Mainlobe Jamming Suppression via Joint Polarization-Range-Doppler Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research on Polarization-Based Anti-Jamming
1.2. Innovative Points of This Paper
- We propose a polarized eigen-element surrogate method (PEES) to estimate jamming polarization. The method enhances the distinguishability between jamming and target signatures through joint time-polarization domain processing. Unlike methods in References [11,19], the proposed method maintains robust estimation accuracy under low jamming-to-signal ratio (JSR) conditions while demonstrating superior computational efficiency compared to References [15,19].
- For the challenging task of target polarization extraction from mixed echoes containing a target, jamming, and noise, this paper proposes a combined feature projection method (CFP) based on phase compensation and coherent accumulation. Compared with the feature projection approach (FP), the proposed method maintains superior performance even in strong jamming environments.
- We design a target polarization projection filter (TPPF) that optimizes the output SINR through noise-constrained processing. Furthermore, we introduce the concept of the signal loss ratio (SLR) metric, and the filter’s performance is comprehensively assessed in terms of both jamming suppression capability and target signal loss.
- Leveraging the aforementioned steps, a method for suppressing mainlobe jamming through joint polarization-range-Doppler processing is constructed, and its effectiveness is verified through six sets of simulation cases.
1.3. Notation
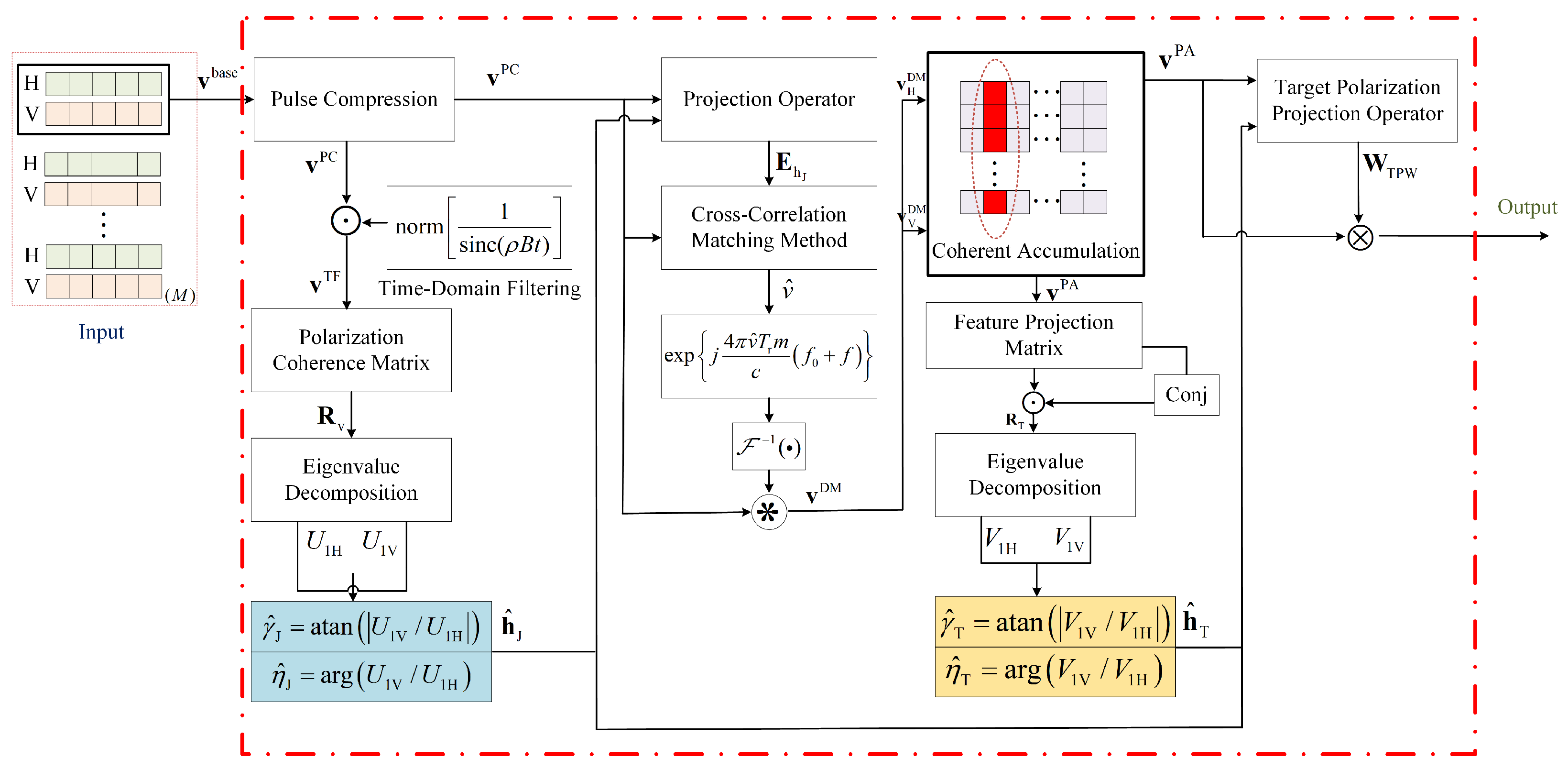
