Abstract
The internal response mechanism of vegetation change in fragile high-altitude ecosystems is pivotal for ecological stability. This study focuses on the Lhasa River Basin (LRB) on the Tibetan Plateau (TP), a typical high-altitude fragile ecosystem where vegetation dynamics are highly sensitive to climate change and human activities. Utilizing MODIS surface reflectance data (MOD09Q1), a general regression neural network (GRNN) was applied to create a 250 m resolution fractional vegetation cover (FVC) dataset from 2001 to 2022, whose accuracy was verified with field survey data. Through methods like the Theil–Sen Median trend analysis, Mann–Kendall significance test, Hurst exponent, and geographical detector, the collaborative mechanism of 14 driving factors was systematically explored. Key conclusions are as follows: (1) The FVC in the LRB evolved in stages, first decreasing and then increasing, with 46.71% of the basin area expected to show an improvement trend in the future. (2) Among natural factors, elevation (q = 0.480), annual mean potential evapotranspiration (q = 0.362), and annual mean temperature (q = 0.361) are the main determinants of FVC spatiotemporal variation. (3) In terms of human activities, land use type has the highest explanatory power (q = 0.365) for FVC. (4) The interaction of two factors on FVC is stronger than that of a single factor, with the elevation–land use interaction being the most significant (q = 0.558). These results deepen our understanding of the interactions among vegetation, climate, and humans in fragile high-altitude ecosystems and provide a scientific basis for formulating zoned restoration strategies on the TP.
1. Introduction
Vegetation, as a core component of terrestrial ecosystems, maintains the multi-interface coupling processes among the atmosphere, hydrosphere, pedosphere, and biosphere by regulating carbon–water cycles and energy balance [1,2]. It not only fulfills critical functions in sustaining ecological stability and driving material cycling and energy transfer but also serves as a core indicator of ecosystem structure and function [3,4]. Under the backdrop of global change, the response mechanisms of vegetation dynamics in ecologically fragile regions to climatic fluctuations and human activities have emerged as a key research focus—these regions face high risks of ecosystem degradation due to their climatic sensitivity and weak resistance to disturbances [5,6,7,8]. Systematically decoding the evolution patterns of vegetation dynamics and their driving mechanisms in fragile ecosystems, particularly clarifying their nonlinear response relationships to climatic variations and human activities [5,9], has become a fundamental scientific basis for predicting ecosystem evolution trends and formulating adaptive management strategies [10,11].
In the research progress exploring vegetation dynamics and influencing factors in ecologically fragile regions, the rapid advancement of remote sensing technology has provided strong support for acquiring large-scale, long-term, and high-resolution vegetation information [12,13,14]. Among these, FVC, a key parameter characterizing the spatial heterogeneity of surface vegetation, has been widely applied in assessing vegetation growth conditions and analyzing ecosystem functions [12,15]. Traditional FVC inversion has mostly relied on Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) empirical models, yet their regional applicability and physical interpretability remain limited [16,17,18]. In recent years, machine learning methods represented by the GRNN have overcome the aforementioned limitations thanks to their nonlinear fitting ability and computational efficiency, making it possible to generate large-scale, high-precision, and spatio-temporally continuous FVC datasets [18,19,20,21,22,23]. For example, Jia et al. (2015) used a GRNN to fuse MODIS and Landsat data, producing a global FVC product with a validation accuracy significantly superior to traditional empirical models [18]. Xiao et al. (2016) derived FVC from GLASS (Global Land Surface Satellite) leaf area index products using GRNN assimilation, achieving a root mean square error (RMSE) with in situ measurements that were over 30% lower than the GEOV1 product [20]. Regarding the analysis of driving mechanisms, correlation analysis, multiple regression, and residual analysis are suitable when linear relationships exist between factors and drivers [24]. The Geodetector model, by quantifying the nonlinear effects of multi-factor interactions, offers a methodological innovation for revealing the coupling mechanisms of complex terrestrial systems [6,25,26].
As the world’s highest and largest plateau ecosystem, the TP’s alpine vegetation serves not only as a key carrier for regional hydrological regulation and carbon storage but also as a typical climate-sensitive fragile ecosystem [9,27]. Factors such as permafrost degradation, altered precipitation patterns, and intensified human activities are exerting complex impacts on vegetation growth by modifying soil moisture and nutrient cycles in this region [28,29]. Previous studies have demonstrated that climatic factors dominate the spatiotemporal differentiation of vegetation by regulating water and heat conditions [2,3,28]. For example, Shi et al. (2023) found that vegetation in northern TP exhibited a greening trend between 2000 and 2020, primarily attributed to rising temperatures and increased precipitation [27]. Temperature increases have prolonged the vegetation growing season to some extent, providing more adequate thermal conditions for plant growth [30]. However, in high-altitude areas of the TP, excessively high temperatures may trigger issues such as excessive water evaporation, which can instead inhibit vegetation growth [31]. Increased precipitation generally improves soil moisture, alleviating water limitations for vegetation and promoting growth and development [3], yet extreme precipitation events like floods or droughts can have adverse effects on plant growth [32]. Topographic factors reshape local water and heat regimes through altitude, slope, and aspect, driving the vertical zonation distribution of vegetation [33,34]. However, Wei et al.’s (2022) study on the NDVI in the TP revealed that the intensity of anthropogenic pressures far exceeds the impacts of climate change [29]. Additionally, human disturbances such as road network expansion and intensified urbanization are profoundly altering the distribution and growth of plateau vegetation [35,36,37].
Although previous studies on the influencing factors of vegetation dynamics in the TP have provided important references for understanding vegetation changes in ecologically fragile regions and achieved notable progress, most existing research focuses on the linear effects of single driving factors. There remains a lack of systematic understanding of the interactions between natural and anthropogenic factors and the spatiotemporal heterogeneous response mechanisms [2,3] as well as a significant shortage of high-resolution, long-term studies at the watershed scale [12,38]. These limitations collectively hinder the formulation of refined ecosystem management strategies for ecologically fragile areas at the watershed scale in the TP. The LRB, serving as a core area for population and economic activities on the TP, faces dual pressures of escalating land desertification and decline in ecosystem services in its middle and lower reaches [39]. Therefore, this study aims to utilize MODIS surface reflectance data and a GRNN to invert and generate a 250 m resolution FVC dataset for the LRB from 2001 to 2022; analyze the spatiotemporal dynamic characteristics of FVC; and employ the Geodetector model to quantify the independent and interactive effects of natural and anthropogenic factors, thereby elucidating the spatial heterogeneous patterns of multi-scale driving mechanisms. These efforts aim to provide a scientific basis for ecosystem protection, restoration, and sustainable development in the LRB and, more broadly, in ecologically fragile regions of the TP.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area Overview
The study area, a typical high-altitude ecologically fragile region within the TP, is located in the LRB of Tibet (Figure 1), spanning coordinates 90°05′–93°20′E and 29°20′–31°15′N. The LRB covers 32,425 km2 and exhibits a plateau temperate semi-arid climate influenced by the Southwest Monsoon, characterized by distinct dry and wet seasons. Precipitation is concentrated between May and September, with annual totals ranging from 257 to 699 mm. The region experiences intense solar radiation, a mean annual temperature of 6.3–9.1 °C, a large daily temperature range, an average elevation exceeding 4500 m, and a mean slope gradient of approximately 0.29%. The Lhasa River originates from Luoburula, flows through Mozhugongka and Dazi, and finally converges into the Yarlung Zangbo River in Qushui, Lhasa. Rapid economic growth and population expansion within the basin have posed unprecedented challenges to its ecological stability [40].
