InfraredStereo3D: Breaking Night Vision Limits with Perspective Projection Positional Encoding and Groundbreaking Infrared Dataset
Abstract
1. Introduction
- •
- An infrared binocular stereo matching dataset is constructed;
- •
- A binocular stereo matching network combined with the transformer and cost volume is created to complete global feature extraction and local feature extraction tasks, respectively;
- •
- The perspective projection model is embedded in the attention mechanism positional encoding part of the transformer network instead of the unrealistic parallel projection model.
2. Related Works
2.1. Datasets
2.2. 3D Reconstruction from Infrared Images
2.3. Stereo Matching
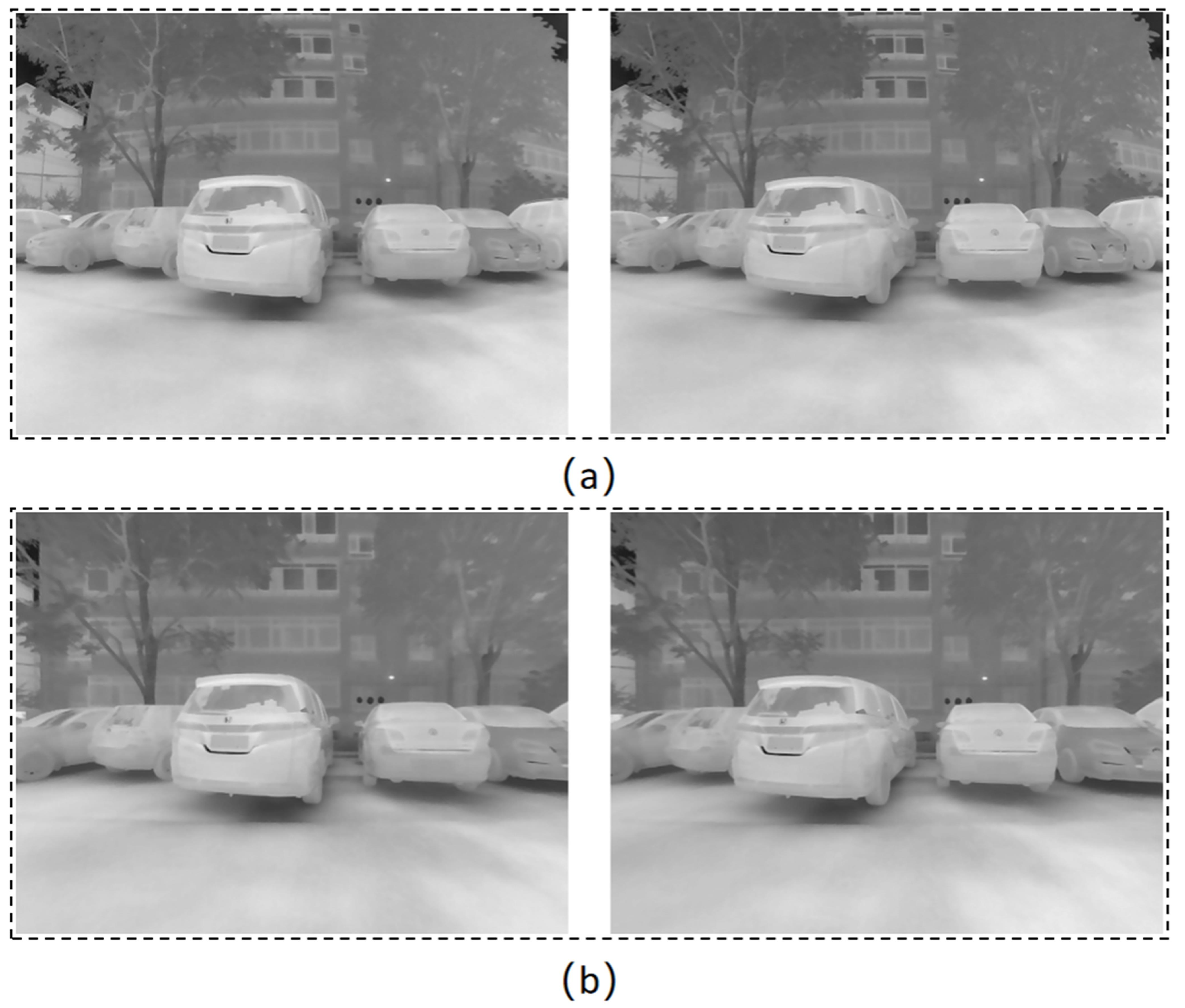
3. Infrared Depth Dataset
3.1. Data Acquisition
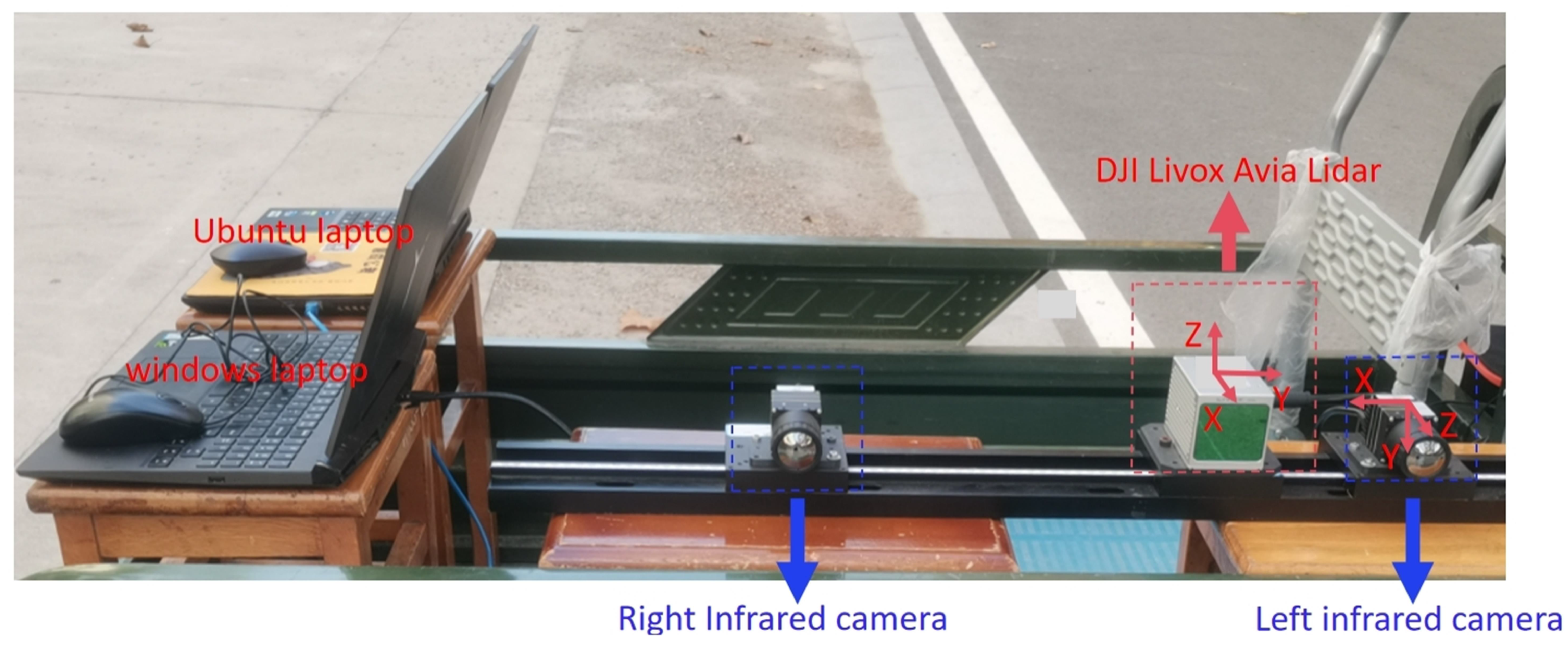
3.1.1. Sensor Setup
- •
- Two long-wave infrared cameras with a resolution of (Huajingkang K26E4) operate in a wavelength range and pixel spacing of 8–14 um and 17 um, respectively.
- •
- DJI Livox Avia Lidar: wavelength is 950 nm, frequency is 10 Hz, ray divergence angle is , built-in IMU (Model: BMI088), 480,000 points/s in double echo mode, of view in the non-repeat scan mode, and the detection distance is 450 m.
