The Optimal Estimation Model for Soil Salinization Based on the FOD-CNN Spectral Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
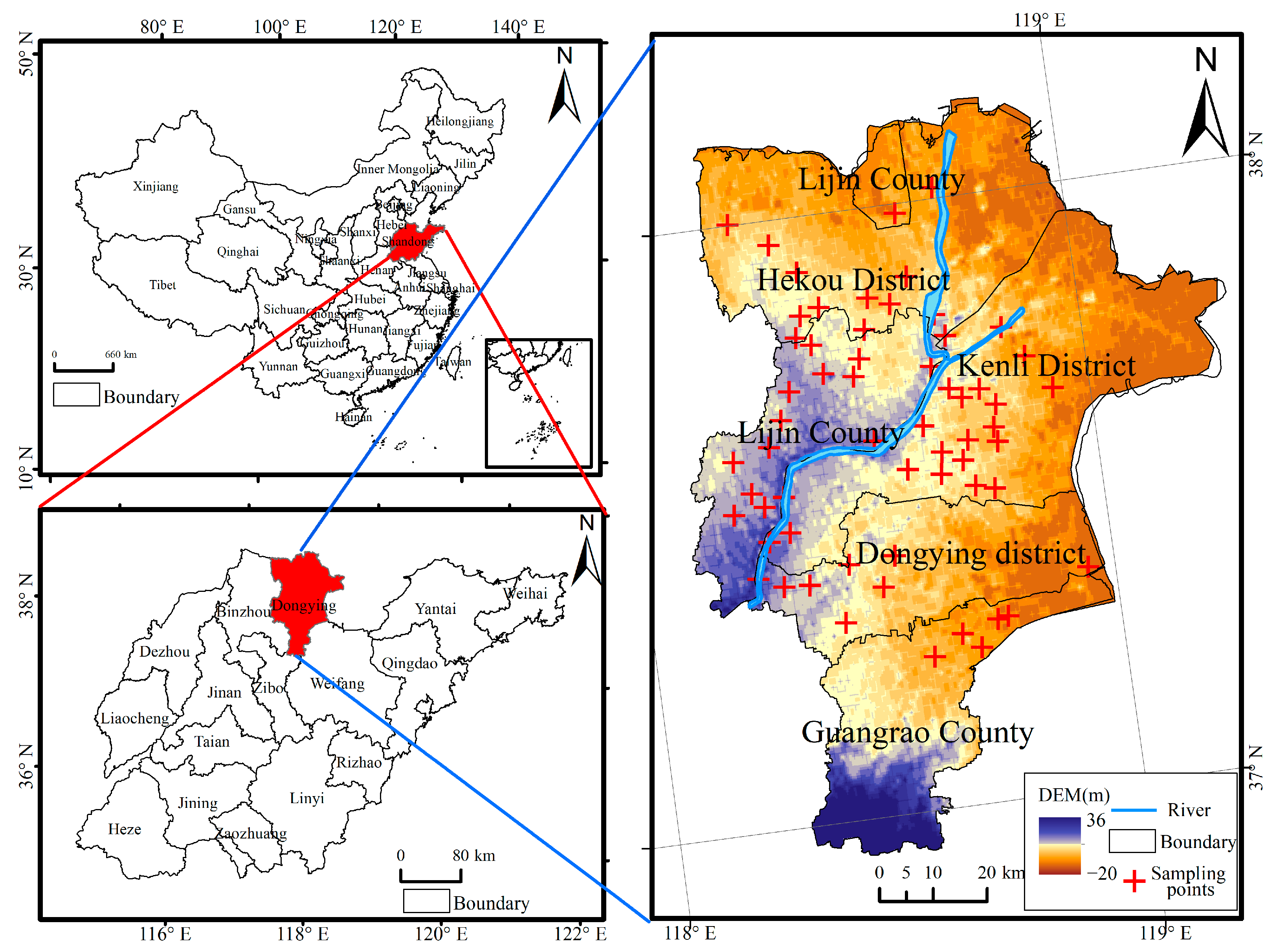
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Data Collection
2.2.2. Data Preprocessing
- (1)
- The first step entails computing the average spectrum of spectra awaiting correction:
- (2)
- The second step involves implementing univariate linear regressions against the reference