Analysis of Tropospheric NO2 Observation Using Pandora and MAX-DOAS Instrument in Xianghe, North China
Abstract
1. Introduction
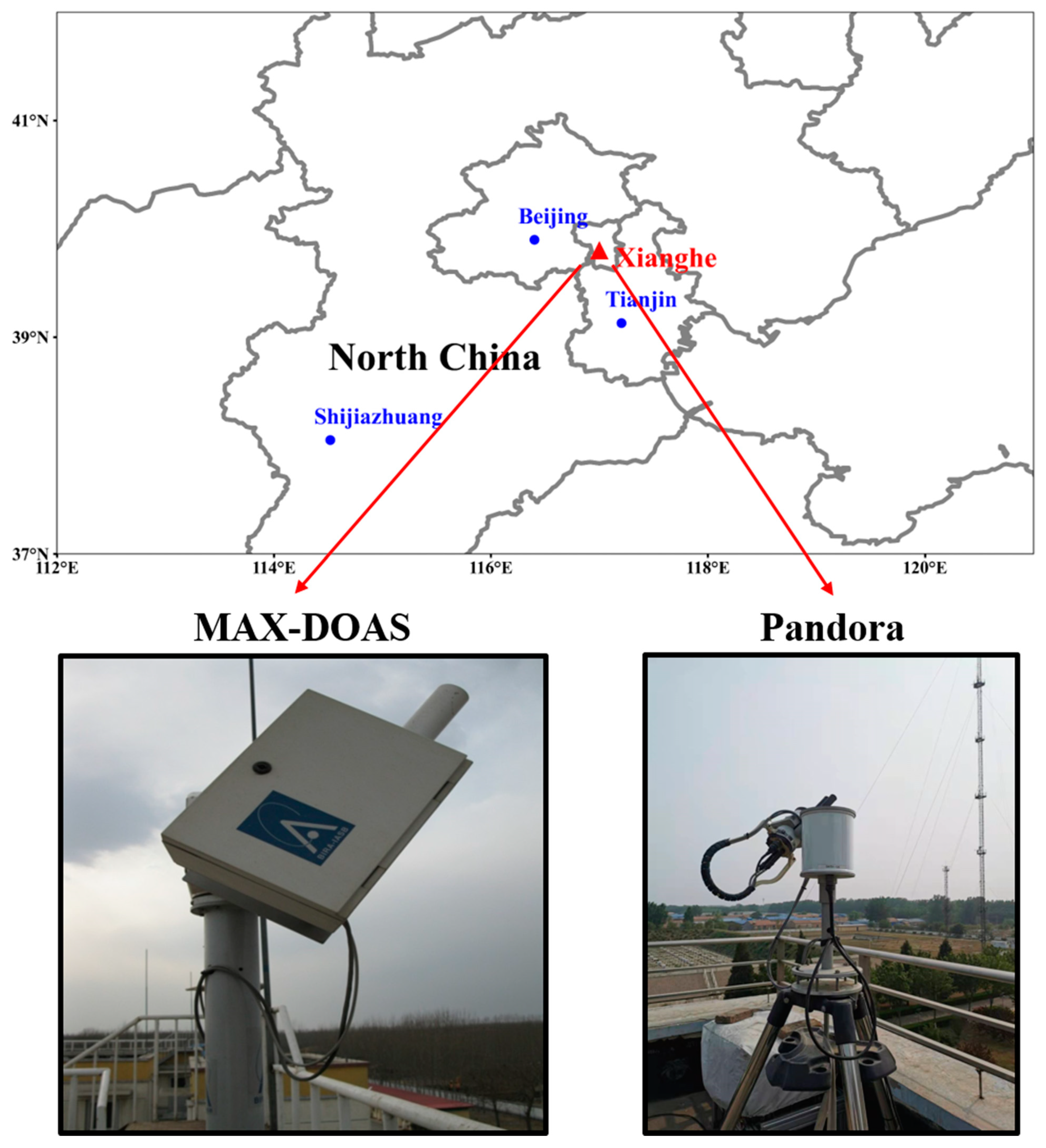
2. Instrumental and Satellite Data
2.1. Pandora Spectrometer
2.2. OMI and TROPOMI NO2 Product
3. Methodology
3.1. Spectral Preprocessing for Pandora Observations
3.1.1. Spectral Preprocessing
3.1.2. Dark Current Calibration
3.1.3. Spectral Analysis
3.2. Inversion Algorithm and Tropospheric NO2 Retrieval
3.2.1. Retrieval of NO2 Slant Column Densities
3.2.2. Retrieval of NO2 Vertical Column Densities
4. Results
4.1. Comparison Experiment Between Ground-Based Pandora and MAX-DOAS
4.1.1. Experimental Scheme
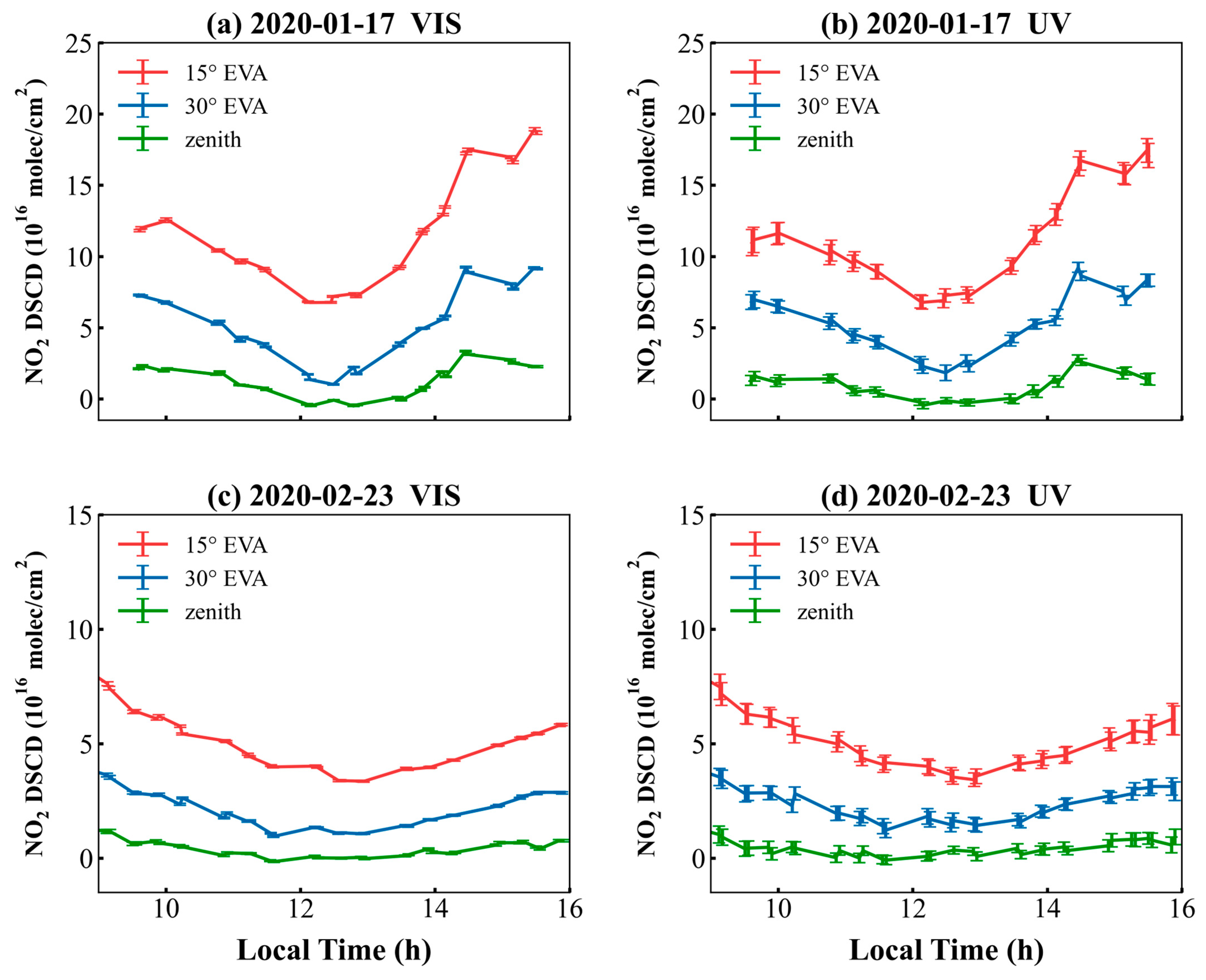
4.1.2. Comparative Analysis of NO2 Differential Slant Column Densities
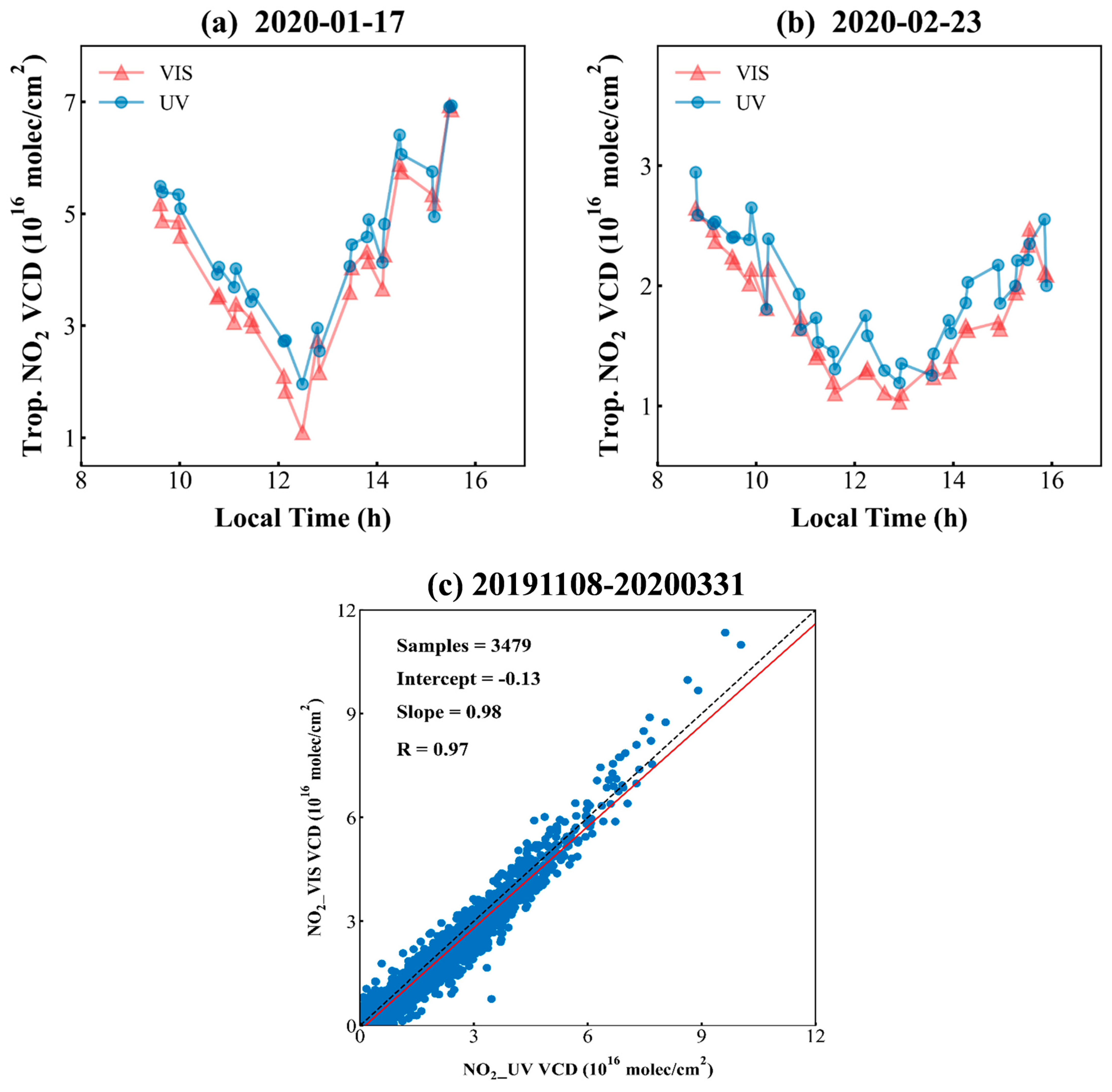
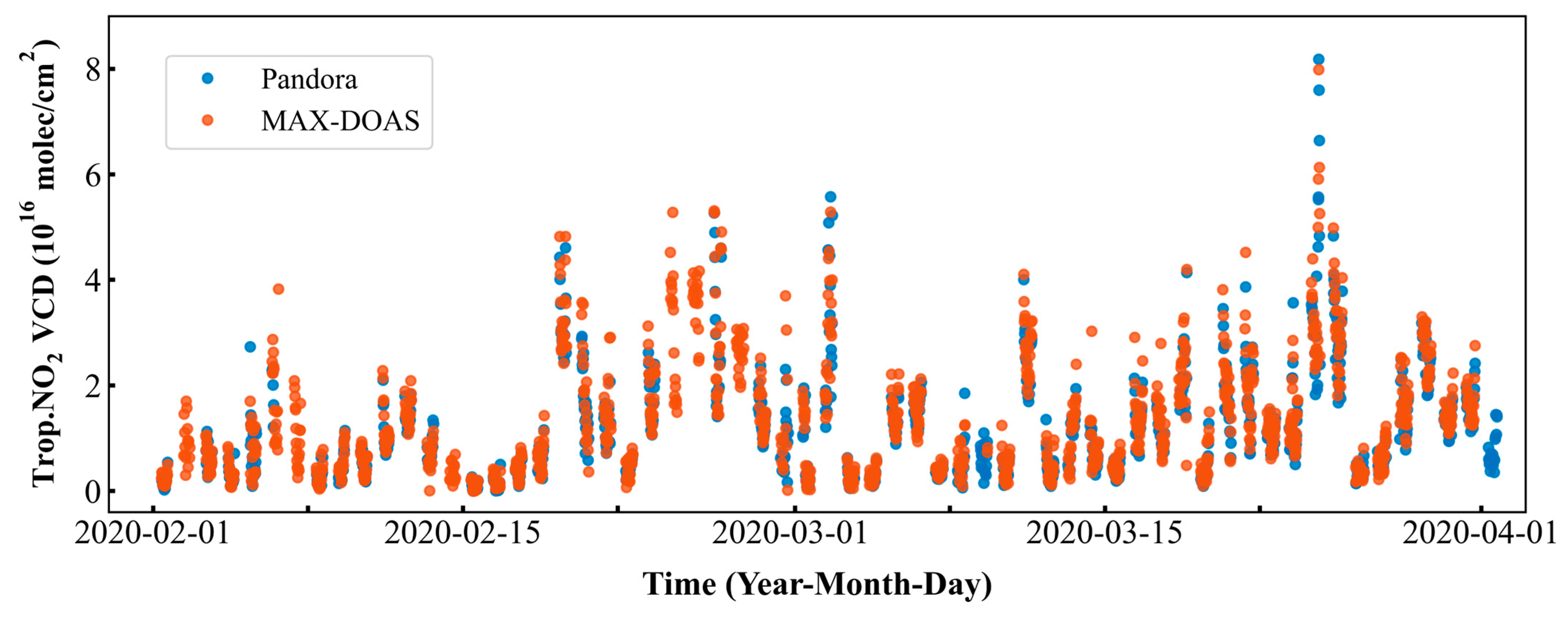
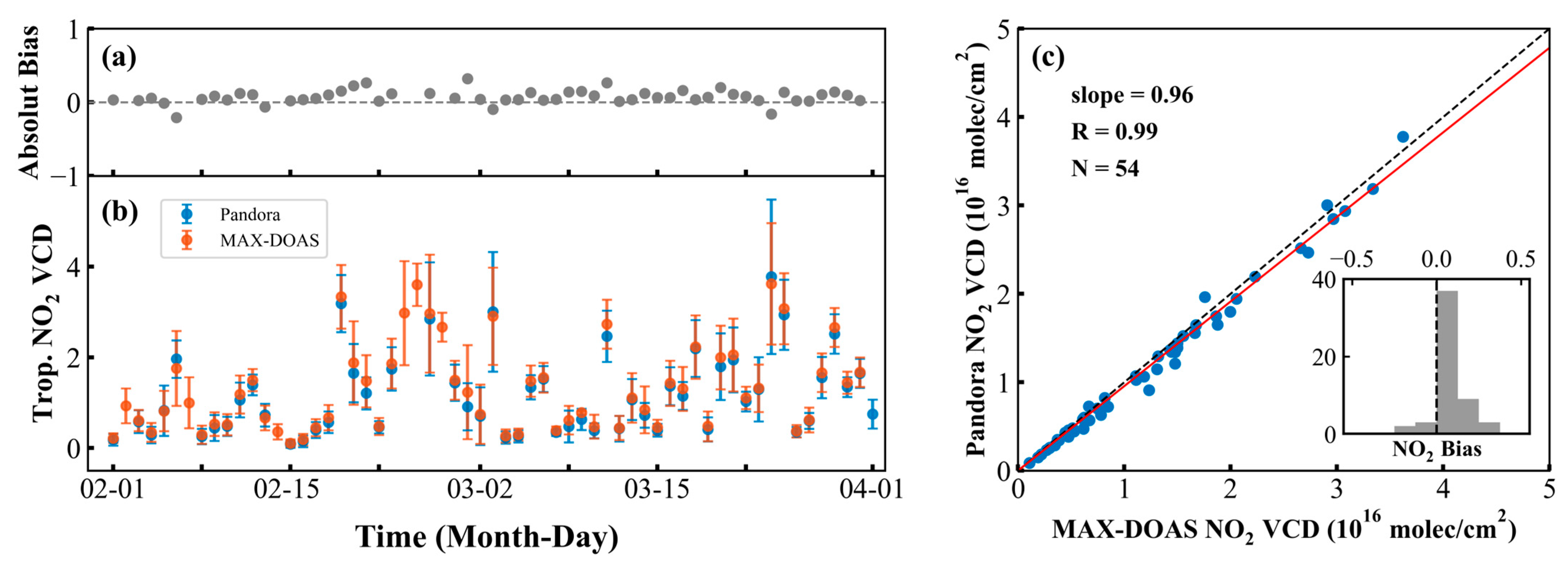
4.1.3. Comparative Analysis of NO2 Vertical Column Densities
4.2. Comparison Between the Ground-Based Pandora and Satellite Observations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, D.; Hakkarainen, J.; Liu, Y.; Ialongo, I.; Cai, Z.; Tamminen, J. Detection of Anthropogenic CO2 Emission Signatures with TanSat CO2 and with Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor (S5P) NO2 Measurements: First Results. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luvsan, M.E. The patterns and health risks of NO2 and SO2 pollution in Mongolia. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Risk, Sydney, Australia, 17–20 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, S.; Ferreira, J.; Silveira, C.; Costa, C.; Lopes, D.; Relvas, H.; Borrego, C.; Roebeling, P.; Miranda, A.I.; Paulo Teixeira, J. Integrating Health on Air Quality Assessment-Review Report on Health Risks of Two Major European Outdoor Air Pollutants: PM and NO2. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2014, 17, 307–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averett, N. Exercising in Polluted Areas: Study Suggests Benefits Outweigh the Health Risks of NO2 Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, A158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heue, K.P.; Richter, A.; Bruns, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Platt, U.; Pundt, I.; Wang, P.; Wagner, T. Validation of SCIAMACHY tropospheric NO2-columns with AMAXDOAS measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2004, 4, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, H.; Kanaya, Y.; Akimoto, H.; Tanimoto, H.; Bucsela, E.J. Validation of OMI tropospheric NO2 column data