The Influence of Viewing Geometry on Hyperspectral-Based Soil Property Retrieval
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
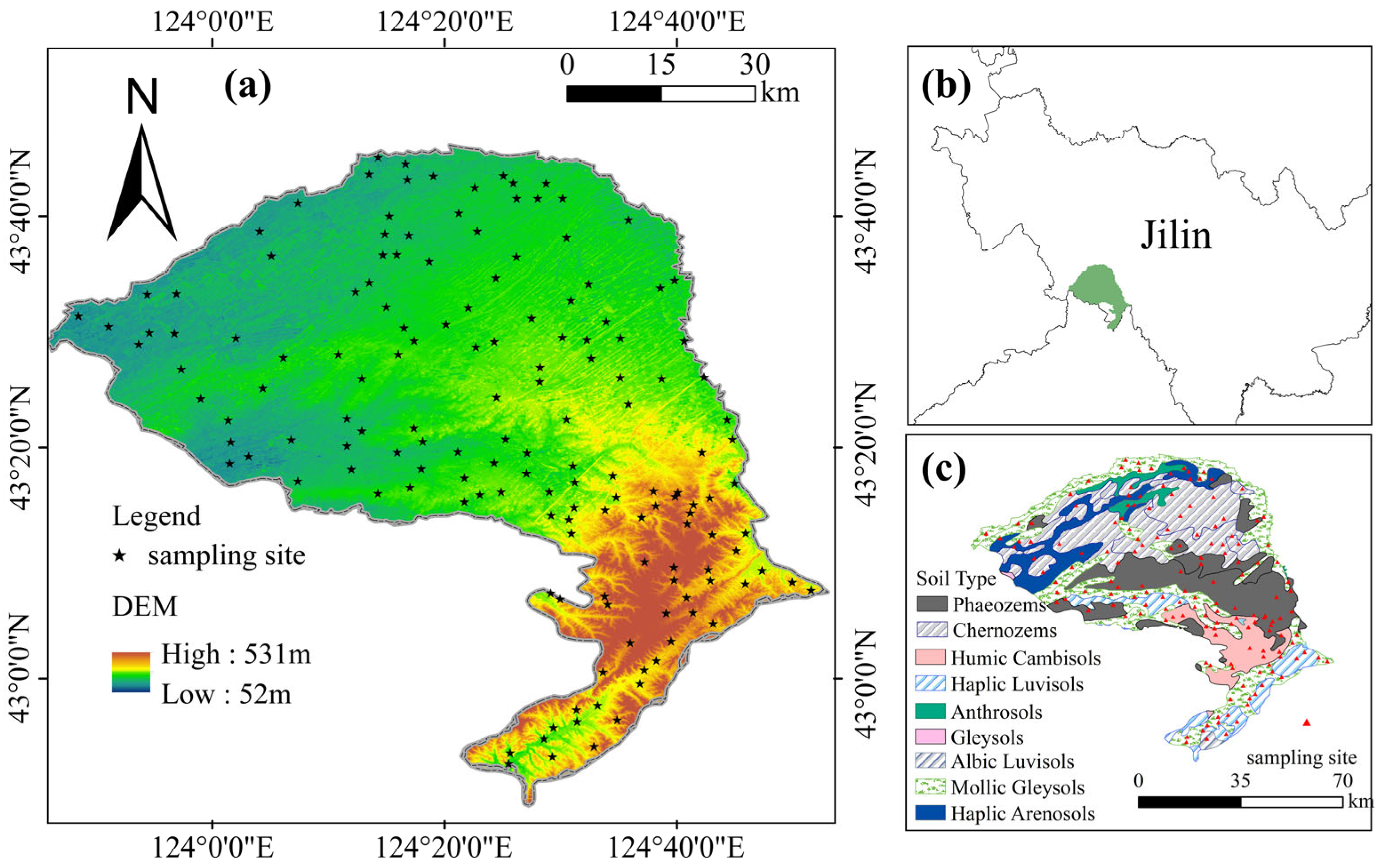
2.1. Soil Sampling Sites
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Soil Properties
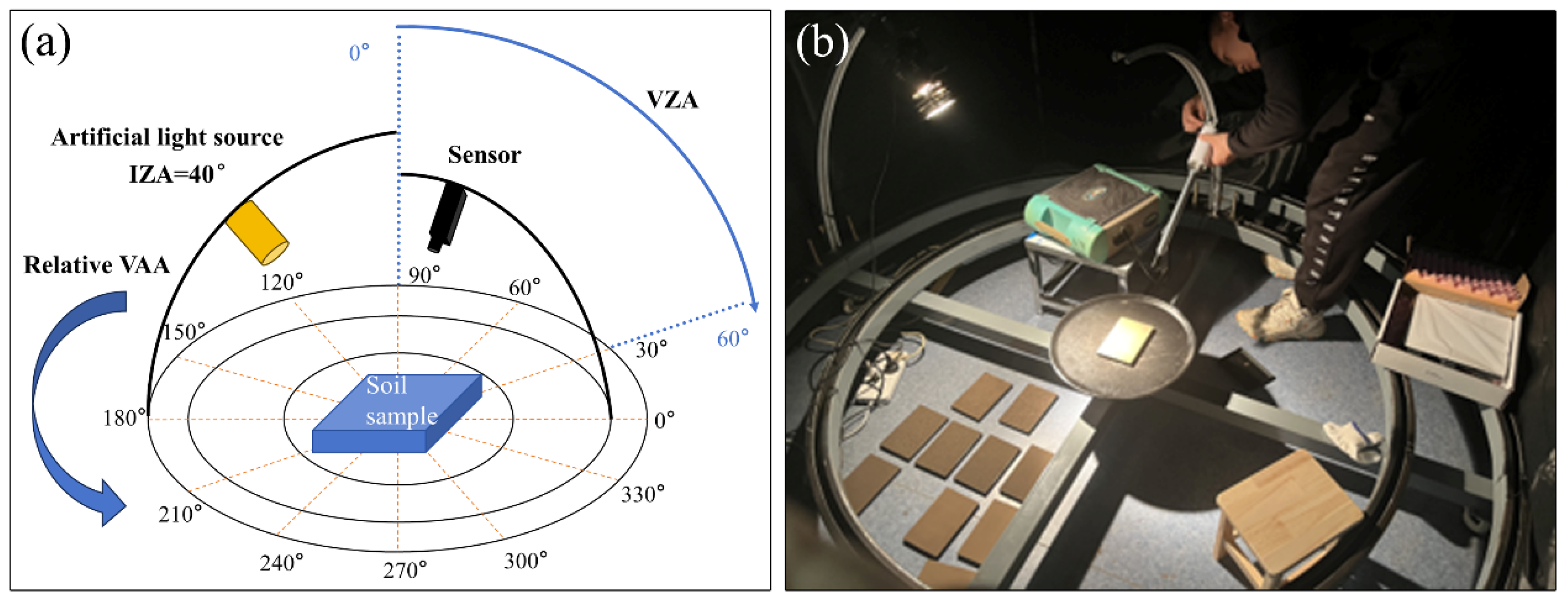
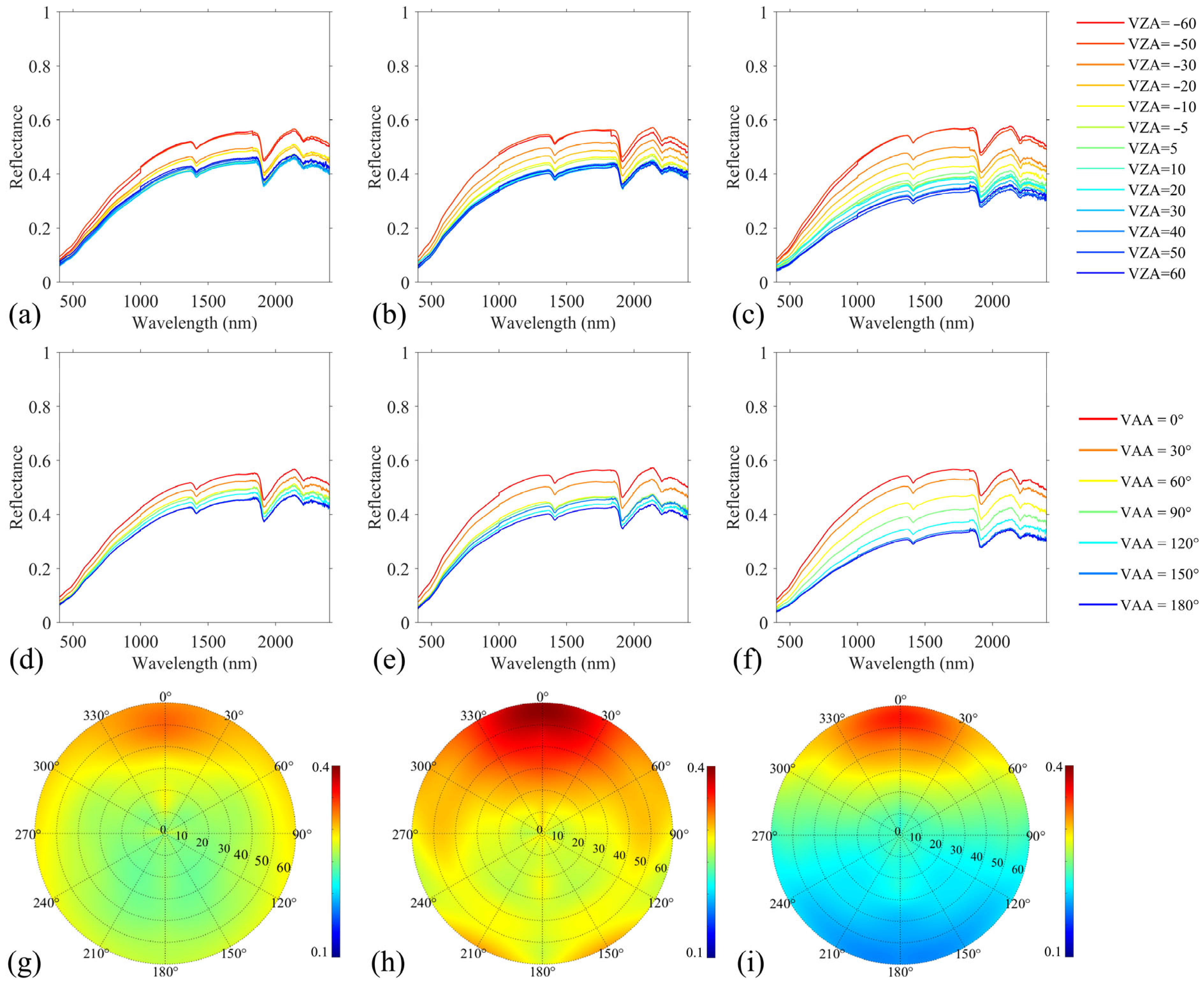
2.2.2. Soil BRF Measurements
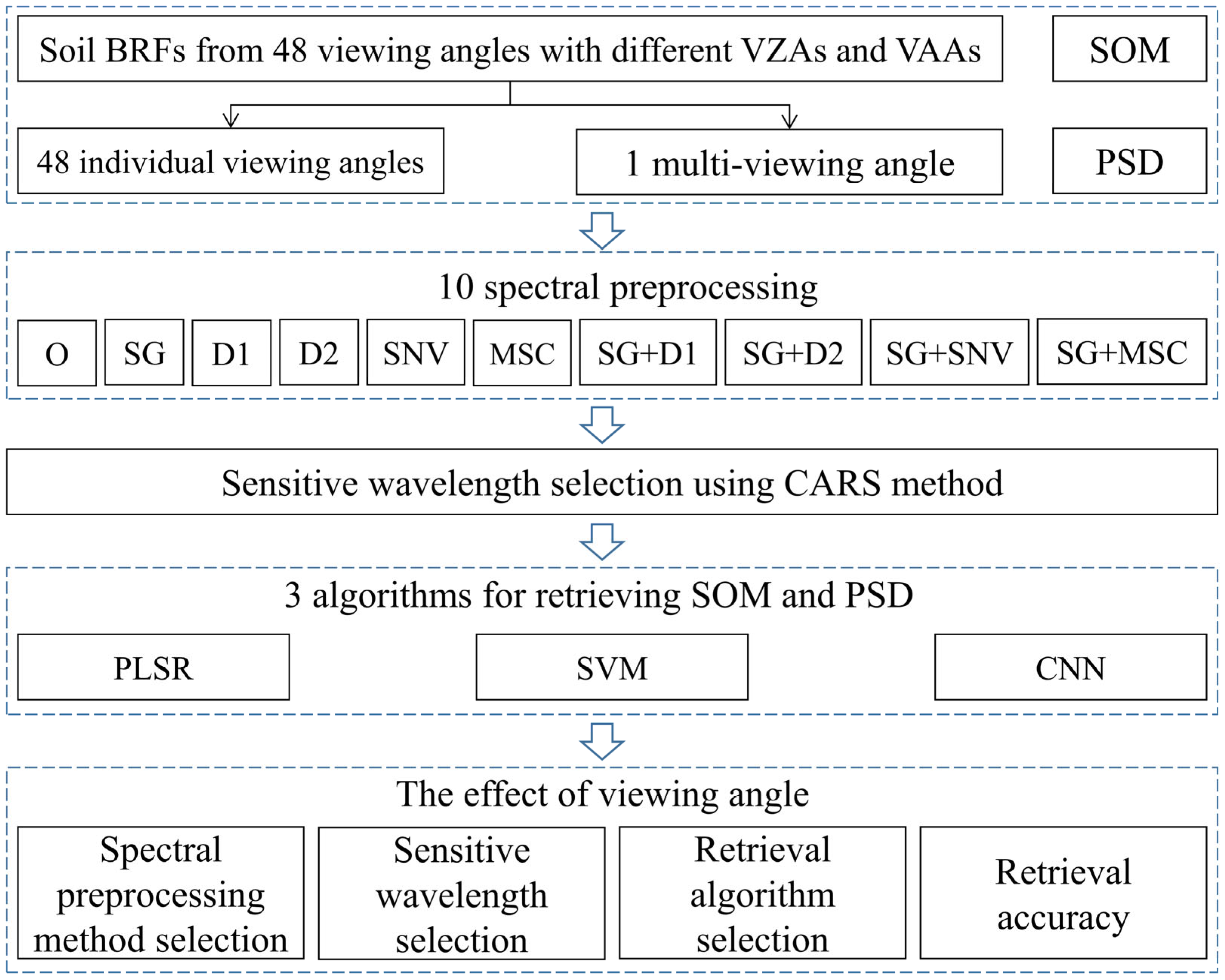
2.3. Method
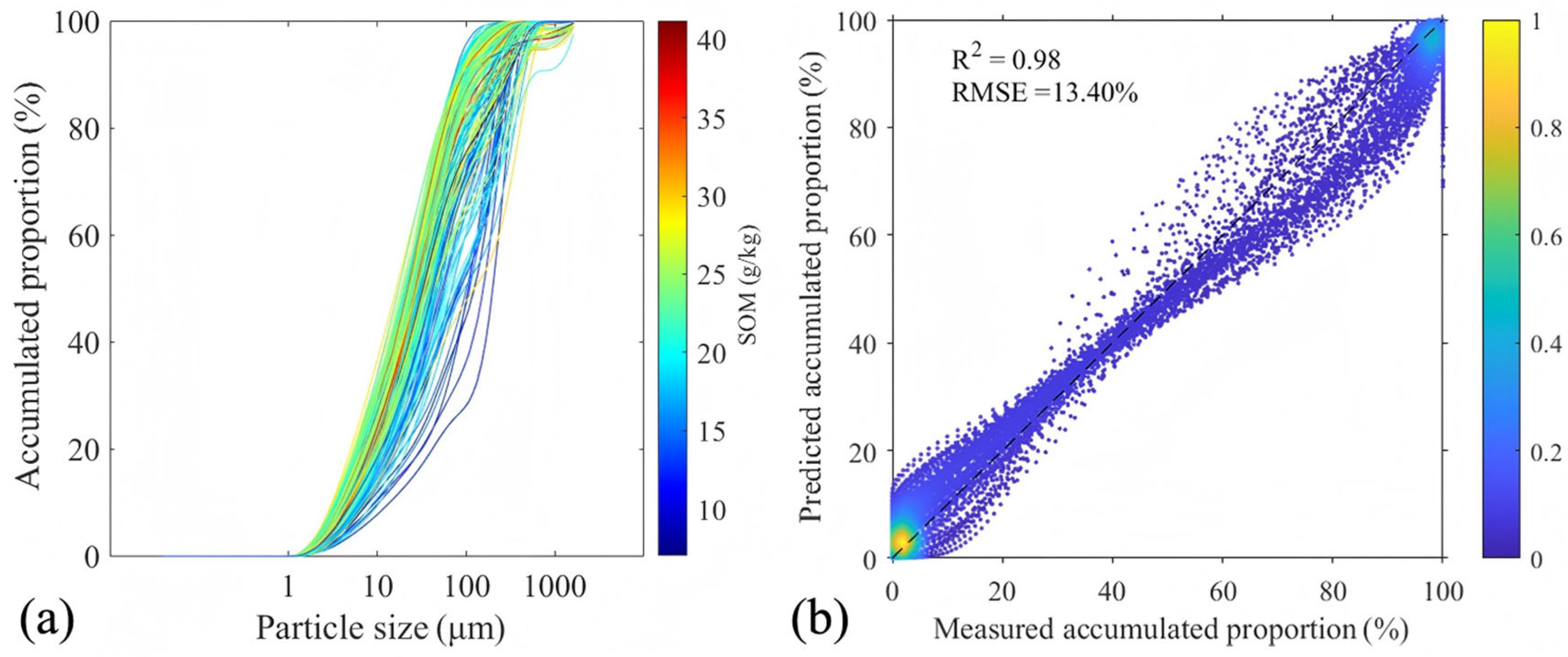
2.3.1. Particle Size Distribution Modeling
2.3.2. Hyperspectral Retrieval of Soil Properties
2.3.3. Viewing Angle Effect Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties and BRFs
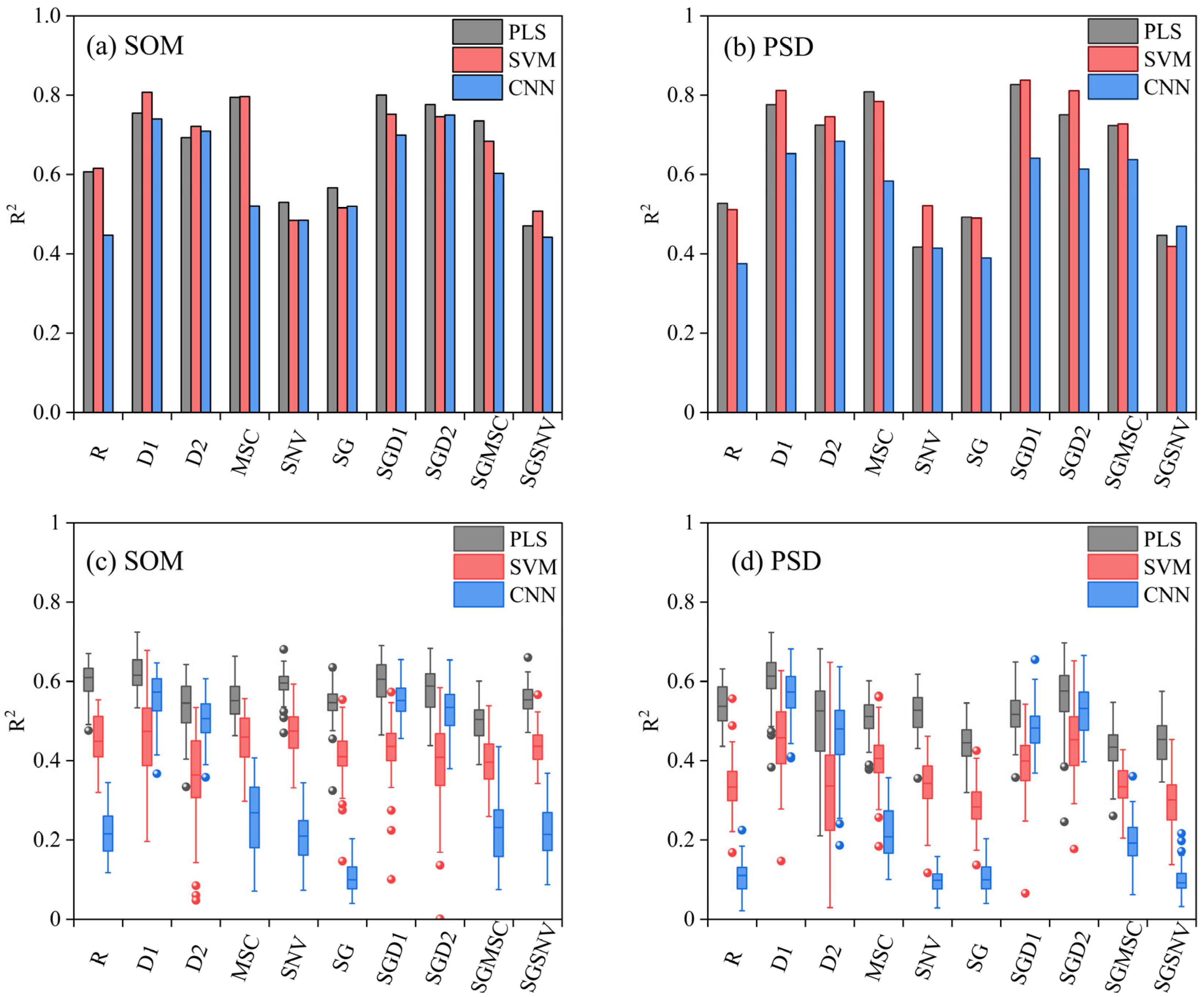
3.2. Variation in Method Selection with Viewing Angle
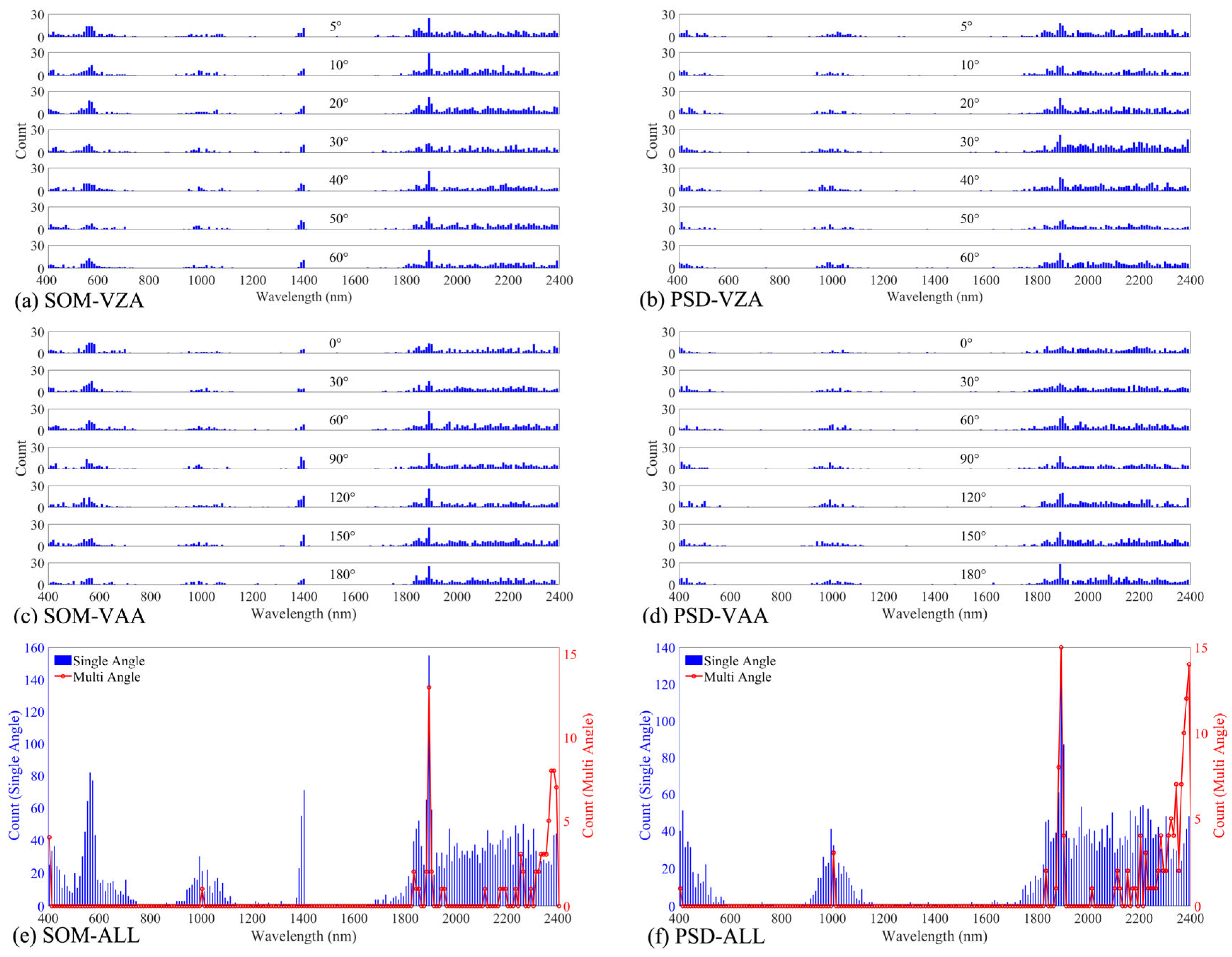
3.3. Variation in Sensitive Wavelength with Viewing Angle
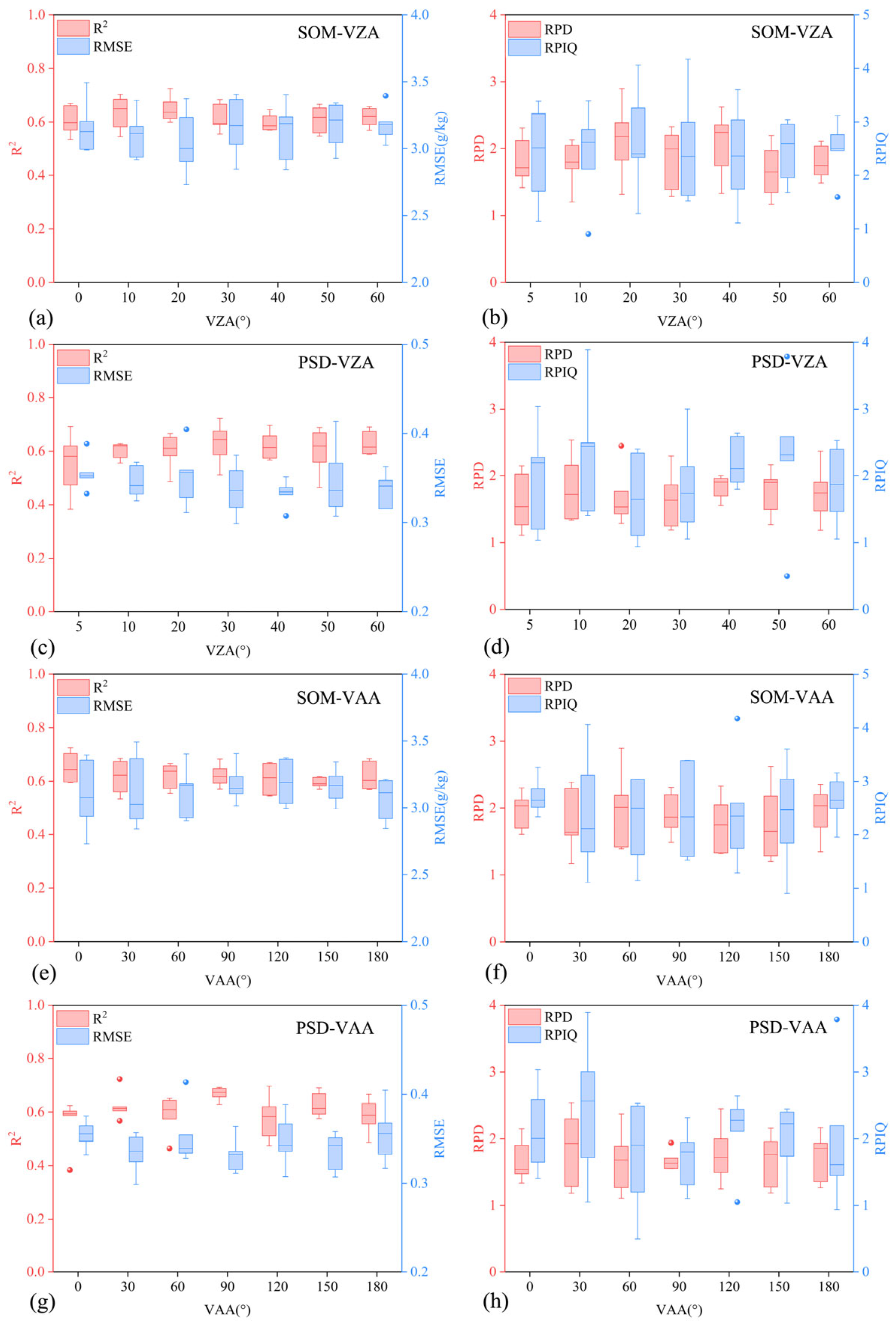
3.4. Variation in Soil Property Retrieval Accuracy with Viewing Angles
4. Discussions
4.1. Effect of Viewing Angle on Method Selection
4.2. Effect of Viewing Angle on Sensitive Wavelength Selection
4.3. Effect of Viewing Angle on Soil Property Retrieval Accuracy
4.4. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruehlmann, J. Soil particle density as affected by soil texture and soil organic matter: 1. Partitioning of SOM in conceptional fractions and derivation of a variable SOC to SOM conversion factor. Geoderma 2020, 375, 114542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Du, P.; et al. Cadmium distribution and availability in different particle-size aggregates of post-harvest paddy soil amended with bio-based materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Cheng, X.; Hu, X. Soil organic matter content prediction in tobacco fields based on hyperspectral remote sensing and generative adversarial network data augmentation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 233, 110164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansen, C.; Knadel, M.; Moldrup, P.; Greve, M.H.; Karup, D.; de Jonge, L.W. Complete Soil Texture is Accurately Predicted by Visible Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, P.; Kocsis, M.; Szatmári, G.; Makó, A.; Mészáros, J.; Laborczi, A.; Magyar, Z.; Takács, K.; Pásztor, L.; Szabó, B. Large-scale mapping of soil particle size distribution using legacy data and machine learning-based pedotransfer functions. Geoderma 2025, 454, 117178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, P. Temporal and spatial distribution of soil water repellency in grassland soils and its relation to soil moisture, hydrophobic matter, and particle size. