Machine Learning-Based Estimation of foF2 and MUF(3000)F2 Using GNSS Ionospheric TEC Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
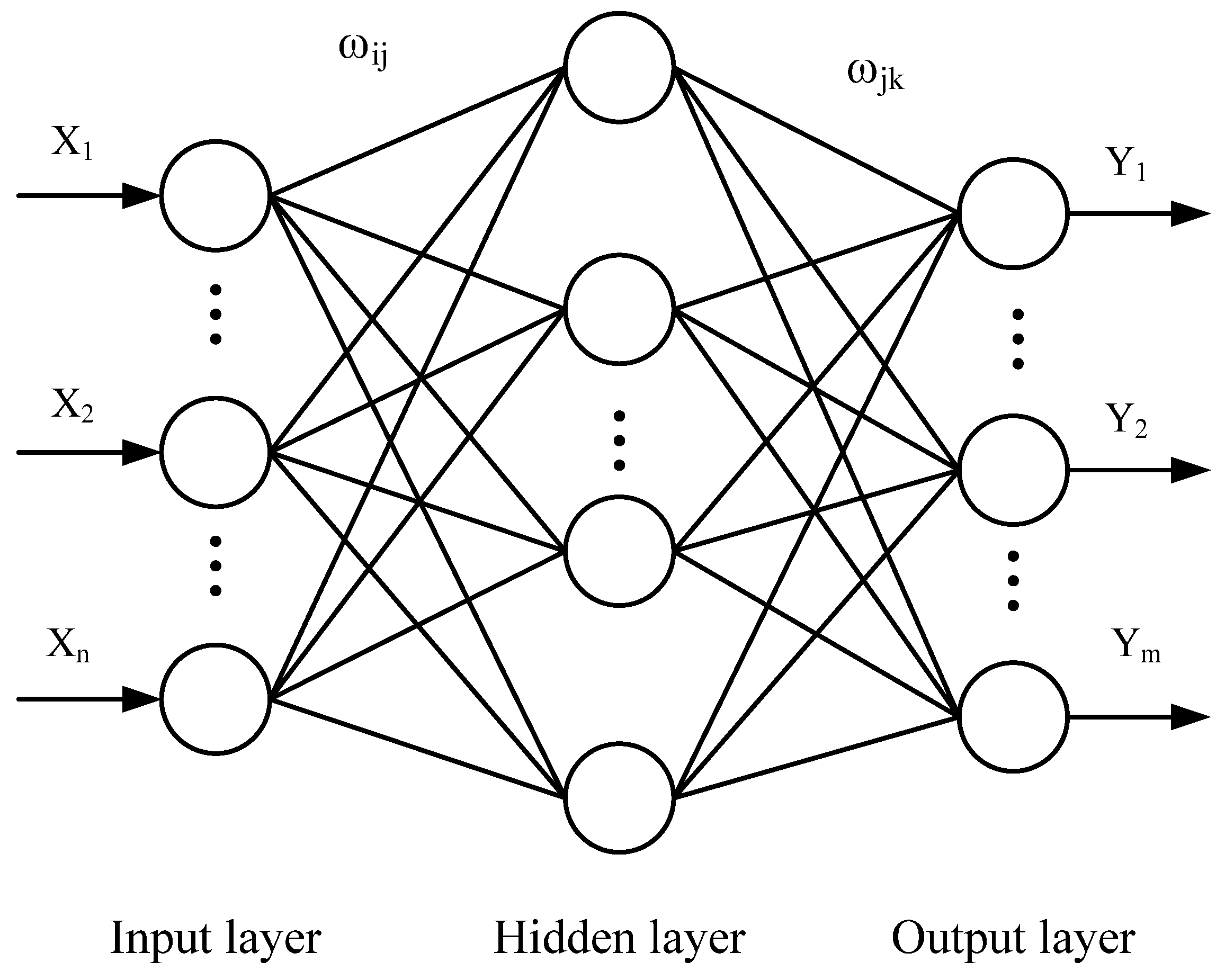
2.1. Description of Machine Learning Algorithms
2.1.1. RF Algorithm
2.1.2. SVM Algorithm
2.1.3. BPNN Algorithm
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Input and Output Parameters
2.3.1. Solar Activity Parameters
2.3.2. Geomagnetic Activity Parameters
2.3.3. Parameters of Spatiotemporal Information
2.4. Model Setting
2.5. Error Analysis Method
3. Results
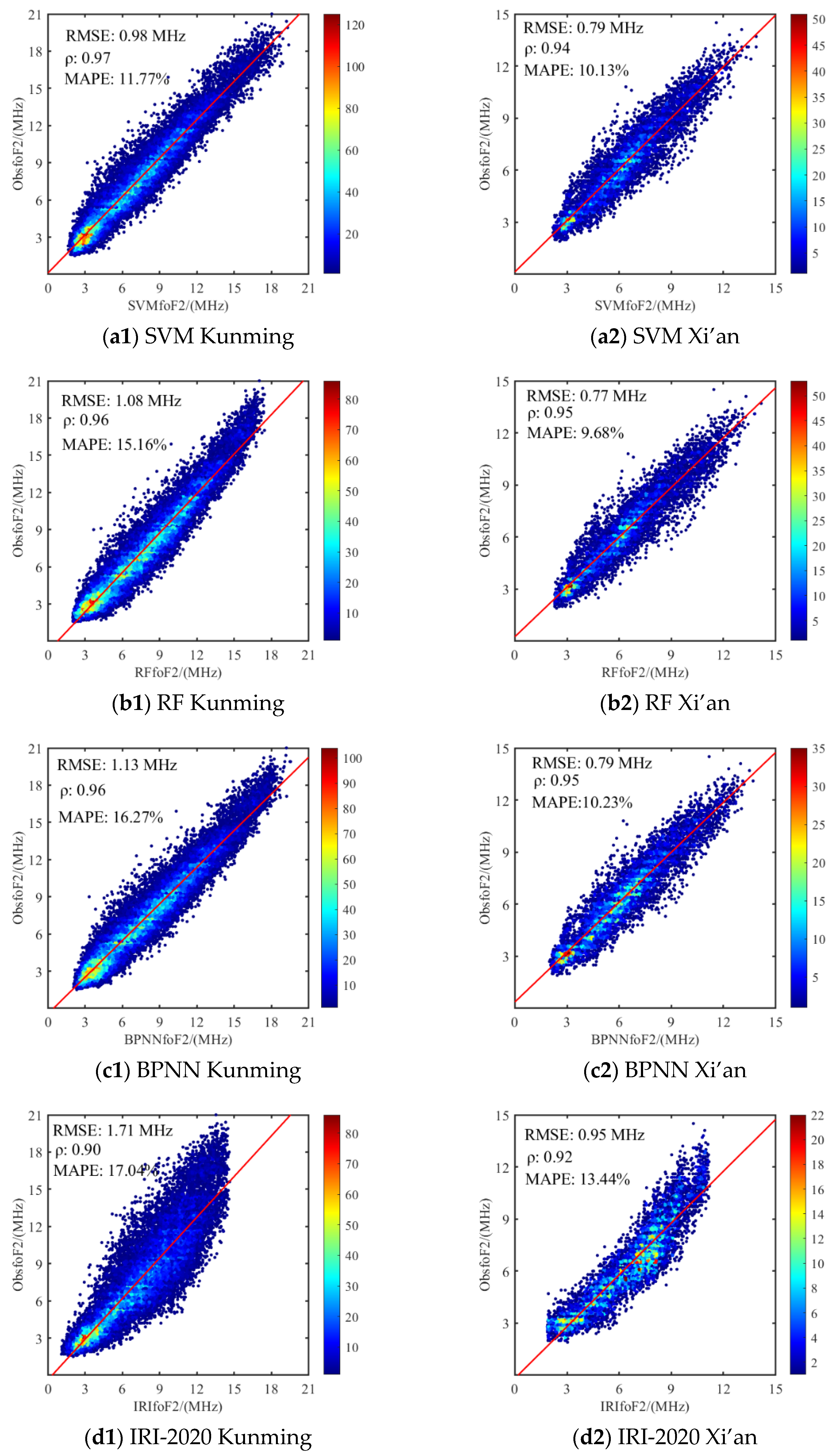
3.1. Model Performance and the foF2 Estimation Error
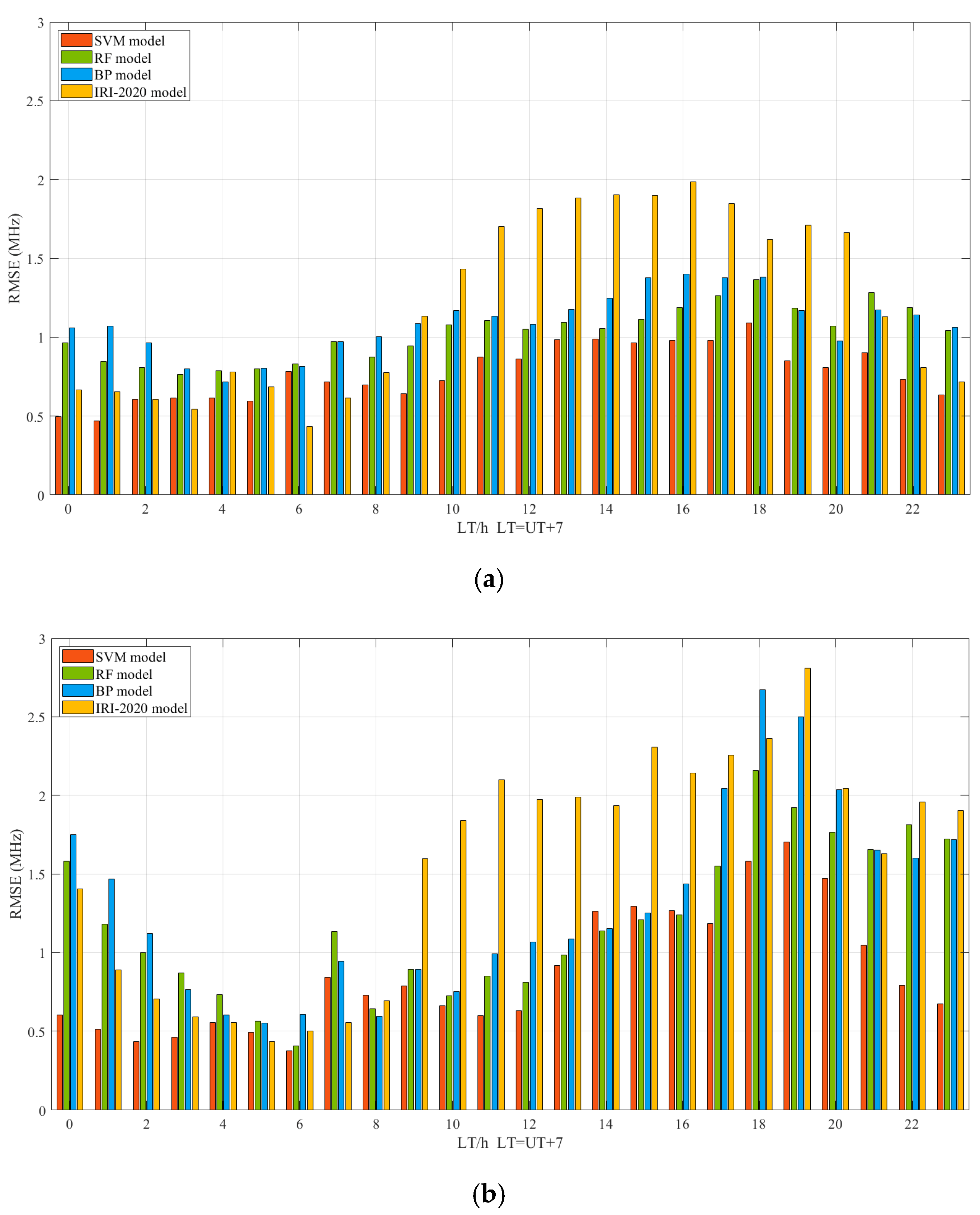
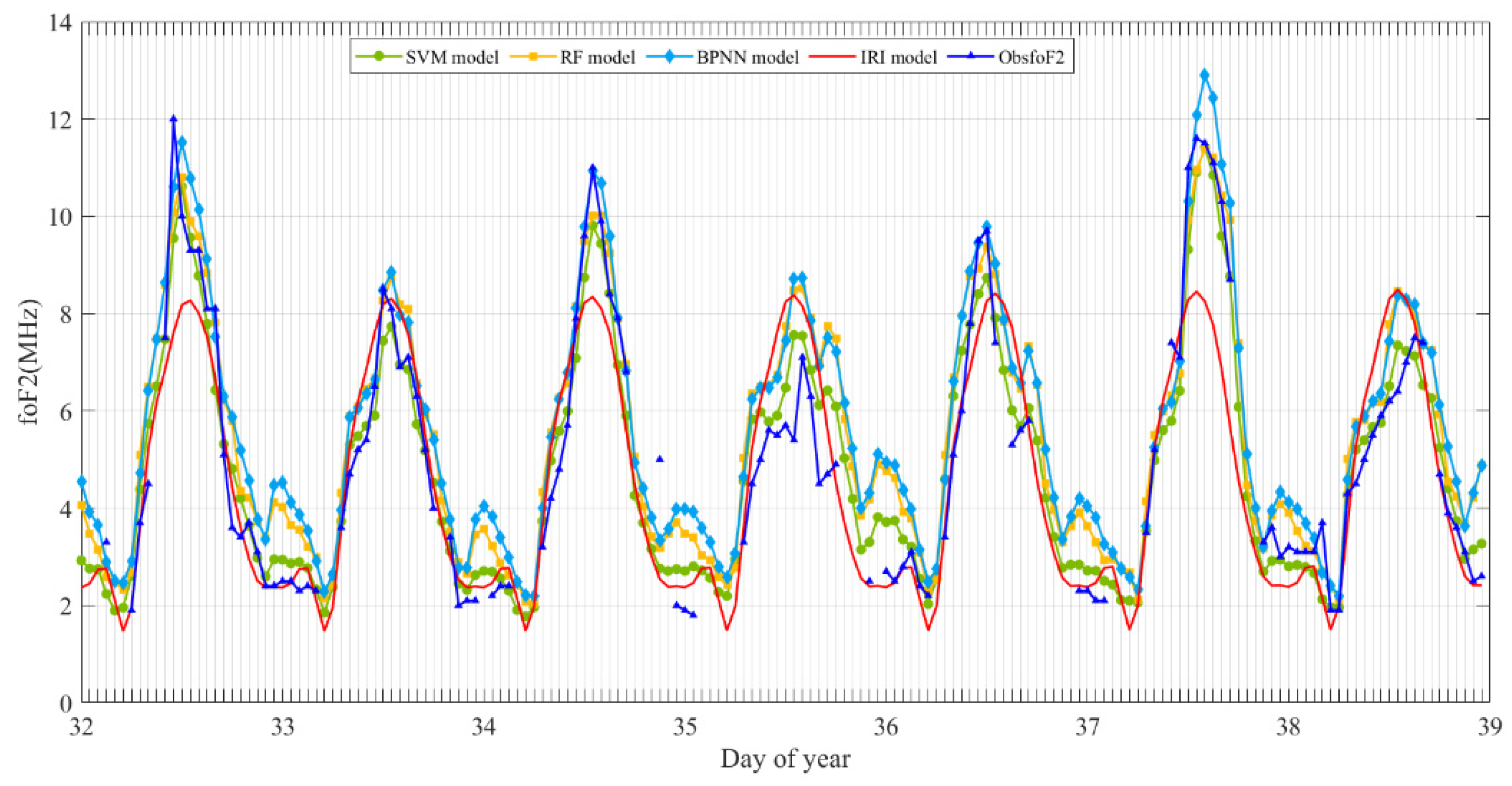
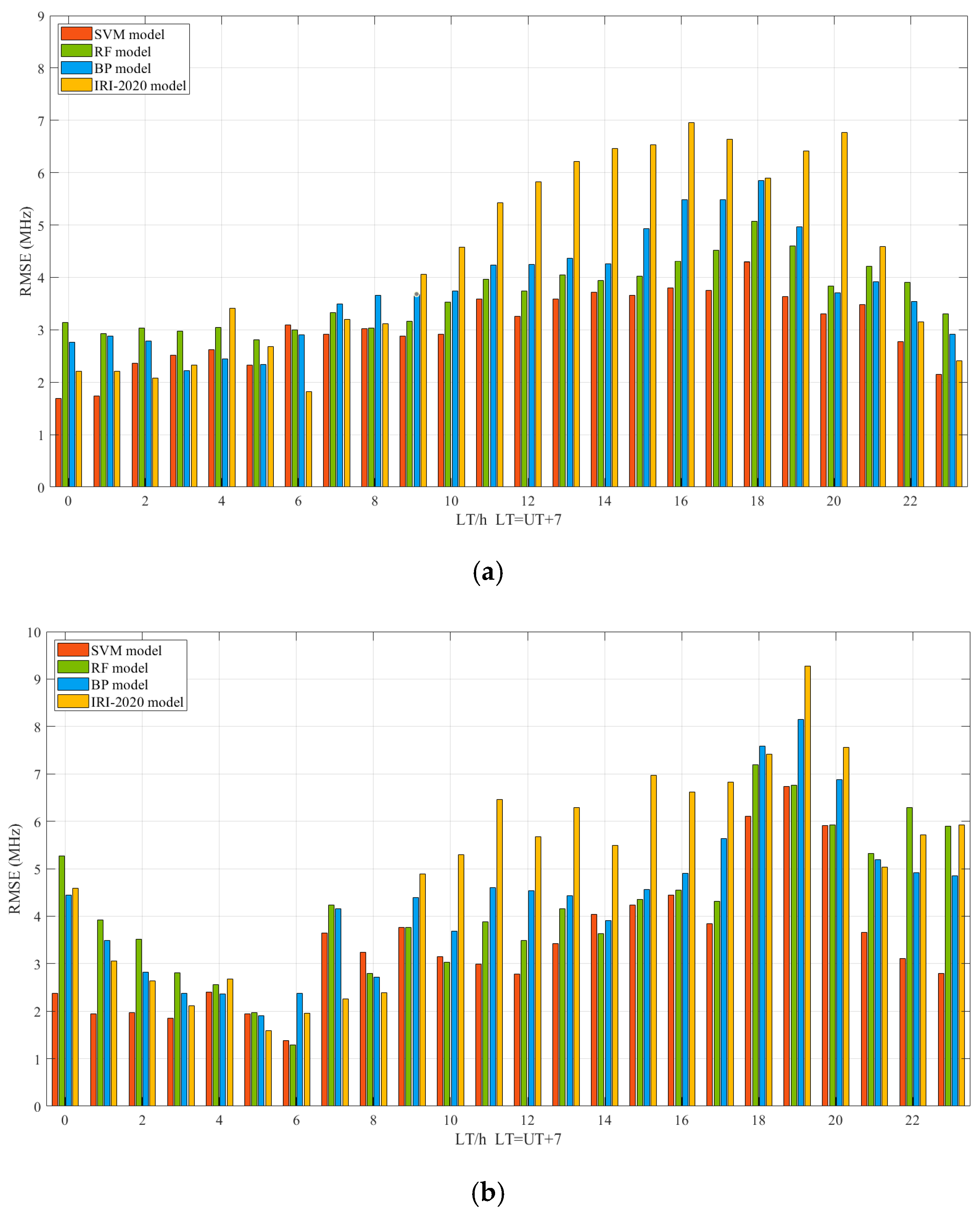
- Diurnal variations of foF2 RMSE values in machine learning models
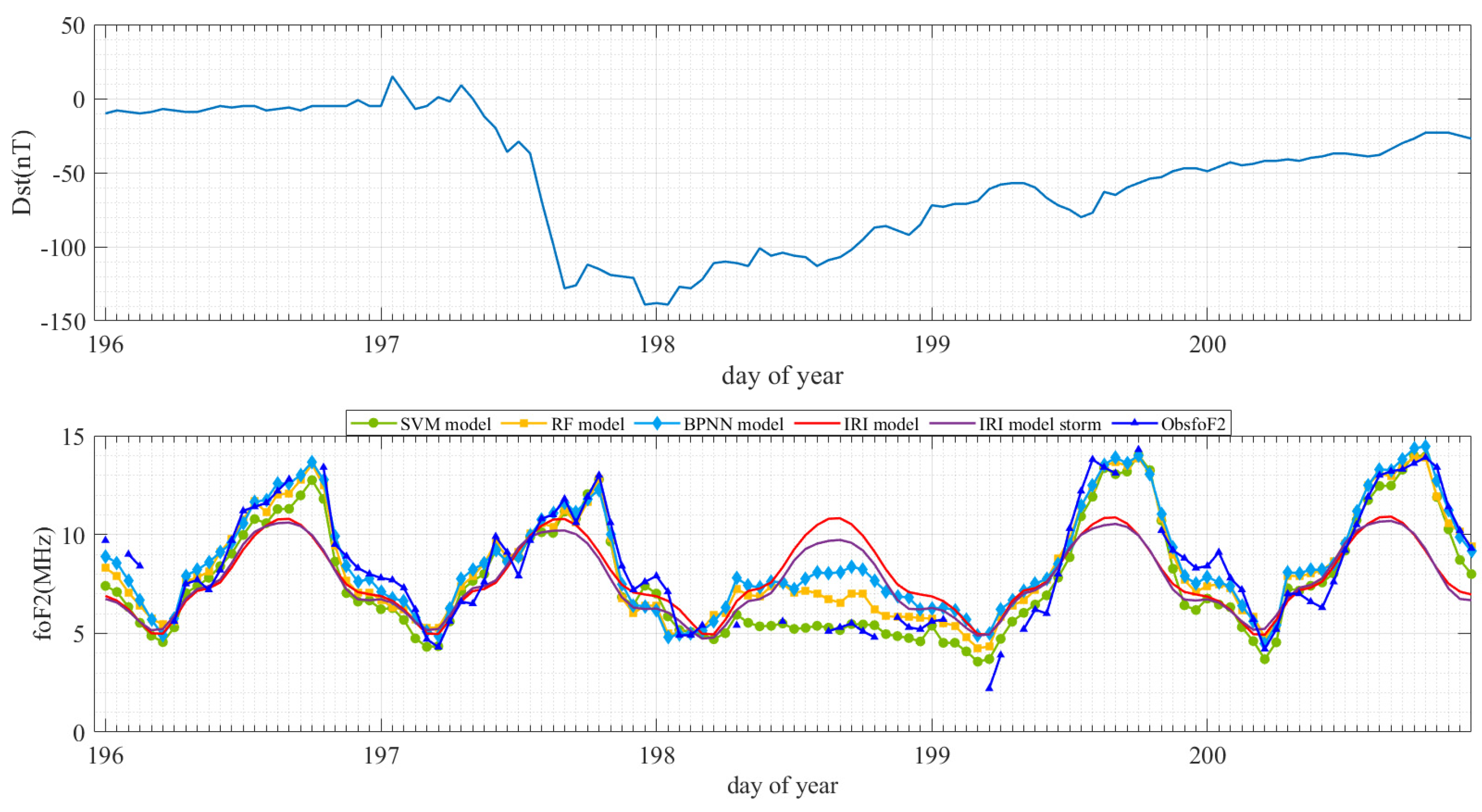
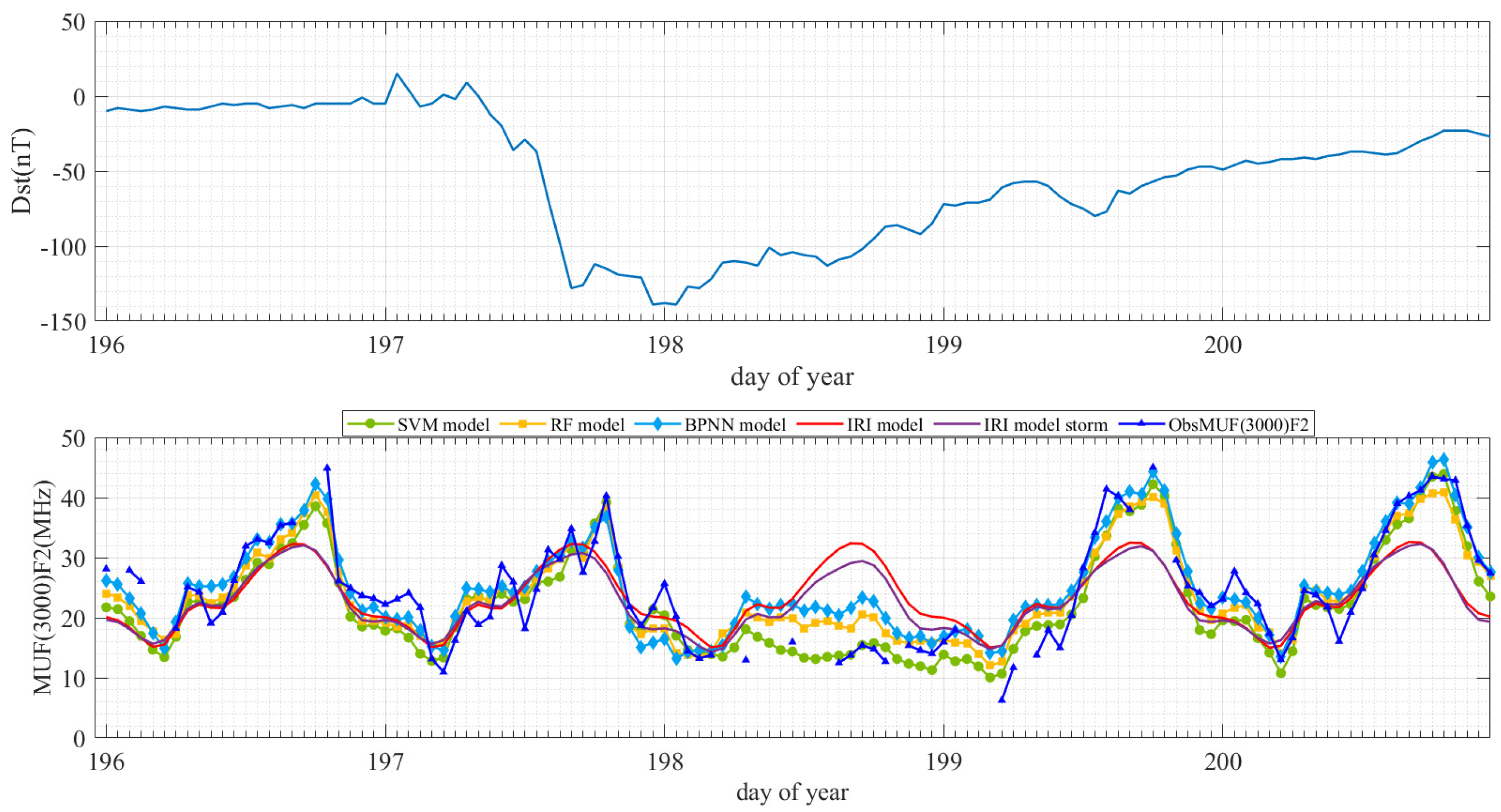
- Performance evaluation of the models in estimating foF2 under quiet and disturbed ionospheric conditions
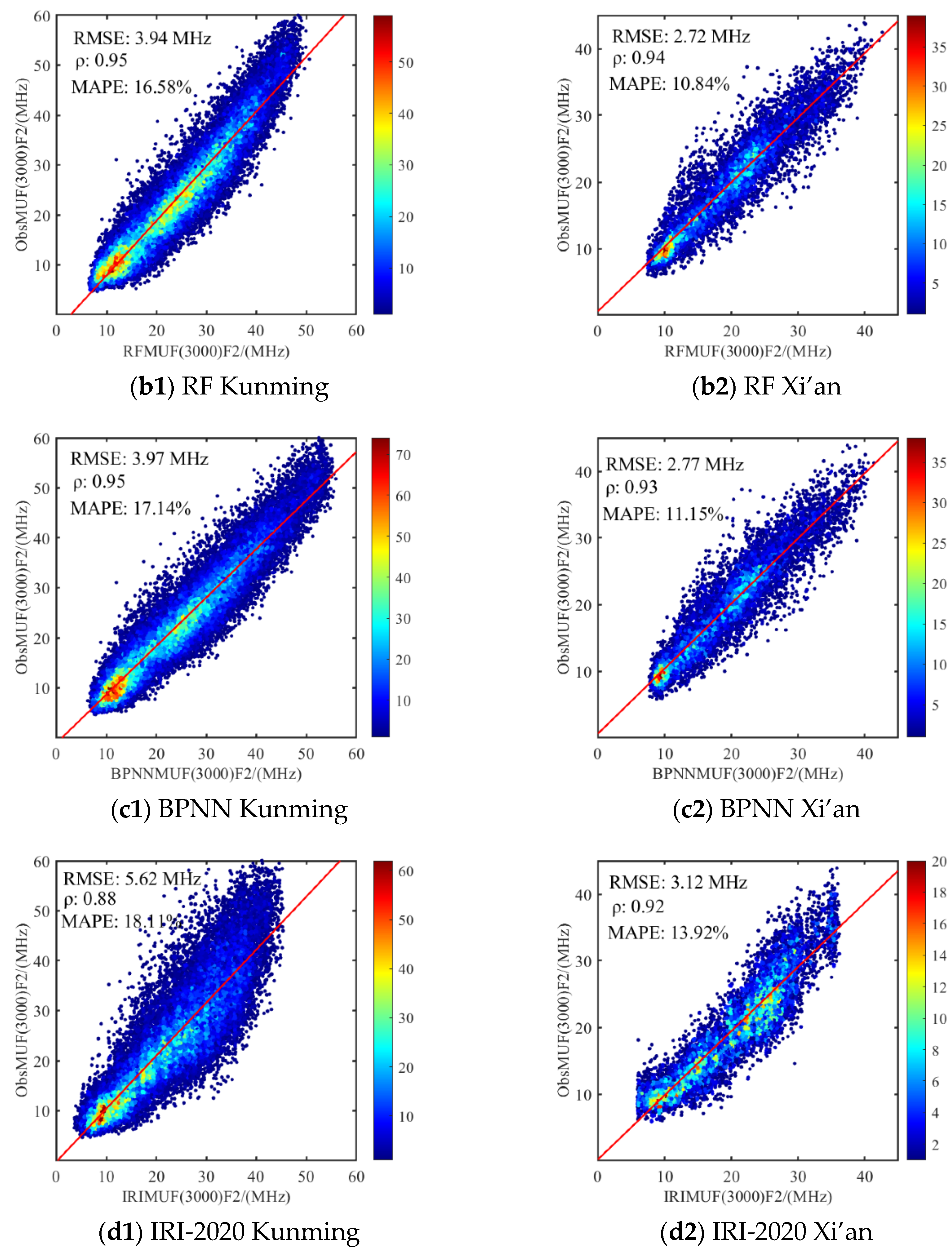
3.2. Estimation Results of MUF(3000)F2 and Model Performance Evaluation
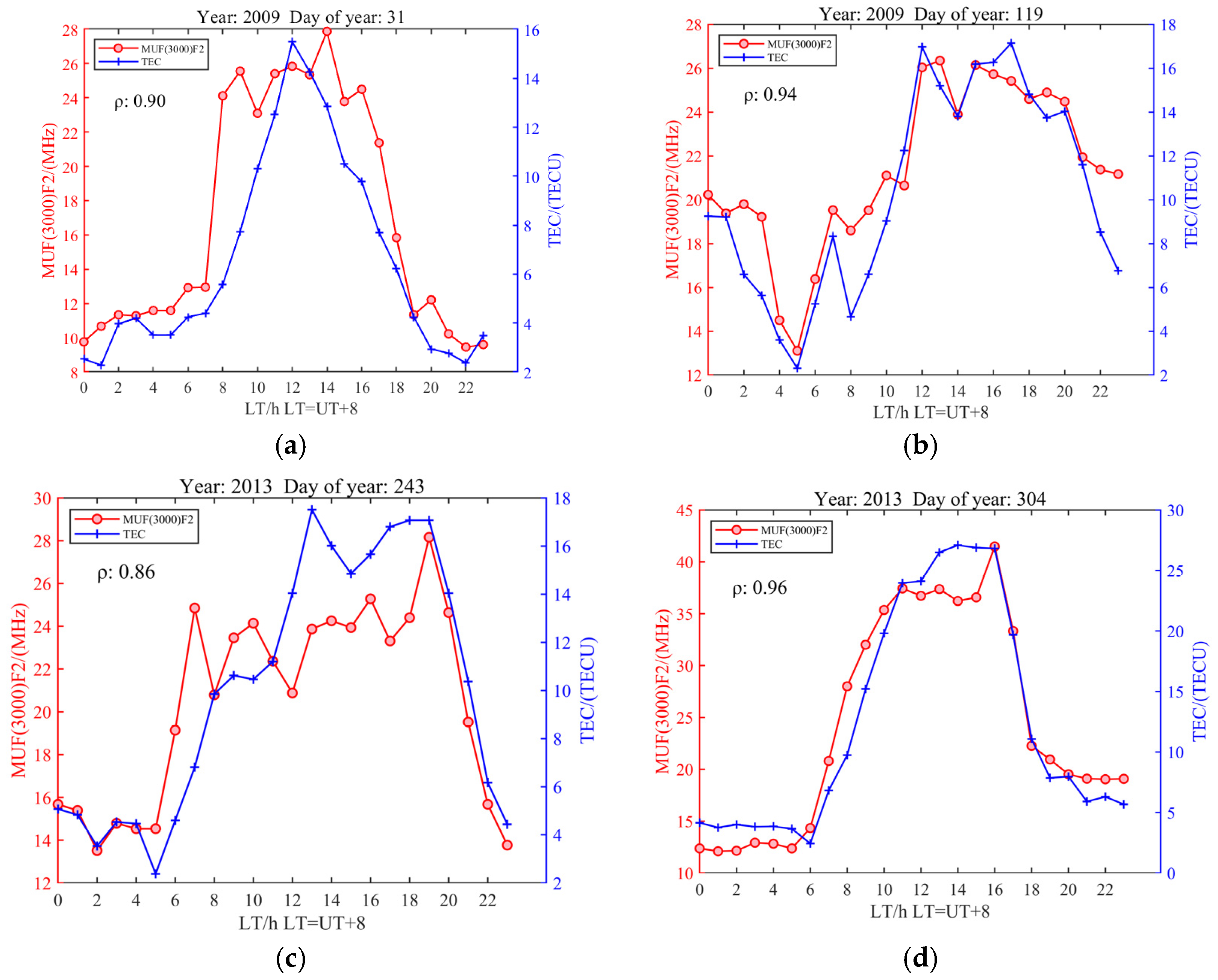
3.2.1. Relationship Between MUF(3000)F2 and TEC
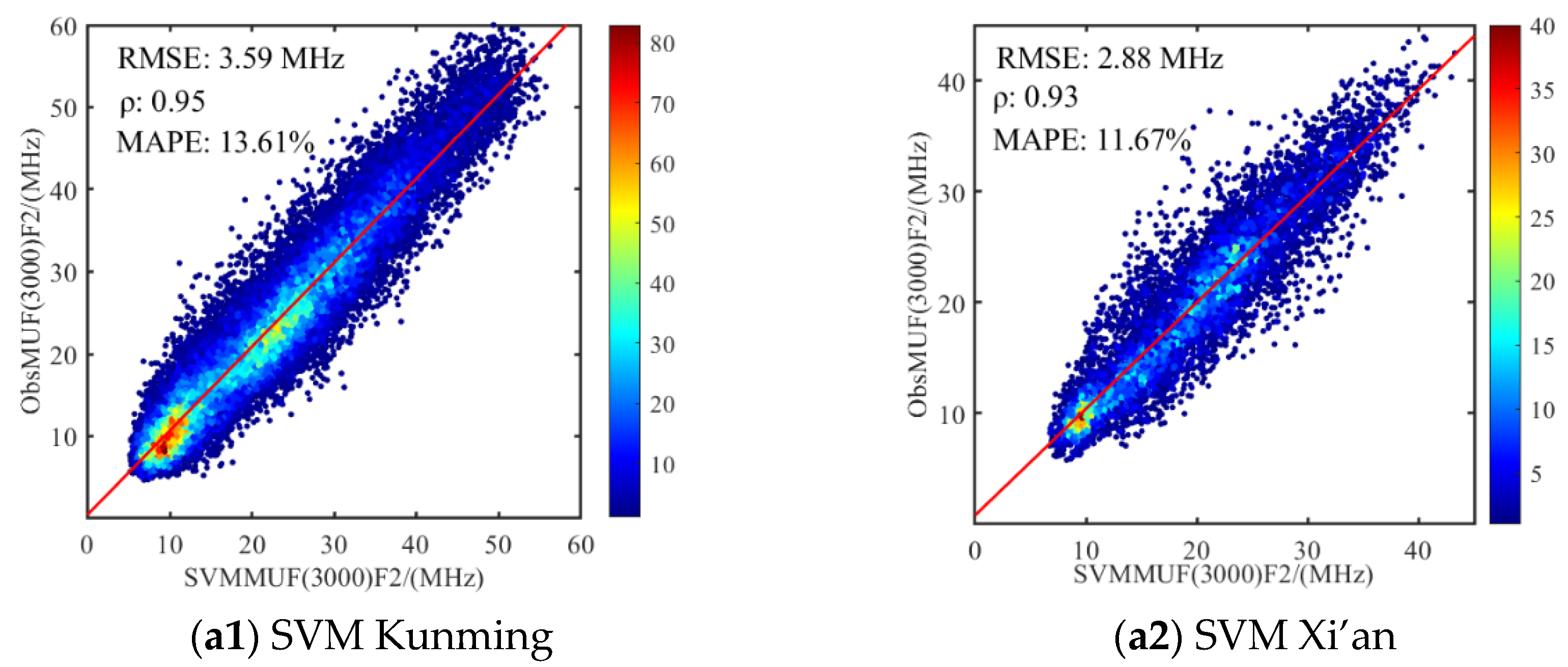
3.2.2. The MUF(3000)F2 Estimation Error and Model Performance
- Diurnal variations of MUF(3000)F2 RMSE values in RMSE of the machine learning models
- Performance evaluation of the models in estimating MUF(3000)F2 under quiet and disturbed ionospheric conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SVM | support vector machine |
| RF | random forest |
