Salinity Fronts in the South Atlantic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Large-Scale Open-Ocean Salinity Fronts
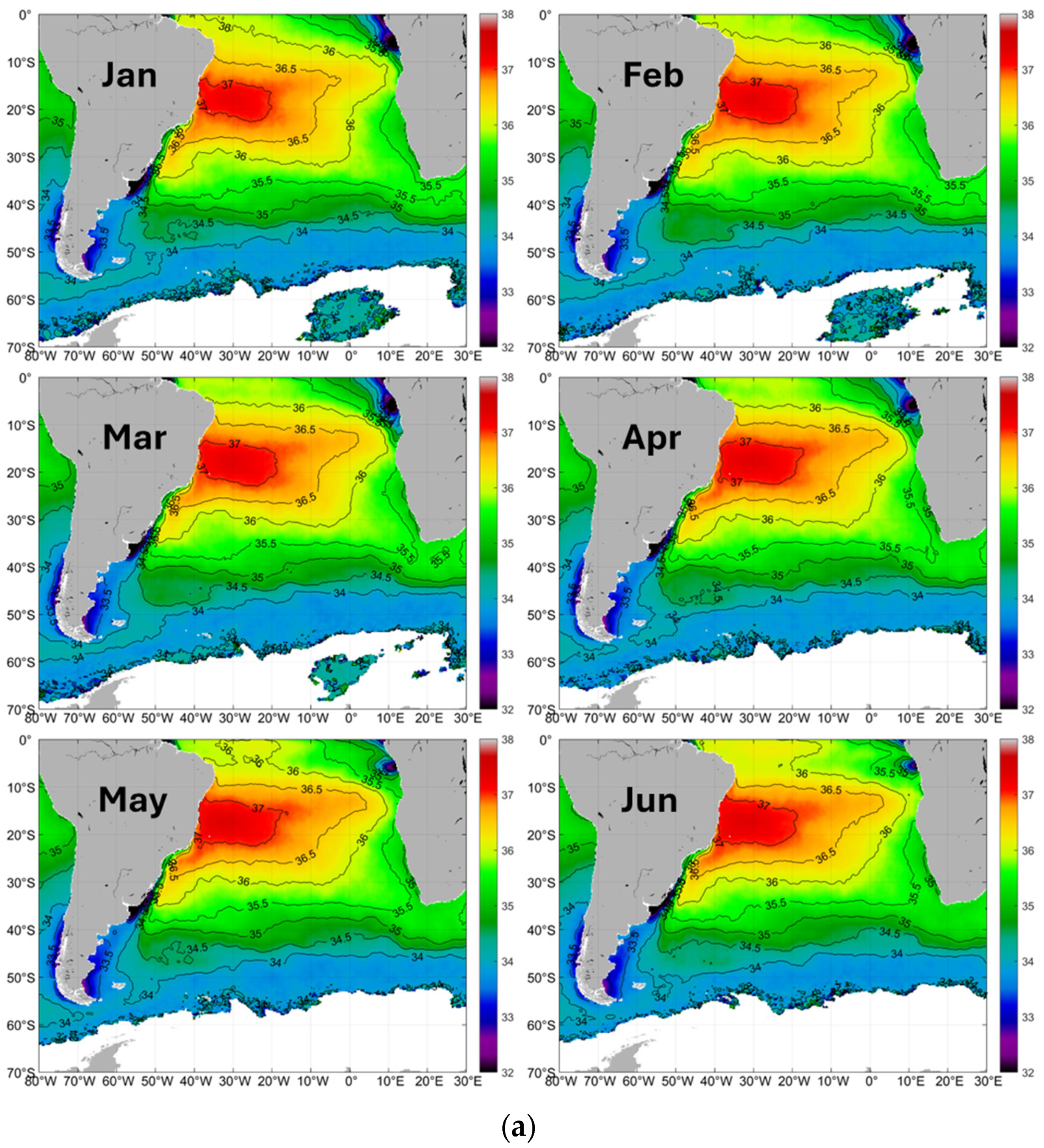
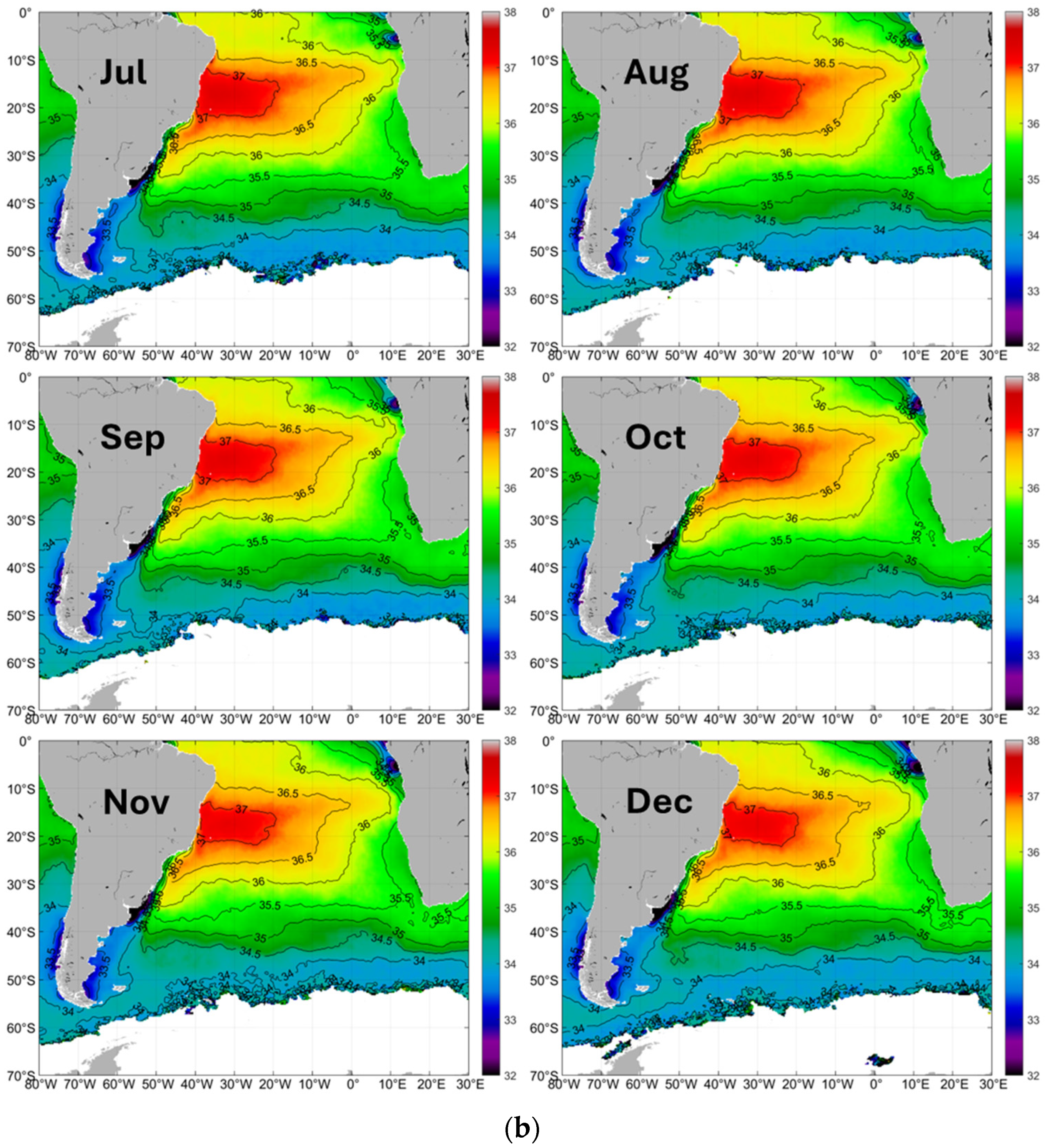
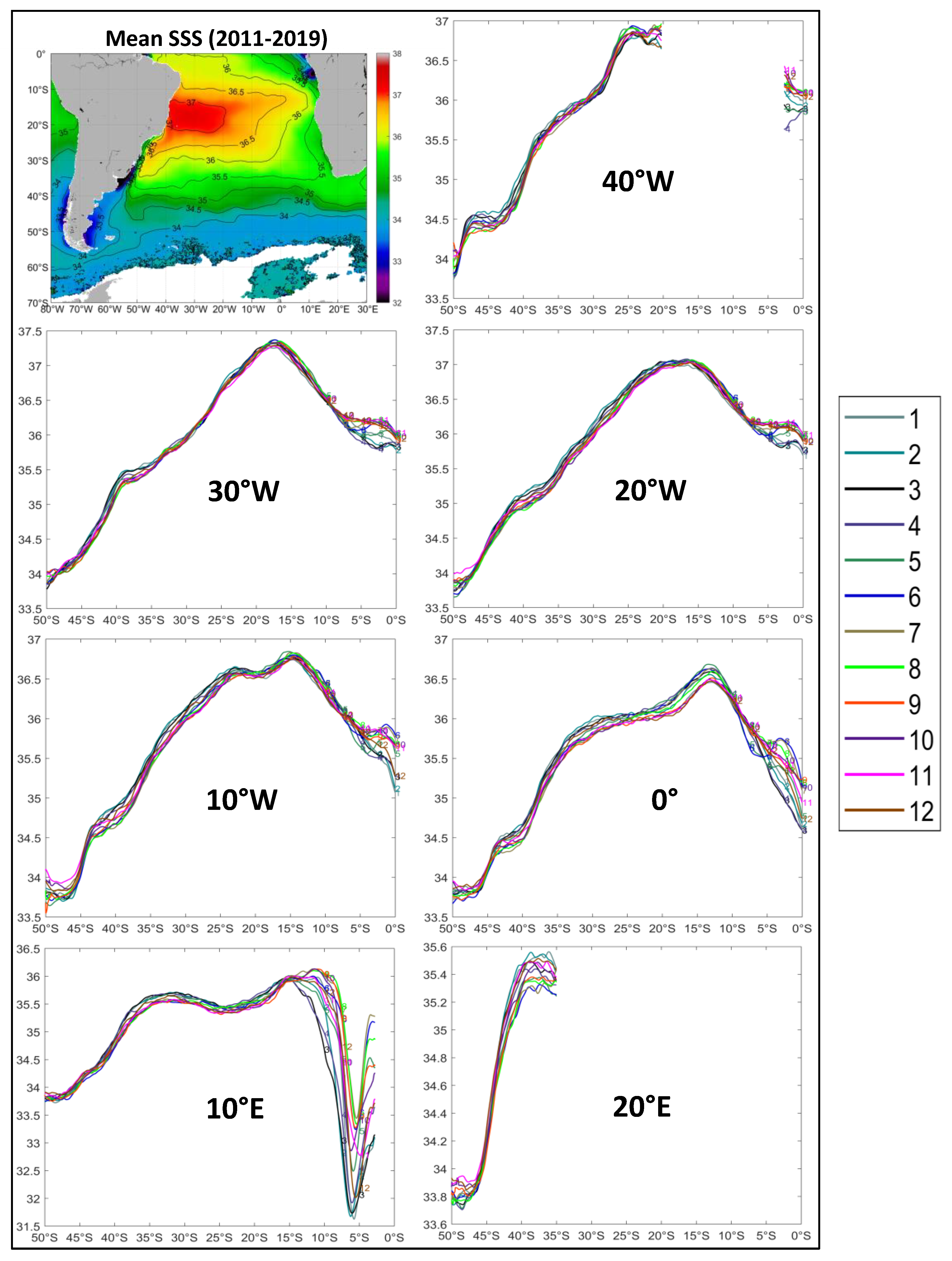
3.1.1. Large-Scale Pattern of Sea Surface Salinity
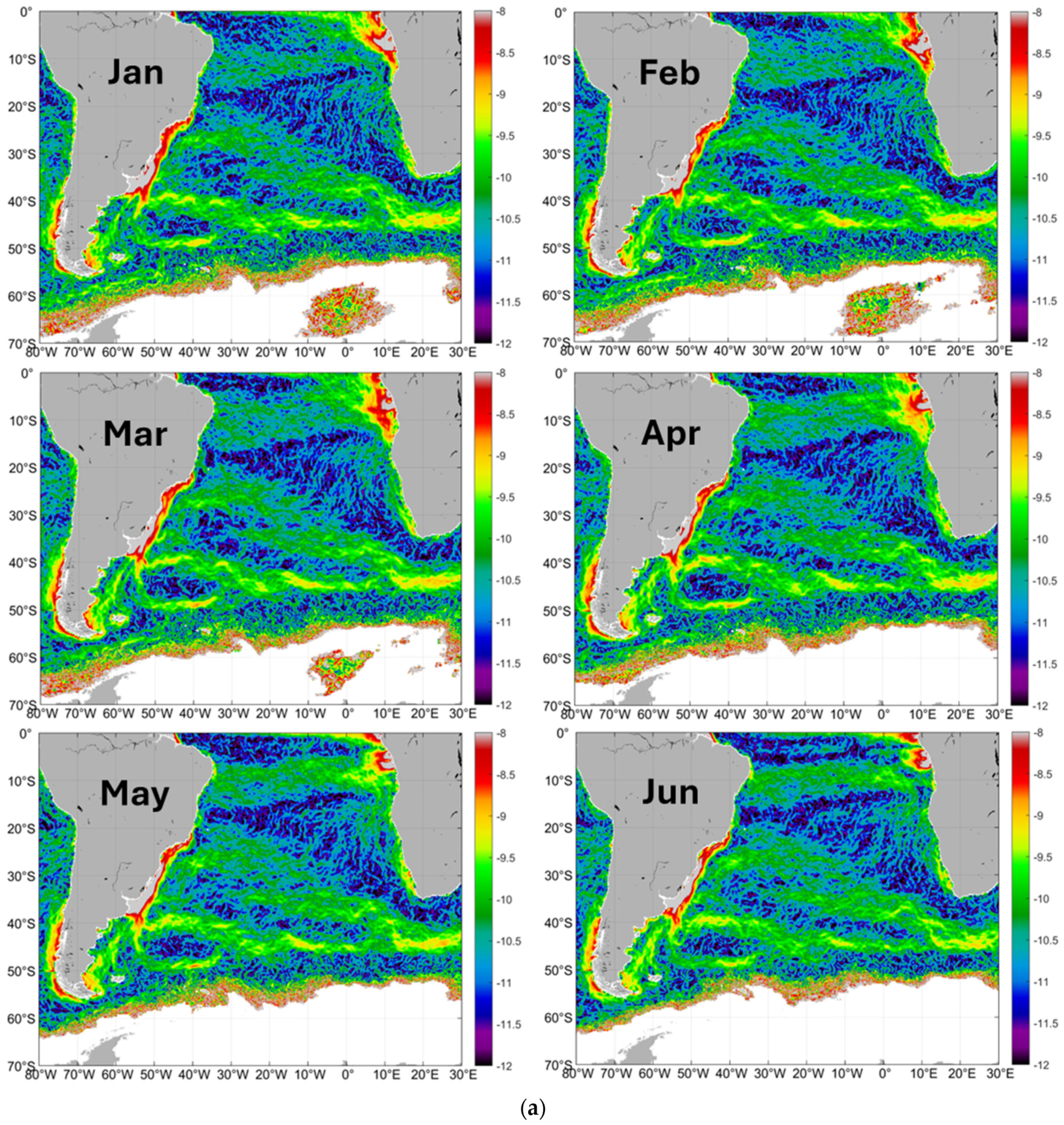
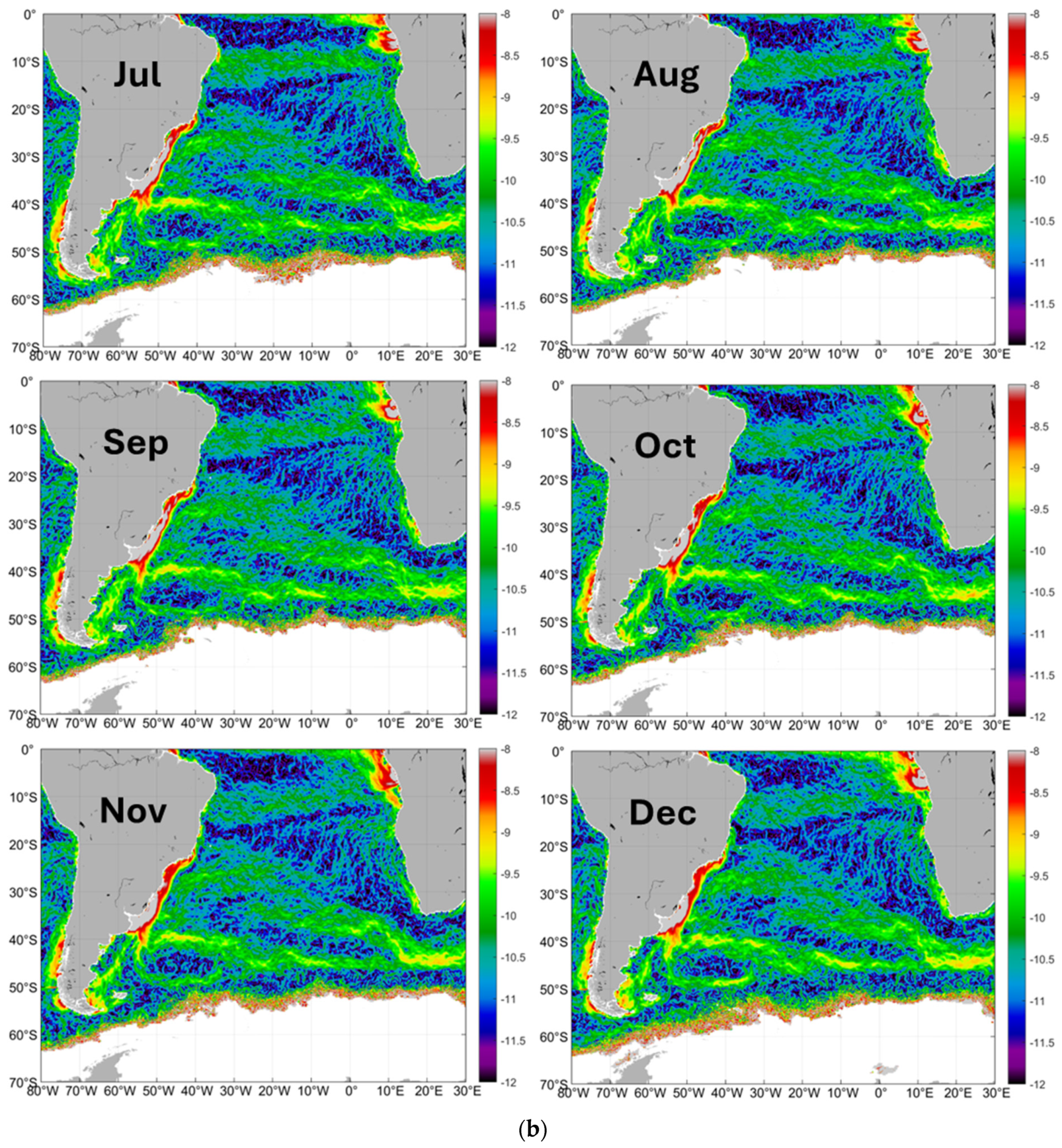
3.1.2. Salinity Fronts: An Overview
3.1.3. Meridional (North-South) and Zonal (West-East) Variations of Surface Salinity
3.1.4. Large-Scale Pattern of Open-Ocean Salinity Fronts
3.1.5. Tropical Front
3.1.6. Meridional Salinity Maximum
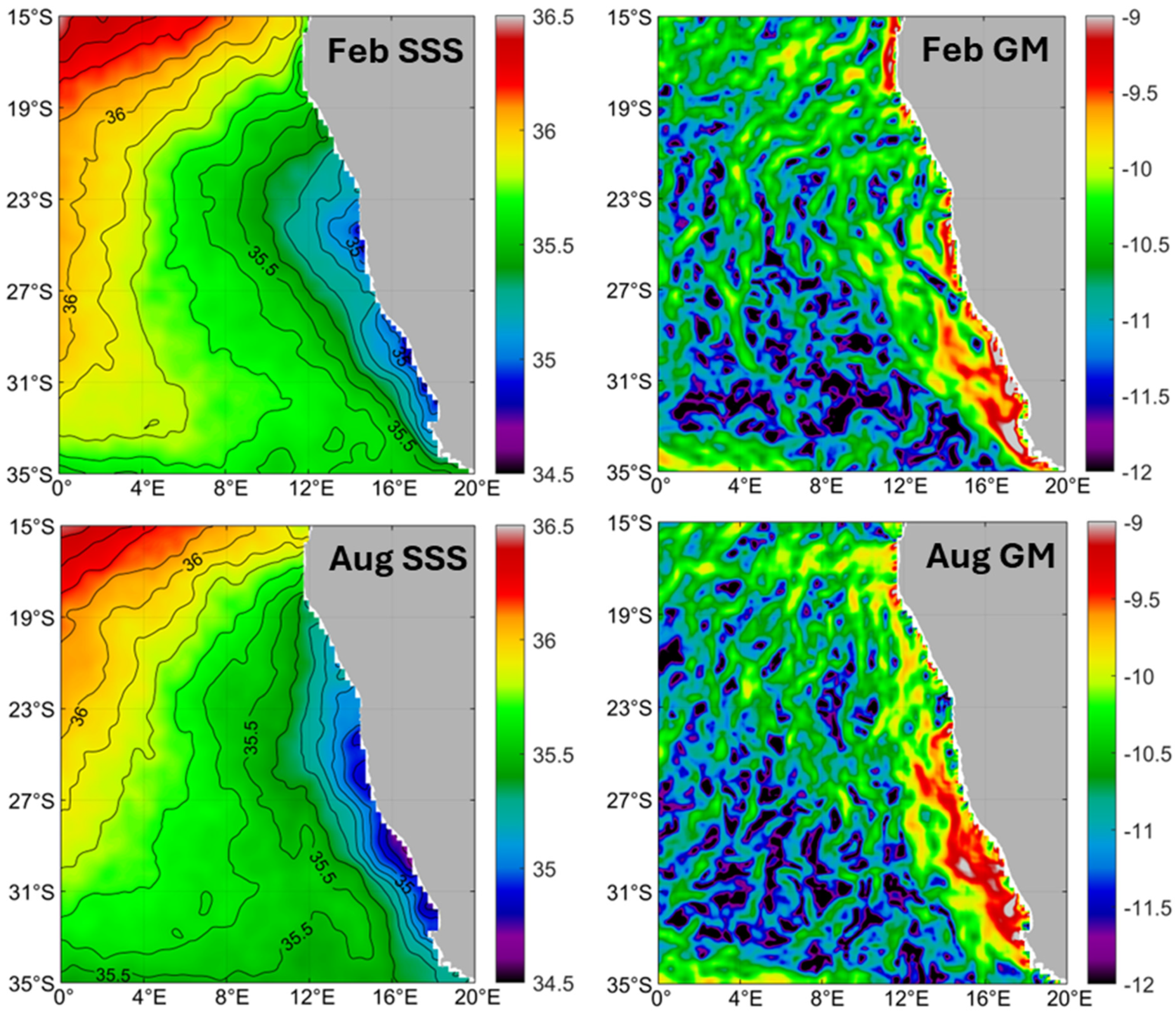
3.1.7. Subtropical Frontal Zone (STFZ)
3.1.8. Subantarctic Front (SAF)
3.1.9. Meso-Scale Quasi-Meridional Tropical-Subtropical Fronts
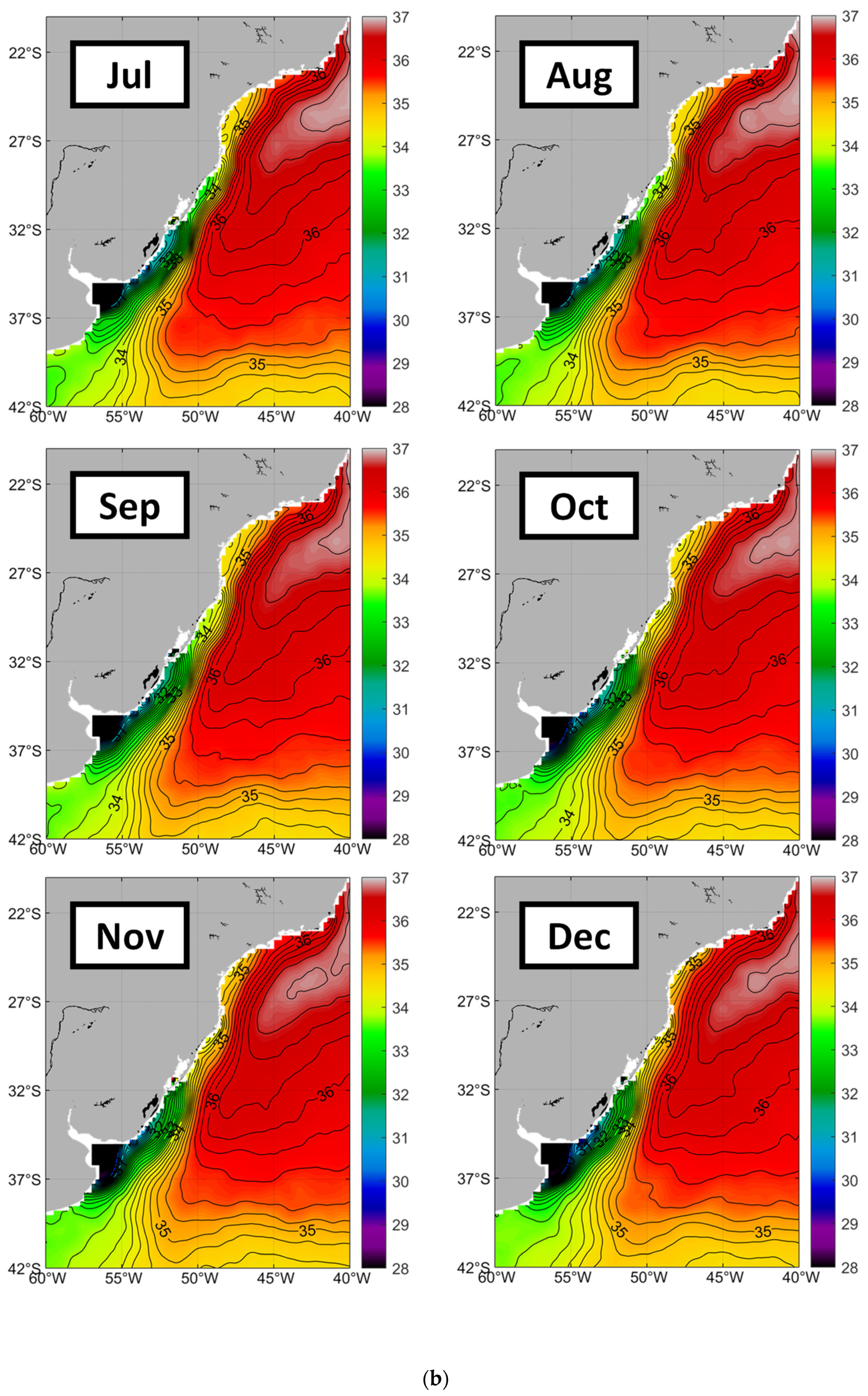
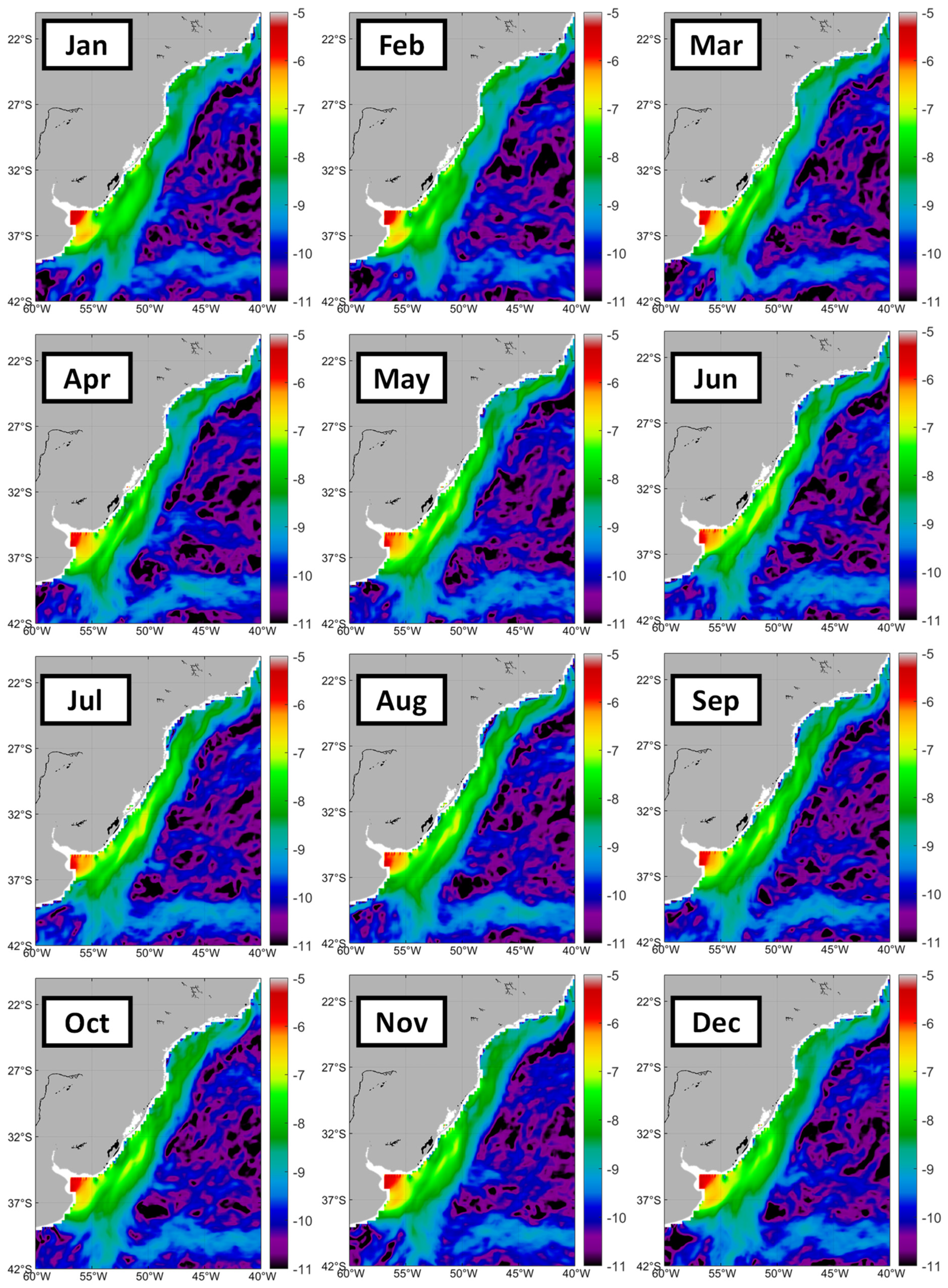
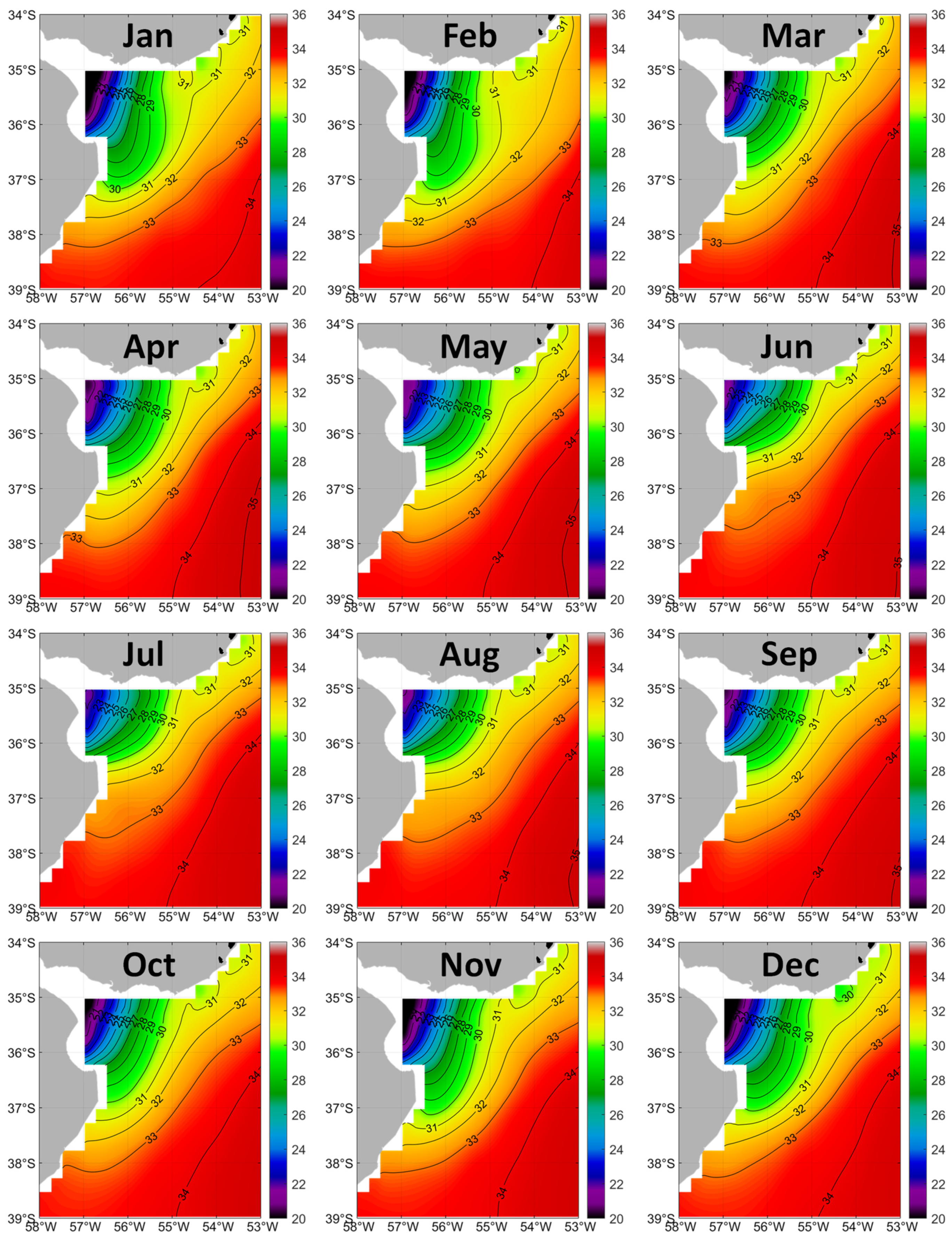
3.2. Rio de la Plata Outflow
3.3. Magellan Strait and Le Maire Strait Outflows
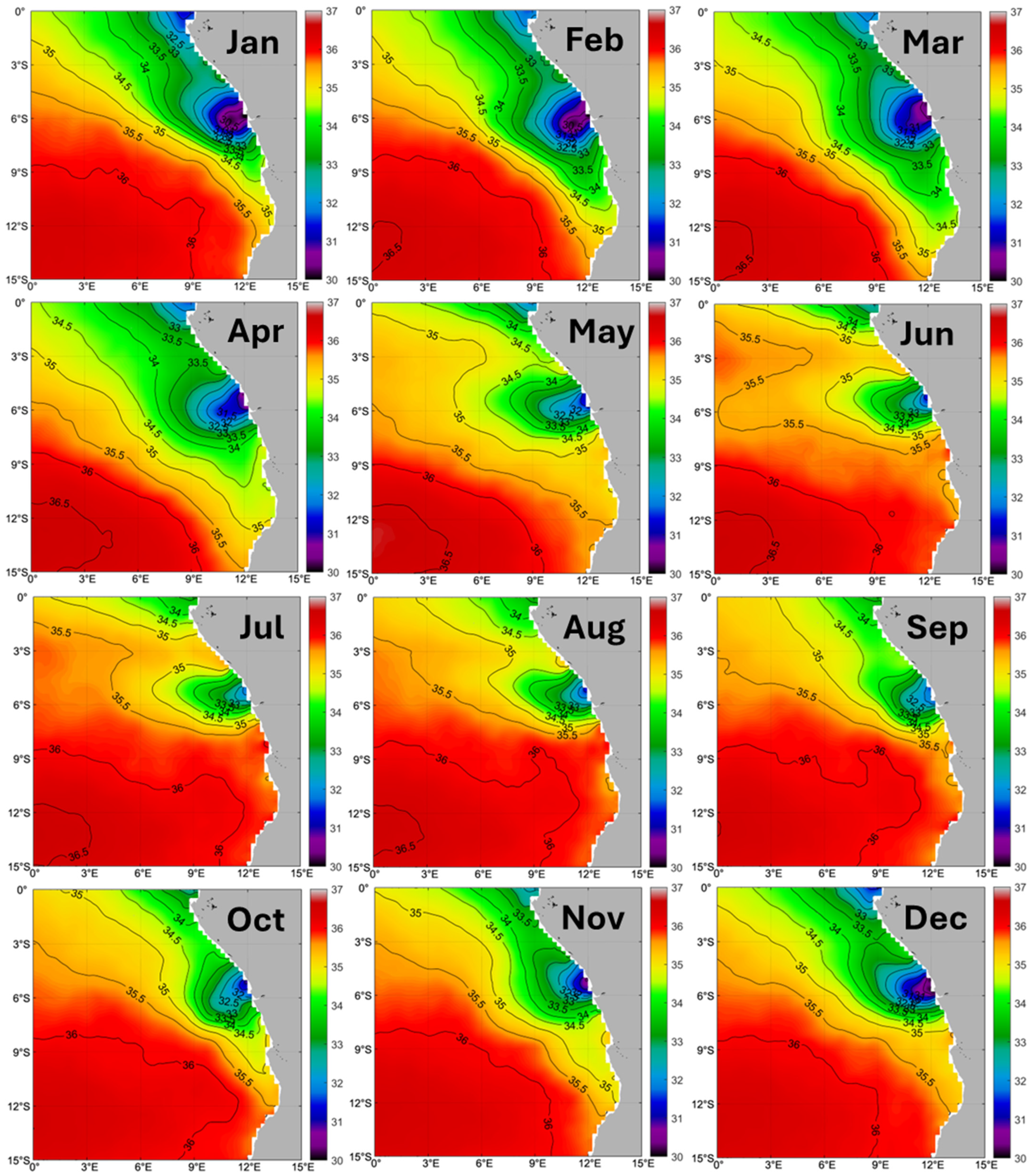
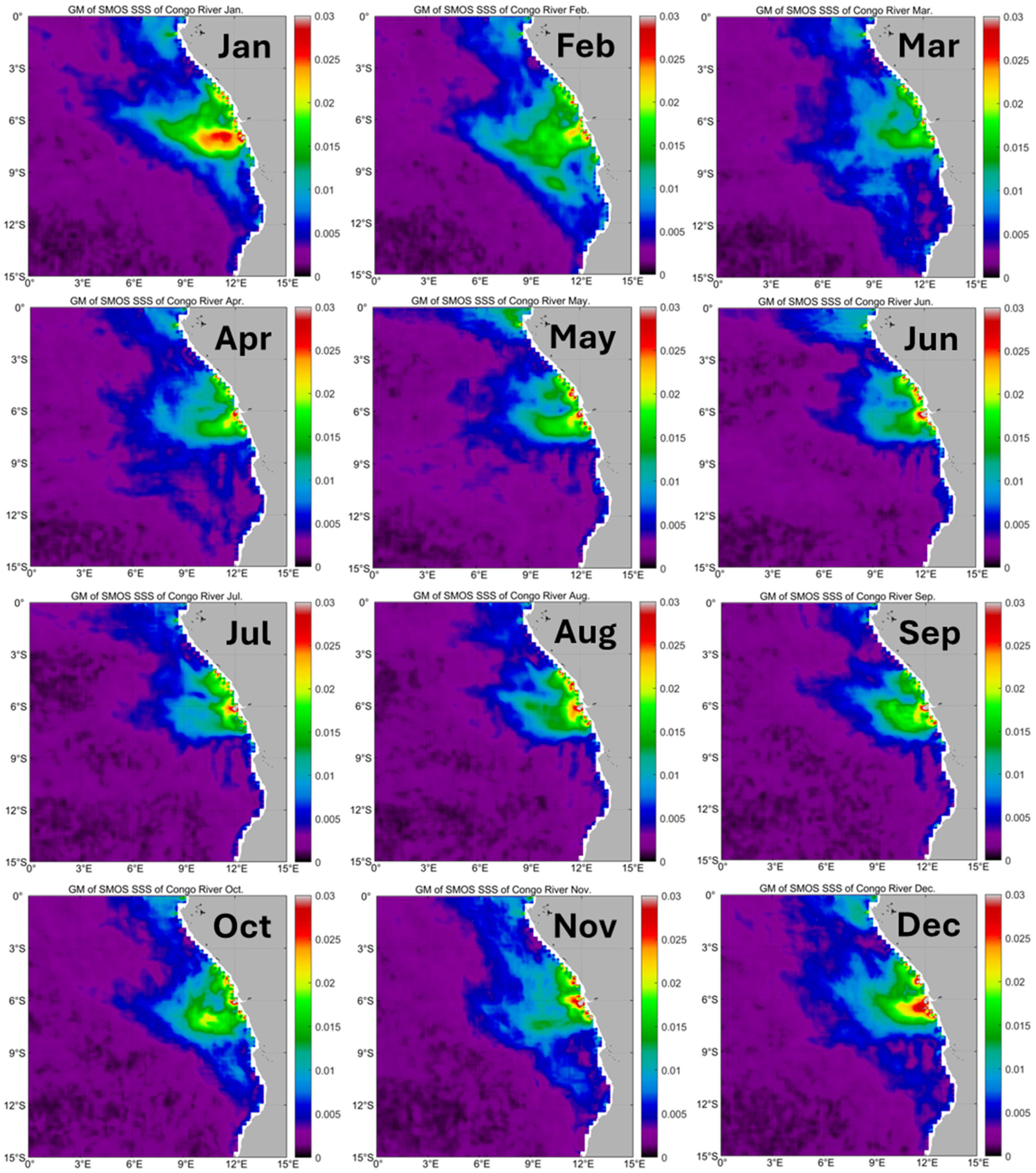
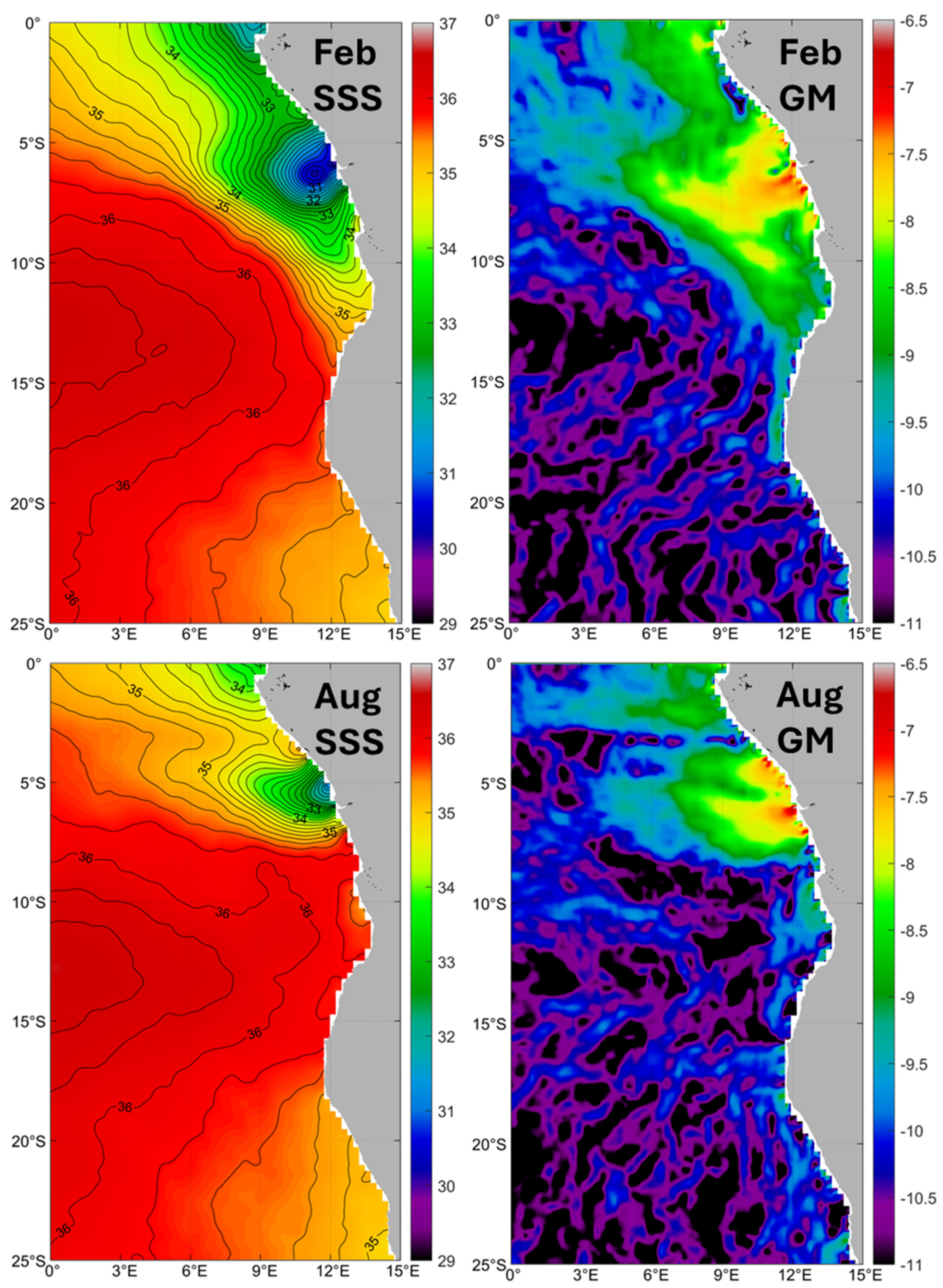
3.4. Congo River Outflow
3.5. Angola-Benguela Front
3.6. Benguela Upwelling Front
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boutin, J.; Yueh, S.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Entekhabi, D.; Kerr, Y.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Lee, T.; Reul, N.; Zribi, M. Soil moisture and sea surface salinity derived from satellite-borne sensors. Surv. Geophys. 2023, 44, 1449–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Fournier, S.; Boutin, J.; Hernandez, O.; Maes, C.; Chapron, B.; Alory, G.; Quilfen, Y.; Tenerelli, J.; Morisset, S.; et al. Sea surface salinity observations from space with the SMOS satellite: A new means to monitor the marine branch of the water cycle. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 681–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.L.; Marchand, S.; d’Amico, F.; Hasson, A.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Reul, N.; Reverdin, G.; Vialard, J. New SMOS Sea Surface Salinity with reduced systematic errors and improved variability. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.; Lee, T.; Boutin, J.; Drushka, K.; Fournier, S.; Sabia, R.; Stammer, D.; Bayler, E.; Reul, N.; Gordon, A.; et al. Satellite salinity observing system: Recent discoveries and the way forward. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Grodsky, S.A.; Arias, M.; Boutin, J.; Catany, R.; Chapron, B.; d’Amico, F.; Dinnat, E.; Donlon, C.; Fore, A.; et al. Sea surface salinity estimates from spaceborne L-band radiometers: An overview of the first decade of observation (2010–2019). Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Reul, N.; Köhler, J.; Martin, A.; Catany, R.; Guimbard, S.; Rouffi, F.; Vergely, J.L.; Arias, M.; Chakroun, M.; et al. Satellite-based sea surface salinity designed for ocean and climate studies. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.D.; Song, Y.T.; Maes, C. Sea surface salinity and barrier layer variability in the equatorial Pacific as seen from Aquarius and Argo. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.Y.; Lagerloef, G.S.E. Salinity fronts in the tropical Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.S. Sea-surface salinity fronts and associated salinity-minimum zones in the tropical ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 4205–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnichenko, O.; Hacker, P.; Maximenko, N.; Lagerloef, G.; Potemra, J. Optimum interpolation analysis of Aquarius sea surface salinity. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyadjro, E.S.; Subrahmanyam, B. Spatial and temporal variability of central Indian Ocean salinity fronts observed by SMOS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asto, C.; Chaigneau, A.; Gutiérrez, D. Spatio-temporal variability of the equatorial front in the eastern tropical Pacific from remote sensing salinity data (2010–2015). Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2019, 169–170, 104640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.L.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, R.; Yan, H.Q.; Chen, J.; Bai, C.Z. Application of phenomena-resolving assessment methods to satellite sea surface salinity products. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Cuervo, J.; García-Reyes, M.; Gómez-Valdés, J. Identification of sea surface temperature and sea surface salinity fronts along the California Coast: Application using Saildrone and satellite derived products. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeckis, R. A survey of worldwide sea surface temperature fronts detected by environmental satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1978, 83, 4501–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allega, L.; Pisoni, J.P.; Cozzolino, E.; Maenza, R.A.; Piccolo, M.C. The variability of sea surface temperature in the