Codesign of Transmit Waveform and Receive Filter with Similarity Constraints for FDA-MIMO Radar
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The codesign model for constant modulus transmit waveforms and receive filters in FDA-MIMO radarIn the existing research on waveform design of FDA-MIMO systems, peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) and total energy constraints are usually considered [20,21]. The total energy constraint is mainly used to control resource costs, while the peak-to-average power ratio constraint avoids nonlinear distortion of the transmitter amplifier while controlling resource costs, but this constraint will also reduce the energy efficiency of the power amplifier. To solve this problem, this paper models the problem as maximizing the signal-to-interference ratio (SINR) of the system under the similarity constraint of the transmitted waveform, the constant modulus constraint, and the norm constraint of the receiving filter. While improving the system performance, it also ensures that the power amplifier maximizes energy efficiency while avoiding distortion and maintaining the excellent characteristics of the reference waveform.
- The adaptive penalty strategyMainstream methods typically use penalty-based strategies to transform similarity constraints. However, most existing methods use fixed penalty factors [13,21,26,27], and selecting an appropriate penalty factor is challenging. A small penalty factor may result in the failure to meet the similarity constraint, while an excessively large penalty factor may significantly degrade system performance. To address this problem, we propose an optimization method based on an adaptive penalty factor. This method starts with a small penalty factor and gradually increases it during the iteration process until it reaches a suitable level. This allows the similarity constraint to be accurately met, maximizing the system’s optimization performance.