spectrum to determine regression coefficients and biases for each sample:
- (3)
- Then, we correct the raw spectra:
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Fractional-Order Differentiation
2.3.2. Index Construction
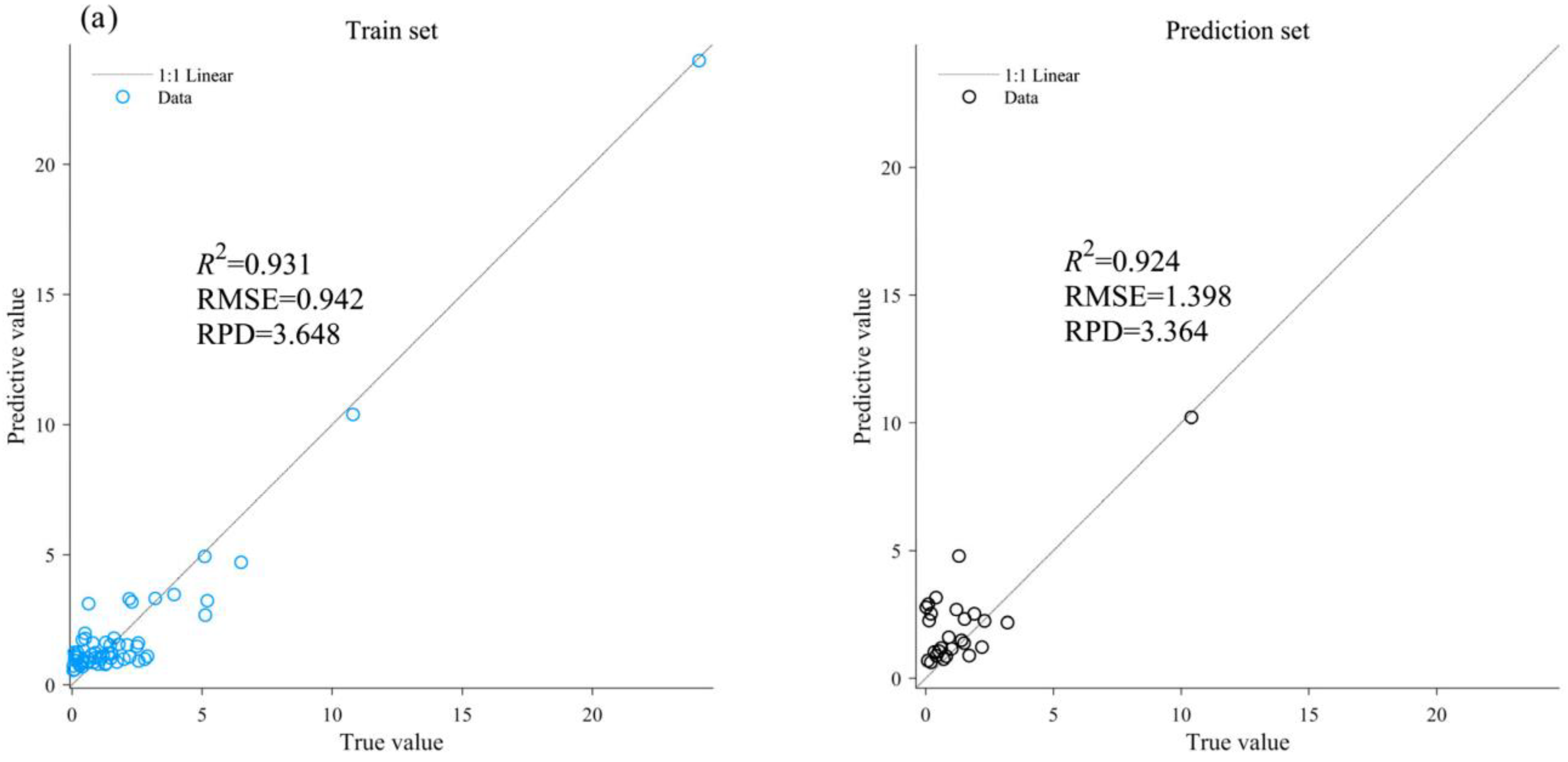
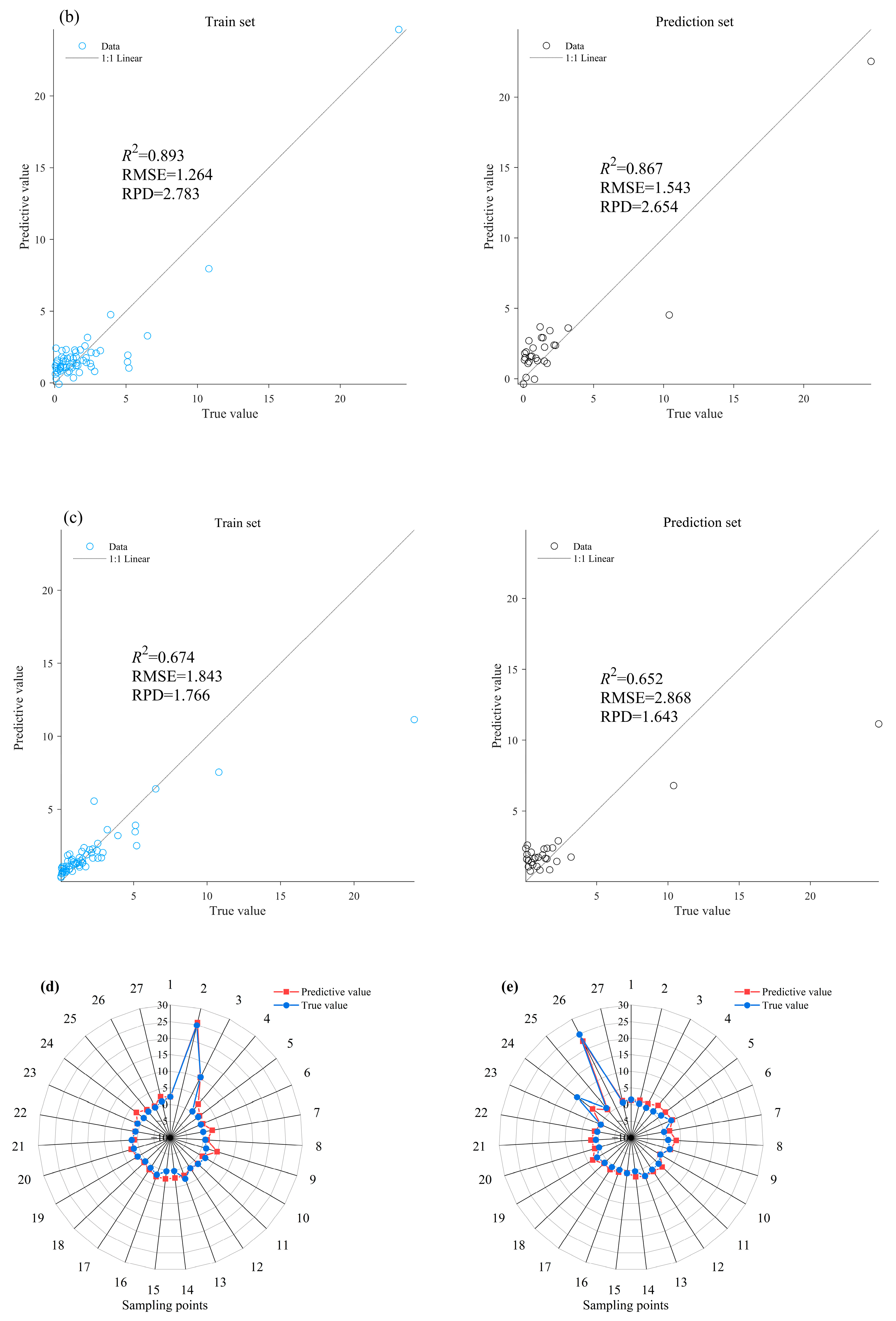
2.3.3. Model Construction and Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Spectral Curve Characteristics
3.2. Feature Extraction