- •
- Two laptops with Intel i7 processors running Ubuntu 18.046 and Windows 10 systems, respectively.
3.1.2. Data Acquisition
3.2. Equipment Calibration
3.2.1. Calibration of Infrared Binocular Cameras
3.2.2. Calibration Between Infrared Camera and Lidar
3.3. Infrared Image Processing
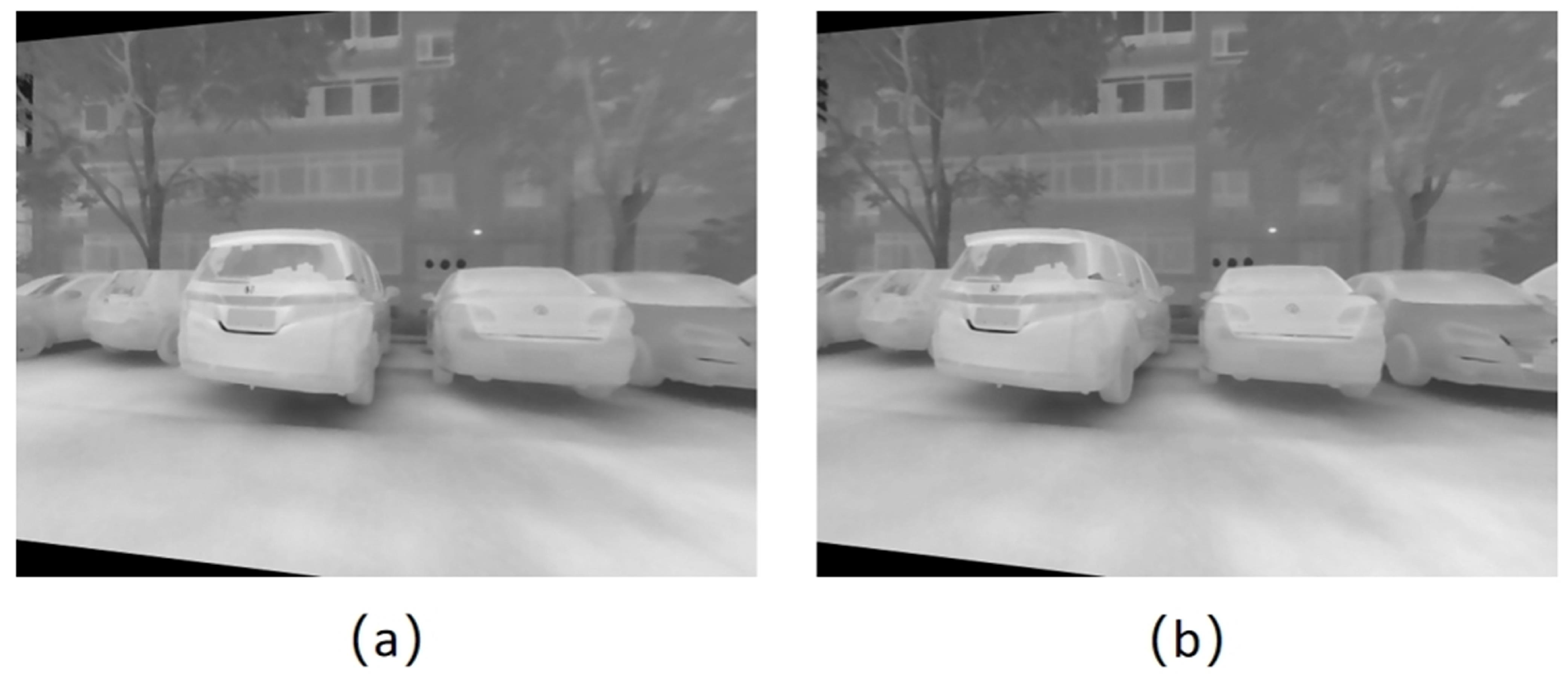
3.3.1. Distortion Removal
3.3.2. Stereo Rectification
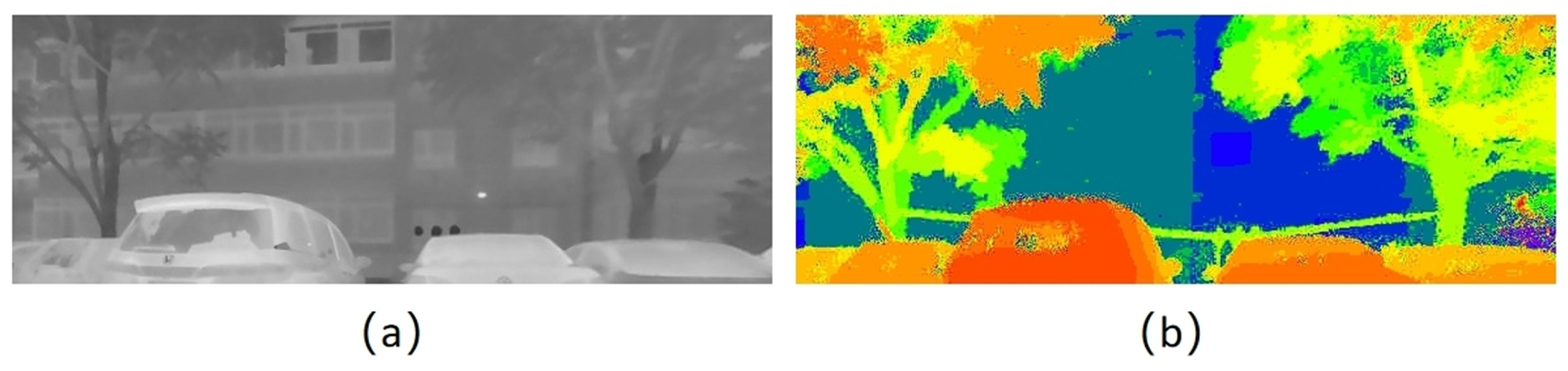
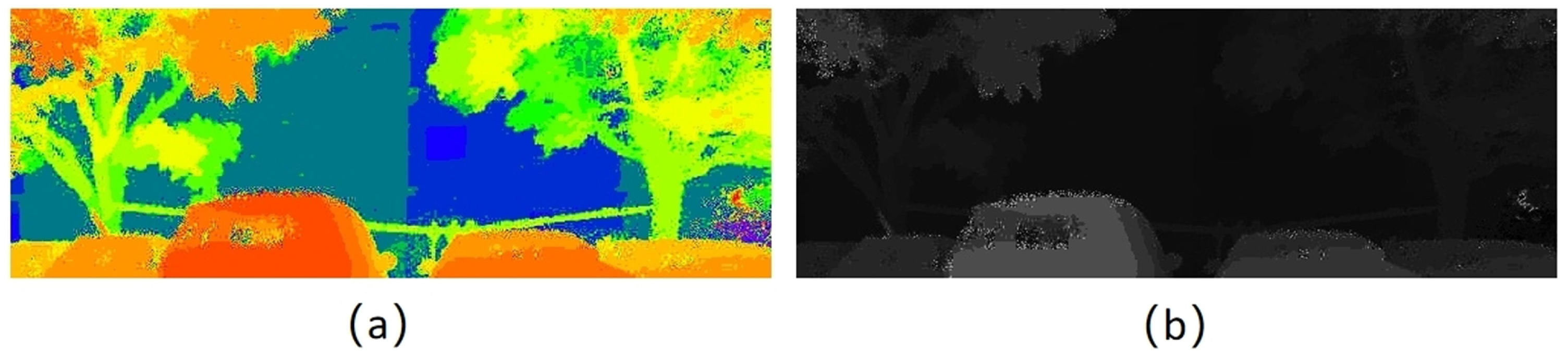
3.4. Generation of Disparity Map
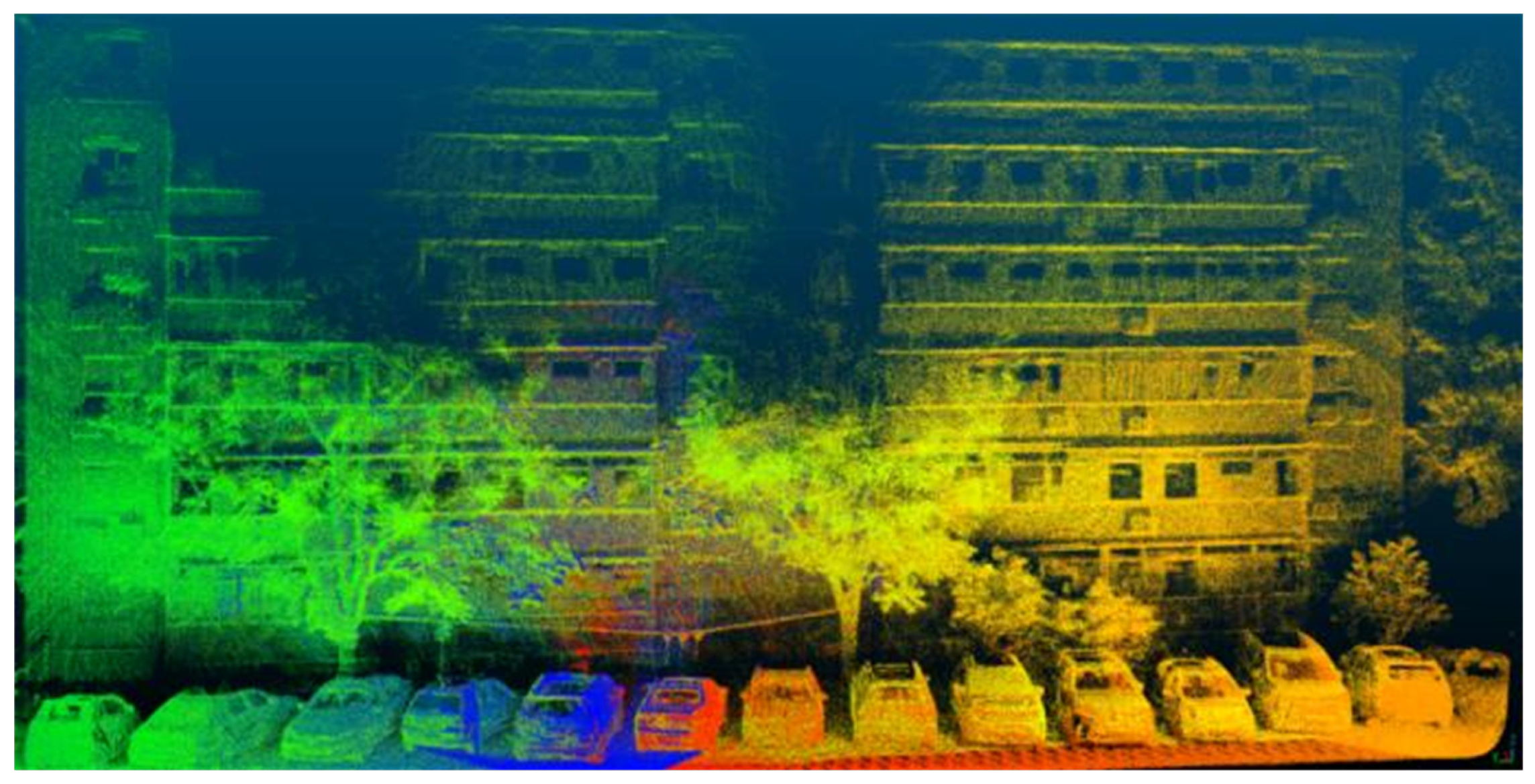
3.4.1. Generation of Lidar Point Cloud Map
3.4.2. Generation of Depth Map
- •
- In the real scene, the object scanned by laser has an occlusion phenomenon. When multiple lidar points cover the same pixel, we select the point with the smaller depth value as the corresponding depth value of the pixel.
- •
- The depth of the surface of an object in a real scene is usually relatively continuous in a local area. So, when the point cloud cannot cover all the pixels, we fill in the void locations with an average depth of 8 pixels to obtain a more complete depth map.
- •
- The semi-solid lidar used in this paper has a detection blind area when it is less than 3 m.
