The Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Urban Heat Islands: A Comparative Study of Beijing and Dalian (2003–2023)
Abstract
1. Introduction
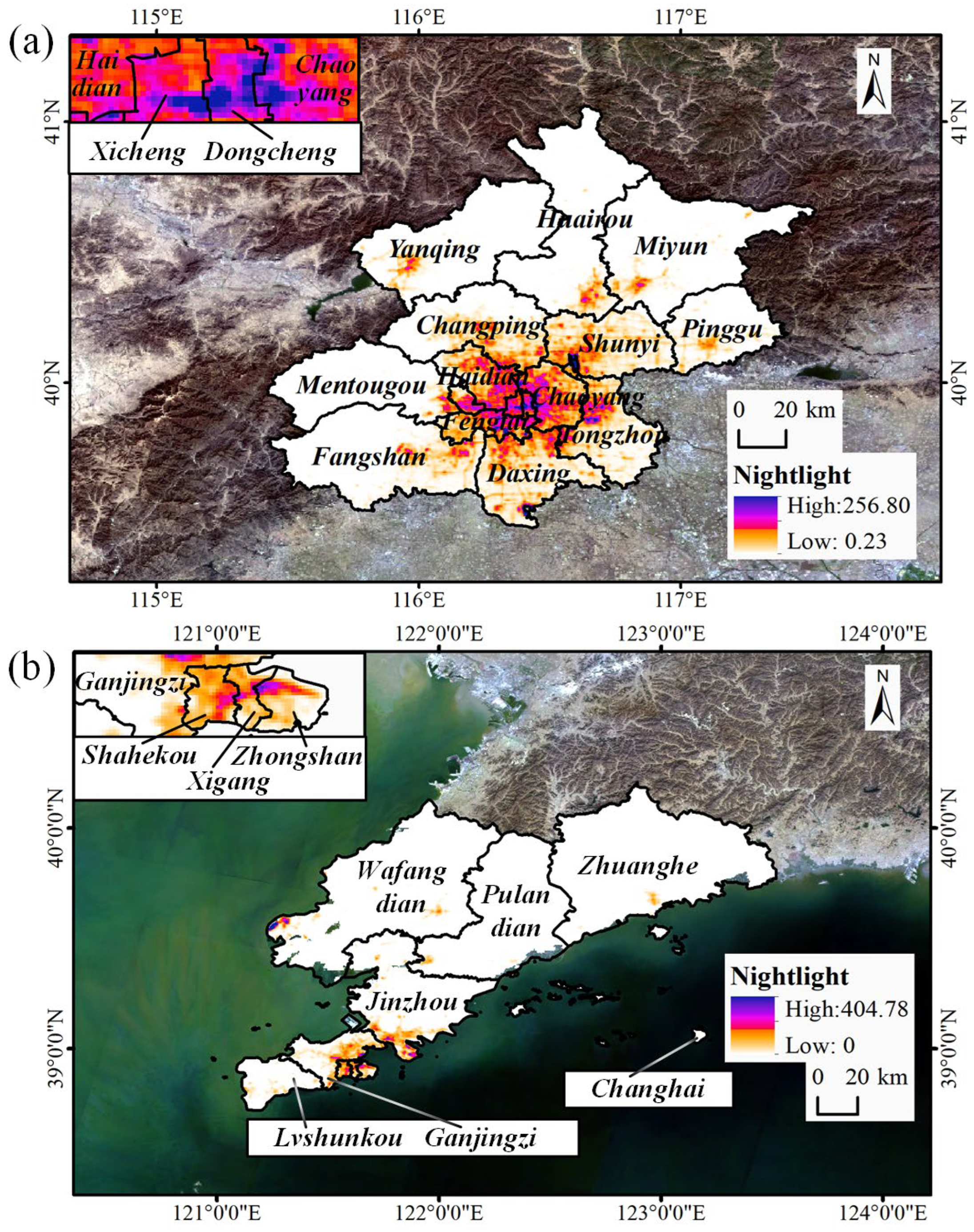
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Methods
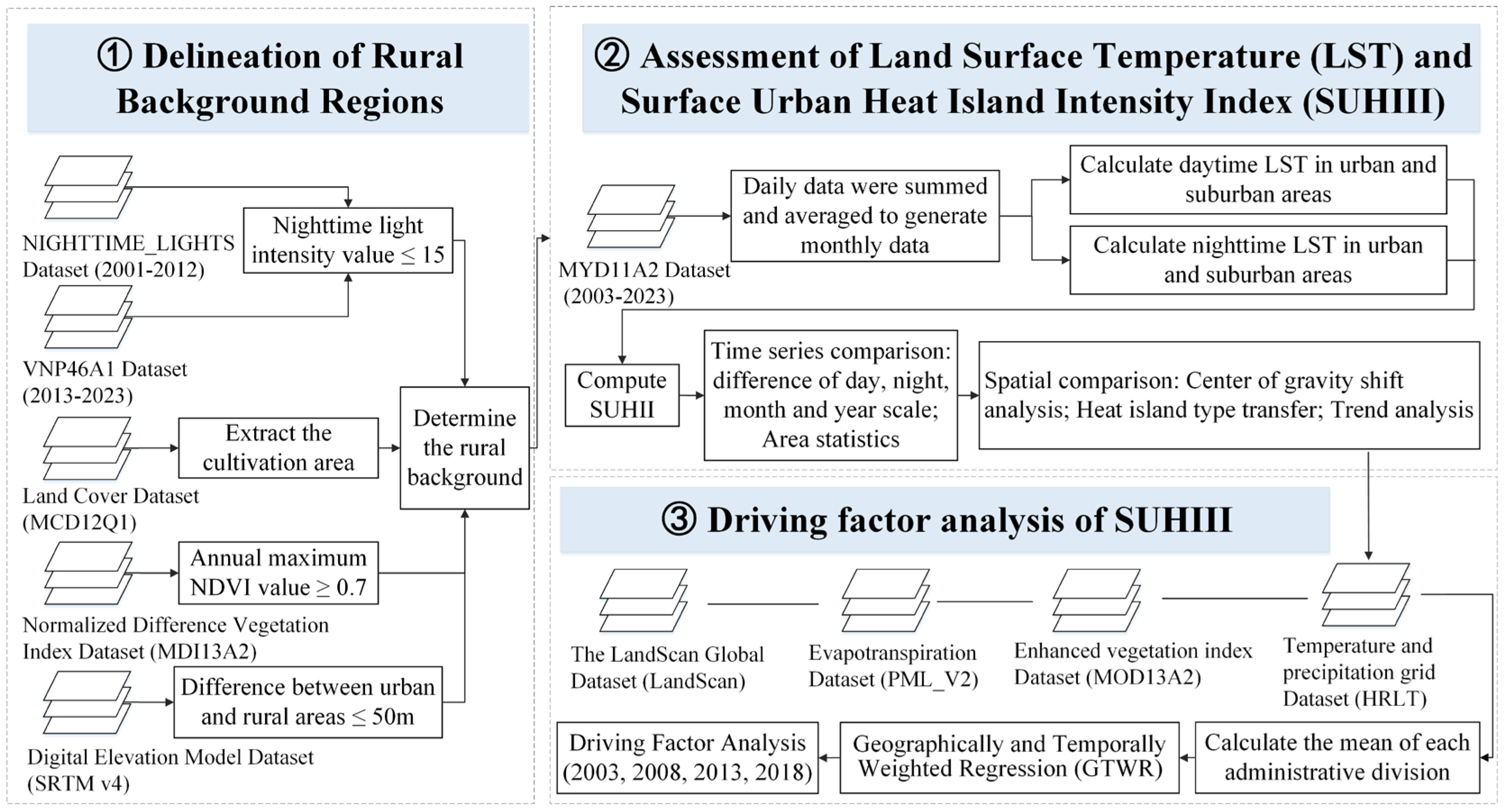
3.2.1. Delineation of Rural Background Regions
3.2.2. Assessment of LST and SUHIII
3.2.3. Driving Factor Analysis of SUHIII
4. Results
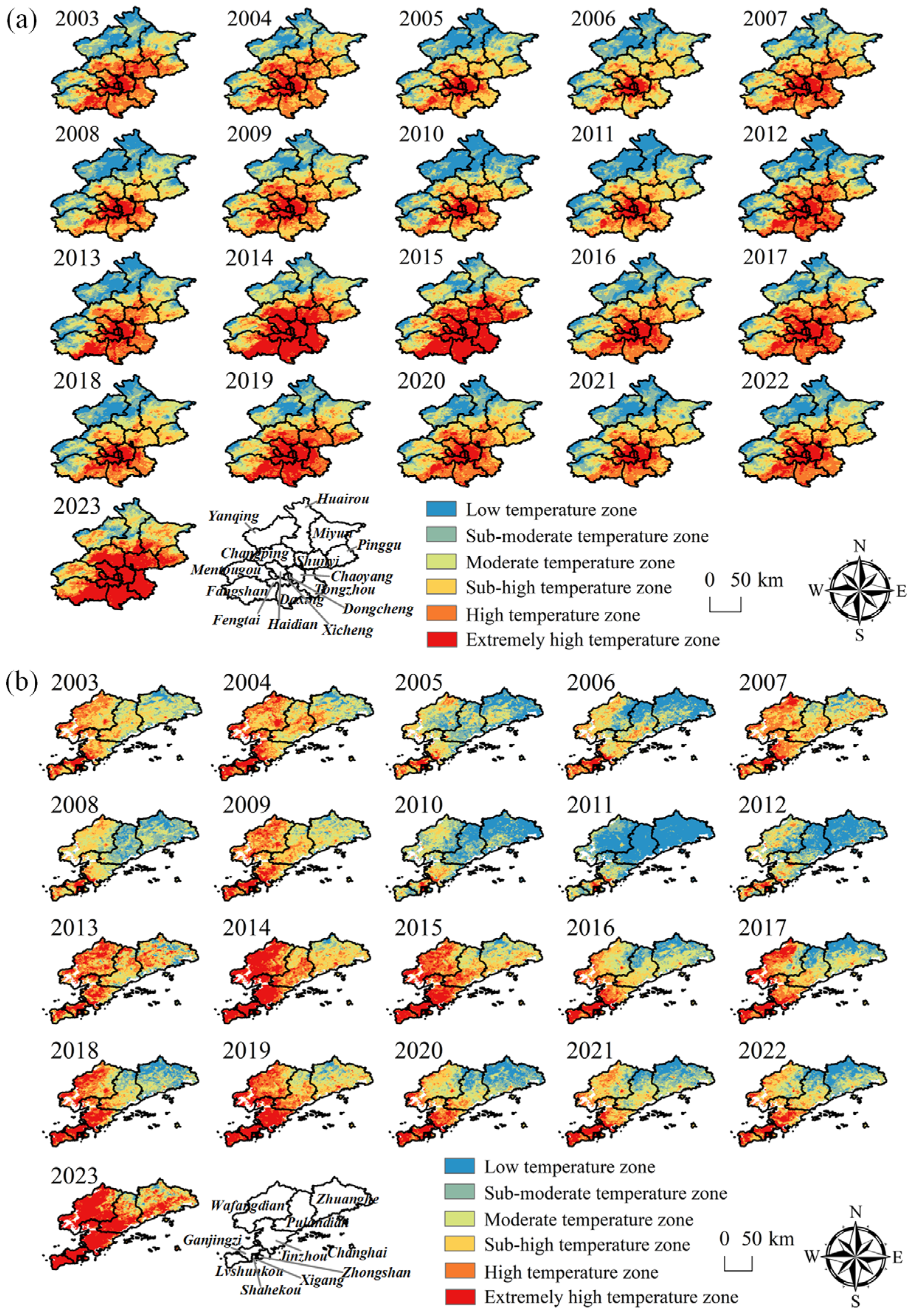
4.1. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of LSTs
4.1.1. Analysis of LSTs at the Monthly Scale
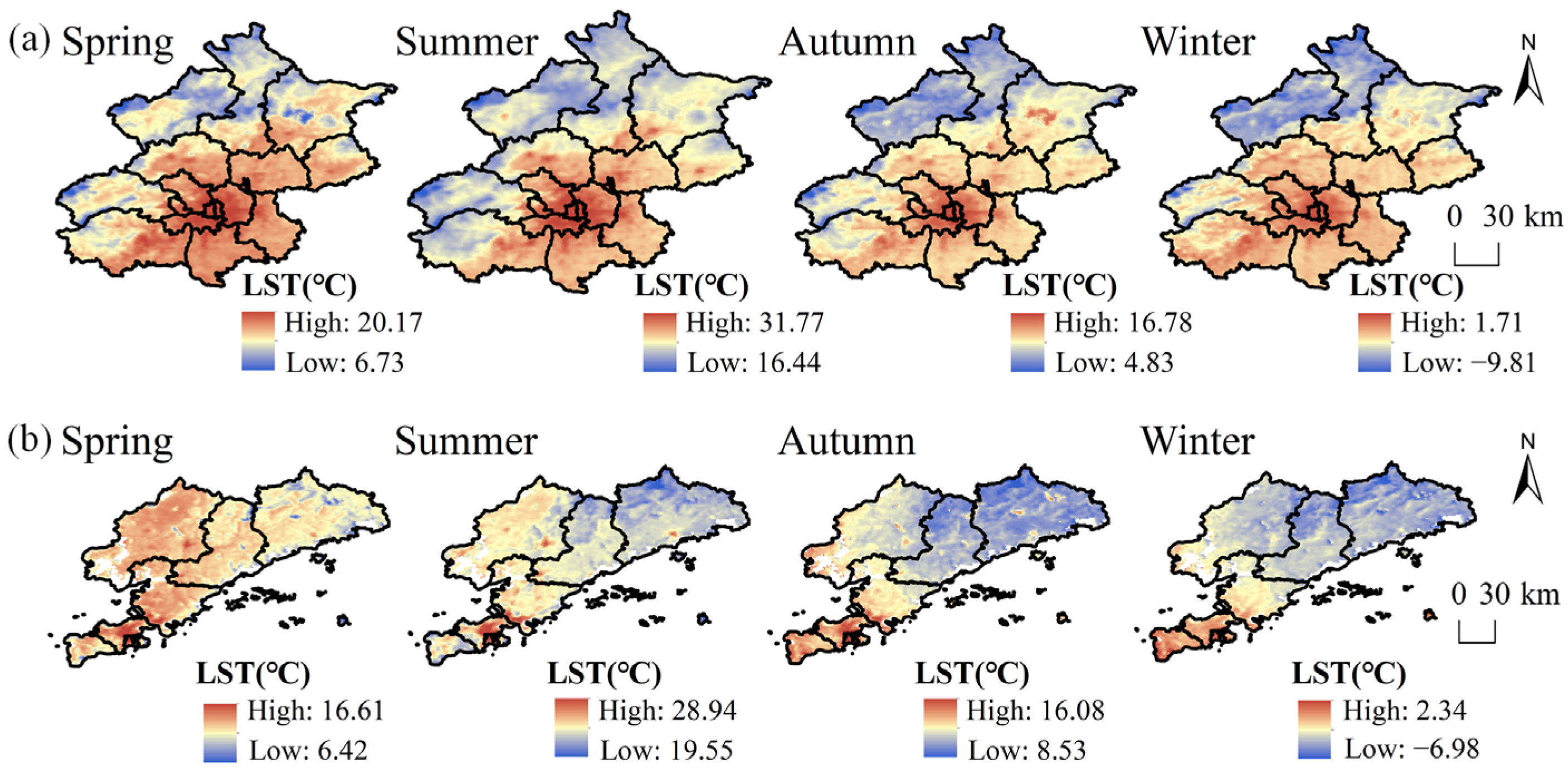
4.1.2. Analysis of LSTs at the Seasonal Scale
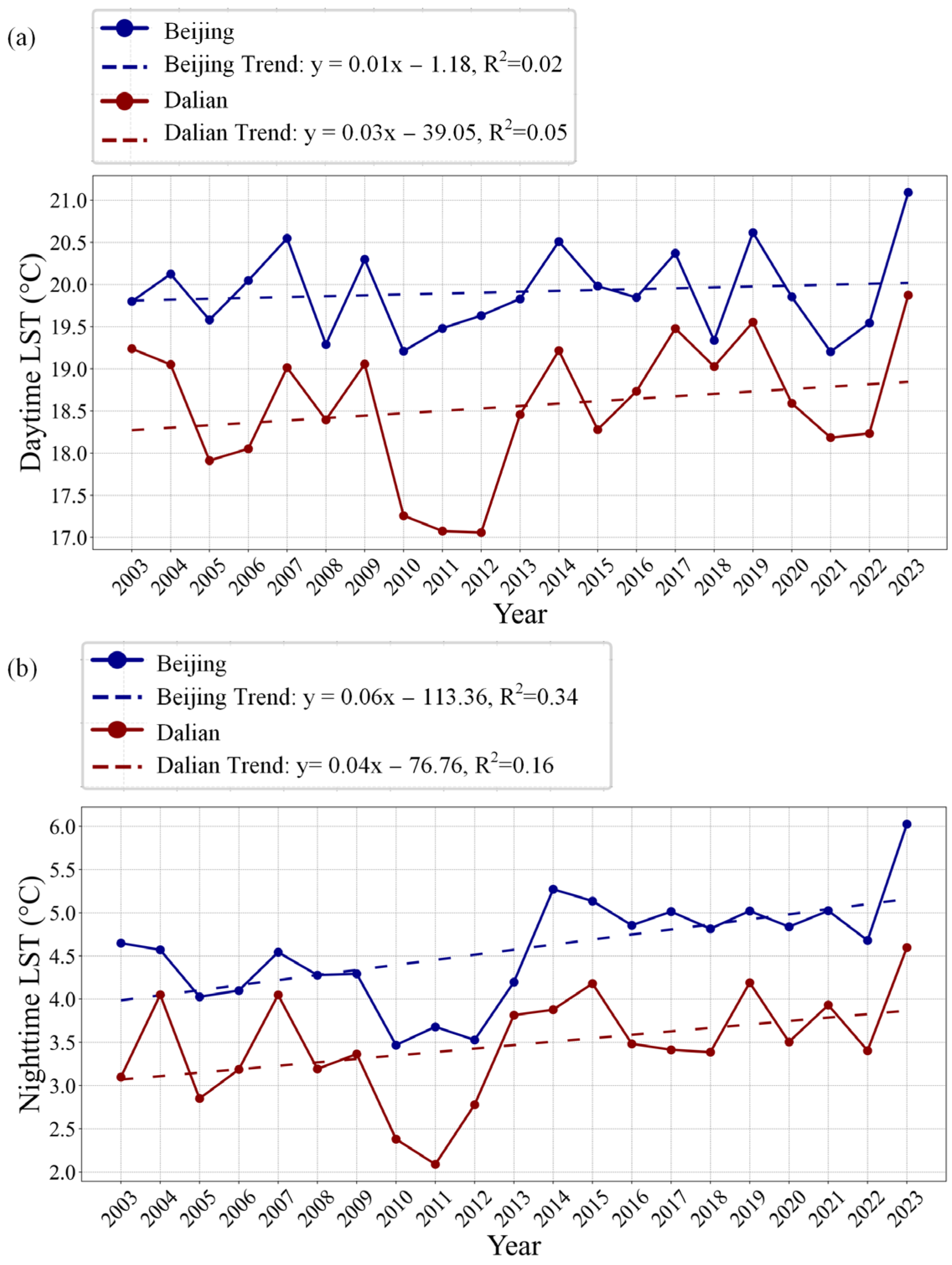
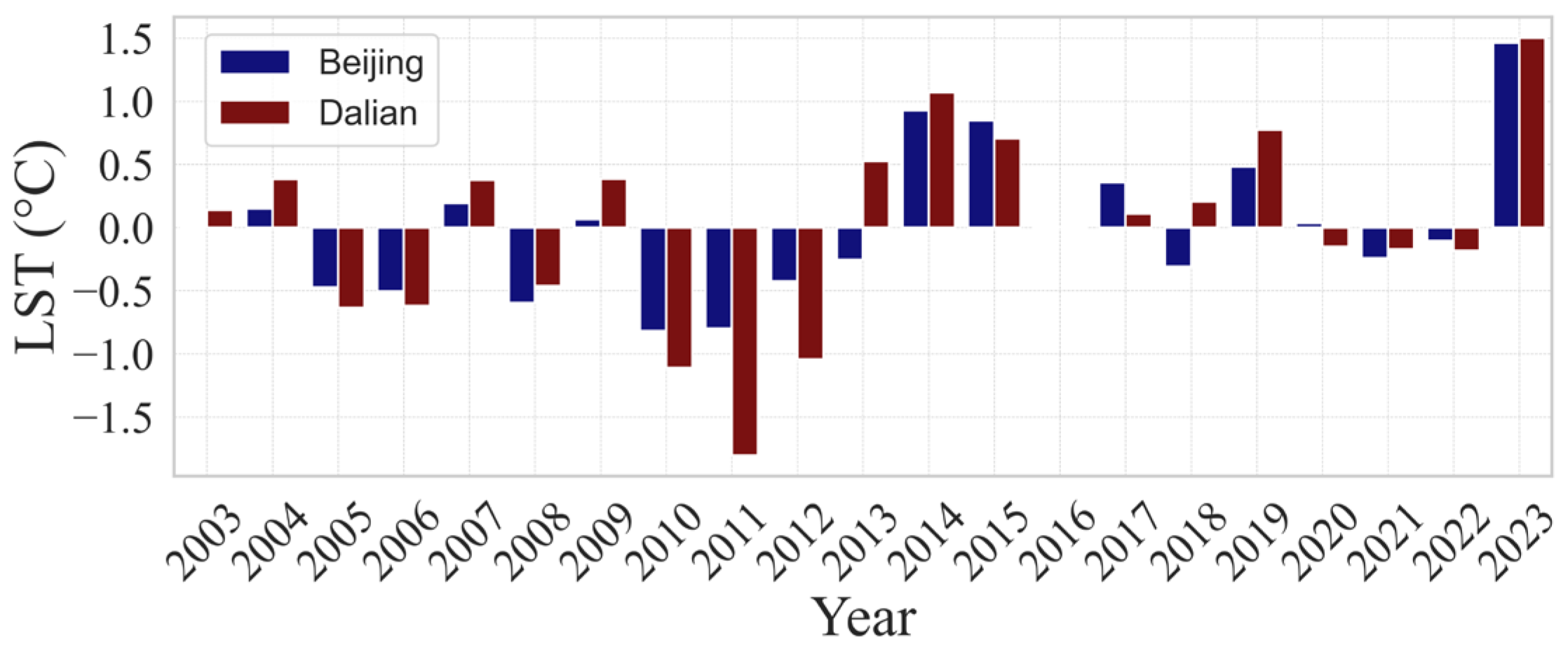
4.1.3. Analysis of LSTs at the Annual Scale
4.2. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of SUHIII
4.2.1. Analysis of SUHIII at the Monthly Scale
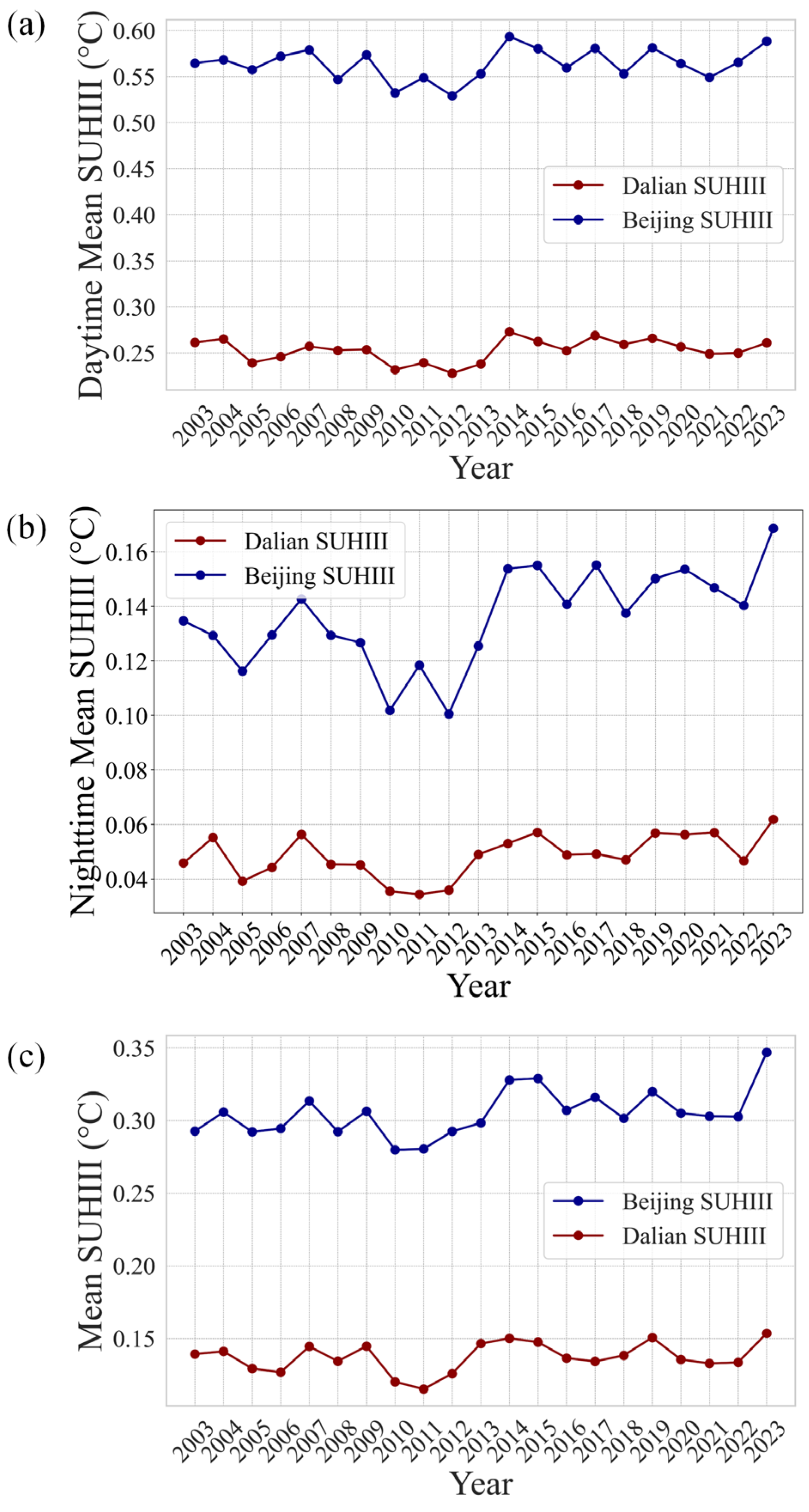
4.2.2. Analysis of SUHIII at the Annual Scale
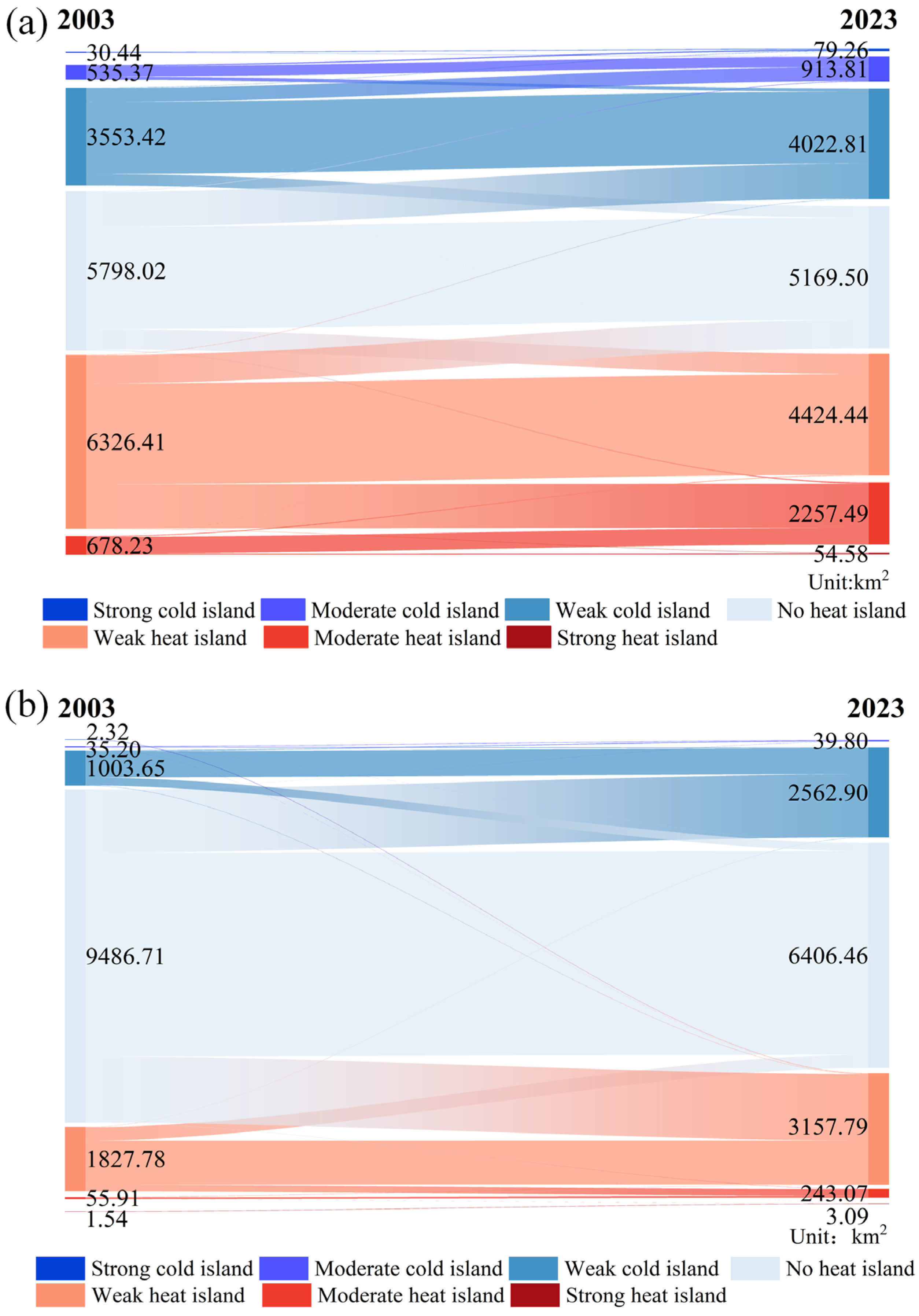
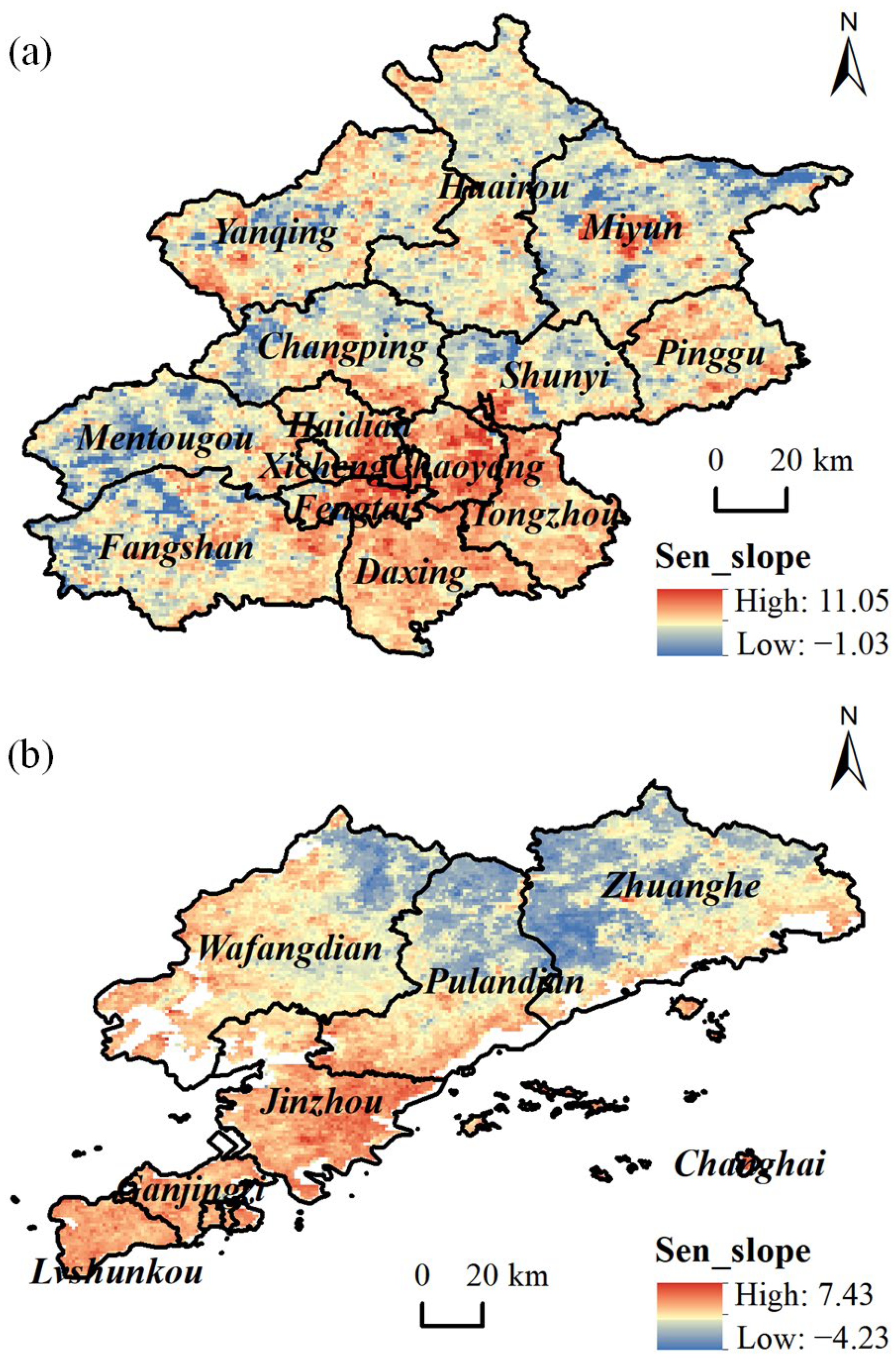
4.2.3. Analysis of SUHIII Centroid Shifts and Transfers
4.3. Driving Factors
4.3.1. Annual Mean Maximum Temperature (TEMP)
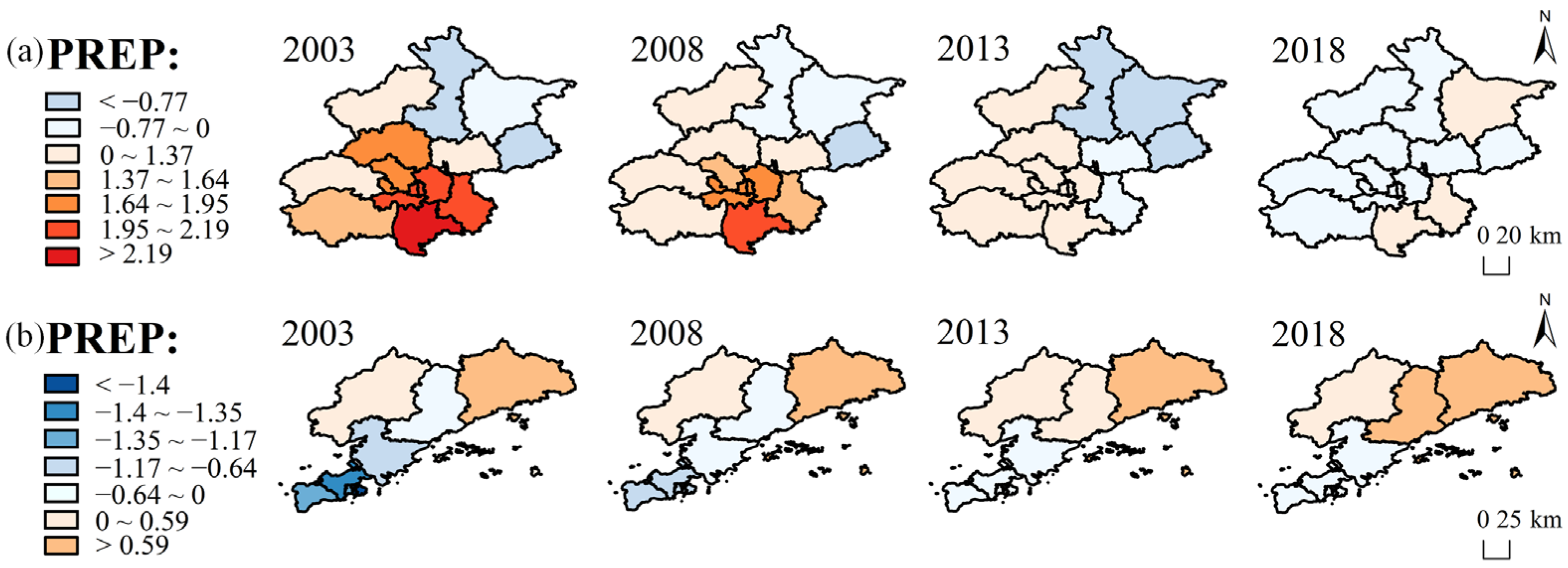
4.3.2. Precipitation (PREP)
4.3.3. Population Density (POP)
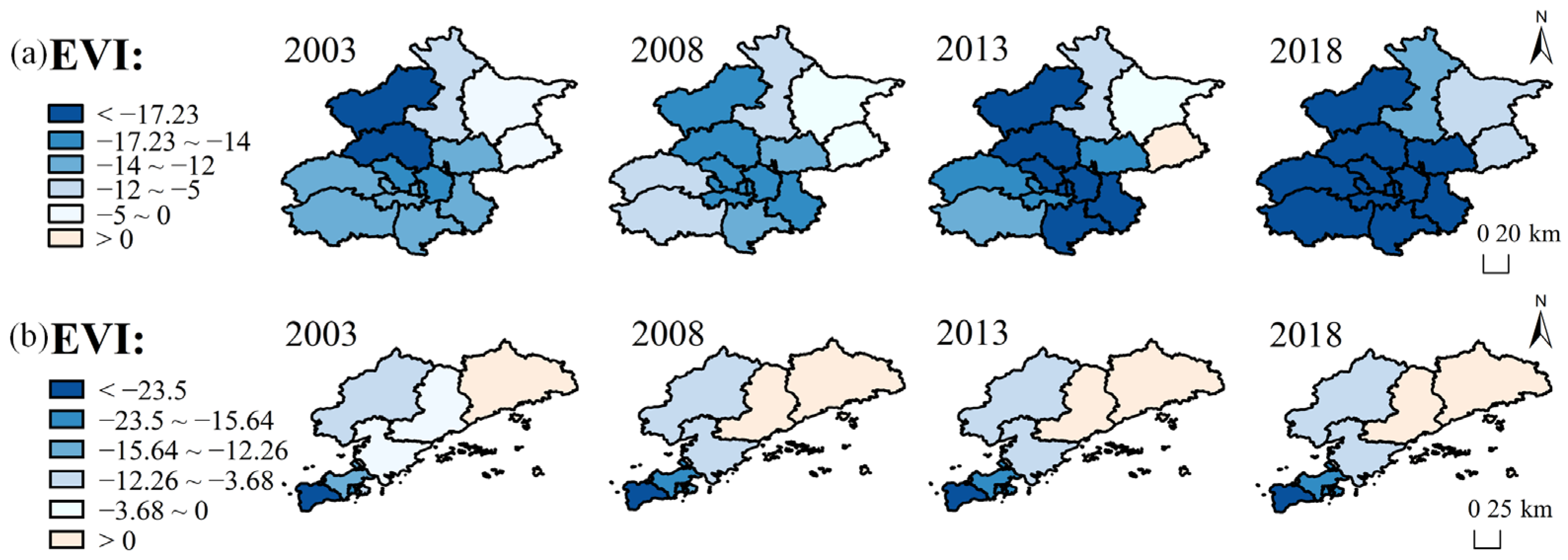
4.3.4. Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI)
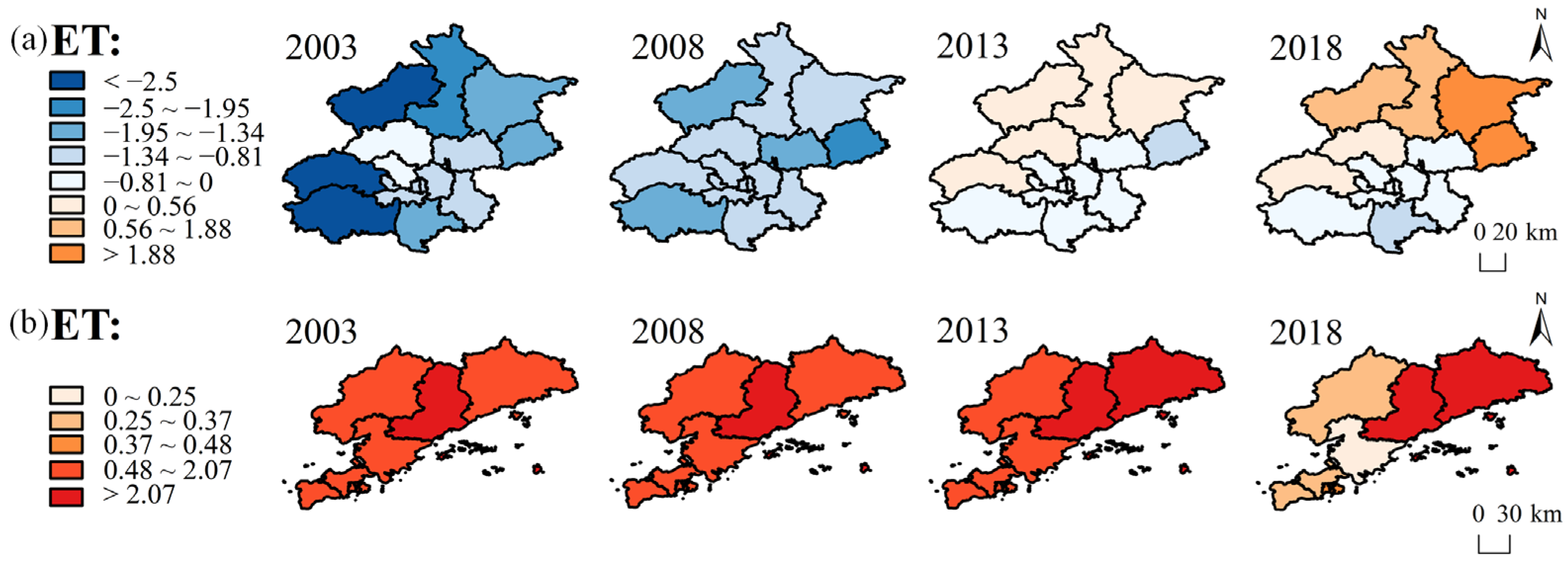
4.3.5. Evapotranspiration (ET)
5. Discussion
5.1. Trend Analysis
5.2. Recommendations for Urban Heat Island Mitigation
5.3. Outlook
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manley, G. On the Frequency of Snowfall in Metropolitan England. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1958, 84, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The Energetic Basis of the Urban Heat Island. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. City Size and the Urban Heat Island. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1973, 7, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarif, M.O.; Rimal, B.; Stork, N.E. Assessment of Changes in Land Use/Land Cover and Land Surface Temperatures and Their Impact on Surface Urban Heat Island Phenomena in the Kathmandu Valley (1988–2018). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un-Habitat. World Cities Report 2020: The Value of Sustainable Urbanization; United Nations Human Settlements Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vujovic, S.; Haddad, B.; Karaky, H.; Sebaibi, N.; Boutouil, M. Urban Heat Island: Causes, Consequences, and Mitigation Measures with Emphasis on Reflective and Permeable Pavements. CivilEng 2021, 2, 459–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, M.; Crisci, A.; Guerri, G.; Messeri, A.; Congedo, L.; Munafò, M. Surface Urban Heat Islands in Italian Metropolitan Cities: Tree Cover and Impervious Surface Influences. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 142334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Trevizo, M.E.; Martinez-Torres, K.E.; Armendariz-Lopez, J.F.; Santamouris, M.; Bojorquez-Morales, G.; Luna-Leon, A. Research Trends on Environmental, Energy and Vulnerability Impacts of Urban Heat Islands: An Overview. Energy Build. 2021, 246, 111051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Z.; Li, M.; He, B. Examination and Evaluation of Urban Heat Island Effect Based on Satellite Remote Sensing: Taking Wuhan as an Example. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2023, 38, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.V.; Paddon, A.; Jimenez, A. Review of World Urban Heat Islands: Many Linked to Increased Mortality. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2013, 135, 022101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Ren, G.; Zhang, P.; Xue, X.; Tysa, S.K.; Jia, W.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, S. PM2.5 Influence on Urban Heat Island (UHI) Effect in Beijing and the Possible Mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD035227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; An, H.; Lei, J.; Li, M.; Song, J.; Han, W. Heat Island Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Urban Ag- Glomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Zone Based on GEE. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; He, T.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xu, X.; Yang, J. Quantifying the Contribution of Land Use Change Based on the Effects of Global Climate Change and Human Activities on Urban Thermal Environment in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 1932–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, N. Positive Discourse Analysis under the Appraisal Theory—A Case Study of the White Paper “China ’s Policies and Actions on Climate Change”. Overseas Engl. 2023, 9, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. 