Constructing an Ecological Spatial Network Optimization Framework from the Pattern–Process–Function Perspective: A Case Study in Wuhan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Methods Framework
- (1)
- According to ecosystem service theory, ecological functions include regulatory, supporting, and provisioning services [46]. In this study, four typical ecosystem services—habitat quality (HQ), water conservation (WC), soil retention (SR), and carbon sequestration (CS)—are selected to represent functional outcomes, reflecting the service capacity of ecological patches. HQ indicates habitat stability and integrity, WC reflects hydrological regulation capacity, which is especially important in lake-dense urban areas [47], and SR and CS capture soil and carbon regulation capacities in response to environmental pressure [48].
- (2)
- According to the LEH framework, process evaluation should capture system vigor, resilience, and sensitivity [34]. Accordingly, process indicators include NDVI (plant vigor), modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI, water dynamics), an eco-elasticity index (comprising resistance, adaptation, and recovery), and ecological sensitivity (represented by soil erosion). These indicators capture the spatiotemporal dynamics and adaptive capacity of the urban ecological system under disturbance. MNDWI is chosen to emphasize the urban hydrological dynamics relevant to Wuhan’s landscape, especially for distinguishing surface water changes where NDVI is limited [49]. The resilience and sensitivity indices reflect the system’s response thresholds and recovery capabilities [50].
- (3)
- From the pattern dimension, based on complex network theory, EN structure is described through four topological indicators: degree centrality, betweenness centrality, closeness centrality, and clustering coefficient. These reflect connectivity, nodal importance, accessibility, and local structural aggregation [33,51], allowing quantitative assessment of network configuration.
2.2.1. Measurement of Ecosystem Services
2.2.2. Assessment of Ecological Process
Vigor
Eco-Elasticity
Sensitivity
2.2.3. Construction of Ecological Security Pattern
Ecological Sources
- (1)
- Landscape Connectivity
- (2)
- Ecological Sensitivity
Ecological Corridors and Key Nodes
- (1)
- Ecological Resistance Surface
- (2)
- Ecological Corridors, Pinch Points, and Barriers
Network Topological Pattern
2.2.4. Optimization and Evaluation of Ecological Network
Network Optimization
Evaluation of Optimization Effectiveness
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ecosystem Services
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Landscape Ecological Processes
3.3. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ecological Network and Topology Characteristics
3.3.1. Ecological Network Construction
3.3.2. Network Topological Characteristics
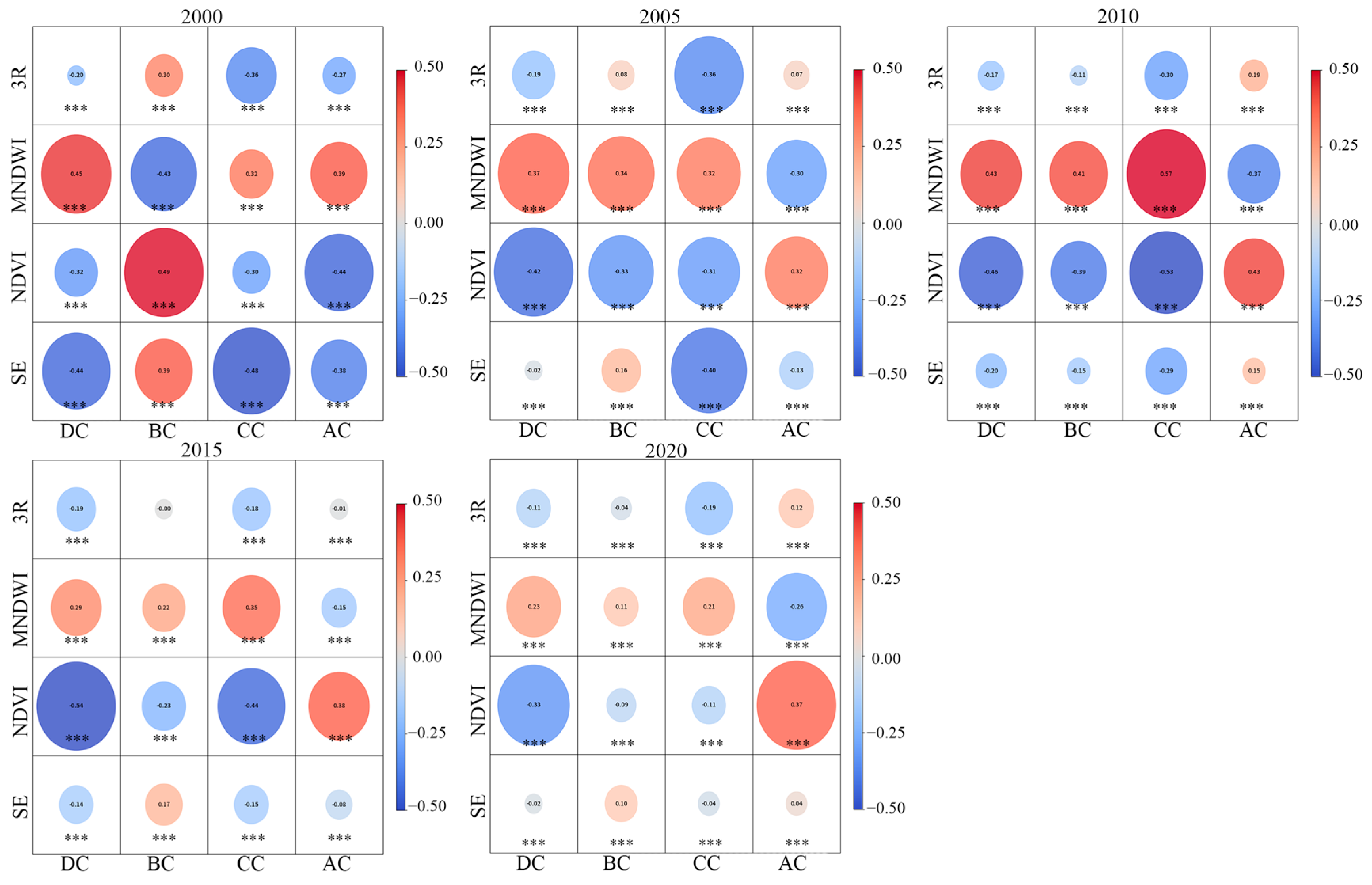
3.4. Correlation Between Ecological Function, Process, and Network Pattern
3.4.1. Pattern–Function Correlation
3.4.2. Pattern–Process Correlation
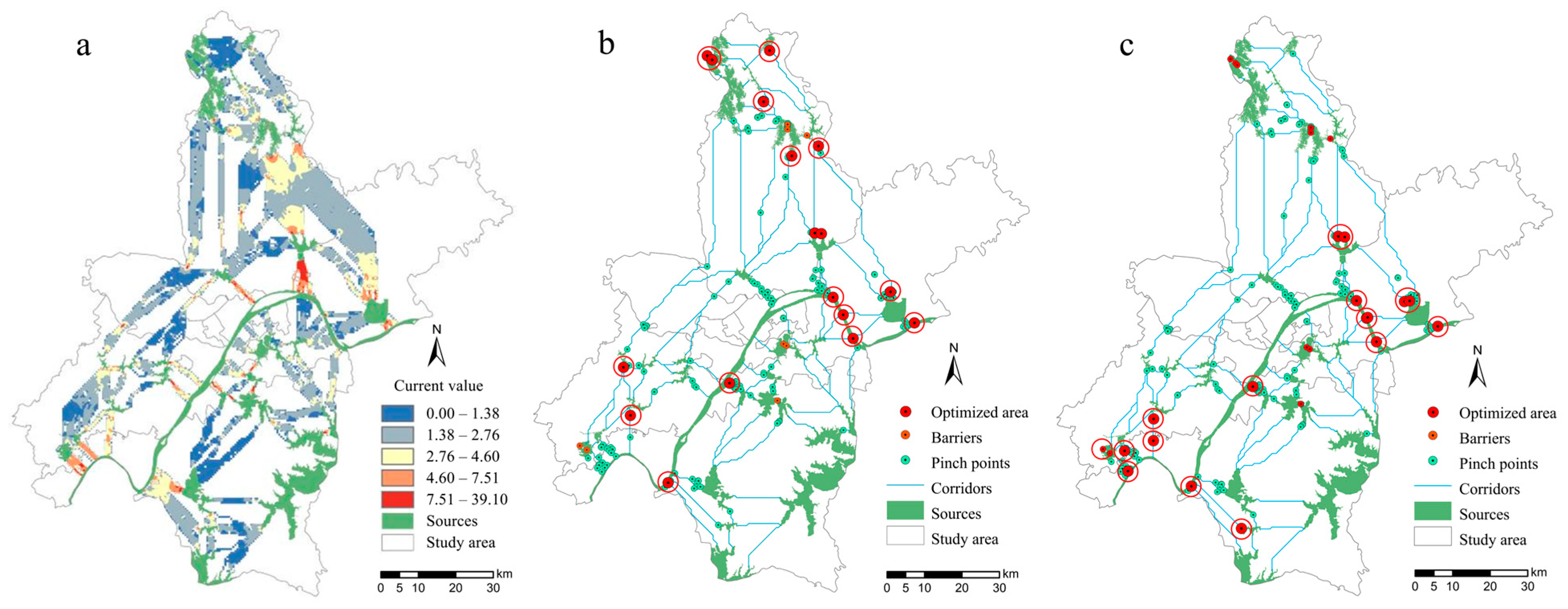
3.5. EN Optimization and Effectiveness Evaluation
3.5.1. Ecological Network Optimization
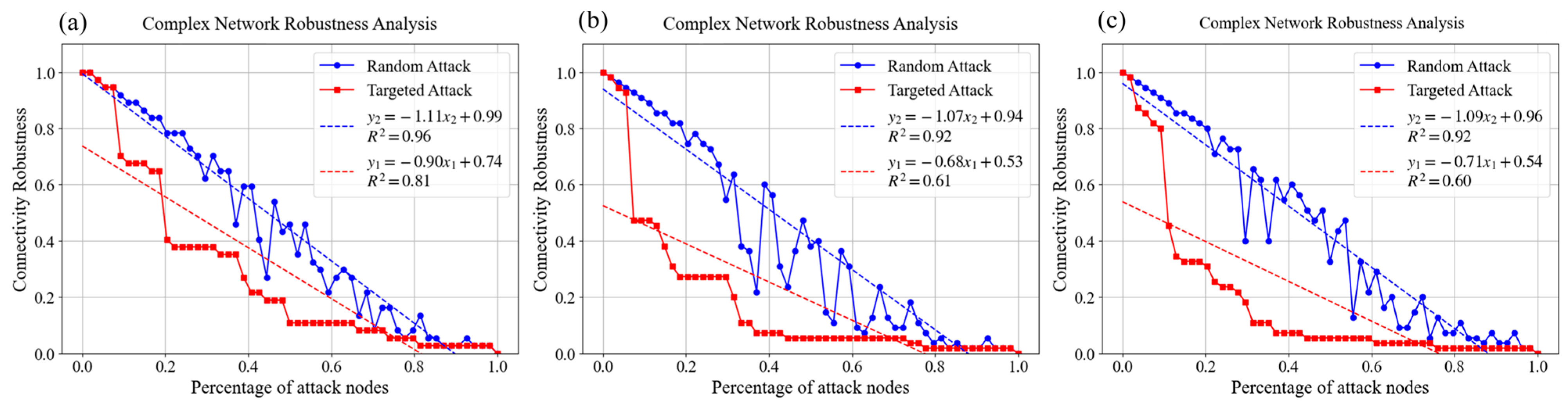
3.5.2. Evaluation of Ecological Network Optimization
4. Discussion
4.1. Value and Necessity of Optimizing Ecological Networks from a Long-Term Pattern–Process–Function Perspective
4.2. Correlation Between Ecosystem Services, Ecological Processes, and Network Topological Characteristics
