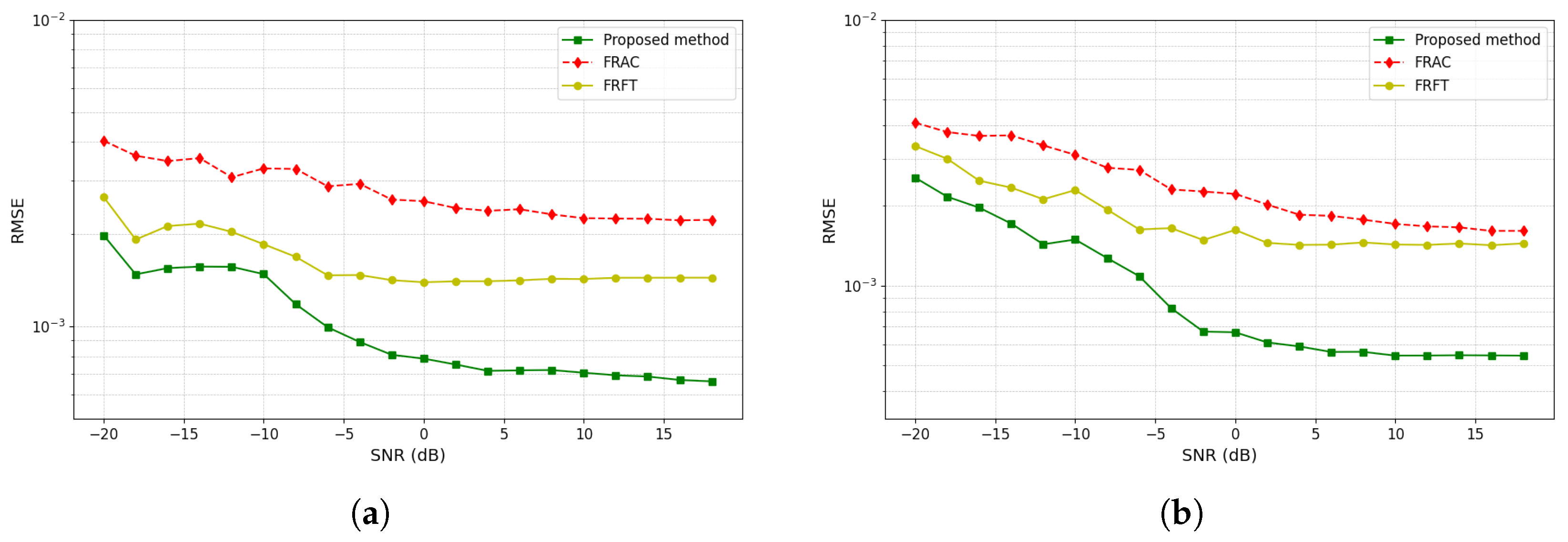
4.4. Parameter Estimation for Multiple Targets
4.5. Comparison of Computational Efficiency
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, S.; Liao, G.L.; Yang, D.; Tao, H. A new method for radar high-speed maneuvering weak target detection and imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, A.; Vorobyov, S.A.; Gershman, A.B. Moving target parameters estimation in noncoherent MIMO radar systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 2354–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, L.; Cui, G.; Yi, W. A fast detection method for maneuvering target in coherent radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 6722–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Tao, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. ISAR imaging of a ship target based on parameter estimation of multicomponent quadratic frequency-modulated signals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Su, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Q.H. ISAR imaging of targets with complex motion based on the chirp rate-quadratic chirp rate distribution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7276–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B. Joint customer assignment, power allocation, and subchannel allocation in a UAV-based joint radar and communication network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 29643–29660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Li, Y.; Cheng, W.; Dong, L.; Tan, Y. Joint DOA-range estimation based on bidirectional extension frequency diverse coprime array. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 4820–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, F.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y. Weak and High Maneuvering UAV Detection via Long-Time Coherent Integration Based on KT-BCS-LSM Method. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, G.H.; Sun, J.P. Polynomial radon-polynomial Fourier transform for near space hypersonic maneuvering target detection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1306–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, N.; Guan, J.; He, Y. Radon-fractional ambiguity function-based detection method of low-observable maneuvering target. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, H.; Jiu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y. Full-dimensional partial-search generalized Radon–Fourier transform for high-speed maneuvering target detection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 5445–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sa’d, M.; Boashash, B.; Gabbouj, M. Design of an optimal piece-wise spline Wigner-Ville distribution for TFD performance evaluation and comparison. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 3963–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chan, A.K.; Chui, C.K. Linear frequency-modulated signal detection using Radon-ambiguity transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1998, 46, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennison, B.K. Detection of polyphase pulse compression waveforms using the Radon-ambiguity transform. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.N.; Xia, X.G. Radon-Fourier transform for radar target detection (II): Blind speed sidelobe suppression. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 2473–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.N.; Xia, X.G. Radon-Fourier transform for radar target detection (III): Optimality and fast implementations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Su, T.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. Radar high-speed target detection based on improved minimalized windowed RFT. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 870–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xia, X.G.; Peng, S.B.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.N.; Qian, L.C. Radar maneuvering target motion estimation based on generalized Radon-Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 6190–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, L. A GRFT-like method for highly maneuvering target detection via neural network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, J.; Liang, Z.; Long, T. Motion parameter estimation and HRRP construction for high-speed weak targets based on modified GRFT for synthetic-wideband radar with PRF jittering. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 23234–23244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Wang, M.; Cui, G.; Yeo, T.S. NU-SCGRFT-Based Coherent Integration Method for High-Speed Maneuvering Target Detection and Estimation in Bistatic PRI-Agile Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Bi, G.; Wan, C.; Xing, M. Lv’s distribution: Principle, implementation, properties, and performance. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3576–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, X.; Cui, G.; Yi, W.; Yichuan, Y. Coherent integration algorithm for a maneuvering target with high-order range migration. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 4474–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. A keystone transform without interpolation for SAR ground moving-target imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Yi, W.; Cui, G.; Kong, L. Fast coherent integration for maneuvering target with high-order range migration via TRT-SKT-LVD. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 2803–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capus, C.; Brown, K.E. Fractional Fourier transform of the Gaussian and fractional domain signal support. IEE Proc.-Image Signal Process. 2003, 150, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capus, C.; Rzhanov, Y.; Linnett, L. The analysis of multiple linear chirp signals. In Proceedings of the IEE Seminar on Time-Scale and Time-Frequency Analysis and Applications, London, UK, 29 February 2000. 4/1–4/7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbes, A.; Durak, L. Optimum signal and image recovery by the method of alternating projections in fractional Fourier domains. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shi, D. Maximum amplitude method for estimating compact fractional Fourier domain. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2010, 17, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbes, A. On the estimation of LFM signal parameters: Analytical formulation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; He, J.; Feng, S. Separation of multicomponent chirp signals using morphological component analysis and fractional Fourier transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldimashki, O.; Serbes, A. Performance of chirp parameter estimation in the fractional Fourier domains and an algorithm for fast chirp-rate estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 3685–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Li, Y.; Cheng, W.; Dong, L.; Kou, Q. High-resolution multicomponent LFM parameter estimation based on deep learning. Signal Process. 