Extinction Coefficient Inversion Algorithm with New Boundary Value Estimation for Horizontal Scanning Lidar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Methodology
2.1. The Error Originating from the Noise
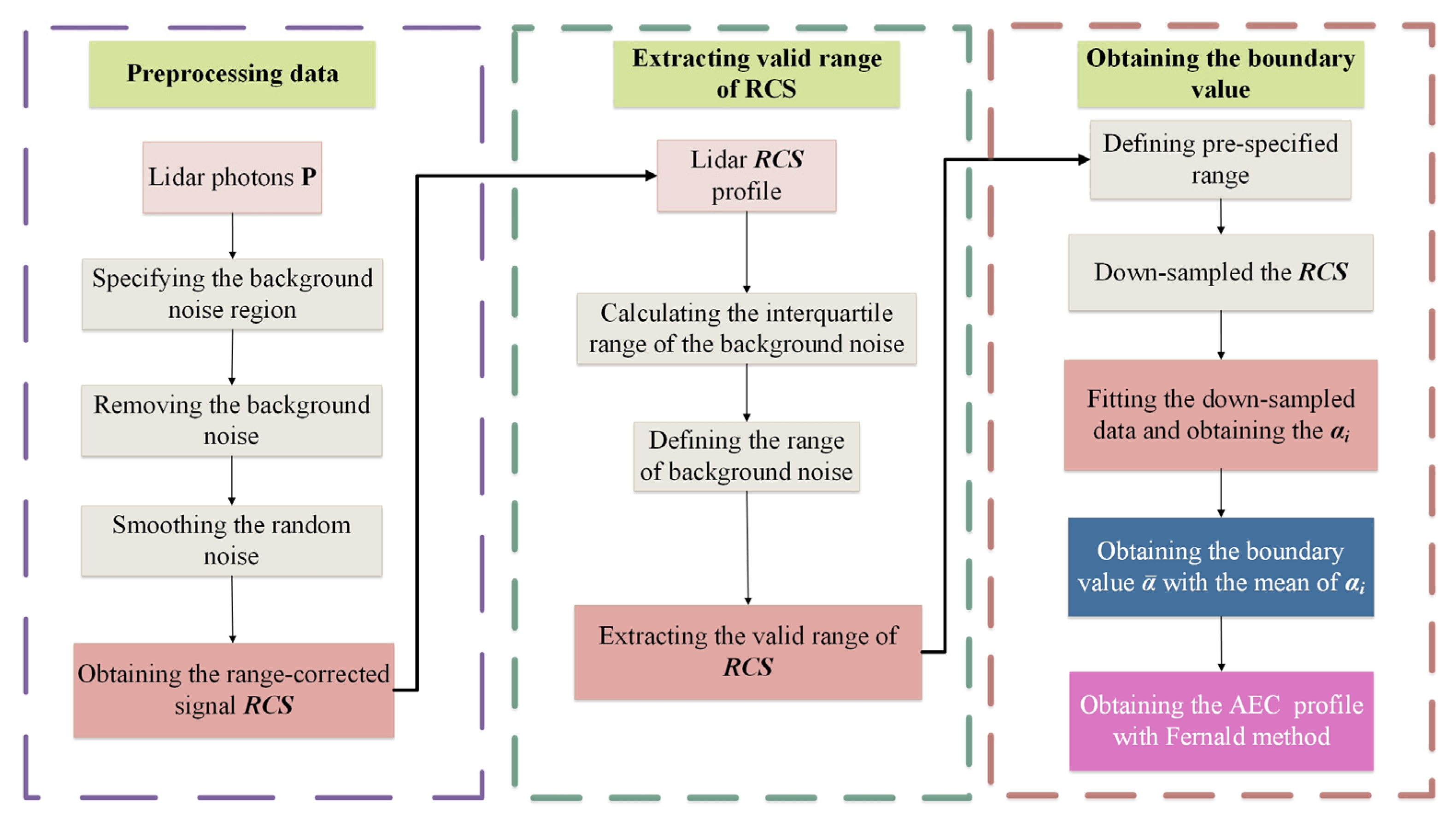
2.2. Extinction Coefficient Profile Inversion Algorithm
2.2.1. Preprocess the Data
2.2.2. Determine the Valid RCS
2.2.3. Estimate the Boundary Extinction Coefficient
3. The Validation Experiments
3.1. Lidar Signal Simulation with Pre-Set Extinction Coefficient
3.2. The Result of the New Boundary Estimation Algorithm
3.3. Error Analysis for the New Algorithm
3.4. The Field Experiment
4. Results
4.1. The Instrument and Observation
4.2. The Detection of Sea Fog
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Lau, W.M.; Ramanathan, V.; Wu, G.; Ding, Y.; Manoj, M.G.; Liu, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; et al. Aerosol and Monsoon Climate Interactions over Asia. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 866–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Deng, M.; Lee, S.S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Zhai, P.; Liu, H.; Lv, W.; Yao, W.; Li, X. Delaying Precipitation and Lightning by Air Pollution over the Pearl River Delta. Part I: Observational Analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6472–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, A.; Imre, K.; Ferenczi, Z.; Kiss, G.; Gelencsér, A. Aerosol Hygroscopicity: Hygroscopic Growth Proxy Based on Visibility for Low-Cost PM Monitoring. Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Yung, Y.L.; Lv, D.; Hansen, J.; Penner, J.E.; Liao, H.; Ramaswamy, V.; Kahn, R.A.; Zhang, P.; et al. Scattering and Absorbing Aerosols in the Climate System. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Müller, D. Lidar and Atmospheric Aerosol Particles. In Lidar; Weitkamp, C., Ed.; Springer Series in Optical Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 102, pp. 105–141. ISBN 978-0-387-40075-4. [Google Scholar]
- Amiridis, V.; Balis, D.S.; Kazadzis, S.; Bais, A.; Giannakaki, E.; Papayannis, A.; Zerefos, C. Four-year Aerosol Observations with a Raman Lidar at Thessaloniki, Greece, in the Framework of European Aerosol Research Lidar Network (EARLINET). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D21203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, H.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Heese, B.; Müller, D.; Artaxo, P.; Paixao, M.; Pauliquevis, T.; Souza, R. Aerosol Profiling with Lidar in the Amazon Basin during the Wet and Dry Season. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Q.; Li, C.C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Yuan, Z.B.; Lu, X.C.; Tse, K.T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, Y.; Yao, T.; Su, L.; et al. Assessment of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth Using Continuous Lidar Observation. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Han, G.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, J. Regional Atmospheric Aerosol Pollution Detection Based on LiDAR Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Yi, F.; Liu, F.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y. Long-Term Variations of Aerosol Optical Properties over Wuhan with Polarization Lidar. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.P.; Pommereau, J.P.; Garnier, A.; Pelon, J.; Larsen, N.; Nielsen, J.; Christensen, T.; Cairo, F.; Thomason, L.W.; Leblanc, T.; et al. Tropical Stratospheric Aerosol Layer from CALIPSO Lidar Observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00H10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Omar, A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hair, J.; Kittaka, C.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D.; Hostetler, C.; et al. CALIPSO Lidar Observations of the Optical Properties of Saharan Dust: A Case Study of Long-range Transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D07207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnai, T.; Marshak, A. Global CALIPSO Observations of Aerosol Changes Near Clouds. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Daniel, J.S.; Neely, R.R.; Vernier, J.