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Xiang, N.; Lv, S.; Zhang, G. Fractal characterization of soil particle-size distribution under different land-use patterns in the Yellow River Delta Wetland in China. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Comparisons of Three Methods for Organic and Inorganic Carbon in Calcareous Soils of Northwestern China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.A. A reevaluation of the chromic acid colorimetric procedure for soil organic carbon. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1998, 29, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size Analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flogeac, K.; Guillon, E.; Aplincourt, M.; Marceau, E.; Stievano, L.; Beaunier, P.; Frapart, Y.-M. Characterization of soil particles by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, L.; Bittelli, M.; Pisa, P.R. Laser diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and image analysis to evaluate a bimodal Gaussian model for particle size distribution in soils. Geoderma 2006, 135, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshel, G.; Levy, G.J.; Mingelgrin, U.; Singer, M.J. Critical Evaluation of the Use of Laser Diffraction for Particle-Size Distribution Analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittelli, M.; Pellegrini, S.; Olmi, R.; Andrenelli, M.C.; Simonetti, G.; Borrelli, E.; Morari, F. Experimental evidence of laser diffraction accuracy for particle size analysis. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, H.; Rastgo, M.; Mansouri Zadeh, M.; Vereecken, H. Particle size distribution models, their characteristics and fitting capability. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 872–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesilind, P.A. The Rosin-Rammler particle size distribution. Resour. Recovery Conserv. 1980, 5, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, M.D.; Fredlund, D.G.; Wilson, G.W. An equation to represent grain-size distribution. Can. Geotech. J. 2000, 37, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Tan, K.