using MAX-DOAS measurements deep inside the North China Plain in June 2006: Mount Tai Experiment 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6577–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenig, M.O.; Cede, A.M.; Bucsela, E.J.; Celarier, E.A.; Boersma, K.F.; Veefkind, J.P.; Brinksma, E.J.; Gleason, J.F.; Herman, J.R. Validation of OMI tropospheric NO2 column densities using direct-Sun mode Brewer measurements at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D16S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ma, J.; Lin, W.; Zhao, H.; Shaiganfar, R.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. MAX-DOAS measurements and satellite validation of tropospheric NO2 and SO2 vertical column densities at a rural site of North China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulou, E.; Hendrick, F.; Pinardi, G.; Friedrich, M.M.; Roozendael, M.V. Validation of TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 columns using dual-scan multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) measurements in Uccle, Brussels. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 5165–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, W. Assessment of the Performance of TROPOMI NO2 and SO2 Data Products in the North China Plain: Comparison, Correction and Application. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Richter, A.; Schnhardt, A.; Meier, A.; Bsch, T.; Seyler, A.; Krause, K.U.; Behrens, L.; Wittrock, F.; Merlaud, A. Validation of Sentinel-5P TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 products by comparison with NO2 measurements from airborne imaging DOAS, ground-based stationary DOAS, and mobile car DOAS measurements during the S5P-VAL-DE-Ruhr campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 1357–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, A.W.; Mcelroy, C.T.; Kerr, J.B. Nitrogen Dioxide Concentrations in the Atmosphere. Nature 1973, 246, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noxon, J.F. Nitrogen Dioxide in the Stratosphere and Troposphere Measured by Ground-Based Absorption Spectroscopy. Science 1975, 189, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönninger, G.; Von Friedeburg, C.; Platt, U. Multi axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 4, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, O.; Platt, U.; Shaiganfar, R.; Wagner, T. Mobile MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric trace gases. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Vlemmix, T.; Piters, A.J.M.; Stammes, P.; Wang, P.; Levelt, P.F. Retrieval of tropospheric NO2 using the MAX-DOAS method combined with relative intensity measurements for aerosol correction. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1287–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leser, H.; Honninger, G.; Platt, U. MAX-DOAS measurements of BrO and NO2 in the marine boundary layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 101029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Beirle, S.; Jin, J.L.; Shaiganfar, R.; Yan, P.; Wagner, T. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities over Beijing: Results of the first three years of ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements (2008–2011) and satellite validation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hendrick, F.; Wang, P.; Tang, G.; Clémer, K.; Yu, H.; Fayt, C.; Hermans, C.; Gielen, C.; Müller, J.F.; et al. Evaluation of tropospheric SO2 retrieved from MAX-DOAS measurements in Xianghe, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11149–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, Q.; Liu, B.; Cao, J.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Y. Evaluation and Evolution of MAX-DOAS-observed Vertical NO2 Profiles in Urban Beijing. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Chen, M.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Li, A.; Ren, B.; Zhang, T.; Fan, G.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; et al. Evaluation of MAX-DOAS Profile Retrievals under Different Vertical Resolutions of Aerosol and NO2 Profiles and Elevation Angles. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinksma, E.J.; Pinardi, G.; Volten, H.; Braak, R.; Levelt, P.F. The 2005 and 2006 DANDELIONS NO2 and aerosol intercomparison campaigns. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.; Cede, A.; Spinei, E.; Mount, G.; Tzortziou, M.; Abuhassan, N. NO2 column amounts from ground-based Pandora and MFDOAS spectrometers using the direct-sun DOAS technique: Intercomparisons and application to OMI validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clémer, K.; Roozendael, M.V.; Fayt, C.; Hendrick, F.; Mazière, M.D. Multiple wavelength retrieval of tropospheric aerosol optical properties from MAXDOAS measurements in Beijing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piters, A.J.M.; Boersma, K.F.; Kroon, M.; Hains, J.C.; Van Roozendael, M.; Wittrock, F.; Abuhassan, N.; Adams, C.; Akrami, M.; Allaart, M.A.F.; et al. The Cabauw Intercomparison campaign for Nitrogen Dioxide measuring Instruments (CINDI): Design, execution, and early results. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 457–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzortziou, M.; Herman, J.R.; Cede, A.; Loughner, C.P.; Abuhassan, N.; Naik, S. Spatial and temporal variability of ozone and nitrogen dioxide over a major urban estuarine ecosystem. J. Atmos. Chem. 2015, 72, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fioletov, V.; Strong, K.; Cede, A.; Davies, J. Accuracy, precision, and temperature dependence of Pandora total ozone measurements estimated from a comparison with the Brewer triad in Toronto. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5747–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.; Lee, H.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.W.; Herman, J.R.; Abuhassan, N.K.; Ahn, J.Y. Regional characteristics of NO2 column densities from Pandora observations during the MAPS-Seoul campaign. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.; Spinei, E.; Fried, A.; Kim, J.; Segal-Rozenhaimer, M. NO2 and HCHO measurements in Korea from 2012 to 2016 from Pandora Spectrometer Instruments compared with OMI retrievals and with aircraft measurements during the KORUS-AQ campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2018, 11, 4583–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.M.; Stauffer, R.M.; Boyle, T.P.; Kollonige, D.E.; Miyazaki, K.; Tzortziou, M.; Herman, J.R.; Abuhassan, N.; Jordan, C.E.; Lamb, B.T. Comparison of Near-Surface NO2 Pollution With Pandora Total Column NO2 During the Korea-United States Ocean Color (KORUS OC) Campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13560–13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, I.; Herman, J.; Krotkov, N.; Lamsal, L.; Tamminen, J. Comparison of OMI NO2 observations and their seasonal and weekly cycles with ground-based measurements in Helsinki. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5203–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.; Abuhassan, N.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Tzortziou, M. Underestimation of column NO2 amounts from the OMI satellite compared to diurnally varying ground-based retrievals from multiple PANDORA spectrometer instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5593–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.M.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Janz, S.J.; Kowalewski, M.G.; Williams, D. Evaluating the impact of spatial resolution on tropospheric NO2 column comparisons within urban areas using high-resolution airborne data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 6091–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, L.M.