-P.; Dutton, E.G.; Thomason, L.W. The Persistently Variable “Background” Stratospheric Aerosol Layer and Global Climate Change. Science 2011, 333, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremser, S.; Thomason, L.W.; Von Hobe, M.; Hermann, M.; Deshler, T.; Timmreck, C.; Toohey, M.; Stenke, A.; Schwarz, J.P.; Weigel, R.; et al. Stratospheric Aerosol-Observations, Processes, and Impact on Climate: Stratospheric Aerosol. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 278–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, Y.; Hua, S.; Zhu, Q.; Shao, T. Estimation of the Aerosol Radiative Effect over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the Latest CALIPSO Product. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G.; Herman, B.M.; Reagan, J.A. Determination of Aerosol Height Distributions by Lidar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1972, 11, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of Atmospheric Lidar Observations: Some Comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Stable Analytical Inversion Solution for Processing Lidar Returns. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasano, Y.; Nakane, H. Significance of the Extinction/Backscatter Ratio and the Boundary Value Term in the Solution for the Two-Component Lidar Equation. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 11_1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocadenbosch, F.; Reba, M.N.M.D.; Sicard, M.; Comerón, A. Practical Analytical Backscatter Error Bars for Elastic One-Component Lidar Inversion Algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 3380–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Sensitivity of Lidar Equation Solution to Boundary Values and Determination of the Values. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Takeuchi, N. Effects of Misestimated Far-End Boundary Values on Two Common Lidar Inversion Solutions. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 6451–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, N.; Yang, F.; Zhu, C. Improving the Accuracy of Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Inversion. Opt. Spectrosc. 2014, 116, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, P.M.; Lagrosas, N.; Shiina, T.; Kuze, H. Surface Aerosol Properties Studied Using a Near-Horizontal Lidar. Atmosphere 2019, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mao, M. An Accurate Inversion Method of Aerosol Extinction Coefficient about Ground-Based Lidar without Needing Calibration. Acta Phys. Sin. 2019, 68, 074205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Qin, L.; Zhang, S.; He, F.; Tan, F.; Jing, X.; Hou, Z. A New Method of Measuring Boundary Value of Atmospheric Extinction Coefficient. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 054205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, N.; Gao, H.; Xiong, X. Determination of the Boundary Value of the Aerosol Extinction Coefficient and Its Effects on the Extinction Coefficient Profile of Aerosol in Lower Atmosphere. Optik 2018, 160, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chang, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Z. An RBF Neural Network Approach for Retrieving Atmospheric Extinction Coefficients Based on Lidar Measurements. Appl. Phys. B 2018, 124, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.A.; Stephens, D.H. Algorithm for Inverting Lidar Returns. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 3673–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, J.; Han, Y.; Huang, S.; Sun, D.; Zheng, J.; Han, F.; Zhou, A.; Yang, S.; Xu, W.; Song, Q.; et al. Novel Lidar Algorithm for Horizontal Visibility Measurement and Sea Fog Monitoring. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 34853–34863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, J.; Sun, D.; Xu, W.; Han, Y.; Zheng, J.; Peng, J.; Yang, S. Urban Air Pollution Monitoring Using Scanning Lidar. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collis, R.T.H. Lidar: A New Atmospheric Probe. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1966, 92, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Xia, H.; Dou, X.; Shangguan, M.; Li, M.; Wang, C. Adaptive Inversion Algorithm for 1.5 μm Visibility Lidar Incorporating in Situ Angstrom Wavelength Exponent. Opt. Commun. 2018, 418, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocadenbosch, F.; Comerón, A.; Albiol, L. Statistics of the Slope-Method Estimator. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 6049–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, G.J.; De Leeuw, G. Inversion of Lidar Signals with the Slope Method. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Wang, W.; Min, Q.; Gong, W. Approach for Selecting Boundary Value to Retrieve Mie-Scattering Lidar Data Based on Segmentation and Two-Component Fitting Methods. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A604–A613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, F.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Gong, W.; Min, Q.; Wang, W. Nonlinear Physical Segmentation Algorithm for Determining the Layer Boundary from Lidar Signal. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A1589–A1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xia, M.; Ge, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, K. On-Site Ocean Horizontal Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Inversion under Different Weather Conditions on the Bo-Hai and Huang-Hai Seas. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 177, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, R.; Kong, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Gong, Z.; Liu, K.; Hua, D.; Mei, L. Retrieval of the Aerosol Extinction Coefficient from Scanning Scheimpflug Lidar Measurements for Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 309, 119945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, A.J.; Minzner, R.A. A Mid-Latitude Ozone Model for the 1976 US Standard Atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 4477–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap Methods: Another Look at the Jackknife. Ann. Stat. 1979, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Qin, B.; Feng, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y. Reducing Poisson Noise and Baseline Drift in X-Ray Spectral Images with Bootstrap Poisson Regression and Robust Nonparametric Regression. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S.J.; Anderson, T.L.; Charlson, R.J. Measurement of the Lidar Ratio for Atmospheric Aerosols with a 180° Backscatter Nephelometer. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeiro, F.M.; Wagner, F.; Ramos, P.M.; Silva, A.M. Atmospheric Visibility Measurements Based on a Low-Cost Digital Camera. In Proceedings of the ConfTele, 6th Conference on Telecommunications, Peniche, Portugal, 9–11 May 2007; pp. 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Liu, H.; Jiang, W.; Huang, J.; Mao, W. Characteristics of the Boundary Layer Structure of Sea Fog on the Coast of Southern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, B.; Yi, L.; Liu, C.; Tu, J.; Wen, G.; Mao, W. Evaluation of the Global and Regional Assimilation and Prediction System for Predicting Sea Fog over the South China Sea. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Sun, D.; Qi, X.; Xian, J. Lidar System with a Fast Scanning Speed for Sea Fog Detection. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 27462–27471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Ma, Y.; Cui, T. MERRA-2 Reanalysis-Aided Sea Fog Detection Based on CALIOP Observation over North Pacific. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 292, 113583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, X.; Feng, Z.; Wu, G.; Yan, X.; Zhai, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Demonstration of Measuring Sea Fog with an SNSPD-Based Lidar System. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.; He, C.; Zhao, M.; Liu, A.; Wang, Z. Extinction Coefficient Inversion Algorithm with New Boundary Value Estimation for Horizontal Scanning Lidar. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101736
Chen L, Yu Z, Wang S, He C, Zhao M, Liu A, Wang Z. Extinction Coefficient Inversion Algorithm with New Boundary Value Estimation for Horizontal Scanning Lidar. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101736
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Le, Zhibin Yu, Shihai Wang, Chunhui He, Mingguang Zhao, Aiming Liu, and Zhangjun Wang. 2025. "Extinction Coefficient Inversion Algorithm with New Boundary Value Estimation for Horizontal Scanning Lidar" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101736
APA StyleChen, L., Yu, Z., Wang, S., He, C., Zhao, M., Liu, A., & Wang, Z. (2025). Extinction Coefficient Inversion Algorithm with New Boundary Value Estimation for Horizontal Scanning Lidar. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101736