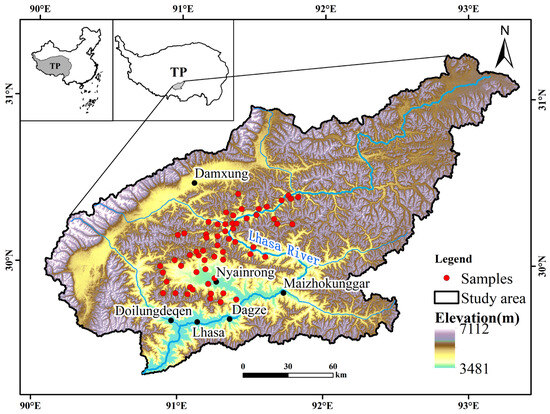
Figure 1.
Location of the LRB.
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. FVC Data
Field survey data: A total of 60 sample plots were surveyed within the study area from July to August 2022 (Figure 1). For each plot, a 250 m × 250 m area was selected, and three 1 m × 1 m subplots were randomly established within it. The FVC of each subplot was obtained via visual estimation, with the average value of the three subplots used to represent the actual FVC of the sample plot [41].
Remote sensing data: The remote sensing data were obtained from the MODIS Surface Reflectance product (MOD09Q1) provided by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA, https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/search/, accessed on 8 July 2024), which has an 8-day temporal resolution and a 250 m spatial resolution, with 46 tiles annually. Data from the vegetation growing season (May–September) of 2001–2022 were selected to generate a 250 m resolution FVC dataset for the LRB using a GRNN. The Maximum Value Composite (MVC) method was applied to derive annual growing season data.
2.2.2. Driving Factors
The primary explanatory variables for the FVC were determined to be ten natural factors (elevation, slope, aspect, annual mean temperature (AMT), annual mean precipitation (AMP), annual mean potential evapotranspiration (AMPE), geomorphological type, vegetation type, soil type, and distance to the rivers) and four anthropogenic factors (distance to the roads, distance to the residences, annual mean nighttime light (AMNL), and land use type) (Table 1). The elevation, slope, and aspect data were derived from 30 m spatial resolution DEM data. The AMT, AMP, and AMPE data came from the National Tibetan Plateau Science Data Center [42,43,44,45,46]. River, road, and residence datasets were sourced from OpenStreetMap, while nighttime light data, at a 1 km resolution, were obtained from the Harvard Dataverse platform [47]. The landform type data, vegetation type data, soil type data, and land use type were all sourced from the Resource and Environment Science Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Distance to the rivers, roads, and residences to each pixel were calculated using the ArcGIS 10.8 Distance Tool.

Table 1.
Driving factors.
This study employed the Jenks natural breaks method to objectively classify the 14 driving factors, with their geographical distributions illustrated in Figure 2. To ensure data consistency, all coordinate systems were projected to WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_48N, and the spatial resolution was resampled to 250 m × 250 m. A total of 8104 2 km × 2 km grid sampling points were generated using the ArcGIS Fishnet Tool, from which attribute tables containing FVC and driving factor values were extracted and constructed.
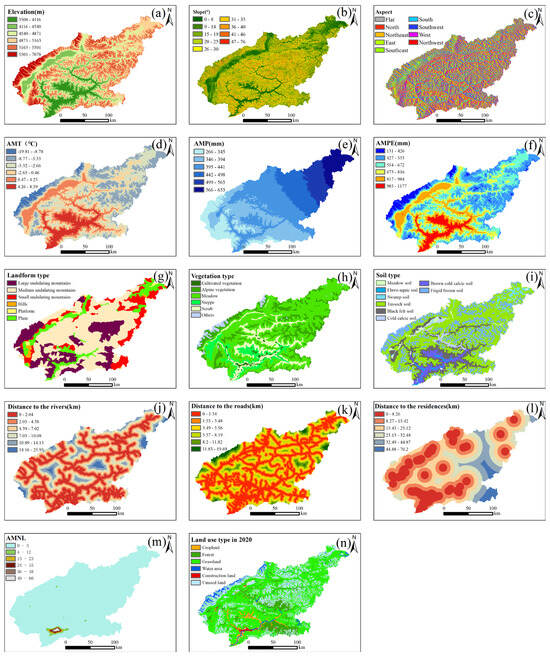
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of influencing factors in the LRB. (a–n) represent Elevation, Slope, Aspect, AMT, AMP, AMPE, Landform type, Vegetation type, Soil type, Distance to rivers, Distance to roads, Distance to residences, AMNL, and Land use type, respectively.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. The Inversion Method of FVC
First, a GRNN was employed for inversion, and FVC was calculated based on vegetation canopy transmittance following the specific workflow described below.
The GRNN can be divided into 4 layers: the input layer, the hidden layer, the summation layer, and the output layer. The input layer distributes the input vector to each unit of the hidden layer. The hidden layer includes all training samples (I = 1, 2, …, n). After determining the input vector, the distance between the input vector and the training samples is computed and substituted into the probability density function. The summation layer is then split into two separate computational units, labeled A and B. The output layer calculates A divided by B to obtain the final prediction result.
The GRNN’s probability density function (kernel function) is calculated via the Gaussian function, with the output expression:
where = (X)T(X), Xi and Yi (i = 1, 2, …, n) are the input and output of i-th sample, respectively; n is number of samples; X is the input vector; (X) is the output when the predicted input is X; and is the corresponding parameter that controls the smoothness of the fitting result. Preprocessing operations such as atmospheric correction, identification of contaminated data, removal of contaminated data, and filling of missing data were carried out on the MODIS surface reflectance data [19]. Then, these data were used as input data, and the trained neural network was employed to invert and generate a long-term time series LAI data product with a resolution of 250 m.
Based on the LAI dataset, the FVC was calculated using the transmittance of the vegetation canopy, where the light passing through the canopy at its top was measured [20]:
where is the solar zenith angle, a is the leaf absorptivity, Ω is the clumping index, LAI is the leaf area index, and is the canopy extinction coefficient, which is calculated by the following formula:
where is the ratio of the average projected area of the horizontal surface of the leaves to that of the vertical surface. According to the definition of FVC, when the vegetation cover is 1, subtract the canopy transmittance when is at 0 degrees, that is:
This method has been directly validated at over 28 sites worldwide [20]. Results indicate that this method outperforms mainstream products (such as GEOV1 and MOD15) in terms of accuracy, spatiotemporal continuity, and physical consistency, thus validating its reliability and applicability [18,19,20,22].
2.3.2. FVC Accuracy Verification
In this study, the confusion matrix and Kappa coefficient were used to validate the accuracy of remotely sensed inverted FVC data. Remotely sensed inverted FVC data close in time to field surveys were selected, and the corresponding remotely sensed inverted FVC values were extracted and compared with the measured values. Both remotely sensed inverted FVC values and measured values were classified into two categories according to a unified classification standard: FVC ≤ 0.5 and FVC > 0.5. A 2 × 2 confusion matrix (Table 2) was constructed, and the Kappa coefficient was calculated to evaluate the consistency of classification results. A paired-samples t-test was conducted using G*Power 3.1.9.7 software [48], with an a priori effect size (Cohen’s d) set at 0.5 and a significance level (α) of 0.05. The power analysis revealed that a minimum of 54 samples were required to achieve a statistical power of 0.95. In this study, 60 samples were used for validation, exceeding the calculated sample size requirement.

Table 2.
The confusion matrix.