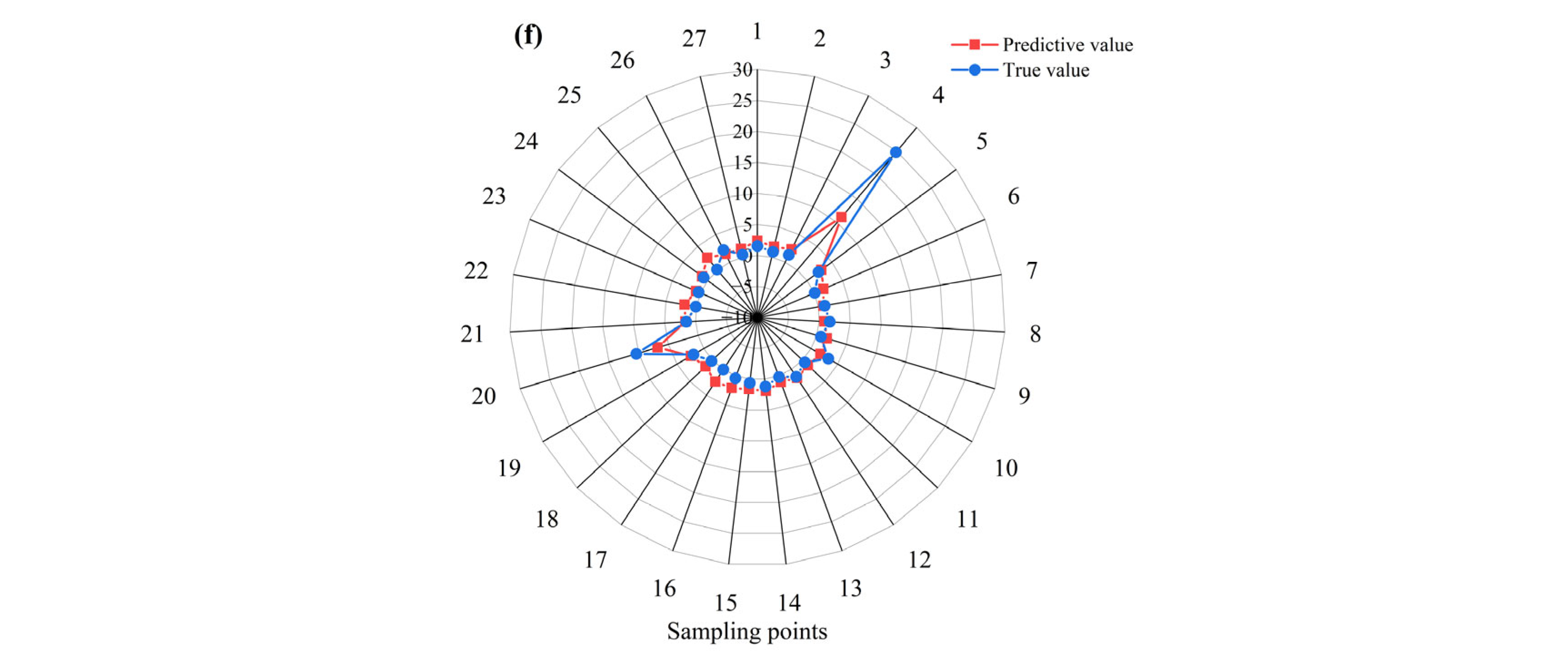
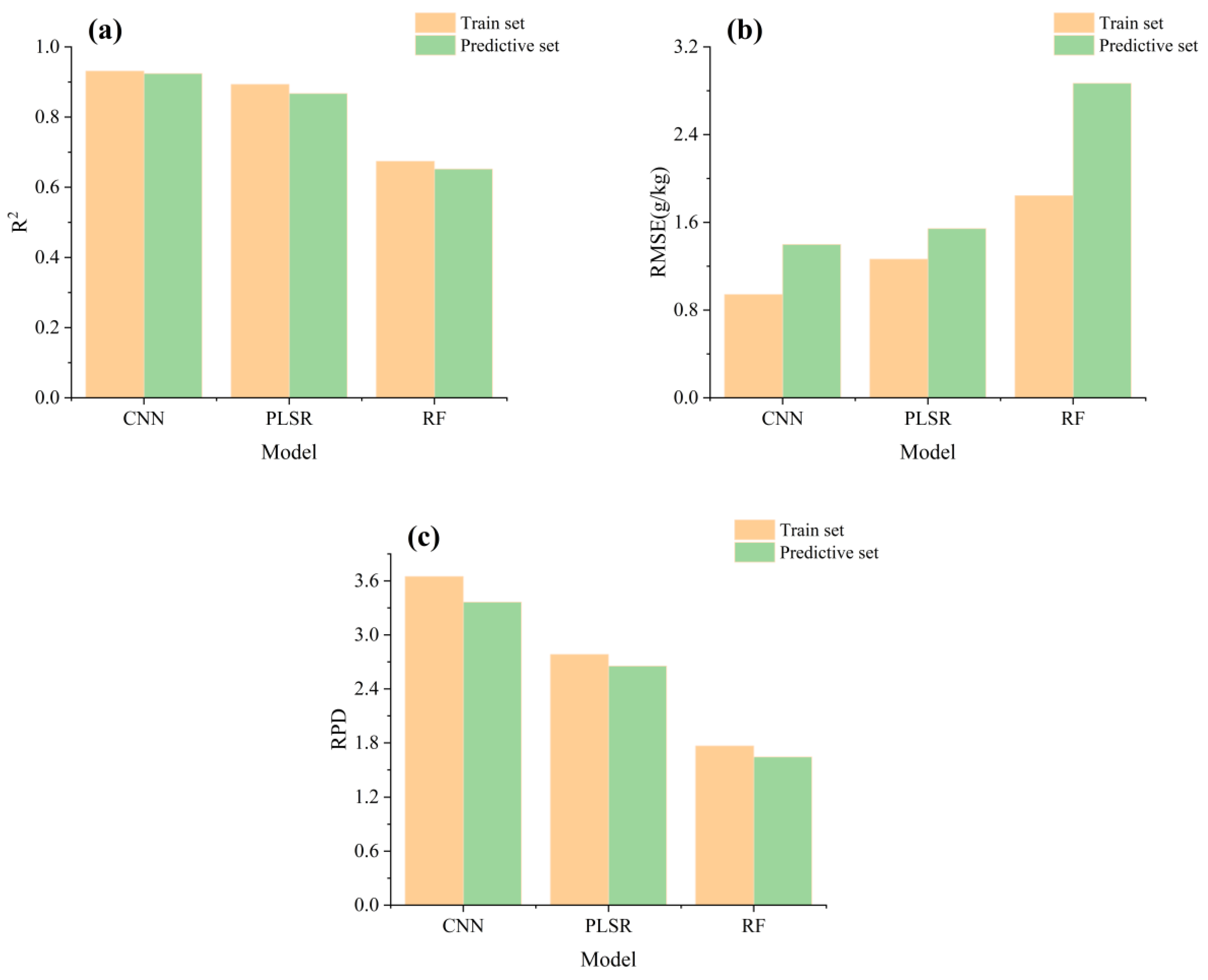
3.3. Model Result Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Merits of Fractional Calculus
4.2. Advantages and Adaptability of Spectral Indices
4.3. Superiority of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Models
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Compared to integer-order differentiation, FOD effectively highlights gradual changes in spectral curve variations.
