Rubber Plantation Expansion Leads to Increase in Soil Erosion in the Middle Lancang-Mekong River Basin During the Period 2003–2022
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Source
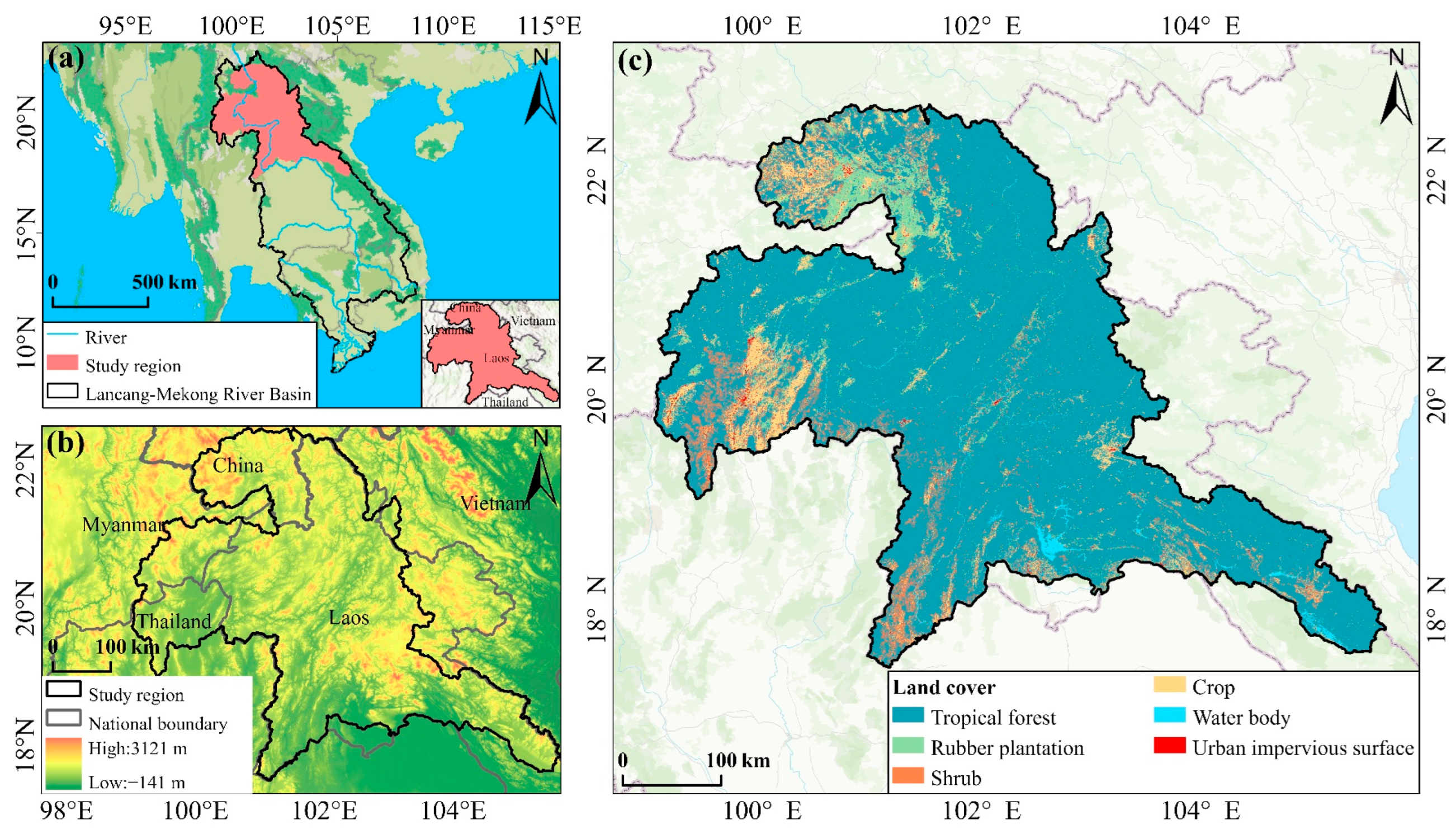
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
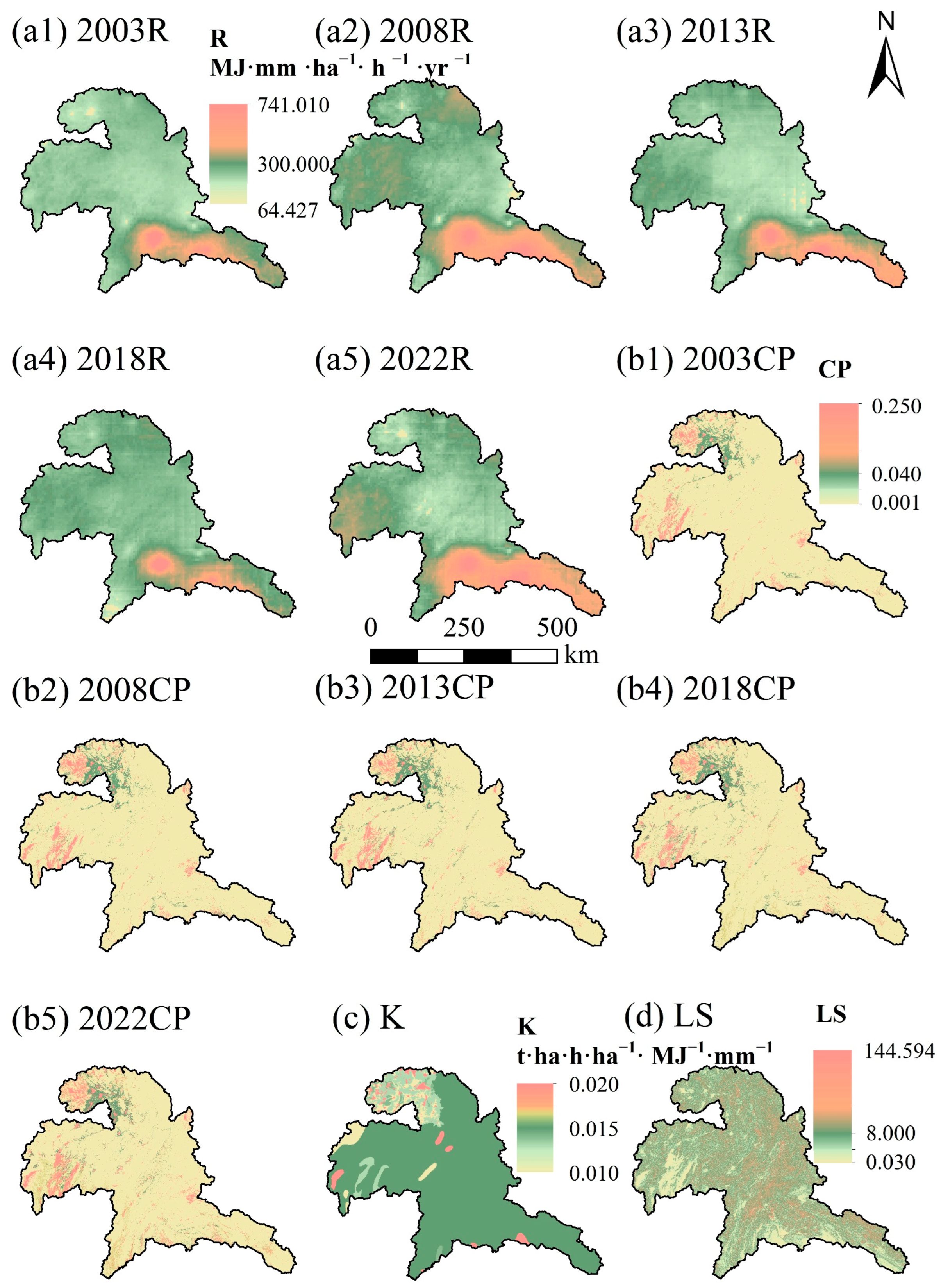
2.2.1. Input Parameters for the RUSLE Model
2.2.2. Data for Driving Factor Analysis
3. Methods
3.1. Rubber Plantation Mapping Framework
3.2. Soil Erosion Calculation by Revising the Universal Soil Loss Equation
3.2.1. Modifying the Universal Soil Loss Equation
- (1)
- Rainfall-runoff (R) factor
- (2)
- Soil erodibility (K) factor
- (3)
- Slope length and steepness (LS) factor
- (4)
- Cover management (C) factor and support practice (P) factor
- (5)
- Cover management and support practice (CP) factor for rubber plantations
3.2.2. Calculation of Total Soil Erosion
3.2.3. Analysis on the Expansion of Rubber Plantations and Changes in Their Soil Erosion Levels
3.3. Analysis on Soil Erosion in Rubber Plantations
3.3.1. Methods of Soil Erosion Trend in Rubber Plantations
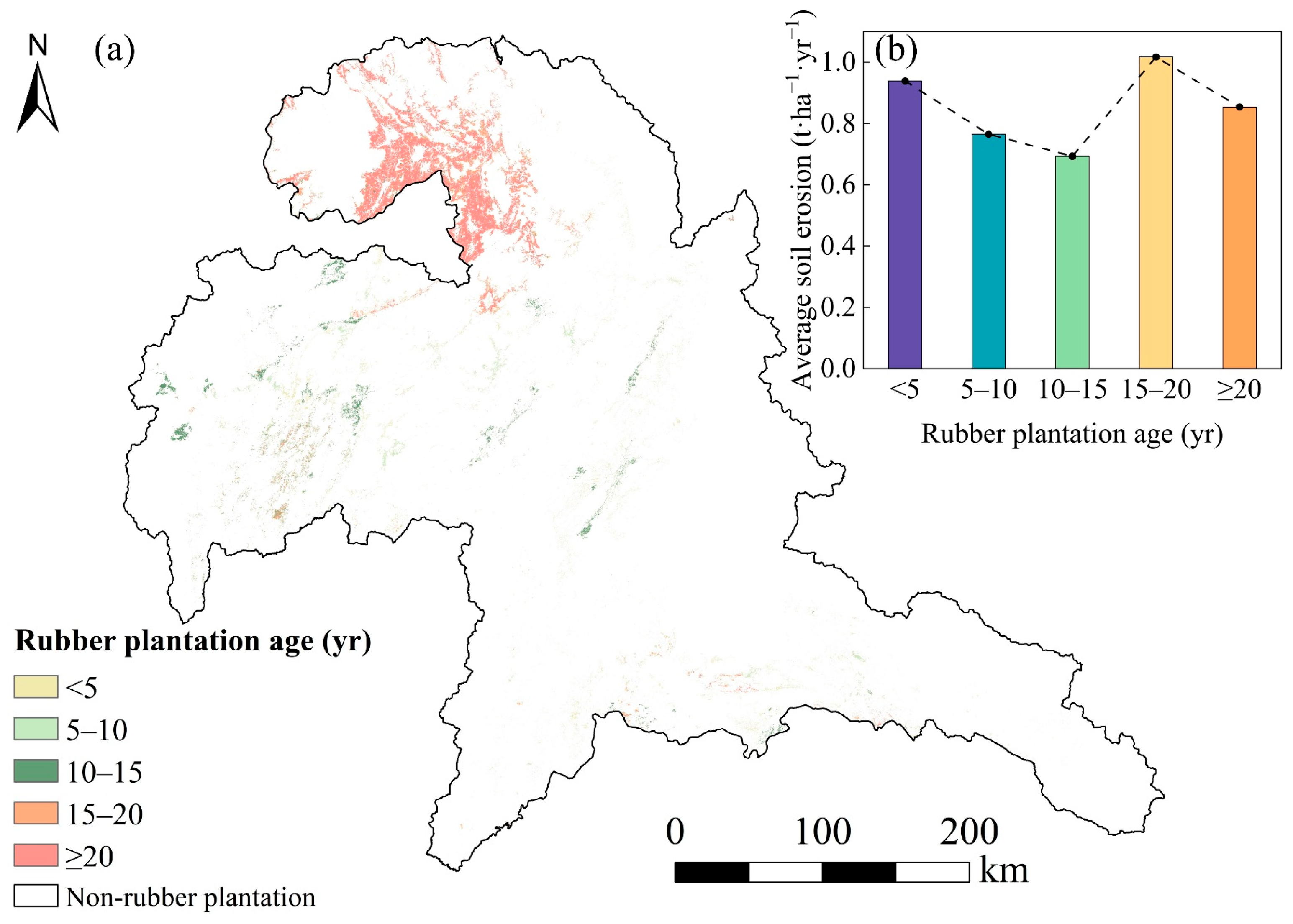
3.3.2. Analysis of Soil Loss in Rubber Plantations of Different Ages
3.4. Methods for Calculating Soil Erosion Caused by Rubber Plantation Expansion
3.5. Analysis of Driving Factor Soil Erosion in Rubber Plantations
4. Results
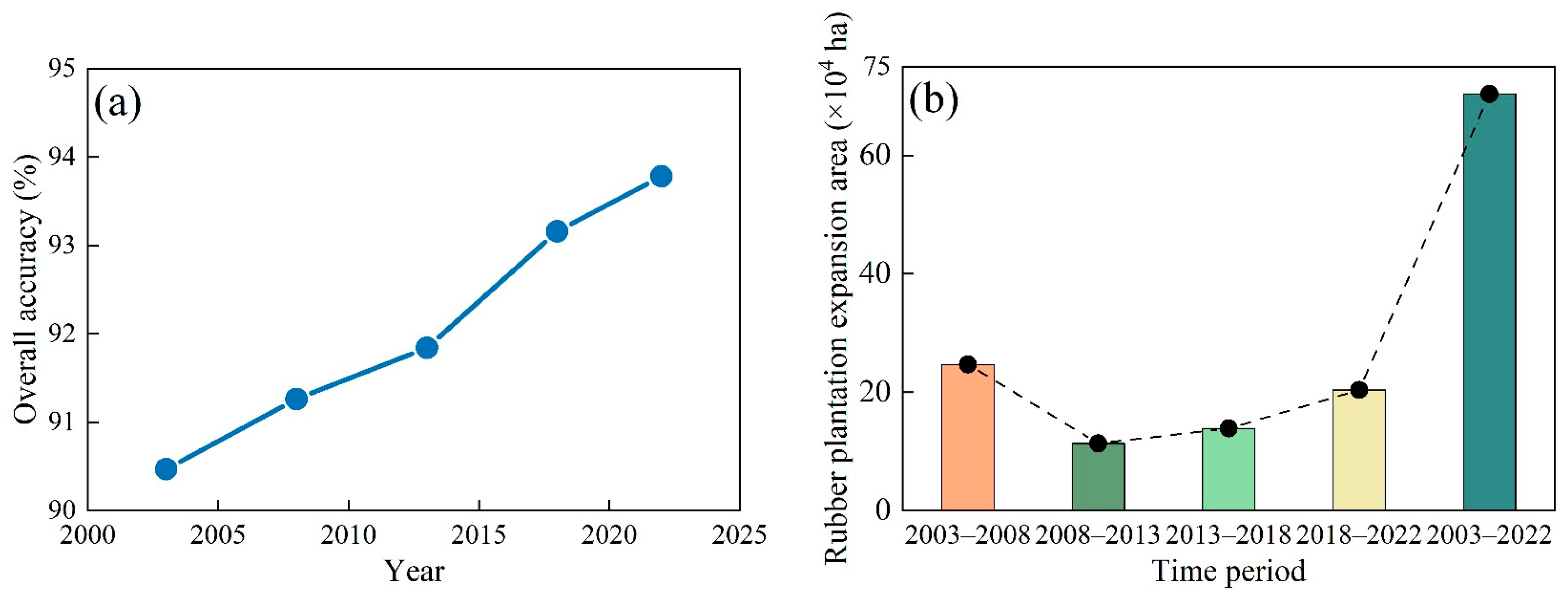
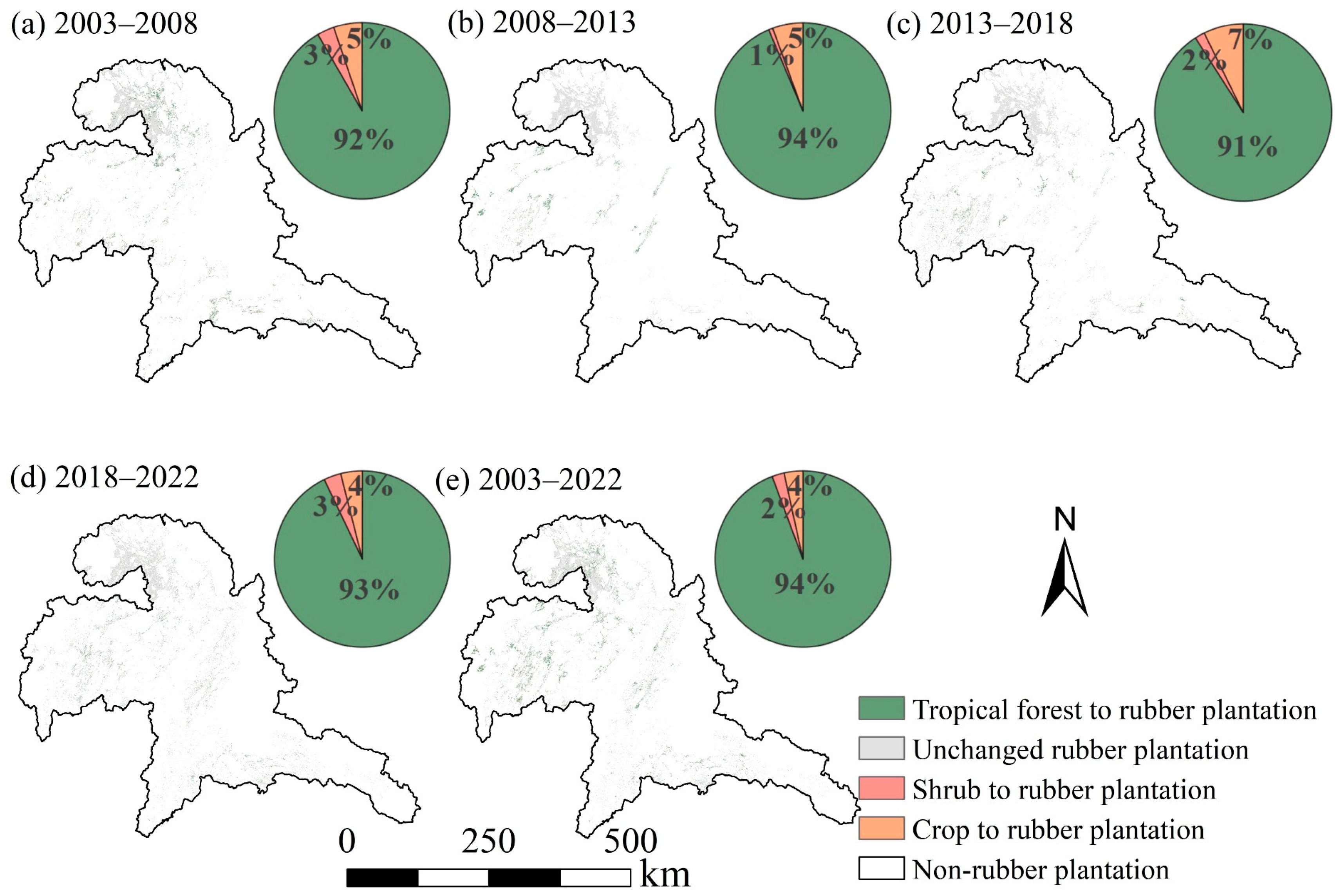
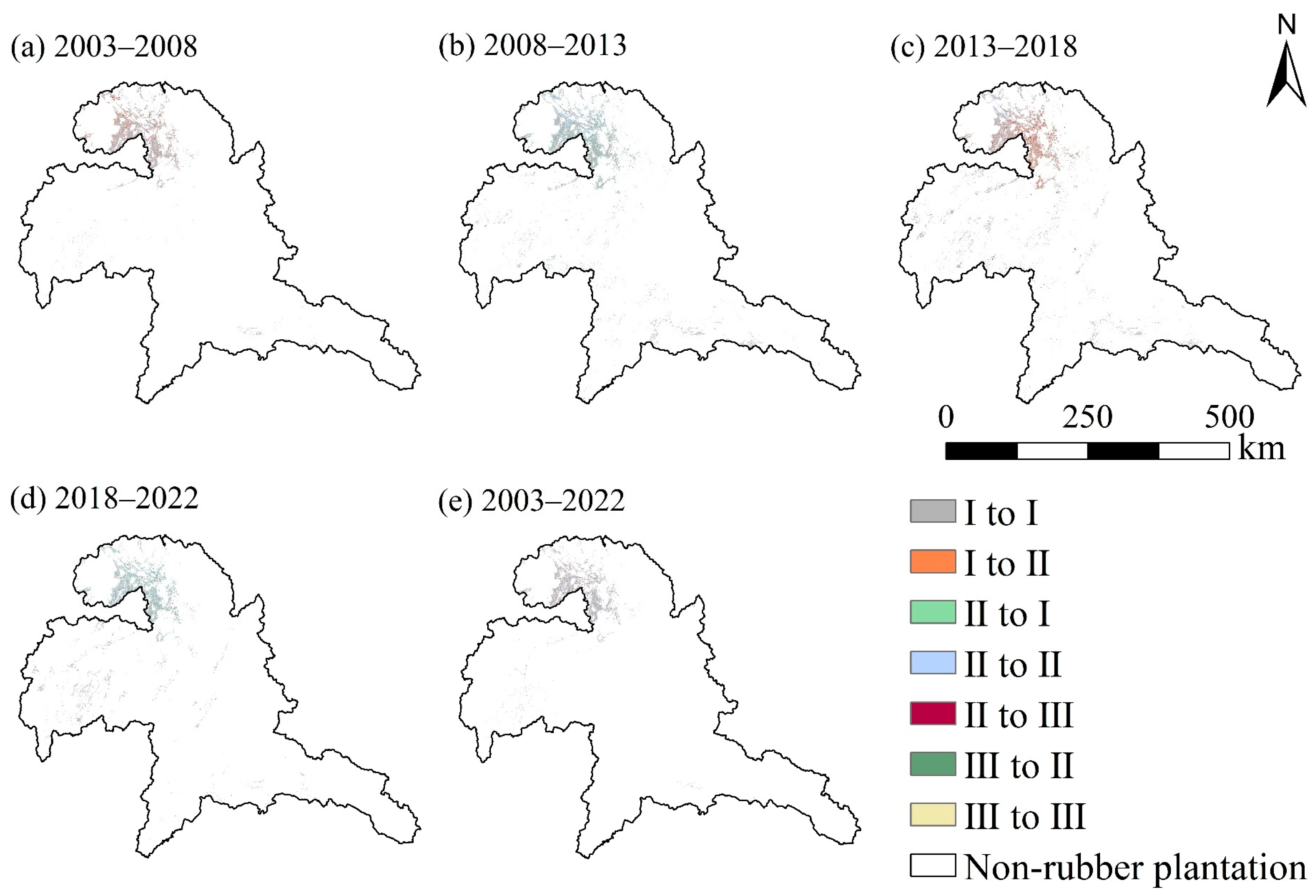
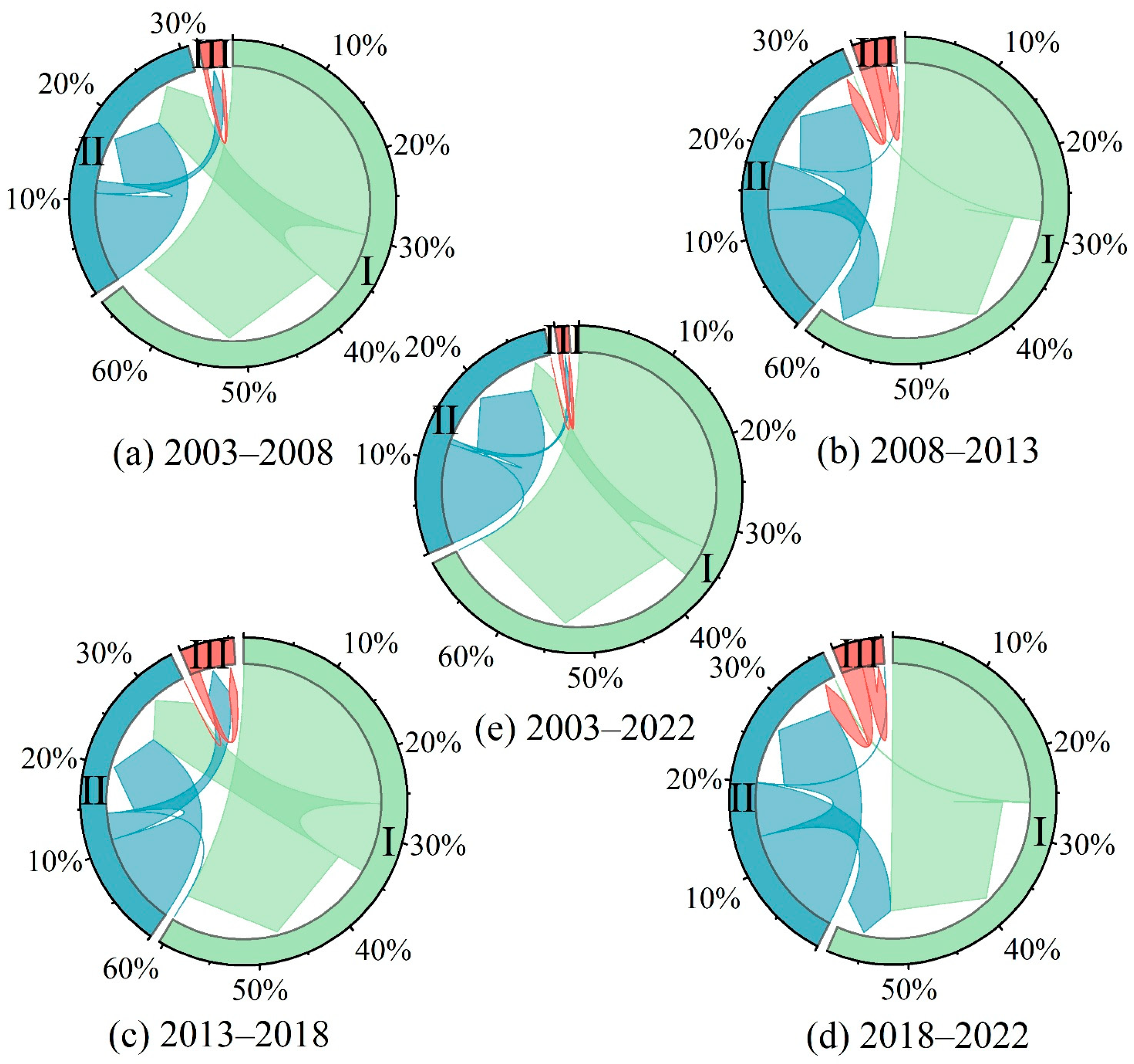
4.1. Rubber Plantation Expansion
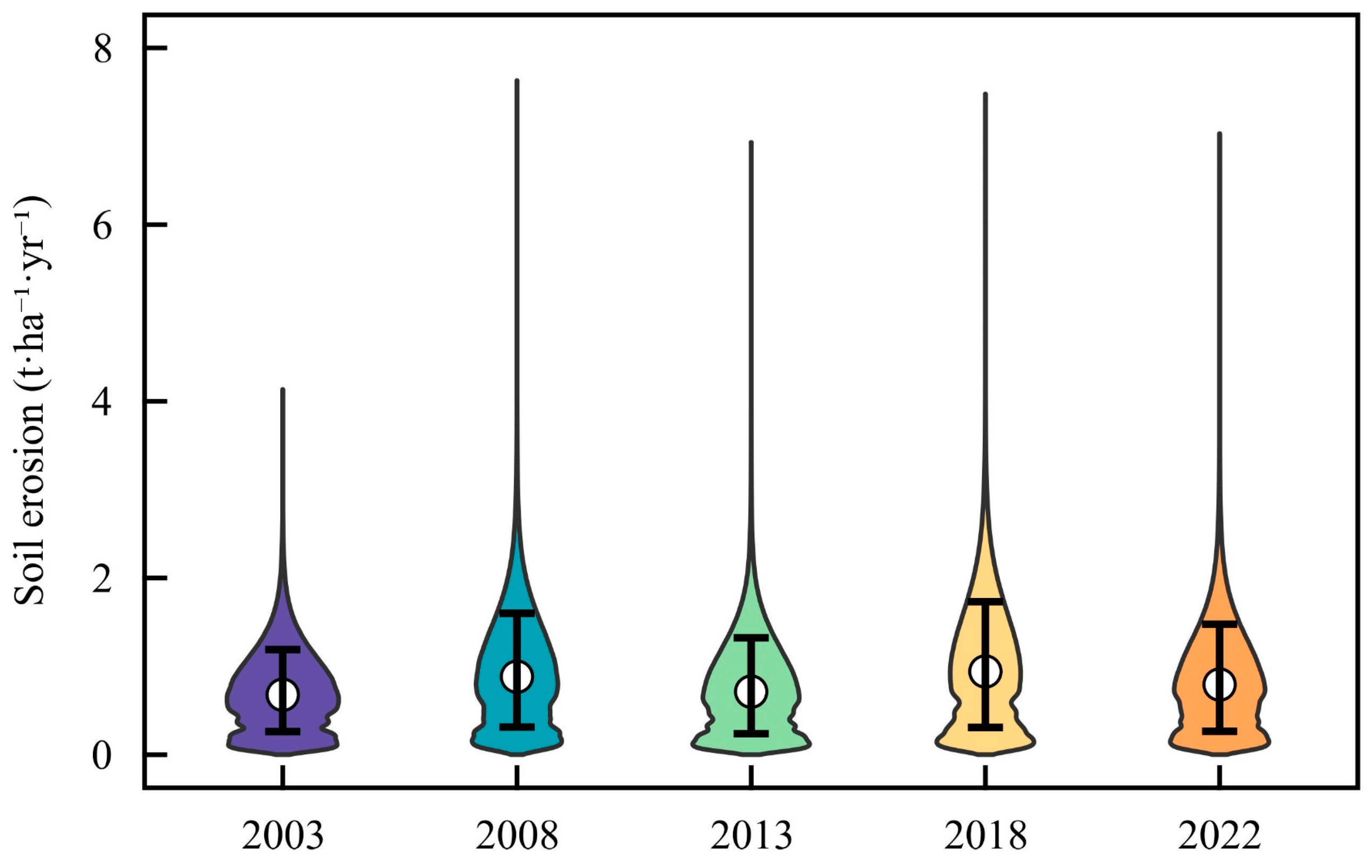
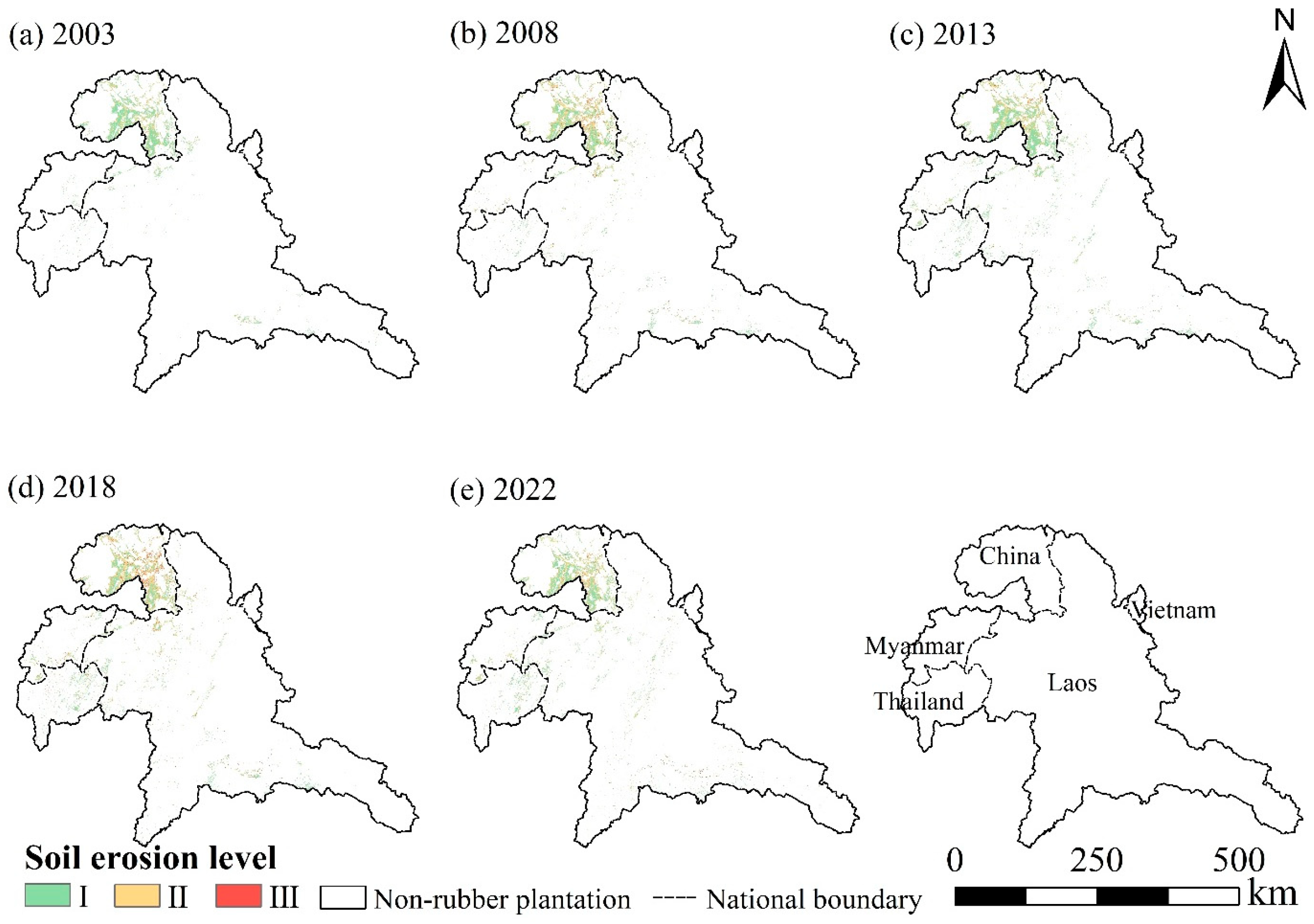
4.2. Soil Erosion in Rubber Plantations
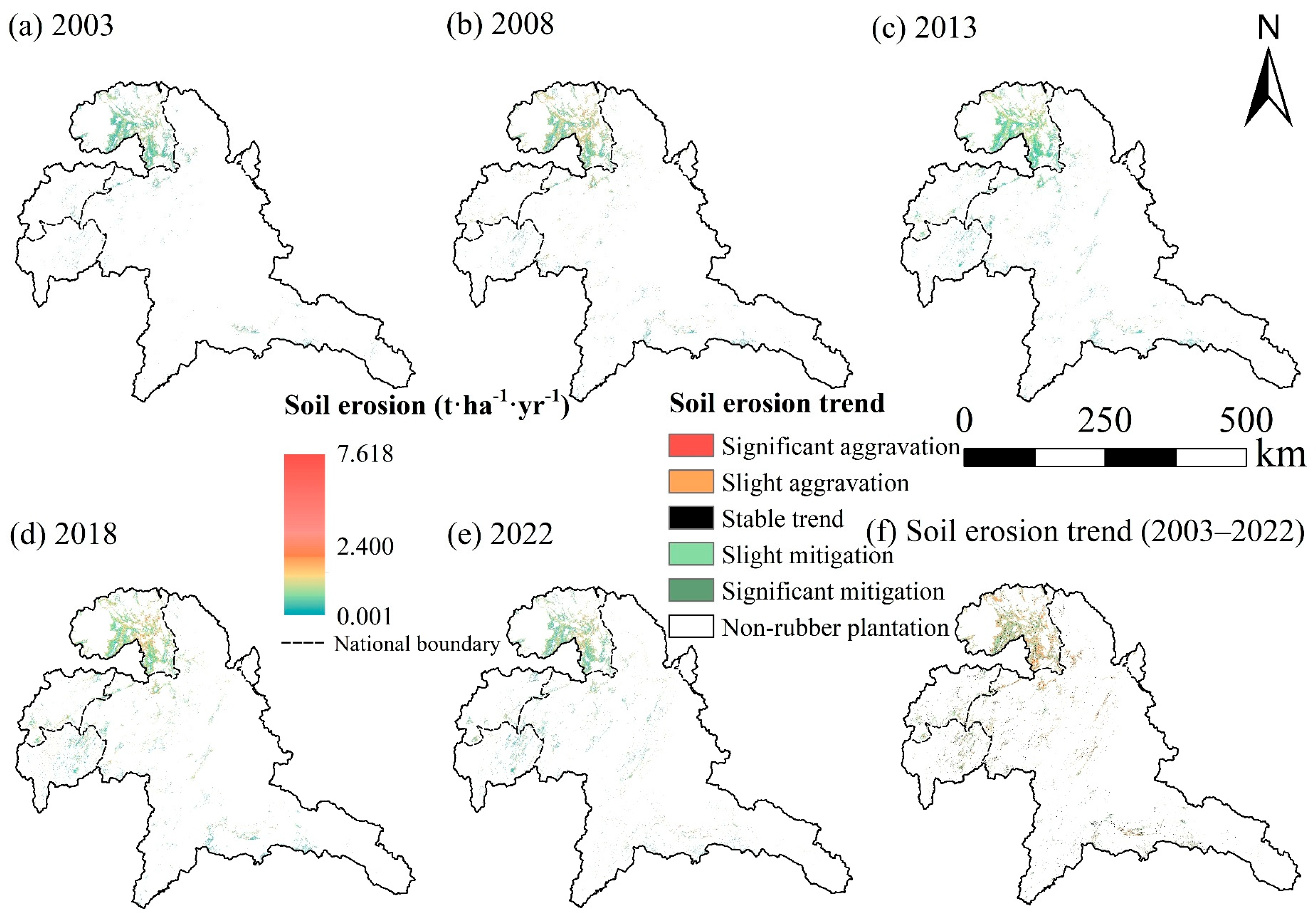
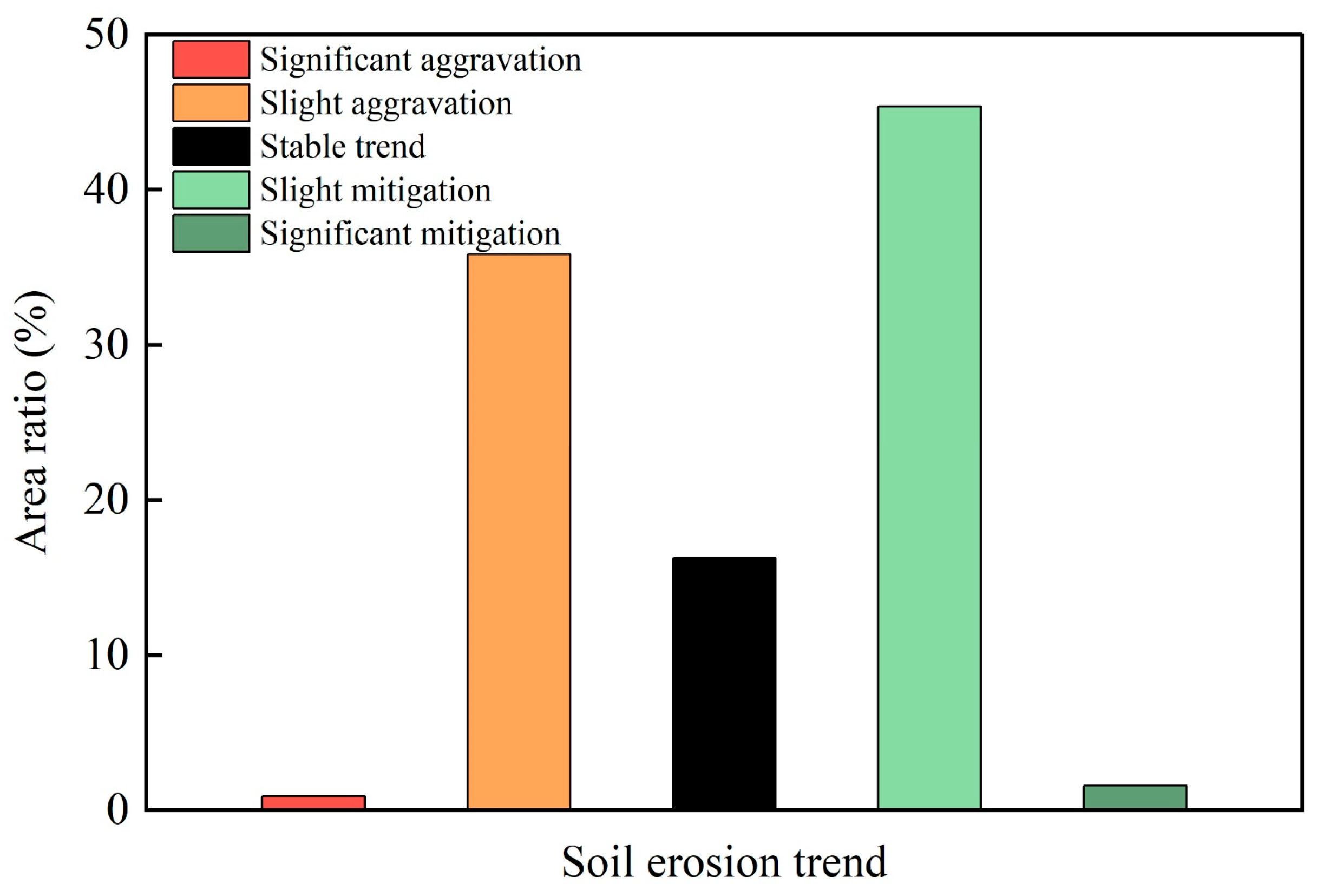
4.3. Temporal and Spatial Variation Trend of Soil Erosion in Rubber Plantations
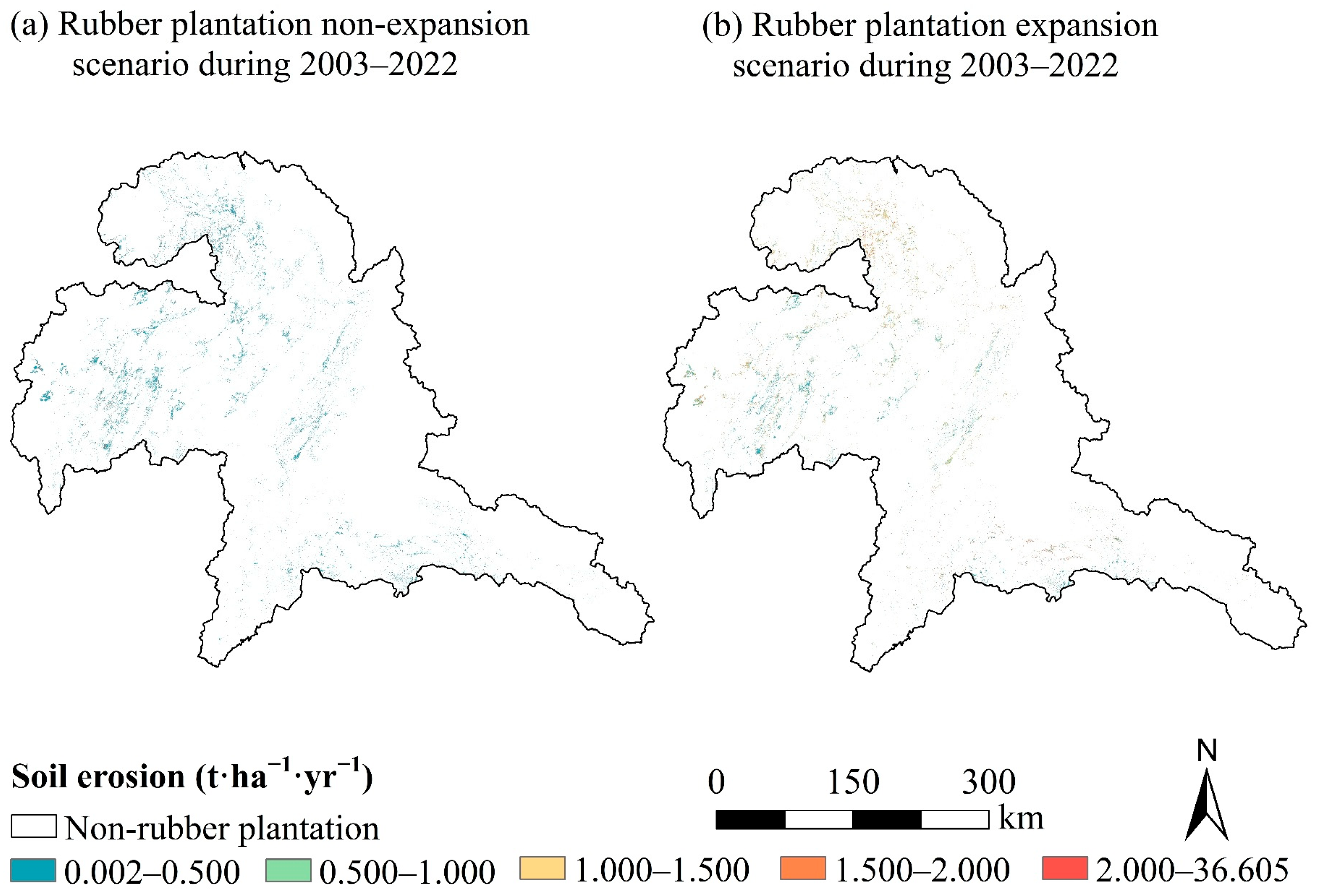
4.4. Soil Erosion Caused by Rubber Plantation Expansion
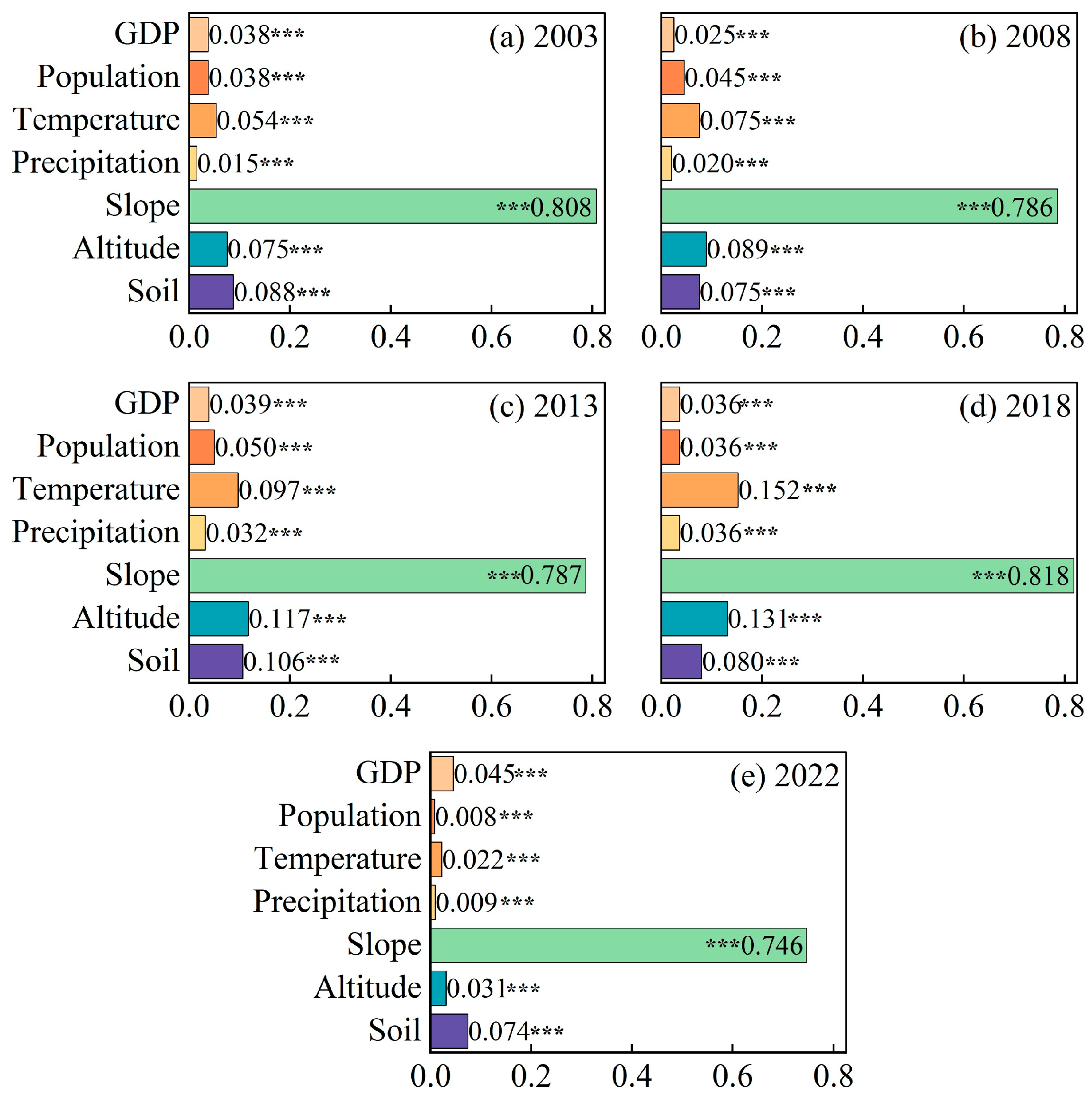
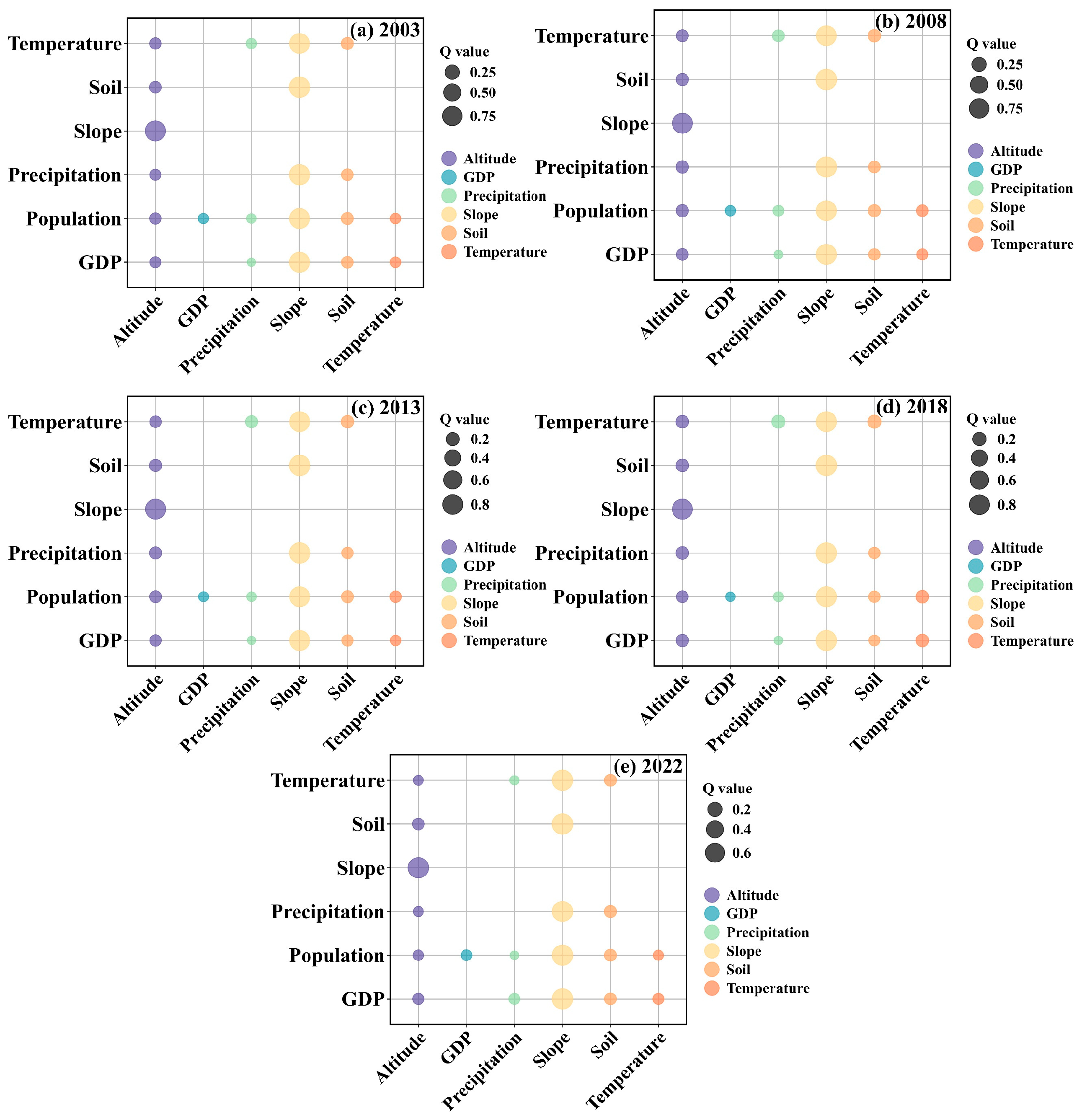
4.5. Driving Factor Analysis
5. Discussions
5.1. Soil Erosion Under the Background of Rubber Plantation Expansion
5.2. Comparison with Existing Studies
5.3. Limitation Analysis and Outlook