Here, a denotes the number of plots where both measured and remotely sensed inverted FVC values are ≤ 0.5; b is the number of plots with measured FVC ≤ 0.5 but remotely sensed inverted FVC > 0.5; c is the number of plots with measured FVC > 0.5 but remotely sensed inverted FVC ≤ 0.5; and d represents the number of plots where both measured and remotely sensed inverted FVC > 0.5 [49].
The Kappa coefficient’s calculation formula is:
where N is the total sample size; xii is the value on the diagonal; and xij and xji are the marginal sums of rows and columns, respectively. The range of the Kappa index is between −1 and 1. Among them, K = 1 indicates a high level of agreement, K = 0 means that the agreement is equivalent to random classification, and K < 0 indicates that the agreement is lower than random classification. Generally, K values exceeding 0.75 suggest strong consistency, those ranging from 0.40 to 0.75 denote moderate consistency, and values at or below 0.40 indicate low consistency.
2.3.3. TSM and M-K Trend Analysis
Theil–Sen median (TSM) trend analysis is a popular technique for analyzing the FVC evolution trend [50]. The Mann–Kendall (M-K) test is used to verify the statistical significance of the trend [51]. Figure 3 shows the process of TSM and M-K trend analysis.
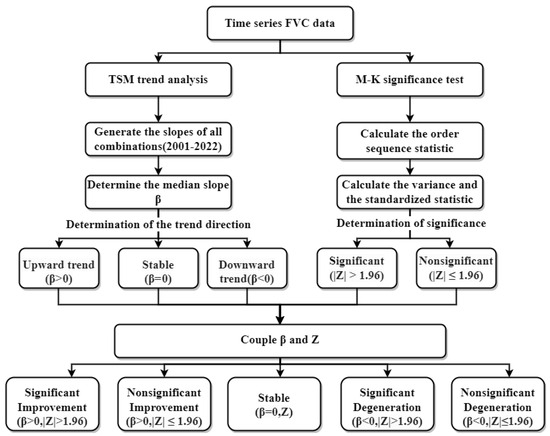
Figure 3.
The process of trend analysis.
2.3.4. Hurst Exponent
The Hurst exponent (H), a crucial parameter in time series analysis [52], can effectively capture the long-term memory effect and the trend persistence characteristics of a data series [53]. In the context of FVC time series, when H lies within the interval (0, 0.5), the FVC time series exhibits anti-persistence. When H equals 0.5, it adheres to the characteristics of Brownian motion. When H is in the range (0.5, 1), the series shows persistence, and notably, the greater the value of H, the stronger the persistence. This is how the computation method is shown:
- (1)
- Create a pixel time series (Vt), where t ranging from 1 to n.
- (2)
- Mean value calculation:
- (3)
- Cumulative fluctuation series:
- (4)
- Range calculation:
- (5)
- Standard deviation calculation:
- (6)
- Hurst exponent calculation:
2.3.5. Geographical Detector
The Geodetector is a set of statistical methods used to detect spatial heterogeneity and dissect its driving factors.
- (1)
- Factor Detection
- (2)
- Interaction Detection
The interaction detector measures the explanatory power of the two driving factors’ interaction on FVC. The intersection of the spatial regions corresponding to the two factors is taken. By comparing the q-values of the two factors’ individual effects on the FVC with the q-value of their combined effect, the type and effect of the interaction can be determined (Figure 4).
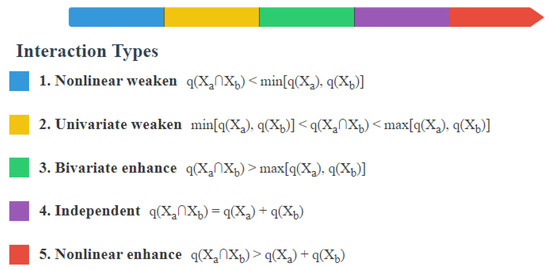
Figure 4.
Types of interaction.
- (3)
- Risk Detection
The risk detection module is used to determine whether there are significant differences in the mean values of FVC between two sub-regions, and a hypothesis verification system of the t-test is constructed for verification [54].
where and represent the mean values of FVC within the two sub-regions, respectively; and are the sample variances; and and are the sample sizes.
3. Results
3.1. Verification of FVC in the LRB
The validation results of the confusion matrix indicate that the Kappa coefficient is 0.78, suggesting a high degree of consistency between the remotely sensed FVC and the measured FVC. According to Figure 5, among the samples with measured FVC ≤ 0.5, nine samples were correctly classified by remote sensing, and there were no misclassified samples. This demonstrates that the remote-sensing classification has a high level of accuracy in identifying cases where FVC ≤ 0.5. Among the samples with measured FVC > 0.5, 47 samples were correctly classified by remote sensing, but 4 samples with measured FVC > 0.5 were misclassified as FVC ≤ 0.5. This indicates that there is some misjudgment in identifying cases where FVC > 0.5, yet the overall number of correct classifications is relatively large.
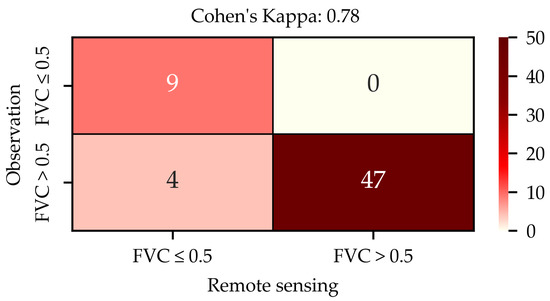
Figure 5.
Confusion matrix of FVC between remote sensing and observation.
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation of FVC in the LRB
Based on the analysis of the FVC time series data in the LRB from 2001 to 2022 (Figure 6), the FVC values during the study period ranged from 0.369 to 0.447, with an average of 0.416, exhibiting pronounced interannual fluctuation characteristics. Specifically, the lowest FVC value (0.369) occurred in 2007, while the peak value (0.447) was observed in 2020. Linear trend analysis revealed a slight upward trend in interannual FVC changes, with a growth rate of 0.5%/10a, though this trend did not pass the significance test (p > 0.05), suggesting that climatic fluctuations or human activities may have obscured the long-term trend signal. To uncover the underlying patterns of change, the original data were further smoothed using a 5-year moving average method. The results indicated that FVC evolution showed a trend of first decreasing and then increasing.
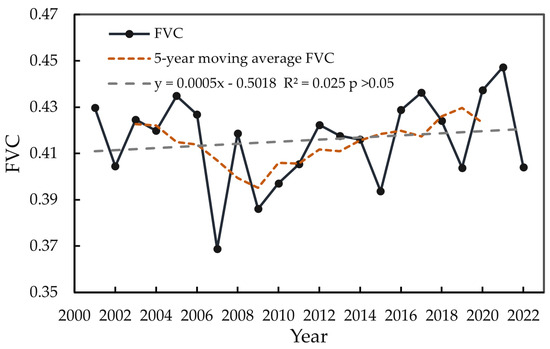
Figure 6.
The trend of the annual mean FVC of LRB, 2001–2022.
The change trends of the FVC in the LRB showed significant differences in space (see Figure 7a). Among them, 15.72% of the area had stable FVC, mostly found in the basin’s northwest high-elevation regions; 4.34% of the area had significant FVC degradation, concentrated around towns with frequent human activities; 8.83% of the area had significant FVC improvement, which was in the valley region of the lower Lhasa River reaches (Figure 7b). In addition, 29.87% of the area had nonsignificant FVC degradation, and 41.24% of the area had nonsignificant FVC improvement. Overall, about 65.79% of the LRB was in a stable or improving state, with a favorable FVC trend.
