Joint Optimization of Carrier Frequency and PRF for Frequency Agile Radar Based on Compressed Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CF-PRF Jointly Agile Radar Signal Model
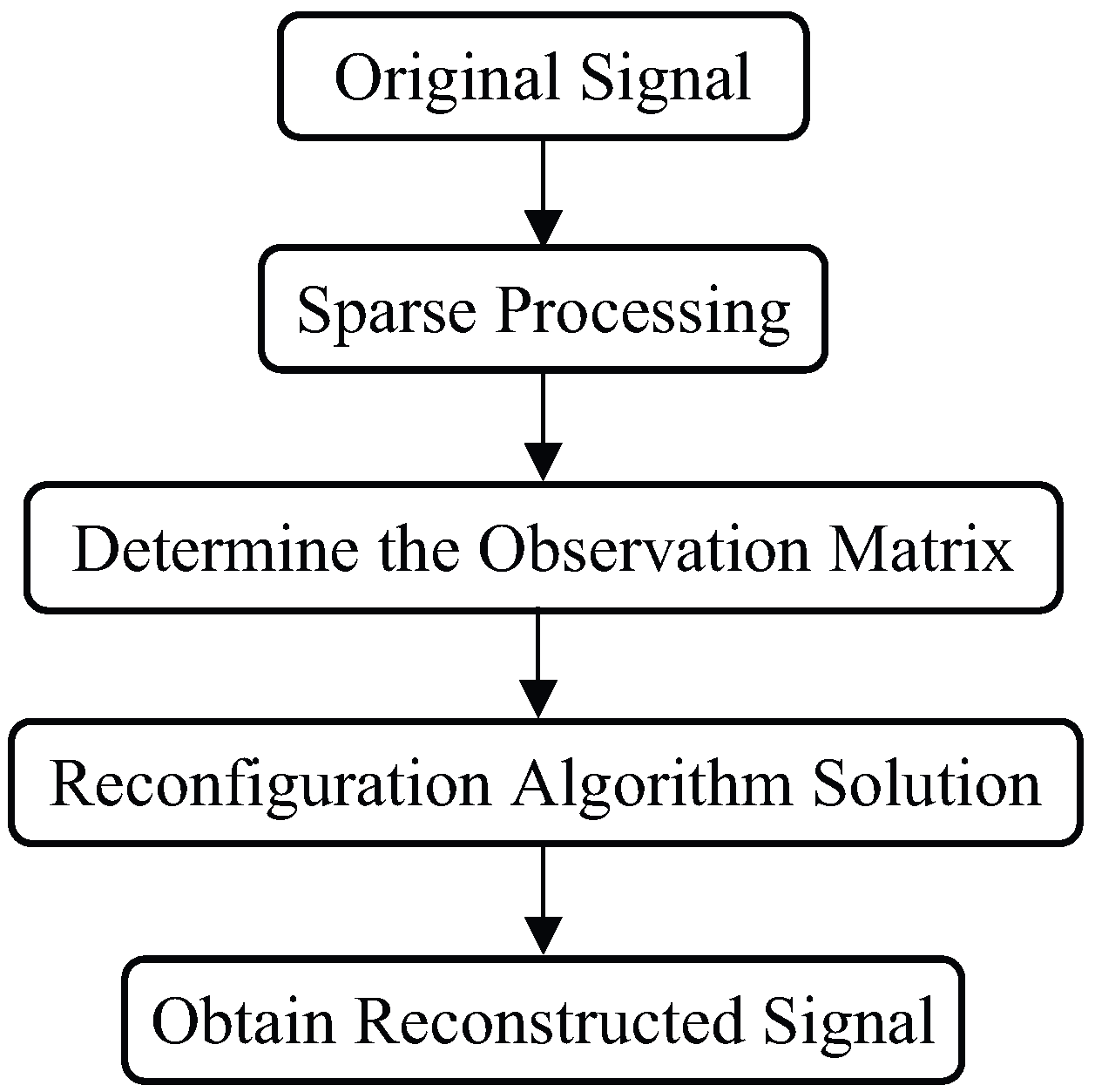
3. CF-PRF Jointly Agile Radar Signal Processing Method
3.1. The Theory Model of CS
3.2. CS Model for CF-PRF Jointly Agile Radar Signal Processing
3.3. CF-PRF Jointly Agile Radar Signal Processing Method Based on ADMM
| Algorithm 1: ADMM Flow |
|
4. GA-Based Dictionary Matrix Optimization Method
4.1. Properties of Dictionary Matrix
- (1)
- RIP
- (2)
- MIP
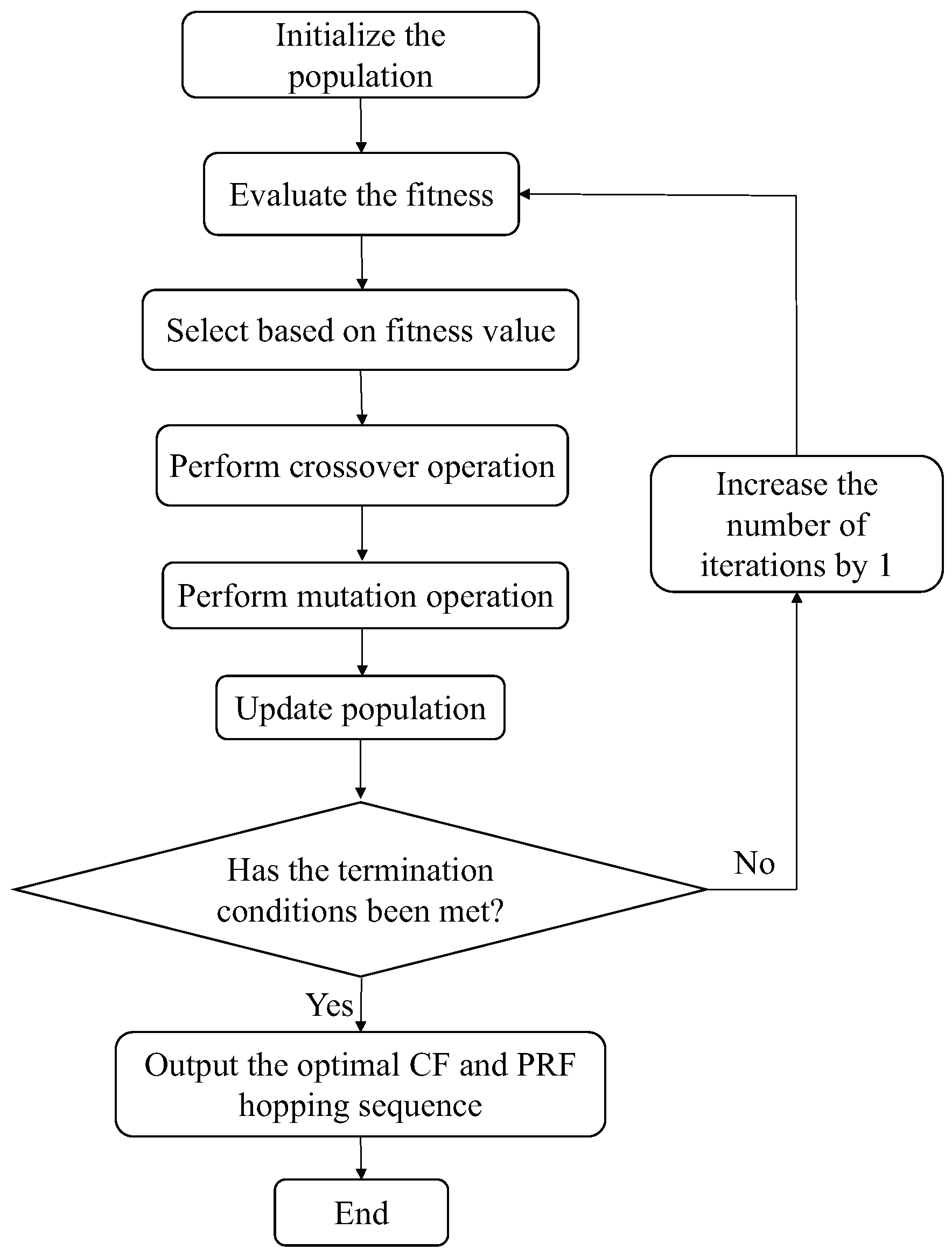
4.2. Joint Optimization of CF-PRF Hopping Sequence for FAR Based on GA
- Step 1:
- Step 2:
- Step 3:
- Step 4:
- Step 5:
- Step 6:
- Step 7:
5. Simulations
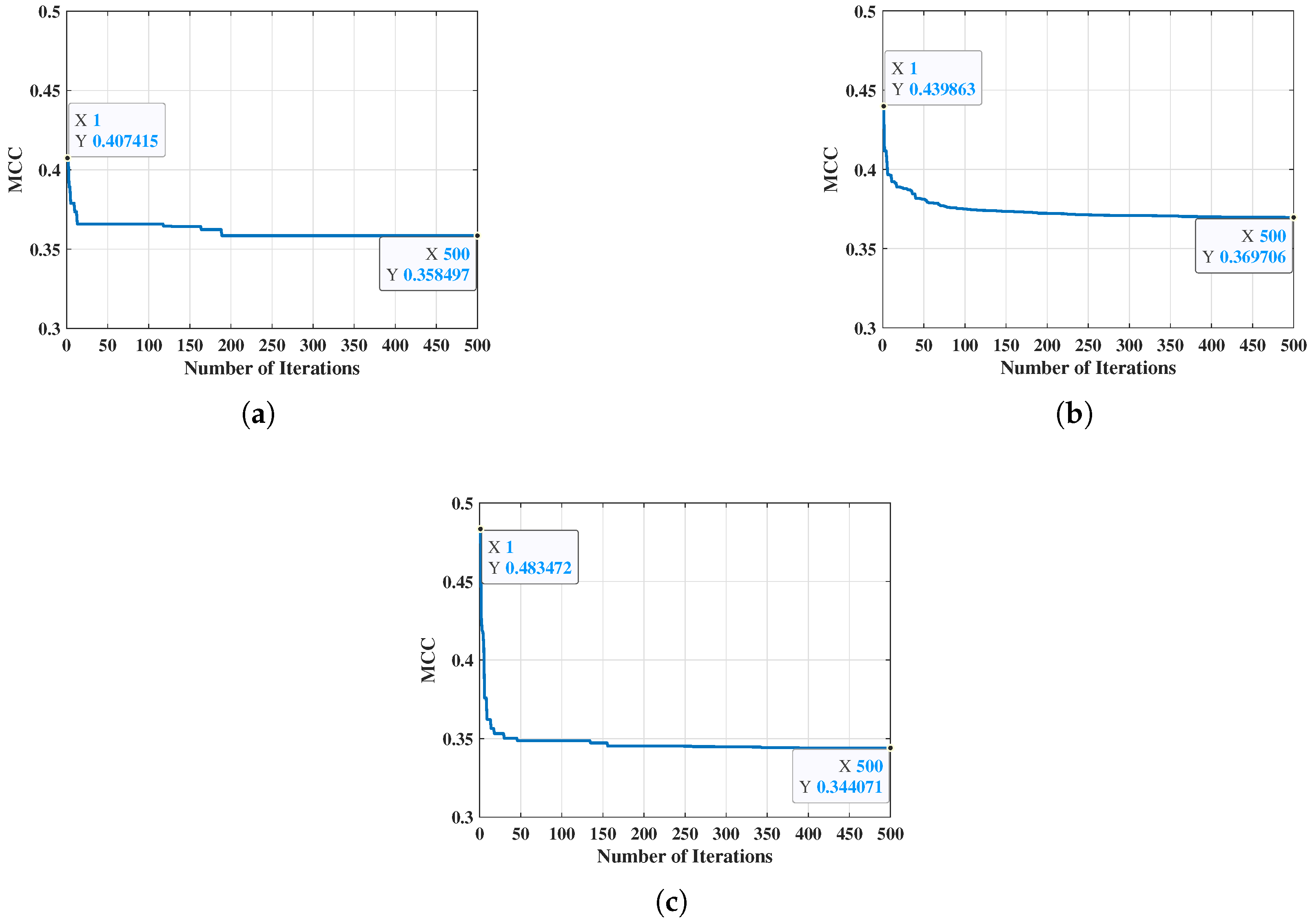
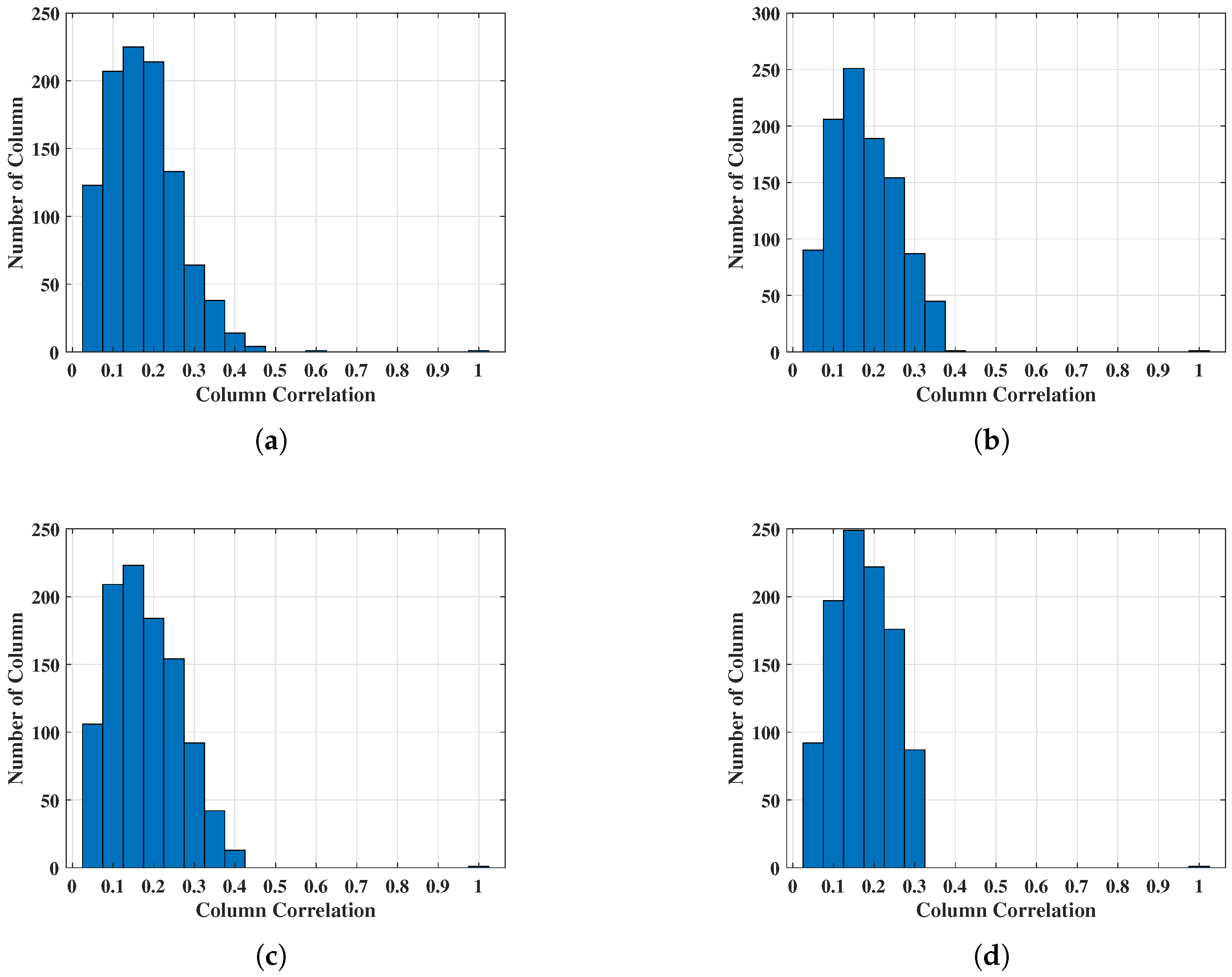
5.1. Optimization Results of Dictionary Matrix
| GA | SA | PSO | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Iteration Time | 58765 s | 74928 s | 17081 s |
| Average MCC | 0.345092 | 0.349563 | 0.361284 |
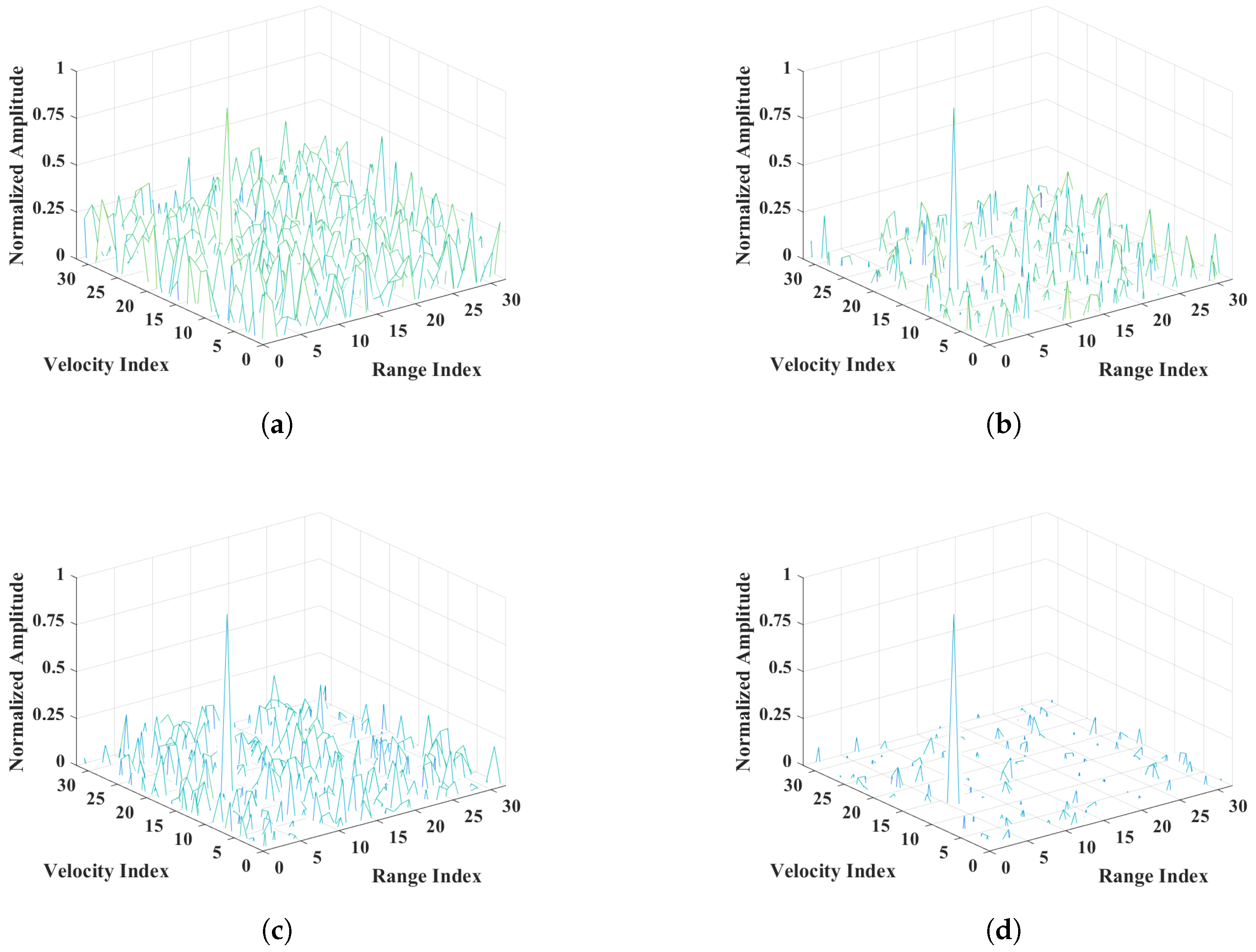