Patagonian Shelf Argentina, from 35 years of satellite information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 6090–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artana, C.; Lellouche, J.M.; Park, Y.H.; Garric, G.; Koenig, Z.; Sennéchael, N.; Ferrari, R.; Piola, A.R.; Saraceno, M.; Provost, C. Fronts of the Malvinas Current System: Surface and subsurface expressions revealed by satellite altimetry, Argo floats, and Mercator operational model outputs. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 5261–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré, N.; Provost, C.; Saraceno, M. Spatial and temporal scales of the Brazil–Malvinas Current confluence documented by simultaneous MODIS Aqua 1.1-km resolution SST and color images. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 37, 770–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billany, W.; Swart, S.; Hermes, J.; Reason, C.J.C. Variability of the Southern Ocean fronts at the Greenwich Meridian. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 82, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, M.; Sato, O.T.; Polito, P.S. Temporal trends in sea surface temperature gradients in the South Atlantic Ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burls, N.J.; Reason, C.J.C. Sea surface temperature fronts in the midlatitude South Atlantic revealed by using microwave satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, C08001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, P.; Olmedo, E.; Pelegrí, J.L.; Turiel, A.; Campos, E.J.D. Seasonal variability of retroflection structures and transports in the Atlantic Ocean as inferred from satellite-derived salinity maps. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Farrara, J.D.; Schumann, G.; Andreadis, K.M.; Moller, D. Sea surface salinity variability in response to the Congo River discharge. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 99, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chai, F. Seasonal variability of SST fronts and winds on the southeastern continental shelf of Brazil. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, I.C.; Pereira, F.; Flierl, G.R.; Simoes-Sousa, I.T.; Palóczy, A.; Borges-Silva, M.; Rocha, C.B. The Brazil Current quasi-stationary unstable meanders at 22°S–23°S. Prog. Oceanogr. 