Rao and Wald Tests in Nonzero-Mean Non–Gaussian Sea Clutter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
- (1)
- denotes the primary data vector in the cell under test, where ; and represents the training data vector received from the kth reference cell, where stands for the number of the secondary data cell.
- (2)
- denotes the target for detection, where is the unknown deterministic complex amplitude of the target, which depends on both the radar cross-section (RCS) of the target and the transmission path. stands for the space-time steering vector, which is associated with the normalized spatial frequency and normalized Doppler frequency .
- (3)
- and represent the sea clutter vectors collected from the test cell and the kth reference cell, respectively. Similarly, k stands for the secondary data cell number.
3. Detector Design
3.1. The Rao Test
- (1)
- with and .
- (2)
- and stand for the real and imaginary parts of , respectively.
- (3)
- represents the maximum likelihood estimate (MLE) of under the hypothesis and is the MLE of under the hypothesis.
- (4)
- represents the conditional pdf of under the hypothesis.
- (5)
- denotes the detection threshold in the Rao test.
- (6)
- is the Fisher information matrix (FIM) withwhere , , , and are given byand
- (7)
- is expressed by
3.1.1. Nonzero-Mean Rao-Based with an Inverse Gamma Texture (Rao-IG-NZ) Detector
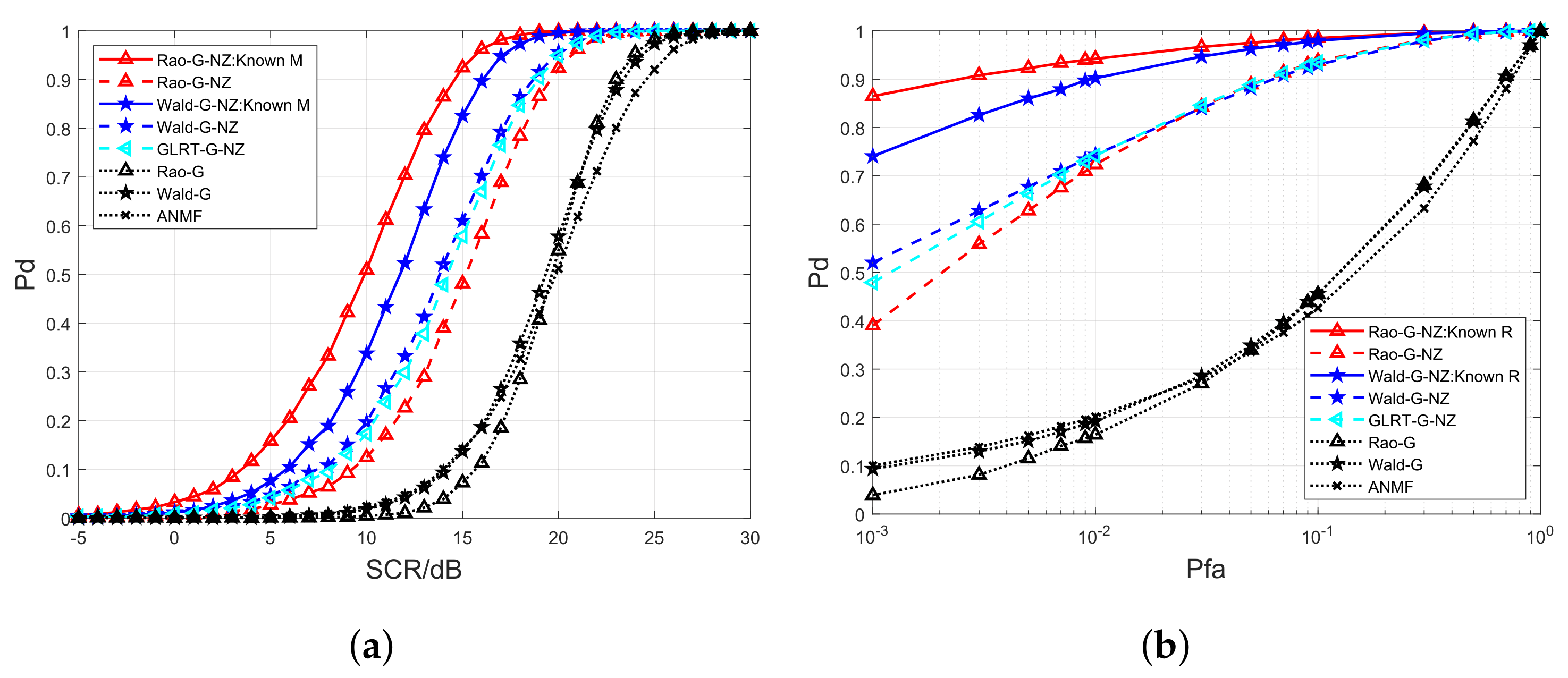
3.1.2. Nonzero-Mean Rao-Based with Gamma Texture (Rao-G-NZ) Detector
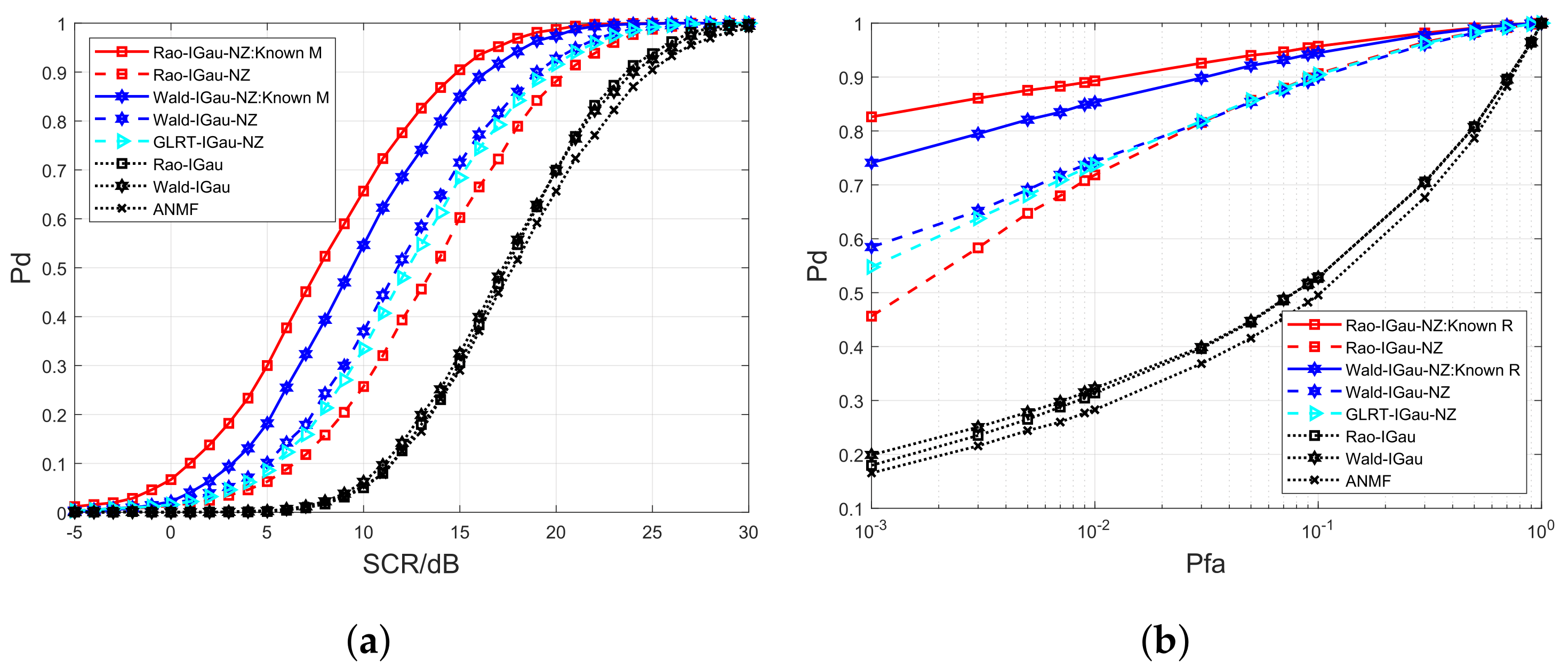
3.1.3. Nonzero-Mean Rao-Based with Inverse Gaussian Texture (Rao-IGau-NZ) Detector
3.2. The Wald Test
- (1)
- , , and are defined in the same way as for the Rao test.