| BPNN | backpropagation neural network |
| MUF(3000)F2 | maximum usable frequency for a 3000 km range circuit |
| foF2 | critical frequency of the F2 layer |
| TEC | total electron content |
| GNSS | global navigation satellite system |
| HF | high frequency |
| DOY | day of year |
| LT | local time |
References
- Buonsanto, M.J. Ionospheric storms—A review. Space Sci. Rev. 1999, 88, 563–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, H.; Tahir, A.; Gul, I.; Waris, B.B.; Ameen, M.A.; Talha, M.; Ali, M.S.; Ansari, A.; Javaid, S. Estimation of MUF(3000)F2 using Earth-ionosphere geometry for Karachi and Multan, Pakistan. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4646–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalla, P.; Cairolo, L. TEC and foF2 comparison. Ann. Geophys. 1994, 37, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otugo, V.N.; Okoh, D.; Okujagu, C.; Onwuneme, S.; Rabiu, B.; Uwamahoro, J.; Habarulema, J.B.; Tshisaphungo, M.; Ssessanga, N. Estimation of Ionospheric Critical Plasma Frequencies From GNSS-TEC Measurements Using Artificial Neural Networks. Space Weather 2019, 17, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J. Neural network modeling of the ionospheric electron content at global scale using GPS data. Radio Sci. 1997, 32, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.W.V.; McKinnell, L.-A. On the predictability of foF2 using neural networks. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyemi, E.O.; Poole, A.W.V.; McKinnell, L.A. On the global model for foF2 using neural networks. Radio Sci. 2005, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyemi, E.O.; Poole, A.; McKinnell, L.A. On the global short-term forecasting of the ionospheric critical frequency foF2 up to 5 hours in advance using neural networks. Radio Sci. 2005, 40, 5347–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.I.; Maruyama, T.; Shidama, Y. Using a neural network to make operational forecasts of ionospheric variations and storms at Kokubunji. Earth Planet Space 2007, 59, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, R.F.; Santos, M.C. A neural network approach for regional vertical total electron content modelling. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2007, 51, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habarulema, J.B.; Mckinnell, L.A.; Cilliers, P.J. Prediction of global positioning system total electron content using Neural Networks over South Africa. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habarulema, J.B.; McKinnell, L.A. Investigating the performance of neural network backpropagation algorithms for TEC estimations using South African GPS data. Ann. Geophys. 2012, 30, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Gowtam, V.; Tulasi Ram, S. An Artificial Neural Network based Ionospheric Model to predict NmF2 and hmF2 using long-term data set of FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC radio occultation observations: Preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res. Space 2007, 122, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, C.; Liu, J.; He, J. Predicting TEC in China based on the neural networks optimized by genetic algorithm. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Liu, C.; Lv, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, J. A Short-Term Forecast Model of foF2 Based on Elman Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C. Ionospheric foF2 disturbance forecast using neural network improved by a genetic algorithm. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 4003–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Liu, Y.; Wei, T.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C. Ionospheric TEC forecast model based on support vector machine with GPU acceleration in the China region. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, T.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Y. Forecasting of ionospheric vertical total electron content (TEC) using LSTM networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), Ningbo, China, 9–12 July 2017; Volume 2, pp. 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Kaselimi, M.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Delikaraoglou, D. A Causal Long Short-Term Memory Sequence to Sequence Model for TEC Prediction Using GNSS Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Xia, G.; Liu, Y. Forecasting Ionospheric foF2 Based on Deep Learning Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; Golowich, S.E.; Smola, A. Support vector method for function approximation, regression estimation, and signal processing. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Systems. 2008, 9, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, C.; Deng, Z.; Ni, B.; Zhao, Z. Predicting foF2 in the China region using the neural networks improved by the genetic algorithm. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 92, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, S.S.; Gilliland, T.R.; Smith, N.; Reymer, S.E. The ionosphere, solar eclipse and magnetic storm. Phys. Rev. 1936, 50, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintoft, P.; Cander, L.R. Ionospheric foF2 storm forecasting using neural networks. Phys. Chem. Earth C Sol. Terr. Planet. Sci. 2000, 25, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wan, W.; Chen, Y.; Le, H. Solar activity effects of the ionosphere: A brief review. Chin Sci Bull. 2011, 56, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, G.; Zherebtsov, G.A.; Pirog, O.M. Responses of ionospheric foF2 to geomagnetic activities in Hainan. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutiev, I.; Muhtarov, P. Modeling of mid-latitude F region response to geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 15501–15509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cander, L.R. Spatial correlation of foF2 and vTEC under quiet and disturbed ionospheric conditions: A case study. Acta Geophys. 2007, 55, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williscroft, L.A.; Poole, A.W. Neural networks, foF2, sunspot number and magnetic activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 3659–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumluca, A.; Tulunay, E.; Topalli, I.; Tulunay, Y. Temporal and spatial forecasting of ionospheric critical frequency using neural networks. Radio Sci. 1999, 34, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo-Pradere, E.A.; Fuller-Rowell, T.J. STORM: An empirical storm-time ionospheric correction model 2. Validation. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krankowski, A.; Shagimuratov, I.I.; Baran, L.W. Mapping of foF2 over Europe based on GPS-derived TEC data. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssessanga, N.; Mckinnell, L.A.; Habarulema, J.B. Estimation of foF2 from GPS TEC over the South African region. J. Atm. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2014, 112, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


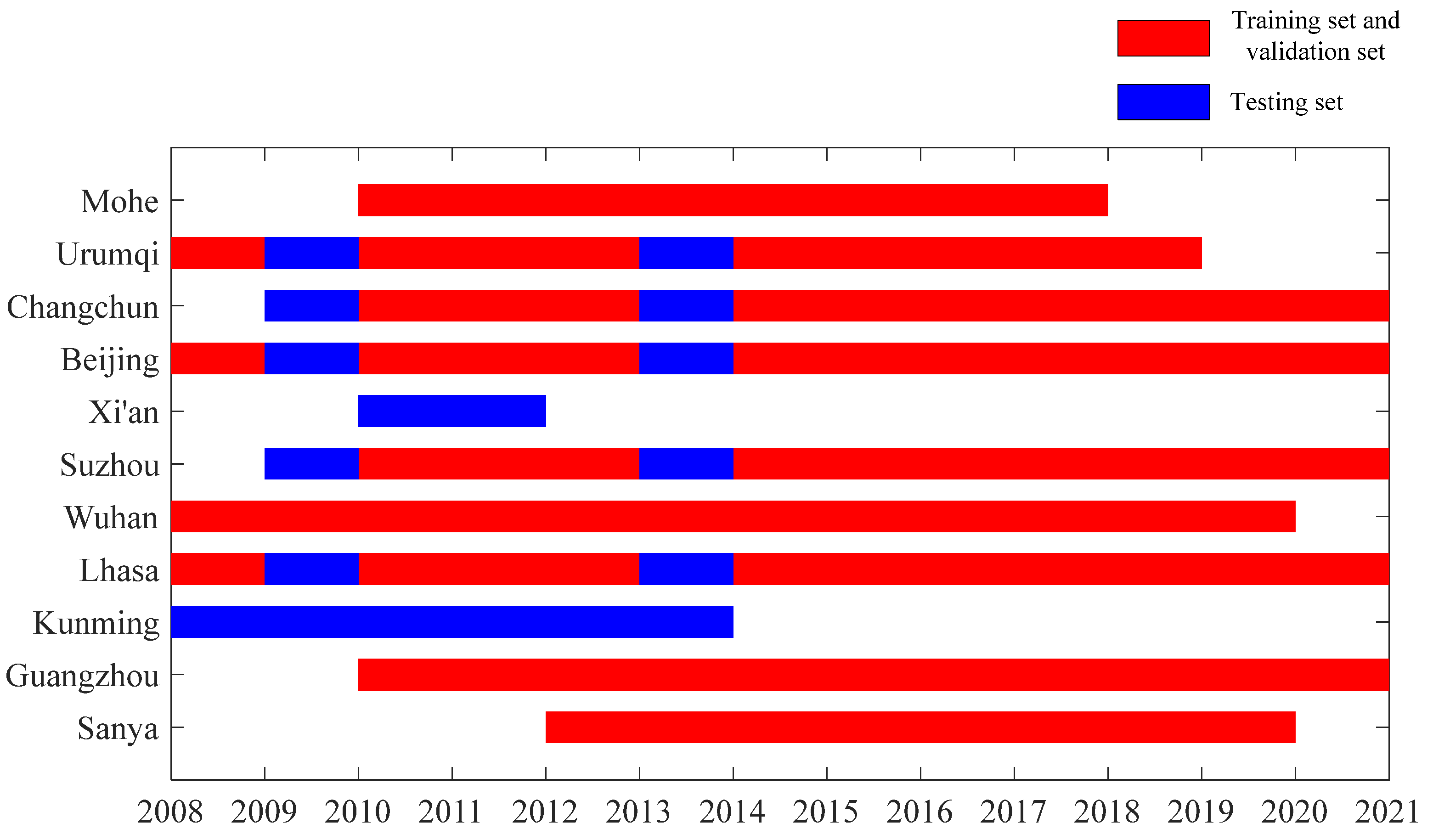




| Site Name | Ionosonde Station | GNSS Receiver Station | Time Span | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | ||
| Mohe | 53.49 | 122.34 | 53.49 | 122.34 | 2011–2017 |
| Urumqi | 43.75 | 87.64 | 43.80 | 87.60 | 2008–2018 |
| Changchun | 43.84 | 125.28 | 43.79 | 125.44 | 2009–2020 |
| Beijing | 40.11 | 116.28 | 39.61 | 115.89 | 2008–2020 |
| Xi’an | 34.13 | 108.83 | 34.37 | 109.22 | 2010–2011 |
| Suzhou | 31.34 | 120.41 | 31.10 | 121.20 | 2009–2020 |
| Wuhan | 30.60 | 114.40 | 30.53 | 114.36 | 2008–2019 |
| Lhasa | 29.64 | 91.18 | 29.66 | 91.10 | 2008–2020 |
| Kunming | 25.64 | 103.72 | 25.03 | 102.80 | 2008–2013 |
| Guangzhou | 23.14 | 113.36 | 22.37 | 113.93 | 2010–2020 |
| Sanya | 18.35 | 109.62 | 18.35 | 109.62 | 2012–2019 |
| Type | Size | Time to Spend |
|---|---|---|
| SVM | 52.5 MB | about 25.8 h |
| RF | 1.25 GB | about 0.58 h |
| BPNN | 11.4 MB | about 1.2 h |
| Site Name | Year | SVM | RF | BPNN | IRI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE /MHz | MAPE | RMSE /MHz | MAPE | RMSE /MHz | MAPE | RMSE /MHz | MAPE | ||