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Two Optimization Scenarios and Their Synergistic Implications
4.4. Deficiencies and Prospects of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EN | Ecological Network |
| ES | Ecosystem Service |
| HQ | Habitat Quality |
| WC | Water Conservation |
| SR | Soil Retention |
| CS | Carbon Sequestration |
| MSPA | Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis |
| NTC | Network Topological Characteristics |
| DC | Degree Centrality |
| BC | Betweenness Centrality |
| CC | Closeness Centrality |
| AC | Clustering Coefficient |
| PFO | Pattern–Function Optimization |
| PPO | Pattern–Process Optimization |
References
- Jiang, J.; Cai, J.; Peng, R.; Li, P.; Chen, W.; Xia, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Z. Establishment and optimization of urban ecological network based on ecological regulation services aiming at stability and connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Leng, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Qiu, Y.A.; Wu, Q.; et al. Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Nie, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Xu, B. Assessment and optimization of urban ecological network resilience based on disturbance scenario simulations: A case study of Nanjing city. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 438, 140812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Bin Xu, B.; Yang, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B.; Wu, R.; Lin, W.; Pei, H.; Bao, Z. Simulating future land use by coupling ecological security patterns and multiple scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, B.; Nie, W. The impact of connectivity in natural protected areas on the resilience of urban ecological networks: A research framework based on hierarchical disturbance scenario simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 164, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, B. Pattern, process, and function in landscape ecology and catchment hydrology—How can quantitative landscape ecology support predictions in ungauged basins? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhao, W.; Pereira, P. Ecosystem restoration along the “pattern-process-service-sustainability” path for achieving land degradation neutrality. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 253, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Jia, K.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, W.; Hu, X.; Cherubini, F. A framework for regional ecosystem authenticity evaluation-a case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 31, e01849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cai, Y. Impact of ecological risk and ecosystem health on ecosystem services. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2024, 79, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, R.T.T. Some general principles of landscape and regional ecology. Landsc. Ecol. 1995, 10, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Du, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Wang, F.; Fu, M. Research progress and prospects for constructing ecological security pattern based on ecological network. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, S. Stepwise Construction and Integration of Ecological Network in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study on Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Li, M. Constructing ecological security patterns using remote sensing ecological index and circuit theory: A case study of the Changchun-Jilin-Tumen region. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizizi, Y.; Kasimu, A.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, B. Evaluation of ecological space and ecological quality changes in urban agglomeration on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, M.; Li, Z.; Zeng, J. Multi-scenario simulation of urban growth boundaries with an ESP-FLUS model: A case study of the Min Delta region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X. The role of land use change in affecting ecosystem services and the ecological security pattern of the Hexi Regions, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Delimitation of ecological corridors in a highly urbanizing region based on circuit theory and MSPA. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Fu, B.; Ma, R.; Yang, Y.; Lü, Y.; Wu, X. Identifying ecological security patterns based on the supply, demand and sensitivity of ecosystem service: A case study in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Deng, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, W.; de Vries, W.T. Construction and optimization of ecological security patterns based on social equity perspective: A case study in Wuhan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wu, X.; Wen, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, F.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, J. Ecological Security Pattern based on XGBoost-MCR model: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 470, 143252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, P.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Rong, T.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Lou, Y. Construction of GI Network Based on MSPA and PLUS Model in the Main Urban Area of Zhengzhou: A Case Study. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 878656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Yue, W.; Wu, T. Optimizing ecological security pattern in the coal resource-based city: A case study in Shuozhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tang, F.; Wang, G.; Li, M. Construction of an ecological security network in the Fenhe River Basin and its temporal and spatial evolution characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 137961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, Q.Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, S.C.; Cao, J.R. Ecological network construction and optimization of typical resource-based regions, and strategies for the enhancement of multiple ecosystem services: Balancing function and structure. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 112951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Pan, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T.; He, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yao, C. Identifying priority areas for ecological conservation and restoration based on circuit theory and dynamic weighted complex network: A case study of the Sichuan Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Jia, G.; Yang, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Svenning, J.; Wen, L. Construction of ecological network and its temporal and spatial evolution characteristics: A case study of Ulanqab. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xiong, H.; Ying, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J. Construction and optimization of watershed-scale ecological network based on complex network method: A case study of Erhai Lake Basin in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Exploring the optimization and management methods of ecological networks based on the cluster mode: A case study of Wuhan Metropolis, China. Land Use Policy 2024, 137, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Song, X.N.; Leng, P.; Zhu, X.M.; Hu, R.H.; Guo, D.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Xue, K. Higher water ecological service values have better network connectivity in the middle Yellow River basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xiu, L.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J. Ecological networks construction and optimization in the Longdong Loess Plateau: The advantages of self-organizing map and complex networks. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Hu, M.; Xia, B. Integrating ecosystem services and landscape connectivity into the optimization of ecological security pattern: A case study of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76051–76065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, D.; Pan, J. Incorporating network topology and ecosystem services into the optimization of ecological network: A case study of the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Y.F. Integrating pattern, process, and function in urban landscape ecological network planning: A case study of Harbin central city. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liang, X.; Guo, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Li, G.; Likulunga, L.E. The analysis of ecological network characteristics of Baiyangdian Basin in China using the complex network theory. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.Y.; Ai, J.W.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, C.H. Exploring the Spatial Relationship between the Ecological Topological Network and Carbon Sequestration Capacity of Coastal Urban Ecosystems: A Case Study of Yancheng City, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Shi, F.; Beazley, R. Construction and optimization of an ecological network based on morphological spatial pattern analysis and circuit theory. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2059–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Xu, C.L.; Ma, J.J.; Liu, H.J. Study on the relationship between topological characteristics of ecological spatial network and soil conservation function in southeastern Tibet, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Li, T.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Lü, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. Variable climatic conditions dominate decreased wetland vulnerability on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Insights from the ecosystem pattern-process-function framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Gao, G.; Fu, B. Spatiotemporal changes and driving forces of ecosystem vulnerability in the Yangtze River Basin, China: Quantification using habitat-structure-function framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Sun, L.; Su, X.; Chen, L. A review on the coupling research of landscape patterns and ecological processes: Consistency and innovation. Shengtai Xuebao 2021, 41, 415–421. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, Y.; Hong, G.; Wu, X. Identifying priority wetlands for the conservation of waterbirds in Wuhan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Wen, X.; Feng, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, W. Optimizing urban ecological space based on the scenario of ecological security patterns: The case of central Wuhan, China. Appl. Geogr. 