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Szykman, J.J.; Valin, L.C.; Janz, S.J.; Kowalewski, M.G.; Eskes, H.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Cede, A.; Mueller, M. Evaluating Sentinel-5P TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 column densities with airborne and Pandora spectrometers near New York City and Long Island Sound. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6113–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Griffin, D.; Fioletov, V.; Mclinden, C.; Lee, S.C. Assessment of the quality of TROPOMI high-spatial-resolution NO2 data products in the Greater Toronto Area. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2131–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.U.; Park, J.S.; Diaz, D.S.; Gebetsberger, M.; Müller, M.; Shalaby, L.; Tiefengraber, M.; Kim, H.; Park, S.S.; Song, C.K. Spatiotemporal inhomogeneity of total column NO2 in a polluted urban area inferred from TROPOMI and Pandora intercomparisons. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijnen, V.; Eskes, H.J.; Poupkou, A.; Elbern, H.; Zerefos, C. Comparison of OMI NO2 tropospheric columns with an ensemble of global and European regional air quality models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 9, 3273–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Yu, T.; Cheng, T.; Gu, X.; Guo, H. Intercomparison of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide retrieved from Ozone Monitoring Instrument over China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Swartz, W.H.; Marchenko, S.V.; Bucsela, E.J.; Chan, K.L.; Wenig, M.; Zara, M. The version 3 OMI NO2 standard product. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3133–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lamsal, L.N.; Follette-Cook, M.; Joiner, J.; Herman, J.R. Assessment of NO2 observations during DISCOVER-AQ and KORUS-AQ field campaigns. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2523–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMNO2 Product Guidance Document. Available online: https://aura.gesdisc.eosdis.nasa.gov/data/Aura_OMI_Level2/OMNO2.003/doc/README.OMNO2.pdf (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- TROPOMI ATBD of the Total and Tropospheric NO2 Data Products. Available online: https://sentiwiki.copernicus.eu/__attachments/1673595/S5P-KNMI-L2-0005-RP%20-%20Sentinel-5P%20TROPOMI%20ATBD%20NO2%20data%20products%202024%20-%202.8.0.pdf?inst-v=11c8ff02-71eb-449c-ab75-3b9180f56695 (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Griffin, D.; Zhao, X.; Mclinden, C.A.; Boersma, K.F.; Bourassa, A.; Dammers, E.; Degenstein, D.A.; Eskes, H.; Fehr, L.; Fioletov, V. High-Resolution