8 Departments Issued the Notice on Deepening the Pilot Construction of Climate-Resilient Cities. Urban Rural Dev. 2023, 17, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. We Should Practice the Important Concept of “People ’s City” and Promote the Construction of Climate-Adaptive Cities. Explor. Free Views 2022, 12, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. A Comparative Study of Atmospheric and Surface Urban Heat Island Effects in China’s Major Cities. Clim. Chang. Res. 2023, 19, 605–615. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J.A. Sobrino Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Urban Heat Islands: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, C. Study on Urbanization and Urban Heat Island of TypicalUrban Agglomerations in China Based on Remote Sensing. J. Gansu Sci. 2021, 33, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, M. Analysis of the Impact of High Temperature Heat Wave on Thecharacteristics of Urban Heat Island Change in Dalian City. J. Hebei Acad. Sci. 2024, 41, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luan, Q. Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Island across China’s Three Main Urban Agglomerations. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, H. A Comparative Study on the Changes in Heat Island Effect in Chinese and Foreign Megacities. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2021, 33, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J. Analysis of SUHI Spatial Differences and Urban Planning Response in Xi’an and Nanjing Based on LCZ. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xi’an, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cheval, S.; Amihăesei, V.-A.; Chitu, Z.; Dumitrescu, A.; Falcescu, V.; Irașoc, A.; Micu, D.M.; Mihulet, E.; Ontel, I.; Paraschiv, M.-G.; et al. A Systematic Review of Urban Heat Island and Heat Waves Research (1991–2022). Clim. Risk Manag. 2024, 44, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Yang, C.; Liao, W.; Hu, L.; Liu, H.; Ren, B.; Li, X. Path Analysis of the Urban Greenspace Landscape Pattern Impacts on Land Surface Temperature: A Case Study in Changsha. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2023, 32, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Luo, T.; Liu, Q. Analysis of the Evolution of Urban Nighttime Light Environment Based on Time Series. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, Y.; Callaghan, C.T.; Ulbrichová, I.; Galanaki, A.; Kominos, T.; Abou Zeid, F.; Ibáñez-Álamo, J.D.; Suhonen, J.; Díaz, M.; Markó, G.; et al. EVI and NDVI as Proxies for Multifaceted Avian Diversity in Urban Areas. Ecol. Appl. 2023, 33, e2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y. Characteristics of Urban Heat Island in Chongqing in Recent 40 Years and Its Association with Weather Conditions. J. Arid Meteorol. 2022, 40, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xie, Y.; Cui, S.; Zhou, P.; Li, Y.; Sun, S. The Characteristics and Driving Forces of Summer Urban Heat Island in Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 3842–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Pei, T.; Cao, S.; Zhang, A.; Fan, Q.; Wang, J. Impacts of Urbanization on Vegetation Growth and Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Eamus, D.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Yu, Q. Use of Satellite Leaf Area Index Estimating Evapotranspiration and Gross Assimilation for Australian Ecosystems. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Gan, R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; McVicar, T.R.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Coupled Estimation of 500 m and 8-Day Resolution Global Evapotranspiration and Gross Primary Production in 2002–2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.-S.; Li, F.-M.; Zhang, F. HRLT: A High-Resolution (1 d, 1 Km) and Long-Term (1961–2019) Gridded Dataset for Surface Temperature and Precipitation across China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4793–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Baudouin, Y.; Gachon, P. An Alternative Method to Characterize the Surface Urban Heat Island. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haashemi, S.; Weng, Q.; Darvishi, A.; Alavipanah, S. Seasonal Variations of the Surface Urban Heat Island in a Semi-Arid City. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ren, G.; Zhou, J. Change of Urban Heat Island Intensity and Its Effect on Surface MeanAir Temperature Records in Southwest China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2008, 19, 722–730. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Luan, Q.; Quan, W.; Zhang, S. Research on Heat Environment of Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan Urban GroupBased on Multisource Satellite Data. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Ren, G.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R. Impact of Urban Heat Island Effect on the Heating and Cooling Loads of Residential Buildings in Tianjin City, China. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Gong, A. Spatial-Temporal Variations of Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity Induced by Different Definitions of Rural Extents in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Shuo, S.; Luan, Q.; Quan, W. Research on Quantitative Evaluations of Heat Islands for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 5818–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liao, S.; Cai, H.; Tian, P.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y. Combined Impacts of the Abnormal and Urban Heat Island Effect in Guiyang, a Typical Karst Mountain City in China. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Huang, N.; Xu, X.; Sun, Z.; Wu, C.; Yang, J. Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Evolution of the Urban Thermallandscape in Metropolitan Beijing between 2003 and 2017. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 475–489. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Song, L.; Xiang, Y. Responses of Extreme High Temperatures to Urbanization in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration in the Context of a Changing Climate. Meteorol. Appl. 2021, 28, e2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, T. Comparision Analyses of Equal Interval Method and Mean-Standard Deviation Method Used to Dalian Itate Urban Heat Island. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 11, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Quan, W. Research on Urban Surface Heat Envronnent Monitoring Indexes and Its Application. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, G. Quantifying Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Urban Expansion in Beijing during 1985–2013 with Rural-Urban Development Transformation. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Zou, W.; Zhao, B.; Fan, W. The Impact of High-Speed Railways on Urban Spatial Evolution: A Case Study of China’s Coastal Areas. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 175, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hou, X.; Yang, L. Study on the Dynamic Evolution and Driving Forces of High-Quality Development of Coal Cities in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Su, M. Relationship between Urban Construction Land Expansion and Population/Economic Growth in Liaoning Province, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Jia, K.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Land Use Change in Yinchuan Plain from 1980 to 2018. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 8008–8018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression for Modeling Spatio-Temporal Variation in House Prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Zhao, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhou, K.; Mu, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Huo, X. Construction of a Seasonal Difference-Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression (SD-GTWR) Model and Comparative Analysis with GWR-Based Models for Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) in Hubei Province (China). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2016, 13, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Driving Mechanisms of Landscape Patterns on Habitat Quality in a City Undergoing Rapid Urbanization Based on GTWR and MGWR: The Case of Nanjing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, P.; Wang, M.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. The Observed Features and Some Possible Reasons of Annual Temperature Extremes over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region for a Century Long-term Based on Newly Constructed Daily Observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 4248–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.-K. Human Influence Can Explain the Widespread Exceptional Warmth in 2023. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esper, J.; Torbenson, M.; Büntgen, U. 2023 Summer Warmth Unparalleled over the Past 2,000 Years. Nature 2024, 631, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.G.; Leblanc, S. Parametric (Modified Least Squares) and Non-Parametric (Theil–Sen) Linear Regressions for Predicting Biophysical Parameters in the Presence of Measurement Errors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ottle, C.; Bréon, F.