- (2)
- and represent the MLEs of parameters and under .
- (3)
- stands for the detection threshold in the Wald test.
3.2.1. Nonzero-Mean Wald-Based with Inverse Gamma Texture (Wald-IG-NZ) Detector
3.2.2. Nonzero-Mean Wald-Based with Gamma Texture (Wald-G-NZ) Detector
3.2.3. Nonzero-Mean Wald-Based with Inverse Gaussian Texture (Wald-IGau-NZ) Detector
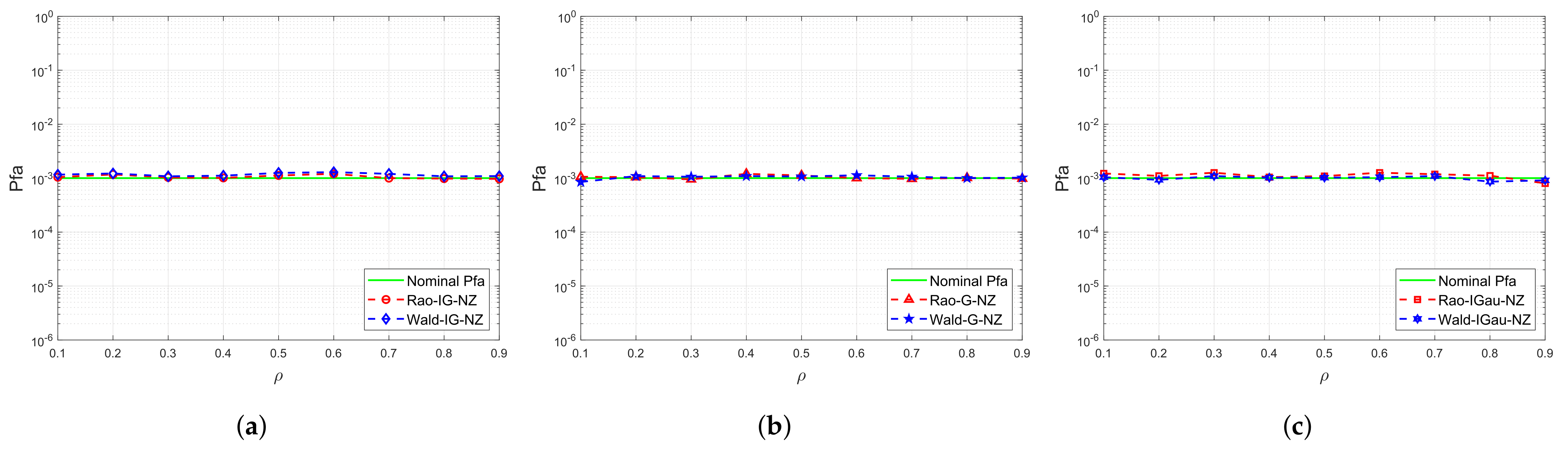
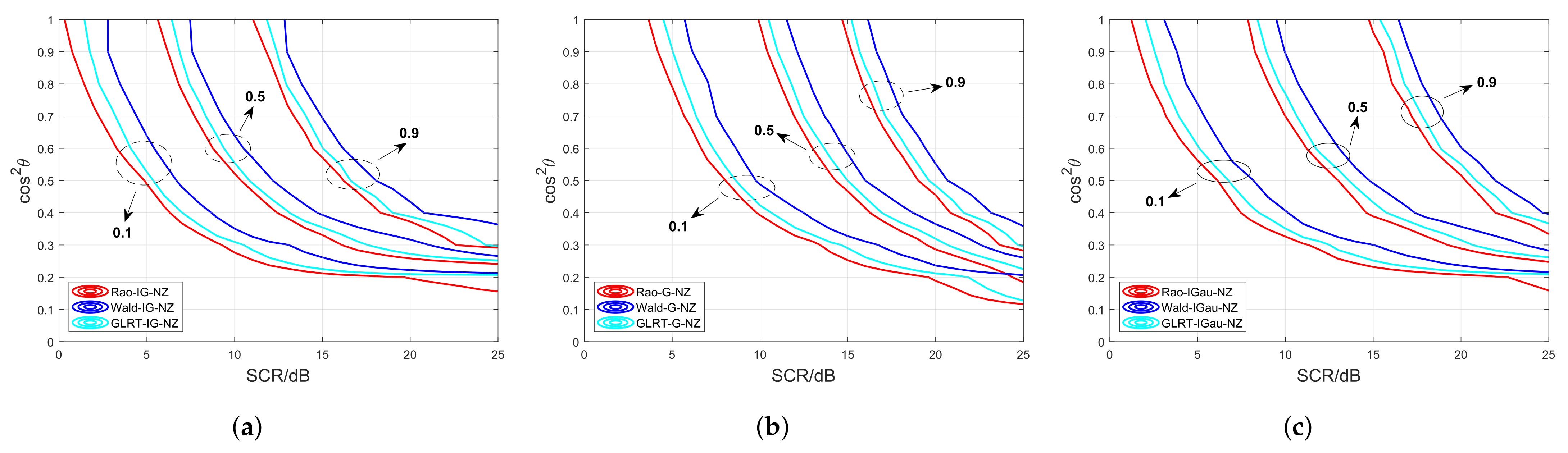
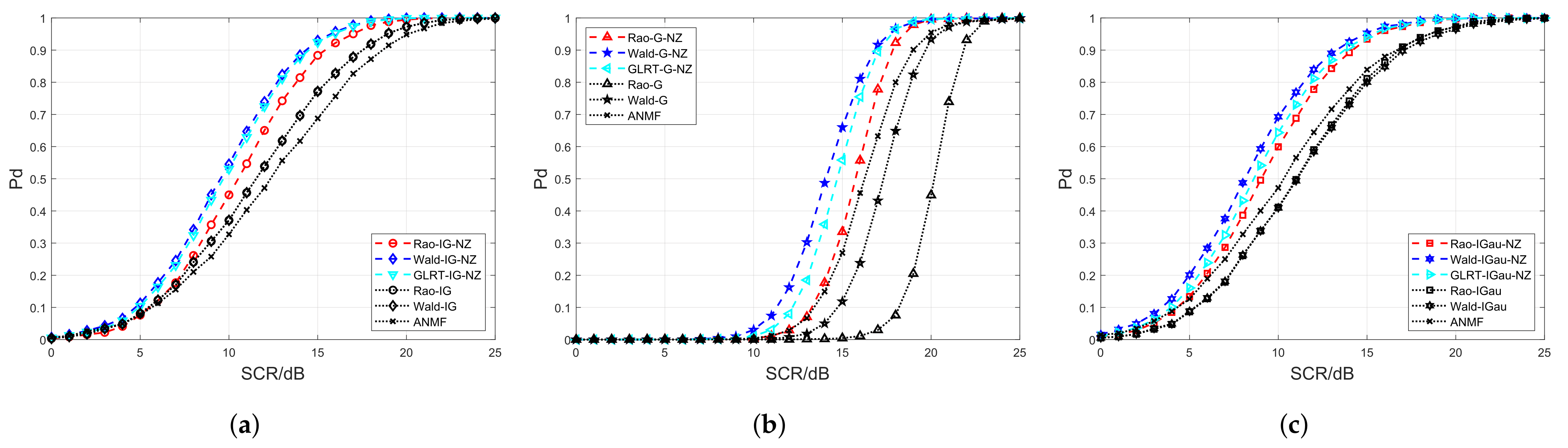
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Simulated Data
4.2. Measured Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of the Inverse of FIM
Appendix B. Proof of CFAR Properties for the Designed Detectors
References
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, W. Adaptive robust radar target detector based on gradient test. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Xu, H. Joint power, bandwidth, and subchannel allocation in a UAV-assisted DFRC network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 11633–11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, W.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Adaptive double subspace signal detection in Gaussian background—part II: Partially homogeneous environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 2358–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B. Joint customer assignment, power allocation, and subchannel allocation in a UAV-based joint radar and communication network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 29643–29660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robey, F.C.; Fuhrmann, D.R.; Kelly, E.J.; Nitzberg, R. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1992, 28, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.J. An adaptive detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1986, 2, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, A.; Kay, S.M.; Chen, H.; Farina, A. On the invariance, coincidence, and statistical equivalence of the GLRT, Rao test, and Wald test. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 58, 1967–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Zou, D.; Wang, Y. Rao tests for distributed target detection in interference and noise. Signal Process. 2015, 117, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Hao, C. Complex parameter Rao, Wald, gradient, and durbin tests for multichannel signal detection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Hao, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.-L. Multichannel adaptive signal detection: Basic theory and literature review. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, W.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Tunable adaptive detection in colocated MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, F.; Orlando, D.; Ricci, G. CFAR detection strategies for distributed targets under conic constraints. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 3305–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Massaro, D.; Orlando, D.; Farina, A. Radar adaptive detection architectures for heterogeneous environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 4307–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, L.; Orlando, D. Polarimetric covariance eigenvalues classification in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Orlando, D.; Ma, X.; Hou, C. Persymmetric Rao and Wald tests for partially homogeneous environment. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2012, 19, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, M. Adaptive detection of distributed target in the presence of signal mismatch in compound Gaussian clutter. Digital Signal Process. 2020, 102, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H. Persymmetric GLRT detection in MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 11913–11923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, B.; Jin, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L. Persymmetric GLRT-based detectors with training data for FDA-MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 61, 4776–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-R.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Polarization-space-time domain generalized likelihood ratio detection of radar targets. Signal Process. 1995, 41, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, A.; Ricci, G. A polarimetric adaptive matched filter. Signal Process. 2001, 81, 2583–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Gazor, S.; Ma, X.; Yan, S.; Hou, C.; Orlando, D. Polarimetric detection and range estimation of a point-like target. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, L.L.; Friedlander, B. Matched subspace detectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2146–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraut, S.; Scharf, L.L.; McWhorter, L.T. Adaptive subspace detectors. IEEE Tran. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Adaptive double subspace signal detection in Gaussian background—part I: Homogeneous environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, D.; Ricci, G.; Scharf, L.L. A unified theory of adaptive subspace detection part I: Detector designs. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 4925–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Du, Q.; Wang, Y.L. Multichannel signal detection based on Wald test in subspace interference and Gaussian noise. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Dung, H. Mixture texture model with weighted generalized inverse Gaussian distribution for target detection. Digital Signal Process. 