2022, 138, 102619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.B.; Huang, Y. The complex ecological network’s resilience of the Wuhan metropolitan area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Wu, X. Nonlinear trade-off relationship and critical threshold between ecosystem services and climate resilience for sustainable urban development. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 103, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Yuan, S.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Ren, C.; Bian, J.; Li, T.; Ping, Z. Spatial and temporal characteristics of water conservation services and rapid response framework for water yield in key ecological zones of the Yiluo River basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 60, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Tian, C.; Yuan, Q.; Deng, W. Effects of different restoration years on soil carbon sequestration and water retention capacity in bamboo forest: A case study in Southwest China Karst. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 210, 107434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Shao, Z.; Dang, C.; Huang, X.; Wu, W.; Zhuang, Q.; Ding, Q. Assessing urban wetlands dynamics in Wuhan and Nanchang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Doyen, L.; Béné, C.; Borgomeo, E.; Brooks, K.; Chu, L.; Cumming, G.S.; Dixon, J.; Dovers, S.; Garrick, D.; et al. Realizing resilience for decision-making. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, K.; Liang, X.F.; Jiang, X.B.; Wang, J.P.; You, Y.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Chang, S.H.; Wei, C.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; et al. Identification of priority areas to provide insights for ecological protection planning: A case study in Hechi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEA. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 1–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, P.; Hu, S.; Frazier, A.E.; Yang, S.; Song, X.; Qu, S. The dynamic relationships between landscape structure and ecosystem services: An empirical analysis from the Wuhan metropolitan area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shi, X.; Wu, Q. Effects of protection and restoration on reducing ecological vulnerability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Guan, T.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Ma, T. The sensitivity of vegetation cover to climate change in multiple climatic zones using machine learning algorithms. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Lin, Y. Assessing ecological vulnerability and resilience-sensitivity under rapid urbanization in China’s Jiangsu province. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Long, Y.; Yang, L.; Ding, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, T. Impacts of urbanization on the spatiotemporal evolution of ecological resilience in the Plateau Lake Area in Central Yunnan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zeng, F.; Loo, B.P.Y.; Zhong, Y. The evolution of urban ecological resilience: An evaluation framework based on vulnerability, sensitivity and self-organization. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Spatial-Temporal Evolutions of Ecological Environment Quality and Ecological Resilience Pattern in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, Y. Construction of an ecological security pattern in Jiangnan water network area based on an integrated Approach: A case study of Gaochun, Nanjing. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Min, M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Liu, T. Optimization of ecological connectivity and construction of supply-demand network in Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, K.; Peng, L. Flood Risk Assessment under Land Use and Climate Change in Wuhan City of the Yangtze River Basin, China. Land 2021, 10, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Huang, M.; Lin, H. Construction of an ecological security pattern in rapidly urbanizing areas based on ecosystem sustainability, stability, and integrity. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Montis, A.; Caschili, S.; Mulas, M.; Modica, G.; Ganciu, A.; Bardi, A.; Ledda, A.; Dessena, L.; Laudari, L.; Fichera, C.R. Urban-rural ecological networks for landscape planning. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Peng, L.; Wang, X.; Deng, W.; Liu, Y. Incorporating circuit theory, complex networks, and carbon offsets into the multi-objective optimization of ecological networks: A case study on karst regions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Li, W.; Yue, R. Integrating spatial carbon factors into ecological network construction in an energy-intensive megaregion toward multi-objective synergy in northern China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Fang, M.Z.; Guo, H.Q.; Liu, H.J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.Y. Restoration and renewal of ecological spatial network in mining cities for the purpose of enhancing carbon Sinks: The case of Xuzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Bai, J.; Lü, Y.; Li, J. The cascade failure model under ecological network is effective for quantifying the resilience of urban regions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 114, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Niu, T.; Yu, Q.; Yang, L.Z.; Ma, J.; Qiu, S. Evaluation of the Spatiotemporal Evolution of China’s Ecological Spatial Network Function-Structure and Its Pattern Optimization. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Gao, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mao, W.; Lu, X. Optimization of ecological network to improve water conservation services in the Nianchu River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 372, 123368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, D.W.; Yin, J.F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Feng, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.J. Regional ecosystem health improvement pathway design based on ecological network optimization. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 173, 113377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, B.; Li, M.; Du, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Identification of priority areas for territorial ecological conservation and restoration based on ecological networks: A case study of Tianjin City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhai, G.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Research on regional terrestrial carbon storage based on the pattern-process-function. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Sun, Q.; Peng, S. Research on synergistic optimization of ecological network under the dual-objective orientation of “blind zone reduction” and “functional structure coordination”: A case study of Wuhan. Shengtai Xuebao 2025, 45, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhai, T.; Cheng, H. An integrated approach towards spatial identification of restored and conserved priority areas of ecological network for implementation planning in metropolitan region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.F.