- (2)
- FOD significantly improves the correlation between spectral indices and soil salinity compared to the original spectrum.
- (3)
- The optimal NDI (1244 nm, 2081 nm) and RI (2242 nm, 1208 nm) spectral indices at the 1.6th order show the highest correlation with soil salinity, with correlation coefficients of 0.90 and 0.882, respectively.
- (4)
- The CNN model achieved the highest inversion accuracy, improving the RPD of the prediction set by 0.710 and 1.721, improving R2 by 0.057 and 0.272, and reducing RMSE by 0.145 g/kg and 1.470 g/kg compared to the PLSR and RF models.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.K.; Song, N.P.; Yang, S.Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.X. Spatial Variation Characteristics of Soil Salinity in Desert Steppe. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 56, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L. Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Li, C.; Tang, R. Estimation of nitrogen concentration in rubber trees using fractional calculus augmented NIR spectra. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 831–839. [Google Scholar]
- Gorji, T.; Yildirim, A.; Hamzehpour, N.; Sertel, E. Soil salinity analysis of Urmia Lake Basin using Landsat-8 OLl and Sentinel-2A based spectral indices and electrical conductivity measurements. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106173. [Google Scholar]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L.; Sinha, P. Mapping and modelling spatial variation in soil salinity in the Al Hassa Oasis based on remote sensing indicators and regression techniques. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1137–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Yue, C.; Yuan, G.L.; Yuan, S.; Pang, W.Q.; Li, J. Salinization inversion model based on ENDVI-SI3 characteristic space and risk assessment. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2022, 34, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zhao, H.Q.; Mao, J.H.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X.F.; Li, M.Y. Study on Hyperspectral Inversion Model of Soil Heavy Metals in TypicalLead-Linc Mining Areas. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2024, 44, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Zhang, S.; Tian, J.; Lu, X. UAV hyperspectral inversion of Suaeda Salsa leaf area index in coastal wetlands combined with multimodal data. Nat. Remote Sens. Bull. 2023, 27, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yu, H.; Cao, Y.Y.; Hao, Z.Y.; Yang, W.; Li, M.Z. Hyperspectral Prediction of Soil Organic Matter Content Using CARS-CNN Modelling. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2024, 44, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z. Inversion of High Spectral Characteristics of Soil Salt in Arid Area Based on Different Transform Forms. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Su, W.Z.; Li, X.G.; Wang, Y.F.; Mao, D.L.; Mamattursum, E. Modeling and Verification of Soil Salt Content Based on Hyperspectral Characteristic Parameter Optimization. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2021, 58, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Gao, X.M.; Bao, S.M.; Li, W.; Fu, Y.; Wu, R.; Wang, J.Y.; Guo, L.Y. Prediction model of salt content in salinized soil based on hyperspectral data. Agric. Eng. 2024, 14, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Ding, J.L.; Li, X.; Yang, A.X. Research of Soil and Water Conservation. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 47, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.M.; Song, L.L.; Wang, J.R.; Wang, F. Estimation of Salt and Water Content in Jingdian Irrigation Area Based on Hyperspectral of Salinized Soils. J. Gansu For. Sci. Technol. 2024, 49, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, A.H.; Zhao, J.S.; Zhang, S.J.; Fu, C.B.; Xiong, H.G. Hyperspectral estimation of saline soil electrical conductivity based on fractional derivative. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2020, 28, 599–607. [Google Scholar]