- The joint optimization method based on JCCM-CSMSThe existing methods addressing the joint design problem of FDA-MIMO radar typically rely on relaxation strategies [17,20,21]. Relaxation transforms an otherwise difficult-to-solve optimization problem into a more tractable form; however, this process inevitably introduces errors, leading to performance loss. We have observed that the complex circle manifold space (CCMS) consists of complex vectors with unit modulus, while the complex sphere manifold space (CSMS) is composed of complex vectors with unit norm. Based on this observation, this paper constructs a joint space of the two, i.e., JCCM-CSMS. Through the projecting of the optimization problem into JCCM-CSMS, the original problem is converted into an unconstrained optimization problem, where the SINR takes the form of a quadratic fractional function that can be optimized using a classic gradient-based algorithm. Therefore, this method eliminates the need for relaxation, avoiding the errors introduced by relaxation and significantly improving optimization performance.
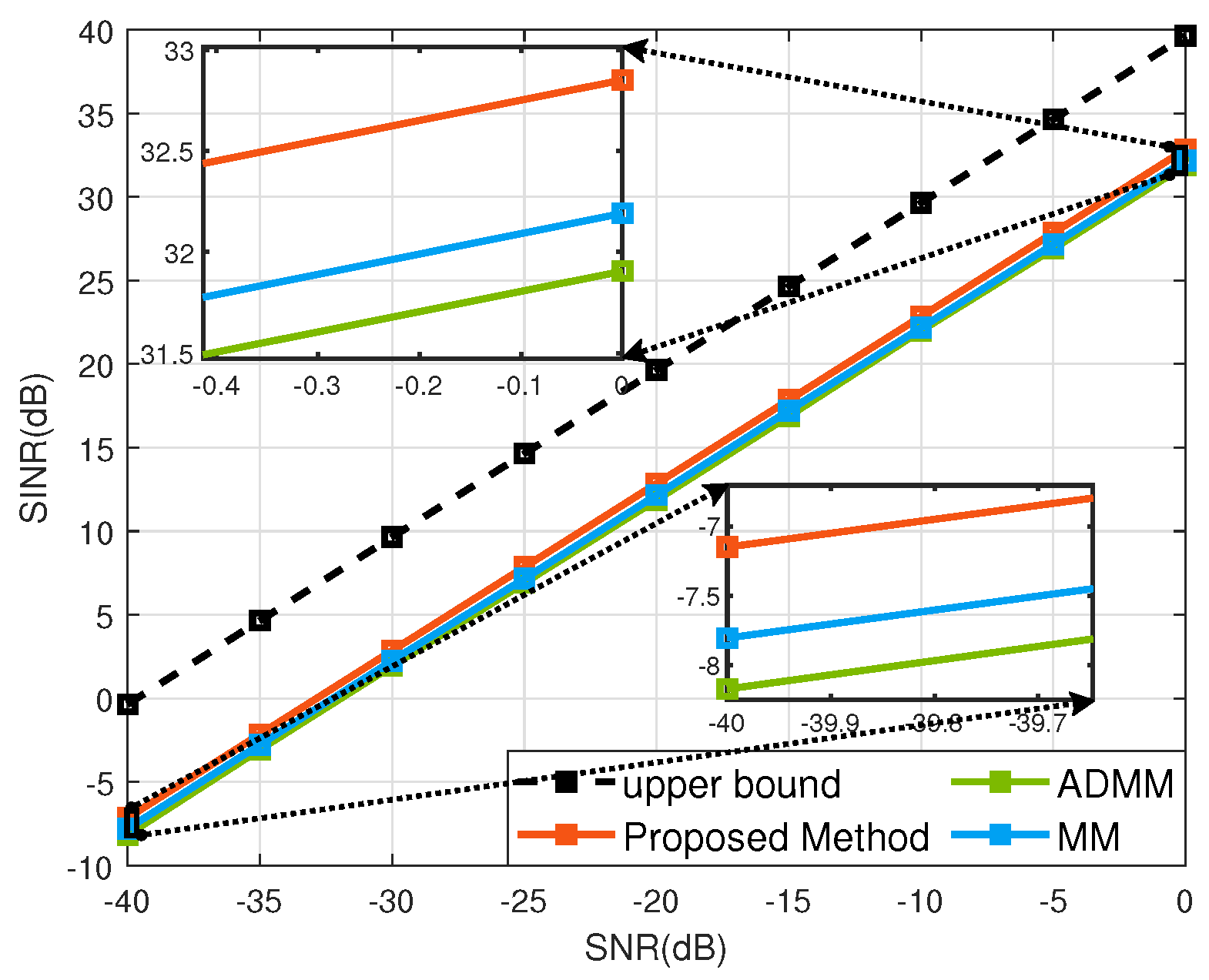
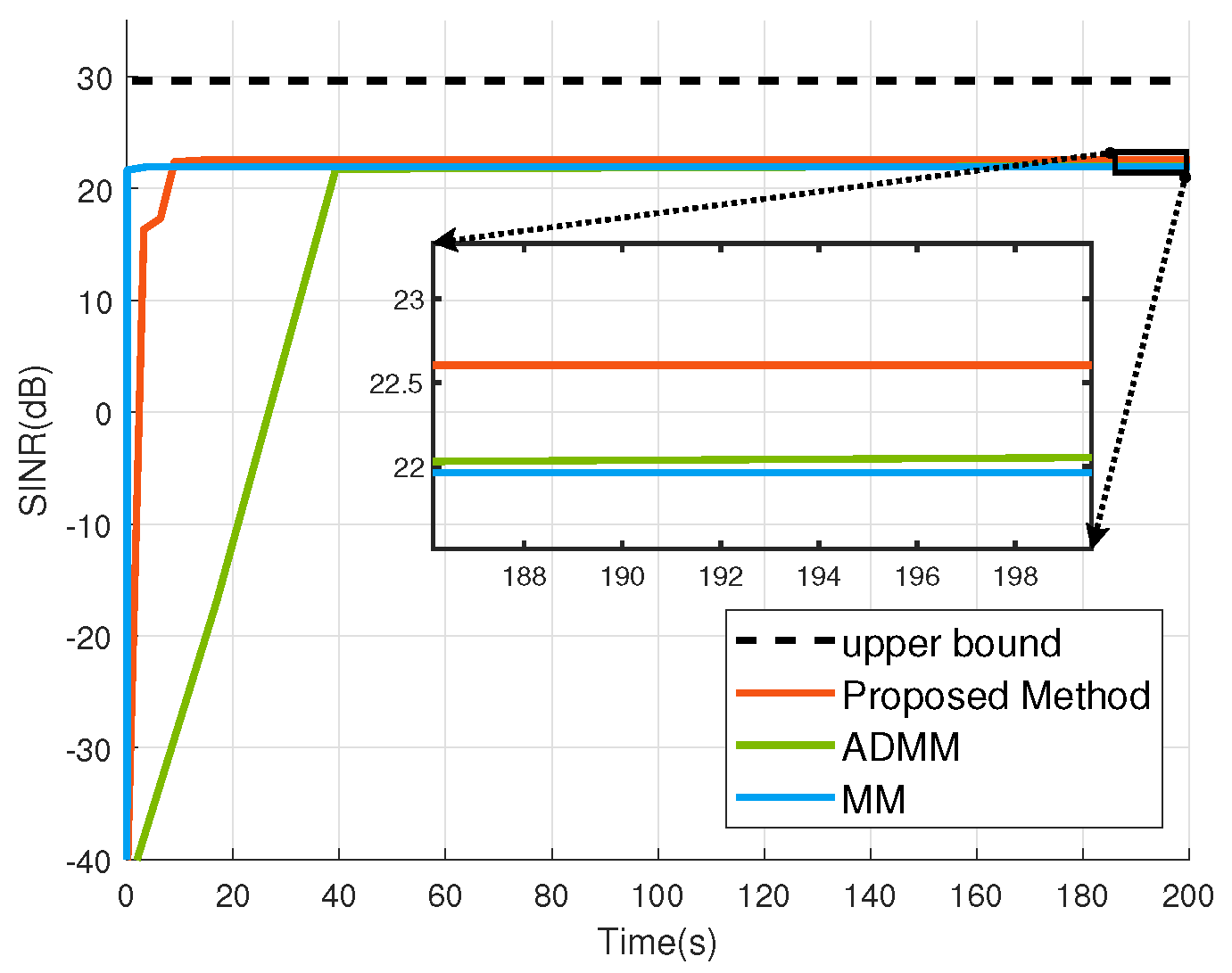
- Superior performanceSimulation results show that the proposed method improves the SINR performance by about 0.7 dB compared with the ADMM-based method proposed in [22]. The performance of the proposed method is improved by about 0.6 dB compared with the MM-based method proposed in [23]. Improving the SINR of the received signal helps improve the accuracy of subsequent target detection and parameter estimation [28,29].