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guerra, C.A.; Rosa, I.M.D.; Valentini, E.; Wolf, F.; Filipponi, F.; Karger, D.N.; Nguyen Xuan, A.; Mathieu, J.; Lavelle, P.; Eisenhauer, N. Global vulnerability of soil ecosystems to erosion. Landsc Ecol. 2020, 35, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.L.; Dos Santos, C.A.C.; de Oliveira, G.; Perez-Marin, A.M.; Santos, C.A.G. Effects of human-induced land degradation on water and carbon fluxes in two different Brazilian dryland soil covers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atoma, H.; Suryabhagavan, K.V.; Balakrishnan, M. Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and GIS in Huluka watershed, Central Ethiopia. Sust. Wat. Resour. Man. 2020, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, K.; Deribew, K.T.; Alemu, G.; Hailu, S. Spatial modeling of soil loss as a response to land use-land cover change in Didessa sub-basin, the agricultural watershed of Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, R.; Sultan, H.; Muse Muhamed, S.; Khan, M.N.; Liao, W.; Li, Q.; Cheng, S.; Tian, J.; Cao, Z.; Tao, Y. Sustainable integration of rubber plantations within agroforestry systems in China: Current research and future directions. Plant Sci. Today 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Liu, W.; Zakari, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, B.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhu, X.; Zou, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; et al. A global review of rubber plantations: Impacts on ecosystem functions, mitigations, future directions, and policies for sustainable cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, T.; Holtkamp, A.M.; Damris, M.; Brümmer, B.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil degradation in oil palm and rubber plantations under land resource scarcity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.; Jessy, M.D.; Mohan, M. Soil carbon pools under rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) based agroforestry systems in South India. Agrofor. Syst. 2022, 96, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrière, N.; Locatelli, B.; Laumonier, Y.; Freycon, V.; Bernoux, M. Soil erosion in the humid tropics: A systematic quantitative review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidle, R.C.; Ziegler, A.D.; Negishi, J.N.; Nik, A.R.; Siew, R.; Turkelboom, F. Erosion processes in steep terrain—Truths, myths, and uncertainties related to forest management in Southeast Asia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 224, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Luo, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Li, H. The effects of conversion of tropical rainforest to rubber plantation on splash erosion in Xishuangbanna, SW China. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 46, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, X. Can intercropping with the cash crop help improve the soil physico-chemical properties of rubber plantations? Geoderma 2019, 335, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.B.; Odeh, I.O.A.; Bishop, T.F.A.; Dunbar, M.S.; Shatar, T.M. An overview of pedometric techniques for use in soil survey. Geoderma 2000, 97, 293–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Kumar, M.; Prasad, S.A.; Narayan, S.; Sandeep, D.S.; Kumar, R.S.; Panigrahi, B. Global-scale application of the RUSLE model: A comprehensive review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 806–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Roy, D.P.; Radeloff, V.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Anderson, M.C.; Johnson, D.M.; Healey, S.; Zhu, Z.; Scambos, T.A.; Pahlevan, N.; et al. Fifty years of Landsat science and impacts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, E.R.; Sridhar, V. Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a Small Mountainous Watershed Using RUSLE: A Case-Study of the Palar Sub-Watershed in Kodaikanal, South India. Water 2018, 10, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, D.M.; Bhat, H.G. Integration of geospatial technologies with RUSLE for analysis of land use/cover change impact on soil erosion: Case study in Rib watershed, north-western highland Ethiopia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P. Assessment of soil erosion in a tropical mountain river basin of the southern Western Ghats, India using RUSLE and GIS. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, H.A.; Shahid, S. Soil erosion susceptibility of Johor River basin. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizeei, H.M.; Saharkhiz, M.A.; Pradhan, B.; Ahmad, N. Soil erosion prediction based on land cover dynamics at the Semenyih watershed in Malaysia using LTM and USLE models. Geocarto Int. 2016, 31, 1158–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, P.V.G.; Silva, M.L.N.; Silva, B.P.C.; Curi, N.; Bueno, I.T.; Acérbi Júnior, F.W.; Davies, J.; Quinton, J. Modelling spatially distributed soil losses and sediment yield in the upper Grande River Basin—Brazil. Catena 2017, 157, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, A. Estimation of soil loss by USLE model using GIS and remote sensing techniques: A case study of Muhuri River Basin, Tripura, India. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2017, 6, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto, F.; Cartes, E.; Mardones, O.; Rubilar, R. Hillslope soil erosion and mobility in pine plantations and native deciduous forest in the coastal range of south-Central Chile. Land. Dedrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.G.; Degener, J.; Kappas, M. Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Blagodatsky, S.; Giese, M.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Cadisch, G. Impact of herbicide application on soil erosion and induced carbon loss in a rubber plantation of Southwest China. Catena 2016, 145, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puktlang, W.; Mongkolsawat, C.; Suwanwerakamtorn, R. The Impact of Expanding Rubber Tree Plantation on Soil Erosion in the Mekong-Sub Basin. In Proceedings of the 34th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Bali, Indonesia, 20–24 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, B.; Seitz, L. Effects of large-scale rubber farm on soil erosion and river bed material in the upper Mekong Basin. In River Flow 2014; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 2305–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Sergey, B.; Feng, L.; Jianchu, X.; Cadisch, G. Impact of rubber plantation age on erosive potential studied with USLE model. J. Appl. Water Eng. Res. 2018, 6, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, T.; Chen, Q.; Han, X.; Weng, X.; He, P.; Zhou, Z.; Du, Y. Spatio-temporal changes in daily extreme precipitation for the Lancang–Mekong River Basin. Nat. Hazards 2023, 115, 641–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. The Physical Geography of Southeast Asia; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IIASA; FAO. Harmonized World Soil Database Version 2.0; FAO: Rome, Italy; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gao, M.; Cheng, S.; Hou, W.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Global 1 km × 1 km gridded revised real gross domestic product and electricity consumption during 1992–2019 based on calibrated nighttime light data. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, A.E.; Stevens, F.R.; Linard, C.; Jia, P.; Tatem, A.J. High resolution population distribution maps for Southeast Asia in 2010 and 2015. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.F.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, B.Q.; R, M.L.; Lu, D.S.; Wang, S.S. A new framework for mapping rubber plantations through the combination of automatic sample migration, dynamic phenology, and change detection variables based on time series Landsat images. 2025; under review. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.J.; Chen, M.H.; Lin, F.X.; Huang, Y.H.; Lu, C.L. The rainfall erosivity index in Fujian Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1995, 9, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chuenchum, P.; Xu, M.; Tang, W. Predicted trends of soil erosion and sediment yield from future land use and climate change scenarios in the Lancang–Mekong River by using the modified RUSLE model. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Mu, Z.; Dong, W.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y. Temporal Spatial Mutations of Soil Erosion in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Lancang River Basin and Its Influencing Mechanisms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Moore, D.; He, P.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Extension of a GIS procedure for calculating the RUSLE equation LS factor. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of land use changes on soil erosion in a fast developing area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zulkar, H.; Wang, D.; Zhao, T.; Xu, W. Changes in Vegetation Coverage and Migration Characteristics of Center of Gravity in the Arid Desert Region of Northwest China in 30 Recent Years. Land 2022, 11, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W. Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jinfeng, W.; Yong, G.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; Zhai, D.; West, C.D.; Green, J.M.H.; Chen, H.; Hurni, K.; Su, Y.; Warren-Thomas, E.; Xu, J.; et al. High-resolution maps show that rubber causes substantial deforestation. Nature 2023, 623, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, S.; Ding, W.; Li, R.; Han, J.; Ge, W.; Chen, H.; Shi, S. Analysis of canopy interception characteristics and influencing factors in typical artificial forest in the Loess Plateau semi-arid region. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliot, W.J.; Page-Dumroese, D.; Robichaud, P.R. The effects of forest management on erosion and soil productivity. In Soil Quality and Soil Erosion; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, D.; McGrouther, K.; Long, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lv, X.; Niazi, N.K.; Song, Z.; Wang, H. Effect of Eucalyptus forests on understory vegetation and soil quality. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Tan, Q.; Liu, G.; Xu, M. Impacts of mixed forests on controlling soil erosion in China. Catena 2022, 213, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Liu, H.; Ning, J.; Zhen, Q.; Zheng, J. Rainwater infiltration and nutrient recharge system significantly enhance the growth of degraded artificial forest in semi-arid areas with shallowly buried soft bedrock. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 539, 121016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Zeng, H. How does a rubber plantation affect the spatial variability and temporal stability of throughfall? Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, C.; Kanali, C.; Owende, P.M.O.; Nieuwenhuis, M.; Ward, S. Characteristic site disturbance due to harvesting and extraction machinery traffic on sensitive forest sites with peat soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 180, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Qi, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Huang, J. The deterioration and restoration of dried soil layers: New evidence from a precipitation manipulation experiment in an artificial forest. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hua, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Ji, W. Effects of artificial restoration and natural recovery on plant communities and soil properties across different temporal gradients after landslides. Forests 2023, 14, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Xu, L.; Teng, W.; Fang, J. Construction of Eco-Compensation Policy Framework for Natural Rubber with Production and Ecological Win–Win. Land 2025, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panklang, P.; Thoumazeau, A.; Chiarawipa, R.; Sdoodee, S.; Sebag, D.; Gay, F.; Thaler, P.; Brauman, A. Rubber, rubber and rubber: How 75 years of successive rubber plantation rotations affect topsoil quality? Land. Dedrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.; Akber, M.A.; Smith, C.; Aziz, A.A. The dynamics of rubber production in Malaysia: Potential impacts, challenges and proposed interventions. For. Policy. Econ. 2021, 127, 102449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, F.; Francksen, R.M.; Zavattaro, L.; Abdalla, M.; Hejduk, S.; Enri, S.R.; Pittarello, M.; Price, P.N.; Schils, R.L.M.; Smith, P.; et al. The role of grassland for erosion and flood mitigation in Europe: A meta-analysis. Agric., Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 348, 108443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, D.; Girindran, R.; Sam, A.S.; Sathyan, A.R.; Kaechele, H. The large-scale expansion of rubber plantations in southern India: Major impacts and the changing nature of drivers. Environ. Monit. Assess 2024, 196, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrends, A.