Abstract
Aurora is caused by the collision of high-energy particles with particles in the Earth’s atmosphere. Recent advances in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) have demonstrated significant potential for ionospheric inversion at various scales, offering new insights into auroral processes. In this study, we present the first reported perturbation of C-band SAR signals induced by auroral activity during the enormous geomagnetic storm of 11 May 2024. The auroral boundaries observed by the Special Sensor Ultraviolet Spectrographic Imager (SSUSI) align closely with Sentinel-1 interferograms, despite the event occurring at mid-latitudes. A novel application of Sentinel-1 is illustrated, namely the inversion of the two-dimensional morphology and boundaries of the aurora at very high resolution and without interference from severe weather. Sentinel-1 promises to become a new method for the detection of precipitation particles, despite operating in the C-band, which is less disturbed by the ionosphere. Interferograms can also capture small-scale sporadic plasma patches associated with aurora. Furthermore, the analysis indicates that distinct polarization channels exhibit varying sensitivity towards auroral boundaries, with cross-polarization displaying heightened responsiveness.
1. Introduction
Auroral physics is an exceedingly intricate and fascinating discipline. A thorough study of the aurora helps to deepen the understanding of solar wind–magnetosphere–ionosphere coupling [1,2]. Although the beautiful aurora is one of the few space weather phenomena on Earth that can be seen with the naked eye, it is mysterious and comes with risks for human activities [3]. Aurora can lead to a very significant increase in ionospheric total electron content (TEC), which can have a serious negative impact on the electromagnetic waves travelling through them [4,5,6]. The challenge in predicting and quantifying auroral activity in the ionosphere at high latitudes stems from its strong correlation with geomagnetic conditions [7,8].
The predominant challenge in current auroral research lies in the scarcity of observational data. Amassing comprehensive measured data proves advantageous for modeling and related investigations. While instruments like the Global Ultraviolet Imager (GUVI), the Special Sensor Ultraviolet Spectrographic Imager (SSUSI), and all-sky cameras possess the capability to capture the two-dimensional structure of aurora [8,9,10], their capabilities are constrained by either resolution or orbits, both of which exhibit certain limitations [11]. Other means seem to focus on the analysis of ionospheric fluctuations, reflecting at most one-dimensional auroral information [12], without going into details here.
With its high resolution and imaging capabilities, spaceborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) stands out as a superior method for inverting the two-dimensional ionospheric structure compared to traditional auroral observation techniques [8]. Over a decade ago, phased array L-band synthetic aperture radar (PALSAR) demonstrated its ability to capture the two-dimensional structure of small-scale aurora on 1 April 2007 [8,13,14]. By leveraging Faraday rotation angles and interferometric phases, it becomes feasible to invert the disturbances caused by aurora in PALSAR, which is an encouraging example. However, it is also the only example of SAR-based detection of auroral morphology to date. Moreover, PALSAR has been decommissioned, and its successors, PALSAR-2 and PALSAR-3, are commercial satellites, limiting the development of related research.
Theoretically, the interference of aurora to the ionosphere can be equated with a localized increase in ionospheric TEC [8], with the lower-frequency SAR satellites being more seriously affected [15,16,17,18]. However, this does not mean that C-band SAR is not affected by ionospheric TEC, although the interference is only about 1/16 of that of L-band PALSAR in terms of group delay. There have been many reports of Sentinel-1 being disturbed by ionospheric interference [19,20,21], even though some of these events are not triggered by geomagnetic storms. With this in mind, we wondered if Sentinel-1 could enable the capture of auroras, which are ultimately an inversion of the structure of the TEC. Furthermore, Sentinel-1 possesses the advantage of being available at no cost, and the constellation of satellites is capable of sustaining uninterrupted observation for extended periods [22].
In this paper, the impact of auroral activity on the C-band Sentinel-1 will be demonstrated and explicitly validated. Utilizing the aurora captured by Sentinel-1 in the mid-latitude Canadian region during the enormous geomagnetic storm of 11 May 2024 as a case study, the effects observed by SAR will be compared with SSUSI measurements to demonstrate that C-band interferograms can invert the two-dimensional structure of aurora. A discussion section analyzes the limitations of the Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (D-InSAR) algorithm in inverting the auroral structure. Additionally, the paper elucidates the varying responses of distinct polarization channels to the aurora.
2. Data and Instrumentation
2.1. DMSP/SSUSI
The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) is a series of sun-synchronous satellites operating at an altitude of approximately 840 km. The orbital period of DMSP is almost 101 min [10]. The inclination of the spacecraft is close to 98.9°, allowing for high-latitude polar observations. Presently, the DMSP F17 and DMSP F18, which remain in orbit, were launched in 2006 and 2009, respectively [23]. Several instruments for the monitoring of the near-Earth plasma environment are to be located at DMSP, with the SSUSI instrument being one of the best known. SSUSI is a far FUV imager, which was designed to observe emissions in five bands: Hydrogen Lyman α (121.6 nm), Oxygen I (OI, 130.4 nm), OI (135.6 nm), Lyman–Birge–Hopfield Short (LBHS, 0–160 nm), and Lyman–Birge–Hopfield Long (LBHL, 60–180 nm) [24].