3.4.3. Generation of Disparity Map
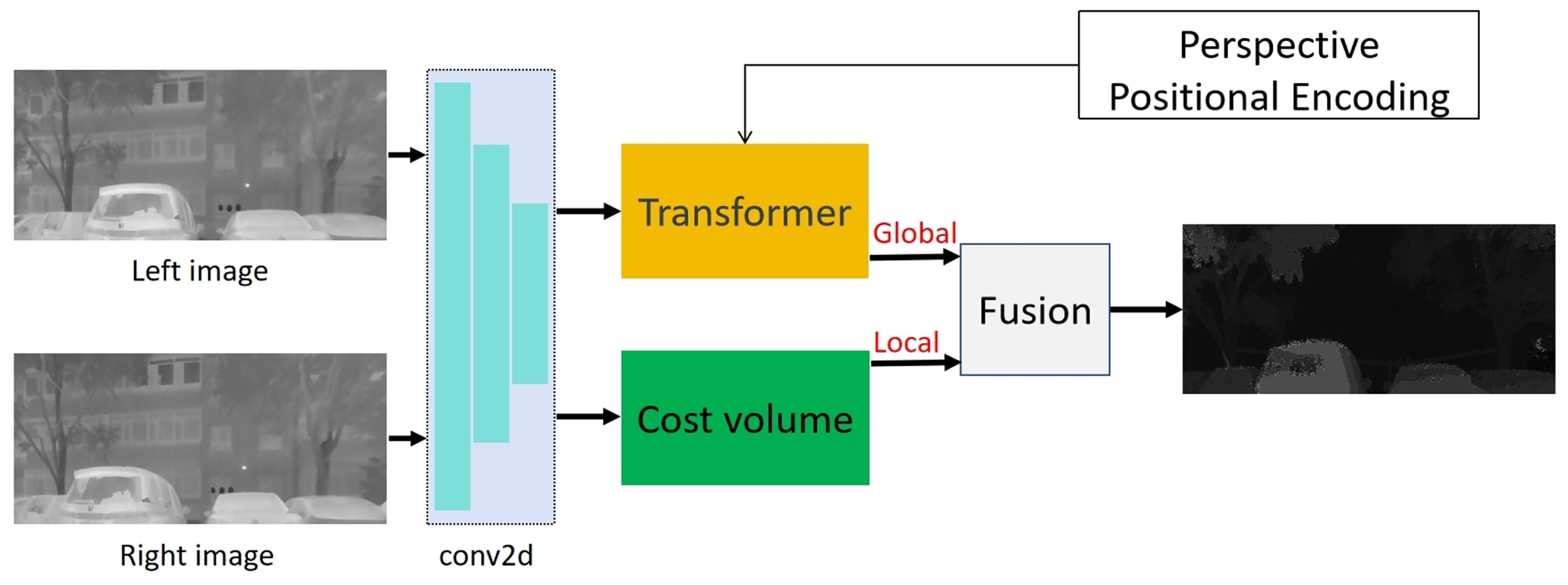
4. Proposed Method
4.1. Stereo Matching Network Combined with Transformer and Cost Volume
4.2. Transformer Network Architecture
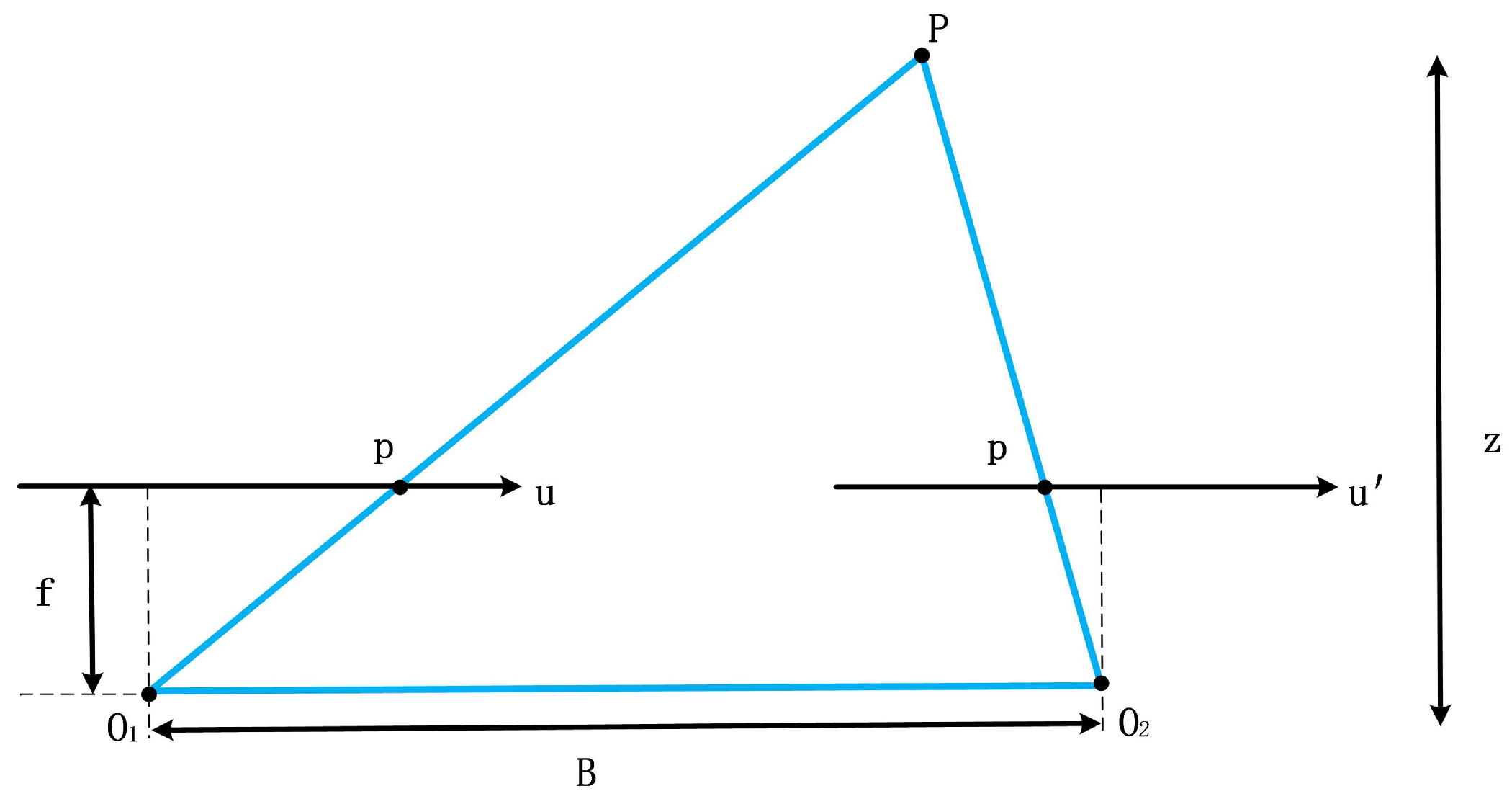
4.3. Perspective Projection for Transformer Positional Encoding
5. Experiments
5.1. Experiments Setup
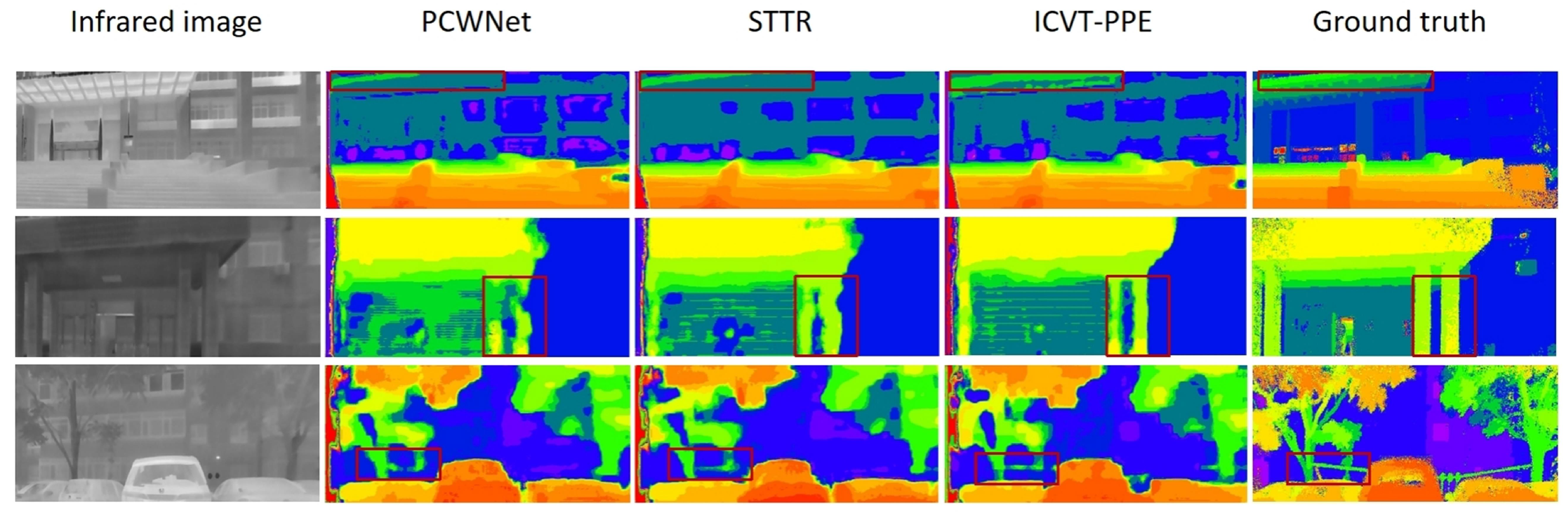
5.2. Comparison with Baselines
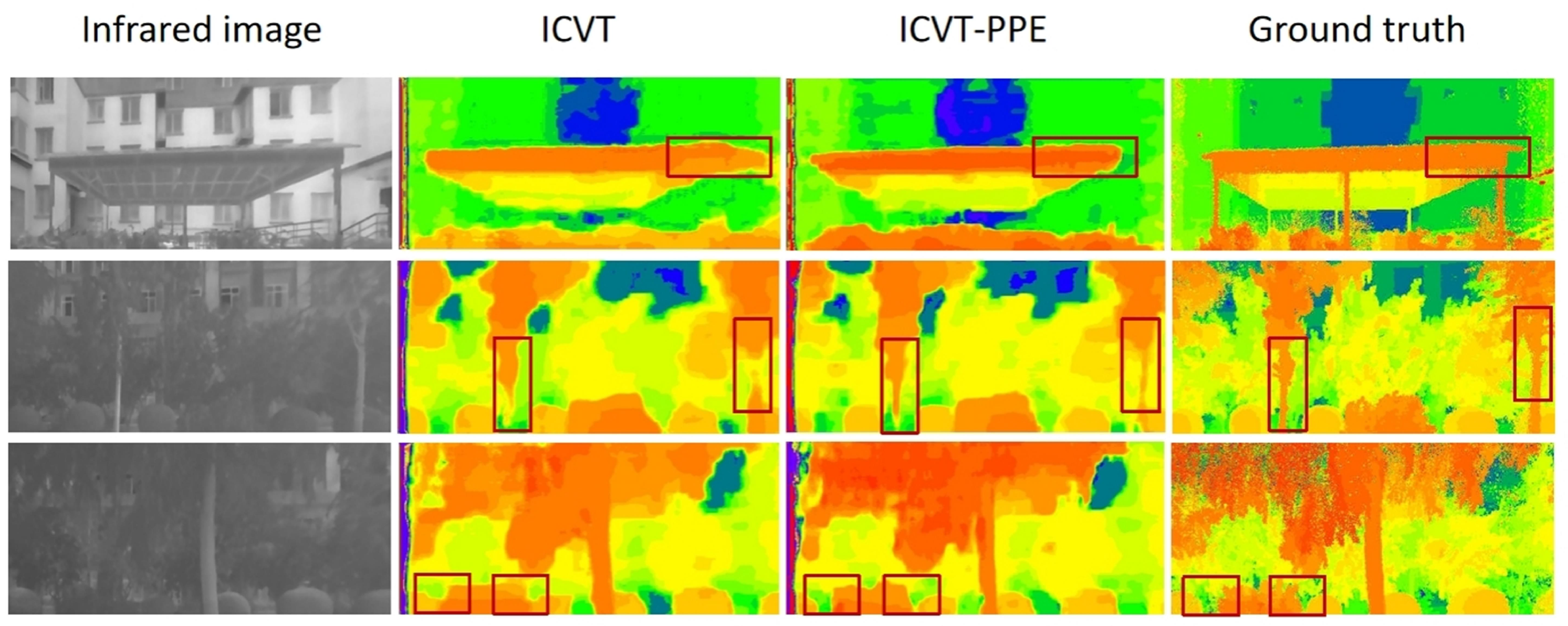
5.3. Ablation Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haris, M.; Watanabe, T.; Fan, L.; Widyanto, M.R.; Nobuhara, H. Superresolution for UAV Images via Adaptive Multiple Sparse Representation and Its Application to 3-D Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4047–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, M.; Fang, Y. Height Estimation From Single Aerial Images Using a Deep Ordinal Regression Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 6000205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, B.; Xiao, W.; Chen, C.; Dong, Z. Automatic 3-D Reconstruction of Indoor Environment With Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3117–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclea, V.-C.; Nedevschi, S. Monocular Depth Estimation With Improved Long-Range Accuracy for UAV Environment Perception. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5602215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, Z.; Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Dong, R.; He, C.; Xia, G.S.; Fu, H.; Lin, D. Weakly Supervised 3-D Building Reconstruction From Monocular Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5615315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Cai, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Peng, Y.; Cheng, L. Phenotypic Parameters Estimation of Plants Using Deep Learning-Based 3-D Reconstruction From Single RGB Image. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 2506705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; You, H.; Xiang, Y. Rethinking the Key Factors for the Generalization of Remote Sensing Stereo Matching Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 4936–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, M.; Shahzad, M.; Khattak, H.A.; Malik, M.I.; Fraz, M.M. Vision-Based 3-D Localization of UAV Using Deep Image Matching. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 12020–12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, G.; Cao, G. Binocular-Vision-Based Structure from Motion for 3-D Reconstruction of Plants. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8019505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Drenkow, N.; Ding, A.; Creighton, F.X.; Taylor, R.H.; Unberath, M. Revisiting Stereo Depth Estimation From a Sequence-to-Sequence Perspective with Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6177–6186. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. TransMVSNet: Global Context-aware Multi-view Stereo Network with Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8575–8584. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Taylor, R.H.; Unberath, M.; Yuille, A.; Li, Y. Context-Enhanced Stereo Transformer. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 263–279. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Bannehr, L.; Ulrich, C.; Maas, H. Evaluating Thermal Attribute Mapping Strategies for Oblique Airborne Photogrammetric System AOS-Tx8. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.; Golparvar-Fard, M. An automated vision-based method for rapid 3D energy performance modeling of existing buildings using thermal and digital imagery. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2013, 27, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidas, S.; Moghadam, P. HeatWave: A handheld 3D thermography system for energy auditing. Energy Build. 2013, 66, 445–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidas, S.; Moghadam, P.; Sridharan, S. Real-Time Mobile 3D Temperature Mapping. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Su, T.; Lin, H. Fusion of Infrared Thermal Image and Visible Image for 3D Thermal Model Reconstruction Using Smartphone Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegner, L.; Stilla, U. Thermal leakage detection on building facades using infrared textures generated by mobile mapping. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegner, L.; Stilla, U. Mobile thermal mapping for matching of infrared images with 3D building models and 3D point clouds. Quant. Infrared. Thermogr. J. 2018, 15, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Ham, Y.; Golpavar-Fard, M. 3D as-is building energy modeling and diagnostics: A review of the state-of-the-art. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, G.; Cao, G. Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Menze, M.; Geiger, A. Object scene flow for autonomous vehicles. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3061–3070. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Flexible camera calibration by viewing a plane from unknown orientations. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; pp. 666–673. [Google Scholar]
- Lepetit, V.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Fua, P. EPnP: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the PnP Problem. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2009, 81, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesch, J.A.; Roumeliotis, S.I. A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) method for PnP. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2011), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2021; pp. 