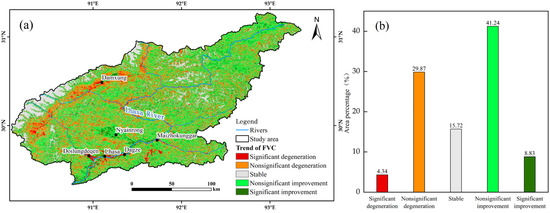
Figure 7.
Change trends of the annual mean FVC in the LRB from 2001 to 2022 (a) and the area ratios of different change levels (b).
3.3. Sustainability of FVC in the LRB
This study utilized the Hurst exponent to determine the sustainability of future vegetation changes in the LRB. Figure 8a shows that Hurst exponents ranged from 0.20 to 0.77, with an average of 0.54, and approximately 70.29% of the region exhibited Hurst exponents greater than 0.5. This indicates that vegetation change trends in the LRB are likely to persist. Areas with Hurst exponents less than 0.5, accounting for 29.71% of the basin, were discretely distributed across the entire LRB. To predict the trend of FVC changes in the study area, the Hurst exponent was coupled with the slope β from the Theil–Sen Median trend analysis (Figure 8b), classifying future changes into six types [55,56,57] (Table 3). Approximately 46.71% of the LRB is projected to exhibit a future improvement trend, concentrated in Linzhou, Maizhokunggar, and the upper reaches of the Lhasa River valley (Figure 8b). Regions with a projected vegetation degradation trend accounted for 37.78%, primarily distributed in the low-altitude areas of the northwestern basin. Additionally, areas with continued stability and random changes accounted for 8.88% and 6.64%, respectively, mainly concentrated in the high-altitude regions of the northwestern basin. Sensitivity analysis revealed that the length of the input data sequence influenced the proportion of areas with vegetation improvement trends (Table 4). Longer data sequences can more comprehensively reflect changes in the research object over extended periods, reducing interference from short-term fluctuations and thus making the results more representative of long-term stable trends.
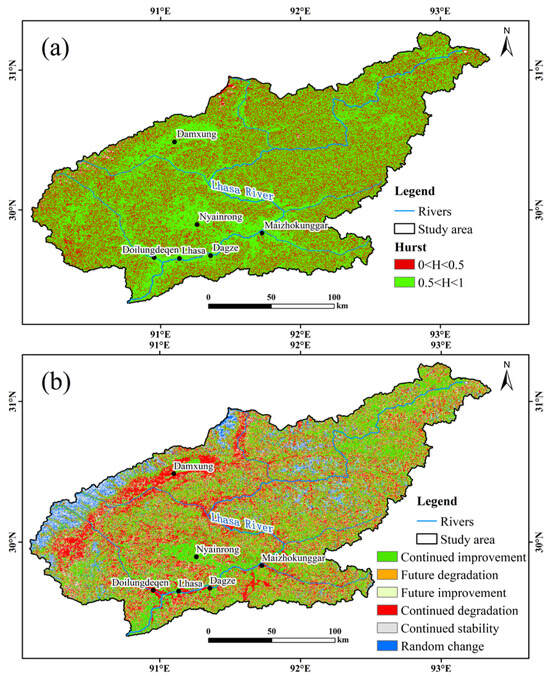
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of the Hurst index (a) and future trends (b) of FVC in the LRB, 2001–2022.

Table 3.
Classification of future sustainability changes of FVC in the LRB.

Table 4.
Hurst exponents and fluctuations in improvement proportion under different data sequence lengths.
3.4. Driving Factors of FVC in the LRB
3.4.1. Factor Detection Analysis
Geodetector analysis was conducted to evaluate the impacts of 14 driving factors on the FVC in the LRB (Figure 9). The results revealed that all factors, except for the AMNL, exhibited extremely significant effects on the FVC in the LRB (p < 0.001). Among them, elevation had the highest q value, with an explanatory power of 0.480, which is the most crucial factor affecting FVC in the LRB. The explanatory powers of land use type, AMPE, and AMT were close, at 0.365, 0.362, and 0.361, respectively. Soil type, vegetation type, distance to roads, and AMP were also key factors for vegetation change in the LRB, with descriptive powers of 0.338, 0.249, 0.115, and 0.087, respectively. Although their effects were minimal, the distance to rivers, landform type, slope, aspect, distance to residences, and AMNL all affected FVC.
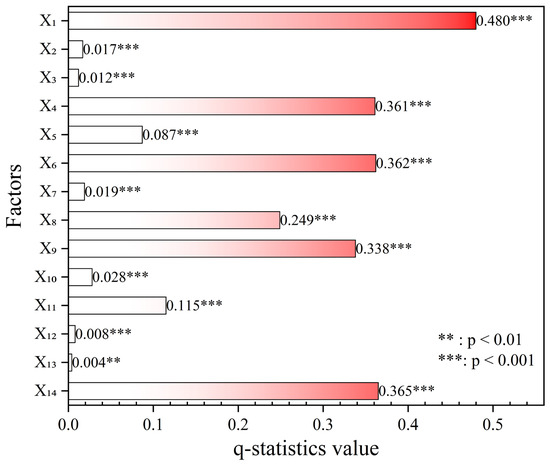
Figure 9.
Factor detection results of FVC change, X1: Elevation; X2: Slope; X3: Aspect; X4: AMT; X₅: AMP; X6: AMPE; X7: Landform type; X8: Vegetation type; X9: Soil type; X10: Distance to rivers; X11: Distance to roads; X12: Distance to residences; X13: AMNL; X14: Land use type.
3.4.2. Interaction Detection Analysis
Interaction detection revealed the types of interactions between two driving factors of FVC. The impact of the two-factor interaction on FVC was significantly greater than that of any single factor (Figure 10). Among the 91 sets of interactions between factors, 37 sets showed two-factor enhancement, and 54 sets exhibited nonlinear increases. Specifically, the interaction between elevation and all other factors had the most significant impact on FVC, with q-values ranging from 0.484 to 0.558. When land use type, AMPE, AMT, and soil type interacted with other factors, the ranges of their q-values were 0.373–0.558, 0.364–0.526, 0.366–0.506, and 0.343–0.520, respectively, indicating the necessity of these four components for vegetation growth (Figure 10). Among them, the interaction between elevation and land use type had the highest interaction effect among all pairwise factor interactions (q = 0.558).
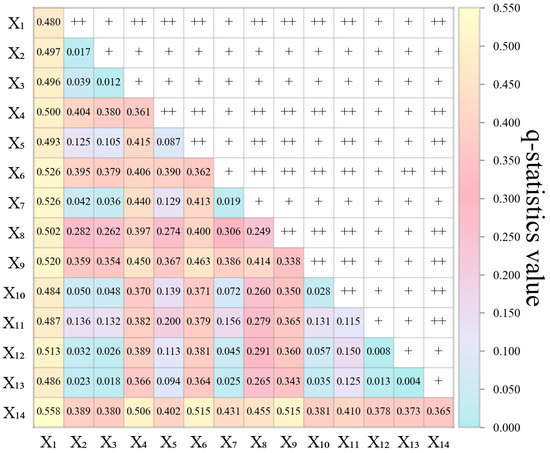
Figure 10.
The q-values of factor interactions in the LRB; ”+” and “++” denote nonlinear enhancement and bivariate enhancement, respectively.