| Urumqi | 2009 | 0.44 | 8.34% | 0.43 | 8.24% | 0.47 | 8.76% | 0.54 | 10.38% |
| 2013 | 0.46 | 6.18% | 0.45 | 6.25% | 0.47 | 6.41% | 0.78 | 10.06% | |
| Changchun | 2009 | 0.41 | 7.57% | 0.41 | 7.56% | 0.45 | 8.54% | 0.58 | 10.46% |
| 2013 | 0.50 | 6.45% | 0.51 | 6.61% | 0.50 | 6.50% | 0.76 | 9.75% | |
| Beijing | 2009 | 0.48 | 8.06% | 0.47 | 7.86% | 0.52 | 8.91% | 0.61 | 10.94% |
| 2013 | 0.50 | 6.29% | 0.52 | 6.56% | 0.51 | 6.42% | 0.84 | 10.80% | |
| Suzhou | 2009 | 0.55 | 8.78% | 0.51 | 8.29% | 0.56 | 9.45% | 1.00 | 17.20% |
| 2013 | 0.66 | 7.13% | 0.70 | 7.48% | 0.70 | 7.65% | 1.30 | 15.90% | |
| Lhasa | 2009 | 0.62 | 9.52% | 0.61 | 9.39% | 0.66 | 10.45% | 1.14 | 17.15% |
| 2013 | 0.74 | 7.83% | 0.75 | 7.76% | 0.77 | 8.43% | 1.43 | 16.46% | |
| Model | Mean (MHz) | Standard Deviation (MHz) | Skewness | Kurtosis | Root Mean Square Error (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | −0.35 | 1.07 | −0.47 | 3.73 | 1.13 |
| RF | 0.19 | 1.09 | −0.40 | 3.41 | 1.11 |
| BPNN | 0.42 | 1.08 | −0.27 | 3.42 | 1.16 |
| Site Name | Year | SVM | RF | BPNN | IRI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE /MHz | MAPE | RMSE /MHz | MAPE | RMSE /MHz | MAPE | RMSE /MHz | MAPE | ||
| Urumqi | 2009 | 1.73 | 9.88% | 1.70 | 9.71% | 1.81 | 10.45% | 2.04 | 11.51% |
| 2013 | 1.78 | 7.59% | 1.73 | 7.42% | 1.81 | 7.64% | 2.48 | 10.45% | |
| Changchun | 2009 | 1.72 | 9.10% | 1.70 | 9.04% | 1.79 | 9.78% | 2.44 | 12.62% |
| 2013 | 1.88 | 7.69% | 1.87 | 7.70% | 1.92 | 7.85% | 2.48 | 11.32% | |
| Beijing | 2009 | 1.93 | 9.69% | 1.86 | 9.36% | 1.96 | 10.01% | 2.38 | 12.36% |
| 2013 | 1.91 | 7.64% | 1.88 | 7.61% | 1.92 | 7.74% | 2.72 | 11.33% | |