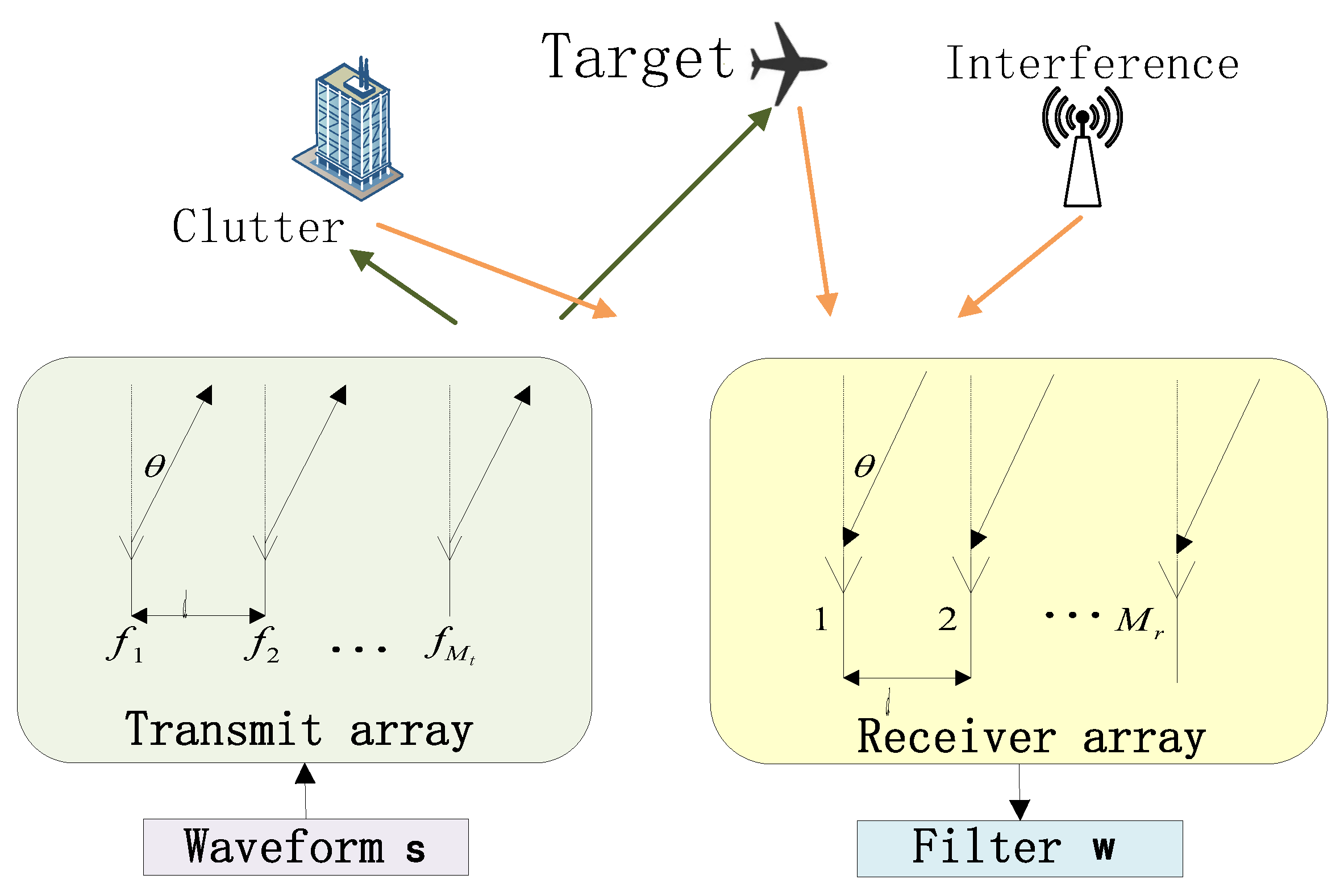
2. Problem Description
2.1. Signal Model
2.2. Problem Modeling
2.2.1. Similarity Constraint
2.2.2. Constant Modulus Constraint
2.2.3. Problem Model
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. Adaptive Exact Penalty Method
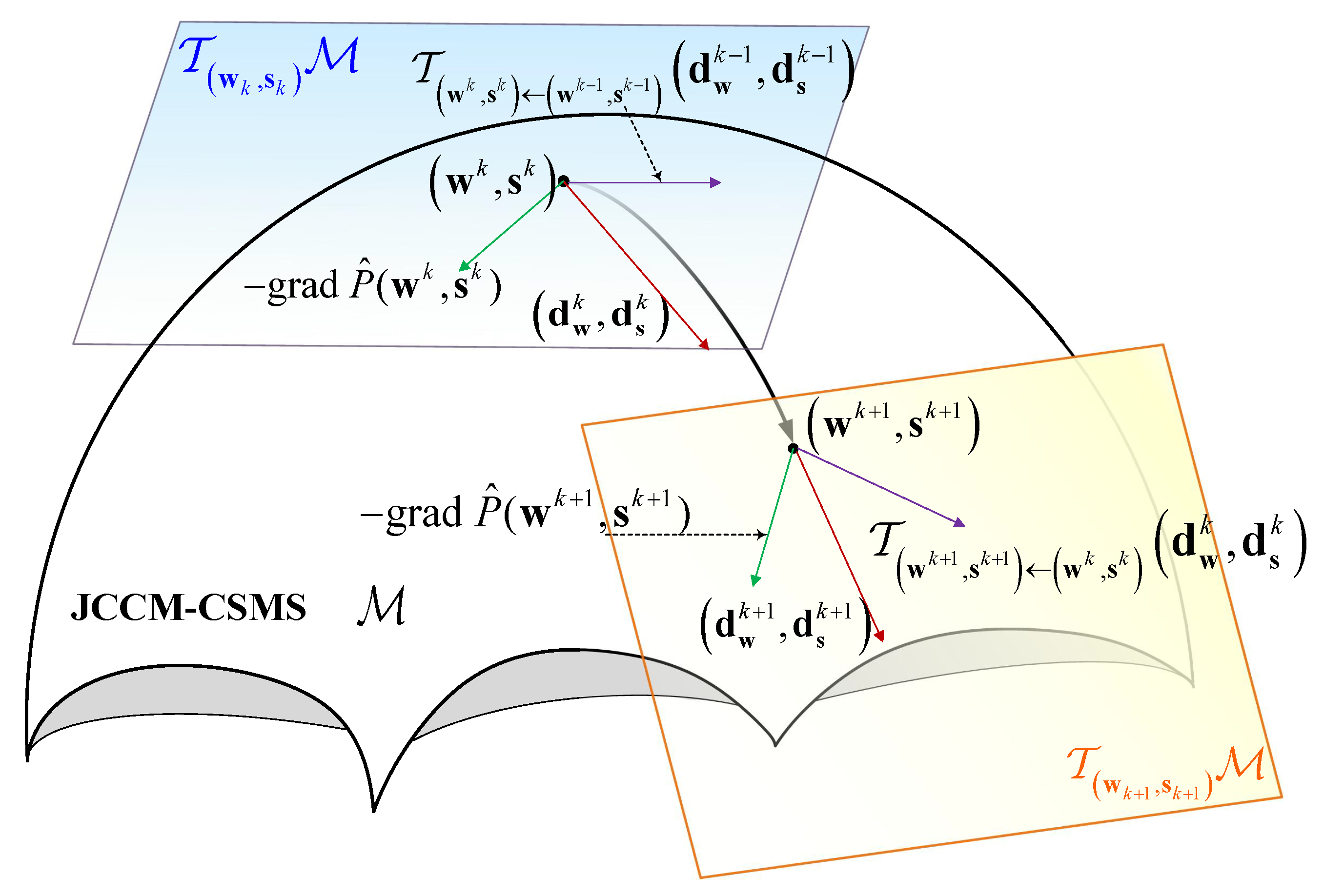
3.2. Construction of the JCCM-CSMS
3.3. RL-BFGS
3.3.1. Calculation of the Riemannian Gradient
