An Accurate LiDAR-Inertial SLAM Based on Multi-Category Feature Extraction and Matching
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A coarse-to-fine two-stage feature correspondence selection strategy is introduced. In the first stage, local geometric consistency is evaluated to reject incorrect correspondences. In the second stage, a greedy selection algorithm is applied to select the most contributive and non-redundant feature correspondences for pose estimation.
- An adaptive weighted pose estimation method is proposed based on distance and directional geometric consistency, enhancing the reliability of feature matching.
- An incremental optimization scheme based on factor graphs is introduced in the back-end optimization stage. This scheme globally integrates multi-category feature matching factors and loop closure factors, effectively reducing cumulative errors and enhancing the performance of the LiDAR-inertial odometry system across diverse environments.
2. Related Work
2.1. LiDAR-Inertial SLAM
2.2. Feature Extraction
2.3. Feature Matching
3. Methods
3.1. System Overview
3.2. Preprocessing Module
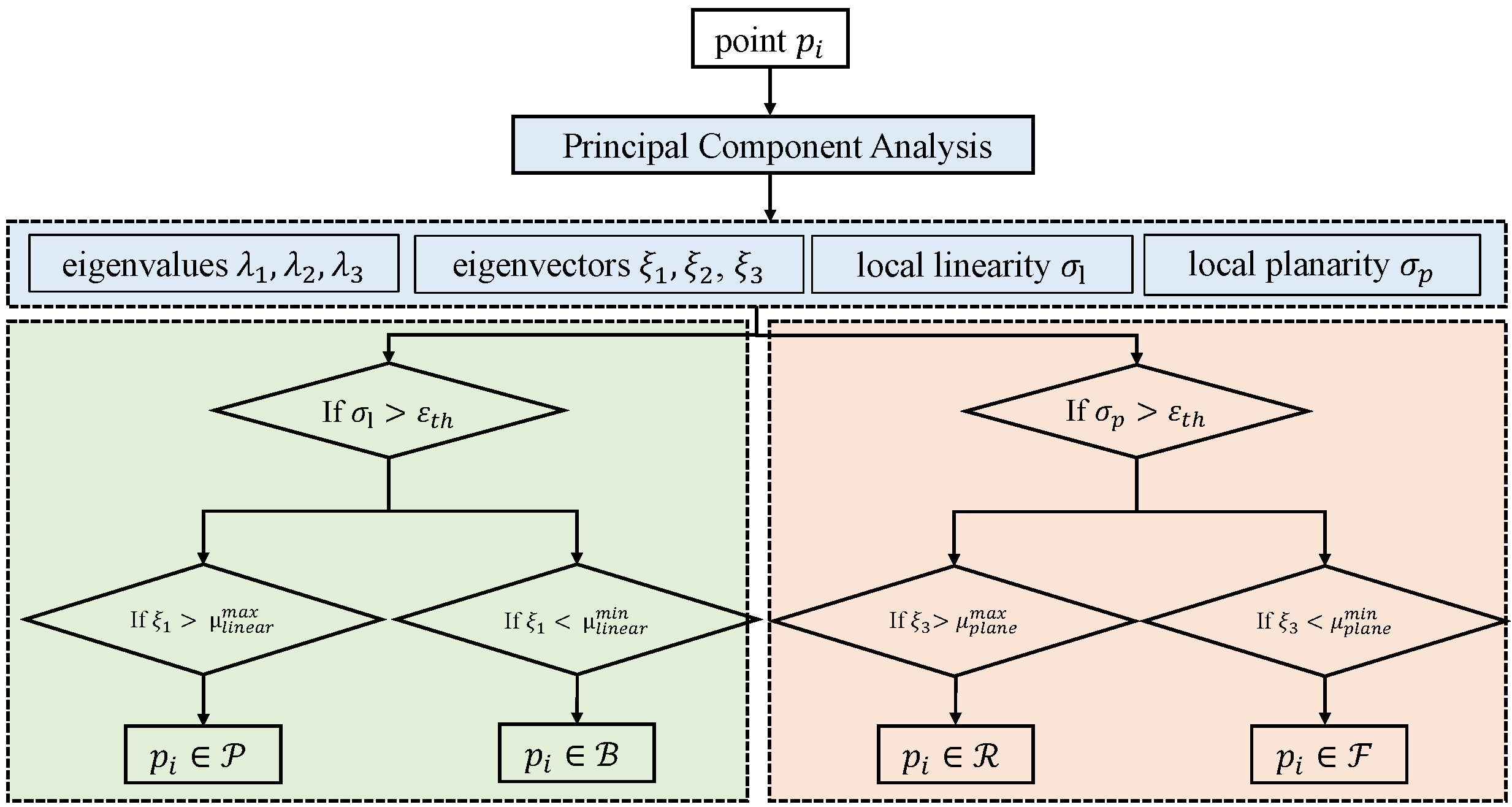
3.3. Multi-Category Feature Extraction Module
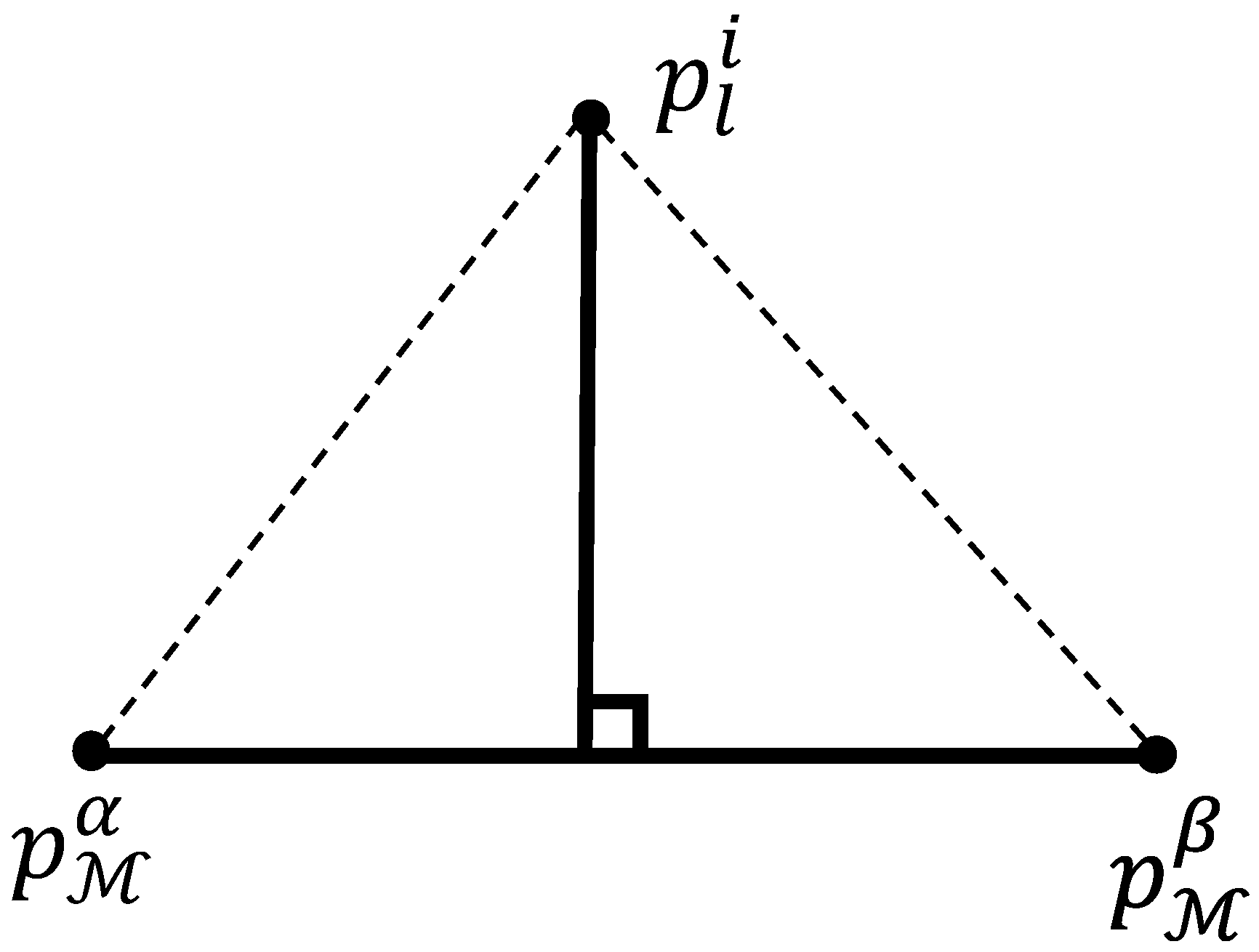
3.4. Two-Stage Feature Correspondence Selection Module