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Ding, J. Modified soil scattering coefficients for organic matter inversion based on Kubelka-Munk theory. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.H.C.A.; Wijewardane, N.K.; Cox, M.S.; Zhang, X. Assessment of different VisNIR and MIR spectroscopic techniques and the potential of calibration transfer between MIR laboratory and portable instruments to estimate soil properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 251, 106555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Whiting, M.; Chen, F.; Sun, Z.; Song, K.; Wang, Q. Convolutional neural network model for soil moisture prediction and its transferability analysis based on laboratory Vis-NIR spectral data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour-Zarnaq, M.; Omid, M.; Sarmadian, F.; Ghasemi-Mobtaker, H. A CNN model for predicting soil properties using VIS–NIR spectral data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Cao, D. Key wavelengths screening using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method for multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 648, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, B. Prediction of soil salinity with soil-reflected spectra: A comparison of two regression methods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gao, B.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Sukhbaatar, C.; Yin, Y.; Feng, Q.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J. Inversion of soil organic carbon content based on the two-point machine learning method. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 943, 173608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Townshend, J.R.G. A modified hapke model for soil bidirectional reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Townshend, J.R.G. A parametric soil BRDF model: A four stream approximation for multiple scattering. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Gu, S. A review of advances in the retrieval of aerosol properties by remote sensing multi-angle technology. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eon, R.S.; Bachmann, C.M.; Lapszynski, C.S.; Tyler, A.C.; Goldsmith, S. Retrieval of Sediment Filling Factor in a Salt Panne from Multi-View Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Huang, W.; Qian, B.; Ye, H.; Jiao, Q.; Cheng, X.; Ruan, C. A hybrid model coupling PROSAIL and continuous wavelet transform based on multi-angle hyperspectral data improves maize chlorophyll retrieval. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Webb, N.P.; Guerschman, J.P.; Thomas, D.T.; Mata, G.; Handcock, R.N.; Leys, J.F.; Butler, H.J. Improving ground cover monitoring for wind erosion assessment using MODIS BRDF parameters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pang, Y.; Jia, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Effective and Universal Pre-Processing for Multi-Angle CHRIS/PROBA Images. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, M.; He, S.; Barbedo, L. Deriving anisotropic correction for upwelling radiance from PACE’s multi-angle polarimetry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 320, 114647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Qin, Q.; Ye, H.; Peng, D.; Dong, Y.; Mortimer, A.H. Estimation of canopy carotenoid content of winter wheat using multi-angle hyperspectral data. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 1988–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Jacquemoud, S.; Lucas, A.; Douté, S.; Ferrari, C.; Coustance, S.; Marcq, S.; Meygret, A. Mapping the surface properties of the Asal-Ghoubbet rift by massive inversion of the Hapke model on Pleiades multiangular images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 322, 114691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lu, S.; Omasa, K. MART-soil: A modified analytical radiative transfer mode for simulating multi-angular reflection of soils with different particle size. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Rome, Italy, 2022; Available online: https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-classification/world-reference-base/en/ (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Yang, S.; Zhao, W.; Pereira, P. Determinations of environmental factors on interactive soil properties across different land-use types on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Theory of Reflectance and Emittance Spectroscopy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, J.M.; Jiménez-Pérez, J.R.; Pádua, L.; Feito, F.R.; Sousa, J.J. An efficient method for acquisition of spectral BRDFs in real-world scenarios. Comput. Graph. 2022, 102, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Lu, Q. Waveband selection for NIR spectroscopy analysis of soil organic matter based on SG smoothing and MWPLS methods. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2011, 107, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempere, A.; Oliver, J.; Ramos, C. Simple determination of nitrate in soils by second-derivative spectroscopy. J. Soil Sci. 1993, 44, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.; Lin, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Pan, T. Changeable moving window-standard normal variable transformation for visible-NIR spectroscopic analyses. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 308, 123726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.R.; Mouazen, A.M.; Ramon, H.; Baerdemaeker, J.D. Multiplicative Scatter Correction during On-line Measurement with Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 96, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowriswari, S.; Brindha, S. Hyperparameters Optimization using Gridsearch Cross Validation Method for machine learning models in Predicting Diabetes Mellitus Risk. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Communication 2022, Computing and Internet of Things (IC3IoT), Chennai, India, 10–11 March 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, F. Analysis of spectral absorption features in hyperspectral imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2004, 5, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C. A review on spectral data preprocessing techniques for machine learning and quantitative analysis. iScience 2025, 28, 112759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamukçu, E. Efficient Wavelength Selection for Limited Near-Infrared Spectral Data via Genetic Algorithm and Hybrid Regression. J. Chemom. 2025, 39, e70015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canero, F.M.; Rodriguez-Galiano, V.; Aragones, D. Machine Learning and Feature Selection for soil spectroscopy. An evaluation of Random Forest wrappers to predict soil organic matter, clay, and carbonates. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiecher, T.; Moura-Bueno, J.M.; Caner, L.; Minella, J.P.G.; Evrard, O.; Ramon, R.; Naibo, G.; Barros, C.A.P.; Silva, Y.J.A.B.; Amorim, F.F.; et al. Improving the quantification of sediment source contributions using different mathematical models and spectral preprocessing techniques for individual or combined spectra of ultraviolet–visible, near- and middle-infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Shi, Y. Enhanced Hyperspectral Forest Soil Organic Matter Prediction Using a Black-Winged Kite Algorithm-Optimized Convolutional Neural Network and Support Vector Machine. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Han, Z.; Liu, X. Characteristics of spatial variability and hyperspectral estimation of soil organic matter in tensile fissure zone of mine area. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 042607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Hong, J.; Song, B.; Wu, S.; Wei, Y.; Wang, T. Feature Variable Selection Based on VIS-NIR Spectra and Soil Moisture Content Prediction Model Construction. J. Spectrosc. 2024, 2024, 8180765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bao, N.; Li, W.; Liu, S.; Fu, Y.; Mao, Y. Soil Nutrient Estimation and Mapping in Farmland Based on UAV Imaging Spectrometry. Sensors 2021, 21, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, T.; Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Cui, Y.; Huang, Y. Evaluating Calibration and Spectral Variable Selection Methods for Predicting Three Soil Nutrients Using Vis-NIR Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasques, G.M.; Grunwald, S.; Sickman, J.O. Comparison of multivariate methods for inferential modeling of soil carbon using visible/near-infrared spectra. Geoderma 2008, 146, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, I.S.; Næs, T.; Isaksson, T. Related versions of the multiplicative scatter correction method for preprocessing spectroscopic data. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1995, 29, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, I.; Haefele, S.M.; Sakrabani, R.; Kebede, F. Soil spectroscopy with the use of chemometrics, machine learning and pre-processing techniques in soil diagnosis: Recent advances–A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 135, 116166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, A.; Pan, K.; Li, Y.; Pan, X. Mapping the Salt Content in Soil Profiles using Vis-NIR Hyperspectral Imaging. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, T.; Tziolas, N.; Balafoutis, A.; Zalidis, G.; Bochtis, D. Remote Sensing Techniques for Soil Organic Carbon Estimation: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E. Quantitative remote sensing of soil properties. In Advances in Agronomy, (Advances in Agronomy); Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 