First-Arrival Tomography for Mountain Tunnel Hazard Assessment Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Seismic Source and Enhanced by Supervirtual Interferometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
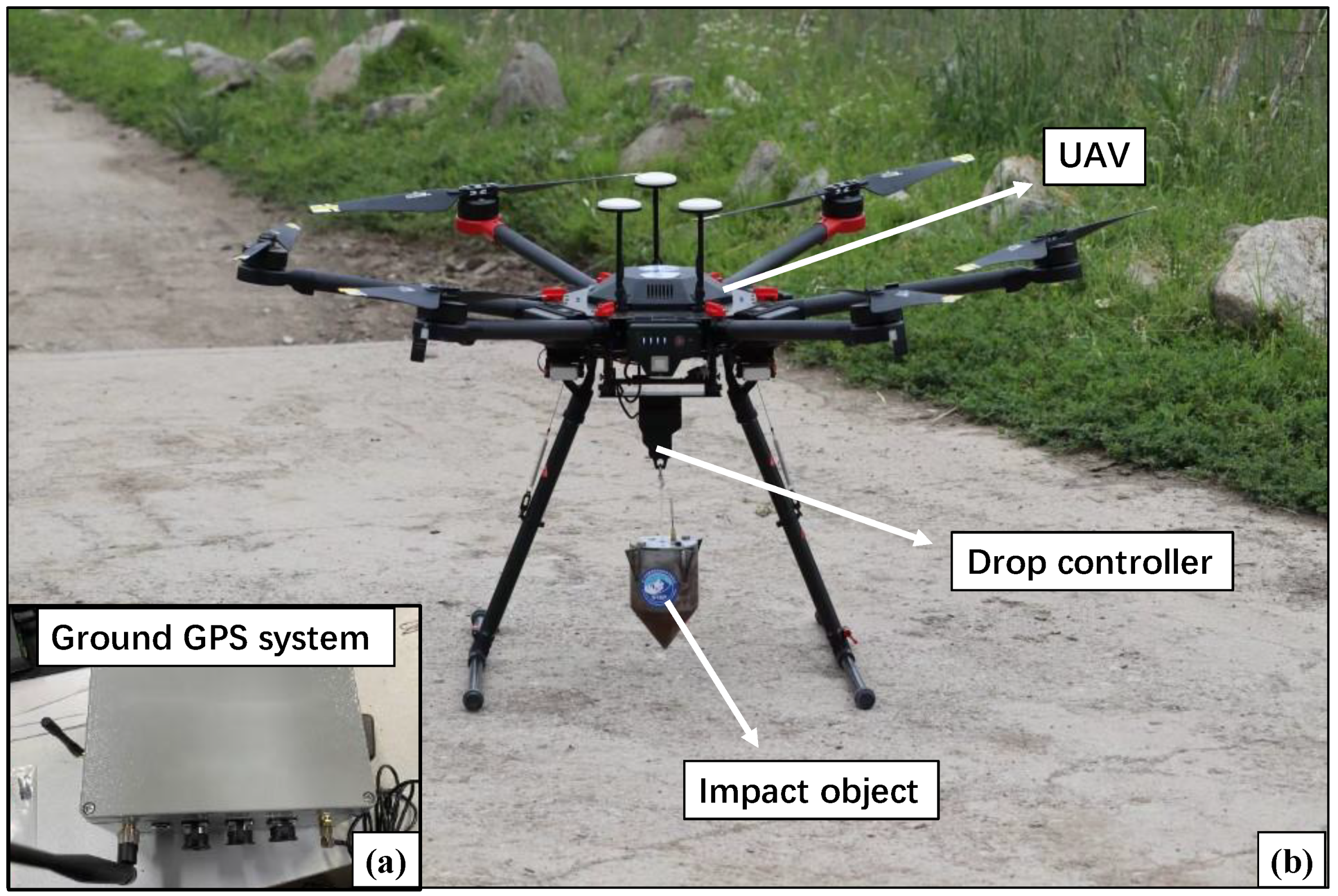
2.1. UAV Seismic Source
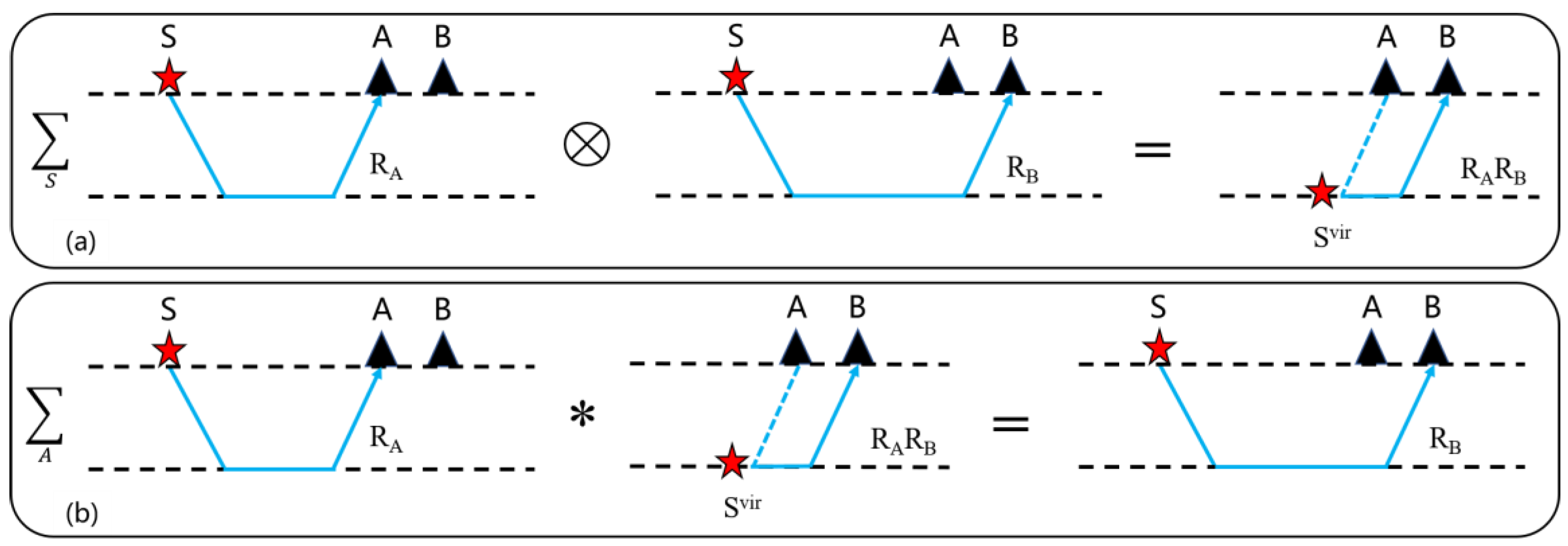
2.2. SVI
3. Case Study
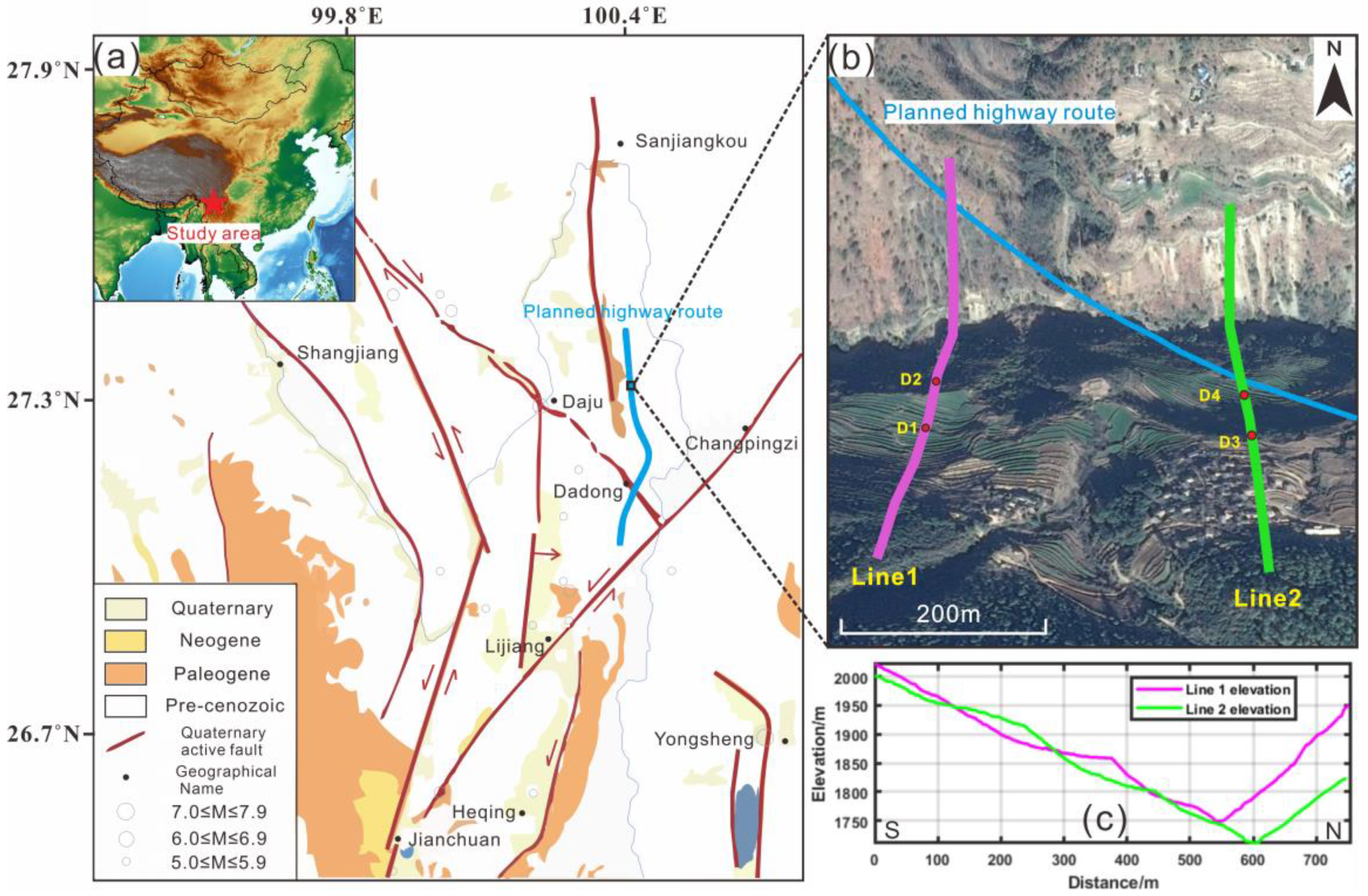
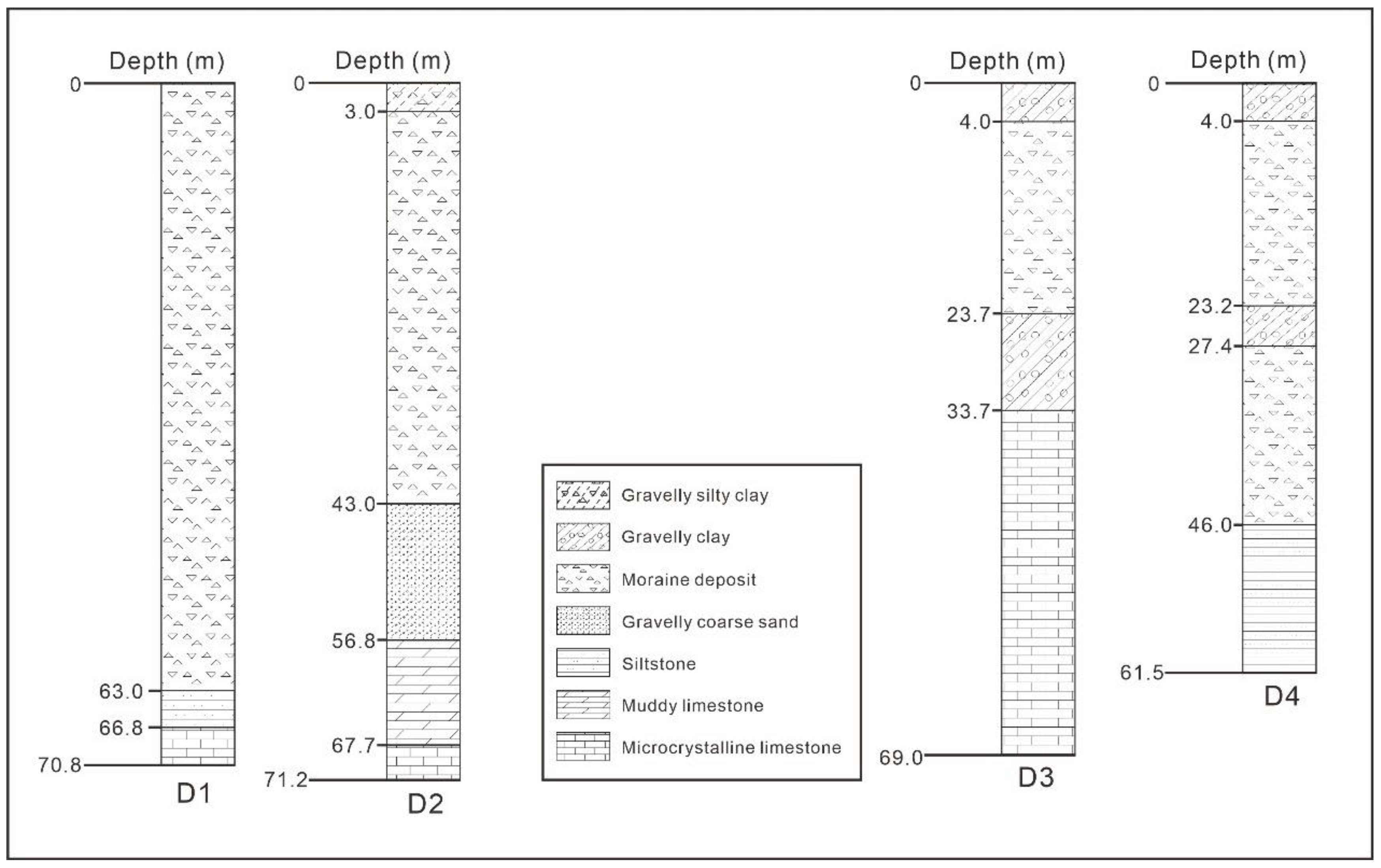
3.1. Geological Setting
3.2. Seismic Data Acquisition
4. Data Processing and Results
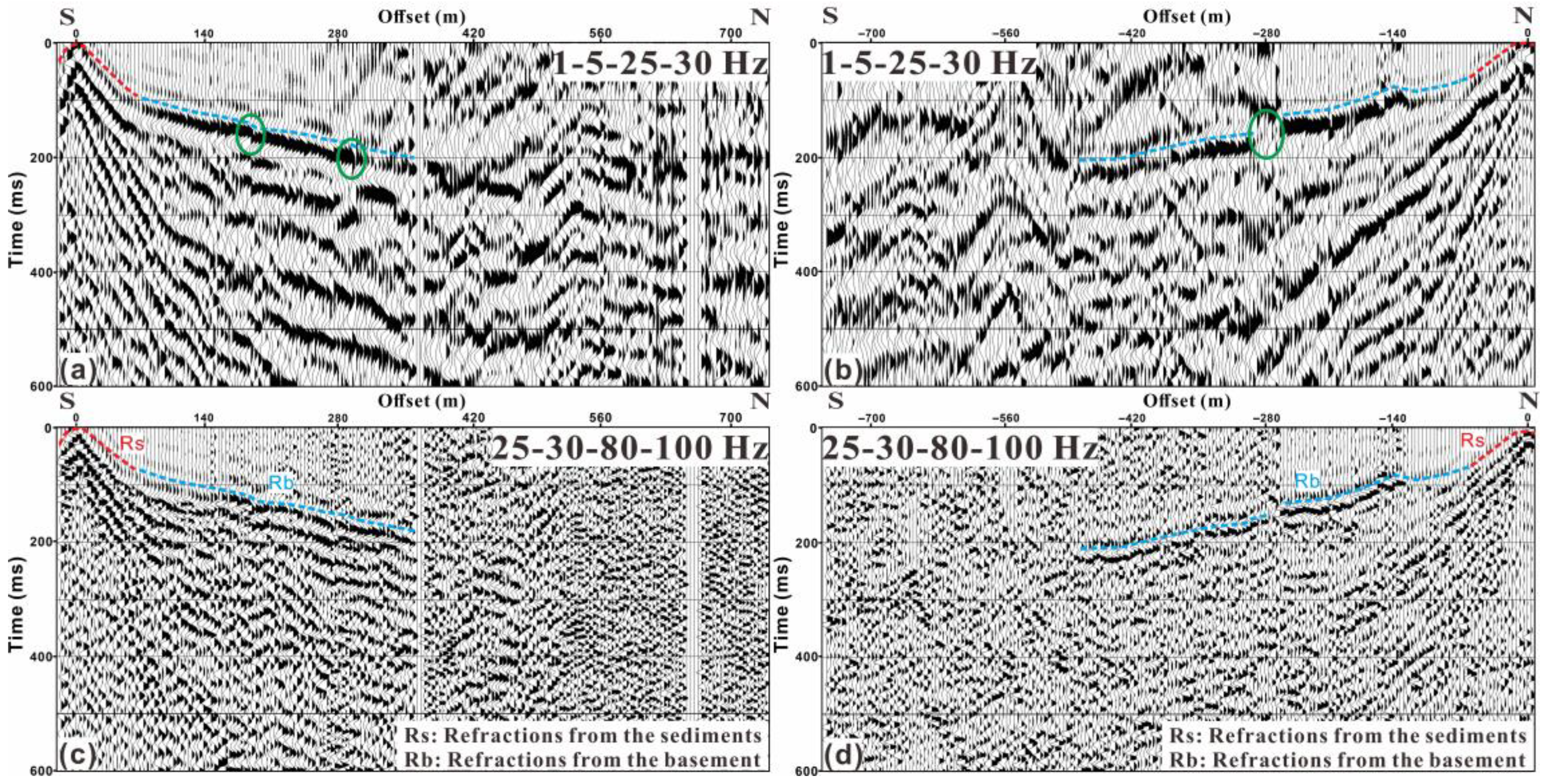
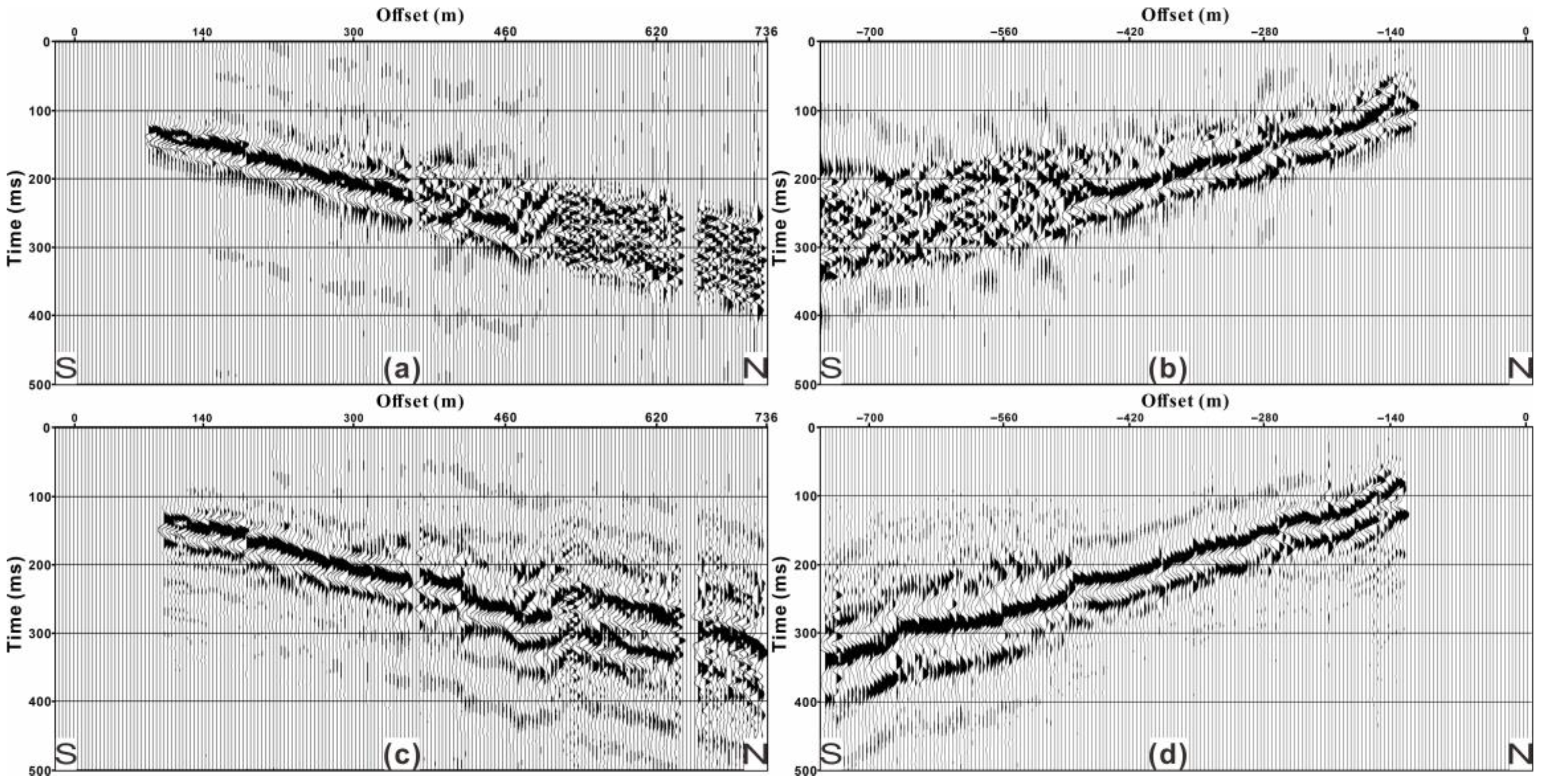
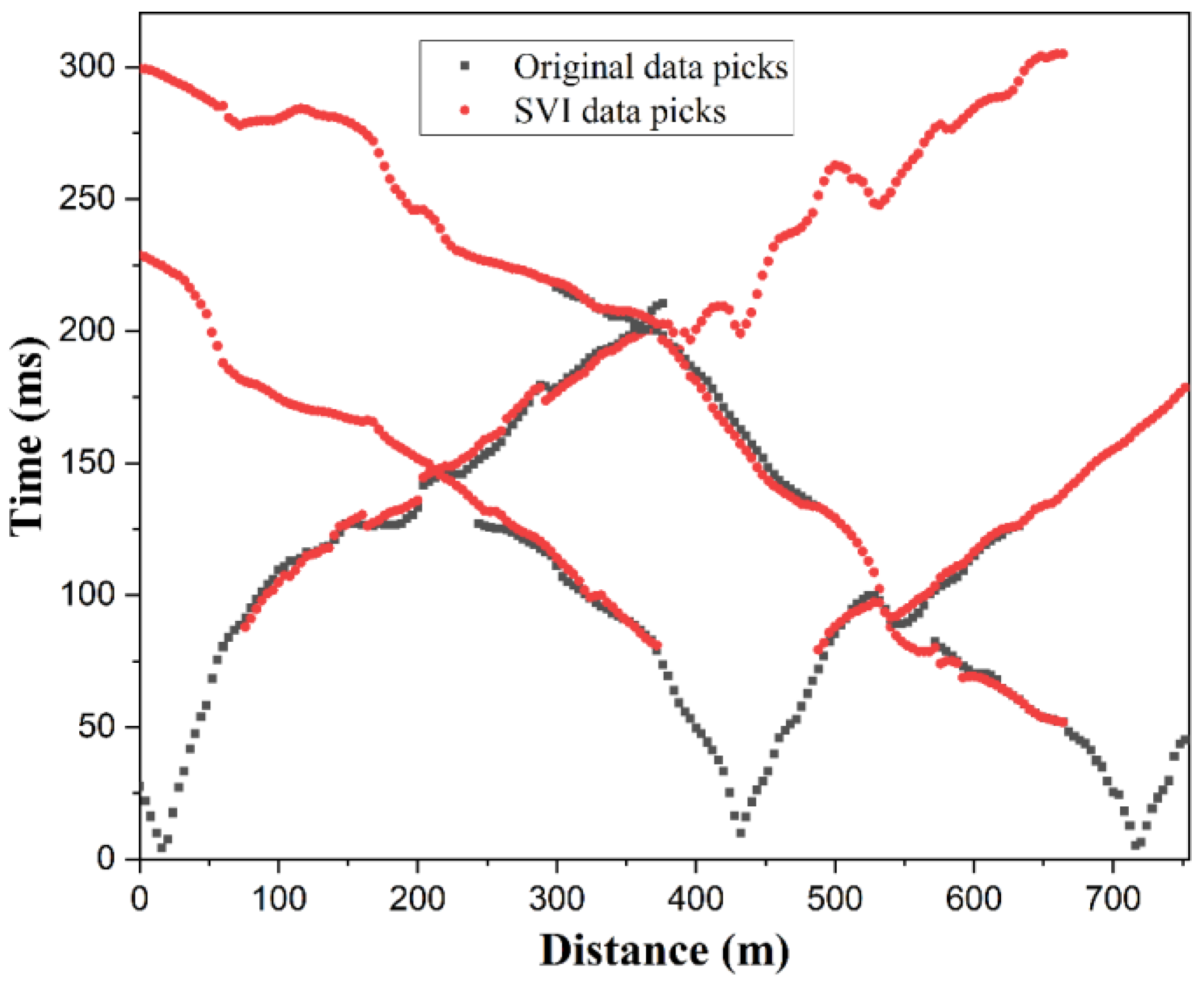
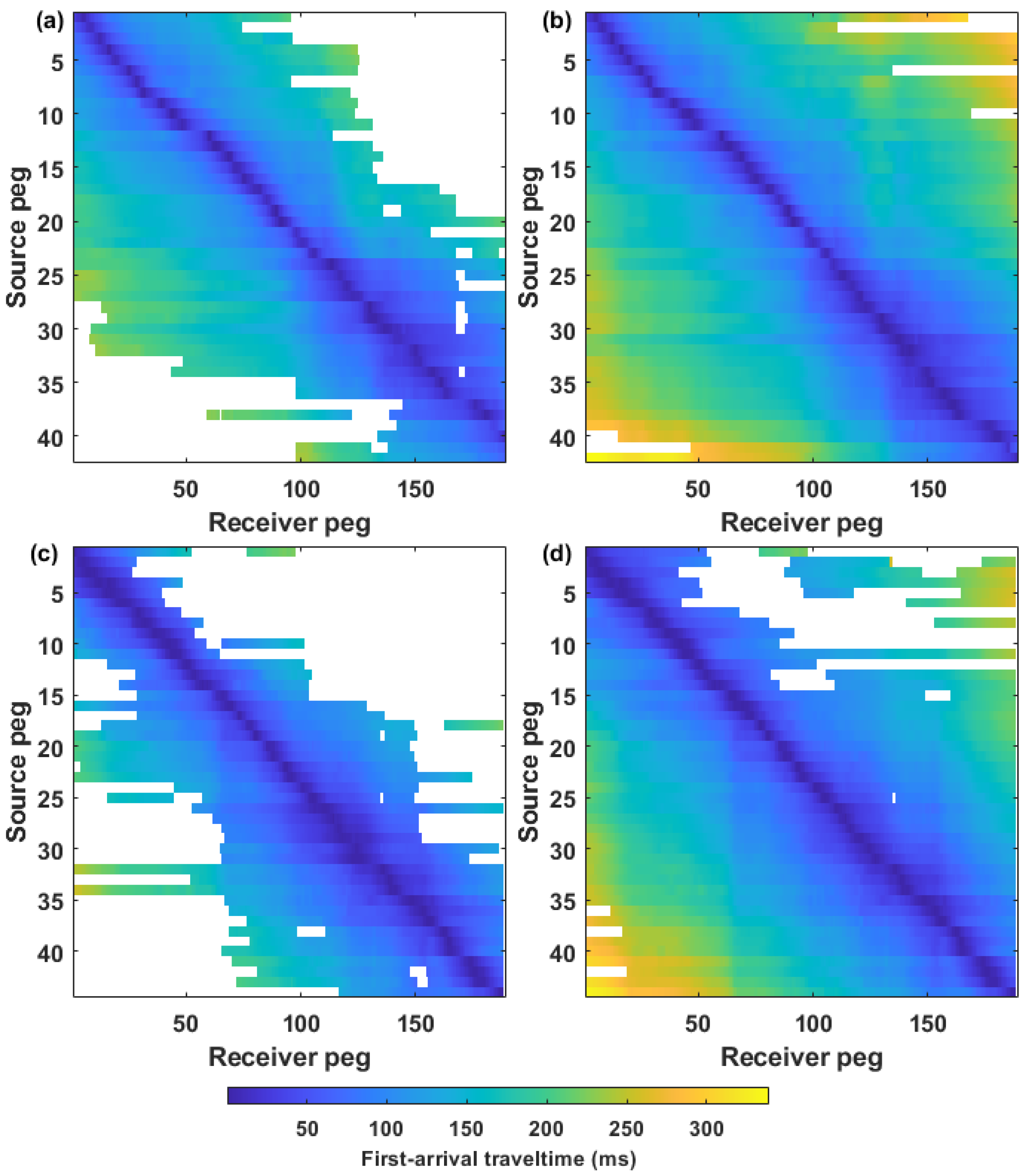
4.1. Supervirtual Refraction Interferometry (SVI) Application and First-Break Picking
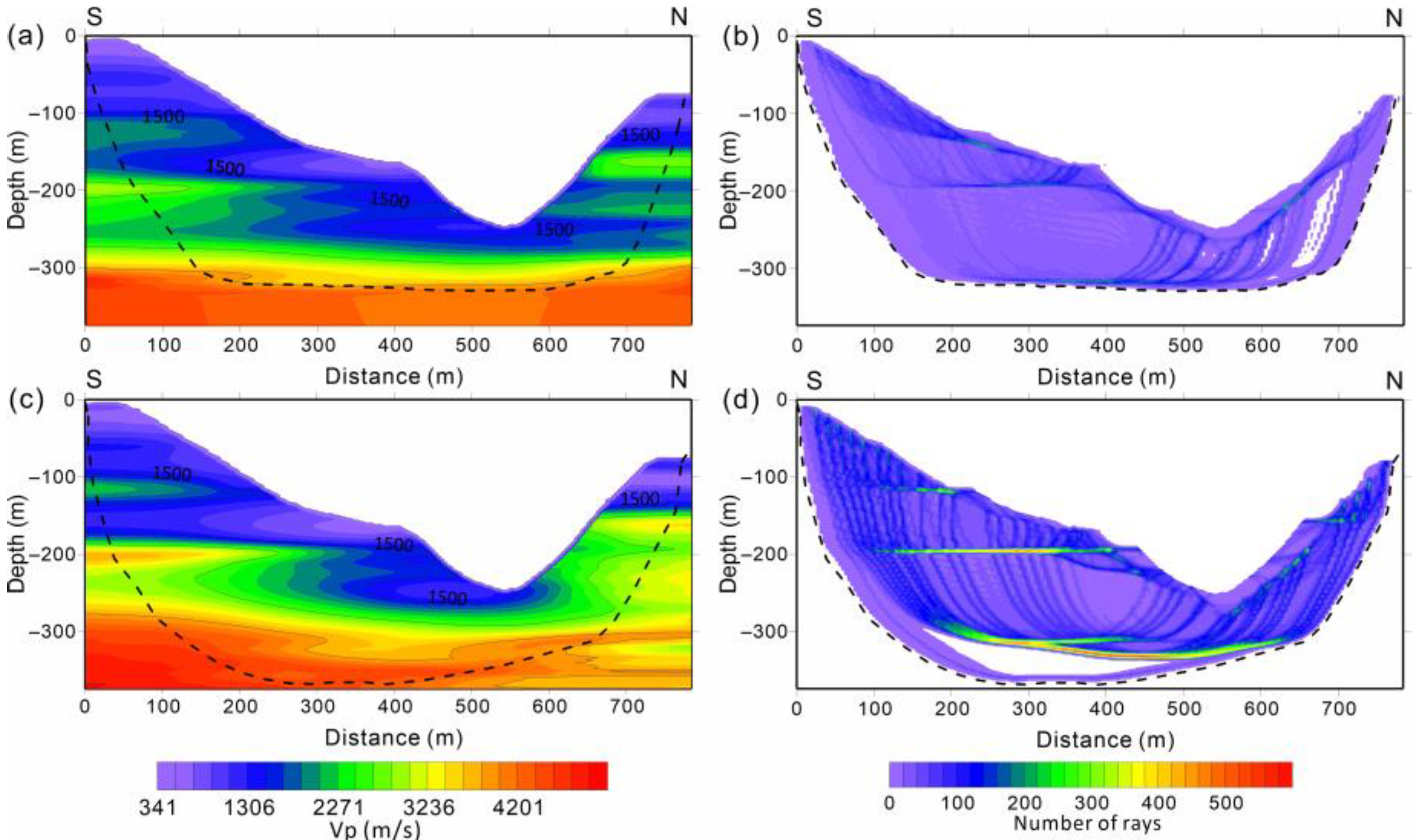
4.2. First-Arrival Traveltime Tomography
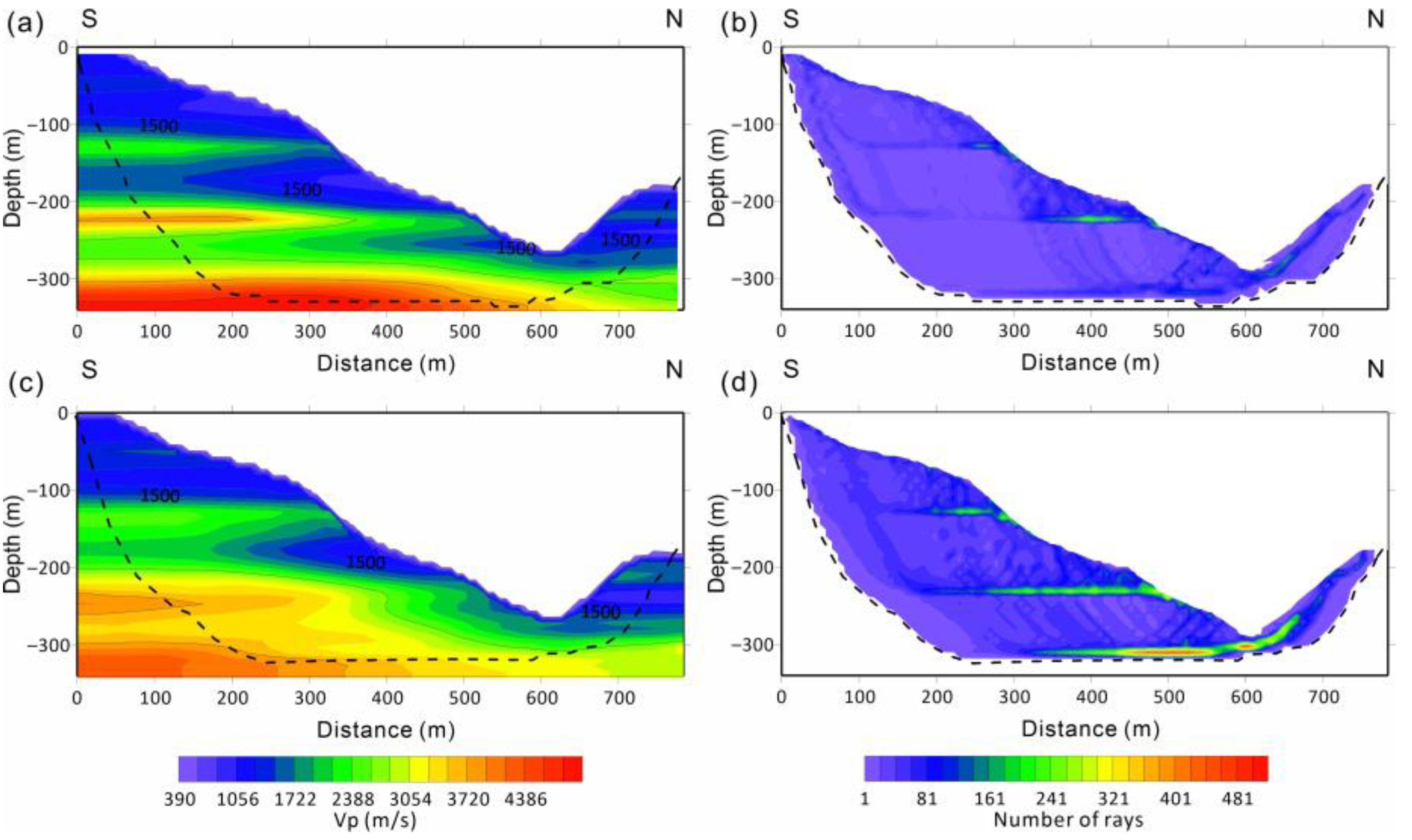
4.3. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Ye, Q. The first semi-airborne transient electromagnetic survey for tunnel investigation in very complex terrain areas. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 132, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Sun, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G.; Sun, H. A joint application of semi-airborne and in-tunnel geophysical survey in complex limestone geology. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X. Three-dimensional inversion of controlled-source electromagnetic data for surveying the Jiutianshan high-speed railway Tunnel, China. J. Appl. Geophys. 2023, 209, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.Q.; Xiao, H.B.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.S. The Effectiveness Experiment Study on The Hidden Karst Detection Method of City Tunnel Engineering. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 168–170, 2416–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogut, A.R.; Samba, N.J. Engineering geological investigations along the Meram railway tunnel, Konya, Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsekian, A.D.; Singha, K.; Minsley, B.J.; Holbrook, W.S.; Slater, L. Multiscale geophysical imaging of the critical zone: Geophysical Imaging of the Critical Zone. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Pei, Z.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, X. Early identification of abnormal regions in rock-mass using traveltime tomography. Engineering 2022, 22, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, J.; Draganov, D.; Malehmir, A.; Juhlin, C.; Wijns, C. Crosscoherence-based interferometry for the retrieval of first arrivals and subsequent tomographic imaging of differential weathering. Geophysics 2019, 84, Q37–Q48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, S.D.; Nolan, J.J.; Broadfoot, S.W.; McKenna, J.R.; Metheny, O.M. Using near-surface seismic refraction tomography and multichannel analysis of surface waves to detect shallow tunnels: A feasibility study. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 99, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegah, E.; Liu, H. Application of near-surface seismic refraction tomography and multichannel analysis of surface waves for geotechnical site characterizations: A case study. Eng. Geol. 2016, 208, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babacan, A.E.; Gelisli, K.; Tweeton, D. Refraction and amplitude attenuation tomography for bedrock characterization: Trabzon case (Turkey). Eng. Geol. 2018, 245, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bery, A.A. High Resolution in Seismic Refraction Tomography for Environmental Study. Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.T.; Hiltunen, D.R. Inversion of Combined Surface and Borehole First-Arrival Time. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2012, 138, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, A.D.; Chardot, L.; Neuberg, J.; Fournier, N.; Scott, B.J.; Sherburn, S. High impact mass drops from helicopter: A new active seismic source method applied in an active volcanic setting. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordkayhun, S.; Na Suwan, J. A university-developed seismic source for shallow seismic surveys. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 82, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.A. GDP: A new source for shallow high-resolution seismic exploration. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 68, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brom, A.; Stan-Kłeczek, I. Comparison of seismic sources for shallow seismic: Sledgehammer and pyrotechnics. Contemp. Trends Geosci. 2015, 4, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Ghosal, D.; Verma, S.N. Enhancement of a thumper source far offset refracted phases using super virtual interferometry (SVI). J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Hu, T.; Cui, D.; Ding, P. Weak signal enhancement using adaptive local similarity and neighboring super-virtual trace for first arrival picking. J. Geophys. Eng. 2020, 17, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Li, J. Integrated System for Geological and Geophysical Survey Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle 2020. US20200393593A1, 17 December 2020. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20200393593A1/en (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Ma, Z.; Qian, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Ling, J. UAV source: A new economical and environmentally friendly source for seismic exploration in complex areas. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 204, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Qian, R.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. The aerodynamic assessment and shotpoint position accuracy of an unmanned aerial vehicle seismic source. Geophysics 2025, 90, P1–P12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinson, I.; Bharadwaj, P.; Schuster, G.; Jakubowicz, H. Enhanced refractor imaging by supervirtual interferometry. Lead. Edge 2011, 30, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, P.; Schuster, G.; Mallinson, I.; Dai, W. Theory of supervirtual refraction interferometry. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 188, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, P.; Wang, X.; Schuster, G.; McIntosh, K. Increasing the number and signal-to-noise ratio of OBS traces with supervirtual refraction interferometry and free-surface multiples. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 192, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, J.; Malehmir, A. Using supervirtual first arrivals in controlled-source hardrock seismic imaging—Well worth the effort. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 206, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zou, Z. Supervirtual interferometry as a tool for slowness estimation of logging-while-drilling multipole acoustic data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Lei, G.; Duan, W.; Zheng, D.; Wang, C. Application of yu’s wavelet and supervirtual seismic refraction interferometry to enhance first arrivals: A case study from kuche mountain. Interpretation 2023, 11, T503–T510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hagan, O.; Hanafy, S.M.; Schuster, G.T. Iterative supervirtual refraction interferometry. Geophysics 2014, 79, Q21–Q30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Hanafy, S.M.; Liu, C. Iterative interferometric denoising filter for traveltime picking. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Gong, X.; Zhang, J. Supervirtual Refraction Interferometry in the Radon Domain. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edigbue, P.; Al-Shuhail, A. Three-dimensional supervirtual seismic refraction interferometry. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Chávez-Pérez, S. 3D supervirtual refraction interferometry. Geophysics 2020, 85, Q1–Q10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edigbue, P.; Al-Shuhail, A.; Hanafy, S.M. Three-dimensional supervirtual seismic refraction interferometry: A case study in western Saudi Arabia. Geophysics 2021, 86, B123–B133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.T. Seismic Interferometry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, S.M.; Al-Hagan, O. Super-virtual refraction interferometry: An engineering field data example. Near Surf. Geophys. 2012, 10, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Survey Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Source | UAV source (500 m height and 5 kg impact object) |
| Source spacing | 16 m |
| Number of source points | 42 |
| Receiver spacing | 4 m |
| Number of channels | 189 |
| Recording length | 1 s |
| Sampling interval | 0.5 ms |
| Geophones | Vertical: natural frequency: 5 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Qian, R.; Ma, Z.; Lei, X.; Ling, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G. First-Arrival Tomography for Mountain Tunnel Hazard Assessment Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Seismic Source and Enhanced by Supervirtual Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101686
Zhang J, Qian R, Ma Z, Lei X, Ling J, Liu X, Zhang G. First-Arrival Tomography for Mountain Tunnel Hazard Assessment Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Seismic Source and Enhanced by Supervirtual Interferometry. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(10):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101686
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jun, Rongyi Qian, Zhenning Ma, Xiaoqiong Lei, Jianyu Ling, Xu Liu, and Guibin Zhang. 2025. "First-Arrival Tomography for Mountain Tunnel Hazard Assessment Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Seismic Source and Enhanced by Supervirtual Interferometry" Remote Sensing 17, no. 10: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101686
APA StyleZhang, J., Qian, R., Ma, Z., Lei, X., Ling, J., Liu, X., & Zhang, G. (2025). First-Arrival Tomography for Mountain Tunnel Hazard Assessment Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Seismic Source and Enhanced by Supervirtual Interferometry. Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17101686