| Suzhou | 2009 | 2.35 | 10.94% | 2.15 | 10.10% | 2.34 | 10.90% | 3.45 | 17.35% |
| 2013 | 2.43 | 8.69% | 2.46 | 8.76% | 2.50 | 8.84% | 4.12 | 16.68% | |
| Lhasa | 2009 | 2.59 | 11.30% | 2.50 | 10.91% | 2.69 | 12.17% | 4.04 | 17.98% |
| 2013 | 2.73 | 9.68% | 2.70 | 9.33% | 2.76 | 9.81% | 4.53 | 17.82% | |
| Model | Mean (MHz) | Standard Deviation (MHz) | Skewness | Kurtosis | Root Mean Square Error (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | −0.98 | 3.87 | −0.20 | 3.45 | 3.99 |
| RF | 0.26 | 4.10 | −0.30 | 3.39 | 4.10 |
| BPNN | 1.54 | 3.89 | −0.09 | 3.41 | 4.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ou, M.; Chen, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Dong, X.; Zhen, W. Machine Learning-Based Estimation of foF2 and MUF(3000)F2 Using GNSS Ionospheric TEC Observations. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101764
Zhang Y, Ou M, Chen L, Hao Y, Zhu Q, Dong X, Zhen W. Machine Learning-Based Estimation of foF2 and MUF(3000)F2 Using GNSS Ionospheric TEC Observations. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101764
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuhang, Ming Ou, Liang Chen, Yi Hao, Qinglin Zhu, Xiang Dong, and Weimin Zhen. 2025. "Machine Learning-Based Estimation of foF2 and MUF(3000)F2 Using GNSS Ionospheric TEC Observations" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101764
APA StyleZhang, Y., Ou, M., Chen, L., Hao, Y., Zhu, Q., Dong, X., & Zhen, W. (2025). Machine Learning-Based Estimation of foF2 and MUF(3000)F2 Using GNSS Ionospheric TEC Observations. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101764