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kneip, L.; Li, H.; Seo, Y. UPnP: An Optimal O(n) Solution to the Absolute Pose Problem with Universal Applicability. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Guan, H.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Spratling, M.; Wang, Y.F. Registration Based Few-Shot Anomaly Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2022), Cham, Switzerland, 6 November 2022; pp. 303–319. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, L.; Lin, C.; Liao, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Depth-Aware Multi-Grid Deep Homography Estimation With Contextual Correlation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2022, 32, 4460–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, H.; He, K.; Sui, C.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.H. Learning Accurate 3D Shape Based on Stereo Polarimetric Imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17287–17296. [Google Scholar]
- Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R.; Zabih, R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Stereo and Multi-Baseline Vision (SMBV 2001), Kauai, HI, USA, 9–10 December 2001; pp. 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R. High-accuracy stereo depth maps using structured light. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; pp. 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Scharstein, D.; Pal, C. Learning Conditional Random Fields for Stereo. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschmuller, H.; Scharstein, D. Evaluation of Cost Functions for Stereo Matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Scharstein, D.; Hirschmüller, H.; Kitajima, Y.; Krathwohl, G.; Nešić, N.; Wang, X.; Westling, P. High-Resolution Stereo Datasets with Subpixel-Accurate Ground Truth. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition: 36th German Conference, GCPR 2014, Münster, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, M.; Mcleod, J.; Wang, C.; Rosenthal, J.C.; Hu, Z.; Gard, N.; Eisert, P.; Fu, K.X.; Zeffiro, T.; Xia, W.; et al. Stereo Correspondence And Reconstruction of Endoscopic Data. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.01133. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Fan, N.; Yeung, D.Y.; Chen, Q. Stereo Waterdrop Removal with Row-wise Dilated Attention. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 3829–3836. [Google Scholar]
- Knapitsch, A.; Park, J.; Zhou, Q.; Koltun, V. Tanks and temples: Benchmarking large-scale scene reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, N.; Ilg, E.; Hausser, P.; Fischer, P.; Cremers, D.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T. A Large Dataset to Train Convolutional Networks for Disparity, Optical Flow, and Scene Flow Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4040–4048. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Martirosyan, H.; Dasgupta, S.; Henry, P.; Kennedy, R.; Bachrach, A.; Bry, A. End-to-End Learning of Geometry and Context for Deep Stereo Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.R.; Chen, Y.S. Pyramid Stereo Matching Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5410–5418. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Yang, K.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Group-Wise Correlation Stereo Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3268–3277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Prisacariu, V.; Yang, R.; Torr, P.H.S. GA-Net: Guided Aggregation Net for End-To-End Stereo Matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J. AANet: Adaptive Aggregation Network for Efficient Stereo Matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1956–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Dai, Y.; Song, X.; Rao, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L. PCW-Net: Pyramid Combination and Warping Cost Volume for Stereo Matching. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 280–297. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Cai, J.; Rezatofighi, H.; Yu, F.; Tao, D.; Geiger, A. Unifying Flow, Stereo and Depth Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13941–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, F. FAST-LIO: A Fast, Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Package by Tightly-Coupled Iterated Kalman Filter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, F.; Ma, J.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, Y.; An, T.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S. InfraredStereo3D: Breaking Night Vision Limits with Perspective Projection Positional Encoding and Groundbreaking Infrared Dataset. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122035
Niu Y, Liu L, Huang F, Ma J, Zheng C, Jiang Y, An T, Zhao Z, Chen S. InfraredStereo3D: Breaking Night Vision Limits with Perspective Projection Positional Encoding and Groundbreaking Infrared Dataset. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(12):2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122035
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Yuandong, Limin Liu, Fuyu Huang, Juntao Ma, Chaowen Zheng, Yunfeng Jiang, Ting An, Zhongchen Zhao, and Shuangyou Chen. 2025. "InfraredStereo3D: Breaking Night Vision Limits with Perspective Projection Positional Encoding and Groundbreaking Infrared Dataset" Remote Sensing 17, no. 12: 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122035
APA StyleNiu, Y., Liu, L., Huang, F., Ma, J., Zheng, C., Jiang, Y., An, T., Zhao, Z., & Chen, S. (2025). InfraredStereo3D: Breaking Night Vision Limits with Perspective Projection Positional Encoding and Groundbreaking Infrared Dataset. Remote Sensing, 17(12), 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17122035