Mapping of Nitrogen Dioxide With TROPOMI: First Results and Validation Over the Canadian Oil Sands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 46, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Rakitin, V. Comparison and Validation of TROPOMI and OMI NO2 Observations over China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, K.; Kurucz, R.L. An improved high-resolution solar reference spectrum for earth’s atmosphere measurements in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandaele, A.C.; Hermans, C.; Simon, P.C.; Carleer, M.; Colin, R.; Fally, S.; Mérienne, M.F.; Jenouvrier, A.; Coquart, B. Measurements of the NO2 absorption cross-section from 42,000 cm−1 to 10,000 cm−1 (238–1000 nm) at 220 K and 294 K. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 59, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogumil, K.; Orphal, J.; Homann, T.; Voigt, S.; Spietz, P.; Fleischmann, O.C.; Vogel, A.; Hartmann, M.; Kromminga, H.; Bovensmann, H. Measurements of molecular absorption spectra with the SCIAMACHY pre-flight model: Instrument characterization and reference data for atmospheric remote-sensing in the 230–2380 nm region. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 157, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, C.; Vandaele, A.C.; Fally, S.; Carleer, M.; Merienne, M.F. Absorption Cross-section of the Collision-Induced Bands of Oxygen from the UV to the NIR. In Weakly Interacting Molecular Pairs: Unconventional Absorbers of Radiation in the Atmosphere; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, L.S.; Barbe, A.; Benner, D.C.; Brown, L.R.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Carleer, M.R.; Chance, K.; Clerbaux, C.; Dana, V.; Devi, V.M. The HITRAN molecular spectroscopic database: Edition of 2000 including updates through 2001. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2003, 82, 5–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, O.C.; Hartmann, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Orphal, J. New ultraviolet absorption cross-sections of BrO at atmospheric temperatures measured by time-windowing Fourier transform spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 168, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, R.; Moortgat, G.K. Temperature dependence of the absorption cross sections of formaldehyde between 223 and 323 K in the wavelength range 225–375 nm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 7089–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaiganfar, R.; Beirle, S.; Sharma, M.; Chauhan, A.; Singh, R.P.; Wagner, T. Estimation