2025, 227, 109714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guan, J.; Liu, N.; He, Y. Maneuvering target detection via Radon-fractional Fourier transform-based long-time coherent integration. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadasian, S.S. A fast and accurate method for parameter estimation of multi-component LFM signals. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, G.; Kong, L.; Yi, W. Fast non-searching method for maneuvering target detection and motion parameters estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Yi, W.; Cui, G.; Kong, L. Detection of maneuvering target with complex motions based on ACCF and FRFT. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 0017–0020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaktas, H.M.; Arikan, O.; Kutay, M.A.; Bozdagt, G. Digital computation of the fractional Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-F.; Liu, F. Spectrum characteristic analysis of linear frequency-modulated signals in the fractional Fourier domain. J. Signal Process. 2010, 26, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Wu, G. Complex-valued frequency estimation network and its applications to superresolution of radar range profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Qi, W. Deep learning-based 2-D frequency estimation of multiple sinusoidals. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 5429–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
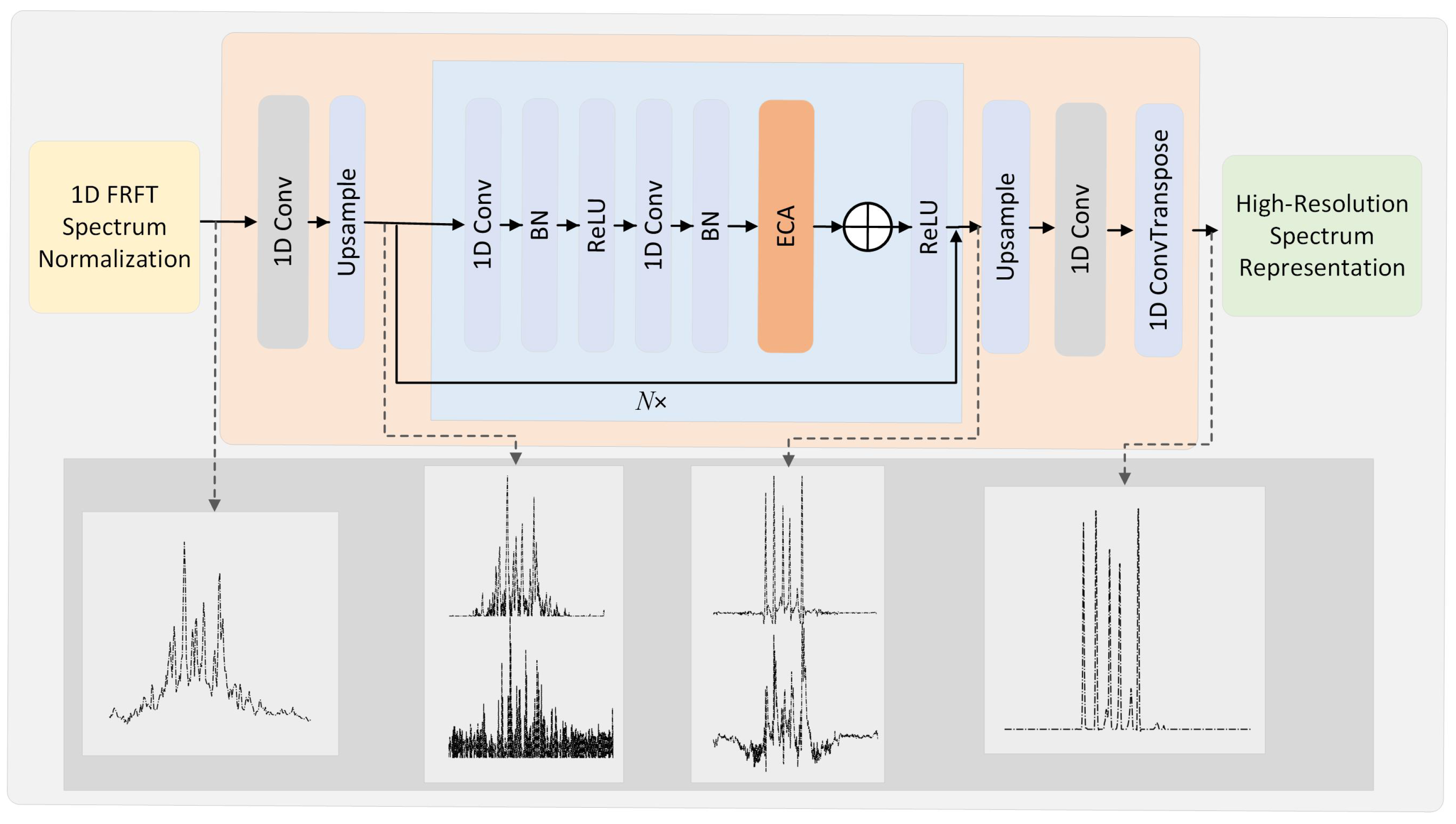

| Model | Layer Number | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| 1D Convolution Layer | 1, 36 | |
| Upsampling Layer | 2, 35 | |
| High Frequency Module | 3–34 | |
| 1D Convolution Transpose | 37 |
| Scenario | Target | Distance (km) | Speed (m/s) | Acceleration (m/s2) | Jerk (m/s3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | Target 1 | 18.0 | 200 | 0 | 6.0 |
| Target 2 | 18.0 | 200 | 0 | 8.0 | |
| Target 3 | 18.0 | 200 | 0 | 9.5 | |
| Scenario 2 | Target 1 | 17.5 | −150 | 0 | −7.5 |
| Target 2 | 17.8 | −150 | 0 | −5.0 | |
| Target 3 | 17.8 | −150 | 0 | −3.0 | |
| Target 4 | 18.0 | −150 | 0 | −1.5 | |
| Target 5 | 18.1 | −150 | 0 | 0.5 | |
| Target 6 | 18.2 | −150 | 0 | 2.0 |
| Methods | Time (ms) |
|---|---|
| FRFT | 47 |
| FRAC | 52 |
| Proposed method | 66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, B.; Li, Y.; Kou, Q.; Chen, R.; Ren, Z.; Cheng, W.; Dong, L.; Luan, L. A Deep Learning-Based Method for Detection of Multiple Maneuvering Targets and Parameter Estimation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152574
Yan B, Li Y, Kou Q, Chen R, Ren Z, Cheng W, Dong L, Luan L. A Deep Learning-Based Method for Detection of Multiple Maneuvering Targets and Parameter Estimation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152574
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Beiming, Yong Li, Qianlan Kou, Ren Chen, Zerong Ren, Wei Cheng, Limeng Dong, and Longyuan Luan. 2025. "A Deep Learning-Based Method for Detection of Multiple Maneuvering Targets and Parameter Estimation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152574
APA StyleYan, B., Li, Y., Kou, Q., Chen, R., Ren, Z., Cheng, W., Dong, L., & Luan, L. (2025). A Deep Learning-Based Method for Detection of Multiple Maneuvering Targets and Parameter Estimation. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152574