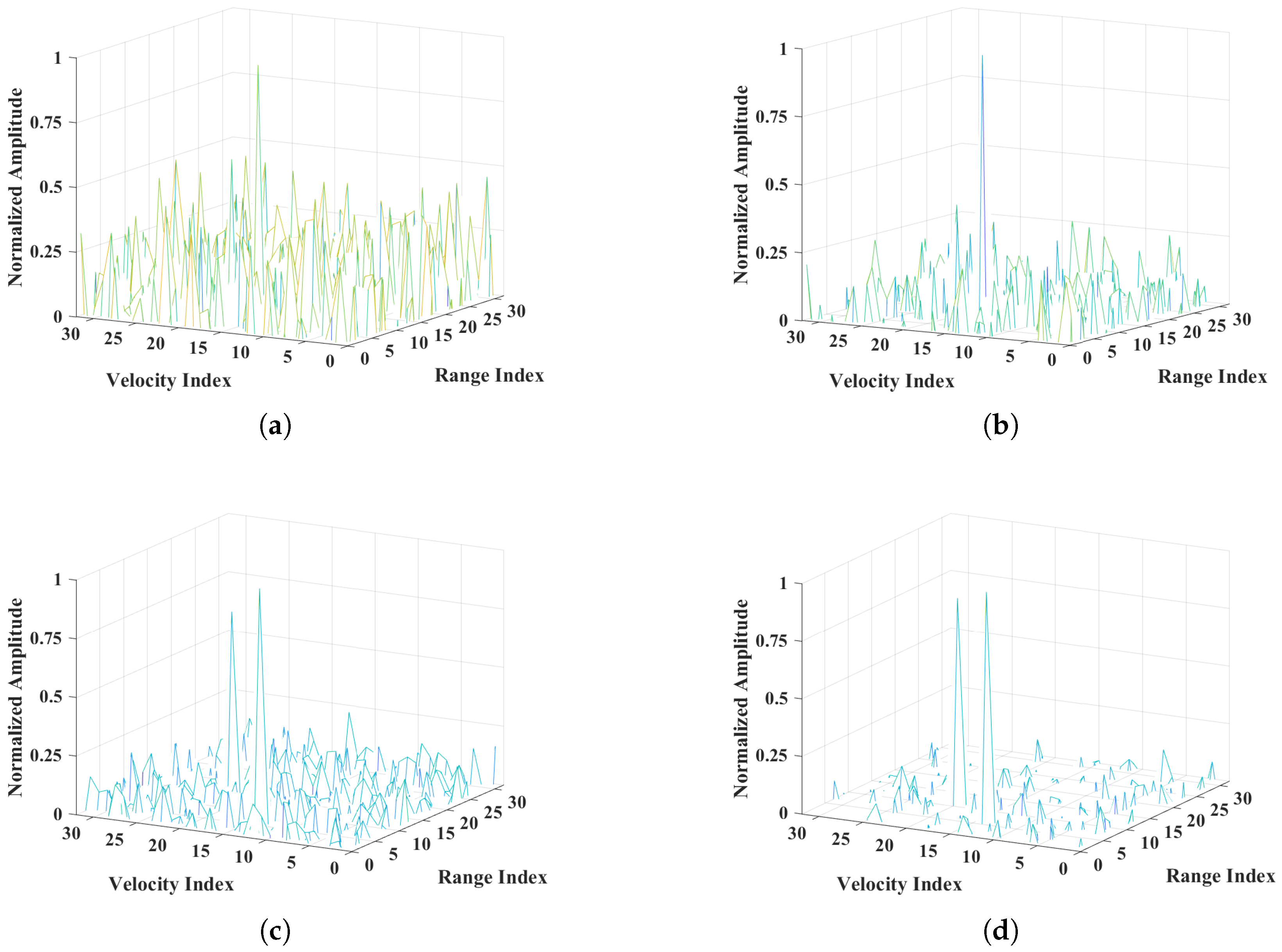
5.2. Reconstruction Results Using ADMM
| Pulse Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF hopping coefficient | 9 | 2 | 11 | 11 | 4 | 24 | 15 | 11 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 26 | 28 | 4 | 22 |
| Pulse Number | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 |
| CF hopping coefficient | 25 | 31 | 10 | 31 | 9 | 8 | 13 | 21 | 7 | 24 | 14 | 0 | 11 | 8 | 31 | 13 |
| Pulse Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRI (μs) | 0 | 605 | 662 | 606 | 601 | 661 | 626 | 657 | 602 | 600 | 644 | 632 | 602 | 612 | 606 | 600 |
| Pulse Number | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 |
| PRI (μs) | 600 | 600 | 600 | 647 | 647 | 663 | 606 | 600 | 663 | 624 | 610 | 625 | 662 | 663 | 602 | 603 |
| Pulse Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF hopping coefficient | 12 | 22 | 17 | 29 | 6 | 15 | 8 | 19 | 19 | 15 | 31 | 10 | 7 | 15 | 6 | 24 |
| PRI (μs) | 0 | 605 | 607 | 600 | 601 | 603 | 626 | 613 | 615 | 653 | 656 | 602 | 609 | 608 | 607 | 647 |