In addition to SSUSI, there are two other significant devices on board the DMSP that facilitate observation of the ionosphere. The Special Sensor J (SSJ) was designed to measure energy fluxes of electrons and ions precipitating into the high-latitude ionosphere. There are 19 logarithmic energy channels in the SSJ which record particles with energies ranging from 30 eV to 30 keV [25]. Additionally, the Special Sensor Ions Electrons and Scintillation (SSIES) is employed to assess plasma characteristics. The SSIES is capable of conducting in situ measurements of plasma density, electron and ion temperatures, and plasma drift velocity. The three instruments previously referenced are frequently utilized in conjunction with one another to analyze the extent to which aurorae affect the ionosphere.
2.2. Sentinel-1
The Sentinel-1 constellation consists of three radar-imaging satellites in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 693 km. Sentinel-1 is one of the few free releases of SAR. Sentinel-1 has a center frequency of 5.4 Ghz and a resolution of 5 by 20 m. Sentinel-1A, -1B, and -1C were launched in 2014, 2016, and 2024, respectively [26]. Operating in unison, these three radar imaging satellites within the same orbit offer uninterrupted, all-weather, day and night C-band SAR imagery of the Earth’s surface. However, Sentinel-1B was retired in 2022. Presently, Sentinel-1C has taken over from Sentinel-1B and is networked with Sentinel-1A to ensure global coverage within six days. It is worth noting that Sentinel-1 has the capacity to remain in service for a considerable period of time, ensuring that this mission will continue uninterrupted [22,27].
Most importantly, Sentinel-1 covers many different applications, such as monitoring surface movement risks, understanding Earth processes, performing infrastructure mapping, and more. It also has many applications in Arctic monitoring [28], such as sea-ice extent and maritime surveillance. An often-overlooked application of Sentinel-1 lies in its adeptness at ionospheric inversion. However, the untapped potential of Sentinel-1 in deciphering auroral patterns awaits further exploration and clarification.
3. Observations and Analyses
3.1. Introduction to the Auroral Event and Areas of Interest
One of the largest and strongest solar storms of the space age occurred on 10–11 May 2024, and there were observations of the aurora reported extending to even middle latitudes [29]. It is inevitable that the quality of numerous Sentinel-1 images will be adversely affected by the geomagnetic storm, which is both protracted and intense. This event could represent a significant opportunity to assess the capability of Sentinel-1 to invert auroral positions and two-dimensional structures.
The region of interest is visually depicted in Figure 1a. This region is selected for the survey because auroras occurring at mid-latitudes are relatively rare. Another reason is that there are more engineering surveys in the mid-latitude region, and the effect of auroras on interferograms is not yet known. The Sentinel-1A VV/VH dual-polarization imaged in the Canadian region, and then four views were used for splicing, with the Dst reaching −397 nT at SAR imaging. VV polarization is co-polarization, where both transmission and reception have electric field vectors oriented in the vertical direction. Conversely, VH polarization is cross-polarization, with the transmission electric field vector oriented vertically and the reception electric field vector oriented horizontally. All images examined in this research were acquired during ascending orbits. Accompanied by a strong substorm, the AE reached 1011 nT at this time. Other corresponding geomagnetic indices are indicated in Figure 1b. The meaning of each of these data is well known and will not be repeated here.
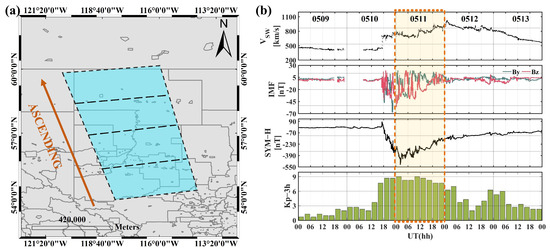
Figure 1.
(a) Location of interest. (b) The magnetic indices for 11 May 2024 and the surrounding dates.
Since Sentinel-1A was imaged at 01:31 UT on 11 May 2024, it almost corresponds to the strongest moment of this geomagnetic storm. The experimental range lies almost exclusively below 60°N, which is geographically in the mid-latitudes, making it certainly a worthwhile and interesting event to study. The location corresponds to a geomagnetic latitude ranging from 59.67° to 66°N.
3.2. Extraction of Ionospheric Disturbances by D-InSAR Techniques
Figure 2a shows the intensity of the two raw Sentinel-1 images without any processing, using the northernmost data before splicing as an example. The interpretation of SAR images that have been distorted by the ionosphere through direct visual inspection is challenging, which is an inherent characteristic of SAR. The analysis of dual-polarization Sentinel-1 imagery necessitates the utilization of the D-InSAR technique, given its inability to invert the Faraday rotation angle. The workflow of D-InSAR technology is presented in Figure 2b, encompassing orbit correction, alignment between master and slave images, generation of interferograms, removal of topographic phases, filtering, and phase unwrapping. The outcome of this processing is an image of the phase differences, termed an interferogram.

Figure 2.
(a) Two raw Sentinel-1 images without any processing. (b) Main flowchart of D-InSAR processing.
Neglecting other factors and atmospheric perturbations [30,31], phase differences can reflect the between the master and slave images [32], allowing the D-InSAR technique to invert the ionospheric structure [33]. One can simply assume that if the perturbation is stronger, it corresponds to a higher interferometric phase. D-InSAR technology is well-established in the field [21,33,34], and we will not delve into its specifics here. The interferometric processing is carried out utilizing the InSAR Scientific Computing Environment (ISCE2) software [35], accessible at https://github.com/isce-framework/isce2, accessed on 1 January 2025. Default values are employed for all parameters in the D-InSAR process.