3.4.3. Risk Detection
The risk detector identified the optimal ranges for factors influencing vegetation growth (Figure 11), with significant differences in mean FVC values across factors. The FVC exhibited a significant gradient variation with elevation, first increasing and then decreasing as elevation changed. Within the 4540–4871 m elevation range, the mean FVC reached a peak of 0.60, representing the most ideal elevation for vegetation growth. When the elevation exceeded 4871 m, vegetation growth was inhibited, reflecting the limiting effect of environmental conditions on vegetation growth. Forest land use type had the highest FVC at 0.62, while water bodies showed the lowest FVC at only 0.17. As AMPE increased, mean FVC first rose and then declined, peaking at 0.61 when AMPE ranged from 673 to 816 mm. The response of FVC to AMT also followed a unimodal trend (Figure 11). When AMT was between −2.54 °C and 0.57 °C, FVC reached 0.58, indicating this temperature range is optimal for vegetation growth. Soil types significantly differed in their impacts on LRB’s FVC: vegetation thrived best in meadow soil and frigid calcic soil (Figure 11), with an annual mean FVC as high as 0.59, while frigid frozen soil showed the lowest FVC. Shrub-dominated areas had the highest vegetation coverage (FVC = 0.57) among vegetation types. As the distance to the roads increased, the average FVC value decreased. Within the region of 0–1.54 km from the road, the average FVC value was the highest at 0.51. The vegetation was not significantly affected by fluctuations in precipitation. AMP had a weaker effect on vegetation growth: mean FVC reached 0.48 when AMP was 345.3–393.7 mm, dropping to the lowest 0.26 when AMP fell below 345.3 mm. Mean FVC declined with increasing distance from rivers. Plains exhibited the best vegetation growth (FVC = 0.47), while hilly areas had the lowest (0.35). As slope gradient increased, mean FVC decreased: slopes of 0–7.74° had the highest mean FVC (0.47). North-facing aspects showed the highest mean FVC (0.46), while southeast-facing aspects had the lowest (0.37), indicating shaded slopes are more favorable for vegetation than sunlit slopes. Distance to residences had a minimal impact, with the mean FVC consistently above 0.35. Vegetation grew best in areas with the lowest AMNL. Table 5 lists the factors associated with optimal vegetation growth conditions.
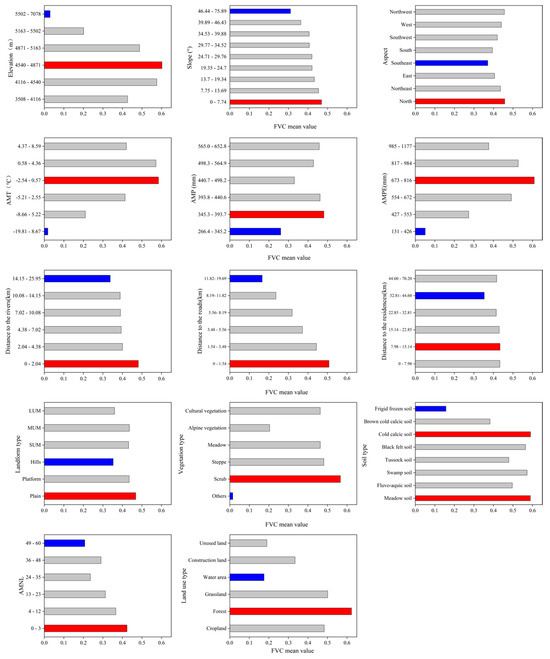
Figure 11.
FVC statistical results of each influencing factor. The red indicates the type or range with the most suitable FVC value, and blue indicates the type or range with the least suitable FVC value. LUM: Large undulating mountains, MUM: Medium undulating mountains, SUM: Small undulating mountains.

Table 5.
Appropriate ranges or types of factors.
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Variation of FVC
As a core indicator of ecosystem structure and function, FVC plays a critical role in maintaining ecological stability, preventing soil erosion, and mitigating climate change by regulating processes such as surface albedo, evapotranspiration, and carbon sink capacity [1,2]. Previous studies have shown that, as a sensitive and vulnerable region to global warming, the TP exhibits a significant increasing trend in its vegetation cover [31,58]. For example, the NDVI across the TP increased at a rate of 0.5%/10a from 1982 to 2020 [31], with a 2.7%/10a increase from 2000 to 2020 [57]. The Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) during the growing season across the TP showed an average increase of 1%/10a from 2000 to 2020 [27], and the Tibet section of the Lancang River Basin experienced a significant 0.4%/10a NDVI increase from 1998–2020 [59]. Similarly, FVC in the Minjiang River Basin of eastern TP trended upward from 2000–2020 [60]. Consistent with these findings, our study revealed a weak positive correlation in overall LRB FVC growth during 2001–2022 (β = 0.5%/10a, p > 0.05), with 50.07% of the basin area showing vegetation improvement higher than the proportion of degraded areas (34.21%) (Figure 7b). It is worth noting that the FVC in the basin increased significantly after 2009, which is highly consistent with the implementation period of the “Tibet Ecological Security Barrier Protection and Construction Plan (2008–2030)” [61], suggesting that the systematic promotion of ecological projects has a positive driving influence on vegetation restoration.
Spatial differentiation characteristics (Figure 7a) revealed the highest FVC stability in the northwestern Nyainqêntanglha Mountains of the basin (elevation > 5500 m) where vegetation communities dominated by alpine meadows and tundra exhibited resilience comparable to the Yangtze River Source region due to low-temperature constraints and minimal human disturbance [62]. A “degradation-improvement” spatial game feature can be seen in the lower reaches of the river valley: the FVC in the built-up areas of Lhasa City and around traffic trunk lines has significantly degraded due to the expansion of construction land, while a series of ecological protection and ecological projects have increased the FVC in the LRB [40]. This spatial heterogeneity confirms the regional characteristics of the coexistence of “stress–restoration” dual mechanisms, indicating that scientifically planned ecological projects can effectively offset the negative impacts of urbanization and provide a practical paradigm for the coordination of human–land relationships in alpine river valleys [63,64,65]. Through the combined analysis of Hurst exponents and TSM trend analysis, this study revealed that approximately 46.71% of the LRB is projected to exhibit a future vegetation improvement trend, while 37.78% is expected to undergo degradation. Although the Hurst exponent is widely used to predict vegetation change trends, it cannot clarify the specific duration of the trend [26,57,66].
4.2. Driving Forces of Vegetation Change
Vegetation dynamics in the TP region are jointly regulated by climate change and human activities [29,57]. Moreover, its spatial heterogeneity mainly originates from natural factors rather than social and economic factors [60,67,68,69]. Findings from this study align with these conclusions: elevation, land use type, AMPE, and AMT collectively dominate variations in FVC in LRB, with the natural factor of elevation exhibiting the highest explanatory power.
4.2.1. Natural Factors
This study reveals that among the 10 natural factors, elevation, AMPE, and AMT are the most influential factors affecting FVC in the LRB, with the q values being 0.480, 0.362, and 0.361, respectively. Elevation determines the vegetation type and its distribution pattern by causing vertical differentiation of hydrothermal conditions [25,70,71]. To further explore the mechanisms by which elevation influences vegetation change in the LRB, this study categorized the elevation of the LRB into three gradients and analyzed the driving factors at each gradient (Figure 12). Changes in LRB vegetation are predominantly affected by the AMPE in the low-elevation area (<4500 m). In this area, the heat conditions are sufficient, and vegetation growth is mainly restricted by the availability of soil moisture [33]. An increase in temperature intensifies evapotranspiration, which may accelerate the depletion of soil moisture, resulting in a water deficit in vegetation and thus inhibiting photosynthesis efficiency and biomass accumulation [71]. The primary determinant of vegetation change in the LRB in the medium-elevation (4500–5500 m) and high-elevation (>5500 m) regions is land use type, underscoring the significance of ecological projects and land management models (converting grazing land back to grassland) [72,73]. Overall, the elevation gradient modifies the action hierarchy of every driving factor by controlling the intensity of human activity and the hydrothermal combination.
