Analysis on GNSS Common View and Precise Point Positioning Time Transfer: BDS-3/Galileo/GPS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
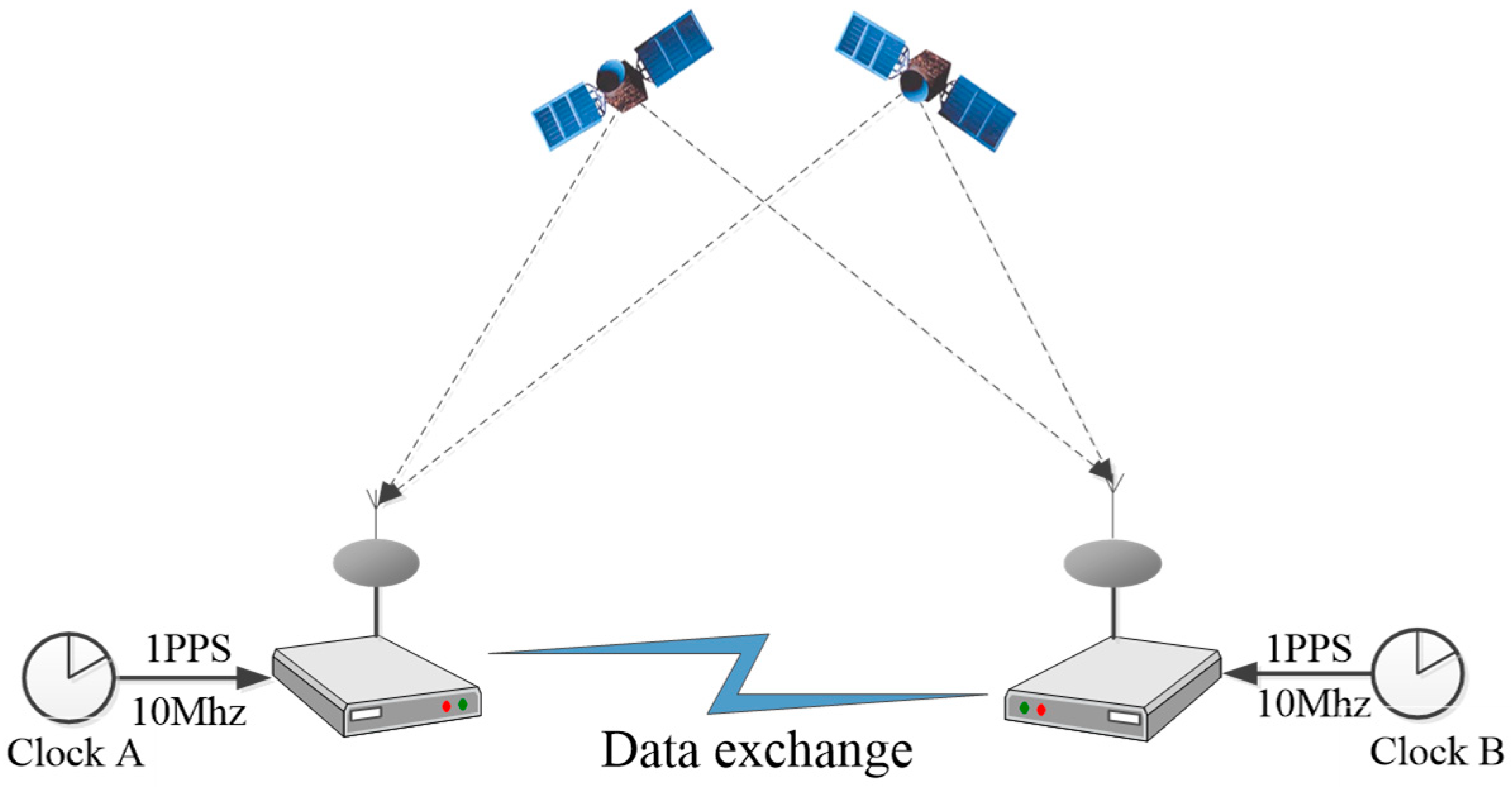
2.1. CV Time Transfer Method