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Yu, Q. Study on the relationship between ecological spatial network structure and regional carbon use Efficiency: A case study of the Wuding river basin. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Du, W.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Bian, H. Evaluation and Optimization of Hydrological Connectivity Based on Graph Theory: A Case Study in Dongliao River Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morino, Y.; Miwa, H. Network Design Method Resistant to Cascade Failure Considering Betweenness Centrality; Barolli, L., Nishino, H., Miwa, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1035, pp. 360–369. [Google Scholar]
- Valdez, L.D.; Shekhtman, L.; La Rocca, C.E.; Zhang, X.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Trunfio, P.A.; Braunstein, L.A.; Havlin, S. Cascading failures in complex networks. J. Complex Netw. 2020, 8, cnaa013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Suh, S.; Kim, J.; Park, H.S. Urban water infrastructure optimization to reduce environmental impacts and costs. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwo, B.E.; Al Kafy, A.; Samuel, A.A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Ayowole, O.E.; Shahrier, M.; Duti, B.M.; Rahman, M.T.; Peter, O.T.; Abosede, O.O. Monitoring and predicting the influences of land use/land cover change on cropland characteristics and drought severity using remote sensing techniques. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 18, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, D.; Pan, J. Integrating key species distribution and ecosystem service flows to build directed ecological network: Evidence from the Shiyang River Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 381, 125183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Lu, Y. A conceptual model for a process-oriented landscape pattern analysis. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yen, H.; Chen, L.; Zhao, F.; Yan, L. Distribution of agricultural land regulates stream water isotopes over multiple spatial scale in a subtropical forested watershed. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Cui, W.; Yang, F. Spatiotemporal variations and driving forces analysis of ecosystem water conservation in coastal areas of China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 112019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yan, W.; Li, Z.; Wende, W.; Xiao, S. A framework for integrating ecosystem service provision and connectivity in ecological spatial networks: A case study of the Shanghai metropolitan area. Sust. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hu, Y.; Bai, Y. Construction of ecological security pattern in national land space from the perspective of the community of life in mountain, water, forest, field, lake and grass: A case study in Guangxi Hechi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Mao, D.; Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Optimizing ecological security patterns considering zonal vegetation distribution for regional sustainability. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 194, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