The master image is derived from the data captured on 11 May 2024, with its first two revisit cycles, occurring on 17 April 2024 and 29 April 2024, respectively, designated as slave images. It is noteworthy that both slave images were captured on magnetostatic days. Referring to Table 1, readers will observe the three sets of interferometric pairs that correspond to the above data. Given that the nature of the data is ascending, the imaging time is based on the southernmost data, corresponding to approximately 17:00 local time.

Table 1.
Three sets of interferometric pairs.
The interferograms generated using the three sets of interferometric pairs in Table 1 are shown separately in Figure 3, using the VV channel of Sentinel-1 as an example for the experiment. The interferograms shown in this paper were all phase-unwrapped by the minimum cost flow (MCF) algorithm [36], which will not be repeated below. To mitigate tropospheric influences within the interferogram, the Generic Atmospheric Correction Online Service for InSAR (GACOS [37]) was employed.
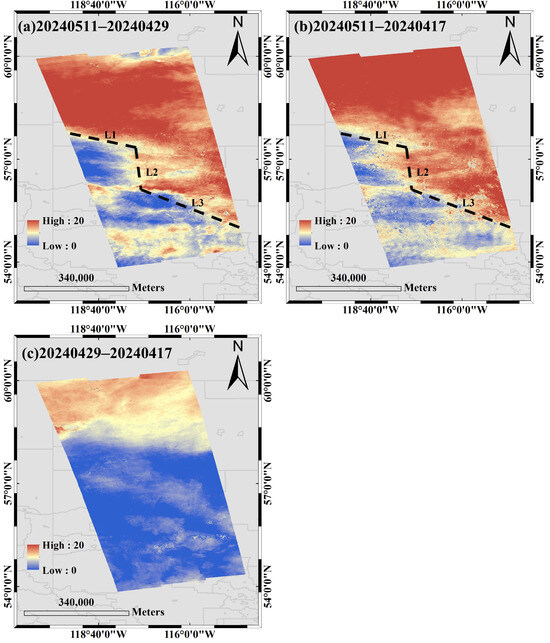
Figure 3.
Three interferograms generated corresponding to Table 1. The black dashed lines in (a) and (b) are auroral boundaries.
Equation (1) demonstrates that the phase advance brought about by the ionosphere is correlated with , where is the constant 40.28 m3/s2, is the speed of light, and is the centre frequency of Sentinel-1. The larger the between the master and slave images, the higher the value of the residual phase in the interferogram. In other words, the distribution of the phase in the interferogram is also equal to the between the master and slave images, with only a multiplicative difference between the two values [33]. Assuming that other interferences are negligible [30,31], it can be hypothesized that the phase in the interferogram is related solely to the ionospheric TEC [32].
Errors induced by the background ionosphere manifest as large-scale streaks, exhibiting a flat trend even after phase unwrapping, as evidenced in the report by Liang et al. [20]. The interferograms depicted in Figure 3a,b demonstrate an absence of background ionospheric interference, as they exhibit significant variability and can only be phase enhancement triggered by ionospheric structures of smaller scales [21,33].
As illustrated in Figure 3a, there is a noticeable increase in phase values in the northeastern section of the interferograms (approximately above 58°N and east of 57°N), exceeding 20 radians. As can be seen from Equation (1), this represents a of approximately more than 6 TECU between the master and slave images. In contrast, the phase values on the southwestern side of the interferograms are notably lower than those in the northern region. The figure clearly marks a distinct boundary line. By excluding the influence of other factors, it becomes apparent that a specific local TEC enhancement exists within the area of phase increase, likely instigated by the interaction with aurora phenomena during SAR imaging. Figure 3b depicts a similar scenario to Figure 3a, with both demonstrating localized enhancements in the northeastern portion of the image. While there are minor discrepancies, these are likely due to variations in the slave images used. To simplify the delineation of suspected auroral boundaries, the figure labels the L1, L2, and L3 structures with black dashed lines. These lines do not represent the actual boundaries of the aurora borealis but are primarily meant as reference points for the subsequent discussion. The genuine boundaries of the aurora borealis are intricately detailed within the interferogram.
In Figure 3c, an interferogram generated without the inclusion of geomagnetic storm data reveals a minor phase enhancement in the upper section of the image, measuring approximately 10 radians. Similarly, when the phase value is 10 rad, the corresponding does not exceed 3 TECU. This enhancement is likely attributed to differences in the background ionosphere between the data from the scenes on 17 April 2024 and 29 April 2024. Additionally, the notably smooth phase transition depicted in Figure 3c further supports the notion of interferometric errors stemming from variations in the background ionosphere. A comparison of the three interferograms in Figure 3 shows that the suspected auroral structure is captured by Sentinel-1 on 11 May 2024.
3.3. Aurora Observed by SSUSI
To ascertain whether the observed interferometric phase enhancements in Figure 3a,b are triggered by aurora or other factors, Figure 4 illustrates the spatial distribution and strength of auroral events recorded by the SSUSI instrument aboard the DMSP F17 satellite at 01:35 UT on 11 May 2024. Given the negligible absorption of LBHL by oxygen molecules and the proportionality of the energy flux of the electronic aurora to the intensity of the radiation from LBHL, it was selected for the demonstration. The data reveal that SSUSI and Sentinel-1 were both operational at nearly the same time, with only a three-minute discrepancy. This close timing suggests that these two satellites might be simultaneously observing the same ionospheric event.