3.3.2. Finding the Descent Direction
3.3.3. Update of Feasible Solutions
3.3.4. Update of Intermediate Variables
3.4. Summary of the Method
| Algorithm 1: RL-BFGS for descent direction determination. |
 |
| Algorithm 2: JCCM-CSMS-based parallel optimization method for waveform and receiver filter. |
 |
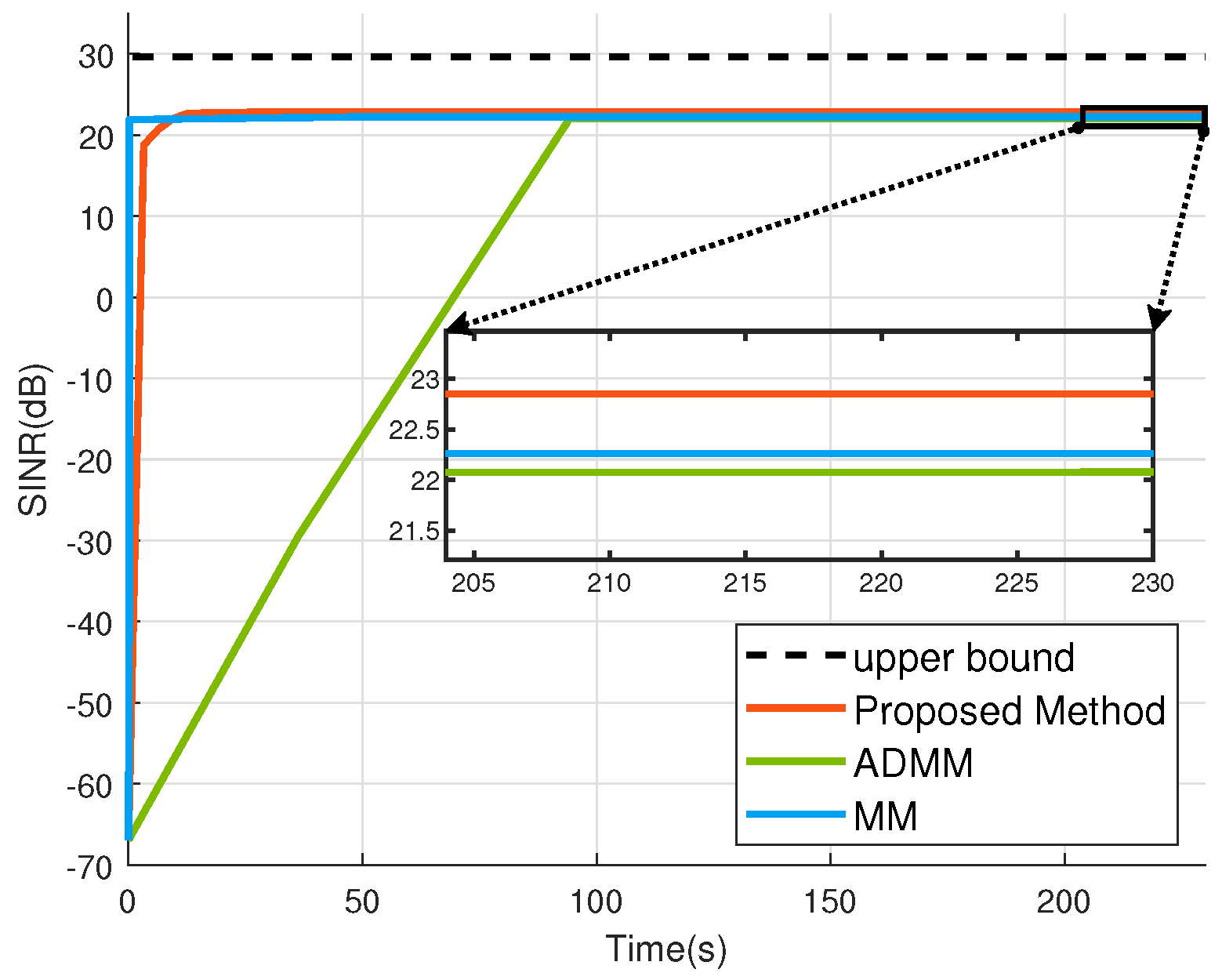
3.5. Convergence Analysis
3.6. Complexity Analysis
4. Numerical Simulations