of NOx emissions from Delhi using Car MAX-DOAS observations and comparison with OMI satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10871–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.J.; Thompson, A.M.; Kollonige, D.E.; Martins, D.K.; Tzortziou, M.A.; Herman, J.R.; Berkoff, T.A.; Abuhassan, N.K.; Cede, A. Effects of local meteorology and aerosols on ozone and nitrogen dioxide retrievals from OMI and pandora spectrometers in Maryland, USA during DISCOVER-AQ 2011. J. Atmos. Chem. 2015, 72, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Wiegner, M.; Alberti, C.; Wenig, M. MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO in Munich and the comparison to OMI and TROPOMI satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4499–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Pinardi, G.; Lambert, J.C.; Zehner, C. Ground-based validation of the Copernicus Sentinel-5P TROPOMI NO2 measurements with the NDACC ZSL-DOAS, MAX-DOAS and Pandonia global networks. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Brinksma, E.J. Error analysis for tropospheric NO2 retrieval from space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Josefsson, W.A.P. Focused sun observations using a Brewer ozone spectrophotometer. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 15813–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondas, A.; Evans, R.; Stuebi, R.; Köhler, U.; Weber, M. Evaluation of the use of five laboratory-determined ozone absorption cross sections in Brewer and Dobson retrieval algorithms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, A.; Koskela, T. On the sources of bias in aerosol optical depth retrieval in the UV range. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabcak, P. Comparison of the optical depth of total ozone and atmospheric aerosols in Poprad-Ganovce, Slovakia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7739–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastiouk, V.; Diémoz, H.; Mcelroy, C.T. A physically based correction for stray light in Brewer spectrophotometer data analysis. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 4785–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, O.; Vaziri, Z.; Mcelroy, C.T.; Tarasick, D.W.; Evans, R.D.; Petropavlovskikh, I.; Feng, K.H. The Effect of Instrumental Stray Light on Brewer and Dobson Total Ozone Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2018, 12, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, Z.V.; Moeini, O.; Mcelroy, T.; Barton, D.; Savastiouk, V. A calibration procedure which accounts for non-linearity in single-monochromator Brewer ozone spectrophotometer measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lampel, J.; Xie, P.