Figure 4.
(a) Relative positions of SSUSI and interferograms, with the black dashed box showing the position of the interferogram. (b) Aerial view of the northern hemisphere, as mapped by SSUSI.
Figure 4a illustrates the distribution of aurora within and surrounding the region of interest, with the position of Sentinel-1 highlighted by the black dashed box. Figure 4b presents an aerial perspective of SSUSI on board the DMSP above the geographic latitude of 50°N, illustrating the distribution of aurora. As illustrated in Figure 4b, the aurora observed in the Canadian example exhibits high levels of intensity, with radiation levels exceeding 5 kilo-Rayleigh (kR). Additionally, auroral events with a radiant brightness of approximately 2 kR were recorded in the European region. However, the intensity of the European aurora is much lower than that observed in North America.
As shown in Figure 4a, the aurora caused disruption in the eastern and northern sectors of Sentinel-1, while the southwestern area remained unaffected. A comparison with Figure 3a reveals a general consistency in trend, though notable differences emerge due to the distinct orbits of SSUSI and Sentinel-1, with the former being processed for the calculation of the puncture point.
When conducting ionospheric studies based on SAR, puncture point projection calculations are a common way to more accurately confirm the interference to which the SAR is subjected [17,18,21,34]. A brief illustration of the principles involved in puncture point calculation is shown in Figure 5a. The calculation of the ionospheric penetration point (IPP) for SAR is inspired by methods commonly employed in GNSS ionospheric studies. In ionospheric research, a single thin-layer approximation is typically used to simplify the model, representing the entire ionosphere as a thin layer located at a certain altitude above the Earth’s surface. This approximation effectively compresses all free electrons into a single layer. The IPP is defined as the intersection of an electromagnetic beam with this ionospheric layer as it propagates through. Accurately determining the IPP is crucial for assessing ionospheric interference on SAR signals. The location of the IPP can be determined by the key parameter, θ, which can be expressed as follows:
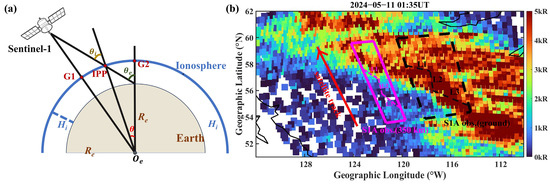
Figure 5.
(a) Schematic diagram of IPP calculation. (b) Relative positions of SSUSI and Sentinel-1A. The dashed black rectangle shows the Sentinel-1A (S1A) ground observation area from Figure 1a. The solid magenta rectangle shows the Sentinel-1A observation area mapped onto 350 km altitude. The footpoint of satellite track is shown by the red line.
According to the law of sines, we have the following:
As demonstrated in Figure 5a, where represents the center of the Earth, is the radius of the Earth, is the height of the background ionosphere, and is the angle of incidence on the ground. Given the knowledge of these parameters, can be expeditiously derived. Furthermore, given the knowledge of the coordinates of positions G1 and G2, in combination with the , the location of the IPP can be determined.
When the ionospheric altitude is set at 350 km [17,18,21], Figure 5b illustrates the position of the Sentinel-1 projection on the ionosphere for the corresponding altitude. The black dashed box denotes the geographic latitude and longitude of the ground observation region corresponding to Sentinel-1, the pink box signifies the projection of Sentinel-1 mapped to the puncture point, and the red line represents the footpoint of the satellite track. As demonstrated in Figure 5b, the interferograms demonstrate a striking congruence with the morphology of SSUSI in the designated pink box (mapped onto 350 km). It is noteworthy that the auroral structures exhibited by L1, L2, and SSUSI demonstrate a remarkable degree of similarity. The west side of L2 corresponds to precipitation particles with radiation levels of approximately 1 kR, thus providing a rationale for the observed lower interferometric phase on the west side of L2 in Figure 3.
It is important to note that while the SSUSI display failed to capture the suspected auroral structure on the western side of L3, DMSP SSJ data confirmed that the region of interest was indeed disturbed by auroral activity at that time. This suggests that SSUSI may not always provide a precise representation of the actual auroral pattern. One possible explanation for this discrepancy is the three-minute time lag between SSUSI and Sentinel-1 observations. Additionally, SSUSI may have been unable to detect lower-energy precipitation particles at that time due to resolution limitations or other factors. In summary, considering the DMSP SSJ measurements (see Section 4.1) alongside our experimental results, there is a strong indication that Sentinel-1 is capable of detecting the auroral boundary.
To further validate our experiments, as demonstrated in Figure 6, the relative positions of corresponding SSUSI and Sentinel-1 for 29 April 2024 and 17 April 2024 are shown. Footprints and other details are not labeled in Figure 6, but they are referenced in Figure 5. As anticipated, there is indeed no interference from the auroral arc for Sentinel-1 at these two times.