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; Ziegler, A.D.; Fox, J.M.; Chen, H.; Su, Y.; Xu, J. Current trends of rubber plantation expansion may threaten biodiversity and livelihoods. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 34, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotiphan, R.; Vaysse, L.; Lacote, R.; Gohet, E.; Thaler, P.; Sajjaphan, K.; Bottier, C.; Char, C.; Liengprayoon, S.; Gay, F. Can fertilization be a driver of rubber plantation intensification? Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefi, M.; Yoshino, K.; Setiawan, Y. Assessment and mapping of soil erosion risk by water in Tunisia using time series MODIS data. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyret, M.; Robain, H.; de Rouw, A.; Janeau, J.-L.; Durand, T.; Kaewthip, J.; Trisophon, K.; Valentin, C. Higher runoff and soil detachment in rubber tree plantations compared to annual cultivation is mitigated by ground cover in steep mountainous Thailand. Catena 2020, 189, 104472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Luo, Q.; Lu, H.; Wu, J.; Duan, W. The effect of litter layer on controlling surface runoff and erosion in rubber plantations on tropical mountain slopes, SW China. Catena 2017, 149, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhong, R.; Yan, K.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Pu, J.; Gao, S.; Qi, J.; Yin, G.; Myneni, R.B. Evaluating the saturation effect of vegetation indices in forests using 3D radiative transfer simulations and satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Dong, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G.; Lai, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Kou, W.; Yun, T. Early identification of immature rubber plantations using Landsat and Sentinel satellite images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2024, 133, 104097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S. The assessment of water-borne erosion at catchment level using GIS-based RUSLE and remote sensing: A review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R)USLE): With a view to increasing its global applicability and improving soil loss estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Land Cover Type | C | P |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical forest | 0.001 | 1 |
| Shrub | 0.08 | 1 |
| Crop | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Water body | 0.01 | 1 |
| Urban impervious surface | 0.1 | 1 |
| SSE | ZSE | Soil Erosion Trend |
|---|---|---|