- Leyden, K.; Goodwine, B. Fractional-order system identification for health monitoring. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 92, 1317–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.W.; Yang, K.M.; Xia, T.; Liu, C.; Sun, T.T. Analysis of fractional-order derivatives and copper content in corn leaves. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2017, 17, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Abulimiti, A.; Cai, L. Estimation of soil salinity using various modeling methods and VIS–NIR spectroscopy, Ebinur Lake Wetland, Northwest China. PeerJ. 2018, 6, e4703. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Gan, S.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, H.; Tian, A. Impact of fractional calculus on correlation coefficients between available po-tassium and spectral data in hyperspectral and Landsat 8 imagery. Mathematics 2019, 7, 488. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.N.; Li, X.Y.; Shi, H.B.; Ma, H.Y.; Wang, W.G.; Cui, J.Q.; Chen, C. Optimizing the inversion of soil salt in salinized wasteland using hyperspectral data from remote sensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. Advancement of hyperspectral image processing and information extraction. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 1062–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. SPA-Based Methods for the Quantitative Estimation of the Soil Salt Content in Saline-Alkali Land from Field Spectroscopy Data: A Case Study from the Yellow River Irrigation Regions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 967. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, J. Modeling risk assessment of soil heavy metal pollution using partial least squares and fuzzy logic: A case study of a gully type coal-based solid waste dumpsite. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124147. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.K.; Zhang, S.A.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, X.F. Feature variable selection combined with SVM for hyperspectral in-version of cultivated soil Hg content. Eng. Surv. Map. 2022, 31, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.K.; Feng, X.X.; Chen, L.B.; Gao, T.Y.; Du, M.J.; Liu, Z.Y. Optimal inversion model for cultivated land soil sality hased on UAV hyperspectral data. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 3085–3094. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Ding, J.L.; Wang, J.Z.; Ge, X.Y.; Li, Z.S. Quantitative Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Content Using Three-Dimensional Spectral Index: A Case Study of the Ebinur Lake Basin in Xinjiang. Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 2020, 40, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.R.; Wu, T.; Tan, S.L.; Yue, S.R. Soil salinization monitoring model based on remote sensing derivative processing and optimal spectral index. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2024, 63, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, G.J.; Xie, J.F.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Z.Q.; Yu, C.L.; Fu, X.B.; Li, X. Monitoring soil salinization of cotton fields in the Aral Reclamation Area using multispectral imaging. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 41, 894–904. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.Y.; Peng, J.B.; Zhu, W.X.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z.; Gong, H.R.; Wang, J.D.; Yang, T.; Lou, J.Y.; Sun, Z.G. Study on retrieval method of soil organic matter in salinity soil using unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing. J. Geoinf. Sci. 2024, 26, 736–752. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W.Y.; Shi, J.F.; Li, S.Y.; Sun, J.J.; Wang, Y.G. Evaluation of multimodel inversion effects on soil salinity in oasis basin. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 41, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Tai, X.; Yang, N.; Zhang, J.R.; Huang, X.Y.; Chen, Q.D. UAV Multispectral Remote Sensing Soil Salinity Inversion Based on Different Fractional Vegetation Coverages. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 220–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, H.Q.; Wang, X.M. Estimation of soil salinity in cultivated layers of oasis in arid areas based on multispectral images. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Xi, H.Y.; Zhao, J.; Ma, K.H.; Cheng, W.J.; Chen, Y.Q. Inversion and spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinity in Alxa area, China. J. Des. Res. 2023, 43, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.X.; Han, X.; Yang, X.; He, Z.J.; Qiao, X.Y.; Zhu, H.L. A prediction model for dynamic alloy addition after converter based on CNN-LSSVM. Iron Steel. 