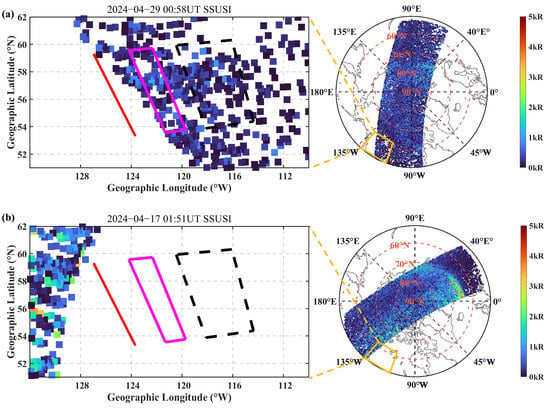
Figure 6.
(a,b) The relative position of SSUSI to the region of interest for 29 April 2024 and 17 April 2024, respectively. Detailed description of the images can be found in Figure 5.
Despite the disparity in the imaging times of SSUSI and Sentinel-1, it is evident in Figure 6a that the presence of auroral precipitation particles on 29 April 2024 had minimal impact on the SAR imaging. While a greater number of auroral precipitation particles with radiant luminance exceeding 2 kR were observed on 17 April 2024, as shown in Figure 6b, their intensity was significantly lower compared to that on 11 May 2024. Even though SSUSI did not coincide with the region of interest, it can still be surmised that Sentinel-1 was not significantly disturbed by the auroral arc. This is because auroral arcs do not typically emerge spontaneously [5], especially since there are no geomagnetic storms occurring. Even if an auroral arc had appeared, it would not have appeared in our region of interest, but further away. The SSUSI map of the previous cycle was taken at 00:21 UT, more than an hour before Sentinel-1, and therefore cannot be used for comparison.
As demonstrated in Figure 3c, the background ionospheric TEC in the region south of 58°N on 17 April 2024 is significantly larger than on 29 April 2024. It can therefore be inferred that the auroral precipitation particles do not appear to be disturbing the background ionosphere at this time. Another possibility is that due to the operation in the C-band, which is insensitive to the ionospheric interferences, the corresponding TEC enhancement is not captured by the Sentinel-1 capture. In any case, the fact that the ionospheric disturbance on 17 April 2024 was apparently less severe than that on 11 May 2024 is not a matter for excessive consideration.
In summary, Sentinel-1 interferograms enable the acquisition of auroral two-dimensional morphology with unparalleled resolution. Zhu et al. [21] have previously reported analogous findings, identifying the presence of small-scale ionospheric irregularities in the mid-latitude United States. Nevertheless, the underlying causes of these irregularities remain uncharacterized. In contrast, the present paper has successfully achieved the first capture of a small-scale irregular structure of known origin using Sentinel-1, which has a finest scale of 22 km in N-S width. A further concern is that prior researchers did not consider Sentinel-1 to be a suitable tool for capturing ionospheric structures due to the higher frequency of C-band. However, the combination of this paper and Zhu et al. [21] has demonstrated that Sentinel-1 is effective for ionospheric structure inversion, even at mid-latitudes. This highlights the necessity for a re-evaluation of the impact of the ionosphere on C-band SAR, especially in this part of the auroral capture application.
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages and Disadvantages of Interferogram-Based Inversion of Auroral Structures
Interferograms play a crucial role in enabling Sentinel-1 to capture small-scale ionospheric structures, as it cannot independently invert ionospheric TEC, unlike fully polarized PALSAR [8,13]. It is important to note that the auroral boundary could not be extracted using the range split-spectrum method in this experiment. Furthermore, azimuthal offset algorithms such as Multiple Aperture InSAR (MAI) failed to yield results due to low coherence.
Under what circumstances can C-band interferograms aid in auroral capture? First, a strong background ionosphere can obscure small-scale ionospheric structures, and the scale of such irregularities is smaller than the map size of SAR images. Therefore, maintaining a low-background ionosphere is essential when conducting imaging with Sentinel-1 [8]. Secondly, the selection of the slave image is of paramount importance. The information in the master image may be compromised if the slave image is significantly affected by ionospheric disturbances, potentially masking auroral signatures. Since the intensity of background ionospheric TEC is inherently uncontrollable and variable, careful image selection is necessary.
A relevant example is illustrated in Figure 7a, where interferograms are generated for the slave image based on Sentinel-1 imaged on 4 June 2024 (Kp = 2) with the master image from 11 May 2024. Only sporadic irregular auroral patterns near ~56°N are visible, while the northeastern aurora resembling Figure 3a is absent. It is most likely that the background ionosphere of 4 June 2024 is much higher than that of the master image, obscuring the interference caused by the auroral energy deposition.

Figure 7.
(a) Interferograms generated from Sentinel-1A imaging on 11 May 2024 and 4 June 2024, respectively. (b) The track of DMSP F17. (c) From top to bottom are the differential electron energy flux, the electron energy flux, the differential ion energy flux, and the ion energy flux. (d) Ne profile along the latitudinal direction.
It is also discussed whether the sporadic structure that occurs around 56°N (marked by the dashed black oval) is linked to auroral activity, a structure that is particularly evident in both Figure 3 and Figure 7a. Although Figure 4 demonstrates the potential for auroral occurrence at this location, the resolution of the SSUSI is significantly lower than that of the interferogram. To utilize the higher-resolution validation data, the energy distributions of the precipitation particles observed in the DMSP Special Sensor J (SSJ) are employed to ascertain the occurrence of aurora at the corresponding locations. As demonstrated in Figure 7b, the orbit of DMSP F17 at a similar time is shown to be in close alignment with the projected position of the puncture point of interest.