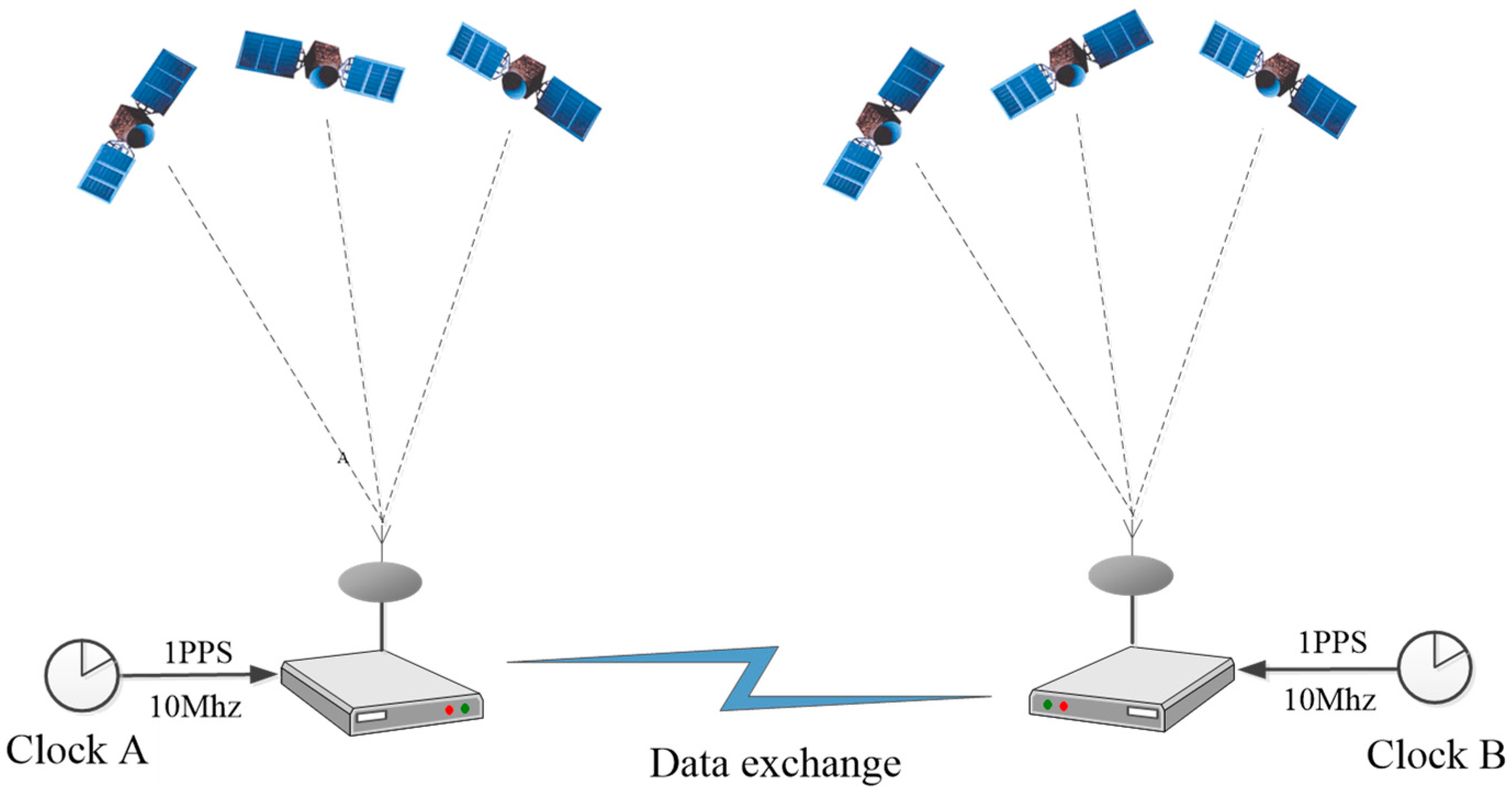
2.2. PPP Time Transfer Method
2.3. Experimental Setup and Data Processing
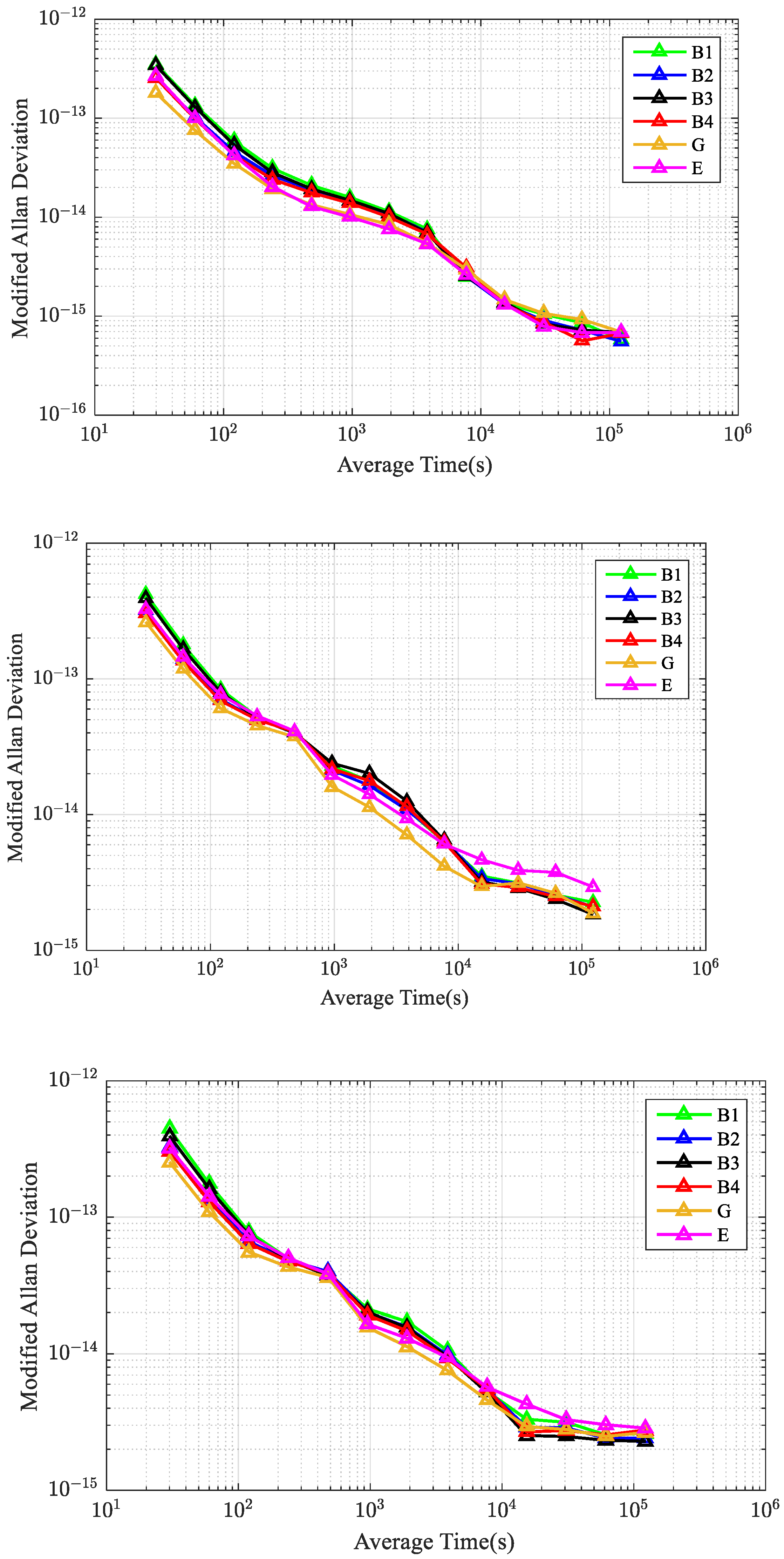
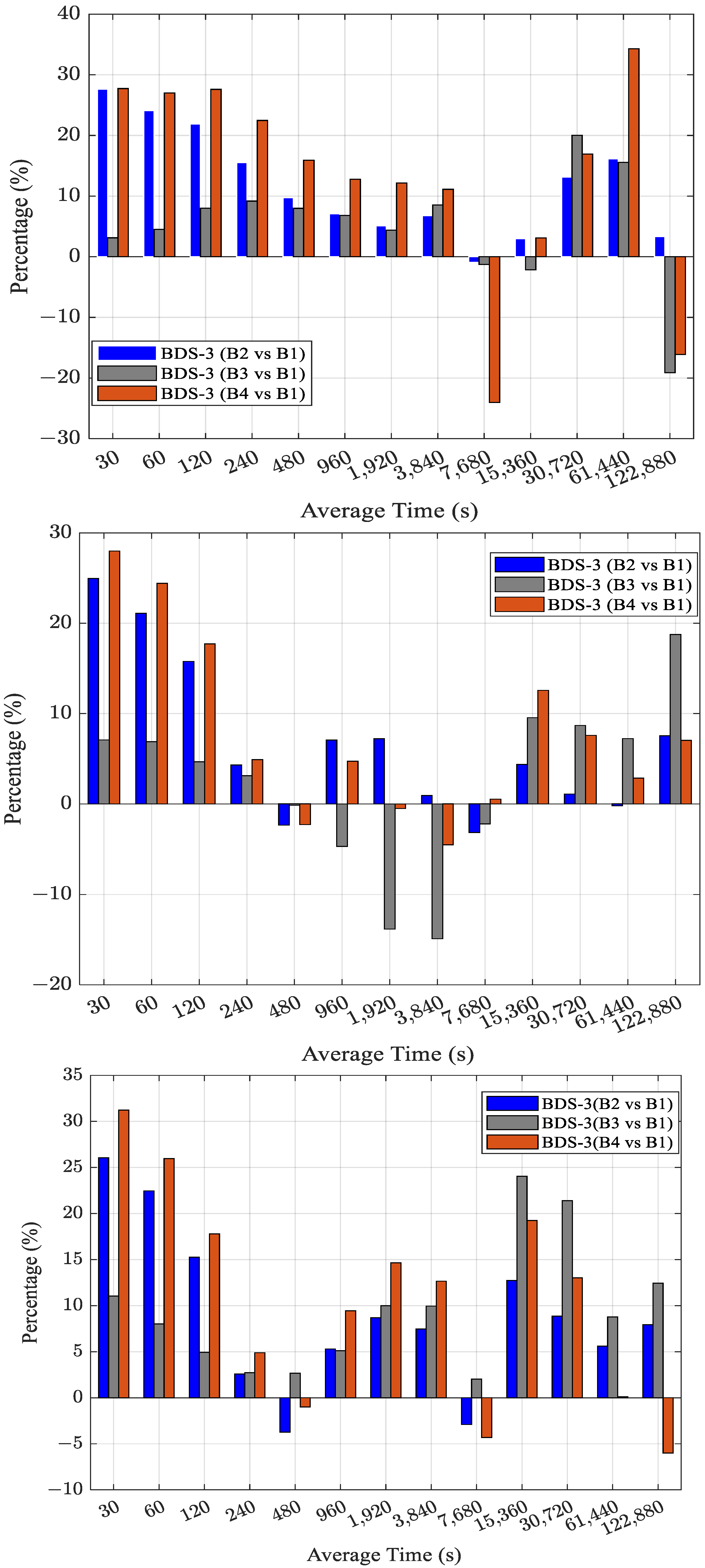