2025, 60, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.J.; Hong, W.W.; Gill, A.; Yu, H.Y.; Chen, X.D. Hyperspectral estimation of coal-derived carbon mass fraction in mine soil based on the CWT-CARS-CNN integrated method. J. Henan Polytech. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 43, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Mashimbye, Z.E.; Cho, M.A.; Nell, J.P.; Clercq, W.P.D. Model-based integrated methods for quantitative estimation of soil salinity from hyperspectral remote sensing data: A case study of selected South African soils. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 640–649. [Google Scholar]
- Kasim, N.; Maihemuti, B.; Sawut, R.; Abliz, A.; Dong, C.; Abdumutallip, M. Quantitative Estimation of Soil Salinization in an Arid Region of the Keriya Oasis Based on Multidimensional Modeling. Water 2020, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaer, Y.; Tashpolat, N.; Shi, Q.; Liu, S. Possibility of Zhuhai-1 hyperspectral imagery for monitoring salinized soil moisture content using fractional order differentially optimized spectral indices. Water 2020, 12, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Meer, F.V.; Atzberger, C.; Carranza, E.J.M. Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: A comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Setia, R.; Jayasree, G.; Das, B.S. A novel method for detecting soil salinity using AVIRIS-NG imaging spectroscopy and ensemble machine learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 200, 191–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, G.M.; Blaschke, T.; Hossein, H.V.; Weng, Q.H.; Kamran, K.V.; Li, Z.L. A comparison between sentinel-2 and landsat 8 OLI satellite images for soil salinity distribution mapping using a deep learning convolutional neural network. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 48, 452–468. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q.; Feng, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, Z.A.; Liu, P.; Liang, Z.Y.; Sun, F.F.; Chen, R. Estimation of soil organic matter and total nitrogen based on hyperspectral technology. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2024, 61, 2491–2499. [Google Scholar]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Zhang, H.; Ling, Y.H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, D.L.; Zhang, N.; Hu, F.J. Multiscale smoothing preprocessing method based on wavelet transform and S-G filtering. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2023, 48, 140–155. [Google Scholar]
- Geladi, P.; MacDougall, D.; Martens, H. Linearization and scatter-correction for near-infrared reflectance spectra of meat. Appl. Spectrosc. 1985, 39, 491–500. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.X.; Teng, X.S.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, L.Y. Applicability of Different Fractional Order Differential Forms in the Hyperspectral Inversion of Saline Soil Conductivity. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2025, 45, 272–281. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.S.; Shen, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.F. Estimating lead and zinc con-centrations in peri-urban agricultural soils using reflectance spectroscopy: Effects of fractional-order derivatives and random forest algorithms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 651, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, X.; Zhang, T.; Zou, Q.; Yan, J.M.; Dong, Y.Y. Construction of remote sensing monitoring model of wheat stripe rust based on fractional-order differential spectral index. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Wang, F.; Han, J.Q.; Ge, W.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Lin, Y.Y. Study on spectral characteristics and quantitative estimation of soil salinity based on Fractional Order Derivative. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2025, 40, 344–358. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.Y.; Ding, Q.D.; Zhang, J.H.; Pan, X.; Zhou, Y.H.; Jia, K.L. Ground-hased hyperspectral inversion of salinization and alkalinization of different soil layers in farmland in Yinbei area, Ningxia, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 3073–3084. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, H. Systems Analysis by Partial Least Squares; IIASA Collaborative Paper; IIASA: Mödling, Austria, 1983; CP-83-046. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.M.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.F.; Luo, D.F.; Peng, J. Estimating soil organic matter content in desert areas using in situ hyper-spectral data and feature variable selection algorithms in southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5221. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Sun, Q.; Yang, G.J.; Zhang, C. Hyperspectral inversion of soil organic matter content in cultivated land based on wavelet transform. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105053. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, T.; Zhan, Y.J. Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Heavy Metal lons Based on Machine Learning. J. Instrum. Anal. 2025, 44, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 1962, 160, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yue, H.; Bi, Y.L.; Peng, S.P.; Jia, Y.H. Remote Sensing Inversion of Soil Carbon Emissions in Desertification Mining Areas. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2024, 44, 2840–2849. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, D. Conditional logit analysis of qualitative choice behavior. In Frontiers in Econometrics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. Contributions to the mathematical theory of evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1894, 185, 71–110. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.C. Variables affecting near-infrared reflectance spectroscopic analysis. In Near-Infrared Technology in the Agricultural and Food Industries; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1987; pp. 143–167. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.R.; Han, Y.; Qin, Y.; Jin, L. Study on the Relationship between Hyperspectral Polarized Information of Soil Salinization and Soil Line. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2015, 35, 2856–2861. [Google Scholar]
- Prashant, K.; Prasoon, T.; Arkoprovo, B. Spatio-temporal assessment of soil salinization utilizing remote sensing derivatives, and prediction modeling: Implications for sustainable development. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101881. [Google Scholar]
- Demattê, J.A.M.; Fabrício, S.T. Spectral pedology: A new perspective on evaluation of soils along pedogenetic alterations. Geoderma 2014, 217, 190–200. [Google Scholar]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Bellon-Maurel, V.; Roger, J.M.; Gobrecht, A.; Ferrand, L.; Joalland, S. Removing the effect of soil moisture from NIR diffuse reflectance spectra for the prediction of soil organic carbon. Geoderma 2011, 167, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Demattê, J.A.M.; Campos, R.C.; Alves, M.C.; Fiorio, P.R.; Nanni, M.R. Visible–NIR reflectance: A new approach on soil evaluation. Geoderma 2004, 121, 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Malone, B.P.; Wheeler, I. Digital mapping of soil carbon. Adv. Agron. 2013, 118, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wadoux, A.M.J.C. Using deep learning for multivariate mapping of soil with quantified uncertainty. Geoderma 2019, 351, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wadoux, A.M.J.C.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Machine learning for digital soil mapping: Applications, challenges and suggested solutions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 210, 103359. [Google Scholar]