The SSJ measurements with the background removed are shown in Figure 7c, with the locations of the sporadic structure circled in orange dashed lines. The SSJ data can be obtained from https://cedar.openmadrigal.org/. Figure 7c shows the differential electron energy flux (jE), electron energy flux (JE), differential ion energy flux, and ion energy flux from top to bottom. The differential energy flux is derived from the measured counts in each channel and represents the particle energy flux at the central energy of that channel. The total energy flux, covering the energy range from 30 eV to 30 keV, is obtained by summing the products of the differential energy flux and the respective energy width of each channel. From the high values and distribution ranges of JE and jE, it is clear that discrete aurora occurs in the region of interest. Consistently, the differential ion energy flux shows that ion aurora occurs here as well. The ion aurora is formed from all spectral data, regardless of the classification of the electron component [5]. Given that ion aurora typically exhibits lower energy than electron aurora, the subsequent analysis will primarily address the contribution of electron aurora to ionospheric processes. As demonstrated in Figure 7c, both electron and ion auroras are observed during this period.
Given that the maximum values of JE and jE both exceed 108 eV/cm2 sr ΔeV s with a wide range of energies, it can be concluded that a broadband aurora occurred in the area of interest [5]. It is well known that broadband aurora is generally triggered by Alfvén waves. The occurrence of the broadband aurora extends from 54°N to 60.5°N, indicating that the entire range of the interferogram is affected by the auroral activity. Being connected to the broadband auroral structure to its west, the sporadic structure proves to be captured by Sentinel-1. Further evidence comes from the electron density (Ne) measurements by DMSP, as shown in Figure 7d. A significant fluctuation in Ne is observed within the region of interest, supporting the presence of ionospheric irregularities in this area. It is clear that the C-band Sentinel-1 has the capability to detect small-scale ionospheric irregularities spanning tens of kilometers, with the finest scales reaching 3 km in N-S width, a capability that other instruments cannot match.
There is a presumption that operating in the C-band does not necessarily constitute a disadvantage for inversion of ionospheric structure. The primary disadvantage is that Sentinel-1 is not a fully polarized satellite and is thus unable to perform ionospheric structure inversion autonomously. From the inclusion of slave images or additional data, it is inevitable that the ionospheric structure extraction will be negatively disturbed.
4.2. Comparison of Auroral Inversion by Different Polarization Channels
Observing the intensity maps firstly shows that there is a slight difference between the ground imaging based on VH and VV polarization [38,39]. The ionospheres influenced by auroral activity may introduce an uneven medium, raising questions about potential differential impacts on the various polarization channels traversing them. Previous researchers have identified discrepancies in the sensitivity of distinct polarization channels to feature classification [40], and it may be highly intriguing to expand this hypothesis to the domain of ionospheric studies. The sensitivity of the different polarization to the ionosphere and the degree of response to the aurora have not been reported, and at most, an explanation is provided in the form of simulations [41].
An interferogram was generated based on VH polarization from the initial set of experimental data presented in Table 1, as shown in Figure 8a. The first conclusion is that the cross-polarized interferogram also has the ability to invert the two-dimensional morphology of the aurora, as it clearly demonstrates an ionospheric structure similar to that described above. Secondly and most importantly, it is evident from the figure that the coverage of the aurora and its intensity detected using VH polarization is slightly larger than that of VV polarization. Furthermore, a comparison between Figure 8a and Figure 3a reveals that the former is more sensitive to the irregular structure located near 57°N.
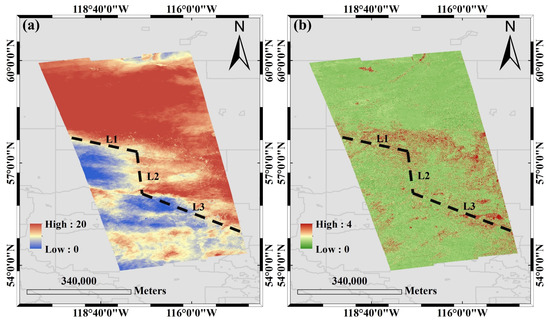
Figure 8.
(a) Interferograms generated by VH polarization. (b) Differences in interferograms for different polarization.
To highlight the discrepancy more distinctly, the absolute value of the difference between the VH interferogram and the VV interferogram is illustrated in Figure 8b. For ease of comparison with the previously discussed figures, the same three reference lines, L1, L2, and L3, are identified in Figure 8. It is evident that the difference tends to localize predominantly at the auroral boundary, reinforcing the notion of varying sensitivity among different polarization channels towards the auroral boundary. This finding further corroborates the efficacy of utilizing Sentinel-1 for the inversion of the aurora’s two-dimensional structure. The interference phase exhibits significant variability at the auroral boundary, likely due to substantial fluctuations in the TEC gradient during these instances.
Ionospheric TEC enhancement induced by aurora will act directly and simultaneously on the interferometric phase and FRA maps [14,42]. Even though Sentinel-1 is a dual-polarization SAR satellite, it is also subject to the Faraday rotation (FR) effect, but there is no way to calculate it. As is well known, the stronger the ionospheric TEC, the stronger the damage to SAR imaging [41,43]. In this case, it can be argued that the FR effect is much more intrusive on SAR than the dispersion effect or other effects [44]. The response of different polarization to FR when an electromagnetic wave travels through the ionosphere varies, as can be seen in Freeman and Saatchi [41], and this is especially a large difference between co-polarization and cross-polarization. This is supposed to be the cause of the appearance of Figure 8b, and it can be surmised that the larger the between the master and slave images, the more pronounced this phase difference is.