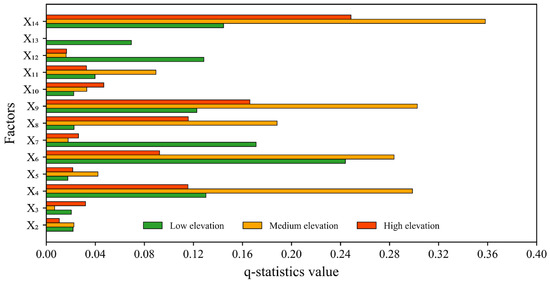
Figure 12.
The q-values of the influence of various factors on vegetation changes under different elevation gradients. Low elevation: Elevation < 4500 m; Medium elevation: 4500 m ≤ Elevation ≤ 5500 m; High elevation: Elevation > 5500 m.
The study also found that among natural factors, AMPE (q = 0.362) and AMT (q = 0.361) exhibited similar explanatory power for vegetation spatial differentiation, closely related to the high sensitivity of plant phenology to temperature changes in high-elevation regions [74]. Under the backdrop of climate warming, vegetation response mechanisms exhibit threshold effects: moderate temperature increases can prolong the vegetation growing season and enhance productivity [25]. However, when temperature rises exceed the physiological tolerance of vegetation, soil water stress induced by increased evapotranspiration may offset the photosynthetic benefits of warming [71]. The influence of soil type is primarily reflected in meadow soil and frigid calcic soil, which exhibited the highest FVC values closely linked to their high organic matter content, cation exchange capacity, and water-holding capacity [75]. The analysis of vegetation types showed that the shrub-covered area has the highest FVC value, mainly distributed at an elevation of 4540–4871 m. This area has the optimal hydrothermal combination conditions [57], and the adaptability of shrubs to the alpine environment has been verified in multiple dimensions [57,76]. Notably, although precipitation is widely regarded as a dominant driver of vegetation change on the TP [57,69], this study showed that its explanatory power for vegetation dynamics was only 0.087. This may be attributed to the hydrological regulation mechanism of deep groundwater recharge to surface ecosystems in the LRB, which mitigates the impact of precipitation on vegetation changes [77]. For example, vegetation in arid regions directly utilizes groundwater through deep roots, with its productivity strongly correlated with groundwater depth rather than precipitation [78,79]. Deep groundwater forms a stable water source by slowly recharging surface ecosystems, thereby mitigating the impact of short-term precipitation fluctuations on vegetation [80]. Vegetation actively acquires groundwater by adjusting root depth, reducing its dependence on precipitation variability [81].
4.2.2. Human Factors
Based on the results of the geographical detector analysis, land use type exhibited the most significant effect among anthropogenic factors on vegetation changes, with a q-value of 0.365, suggesting the ecological effects of human intervention [82]. This study quantitatively analyzed the process of land use transition to deeply explore its driving mechanisms for FVC changes (Figure 13). From 2005 to 2020, the grassland area decreased by 11.20%, while the areas of cultivated land, forest, water area, construction land, and unused land increased by 0.64%, 6.67%, 1.24%, 0.36%, and 2.22%, respectively (Figure 13a). The reduction of grassland area was mainly converted into unused land (9.65%) and forest (8.56%), which led to a decrease of 0.346 and an increase of 0.126 in FVC, respectively (Figure 13b). Grassland degradation and irrational utilization may have contributed to vegetation degradation to some extent [83]. In contrast, ecological measures such as afforestation have significantly promoted vegetation restoration [84]. Urbanization in the LRB has converted cultivated land, forest, and grassland into construction land, resulting in a decrease of 0.397, 0.438, and 0.309, respectively, in the annual average FVC of the LRB (Figure 13b). The direct impacts of urbanization on vegetation are primarily reflected in the reduction of vegetation cover caused by urban expansion [65]. Previous studies have noted that a series of ecological projects were implemented in the LRB to promote vegetation restoration (e.g., afforestation, mine restoration, riparian ecological restoration, and grassland ecological restoration), which offset the negative impacts of urbanization on basin ecology [40,85]. This study also confirmed this (Figure 13b). Furthermore, this study revealed that the FVC value reaches a peak (0.51) within the 0–1.5 km buffer zone from the road, suggesting that moderate human activities may have a positive ecological effect. This phenomenon may be due to the improvement of the micro-habitat brought by the road corridor [86] and the associated effect of the artificial irrigation system.
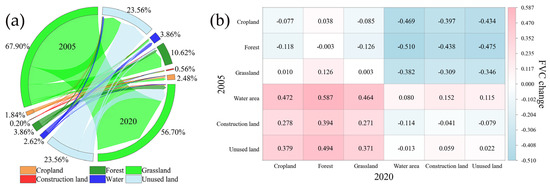
Figure 13.
FVC change (b) as a result of land use type conversion (a). The values in the brackets represent the proportion of specific land use transformations in the basin area.
4.2.3. Impact of Factor Interactions on FVC
The interaction detector results showed that the interactions between the two driving factors in the LRB significantly enhanced the explanatory power for vegetation changes, indicating that interactions among multiple factors impose complex impacts on vegetation dynamics [87,88]. This also confirms the nonlinear influence mechanism of multi-factor synergies on vegetation changes [57,69,87]. The LRB’s vegetation change is most significantly influenced by the interaction between elevation and land use type, with an explanatory power of 0.558, further demonstrating that both natural and human influences affect vegetation change. This conclusion aligns with Mukhtar et al.’s research findings on the Himalayas’ southern slope [34].
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
This study systematically revealed the driving mechanism of vegetation change in alpine regions by integrating the vegetation cover data inverted by the GRNN and the geographical detector method. Compared with traditional linear statistical models, this method has unique advantages in measuring spatial differentiation and analyzing the interactions of explanatory variables [89]. However, this study still has the following limitations: First, during the FVC validation stage, due to transportation constraints and environmental limitations on the TP, validation points were primarily distributed in mid-lower reaches below 4500 m altitude, which may introduce biases in validation accuracy for high-altitude regions. Second, while the Hurst exponent can predict the persistence of vegetation change trends, it cannot determine the specific duration of these trends [26,57,66]. Third, the q-value of the geographical detector is sensitive to data aggregation scales, potentially affecting the absolute values of factor influence while maintaining stable relative rankings [90]. Additionally, the driving factor system does not quantify the impacts of soil moisture, CO2 fertilization, and ecological projects on vegetation, which may weaken the completeness of causal analysis. Furthermore, the insufficient integration of high-resolution urban vegetation mapping data (e.g., Sentinel-2, WorldView-3) may limit the in-depth analysis of interactive mechanisms between small-scale driving factors and FVC [91,92]. Finally, existing driving factor analysis methods still have room for improvement in capturing nonlinear relationships, necessitating the integration of techniques such as machine learning and geographically weighted regression to construct hybrid models [87,93,94], thereby enhancing the comprehensiveness and practical utility of the research.
Future work is recommended to be carried out in the following aspects: Obtain higher-resolution and multi-source integrated surface reflectance data to more accurately invert vegetation cover and improve the ability to capture the details of vegetation change. At the same time, increase the sample plot survey data to improve the accuracy of the verified FVC dataset. Consider driving factors more comprehensively, and introduce advanced models to deeply analyze the interaction mechanism. Expand the research scope to provide universal experience for vegetation protection in ecologically vulnerable areas, and support the construction of the ecological barrier function of the TP.