- Demattê, J.A.M.; Nanni, M.R. Weathering sequence of soils developed from basalt as evaluated by laboratory (IRIS), airborne (AVIRIS) and orbital (TM) sensors. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4715–4738. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Ding, J.L.; Wang, J.Z.; Ge, X.Y. Prediction of soil organic matter in northwestern China using fractional-order derivative spectroscopy and modified normalized difference indices. Catena 2020, 185, 104257. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yang, X.Z.; Zhang, B.; Huang, J.L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.X.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Geng, H.S.; Chen, H.R.; Chen, J.Y. Estimation model of soil moisture content in root domain of winter wheat using a fractional-order differential spectral index. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.G.; Jin, W.G.; Mamattursun, E.; Niu, F.P. Fractional differential based hyperspectral estimation model of soil electrical conductivity of Bosten Lake oasis. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2021, 56, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Li, X.G.; Lai, N.; Asiyemu, T. Hyper-spectral quantification of soil salinity in the west lakeside of Bosten Lake. J. Yangzhou Univ. (Agric. Life Sci. Ed.) 2014, 35, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.M.; Qin, J.Z.; Xu, X.H.; Liu, W.B.; Shi, W.J.; Jiang, H. The relationship between vitrinite reflectance suppression and source rock quality—A case study on source rocks from the Dongying sag Bohai Bay Basin. Petrol. Geol. Exp. 2008, 30, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Tashpolat, T.; Zhang, F.; Ardak, K. Application of fractional differential in preprocessing hyperspectral data of saline soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Chen, S.Y.; Li, W.S.; Li, Y.X.; Cao, H.T.; Liu, J. Applicability of fractional-order differential transformation for salini-zation monitoring in coastal saline soils. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, A.H.; Xiong, H.G.; Zhao, J.S.; Fu, C.B. Mechanism Improvement for Pretreatment Accuracy of Field Spectra of Saline Soil Using Fractional Differential Algorithm. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H. Remote Sensing Monitoring of the Degree of Damage to Cnaphalocrocis Medinalis Based on UAV Hyperspectral Technology. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.H. Inversion Study of Soil Salinization in the Yinchuan Plain Based on Spectral Index and Elimination of Moisture Effects. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Zhou, B.C.; Wong, H.Y.; Zhou, B.B.; Ye, D.P.; Qu, F.F. Inversing soil salinity in cotton fields using spec-troscopy sample augmentation and moisture correction. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Dujaili, A.A.; Duan, Y.; Shamma, O.A.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Amidie, M.A.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.H.; Feng, X.Q.; Nie, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, E.H. Hyperspectral estimation of soil phosphorus content in mining area based on CARS-CNN. Chin. J. Ecol. 2024, 43, 3553. [Google Scholar]


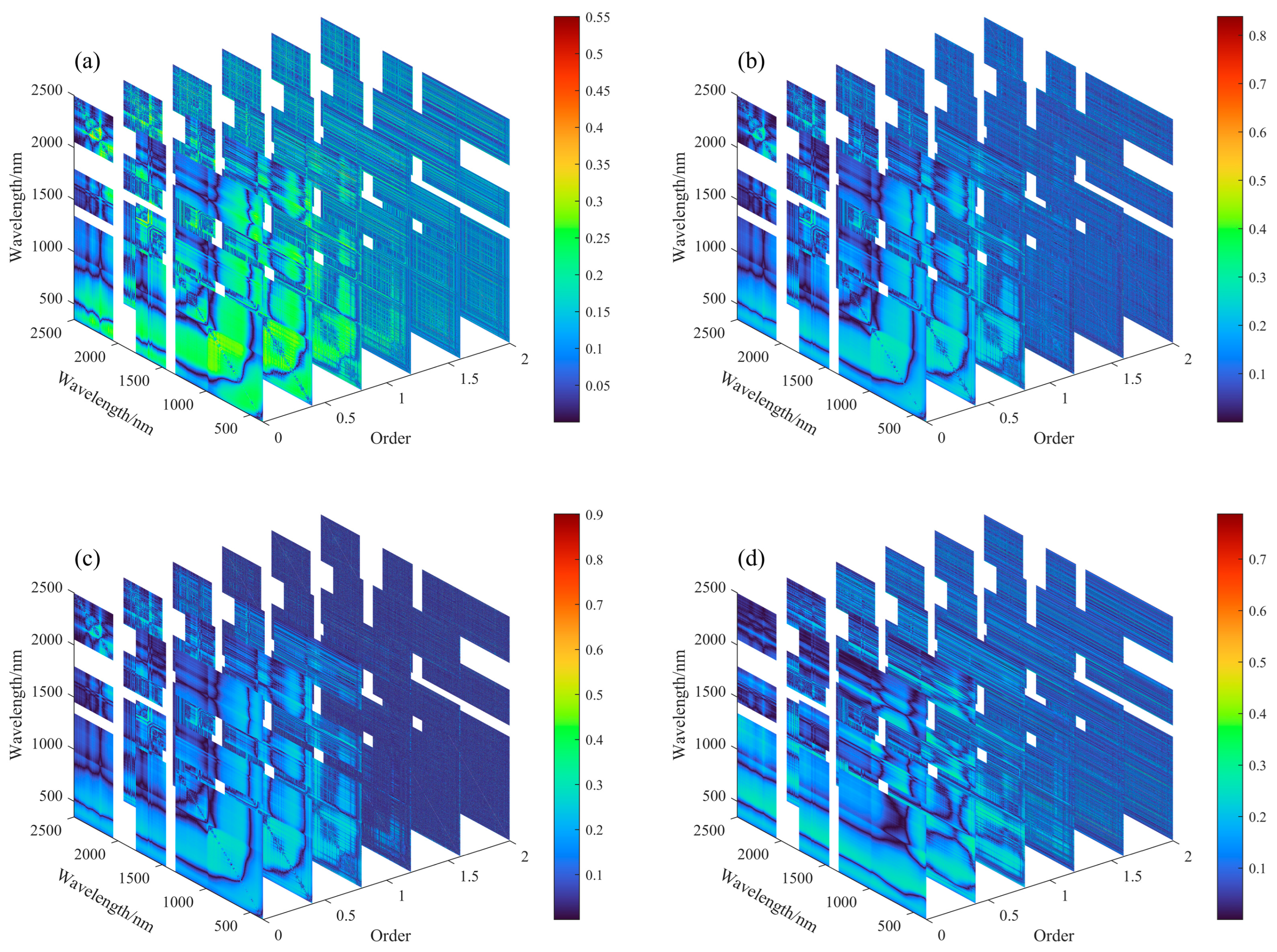
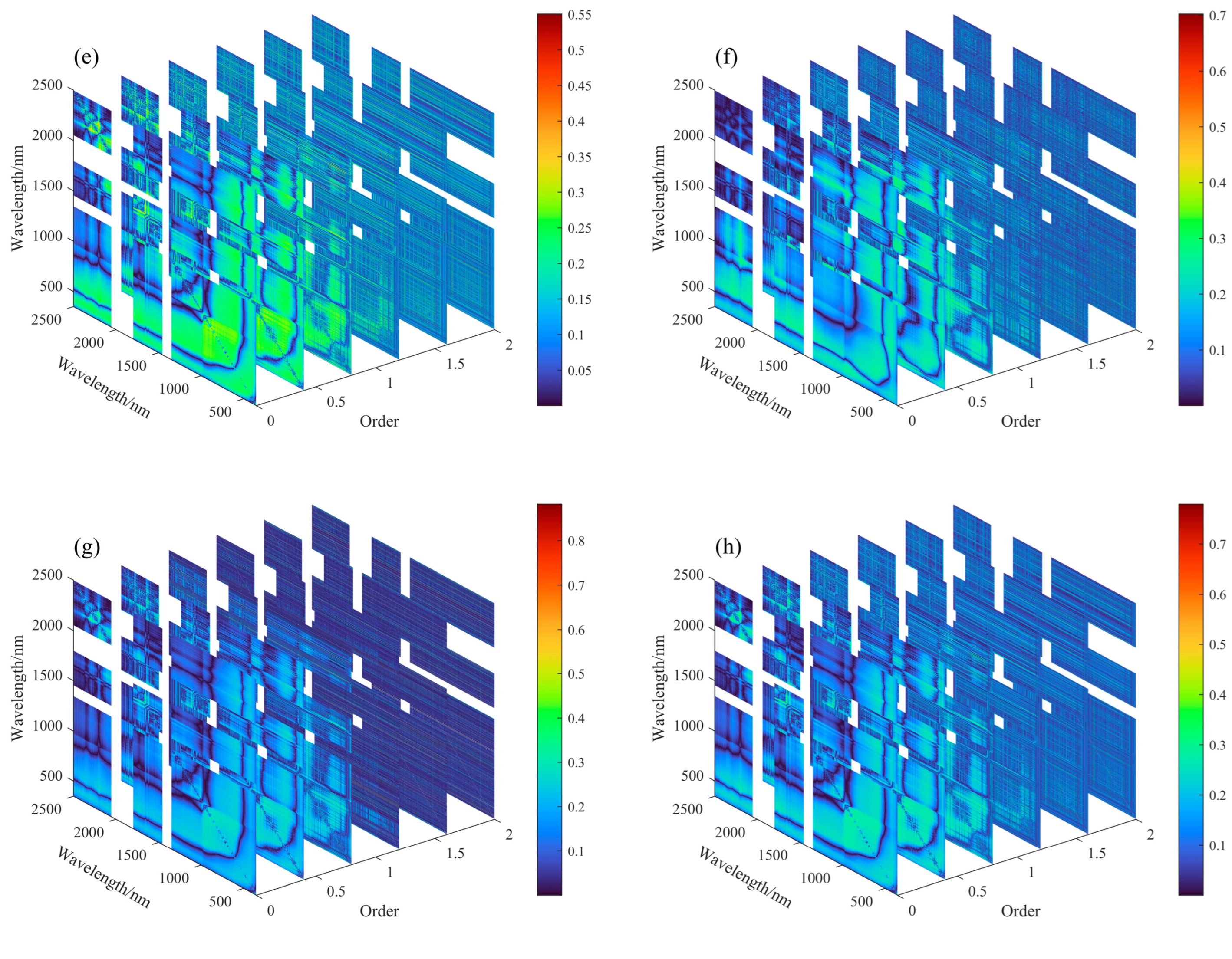

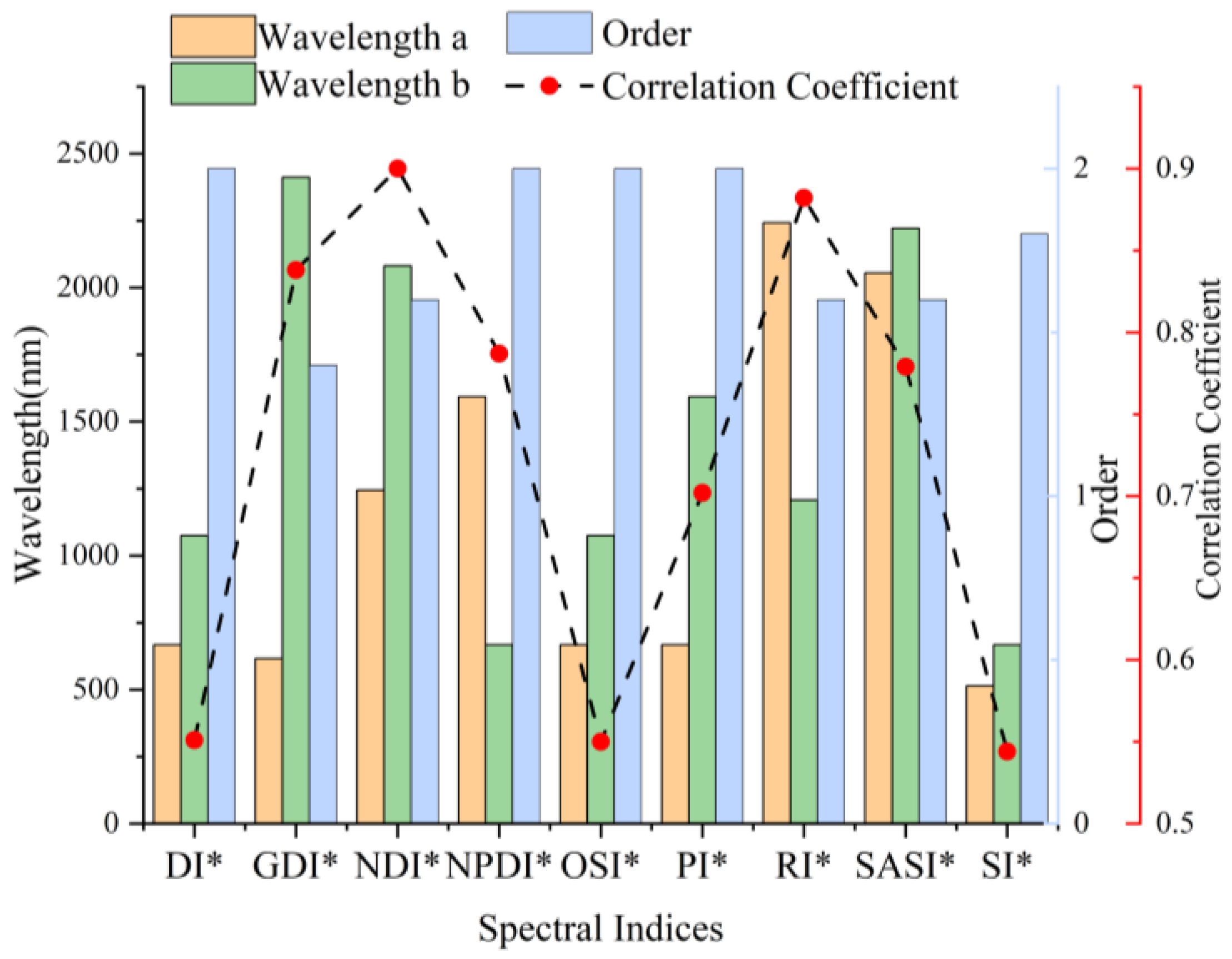
| Spectral Index | Calculation Formula | Spectral Index | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normalized Difference Index (NDI) [20] | Difference Index (DI) [20] | ||
| Optimal Spectral Index (OSI) [50] | Ratio Index (RI) [20] | ||
| Soil-Adjusted Spectral Index (SASI) [50] | Product Index (PI) [50] | ||
| Generalized Difference Index (GDI) [50] | Sum Index (SI) [50] | ||
| Nitrogen Plane Domain Index (NPDI) [50] |
| Model | Train Set | Predictive Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RPD | RMSE (g/kg) | R2 | RPD | RMSE (g/kg) | |
| CNN | 0.931 | 3.648 | 0.942 | 0.924 | 3.364 | 1.398 |
| PLSR | 0.893 | 2.783 | 1.264 | 0.867 | 2.654 | 1.543 |
| RF | 0.674 | 1.766 | 1.843 | 0.652 | 1.643 | 2.868 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Guo, B.; Zhang, R. The Optimal Estimation Model for Soil Salinization Based on the FOD-CNN Spectral Index. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142357
Yang J, Guo B, Zhang R. The Optimal Estimation Model for Soil Salinization Based on the FOD-CNN Spectral Index. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142357
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jicun, Bing Guo, and Rui Zhang. 2025. "The Optimal Estimation Model for Soil Salinization Based on the FOD-CNN Spectral Index" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142357
APA StyleYang, J., Guo, B., & Zhang, R. (2025). The Optimal Estimation Model for Soil Salinization Based on the FOD-CNN Spectral Index. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142357