4.1. Receive Beampattern Results
4.2. SINR Performance Evaluation
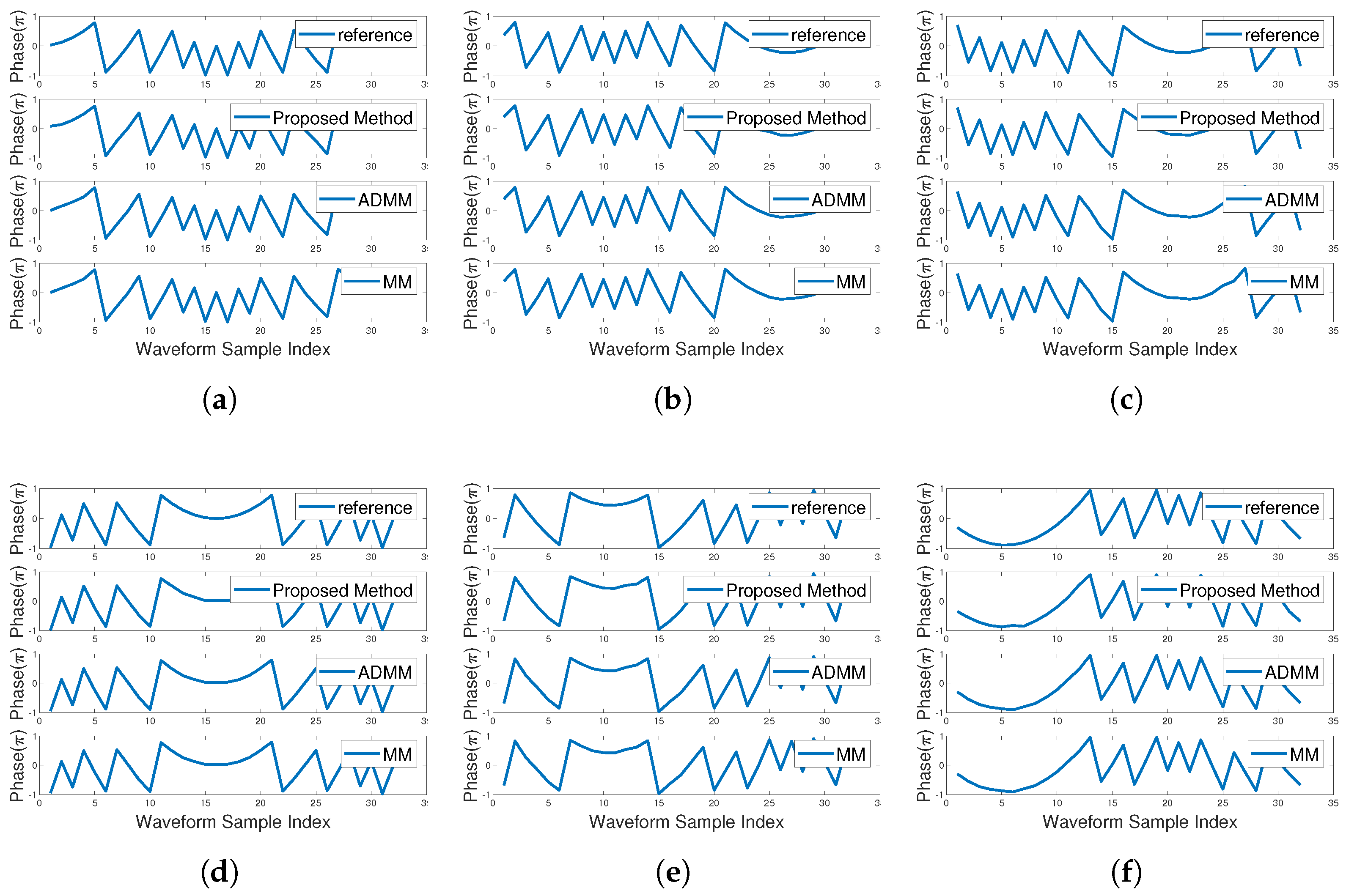
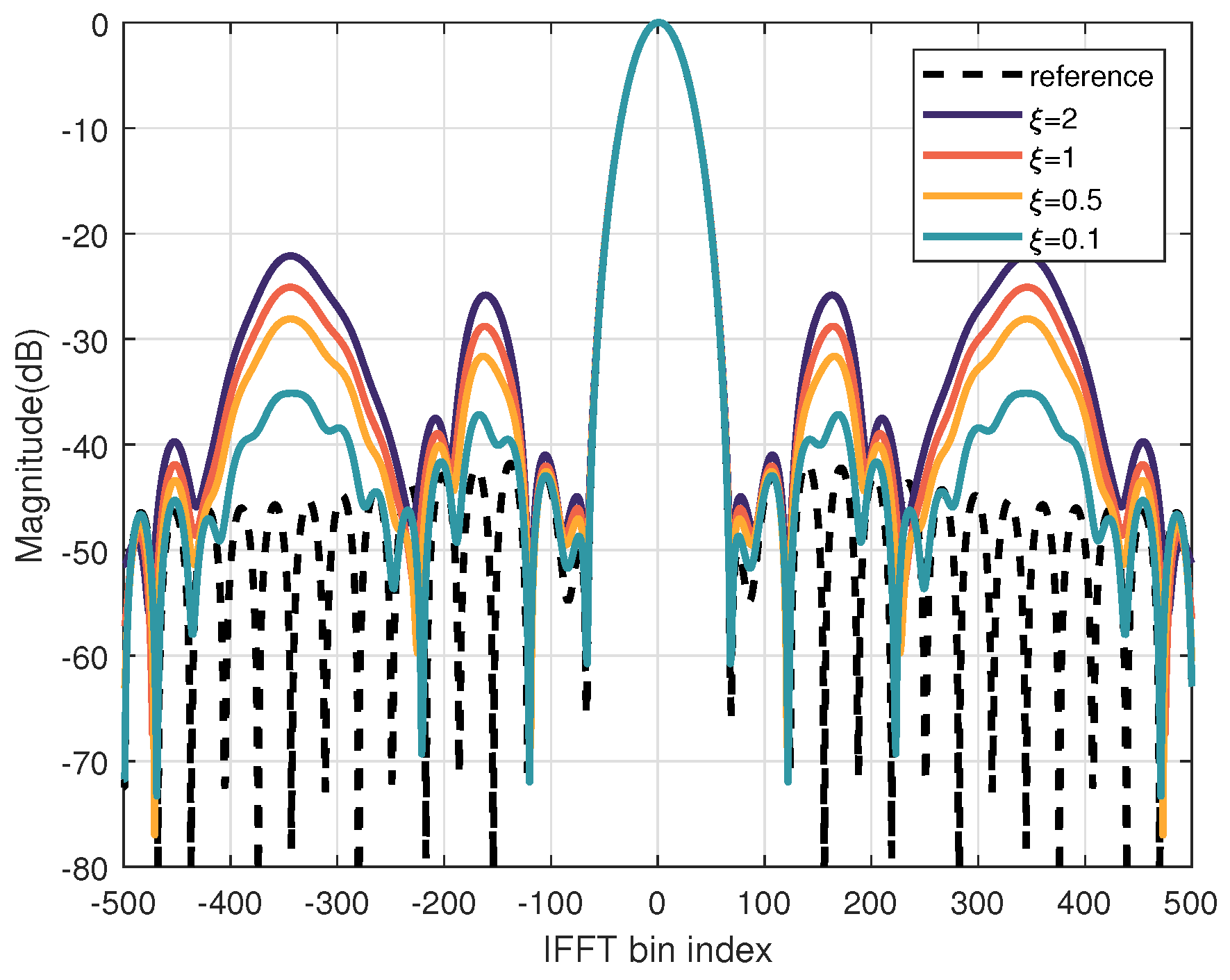
4.3. Analysis of Similarity
4.4. Performance Analysis of a Scenario with More Clutter
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
- When andTransform past variables to the tangent space of the current new iteration point and store the updated variables in the storage space until the storage capacity is reached:Update the coefficient storage space to the following:
- When andDiscard the oldest data and place the updated variables into storage.The coefficient storage space is updated to the following:
- whenThe coefficient storage space has ceased updating, and the intermediate variable storage space will also halt updates while transitioning to the current update point’s tangent space.