75, pp. 173–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Babaeian, E.; Tuller, M.; Jones, S.B. Particle size effects on soil reflectance explained by an analytical radiative transfer model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvdo, L.S.; Vitorello, Í.; Formaggio, A.R. Relationships of spectral reflectance and color among surface and subsurface horizons of tropical soil profiles. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Meng, T.; Dong, H. Organic matter estimation of surface soil using successive projection algorithm. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abbas, A.H.; Swain, P.H.; Baumgardner, M.F. Relating Organic Matter and Clay Content to the Multispectral Radiance of Soils. Soil Sci. 1972, 114, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, L.; Wehrens, R.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Buydens, L.M.C. Possibilities of visible–near-infrared spectroscopy for the assessment of soil contamination in river floodplains. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 446, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, M.F.; Silva, L.F.; Biehl, L.L.; Stoner, E.R. Reflectance Properties of Soils. In Advances in Agronomy; Brady, N.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; Volume 38, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Content Based on Multi-Angle Spectral Reflectance Information. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2023. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27011/d.cnki.gdbsu.2023.000299 (accessed on 10 May 2025). (In Chinese).
- He, L.; Coburn, C.A.; Wang, Z.-J.; Feng, W.; Guo, T.-C. Reduced Prediction Saturation and View Effects for Estimating the Leaf Area Index of Winter Wheat. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1637–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, M.-R.; Guo, Y.-L.; Wei, Y.-K.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Song, X.; Feng, W.; Guo, T.-C. Angular effect of algorithms for monitoring leaf nitrogen concentration of wheat using multi-angle remote sensing data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 195, 106815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Monitoring of leaf nitrogen content of winter wheat using multi-angle hyperspectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4672–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mruthyunjaya, P.; Shetty, A.; Umesh, P.; Gomez, C. Impact