5. Conclusions
This study employed the GRNN and Geodetector to comprehensively analyze vegetation dynamics in the ecologically fragile high-altitude LRB. The findings offer novel perspectives on the complex interactions between natural and human driving forces in this vulnerable region. The principal conclusions are as follows: (1) The LRB’s FVC first declined and then rose between 2001 and 2022. In the study area, the majority of vegetation changes are sustainable, and 46.71% of the area is expected to exhibit an improving trend in the future. (2) Among natural factors, elevation (q = 0.480), AMPE (q = 0.362), and AMT (q = 0.361) form a dominant driving framework. The three factors shape the vegetation distribution pattern by regulating hydrothermal redistribution and nutrient supply. (3) Among human factors, land use type (0.365) is the most important, confirming that ecological improvement projects have offset the negative impacts of urbanization. (4) The two-factor interaction generally shows a non-linear enhancement feature, and the interaction between elevation and land use type is the strongest (q = 0.558), revealing that vegetation changes are influenced by both natural and human factors.
This research advances understanding of vegetation–climate–human dynamics in data-scarce alpine regions and provides a methodological framework for quantifying synergistic drivers using GRNN and Geodetector. The results highlight the necessity of zonal policies: optimizing water management in low-altitude areas, enhancing land use planning in mid-elevation zones, and prioritizing cryosphere vegetation protection in high-altitude regions. These insights are critical for maintaining ecological security on the TP and inform adaptive governance in fragile high-altitude ecosystems globally.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.D. and L.L.; methodology, Y.D., Z.X. and L.L.; data curation, Y.D., X.Z. and Z.X.; investigation X.Y. and X.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.D.; project administration, Y.Z.; visualization, B.Y. and X.P.; writing—original draft, Y.D.; writing—review and editing, L.L., H.Z. and C.P.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript and analysis.
Funding
This study was funded by Open Foundation of the Key Laboratory of Natural Resource Coupling Process and Effects under Grant No. 2023KFKTB006; Tibet Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan Projects under Grant No. XZ202401JD0024; National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 42471146; the Belt and Road Special Foundation of National Key Laboratory of Water Disaster Prevention under Grant No. 2023nkms01; and the China Geological Survey’s Tibetan Plateau Alpine Resources and Environment Investigation, Monitoring, and Evaluation Project under Grant No. DD20220881.
Data Availability Statement
All data will be made available on request to the corresponding author’s email with appropriate justification.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Park, T. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Hong, S. The interactive feedback mechanisms between terrestrial water storage and vegetation in the Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 1004846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xi, G. Effects of Climate Variability and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics across the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1982 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guan, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Bao, Z. Identifying and Predicting the Responses of Multi-Altitude Vegetation to Climate Change in the Alpine Zone. Forests 2024, 15, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Qiu, T. Response of vegetation dynamics in environmentally sensitive and fragile areas to natural and anthropogenic factors: A case study in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Anthropocene 2023, 44, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, W. Using the Geodetector Method to Characterize the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Vegetation and Its Interaction with Environmental Factors in the Qinba Mountains, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, J.; Fang, H.; Niu, Z. Characterization and attribution of vegetation dynamics in the ecologically fragile South China Karst: Evidence from three decadal Landsat observations. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1043389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ye, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Tan, W. Evolution of vegetation dynamics and its response to climate in ecologically fragile regions from 1982 to 2020: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Catena 2022, 219, 106601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yan, D.; Weng, B.; Lai, Y.; Zhu, L.; Qin, T.; Dong, Z.; Bi, W. Nonlinear effects of surface soil moisture changes on vegetation greenness over the Tibetan plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Yang, Y.; You, H.; Han, X. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Alpine Vegetation Phenology and Its Response to Climatic and Topographic Factors on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, J.; Pei, X.; Bian, L.; Zhang, T.; Yi, G.; Bie, X.; Peng, P. Dominance of Topography on Vegetation Dynamics in the Mt. Qomolangma National Nature Reserve: A UMAP and PLS-SEM Analysis. Forests 2023, 14, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Chen, J.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; You, H.; Han, X. Fitness for Purpose of Several Fractional Vegetation Cover Products on Monitoring Vegetation Cover Dynamic Change—A Case Study of an Alpine Grassland Ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J. Responses of runoff processes to vegetation dynamics during 1981–2010 in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Yuan, W. Widespread increase in sensitivity of vegetation growth to climate variability on the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 358, 110260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Quantifying the Contributions of Vegetation Dynamics and Climate Factors to the Enhancement of Vegetation Productivity in Northern China (2001–2020). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A.J. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Moody, A. A comparison of methods for estimating fractional green vegetation cover within a desert-to-upland transition zone in central New Mexico, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Global Land Surface Fractional Vegetation Cover Estimation Using General Regression Neural Networks From MODIS Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4787–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, J. Use of General Regression Neural Networks for Generating the GLASS Leaf Area Index Product From Time-Series MODIS Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, T.; Liang, S.; Sun, R. Estimating the Fractional Vegetation Cover from GLASS Leaf Area Index Product. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Comparison of Four Machine Learning Methods for Generating the GLASS Fractional Vegetation Cover Product from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Song, J.; Yang, H.; Sun, R.; Li, J. A 250 m resolution global leaf area index product derived from MODIS surface reflectance data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 1409–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Jiang, B. Evaluation of four long time-series global leaf area index products. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 246, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, A. Quantitatively distinguishing the impact of climate change and human activities on vegetation in mainland China with the improved residual method. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Cao, X.; Huang, L.; Zhu, J. Temporal-Spatial Changes in Vegetation Coverage under Climate Change and Human Activities: A Case Study of Central Yunnan Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ding, A.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, S. Geodetector model-based quantitative analysis of vegetation change characteristics and driving forces: A case study in the Yongding River basin in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, P.; Zhan, X.; Han, J.; Guo, M.; Wang, F. Warming and increasing precipitation induced greening on the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 2023, 233, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Mo, X.; Liu, S.; Lu, C. Impacts of climate change on grassland fractional vegetation cover variation on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. Dual Influence of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities on the Spatiotemporal Vegetation Dynamics Over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau From 1981 to 2015. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, B. Decadal Change of the Spring Snow Depth over the Tibetan Plateau: The Associated Circulation and Influence on the East Asian Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2780–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Huang, B.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J. Impact of Extreme Climate Indices on Vegetation Dynamics in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: A Comprehensive Analysis Utilizing Long-Term Dataset. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Piao, S.; Jeong, S.J.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Z.; Ciais, P.; Chen, D.; Huang, M.; Jin, C.S.; Li, L.Z.; et al. Evaporative cooling over the Tibetan Plateau induced by vegetation growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9299–9304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Ni, F.; Han, X.; Qiao, X.; Sun, X. Elevation-dependent patterns of temporally asymmetrical vegetation response to climate in an alpine basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Abbas, S.; Wei, D.; Zhao, W. Elevation-Dependent Vegetation Greening and Its Responses to Climate Changes in the South Slope of the Himalayas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2024GL113276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Kong, L.; Ouyang, Z. Identifying suitable areas for cropland and urban development in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Use Policy 2025, 150, 107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Y.; Wu, S. The Compound Effects of Highway Reconstruction and Climate Change on Vegetation Activity over the Qinghai Tibet Plateau: The G318 Highway as a Case Study. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Zhang, W.; Dong, J.; Yang, X.; Xia, S.; Chen, H. Impact of road corridors on soil properties and plant communities in high-elevation fragile ecosystems. Eur. J. For. Res. 2024, 143, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhuo, G.; Zhang, Y. Regional-scale vegetation-climate interactions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 65, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Zhao, W.; Yang, M.; Xiong, D. A long-term record (1995–2019) of the dynamics of land desertification in the middle reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River basin derived from Landsat data. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, T. Assessing the impacts of historical and future land-use/cover change on habitat quality in the urbanizing Lhasa River Basin on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudureheman, W.; Yusufujiang, R.; Zhang, F.; Rukeya, S.; Zhang, X. Temporal and spatial characteristics of grassland degradation in Xinjiang Section of Tianshan Mountains based on remote sensing monitoring and its relationship with climate factors. Pratacultural Sci. 2023, 40, 1779–1792. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Gang, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Assessment of climate change trends over the Loess Plateau in China from 1901 to 2100. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhi, L.I. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, S. Spatiotemporal trends and attribution of drought across China from 1901–2100. Sustainability 2020, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, S. Spatiotemporal change and attribution of potential evapotranspiration over China from 1901 to 2100. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 145, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Chang, Z. Developing improved time-series DMSP-OLS-like data (1992–2019) in China by integrating DMSP-OLS and SNPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4407714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Luo, L. Combined Use of Multiple Cloud-Free Snow Cover Products in China and Its High-Mountain Region: Implications From Snow Cover Identification to Snow Phenology Detection. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR036274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, J.; Xu, C.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, S.; Duan, Z. The response of lake area and vegetation cover variations to climate change over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the past 30 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-Term Storage Capacity of Reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayisaba, F.; Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Guo, H.; Karamage, F.; Kayiranga, A. Understanding the Spatial Temporal Vegetation Dynamics in Rwanda. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying Geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xiu, L.; Yao, X.; Yu, Z.; Huang, X. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors analysis of the eco-quality in the Lanxi urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, G.; Jia, Y.; et al. Disentangling the Response of Vegetation Dynamics to Natural and Anthropogenic Drivers over the Minjiang River Basin Using Dimensionality Reduction and a Structural Equation Model. Forests 2024, 15, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, L.; Li, D.; Shang, H.; Gao, F. Analysis of Vegetation Dynamics and Driving Mechanisms on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in the Context of Climate Change. Water 2023, 15, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Penuelas, J.; Liu, L.; Ge, Q. Weakening warming on spring freeze-thaw cycle caused greening Earth’s third pole. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319581121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Suo, M.; Wang, Y. The Influence of Different Climate and Terrain Factors on Vegetation Dynamics in the Lancang River Basin. Water 2022, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhuo, P.; Ao, T. Development of Fractional Vegetation Cover Change and Driving Forces in the Min River Basin on the Eastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Forests 2025, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Huang, L. Assessment on protection and construction of ecological safety shelter for Tibet. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2017, 32, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ju, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhao, W.; Du, Y.; Jiang, P.; Hao, Z. Regional Patterns of Vegetation Dynamics and Their Sensitivity to Climate Variability in the Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, X. Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and anthropogenic activities in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dai, E. Vegetation cover dynamics and its constraint effect on ecosystem services on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under ecological restoration projects. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zohner, C.M.; Crowther, T.W.; Li, M.; Shen, F.; Guo, M.; Qin, J.; Yao, L.; Zhou, C. Direct and indirect impacts of urbanization on vegetation growth across the world’s cities. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo0095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, Y. Trend analysis of vegetation dynamics in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau using Hurst Exponent. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, W. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Influencing Factors of Ecosystem Vulnerability on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Env. Res Public Health 2021, 18, 6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Kuang, T.; Tao, S. Quantifying influences of natural factors on vegetation NDVI changes based on geographical detector in Sichuan, western China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wu, H. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Vegetation Cover in Relation to Its Driving Forces in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Forests 2023, 14, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.K.; Sylvester, K.M. Identification of “ever-cropped” land (1984–2010) using Landsat annual maximum NDVI image composites: Southwestern Kansas case study. Remote Sens Env. 2012, 121, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, S. Response of vegetation to drought in the Tibetan Plateau: Elevation differentiation and the dominant factors. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 306, 108468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, J.; Feng, Y.; Niu, B.; He, Y.; Zhang, X. Climate Variability Rather Than Livestock Grazing Dominates Changes in Alpine Grassland Productivity Across Tibet. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 631024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, W.; Xue, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, R.; Zeng, H.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; et al. Grassland changes and adaptive management on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liang, E.; Camarero, J.J.; Rossi, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Fu, Y.H.; Sun, J.; Wang, T.; Piao, S. Warming-induced phenological mismatch between trees and shrubs explains high-elevation forest expansion. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Sun, C. Spatiotemporal variation and influencing factors of vegetation dynamics based on Geodetector: A case study of the northwestern Yunnan Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Han, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, P.; Ban, C.; Sun, W.; Pang, B.; Peng, D.; Kan, G.; Zhang, R.; et al. Time-lag effects of climatic change and drought on vegetation dynamics in an alpine river basin of the Tibet Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kuang, X.; Lancia, M.; Yao, Y.; Zheng, C. Analysis of the groundwater flow system in a high-altitude headwater region under rapid climate warming: Lhasa River Basin, Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 36, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanville, K.; Sheldon, F.; Butler, D.; Capon, S. Effects and significance of groundwater for vegetation: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jackson, R.B. A Global Analysis of Groundwater Recharge for Vegetation, Climate, and Soils. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11, vzj2011.0021RA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood Lollar, B.; Warr, O.; Higgins, P.M. The Hidden Hydrogeosphere: The Contribution of Deep Groundwater to the Planetary Water Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2024, 52, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Miguez-Macho, G.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Otero-Casal, C. Hydrologic regulation of plant rooting depth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10572–10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Song, W. Ecological and Environmental Effects of Land Use and Cover Changes on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A Bibliometric Review. Land 2022, 11, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, H.; Peng, C.; Liu, J.; Piao, S.; He, J.-S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; et al. An early warning signal for grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, E.; Zhao, Z.; Jia, L.; Jiang, X. Contribution of ecosystem services improvement on achieving Sustainable development Goals under ecological engineering projects on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 199, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, P.; Luo, H.; Hu, T.; Dong, B.; Cui, Y.; Khan, S.; Luo, Y. Impacts of land use and land cover changes on regional climate in the Lhasa River basin, Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monasterolo, M.; Poggio, S.L.; Medan, D.; Devoto, M. Wider road verges sustain higher plant species richness and pollinator abundance in intensively managed agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Xu, C.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.; Xing, X.; Yang, D.; Xu, B.; Yang, X. Cross-scale mapping of above-ground biomass and shrub dominance by integrating UAV and satellite data in temperate grassland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 304, 114024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Land use change and driving factors in rural China during the period 1995–2015. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Dong, G.; Jiang, X.; Lei, Y. Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Forces of Vegetation Coverage on the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.-F. Optimal discretization for geographical detectors-based risk assessment. GISci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deventer, H.; Linström, A.; Naidoo, L.; Job, N.; Sieben, E.J.J.; Cho, M.A. Comparison between Sentinel-2 and WorldView-3 sensors in mapping wetland vegetation communities of the Grassland Biome of South Africa, for monitoring under climate change. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 28, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganem, K.A.; Xue, Y.; Rodrigues, A.D.A.; Franca-Rocha, W.; Oliveira, M.T.D.; Carvalho, N.S.D.; Cayo, E.Y.T.; Rosa, M.R.; Dutra, A.C.; Shimabukuro, Y.E. Mapping South America’s Drylands through Remote Sensing—A Review of the Methodological Trends and Current Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Xu, G.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Quantifying the relative contribution of natural and human factors to vegetation coverage variation in coastal wetlands in China. Catena 2020, 188, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Cao, A. Analysis of the heterogeneity of landscape risk evolution and driving factors based on a combined GeoDa and Geodetector model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 108832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).