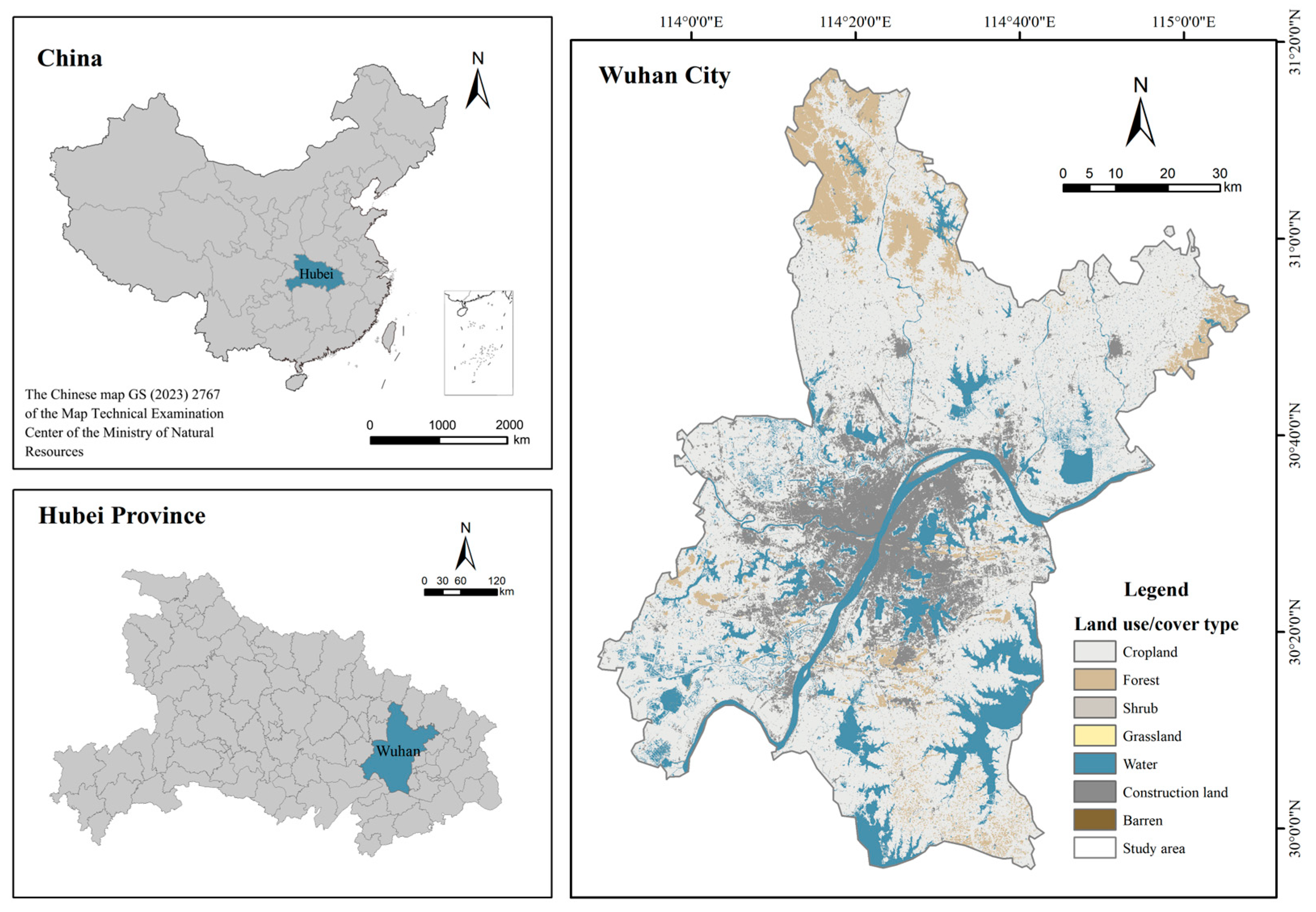










| Data | Data Format | Spatial Resolution | Data Sources/Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | Raster | 250 m | Calculated in Google Earth Engine based on Landsat 8 TM (USGS) |
| Precipitation | Raster | 1 km | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 28 June 2024)) |
| Evapotranspiration | Raster | 1 km | National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center (https://doi.org/10.11866/db.loess.2021.001 (accessed on 20 November 2024)) |
| Soil data | Raster | 1 km | Harmonized World Soil Database (HWSD) version 2, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) (https://iiasa.ac.at/ (accessed on 22 July 2024)) |
| Net Primary Production (NPP) | Raster | 500 m | NASA MODIS_MOD17A3 (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search (accessed on 1 July 2024)) |
| Land use data | Raster | 30 m | China’s Land-Use/Cover Datasets (CLUD) (https://zenodo.org/records/5210928#.Y-99ymlBxPb (accessed on 21 July 2024)) |
| Digital elevation model (DEM) | Raster | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 20 November 2024)) |
| Road | Vector | - | Open Street Map (http://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 21 July 2024)) |
| Population density | Raster | 1 km | Center for International Earth Science Information Network (http://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/data/collection/gpw-v4/documentation (accessed on 22 July 2024)) |
| Nighttime lighting | Raster | 1 km | China Long Time Series Artificial Nighttime Lighting Dataset (PANDA-China) (https://data.casearth.cn/sdo/detail/66693dd3819aec0d5564a3f9 (accessed on 20 November 2024)) |
| Optimization Objective | PFO | PPO | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synergy core ES and connectivity | Strong | Moderate | Functionality: Attention to ecosystem services |
| Synergy peripheral ecological processes and connectivity | Moderate | Strong | Functionality: Attention to ecological processes |
| Resistance to targeted attacks | Stronger (24%) | Strong (21%) | Robustness: Slope performance under targeted attacks (Figures in brackets indicate slope improvement, the same below) |
| Resistance to random attacks | Moderate (4%) | Moderate (2%) | Robustness: Slope performance under random attacks |
| Spatial balance and edge redundancy | Centralized | Enhanced | Spatial distribution: Equilibrium and dispersion of new corridors |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, A.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Qu, Z. Constructing an Ecological Spatial Network Optimization Framework from the Pattern–Process–Function Perspective: A Case Study in Wuhan. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152548
Tong A, Zhou Y, Chen T, Qu Z. Constructing an Ecological Spatial Network Optimization Framework from the Pattern–Process–Function Perspective: A Case Study in Wuhan. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152548
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, An, Yan Zhou, Tao Chen, and Zihan Qu. 2025. "Constructing an Ecological Spatial Network Optimization Framework from the Pattern–Process–Function Perspective: A Case Study in Wuhan" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152548
APA StyleTong, A., Zhou, Y., Chen, T., & Qu, Z. (2025). Constructing an Ecological Spatial Network Optimization Framework from the Pattern–Process–Function Perspective: A Case Study in Wuhan. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152548