of Atmospheric Correction Methods Parametrization on Soil Organic Carbon Estimation Based on Hyperion Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, O.G.E.N.; Faigenbaum-Golovin, S.; Granot, A.; Shkolnisky, Y.; Goldshleger, N.; Eyal, B.D. Removing Moisture Effect on Soil Reflectance Properties: A Case Study of Clay Content Prediction. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variation | Number | |
|---|---|---|
| Soil type | Phaeozems | 29 |
| Chernozems | 27 | |
| Albicc Luvisols | 1 | |
| Mollic Gleysols | 54 | |
| Humic Cambisols | 14 | |
| Haplic Arenosols | 13 | |
| Haplic Arenosols | 12 | |
| Anthrosols | 4 | |
| Slope position | Hilltop | 17 |
| Upper slope | 38 | |
| Middle slope | 31 | |
| Downslope | 41 | |
| Footslope | 27 | |
| Land use | Dryland | 144 |
| Paddy | 10 | |
| Relative View Azimuthal Angle | View Zenith Angle |
|---|---|
| 0° | 5°; 10°; 20°; 30°; 50°; 60° |
| 30° | 5°; 10°; 20°; 30°; 40°; 50°; 60° |
| 60° | 5°; 10°; 20°; 30°; 40°; 50°; 60° |
| 90° | 5°; 10°; 20°; 30°; 40°; 50°; 60° |
| 120° | 5°; 10°; 20°; 30°; 40°; 50°; 60° |
| 150° | 5°; 10°; 20°; 30°; 40°; 50°; 60° |
| 180° | 5°; 10°; 20°; 30°; 40°; 50°; 60° |
| Model | Key Parameter | Range |
|---|---|---|
| PLS | Latent Variables (LVs) | [2, 15] |
| SVM | Penalty Factor | [1, 5] |
| Radial Basis Function | [1, 5] | |
| Epsilon | [0.001, 0.1] | |
| CNN | Filters | [3, 8, 16, 32] |
| Kernel Size | [1, 5] | |
| Learning Rate | [0.01, 0.1] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, D. The Influence of Viewing Geometry on Hyperspectral-Based Soil Property Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142510
Gao Y, Ma L, Zhang Z, Pan X, Yuan Z, Wang C, Yu D. The Influence of Viewing Geometry on Hyperspectral-Based Soil Property Retrieval. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142510
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yucheng, Lixia Ma, Zhongqi Zhang, Xianzhang Pan, Ziran Yuan, Changkun Wang, and Dongsheng Yu. 2025. "The Influence of Viewing Geometry on Hyperspectral-Based Soil Property Retrieval" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142510
APA StyleGao, Y., Ma, L., Zhang, Z., Pan, X., Yuan, Z., Wang, C., & Yu, D. (2025). The Influence of Viewing Geometry on Hyperspectral-Based Soil Property Retrieval. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142510