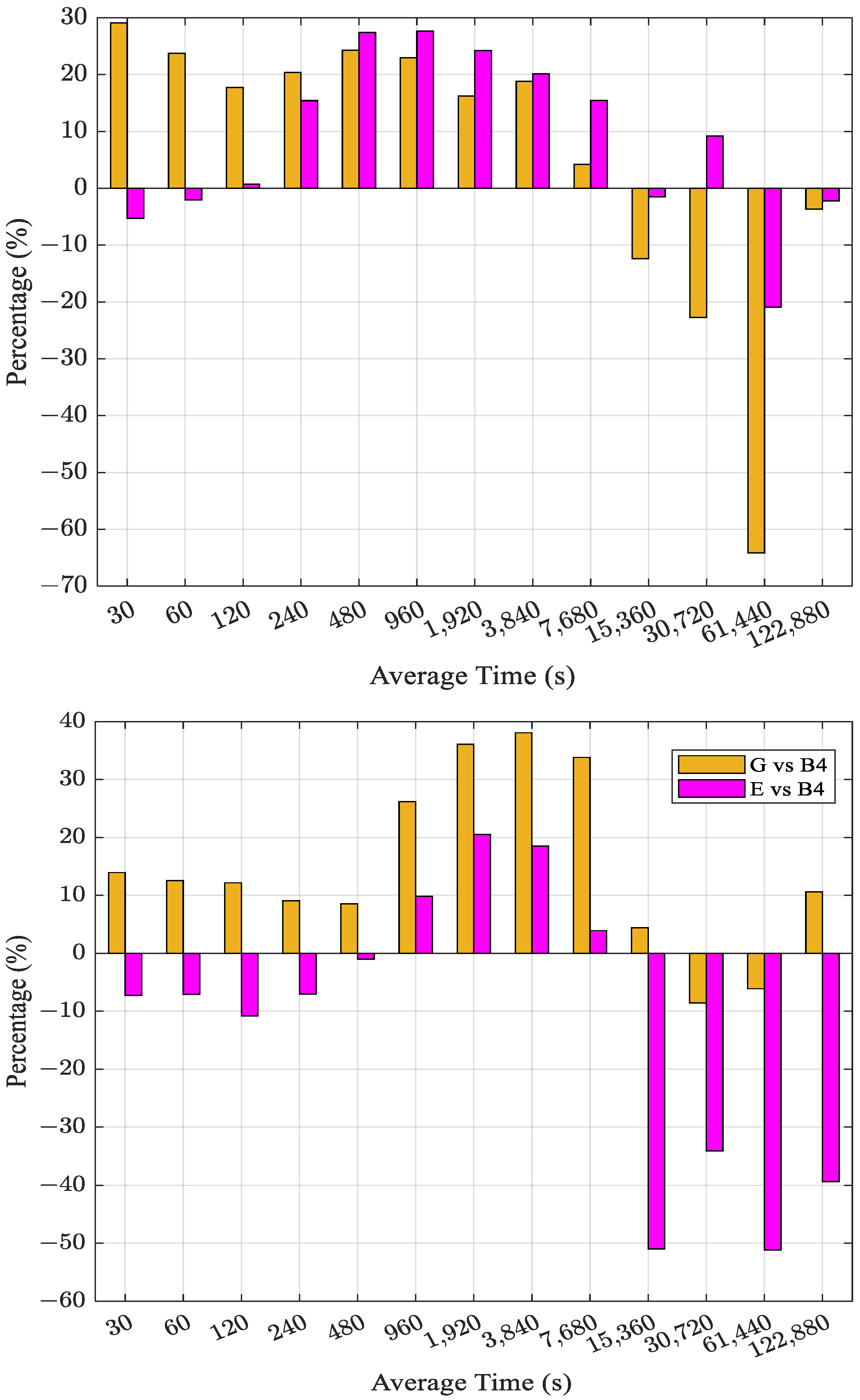
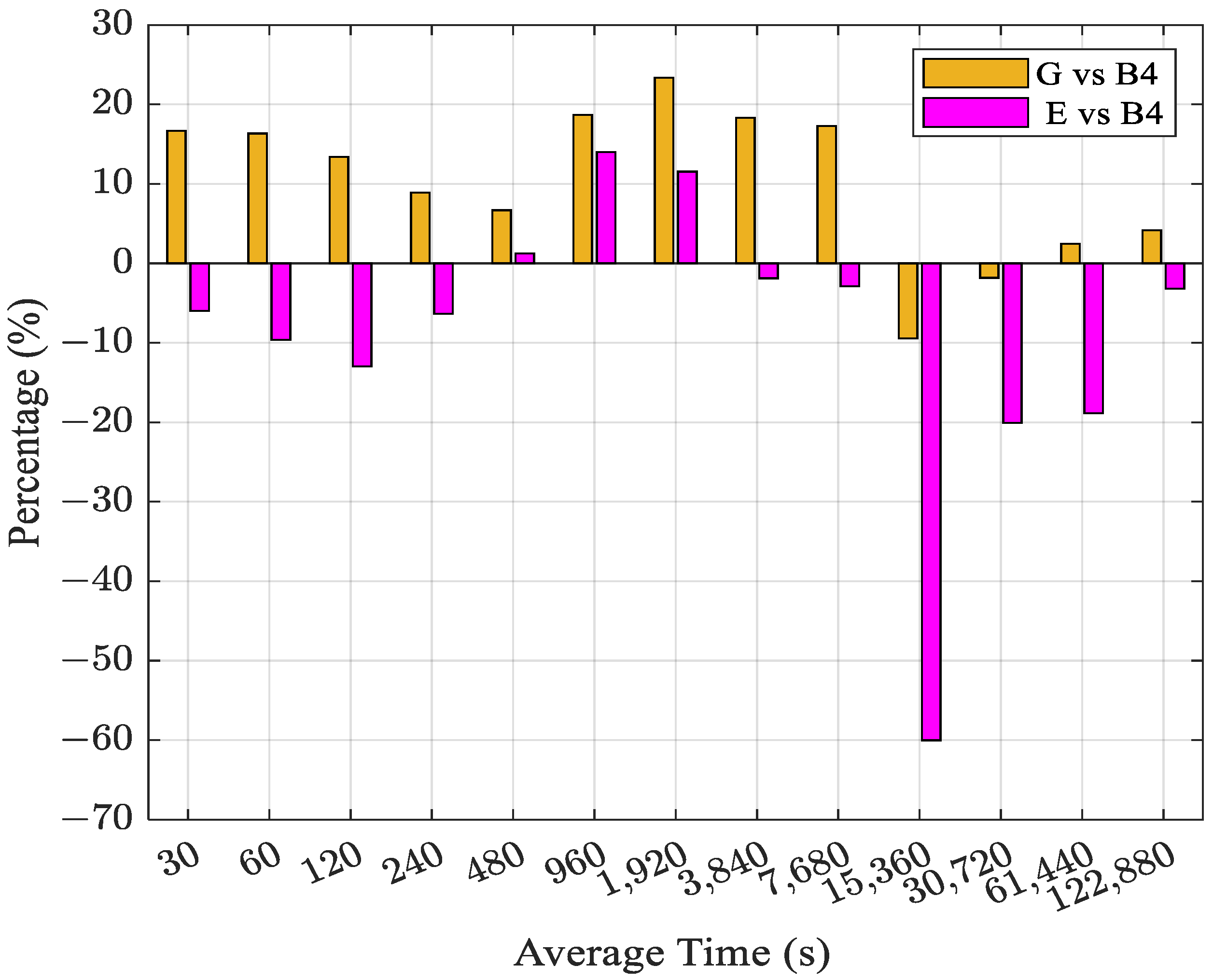
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CV Time Transfer
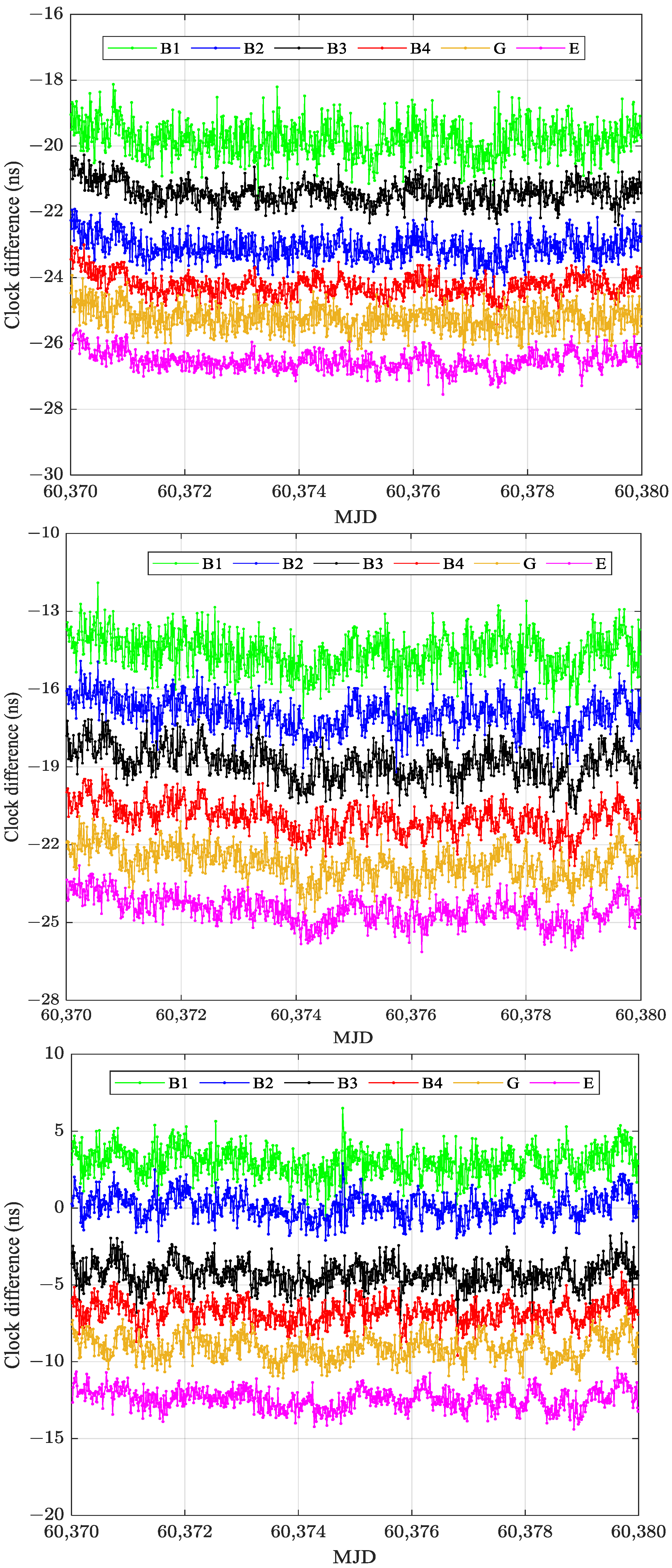
3.2. PPP Time Transfer
4. Conclusions
- The precision and the AFT of the Galileo (E1 & E5a) CV links are better than those of GPS (L1 & L2) and BDS-3 (B1I & B3I, B1I & B2a, B1C & B3I, and B1C & B2a) CV links.