| ≥0.0005 | ≥1.96 | Significant aggravation |
| ≥0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | Slight aggravation |
| −0.0005–0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | Stable trend |
| <0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | Slight mitigation |
| <0.0005 | <−1.96 | Significant mitigation |
| Average Soil Erosion (t·ha−1·yr−1) | Rubber Plantation Non-Expansion Scenario | Rubber Plantation Expansion Scenario | Exacerbated Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2003–2008 | 0.233 | 1.030 | 342.060 |
| 2008–2013 | 0.120 | 0.606 | 405.000 |
| 2013–2018 | 0.241 | 0.976 | 304.979 |
| 2018–2022 | 0.204 | 0.943 | 362.255 |
| 2003–2022 | 0.148 | 0.902 | 509.459 |
| Methods | Study Site | Data Year | Age of Rubber Plantation | Rubber Plantation Soil Erosion (t·ha−1·yr−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USLE | Xishuangbanna | 2014 | 4, 12, 18, 25 and 36 years | 0.330–2.800 | [31] |
| Field experiments | Xishuangbanna | 2011 | 22 years | 0.910–4.730 | [70] |
| Field experiments | Xishuangbanna | 2014 | 12 years | 0.500–4.250 | [28] |
| Field experiments | Thailand | 2015 | Mature/young | 3.600/57.000 | [69] |
| RUSLE | Thailand | 2013 | all ages | 0.021–4.767 | This study |
| RUSLE | Xishuangbanna | 2013 | all ages | 0.003–6.917 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Pham, T.D.; Wu, Q.; Chai, P.; Lu, D.; Li, D.; Chen, Y. Rubber Plantation Expansion Leads to Increase in Soil Erosion in the Middle Lancang-Mekong River Basin During the Period 2003–2022. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132220
Xu H, Pham TD, Wu Q, Chai P, Lu D, Li D, Chen Y. Rubber Plantation Expansion Leads to Increase in Soil Erosion in the Middle Lancang-Mekong River Basin During the Period 2003–2022. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(13):2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132220
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hongfeng, Tien Dat Pham, Qingquan Wu, Peng Chai, Dengsheng Lu, Dengqiu Li, and Yaoliang Chen. 2025. "Rubber Plantation Expansion Leads to Increase in Soil Erosion in the Middle Lancang-Mekong River Basin During the Period 2003–2022" Remote Sensing 17, no. 13: 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132220
APA StyleXu, H., Pham, T. D., Wu, Q., Chai, P., Lu, D., Li, D., & Chen, Y. (2025). Rubber Plantation Expansion Leads to Increase in Soil Erosion in the Middle Lancang-Mekong River Basin During the Period 2003–2022. Remote Sensing, 17(13), 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132220