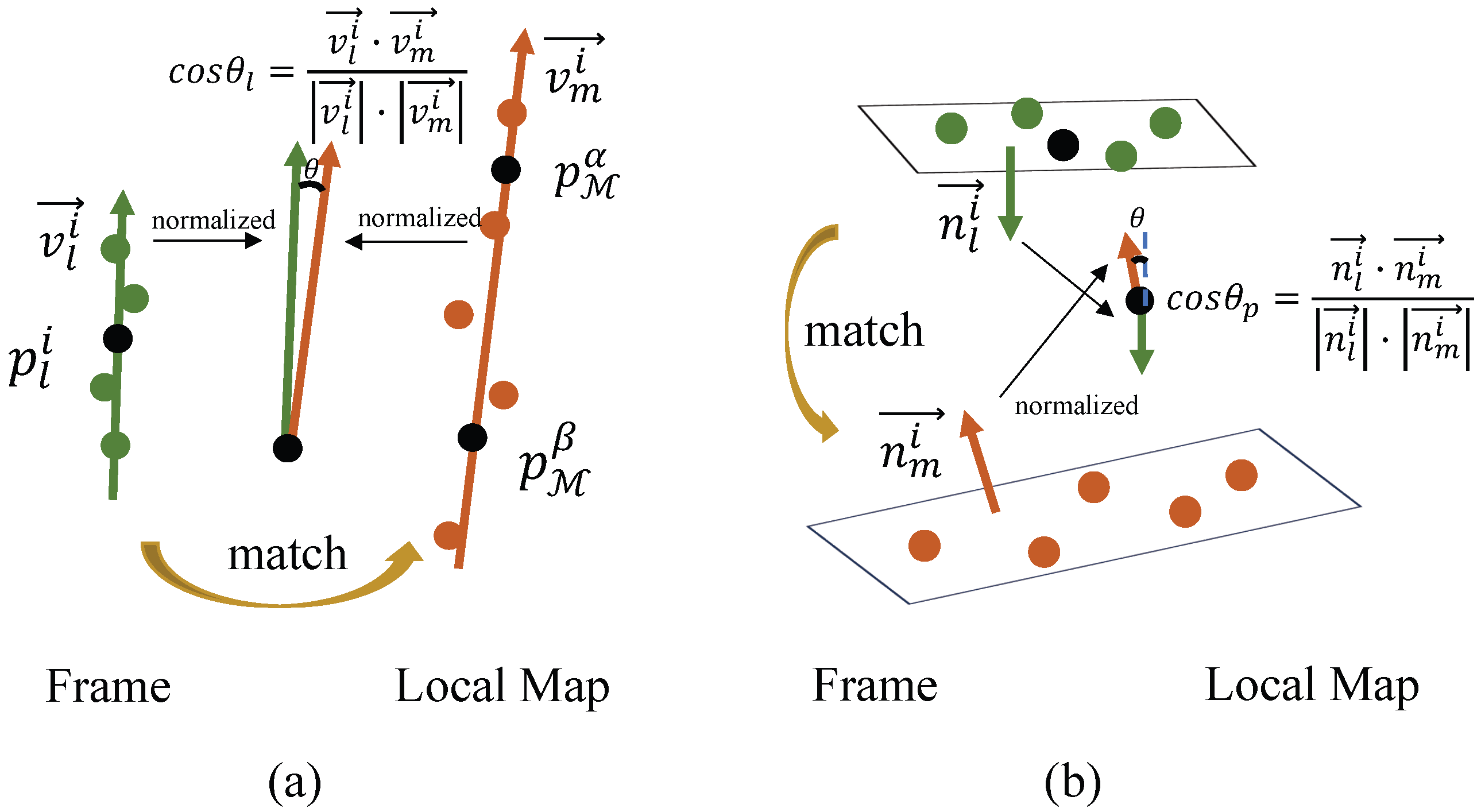
3.5. Adaptive Weighted Feature Matching Module
3.6. Factor Graph Optimization Module
3.6.1. IMU Pre-Integration Factor
3.6.2. Multi-Category Feature Matching Factor
3.6.3. Loop Factor
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset Description
4.2. Performance Evaluation
4.3. Ablation Experiments Comparison
4.4. Time Efficiency Evaluation
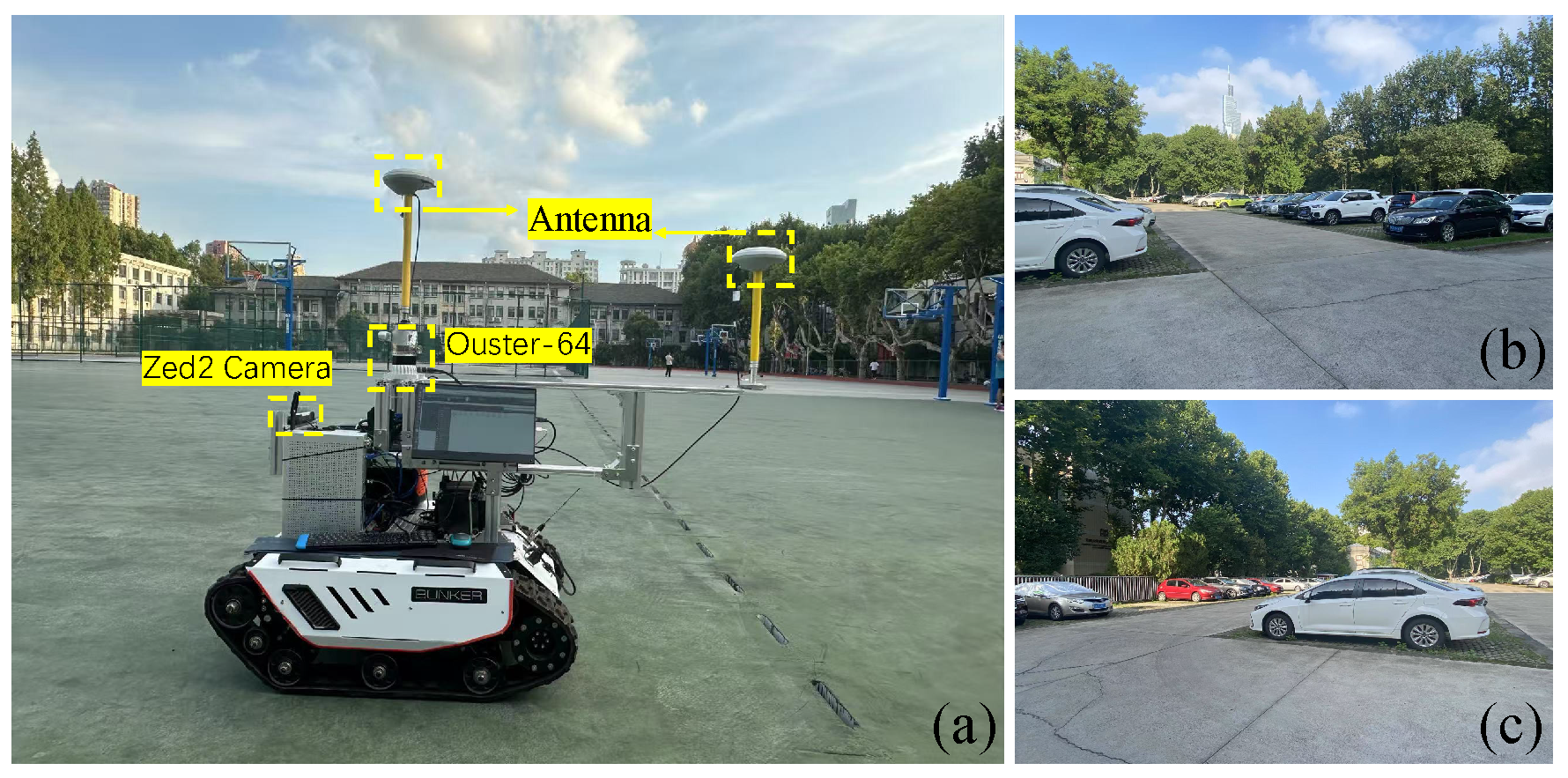
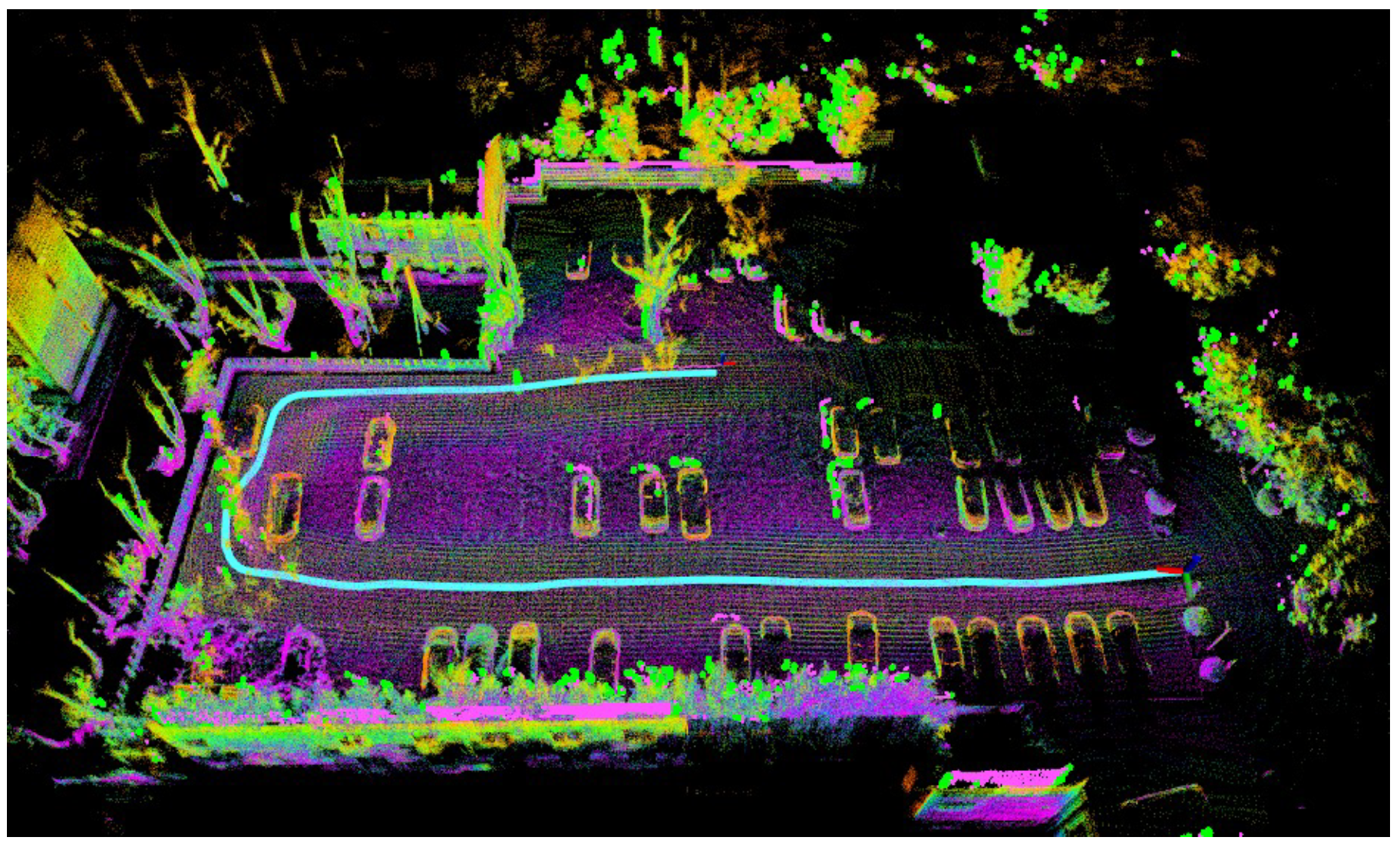
4.5. Campus Experiment
4.6. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, S.; Yao, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, C.; Kong, H. LiDAR-SGMOS: Semantics-guided moving object segmentation with 3D LiDAR. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, C.A.; Zhang, H. Cooperative decision-making in decentralized multiple-robot systems: The best-of-n problem. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2009, 14, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterovitz, R.; Koenig, S.; Likhachev, M. Robot planning in the real world: Research challenges and opportunities. Ai Mag. 2016, 37, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Singh, S. LOAM: Lidar odometry and mapping in real-time. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Berkeley, CA, USA, 12–16 July 2014; Volume 2, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Deng, B. Fast and robust iterative closest point. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3450–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B. Lego-loam: Lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4758–4765. [Google Scholar]
- Bundy, A.; Wallen, L. Breadth-first search. In Catalogue of Artificial Intelligence Tools; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Rong, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y. A LiDAR SLAM with PCA-based feature extraction and two-stage matching. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Zhang, R.; Huang, S.; Hu, M.; Ding, R.; Qin, X. WiCRF: Weighted bimodal constrained LiDAR odometry and mapping with robust features. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 8, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xiao, P.; He, Y.; Shao, Z.; Li, Z. MULLS: Versatile LiDAR SLAM via multi-metric linear least square. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 11633–11640. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Cao, Z.; Guan, P.; Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, S. A novel sparse geometric 3-d lidar odometry approach. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 15, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y. A 3D Lidar Odometry and Mapping Method Based on Clustering-Directed Feature Point. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 18391–18401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, X. Kfs-lio: Key-feature selection for lightweight lidar inertial odometry. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 5042–5048. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, I.; Yu, K.; Guo, Y.J. GDOP analysis for positioning system design. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 3371–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, H.; Huang, H.; Yun, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, M. Greedy-based feature selection for efficient lidar slam. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 5222–5228. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Meyers, D.; Wang, W.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. Lio-sam: Tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 5135–5142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Fang, Z.; Li, H.; Scherer, S. A robust laser-inertial odometry and mapping method for large-scale highway environments. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 1285–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C.; Ye, H.; Pranata, C.E.; Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M. Lins: A lidar-inertial state estimator for robust and efficient navigation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 8899–8906. [Google Scholar]
- Júnior, G.P.C.; Rezende, A.M.; Miranda, V.R.; Fernandes, R.; Azpúrua, H.; Neto, A.A.; Pessin, G.; Freitas, G.M. EKF-LOAM: An adaptive fusion of LiDAR SLAM with wheel odometry and inertial data for confined spaces with few geometric features. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 1458–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, F. Fast-lio: A fast, robust lidar-inertial odometry package by tightly-coupled iterated kalman filter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cai, Y.; He, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F. Fast-lio2: Fast direct lidar-inertial odometry. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 2053–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Jing, F.; Tan, M. RI-LIO: Reflectivity image assisted tightly-coupled LiDAR-inertial odometry. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, M.; Hanebeck, U.D. Towards high-performance solid-state-lidar-inertial odometry and mapping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 5167–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Duberg, D.; Jensfelt, P.; Yuan, S.; Xie, L. Slict: Multi-input multi-scale surfel-based lidar-inertial continuous-time odometry and mapping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Lyu, Y.; Hua, L.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, C. Light-LOAM: A lightweight lidar odometry and mapping based on graph-matching. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 3219–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y. E-LOAM: LiDAR odometry and mapping with expanded local structural information. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2022, 8, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Lin, W.C.; Wang, C.C. K-closest points and maximum clique pruning for efficient and effective 3-d laser scan matching. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, A.; Li, T.; Yu, W.; Zou, D. M2dgr: A multi-sensor and multi-scenario slam dataset for ground robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 7, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Vizzo, I.; Guadagnino, T.; Mersch, B.; Wiesmann, L.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. Kiss-icp: In defense of point-to-point icp–simple, accurate, and robust registration if done the right way. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Xu, W.; Chen, N.; Kong, F.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, F. Point-LIO: Robust high-bandwidth light detection and ranging inertial odometry. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

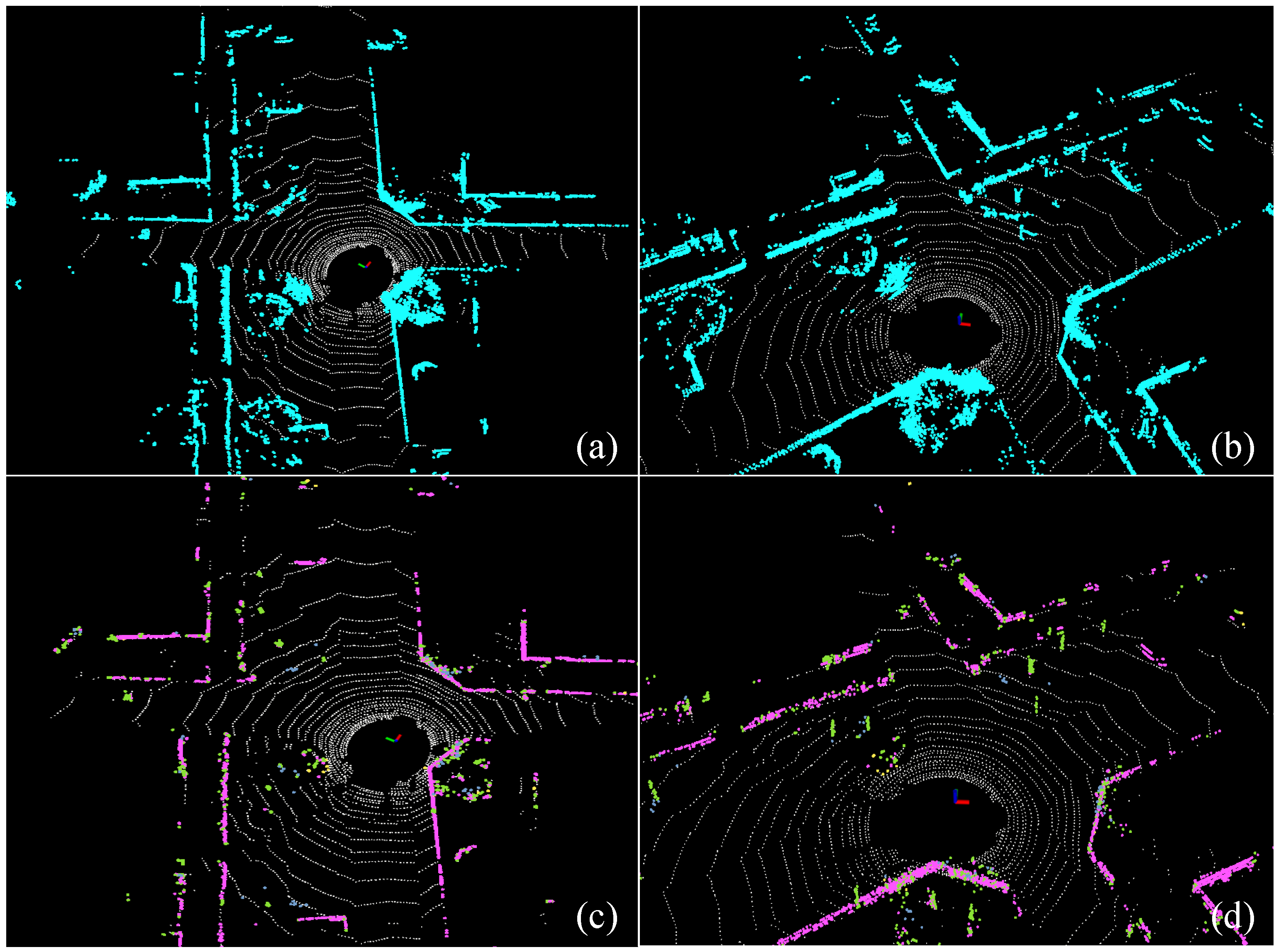



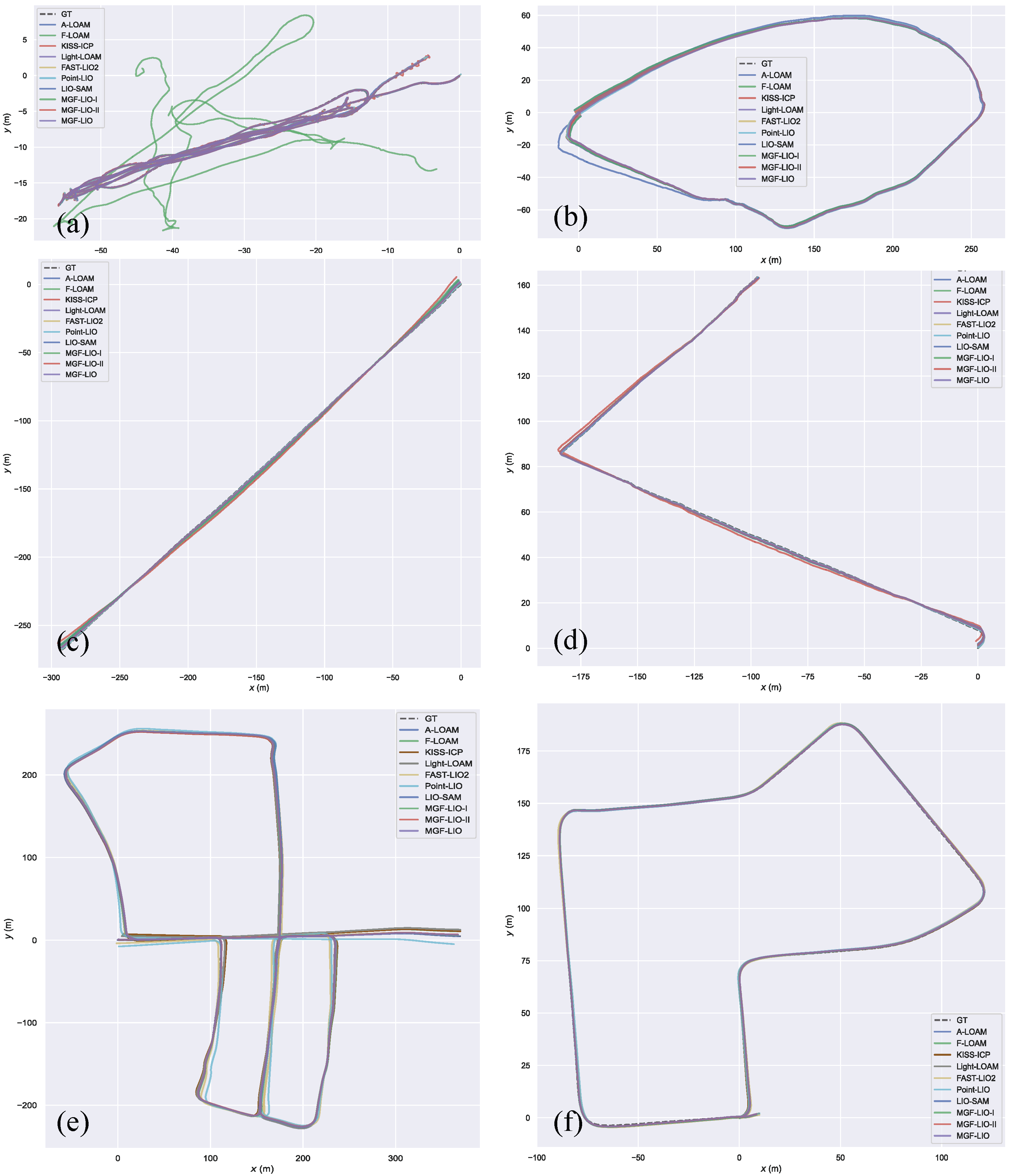
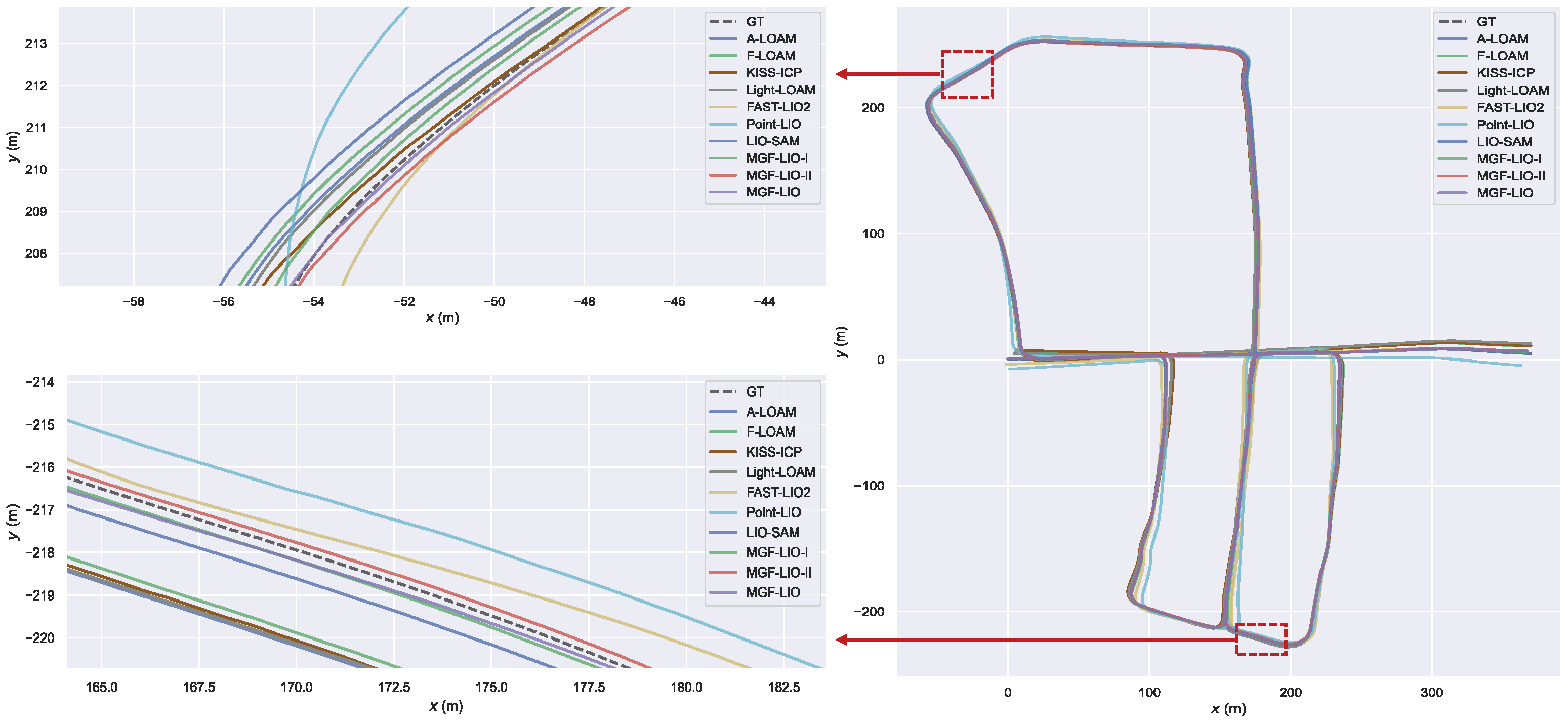
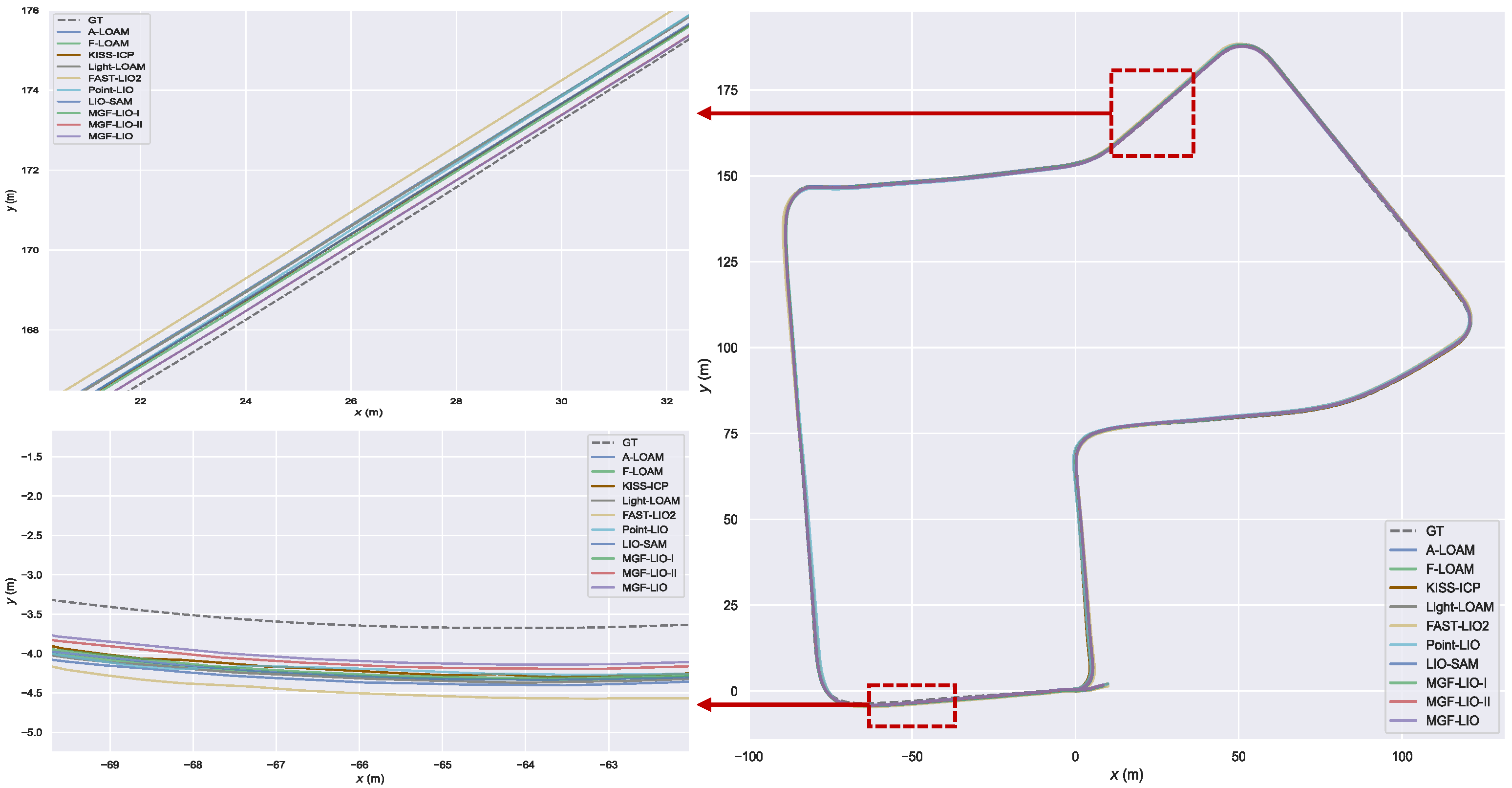

| Method | street03 | street04 | street05 | street06 | KITTI05 | KITTI07 | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-LOAM | 0.155 | 3.391 | 0.715 | 0.540 | 3.214 | 0.533 | 1.425 |
| F-LOAM | 15.629 | 1.080 | 2.356 | 0.925 | 3.610 | 0.590 | 4.032 |
| KISS-ICP | 0.166 | 1.528 | 3.353 | 2.182 | 3.327 | 0.618 | 1.862 |
| Light-LOAM | 0.146 | 0.520 | 1.215 | 0.742 | 3.482 | 0.528 | 1.106 |
| FAST-LIO2 | 0.182 | 0.435 | 0.364 | 0.397 | 4.031 | 1.423 | 1.139 |
| Point-LIO | 0.186 | 0.551 | 0.298 | 0.303 | 5.606 | 1.152 | 1.349 |
| LIO-SAM | 0.144 | 1.924 | 1.741 | 0.913 | 1.322 | 0.466 | 1.085 |
| MGF-LIO-I | 0.141 | 1.879 | 1.678 | 0.730 | 1.056 | 0.455 | 0.990 |
| MGF-LIO-II | 0.139 | 1.149 | 0.723 | 0.749 | 0.815 | 0.380 | 0.659 |
| MGF-LIO | 0.141 | 1.074 | 0.718 | 0.569 | 0.987 | 0.367 | 0.643 |
| Method | Feature Extraction | Feature Matching | Total Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIO-SAM | 7.416 | 38.206 | 45.622 |
| MGF-LIO | 37.263 | 14.978 | 52.241 |
| Method | A-LOAM | F-LOAM | LIO-SAM | MGF-LIO-I | MGF-LIO-II | MGF-LIO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parking lot | 0.183 | 0.165 | 0.158 | 0.156 | 0.153 | 0.151 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Yao, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, S.; Yang, T. An Accurate LiDAR-Inertial SLAM Based on Multi-Category Feature Extraction and Matching. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142425
Li N, Yao Y, Xu X, Zhou S, Yang T. An Accurate LiDAR-Inertial SLAM Based on Multi-Category Feature Extraction and Matching. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142425
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Nuo, Yiqing Yao, Xiaosu Xu, Shuai Zhou, and Taihong Yang. 2025. "An Accurate LiDAR-Inertial SLAM Based on Multi-Category Feature Extraction and Matching" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142425
APA StyleLi, N., Yao, Y., Xu, X., Zhou, S., & Yang, T. (2025). An Accurate LiDAR-Inertial SLAM Based on Multi-Category Feature Extraction and Matching. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142425