- The GPS PPP link is the most precise compared to other links. When the average time is less than 2.1 h, the FT of the GPS link is significantly improved compared with the BDS-3 B1C & B2a link. When the average time is greater than 4.3 h, the FT of the BDS-3 B1C & B2a PPP link is slightly better than that of the Galileo PPP links. Meanwhile, the performance of the Galileo PPP time transfer is affected by the distribution of stations.
- For BDS-3 dual-frequency time transfer utilizing four IF combinations, the precision and AFT of the B1C & B2a combination CV and PPP links are superior to those of other BDS-3 IF combinations. This could be explained by the fact that the dual-frequency IF combination of BDS-3 B1C & B2a has the smallest noise amplification factor.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Defraigne, P.; Bruyninx, C. On the link between GPS pseudorange noise and day-boundary discontinuities in geodetic time transfer solutions. GPS Solut. 2007, 11, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Schutz, B.; Lee, C.; Yang, S. A study on the Common-View and All-in-View GPS time transfer using carrier-phase measurements. Metrologia 2008, 45, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G. The TAIPPP pilot experiment. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Meeting of the 23rd European Frequency and Time Forum/IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium, Besancon, France, 20–24 April 2009; pp. 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Jiang, Z. GPS All in View time transfer for TAI computation. Metrologia 2008, 45, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.; Weiss, M. Accurate time and frequency transfer during common-view of a GPS satellite. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Symposium on Frequency Control, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 28–30 May 1980; pp. 334–346. [Google Scholar]
- Defraigne, P.; Achkar, J.; Coleman, M.J.; Gertsvolf, M.; Ichikawa, R.; Levine, J.; Uhrich, P.; Whibberley, P.; Wouters, M.; Bauch, A. Achieving traceability to UTC through GNSS measurements. Metrologia 2022, 59, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraigne, P.; Petit, G. CGGTTS-Version 2E: An extended standard for GNSS time transfer. Metrologia 2015, 52, G1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Harmegnies, A. Tests of Galileo and BeiDou links for UTC. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and European Frequency and Time Forum (EFTF/IFC), Orlando, FL, USA, 14–18 April 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Defraigne, P. BeiDou time transfer with the standard CGGTTS. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Wu, W.; Dong, S. Analysis on the time transfer performance of BDS-3 signals. Metrologia 2020, 57, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tu, R.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Initial accuracy and reliability of current BDS-3 precise positioning, velocity estimation, and time transfer (PVT). Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIPM. BIPM Annual Report on Time Activities. Available online: https://webtai.bipm.org/ftp/pub/tai/annual-reports/bipm-annual-report/annual_report_2020.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Defraigne, P.; Tagliaferro, G. CGGTTS-Version 2E: Integration of BDS-3. Metrologia 2024, 61, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Cao, X.; Lyu, D.; He, Z.; Ye, F.; Xiao, G.; Shen, F. An investigation of PPP time transfer via BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tu, R.; Lu, X.; He, Z.; Guan, W.; Xiao, G. Initial and comprehensive analysis of PPP time transfer based on Galileo high accuracy service. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, W.; Dong, S.; Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, S. Progress of BeiDou time transfer at NTSC. Metrologia 2018, 55, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraigne, P.; Huang, W.; Bertrand, B.; Rovera, D. Study of the GPS in-ter-frequency calibration of timing receivers. Metrologia 2018, 55, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Dai, P.; Qin, W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, F.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X. Performance of Multi-GNSS precise point positioning time and frequency transfer with clock modeling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, K.; Fu, W.; Xie, S.; Cui, B.; Li, M. Real-Time Estimation of BDS-3 Satellite Clock Offset with Ambiguity Resolution Using B1C/B2a Signals. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Heroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbits and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ling, K.; Qin, H. Performance analysis of familiar elevation-dependent stochastic models with error variance compensation and posteriori unit weight in GPS/BDS precise point positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 3655–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vondrάk, J.; Čepek, A. Combined smoothing method and its use in combining Earth orientation parameters measured by space techniques. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 2000, 147, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Yin, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Yi, R.; Suya, R. BDS/QZSS integrated PPPAR time-frequency transfer. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
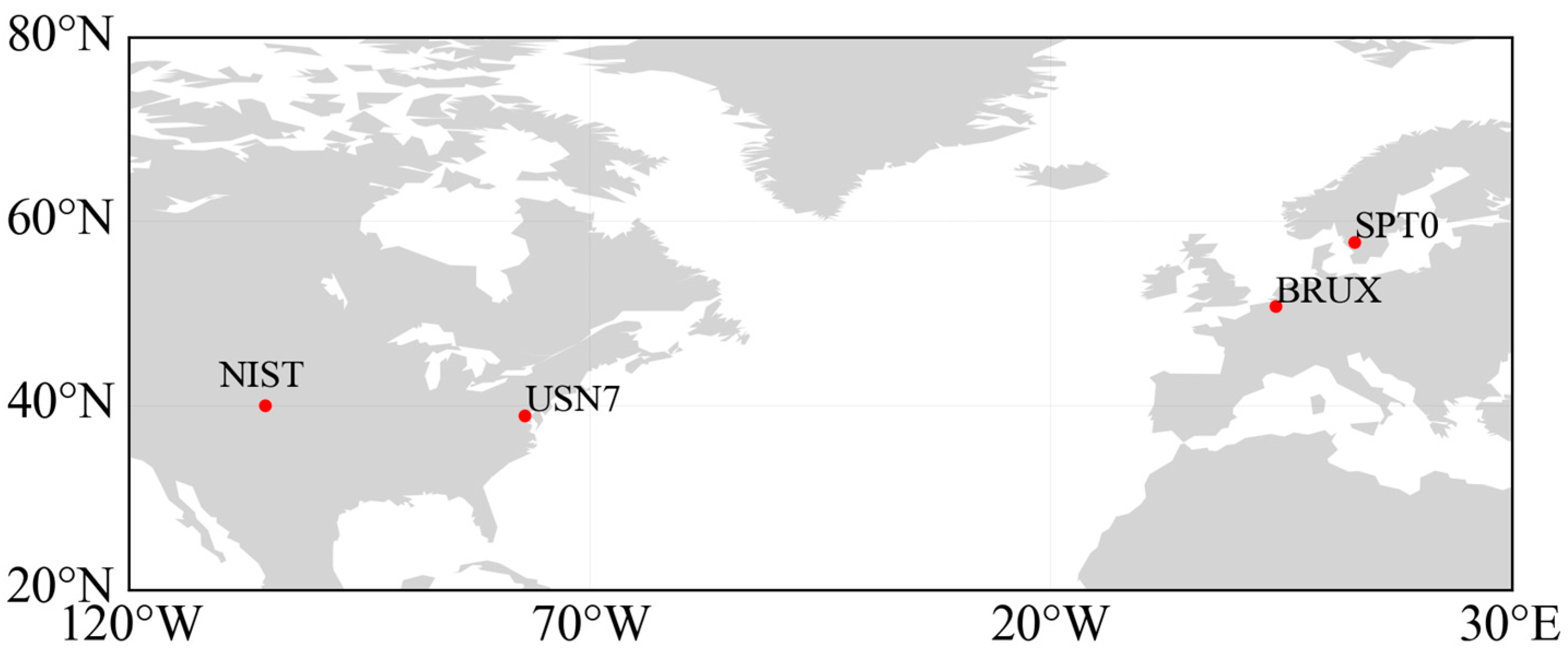
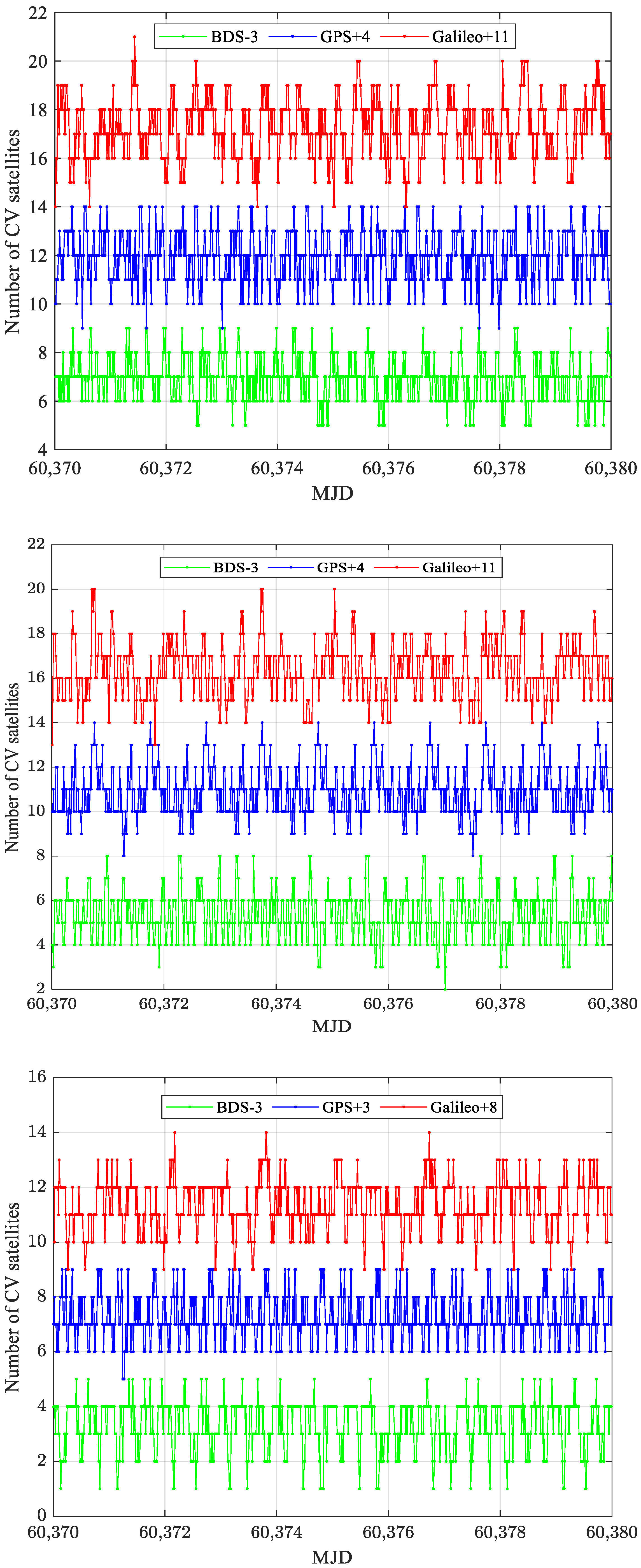
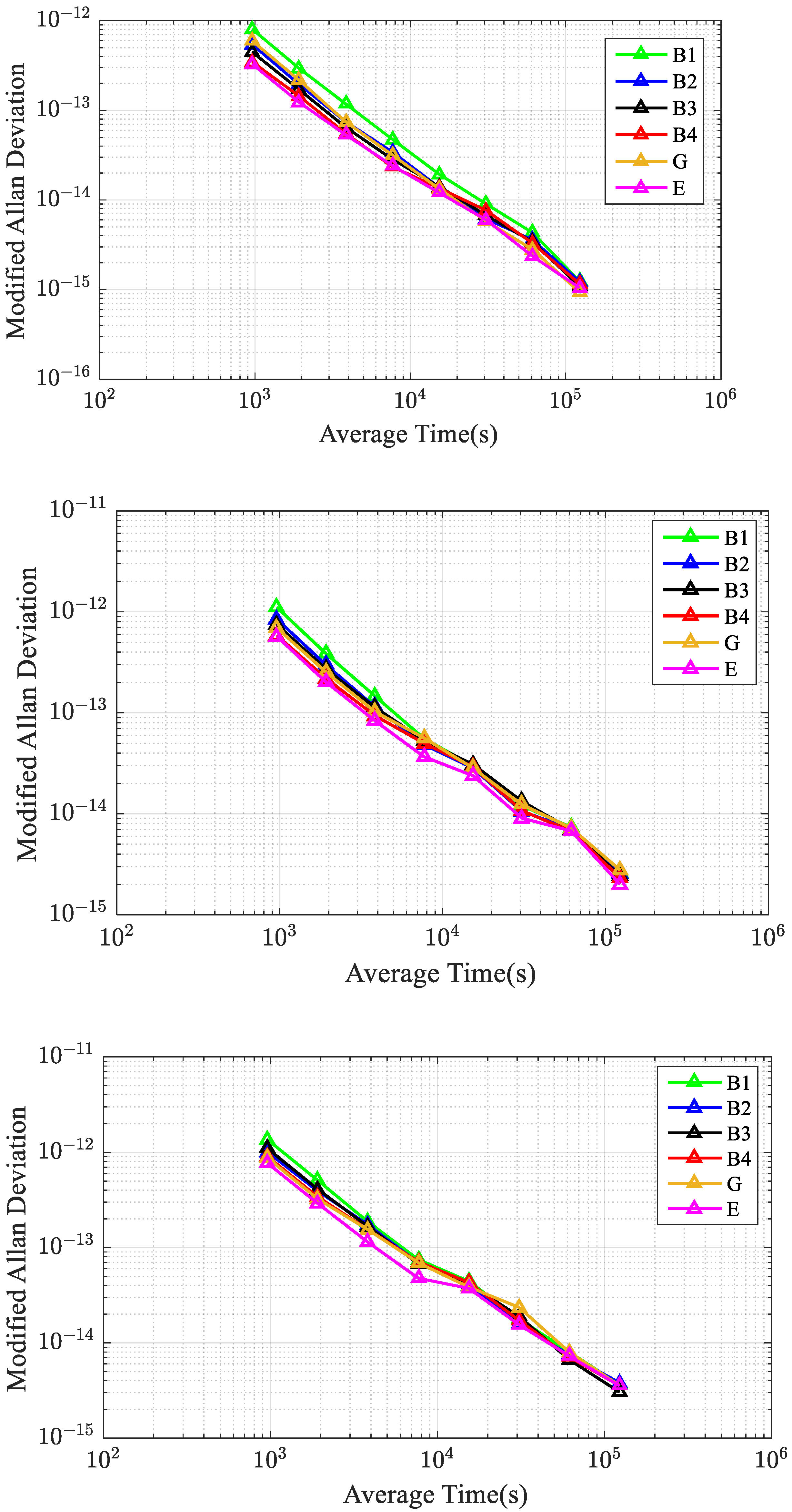
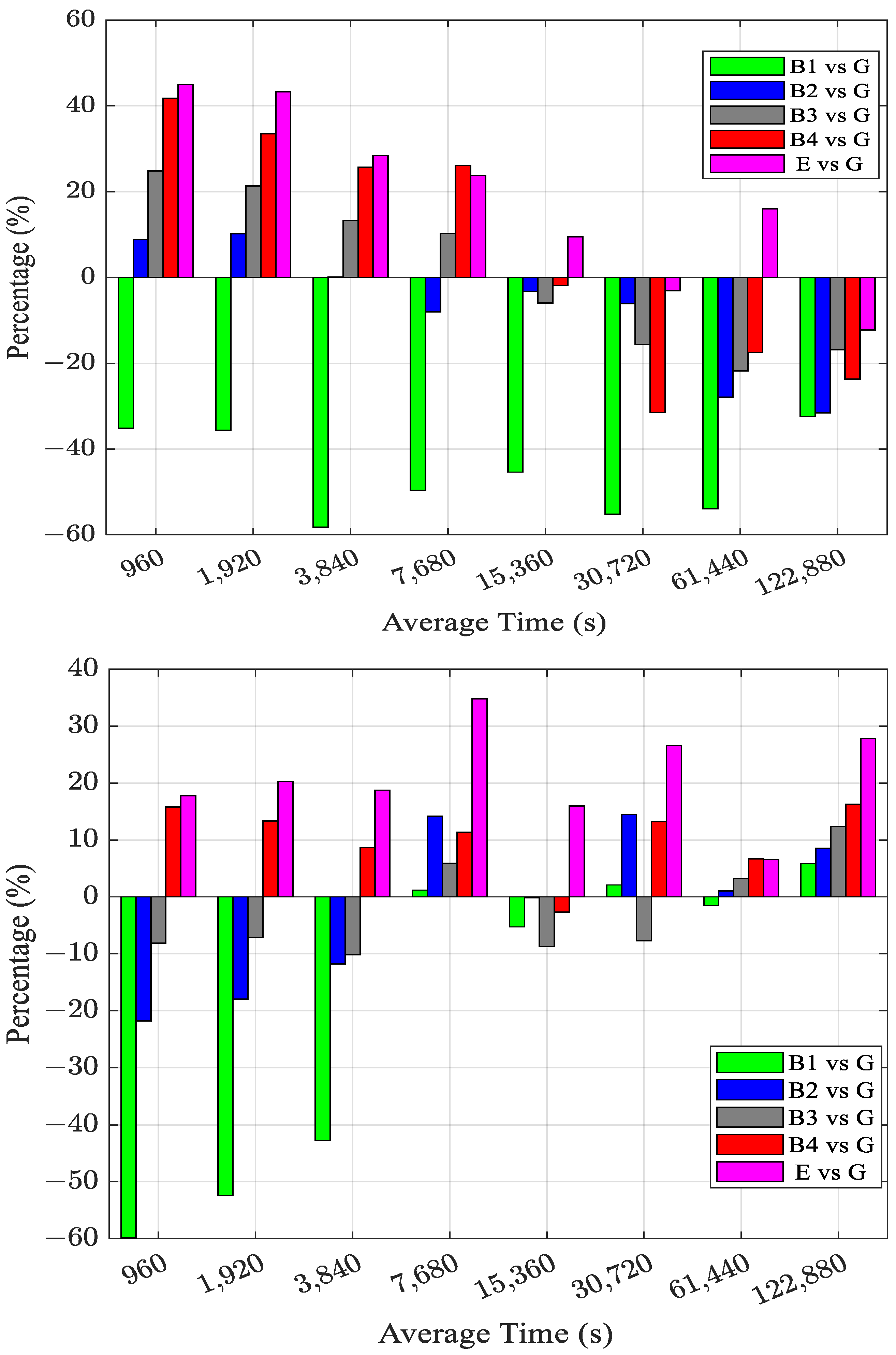

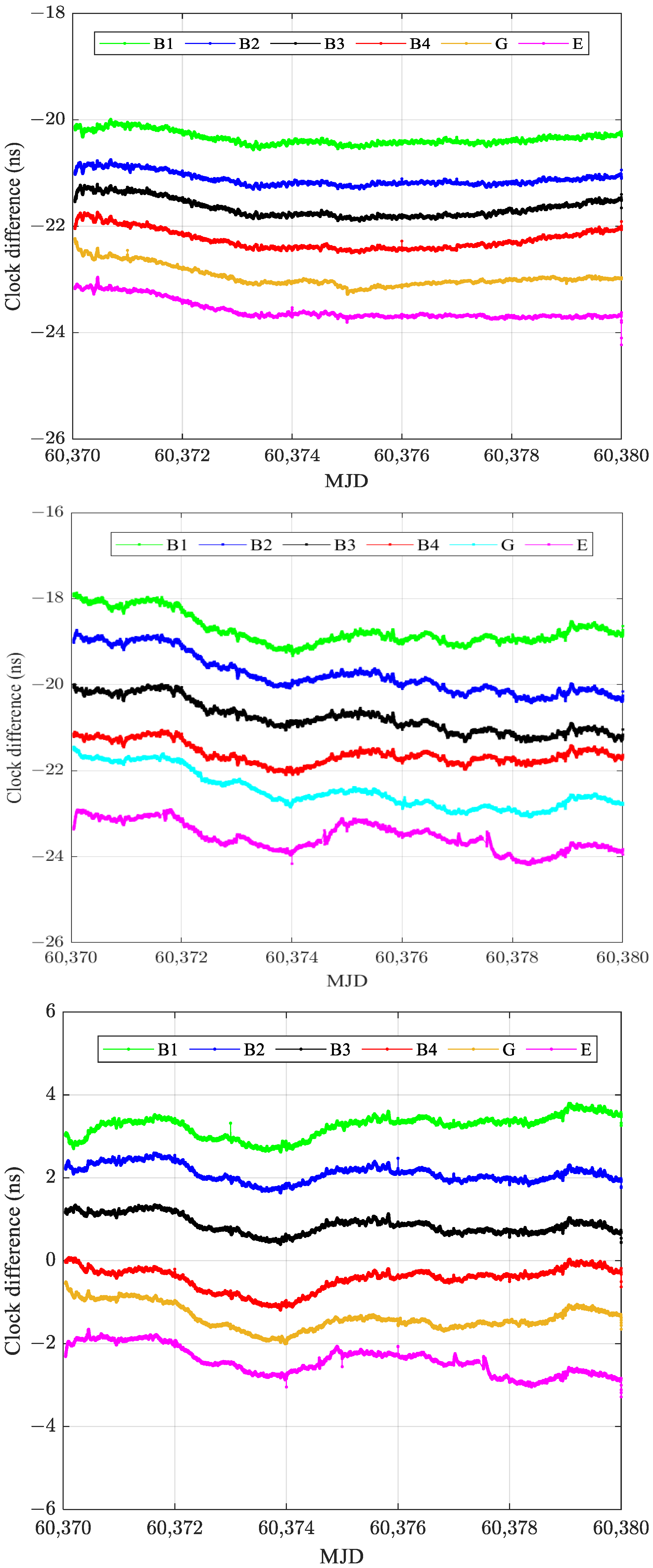
| Station | Country | Receiver Type | Antenna Type | UTC(K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUX | Belgium | SEPT POLARX5TR | JAVRINGANT_DM | UTC(ROB) |
| SPT0 | Sweden | SEPT POLARX5TR | TRM59800.00 | UTC(SP) |
| USN7 | America | SEPT POLARX5TR | TPSCR.G5 | UTC(USNO) |
| NIST | America | SEPT POLARX5TR | NOV750.R4 | UTC(NIST) |
| Link | Time Transfer Method | Distance/km |
|---|---|---|
| BRUX-SPT0 | CV/PPP | 947 |
| NIST-USN7 | CV/PPP | 2405 |
| BRUX-USN7 | CV/PPP | 5991 |
| Content | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Observation | Pseudorange carrier phase observations |
| Signal frequency | GPS L1 & L2; Galileo E1 & E5a; BDS-3 B1I & B3I; B1I & B2a; B1C & B3I; B1C & B2a |
| Sample rate | 30 s |
| Cut-off elevation | 7° |
| Satellite orbits, clock | GBM precise products |
| Ionospheric delay | Dual-frequency IF combination |
| Tropospheric delay | Saastamoinen model + random walk process |
| Receiver clock offset PCO/PCV | White noise estimation IGS20_2247.atx |
| Tides effect Phase wind-up | Model correction [20] Model correction [20] |
| Parameter estimation | Extended Kalman filter [21] |
| Link | Constellation | Frequency Selection | STD/ns |
|---|---|---|---|
| BRUX-SPT0 | BDS-3 | B1I & B3I | 0.43 |
| B1I & B2a | 0.29 | ||
| B1C & B3I | 0.24 | ||
| B1C & B2a | 0.20 | ||
| GPS | L1 & L2 | 0.31 | |
| Galileo | E1 & E5a | 0.18 | |
| NIST-USN7 | BDS-3 | B1I & B3I | 0.57 |
| B1I & B2a | 0.44 | ||
| B1C & B3I | 0.41 | ||
| B1C & B2a | 0.32 | ||
| GPS | L1 & L2 | 0.38 | |
| Galileo | E1 & E5a | 0.30 | |