| Pulse Number | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 |
| CF hopping coefficient | 2 | 12 | 10 | 16 | 8 | 17 | 19 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 10 | 0 | 25 | 28 | 9 |
| PRI (μs) | 651 | 604 | 600 | 603 | 620 | 626 | 615 | 602 | 633 | 654 | 640 | 600 | 630 | 605 | 636 | 625 |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skolnik, M. An introduction and overview of radar. In Radar Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 3, pp. 1.1–1.24. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, P.C.; Tao, S.; Tao, R.; Nan, Z. Detection of high-speed and accelerated target based on the linear frequency modulation radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2014, 8, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, S.R. Analysis of random step frequency radar and comparison with experiments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alland, S.; Stark, W.; Ali, M.; Hegde, M. Interference in automotive radar systems: Characteristics, mitigation techniques, and current and future research. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2019, 36, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, Z.j.; Xing, M.; Li, Y.; Bao, Z. High-resolution ISAR imaging with sparse stepped-frequency waveforms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4630–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, D.R. High Resolution Radar; Artech House, Inc.: Norwood, MA, USA, 1987; 484p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, H.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Range-velocity estimation of multiple targets in randomised stepped-frequency radar. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 1032–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, Y.C.; Kutyniok, G. Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eldar, Y.C. Sampling Theory: Beyond Bandlimited Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ruixue, Z.; Guifen, X.; Yue, Z.; Hengze, L. Coherent signal processing method for frequency-agile radar. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Qingdao, China, 16–18 July 2015; Volume 1, pp. 431–434. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L. Maximum unambiguous frequency of random PRI radar. In Proceedings of the 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Chen, Z.; Hu, P.; Bao, Q.; Xu, S. Coherent integration method of high-speed target for random PRI and staggered PW radar. In Proceedings of the 2019 PhotonIcs & Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Spring (PIERS-Spring), Rome, Italy, 17–20 June 2019; pp. 1037–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Thompson, J.; Huang, X.; Jin, T.; Zhou, Z. Random-frequency SAR imaging based on compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ran, L.; Xing, M.; Liu, M. Moving target detection for frequency agility radar by sparse reconstruction. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 094703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, J.; Olsen, K.E. Frequency agility radar with overlapping pulses and sparse reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 0061–0066. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Liu, Y. Compressed sensing for a frequency agile radar with performance guarantees. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (ChinaSIP), Chengdu, China, 12–15 July 2015; pp. 1057–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tao, T.; Leng, Y.; Leung, H. Frequency-agile coherent radar target Sidelobe suppression based on sparse Bayesian learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Nanjing, China, 6–8 May 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, L.; Wei, X.-z.; Li, X. Novel method of unambiguous moving target detection in pulse-Doppler radar with random pulse repetition interval. J. Radars 2012, 1, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Li, X. Aliasing-free moving target detection in random pulse repetition interval radar based on compressed sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Li, X. Velocity false target identification based on random pulse repetition interval compressed sensing radar. Acta Electron. Sin 2017, 45, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Quan, H.; Sha, M. Waveform optimization for SFA radar based on evolutionary particle swarm optimization. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2022, 44, 834–840. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L.; Tanner, J. Neighborliness of randomly projected simplices in high dimensions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9452–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Yin, W. On the global and linear convergence of the generalized alternating direction method of multipliers. J. Sci. Comput. 2016, 66, 889–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J. Genetic algorithms in machine learning. In Advanced Course on Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 146–168. [Google Scholar]
- Candes, E.J.; Romberg, J.K.; Tao, T. Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2006, 59, 1207–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambora, A.; Gupta, K.; Chopra, K. Genetic algorithm-A literature review. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COMITCon), Faridabad, India, 14–16 February 2019; pp. 380–384. [Google Scholar]
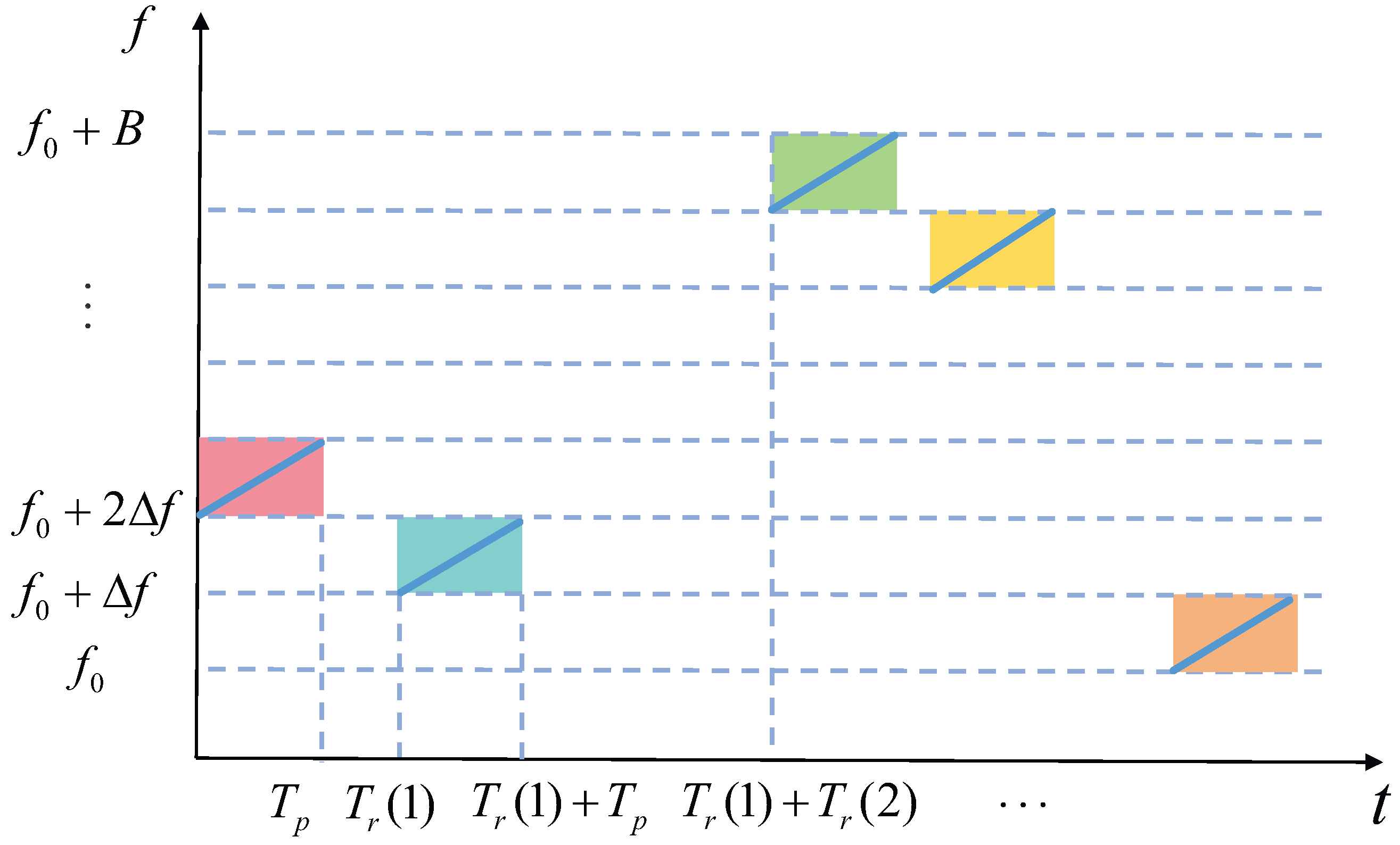


| PRI () | 600–663 s |
| Pulse width () | 20 s |
| Initial CF () | 3 GHz |
| Number of pulses () | 32 |
| Number of available CF points () | 32 |
| Pulse bandwidth () | 2 MHz |
| Frequency hopping Interval () | 2 MHz |
| Signal-to-noise ratio () | 0 dB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Jiang, Y. Joint Optimization of Carrier Frequency and PRF for Frequency Agile Radar Based on Compressed Sensing. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101796
Yang Z, Zheng H, Zhang Y, Yan J, Jiang Y. Joint Optimization of Carrier Frequency and PRF for Frequency Agile Radar Based on Compressed Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101796
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhaoxiang, Hao Zheng, Yongliang Zhang, Junkun Yan, and Yang Jiang. 2025. "Joint Optimization of Carrier Frequency and PRF for Frequency Agile Radar Based on Compressed Sensing" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101796
APA StyleYang, Z., Zheng, H., Zhang, Y., Yan, J., & Jiang, Y. (2025). Joint Optimization of Carrier Frequency and PRF for Frequency Agile Radar Based on Compressed Sensing. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101796