A prospective solution that may come to fruition in the future involves the collaborative observation of auroras utilizing both cross-polarization and co-polarization channels. Despite Sentinel-1 not being a fully polarized satellite, it has leveraged all available information for the inversion of auroral patterns. Previous reports have touched upon co-observations for enhancing interferometric accuracy [39], albeit not specifically in the realm of the ionosphere. Nonetheless, following the analyses presented in this section, the feasibility of employing this approach for ionospheric studies emerges. There is an absence of higher-precision data to determine which polarization (VH or VV) captures the aurora more accurately, which is a regrettable limitation that precludes a detailed discussion of this topic.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we reported for the first time that the interferogram from C-band Sentinel-1 clearly showed the effect on the auroral region during the intense geomagnetic storm on 11 May 2024. By further comparing with the SSUSI observation from the DMSP satellite, we demonstrated that the interferogram can map the structure of the aurora in two-dimensions on a scale as fine as 22 km. The main findings are summarized below:
- It is demonstrated that Sentinel-1 is expected to be a new data source for detecting the presence of precipitating charged particles in the aurora. Notably, the boundary of broadband aurora can be inverted and performed at a high resolution even at mid-latitudes.
- Cross-polarization emerges as a method with considerable potential for auroral studies. It is noteworthy that the cross-polarized and co-polarized channels exhibit divergent sensitivities in capturing auroral phenomena, suggesting the potential for future observations of the ionosphere through a combination of these two channels.
- Through comparison with DMSP SSJ, it has been illustrated that Sentinel-1 interferograms possess the capability to capture small-scale sporadic plasma patches of 3 km in N-S width triggered by auroras.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z., C.X. and F.W.; methodology, Y.Z.; validation, Y.J., S.W. and F.W.; investigation, Y.Z.; data curation, F.T. and S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.X., Y.J. and B.S.; visualization, Y.Z. and S.W.; funding acquisition, C.X. and Y.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42174191 and 62471474), and the Dragon 6 cooperation 2024–2028 (project No. 95437).
Data Availability Statement
Sentinel-1 is provided free of charge by ASF: https://search.asf.alaska.edu/#/, accessed on 1 January 2025. The DMSP/SSUSI data are available from https://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/data/dmsp, accessed on 1 January 2025. The high-resolution GACOS products are available from http://www.gacos.net/, accessed on 1 January 2025. All geomagnetic indices in the manuscript are provided by https://omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov, accessed on 1 January 2025. The MIT GNSS-TEC data are available from https://cedar.openmadrigal.org/ftp/fullname/X/email/XX/affiliation/none/kinst/8000, accessed on 1 January 2025.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the availability of the data online.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bhaskar, A.; Pradeep, J.; Narendranath, S.; Nandy, D.; Vaidya, B.; Hari, P.; Thampi, S.V.; Yadav, V.K.; Vichare, G.; Raghav, A.; et al. AuroraMag: Twin Explorer of Asymmetry in Aurora and Solar Wind-Magnetosphere Coupling. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 75, 6687–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K.; Newell, P.T.; Meng, C.-I.; Brittnacher, M.; Parks, G. Characteristics of the Solar Wind Controlled Auroral Emissions. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 17543–17557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapgood, M.A. Towards a Scientific Understanding of the Risk from Extreme Space Weather. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, E.M.; LaBelle, J. Measurement and Modeling of Auroral Absorption of HF Radio Waves Using a Single Receiver. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, P.T.; Sotirelis, T.; Wing, S. Diffuse, Monoenergetic, and Broadband Aurora: The Global Precipitation Budget. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, R.J.; Seaton, D.B.; Steenburgh, R.; He, J.; Rodriguez, J.V. September 2017′s Geoeffective Space Weather and Impacts to Caribbean Radio Communications During Hurricane Response. Space Weather 2018, 16, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.; Smith, E.K. Ionospheric Effects on Satellite Land Mobile Systems. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2002, 44, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Nicoll, J.; Bristow, B. Mapping Aurora Activity with SAR—a Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 4, pp. IV-1–IV-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.-X.; He, F.; Zhang, X.-X.; Chen, B. A New Auroral Boundary Determination Algorithm Based on Observations from TIMED/GUVI and DMSP/SSUSI. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Shiokawa, K.; Poddelsky, I.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Probing Afternoon Detached Aurora and High-Latitude Trough Based on DMSP Observations. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgemore, K.J.F.; Williams, P.J.S.; Jones, G.O.L.; Wright, J.W. A Comparison of EISCAT and Dynasonde Measurements of the Auroral Ionosphere. Ann. Geophys. 1997, 14, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xiong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y. Small-Scale Field-Aligned Currents of Intense Amplitude Resolved by the Swarm Satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2023JA032198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Freeman, A.; Chapman, B.; Rosen, P.; Li, Z. Imaging Ionospheric Inhomogeneities Using Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Jung, H.-S.; Chen, J.-Y. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (InSAR) Ionospheric Correction Based on Faraday Rotation: Two Case Studies. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomba, G. Estimation and Compensation of Ionospheric Propagation Delay in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Signals, 2016. Available online: https://elib.dlr.de/109038/1/Thesis_compressed.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Ji, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, C.; Xu, Z. Transionospheric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observation: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024, 2–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, F.; Mao, W.