-M.; Nan, H.; Zhou, L.; Myneni, R.B. Surface Urban Heat Island Across 419 Global Big Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Hao, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Liao, C. Influence of Urban Development on Surface Heat Island Effect and Its Relationship: A Case of Hefei and Nanchang. J. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 18, 602–616. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, G. Assessing the Value of Urban Green Infrastructure Ecosystem Services for High-Density Urban Management and Development: Case from the Capital Core Area of Beijing, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzini, S.; Despini, F.; Beltrami, L.; Fabbi, S.; Muscio, A.; Teggi, S. Identification of SUHI in Urban Areas by Remote Sensing Data and Mitigation Hypothesis through Solar Reflective Materials. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Nichol, J.E.; To, P.H.; Wang, J. A Simple Method for Designation of Urban Ventilation Corridors and Its Application to Urban Heat Island Analysis. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iungman Bensignor, T. Urban Heat Islands and Nature-Based Solutions: Insights into Health Impacts and Urban Planning Determinants. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Pompeu Fabra: Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, 2024. [Google Scholar]









| Corresponding Variable | Data | Resolution | Band | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation | CGIAR/SRTM90_V4 | 90 m | Elevation | 2000 |
| NDVI | MODIS/061/MOD13A2 | 1000 m | NDVI, Detailed QA | 2003–2023 year by year |
| Cultivation area | MODIS/006/MCD12Q1 | 500 m | LC_Type1, QC | 2003–2020 year by year |
| Nightlight | NOAA/DMSP-OLS/NIGHTTIME_LIGHTS | 927.67 m | stable_lights | 2003–2012 year by year |
| Nightlight | NOAA/VIIRS/001/VNP46A2 | 500 m | Gap_Filled_DNB_BRDF_Corrected_NTL | 2013–2023 year by year |
| ET | CAS/IGSNRR/PML | 500 m | Ec, Es, Ei, ET_water | 2003, 2008, 2013, 2018 |
| POP | LandScan Global | 1000 m | / | 2003, 2008, 2013, 2018 |
| EVI | MODIS/061/MOD13A2 | 1000 m | EVI | 2003, 2008, 2013, 2018 |
| TEMP and PREP | HRLT | 1000 m | Maxtmp, prep | 2003, 2008, 2013, 2018 |
| Impervious surface | CLCD | 30 m | Impervious surface | 2003, 2008, 2013, 2018 |