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric aerosols, NO2, SO2 and HCHO in Wuxi, China, from 2011 to 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2189–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
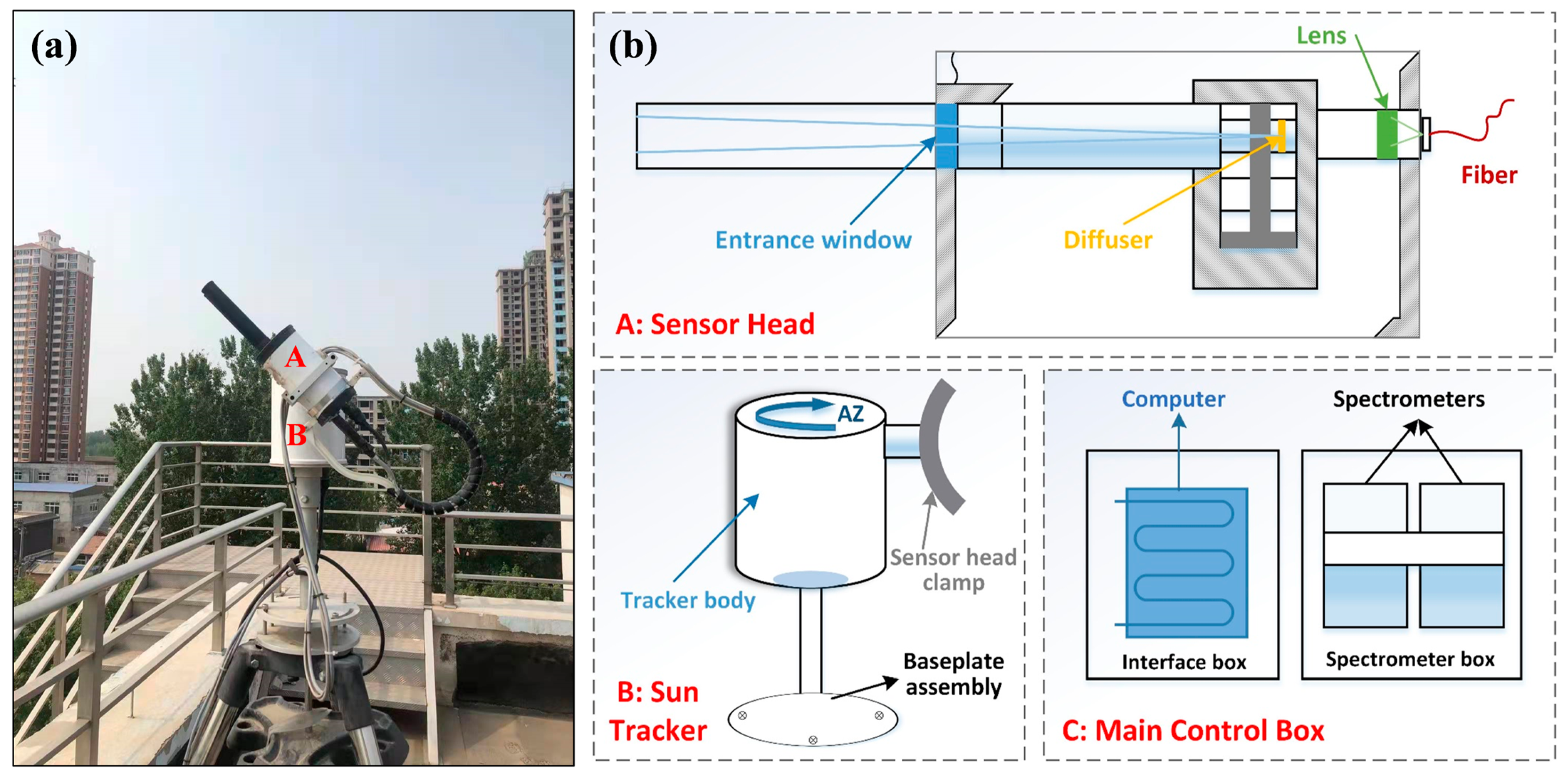

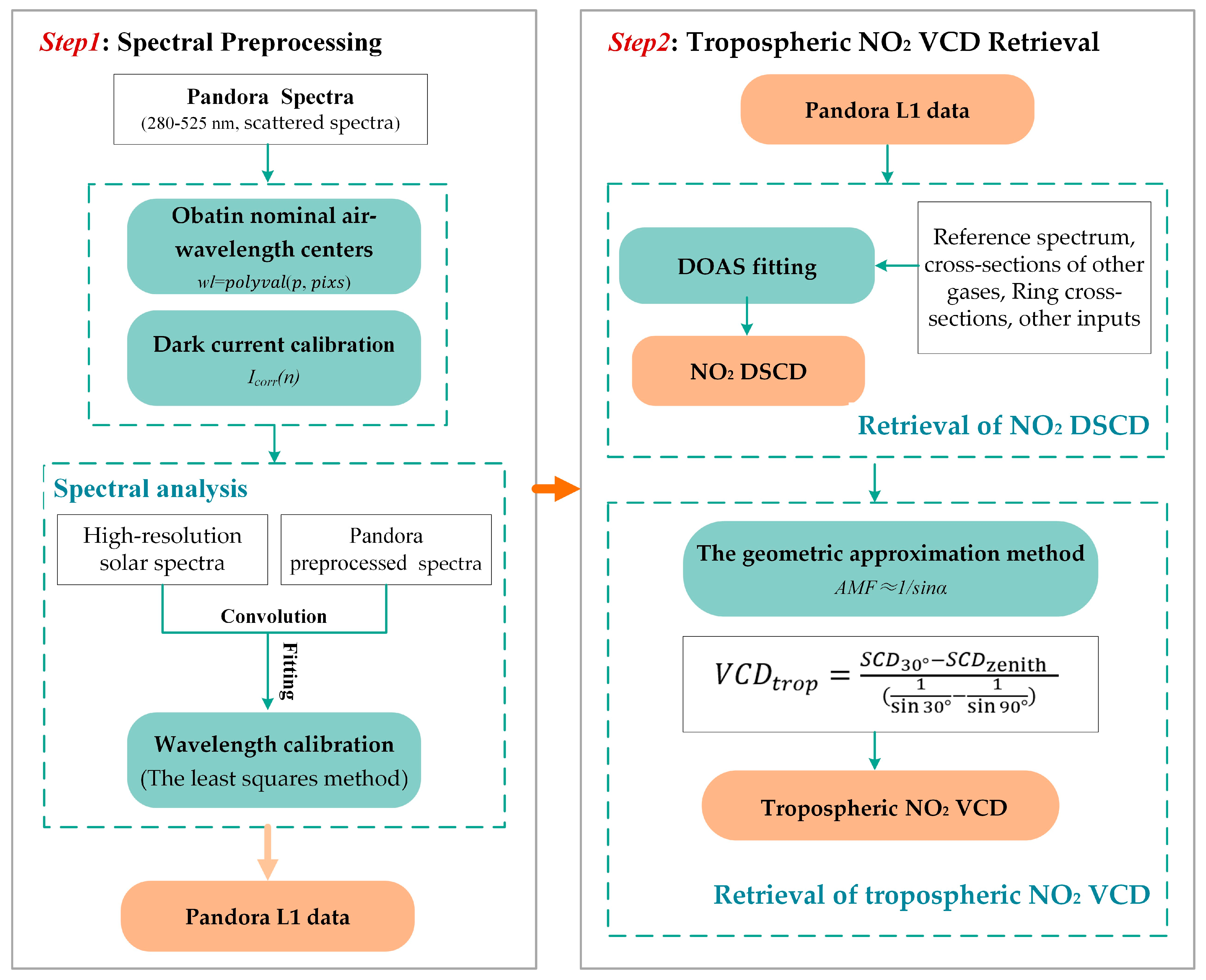

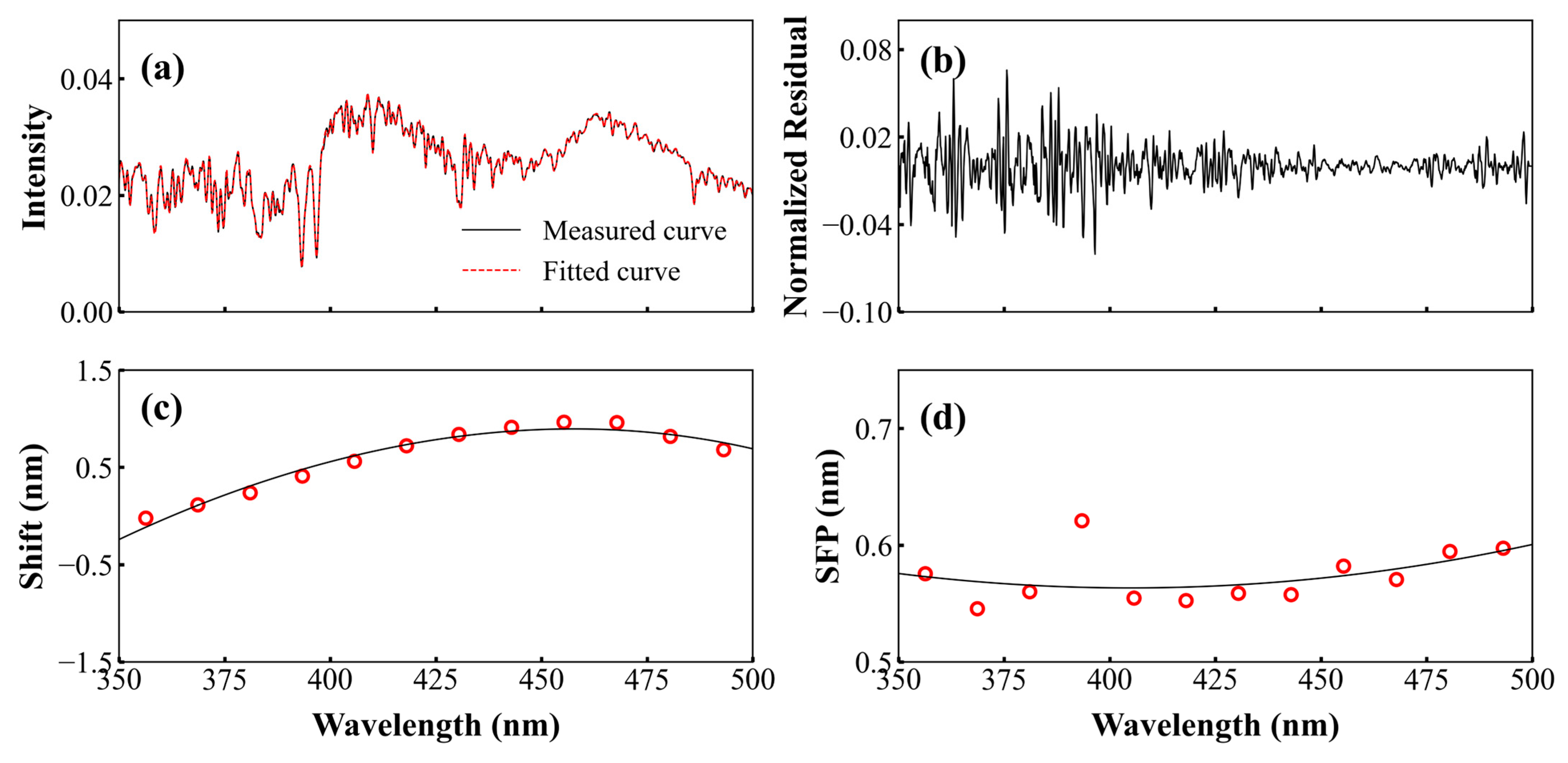
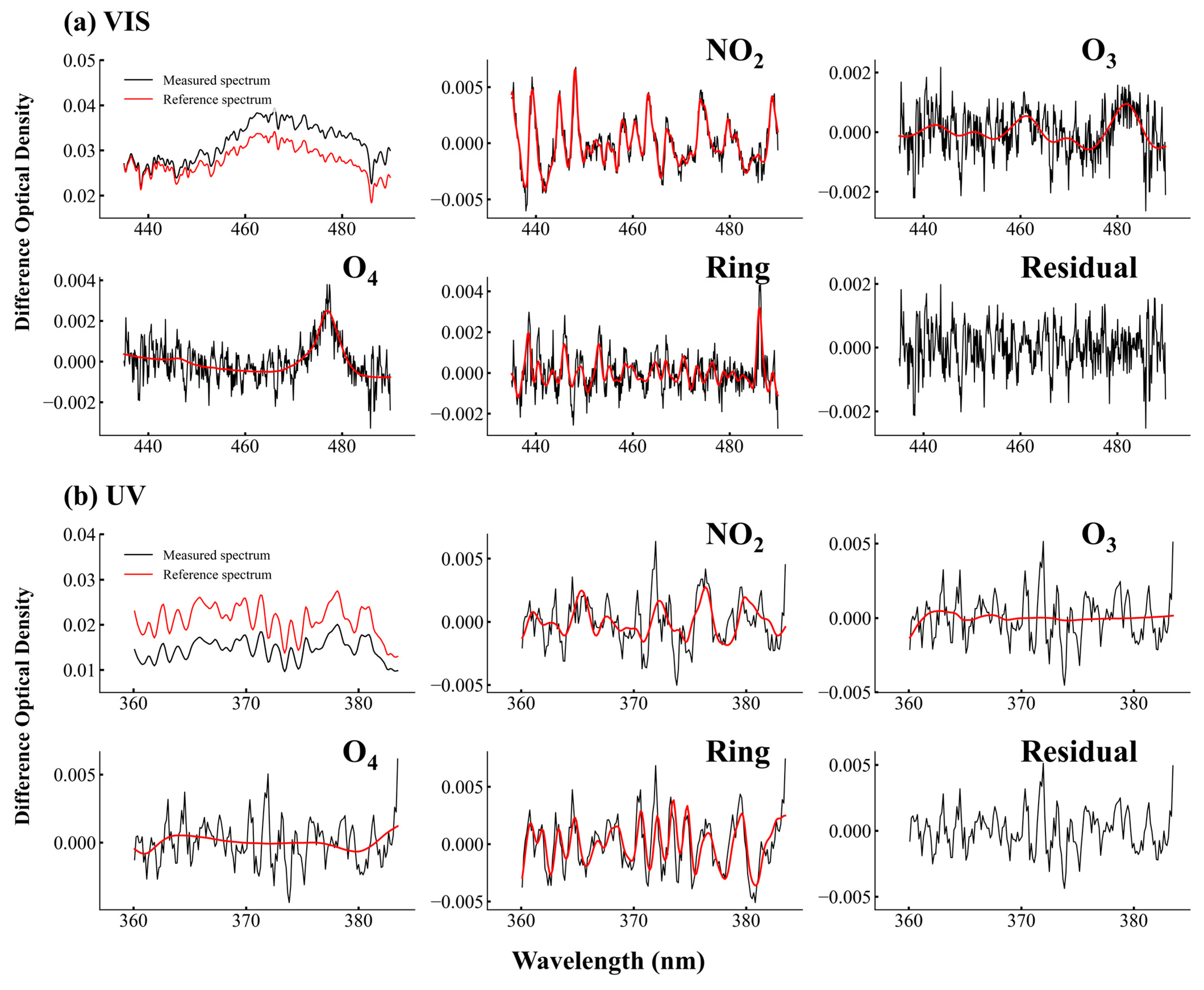


| Characteristics | Pandora | MAX-DOAS |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength interval | 290–380 nm (UV) | 300–390 nm (UV) |
| 280–525 nm (UV–VIS) | 400–720 nm (VIS) | |
| Spectral resolution (UV–VIS) | 0.6 nm | 0.4 nm (UV) |
| 0.9 nm (VIS) | ||
| Array size (pixels) | 2048 | 2048 × 512 |
| 1340 × 100 | ||
| Detector type | CCD | CCD |
| Sky FOV | 1.5° | 0.8° |
| Elevation viewing angles | 1, 2, 15, 30, 90° | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 30, 90° |
| Azimuth angle | North (0°) | North (0°) |
| Parameter | Description | NO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIS | UV | ||
| Wavelength range | 435–490 nm | 360–383.5 nm | |
| Polynomial degree | 5 | 5 | |
| Reference spectrum | Zenith spectrum at solar noon | Zenith spectrum at solar noon | |
| NO2 | 220 K [46], 294 K [46] | √ 1 | √ |
| O3 | 223 K [47], 243 K [47] | √ | √ |
| O4 | 296 K [48] | √ | √ |
| H2O | 298 K [49] | √ | × |
| BrO | 223 K [50] | × 2 | √ |
| HCHO | 293 K [51] | × | √ |
| Ring | QDOAS Ring tool | √ | √ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P. Analysis of Tropospheric NO2 Observation Using Pandora and MAX-DOAS Instrument in Xianghe, North China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101695
Wang C, Wang T, Cai Z, Zhao X, Wang W, Liu Y, Wang P. Analysis of Tropospheric NO2 Observation Using Pandora and MAX-DOAS Instrument in Xianghe, North China. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101695
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chunjiao, Ting Wang, Zhaonan Cai, Xiaoyi Zhao, Wannan Wang, Yi Liu, and Pucai Wang. 2025. "Analysis of Tropospheric NO2 Observation Using Pandora and MAX-DOAS Instrument in Xianghe, North China" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101695
APA StyleWang, C., Wang, T., Cai, Z., Zhao, X., Wang, W., Liu, Y., & Wang, P. (2025). Analysis of Tropospheric NO2 Observation Using Pandora and MAX-DOAS Instrument in Xianghe, North China. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101695