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Gao, H. Equatorial Ionospheric Scintillation Measurement in Advanced Land Observing Satellite Phased Array-Type L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations. Engineering 2025, 47, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Gao, H. Drifting Ionospheric Scintillation Simulation for L-Band Geosynchronous SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomba, G.; Rodriguez, G.F.; De Zan, F. Ionospheric Phase Screen Compensation for the Sentinel-1 TOPS and ALOS-2 ScanSAR Modes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Agram, P.; Simons, M.; Fielding, E.J. Ionospheric Correction of Insar Time Series Analysis of C-Band Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6755–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiong, C.; Wan, X.; Ji, Y.; Tao, Z.; Tang, F.; Gao, S.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y. Observations of Ionospheric Irregularities during a Geomagnetic Storm Based on the C-Band Sentinel-1. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 6425–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenk, P.; Giez, J.; Schmidt, K.; Nannini, M.; Schwerdt, M. Independent Calibration of the Sentinel-1C SAR System. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2024, 15th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Munich, Germany, 23–26 April 2024; pp. 591–594. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, C.; Stolle, C.; Alken, P.; Rauberg, J. Relationship between Large-Scale Ionospheric Field-Aligned Currents and Electron/Ion Precipitations: DMSP Observations. Earth Planets Space 2020, 72, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, L.J.; Morrison, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kil, H.; Wolven, B.; Ogorzalek, B.S.; Humm, D.C.; Meng, C.-I. Validation of Remote Sensing Products Produced by the Special Sensor Ultraviolet Scanning Imager (SSUSI): A Far UV-Imaging Spectrograph on DMSP F-16; Larar, A.M., Mlynczak, M.G., Eds.; International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 338–348. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, R.J.; Denig, W.F.; Kilcommons, L.M.; Knipp, D.J. New DMSP Database of Precipitating Auroral Electrons and Ions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 9056–9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.; Navas-Traver, I.; Bibby, D.; Lokas, S.; Snoeij, P.; Rommen, B.; Osborne, S.; Ceba-Vega, F.; Potin, P.; Geudtner, D. Sentinel-1 SAR System and Mission. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 1582–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.; Geudtner, D.; Davidson, M.; Bibby, D.; Navas-Traver, I.; Garcia Hernandez, A.I.; Laduree, G.; Poupaert, J.; Bollian, T.; Graham, S. Sentinel-1 Next Generation: Enhanced C-Band Data Continuity. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2024, 15th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Munich, Germany, 23–26 April 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dammann, D.O.; Eriksson, L.E.B.; Mahoney, A.R.; Eicken, H.; Meyer, F.J. Mapping Pan-Arctic Landfast Sea Ice Stability Using Sentinel-1 Interferometry. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.C.; Erickson, P.J.; Nishimura, Y.; Zhang, S.R.; Bush, D.C.; Coster, A.J.; Meade, P.E.; Franco-Diaz, E. Imaging the May 2024 Extreme Aurora With Ionospheric Total Electron Content. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; He, M. Resonant Waves Play an Important Role in the Increasing Heat Waves in Northern Hemisphere Mid-Latitudes Under Global Warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL104839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; He, M. Identification of Stratospheric Disturbance Information in China Based on the Round-Trip Intelligent Sounding System. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 3839–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brcic, R.; Parizzi, A.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R.; Meyer, F. Ionospheric Effects in SAR Interferometry: An Analysis and Comparison of Methods for Their Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 1497–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, J.; Suzuki, T.; Furuya, M.; Heki, K. Imaging the Midlatitude Sporadic E Plasma Patches with a Coordinated Observation of Spaceborne InSAR and GPS Total Electron Content. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Kim, J.S.; Otsuka, Y.; Wrasse, C.M.; Rodrigues de Paula, E.; Rodrigues de Souza, J. L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Observation of Ionospheric Density Irregularities at Equatorial Plasma Depletion Region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Gurrola, E.; Sacco, G.F.; Zebker, H. The InSAR Scientific Computing Environment. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2012, 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 730–733. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, A.V. An Efficient Implementation of a Scaling Minimum-Cost Flow Algorithm. J. Algorithms 1997, 22, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T.; Crippa, P. Generic Atmospheric Correction Model for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshiri, R.; Nahavandchi, H.; Motagh, M. Persistent Scatterer Analysis Using Dual-Polarization Sentinel-1 Data: Contribution From VH Channel. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Feng, H.; Yan, S.; Fan, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y. Polarimetric Persistent Scatterer Interferometry for Ground Deformation Monitoring with VV-VH Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, J.; Musekiwa, C.; Kemp, J.; Inggs, M.R. Parameters Affecting Interferometric Coherence—The Case of a Dynamic Agricultural Region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Saatchi, S.S. On the Detection of Faraday Rotation in Linearly Polarized L-Band SAR Backscatter Signatures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.J.; Nicoll, J. The Impact of the Ionosphere on Interferometric SAR Processing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008—2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; Volume 2, pp. II-391–II-394. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, A.L.; Mattar, K.E.; Sofko, G. Influence of Ionospheric Electron Density Fluctuations on Satellite Radar Interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, S.H.; Bates, R.H.T. Effects of Magneto-Ionic Propagation on the Polarization Scattering Matrix. Proc. IEEE 1965, 53, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).