| Beijing LSTs (°C) | Dalian LSTs (°C) | |
|---|---|---|
| Spring | 15.28 | 13.05 |
| Summer | 25.12 | 23.90 |
| Autumn | 11.77 | 11.67 |
| Winter | 0.54 | 0.77 |
| Mean | 13.18 | 12.35 |
| Standard Deviation | 10.15 | 9.46 |
| 2003 | 2008 | 2013 | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing TEMP | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.75 |
| Dalian TEMP | 2.15 | 2.28 | 2.38 | 2.48 |
| Beijing PREP | 1.34 | 1.07 | −0.06 | −0.23 |
| Dalian PREP | −0.62 | −0.27 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| Beijing POP | 0.08 | 0.03 | −0.01 | −0.04 |
| Dalian POP | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Beijing EVI | −11.46 | −12.38 | −14.33 | −17.89 |
| Dalian EVI | −7.74 | −9.15 | −10.04 | −10.56 |
| Beijing ET | −1.41 | −1.25 | −0.15 | 0.40 |
| Dalian ET | 1.89 | 1.69 | 1.34 | 1.05 |
| Year | Beijing ET (mm/d) | Beijing SUHIII (°C) | Dalian ET (mm/d) | Dalian SUHIII (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 1.38 | 1.34 | 1.46 | 0.70 |
| 2008 | 1.48 | 1.59 | 1.40 | 0.93 |
| 2013 | 1.41 | 1.50 | 1.47 | 0.45 |
| 2018 | 1.31 | 1.56 | 1.26 | 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Y.; Gao, C.; Yu, W.; Zhao, E.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, J. The Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Urban Heat Islands: A Comparative Study of Beijing and Dalian (2003–2023). Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101793
Meng Y, Gao C, Yu W, Zhao E, Li W, Wang R, Zhao Y, Zhao H, Zeng J. The Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Urban Heat Islands: A Comparative Study of Beijing and Dalian (2003–2023). Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101793
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Yaru, Caixia Gao, Wenping Yu, Enyu Zhao, Wan Li, Renfei Wang, Yongguang Zhao, Hang Zhao, and Jian Zeng. 2025. "The Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Urban Heat Islands: A Comparative Study of Beijing and Dalian (2003–2023)" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101793
APA StyleMeng, Y., Gao, C., Yu, W., Zhao, E., Li, W., Wang, R., Zhao, Y., Zhao, H., & Zeng, J. (2025). The Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Urban Heat Islands: A Comparative Study of Beijing and Dalian (2003–2023). Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101793