2024, 154, 104677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Fei, T. A robust joint frequency spectrum and power allocation strategy in a coexisting radar and communication system. Chinese J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Maio, A.D.; Galdi, C. Statistical analysis of real clutter at different range resolutions. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 40, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K. Compound representation of high resolution sea clutter. Electron. Lett. 1981, 16, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezache, A.; Soltani, F.; Sahed, M.; Chalabi, I. Model for non-Rayleigh clutter amplitudes using compound inverse Gaussian distribution: An experimental analysis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.-J. Persymmetric adaptive detection of distributed targets in compound-Gaussian sea clutter with Gamma texture. Signal Process. 2018, 152, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Z.; He, Q.; Xiong, B.; Cheng, Z. Persymmetric adaptive target detection with dual-polarization in compound Gaussian sea clutter with inverse Gamma texture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xue, J.; Shui, P. Adaptive detection of range-spread targets in compound Gaussian clutter with the square root of inverse Gaussian texture. Digital Signal Process. 2016, 56, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera-Pons, J.; Pascal, F.; Ovarlez, J.P. Adaptive nonzero-Mean Gaussian detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; He, Z. Adaptive radar target detection in nonzero-mean compound Gaussian sea clutter with random texture. Signal Process. 2025, 227, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L.; Bocquet, S. Non-coherent radar detection performance in medium grazing angle X-Band sea clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.Y.; Shui, P.L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Li, X.; Xu, X.Y. An empirical model of shape parameter of sea clutter based on X-band island-based radar database. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Hao, C. Modified Rao test for multichannel adaptive signal detection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, F.; Forster, P.; Ovarlez, J.P.; Larzabal, P. Performance analysis of covariance matrix estimates in impulsive noise. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 2206–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xu, S.; Shui, P. Coincidence of the Rao Test, Wald Test and gLRT for Radar Target Detection in Generalized Pareto Clutter. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Dalian, China, 20–22 September 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; He, Z.; He, Q.; Zhuang, Y. Adaptive CFAR Rao and Wald Detectors for Compound Gaussian Sea Clutter with Inverse Gaussian Texture. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 5028–5031. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, E.; Lops, M.; Ricci, G. Asymptotically optimum radar detection in compound-Gaussian clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1995, 31, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Moya, J.; Gismero-Menoyo, J.; Asensio-Lopez, A.; Blanco-Del-Campo, A. Small-target detection in high-resolution heterogeneous sea-clutter: An empirical analysis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 1880–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, F.; Besson, O.; Ricci, G. An ABORT-like detector with improved mismatched signals rejection capabilities. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 56, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, A.D.; Iommelli, S. Coincidence of the Rao Test, Wald Test, and GLRT in Partially Homogeneous Environment. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2008, 15, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, B.; Bakker, R. McMaster IPIX Radar Sea Clutter Database. 1998. Available online: http://soma.mcmaster.ca/ipix.php (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Shui, P.L.; Shi, L.X.; Yu, H.; Huang, Y.T. Iterative maximum likelihood and outlier-robust bipercentile estimation of parameters of compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian texture. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, A.D. Rao Test for Adaptive detection in Gaussian interference with unknown covariance matrix. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 3577–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Detectors | Average Time Costs |
|---|---|
| Rao-IG-NZ | s |
| Wald-IG-NZ | s |
| GLRT-IG-NZ | s |
| Range Cell | Shape Parameters | Scale Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Cell 9 (file 84, VV) | ||
| Cell 9 (file 86, HV) | ||
| Cell 18 (file 84, VV) |
| Range Cell | MSEs |
|---|---|
| Cell 9 (file 84, VV) | |
| Cell 9 (file 86, HV) | |
| Cell 18 (file 84, VV) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; He, Z. Rao and Wald Tests in Nonzero-Mean Non–Gaussian Sea Clutter. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101696
Wu H, Guo H, Wang Z, He Z. Rao and Wald Tests in Nonzero-Mean Non–Gaussian Sea Clutter. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101696
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Haoqi, Hongzhi Guo, Zhihang Wang, and Zishu He. 2025. "Rao and Wald Tests in Nonzero-Mean Non–Gaussian Sea Clutter" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101696
APA StyleWu, H., Guo, H., Wang, Z., & He, Z. (2025). Rao and Wald Tests in Nonzero-Mean Non–Gaussian Sea Clutter. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101696