Appendix C
References
- Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Gong, J.; Xu, J.; Tan, M. Fast and Efficient Single-Snapshot Range and Angle Estimation for FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 3509405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Huang, Q.; Huang, B.; Wang, W.Q. FDA-MIMO-Based Integrated Sensing and Communication System with Frequency Offsets Permutation Index Modulation. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2024, 72, 6707–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hao, C.; Hu, Q.; Orlando, D. Sparsity-Based Processing to Enhance the Reverberation Suppression for FDA-MIMO Sonars. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 1556–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Huang, B.; Wang, W.Q.; Sun, Y. Generalized Ambiguity Function for FDA Radar Joint Range, Angle and Doppler Resolution Evaluation. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 3502305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Xu, J.; Lan, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F. Interference Suppression With MR-FDA-MIMO Radar Using Virtual Samples Based Beamforming. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 5211–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Xu, J.; Lan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Frequency Increment Design Method of MR-FDA-MIMO Radar for Interference Suppression. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhu, S.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Lan, L.; Liang, J. Fast Repeater Deception Jamming Suppression With DFI-FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 4271–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Hu, J.; Zuo, Y.; Zhong, K.; Xiao, X.; Li, H.; Li, L. Robust Transceiver Design for ISAC Systems via Product Complex Circle-Sphere Manifold Method. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5501914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.; An, D.; Pan, C.; Teh, K.C.; Yu, X.; Li, H. P2C2M: Parallel Product Complex Circle Manifold for RIS-Aided ISAC Waveform Design. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2024, 10, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cui, G.; Kong, L.; Li, J.; Gui, G. Constrained Waveform Design for Colocated MIMO Radar With Uncertain Steering Matrices. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liang, J.; Li, J. Constant Modulus MIMO Radar Waveform Design With Minimum Peak Sidelobe Transmit Beampattern. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 4207–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dai, W.; Wang, H.; Li, G.Y. Robust Waveform Design for Integrated Sensing and Communication. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2024, 72, 3122–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, F.; Sun, P.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Z. Joint Design of Transmitting Waveform and Receiving Filter via Novel Riemannian Idea for DFRC System. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Cheng, Z. Constrained waveform design for dual-functional MIMO radar-Communication system. Signal Process. 2020, 171, 107530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Jakobsson, A.; Wang, W.Q. Designing FDA Radars Robust to Contaminated Shared Spectra. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Jakobsson, A.; Wang, W.Q. Waveform optimization with SINR criteria for FDA radar in the presence of signal-dependent mainlobe interference. Signal Process. 2023, 204, 108851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.Q. Joint LPI waveform and passive beamforming design for FDA-MIMO-DFRC systems. Signal Process. 2025, 227, 109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q. Joint Transceiver Beamforming for Multi-Target Single-User Joint Radar and Communication. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, W.; Pan, J.; Li, B. Robust Joint Design of Transmit Waveform and Receive Filter for MIMO-STAP Radar Under Target and Clutter Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 1156–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Rosamilia, M.; Aubry, A.; De Maio, A.; Liao, G. FDA-MIMO Transmitter and Receiver Optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2024, 72, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.Q. Joint Design of Transmit Waveform and Receive Beamforming for LPI FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1938–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Tang, B.; Wang, X. Constant-Modulus Waveform Design for Dual-Function Radar-Communication Systems in the Presence of Clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 4005–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Babu, P.; Palomar, D.P. Transmit Waveform/Receive Filter Design for MIMO Radar With Multiple Waveform Constraints. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 1526–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Hu, J.; Cong, Y.; Cui, G.; Hu, H. RMOCG: A Riemannian Manifold Optimization-Based Conjugate Gradient Method for Phase-Only Beamforming Synthesis. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2022, 21, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Huang, W.; Absil, P.A.; Gallivan, K. A Riemannian Limited-Memory BFGS Algorithm for Computing the Matrix Geometric Mean. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 80, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Jiang, H.; Qu, L. Joint Constant-Modulus Waveform and RIS Phase Shift Design for Terahertz Dual-Function MIMO Radar and Communication System. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Sun, G.; Ji, Y.; Ding, Z.; Chen, W. Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Synthetic Aperture Radar Waveform and Filter Design in the Presence of Uncertain Interference Environment. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y. Dynamic Spectrum Tracking of Multiple Targets With Time-Sparse Frequency-Hopping Signals. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Duan, C.; Chen, A. A Contrast-Enhanced Approach for Aerial Moving Target Detection Based on Distributed Satellites. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Tao, H.; Cao, H.; Liao, H. Multiparameter Estimation for Monostatic FDA-MIMO Radar With Polarimetric Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liao, B.; Li, X.; Liao, G. Target Localization With Bistatic MIMO and FDA-MIMO Dual-Mode Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Xie, J.; Lan, L.; Qi, C.; Gao, X. An Intelligent Anti-Interference Scheme for FDA-MIMO Radar Under Nonideal Condition. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 3269–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, W.Q. Performance Analysis of Joint Radar-Communication System Based on FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 48774–48787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wen, F.; He, J.; Truong, T.K. Coarray Tensor Train Decomposition for Bistatic MIMO Radar with Uniform Planar Array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2025, early access, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Wang, W.Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S. Effects of Spatial Position on Mainlobe Interference Suppression Performance of FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 9437–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Hu, T.; Shao, X.; Wu, L.; Xiao, Z. A Single-Snapshot Robust Beamforming for FDA-MIMO Radar Based on AID3. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Xu, J.; Lan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of interference suppression performance in MR-FDA-MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2025, 230, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, W.Q. Moving Target Detection Using FDA-MIMO Radar With Planar Array. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, X.; Pan, C.; Teh, K.C.; Cui, G. Joint Design of Power Allocation and Unimodular Waveform for Polarimetric Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2025, 63, 5100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsinos, C.G.; Arora, A.; Chatzinotas, S.; Ottersten, B. Joint Transmit Waveform and Receive Filter Design for Dual-Function Radar-Communication Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2021, 15, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Feng, X.; Wei, T.; Du, J.; Yu, W. Anti-Maneuvering Repeater Jamming Using Up- and Down-Chirp Modulation in Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Cai, B.; Xia, M.; Yang, L. Research on Optimization Design Method of MIMO Radar Waveform Based on Frequency-Orthogonal LFM. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 160835–160845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; You, P.; An, M. Algorithm for Designing Waveforms Similar to Linear Frequency Modulation Using Polyphase-Coded Frequency Modulation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Hu, J.; Pan, C.; Deng, M.; Fang, J. Joint Waveform and Beamforming Design for RIS-Aided ISAC Systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Cui, G.; Liao, B.; Hu, H. MIMO Radar Unimodular Waveform Design With Learned Complex Circle Manifold Network. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; An, D.; Zhu, G.; Teh, K.C.; Pan, C.; Eldar, Y.C. RIS-Aided Beamforming Design for MIMO Systems via Unified Manifold Optimization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, W.; Wirth, B. Optimization Methods on Riemannian Manifolds and Their Application to Shape Space. SIAM J. Optim. 2012, 22, 596–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Xu, H.X. Joint Power, Bandwidth, and Subchannel Allocation in a UAV-Assisted DFRC Network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 11633–11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B. Joint Customer Assignment, Power Allocation, and Subchannel Allocation in a UAV-Based Joint Radar and Communication Network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 29643–29660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Computational Complexity |
|---|---|
| Proposed Method | |
| ADMM [22] | |
| MM [23] |
| Method | SINR | Similarity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Clutter Scattering Points | 4 Clutter Scattering Points | ||
| Proposed Method | 22.85 dB | 22.60 dB | 1.00 |
| ADMM | 22.12 dB | 22.05 dB | 1.00 |
| MM | 22.26 dB | 21.96 dB | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Tai, X.; Zuo, Y.; Li, H.; Zhong, K.; Li, C. Codesign of Transmit Waveform and Receive Filter with Similarity Constraints for FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101800
Zhang Q, Hu J, Tai X, Zuo Y, Li H, Zhong K, Li C. Codesign of Transmit Waveform and Receive Filter with Similarity Constraints for FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101800
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiping, Jinfeng Hu, Xin Tai, Yongfeng Zuo, Huiyong Li, Kai Zhong, and Chaohai Li. 2025. "Codesign of Transmit Waveform and Receive Filter with Similarity Constraints for FDA-MIMO Radar" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101800
APA StyleZhang, Q., Hu, J., Tai, X., Zuo, Y., Li, H., Zhong, K., & Li, C. (2025). Codesign of Transmit Waveform and Receive Filter with Similarity Constraints for FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101800