| BRUX-USN7 | BDS-3 | B1I & B3I | 0.69 |
| B1I & B2a | 0.55 | ||
| B1C & B3I | 0.58 | ||
| B1C & B2a | 0.48 | ||
| GPS | L1 & L2 | 0.50 | |
| Galileo | E1 & E5a | 0.41 |
| Link | B1 vs. G | B2 vs. G | B3 vs. G | B4 vs. G | E vs. G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRUX-SPT0 | −45.7 | −7.2 | 1.2 | 6.5 | 18.8 |
| NIST-USN7 | −19.1 | −1.6 | −2.5 | 10.3 | 21.1 |
| BRUX-USN7 | −16.7 | −2.5 | −1.8 | 2.0 | 15.8 |
| Link | Constellation | Frequency Selection | STD/ps |
|---|---|---|---|
| BRUX-SPT0 | BDS-3 | B1I & B3I | 14.0 |
| B1I & B2a | 12.6 | ||
| B1C & B3I | 13.3 | ||
| B1C & B2a | 11.7 | ||
| GPS | L1 & L2 | 9.4 | |
| Galileo | E1 & E5a | 10.0 | |
| NIST-USN7 | BDS-3 | B1I & B3I | 21.6 |
| B1I & B2a | 19.9 | ||
| B1C & B3I | 20.7 | ||
| B1C & B2a | 17.2 | ||
| GPS | L1 & L2 | 15.7 | |
| Galileo | E1 & E5a | 18.2 | |
| BRUX-USN7 | BDS-3 | B1I & B3I | 20.8 |
| B1I & B2a | 19.2 | ||
| B1C & B3I | 19.4 | ||
| B1C & B2a | 18.5 | ||
| GPS | L1 & L2 | 15.3 | |
| Galileo | E1 & E5a | 17.0 |
| Links | B2 vs. B1 | B3 vs. B1 | B4 vs. B1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BRUX-SPT0 | 11.7 | 5.0 | 13.1 |
| NIST-USN7 | 6.8 | 2.3 | 7.9 |
| BRUX-USN7 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 10.6 |
| Link | G vs. B4 | E vs. B4 |
|---|---|---|
| BRUX-SPT0 | 5.7 | 8.3 |
| NIST-USN7 | 14.6 | −12.0 |
| BRUX-USN7 | 10.4 | −8.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Pang, C.; Guo, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, X. Analysis on GNSS Common View and Precise Point Positioning Time Transfer: BDS-3/Galileo/GPS. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101725
Wang M, Pang C, Guo D, Wang S, Zhang Y, Gao J, Zhao X. Analysis on GNSS Common View and Precise Point Positioning Time Transfer: BDS-3/Galileo/GPS. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101725
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Meng, Chunlei Pang, Dong Guo, Shize Wang, Yang Zhang, Jinglong Gao, and Xiubin Zhao. 2025. "Analysis on GNSS Common View and Precise Point Positioning Time Transfer: BDS-3/Galileo/GPS" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101725
APA StyleWang, M., Pang, C., Guo, D., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Gao, J., & Zhao, X. (2025). Analysis on GNSS Common View and Precise Point Positioning Time Transfer: BDS-3/Galileo/GPS. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101725