2. Polarization State Estimation of Jamming
2.1. Signal Polarization Reception Model
2.2. Polarized Eigen-Element Surrogate
3. Polarization Feature Extraction of Target
- (1)
- Estimating the target’s polarization parameters in the underdetermined case (limited by dual-polarization antenna DOF, typically only one desired signal can be estimated).
- (2)
- Accurate extraction of polarization characteristics from target signals in suppression jamming environments.
3.1. Feature Projection
3.2. Coherent Integration Under Jamming
- (1)
- Radial Velocity Estimation
- (2)
- Phase Compensation
- (3)
- Coherent Integration
4. Polarization Suppression of Mainlobe Jamming
4.1. Target Polarization Projection Filtering
4.2. Filter Performance Analysis
- (1)
- Suppression Capability of Jamming
- (2)
- Signal Loss of Target
5. Simulation
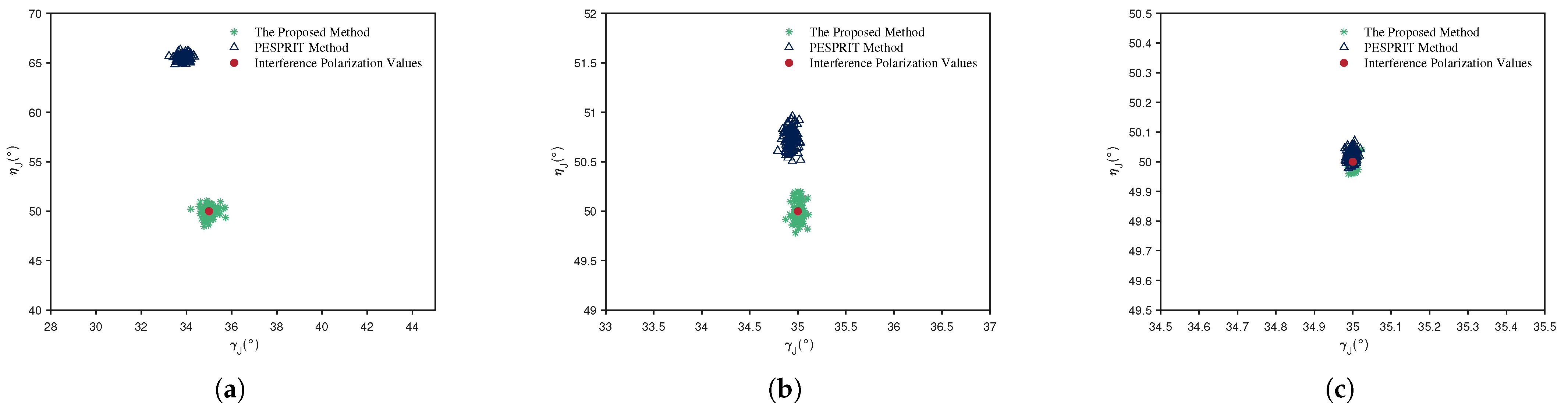
5.1. Polarization Estimation Analysis of Jamming
- (1)
- Effectiveness
- (2)
- Robustness
- (3)
- Complexity
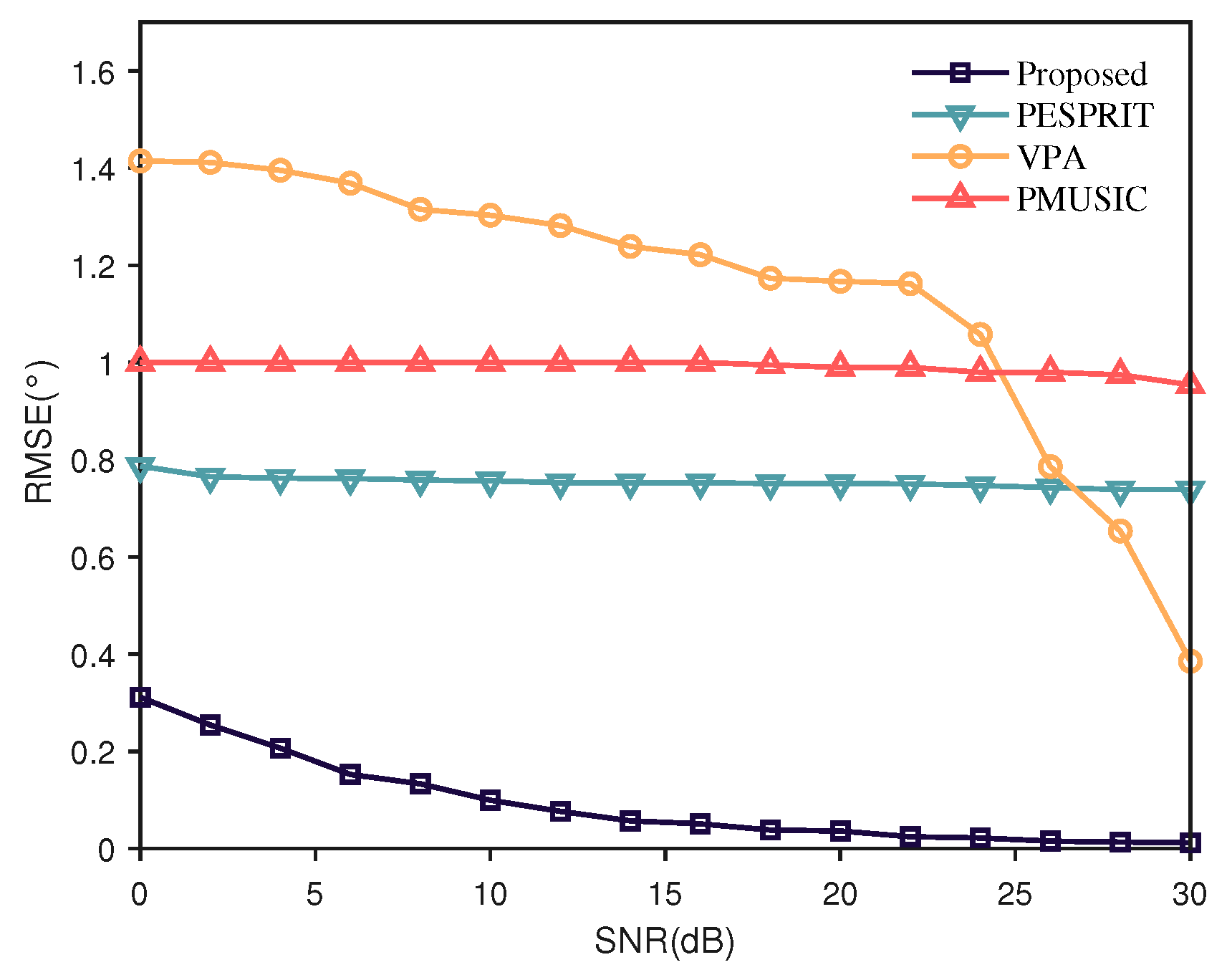
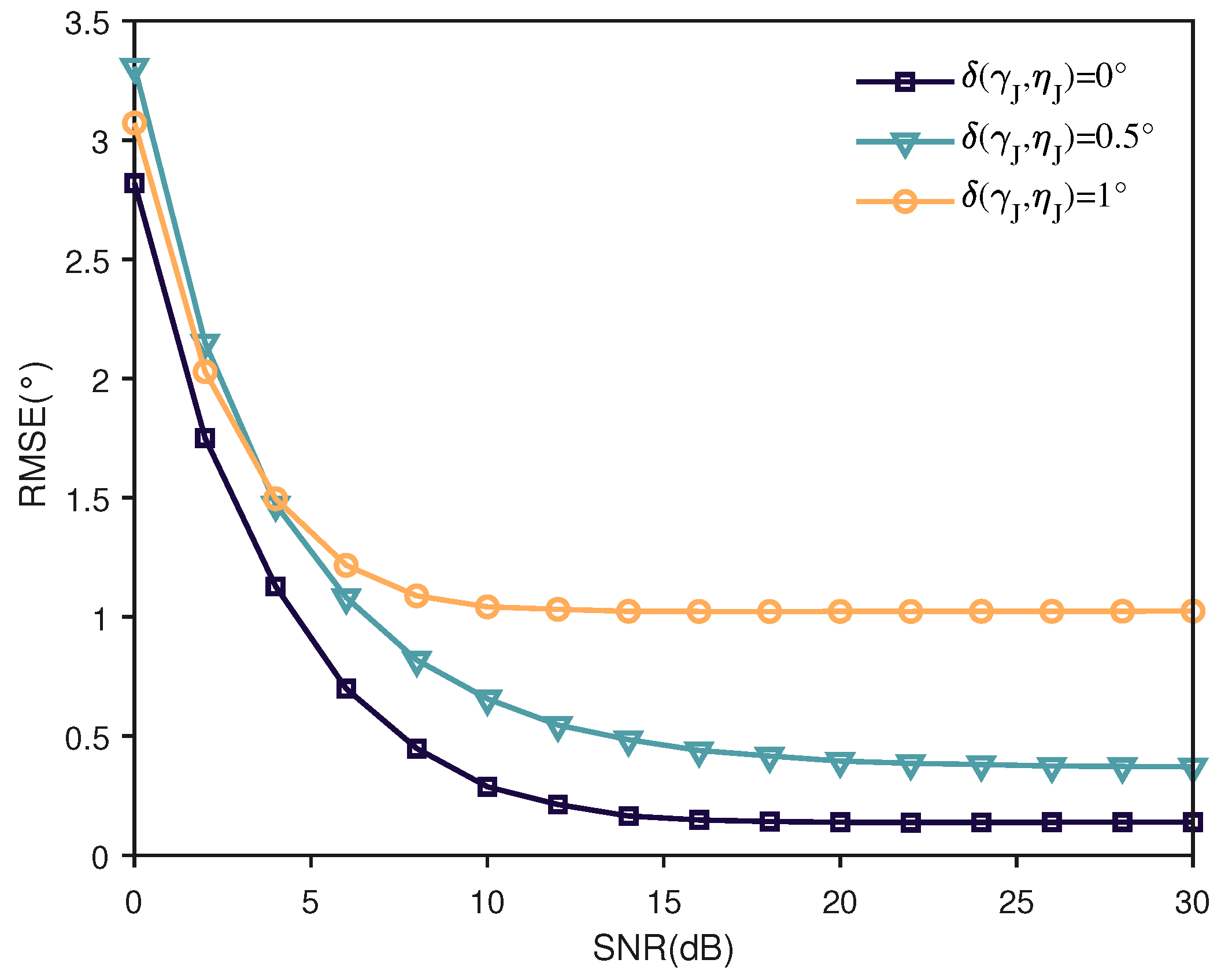
5.2. Polarization Estimation Analysis of Target
- (1)
- Robustness
- (2)
- Applicability
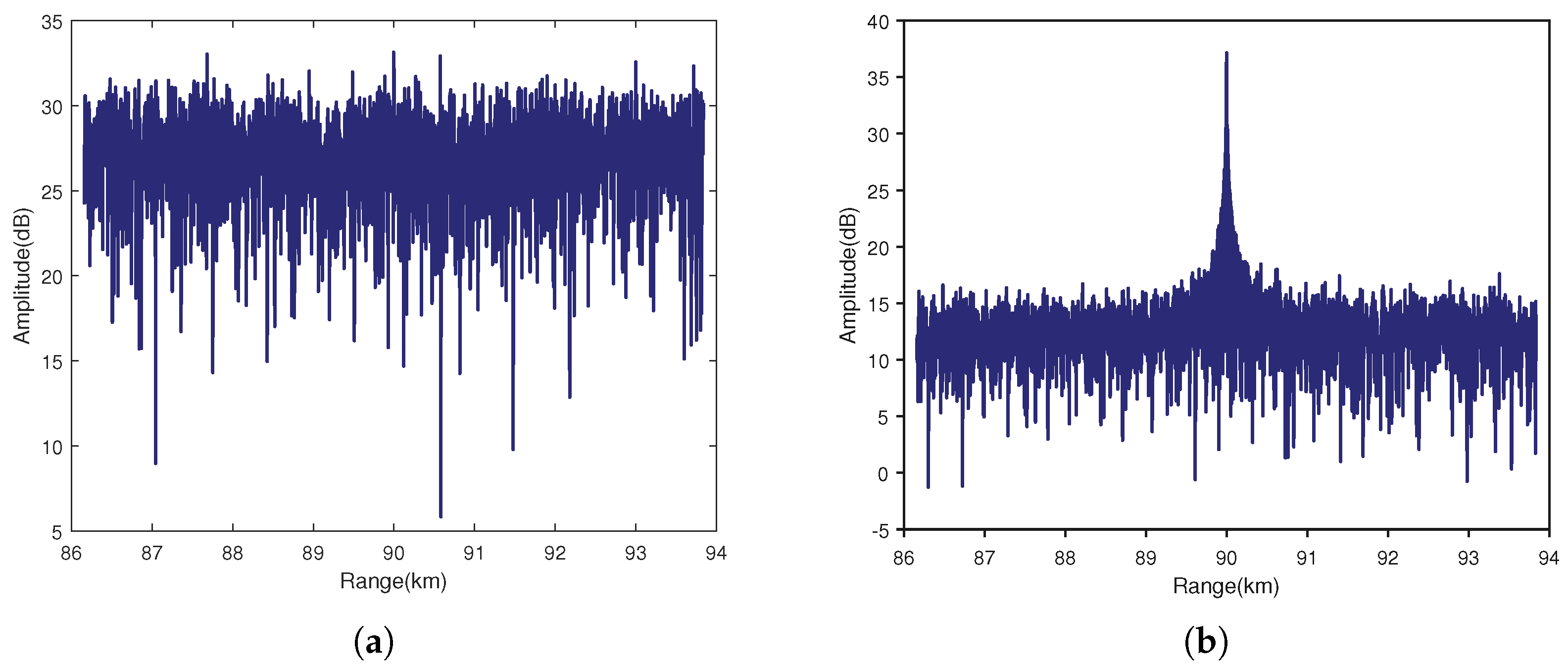
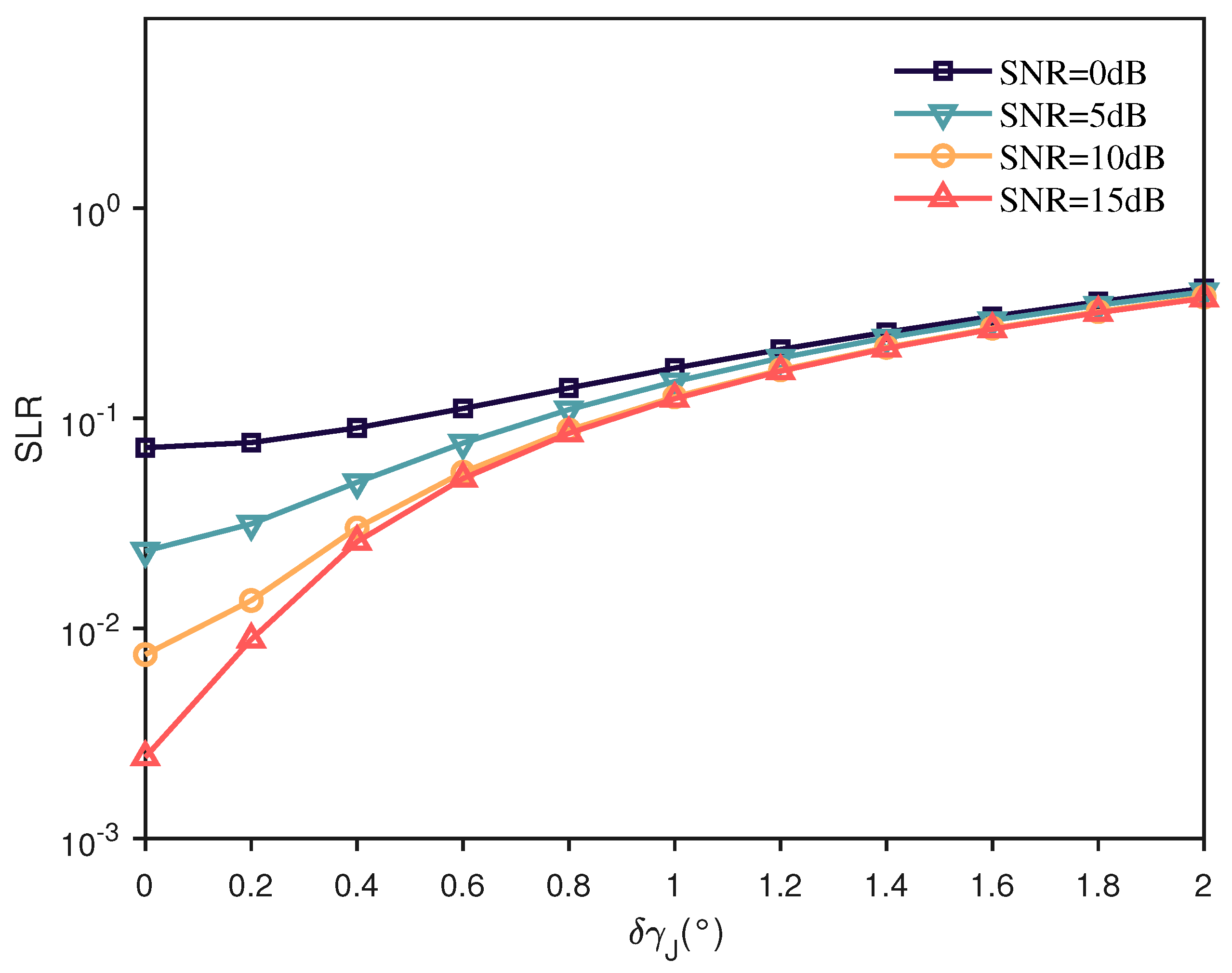
5.3. Polarization Suppression of Jamming
- (1)
- Jamming Suppression Capability
- (2)
- Target Signal Loss
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.D.; Lu, J.H.; Xu, J.W.; Li, S.Y. Mainlobe Deceptive Interference Suppression with Planar Frequency Diverse Array MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Lan, Z.Y.; Lu, X.F.; Gao, Y.C.; Mao, L.L. Joint Transmit–Receive Filter Design with Lower APSL and ICPL to Suppress Interference. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 3673–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Wang, W.Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.S. Effects of Spatial Position on Mainlobe Interference Suppression Performance of FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 9437–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, L.H.; Wang, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q. Mainlobe Interference Suppression for Radar Network via RPCA-Based Covariance Matrix Reconstruction. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 5094–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Zheng, Z.M.; Zhang, K.X.; Chang, S.Q.; Liu, Q.H. Adaptive Main-Lobe Jamming Suppression Based on Cascaded LMS Filter with Low Cost Distributed Radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 26292–26301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.W.; Shu, G.F.; Li, N. Radar Jamming Recognition: Models, Methods, and Prospects. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 3315–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, G. The transmission and reception of elliptically Polarized Waves. Proc. IRE 1950, 38, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennaugh, E.M. Polarization Properties of Radar Reflections. Ph.D. Thesis, Ohio State University, Columbus, UK, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Huynen, J.R. Phenomenological Theory of Radar Targets. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Boerner, W.M. Direct and Inverse Methods in Radar Polarimetry; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Compton, R.T. Angle and polarization estimation using ESPRIT with a polarization sensitive array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1991, 9, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G. Direction and polarization estimation using arrays with small loops and short dipoles. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1993, 41, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Compton, R.T. Two dimensional angle and polarization estimation using the ESPRIT algorithm. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1992, 5, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Compton, R.T. Angle and polarization estimation in a coherent signal environment. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1993, 3, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.; Zoltowski, M.D. Self-initiating MUSIC-based direction finding and polarization estimation in spatio-polarizational beamspace. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2000, 8, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.T.; Li, L.S.; Zoltowski, M.D. Root-MUSIC-based direction-finding and polarization estimation using diversely polarized possibly collocated antennas. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2004, 1, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, M.; Nehorai, A. Polarimetric detection of targets in heavy inhomogeneous clutter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.C.; Si, W.J.; Liu, R.Z. Oblique Projection DOA Estimation Algorithm Based on Spatial Polarization Characteristics. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 10809–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.M.; Yang, J. Polarization Estimation with a Single Vector Sensor for Radar Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, X. Underdetermined estimation of multiple parameters for partially polarized signals with dual-polarized coprime array. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2923–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Jiang, G.J. Efficient DOA and Polarization Estimation for Dual-Polarization Synthetic Nested Arrays. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 6277–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Shan, M.R.; Jiang, G.J. 2D DOA and Polarization Estimation Using Parallel Synthetic Coprime Array of Non-Collocated EMVSs. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Shan, M.R.; Jiang, G.J. 2D DOA and polarization estimation via synthetic nested dual-polarized array with scalable aperture in the presence of unknown nonuniform noise. Digit. Signal Process. 2025, 158, 104932. [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson, F.E. Adaptive circular polarization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 21–23 April 1975; pp. 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.P.; Liu, Y.T. Null phase-shift polarization filtering for high-frequency radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.P.; Liu, A.J.; Hou, H.J. Oblique projection polarization filtering for interference suppression in high-frequency surface wave radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2012, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.J.; Mao, X.P.; Deng, W.B. Oblique projection polarization filtering and its performance in high frequency surface wave radar. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Chengdu, China, 8–11 May 2010; pp. 1618–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, D.; Xu, L. Joint polarization and frequency diversity for deceptive jamming suppression in MIMO radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2012, 13, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Shi, L.F.; Xiao, S.P.; Wang, X.S. Mitigation of cross-eye jamming using a dual-polarization array. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2018, 29, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.Y.; Wang, X.S.; Li, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.P. Main-Lobe Jamming Suppression Method of using Spatial Polarization Characteristics of Antennas. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.M.; Zhang, T.; He, H.F.; Zhang, P.R.; Yang, J. Polarization Anti-Jamming Interference Analysis with Pulse Accumulation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 4772–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelman, A.J.; Guy, J.R.F. Multinotch logic product polarization suppression filters: A typical design example and its performance in a rain clutter environment. IEE Proc. F Commun. Radar Signal Process. 1984, 131, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luo, X.X.; Dong, J. Anti-Jamming Algorithm of Polarization-Sensitive Array Based on Improved Constraint Matrix and Orthogonal Subspace Projection. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 30835–30846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Xiao, S.P.; Tao, H.M.; Zhuang, Z.W. Nonlinear optimization method of radar target polarization enhancement. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2000, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.J.; Mao, X.P.; Li, S.B. A generalized oblique projection operator for interference suppression under colored noise. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–11 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Veen, B.V.; Buckley, K.M. Beamforming: A versatile approach to spatial filtering. IEEE Acoust. Speech Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 5, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Method | Computational Complexity | Average Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Proposed | 3.8 | |
| PESPRIT | 4.2 | |
| PMUSIC | 41.1 | |
| VPA | 665.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Xiao, B.; Zhou, T. Mainlobe Jamming Suppression via Joint Polarization-Range-Doppler Processing. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17121995
Wang L, He H, Li Z, Xiao B, Zhou T. Mainlobe Jamming Suppression via Joint Polarization-Range-Doppler Processing. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(12):1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17121995
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liyuan, Huafeng He, Zhen Li, Buma Xiao, and Tao Zhou. 2025. "Mainlobe Jamming Suppression via Joint Polarization-Range-Doppler Processing" Remote Sensing 17, no. 12: 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17121995
APA StyleWang, L., He, H., Li, Z., Xiao, B., & Zhou, T. (2025). Mainlobe Jamming Suppression via Joint Polarization-Range-Doppler Processing. Remote Sensing, 17(12), 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17121995