2023, 210, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dencausse, G.; Arhan, M.; Speich, S. Is there a continuous Subtropical Front south of Africa? J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C02027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dong, S.; Sprintall, J.; Gille, S.T. Location of the Antarctic polar front from AMSR-E satellite sea surface temperature measurements. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, B.C.; Piola, A.R.; Rivas, A.L.; Baldoni, A.; Pisoni, J.P. Multiple thermal fronts near the Patagonian shelf break. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L02607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, B.C.; Ruiz-Etcheverry, L.A.; Marrari, M.; Piola, A.R.; Matano, R.P. Climate change Impacts on the Patagonian shelf break front. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, N.M.; Lovenduski, N.S. Mapping the Antarctic Polar Front: Weekly realizations from 2002 to 2014. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.M.; de Boer, A.M. The Dynamical Subtropical Front. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 5676–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, R.A.; Piola, A.R.; Fenco, H.; Matano, R.P.; Combes, V.; Chao, Y.; James, C.; Palma, E.D.; Saraceno, M.; Strub, P.T. The salinity signature of the cross-shelf exchanges in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean: Satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 7794–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, J.; Lucas, M.; Dufau, C.; Sutton, M.; Stum, J.; Lauret, O.; Channelliere, C. Detection and variability of the Congo River plume from satellite derived sea surface temperature, salinity, ocean colour and sea level. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hösen, E.; Möller, J.; Jochumsen, K.; Quadfasel, D. Scales and properties of cold filaments in the Benguela upwelling system off Lüderitz. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 1896–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houndegnonto, O.J.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Maes, C.; Bourlès, B.; Da-Allada, C.Y.; Reul, N. Seasonal variability of freshwater plumes in the eastern Gulf of Guinea as inferred from satellite measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC017041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Orsi, A.H. On the variability of Antarctic Circumpolar Current fronts inferred from 1992–2011 altimetry. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 3054–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeckis, R.; Gordon, A.L. Satellite observations of the Brazil and Falkland currents—1975 1976 and 1978. Deep-Sea Res. 1982, 29, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzzetti, J.A.; Stech, J.L.; Mello Filho, W.L.; Assireu, A.T. Satellite observation of Brazil Current inshore thermal front in the SW South Atlantic: Space/time variability and sea surface temperatures. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luko, C.D.; da Silveira, I.C.A.; Simoes-Sousa, I.T.; Araujo, J.M.; Tandon, A. Revisiting the Atlantic South Equatorial Current. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Meeuwis, J.M. The extent and variability of South-East Atlantic upwelling. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1987, 5, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Valentine, H.R.; van Ballegooyen, R.C. On the Subtropical Convergence in the South Atlantic Ocean. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1993, 89, 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, M.S.; Stammer, D. Interannual variability of the Congo River Plume-induced sea surface salinity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeuwis, J.M.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E. Surface thermal characteristics of the Angola-Benguela front. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1990, 9, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeuwis, J.M. Geographic Characteristics of Circulation Patterns and Features in the South Atlantic and South Indian Oceans Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa, 1991; 418p. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10210/10106 (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Moore, J.K.; Abbott, M.R.; Richman, J.G. Variability in the location of the Antarctic Polar Front (90°–20°W) from satellite sea surface temperature data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 27825–27833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.K.; Abbott, M.R.; Richman, J.G. Location and dynamics of the Antarctic Polar Front from satellite sea surface temperature data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 3059–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.B.; Podestá, G.P.; Evans, R.H.; Brown, O.B. Temporal variations in the separation of Brazil and Malvinas Currents. Deep Sea Res. 1988, 35, 1971–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, A.R.; Romero, S.I.; Zajaczkovski, U. Space-time variability of the Plata plume inferred from ocean color. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.L. Spatial and temporal variability of satellite-derived sea surface temperature in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.L.; Pisoni, J.P. Identification, characteristics and seasonal evolution of surface thermal fronts in the Argentinean Continental Shelf. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 79, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Etcheverry, L.A.; Saraceno, M. Sea level trend and fronts in the South Atlantic Ocean. Geosciences 2020, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, M.; Provost, C.; Piola, A.R.; Bava, J.; Gagliardini, A. Brazil Malvinas Frontal System as seen from 9 years of advanced very high resolution radiometer data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109, C05027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, M.; Provost, C.; Piola, A.R. On the relationship between satellite-retrieved surface temperature fronts and chlorophyll a in the western South Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2005, 110, C11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, J.A.; Florenchie, P.; Shillington, F.A. Seasonal and interannual fluctuations of the Angola-Benguela Frontal Zone (ABFZ) using 4.5 km resolution satellite imagery from 1982 to 1999. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Han, Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Lv, M. Southwestern Atlantic Ocean fronts detected from satellite-derived SST and chlorophyll. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Ma, C.Y.; Liu, Y.L. Southwestern Atlantic Ocean fronts detected from the fusion of multi-source remote sensing data by a deep learning model. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1140645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnett, P.J.; Alvera-Azcárate, A.; Chin, T.M.; Corlett, G.K.; Gentemann, C.L.; Karagali, I.; Li, X.; Marsouin, A.; Marullo, S.; Maturi, E.; et al. Half a century of satellite remote sensing of sea-surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provost, C.; Garçon, V.; Falcon, L.M. Hydrographic conditions in the surface layers over the slope-open ocean transition area near the Brazil-Malvinas confluence during austral summer 1990. Cont. Shelf Res. 1996, 16, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artana, C.; Provost, C.; Lellouche, J.M.; Rio, M.H.; Ferrari, R.; Sennéchael, N. The Malvinas Current at the Confluence with the Brazil Current: Inferences from 25 years of Mercator Ocean reanalysis. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 7178–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, R.A.; Acha, E.M.; Framiñan, M.B.; Lasta, C.A. Physical oceanography of the Río de la Plata estuary, Argentina. Cont. Shelf Res. 1997, 17, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, A.R.; Matano, R.P.; Palma, E.D.; Möller, O.O., Jr.; Campos, E.J.D. The influence of the Plata River discharge on the western South Atlantic shelf. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L01603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acha, E.M.; Mianzan, H.; Guerrero, R.; Carreto, J.; Giberto, D.; Montoya, N.; Carignan, M. An overview of physical and ecological processes in the Rio de la Plata Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.J.D.; Piola, A.R.; Matano, R.P.; Miller, J.L. PLATA: A synoptic characterization of the southwest Atlantic shelf under influence of the Plata River and Patos Lagoon outflows. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogliotti, A.I.; Ruddick, K.; Guerrero, R. Seasonal and inter-annual turbidity variability in the Río de la Plata from 15 years of MODIS: El Niño dilution effect. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 182, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borús, J.; Giacosa, J. Evaluación de Caudales Diarios Descargados Por Los Grandes Ríos Del Sistema Del Plata al Río de La Plata. In Direccion y Alerta Hidrológico; Instituto Nacional del Agua: Ezeiza, Argentina, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Burrage, D.; Wesson, J.; Martinez, C.; Pérez, T.; Möller, O., Jr.; Piola, A. Patos Lagoon outflow within the Río de la Plata plume using an airborne salinity mapper: Observing an embedded plume. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.J.D.; Lorenzzetti, J.A.; Stevenson, M.R.; Stech, J.L.; de Souza, R.B. Penetration of waters from the Brazil–Malvinas Confluence region along the South American continental shelf up to 23°S. An. Da Acad. Bras. De Ciências 1996, 68 (Suppl. 1), 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, E.J.D.; Lentini, C.A.D.; Miller, J.L.; Piola, A.R. Interannual variability of the sea surface temperature in the South Brazil Bight. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.D.; Matano, R.P.; Piola, A.R. A numerical study of the Southwestern Atlantic Shelf circulation: Stratified ocean response to local and offshore forcing. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, N.O.; Vargas, W.M. The temporal climatic variability in the ‘Río de la Plata’ basin displayed by the river discharges. Clim. Chang. 1998, 38, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Framiñan, M.B.; Etala, M.P.; Acha, E.M.; Guerrero, R.A.; Lasta, C.A.; Brown, O.B. Physical characteristics and processes of the Río de la Plata Estuary. In Estuaries of South America, Their Geomorphology and Dynamics; Perillo, G.M.E., Piccolo, M.C., Pino-Quivira, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 161–194. [Google Scholar]
- Simionato, C.G.; Nuñez, M.N.; Engel, M. The salinity front of the Río de la Plata—A numerical case study for winter and summer conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2641–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, O.O., Jr.; Piola, A.R.; Freitas, A.C.; Campos, E.J.D. The effects of river discharge and seasonal winds on the shelf off southeastern South America. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1607–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.; Simionato, C. The Río de la Plata estuary hydrology and circulation. Meteorologica 2019, 44, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lisboa, P.V.; Fernandes, E.H.; Sottolichio, A.; Huybrechts, N.; Bendo, A.R. Coastal plumes contribution to the suspended sediment transport in the Southwest Atlantic inner continental shelf. J. Mar. Syst. 2022, 236, 103796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, A.R.; Palma, E.D.; Bianchi, A.A.; Castro, B.M.; Dottori, M.; Guerrero, R.A.; Marrari, M.; Matano, R.P.; Möller, O.O.; Saraceno, M. Physical oceanography of the SW Atlantic Shelf: A review. In Plankton Ecology of the Southwestern Atlantic: From the Subtropical to the Subantarctic Realm; Hoffmeyer, M.S., Sabatini, M.E., Brandini, F.P., Calliari, D.L., Santinelli, N.H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Framiñan, M.B.; Brown, O.B. Study of the Río de la Plata turbidity front, Part 1: Spatial and temporal distribution. Cont. Shelf Res. 1996, 16, 1259–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, F.P.; Santoro, P.E.; Pedocchi, F. Spatio-temporal dynamics of the Río de la Plata turbidity front; combining remote sensing with in-situ measurements and numerical modeling. Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 213, 104301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, R.P.; Combes, V.; Piola, A.R.; Guerrero, R.; Palma, E.D.; Strub, P.T.; James, C.; Fenco, H.; Chao, Y.; Saraceno, M. The salinity signature of the cross-shelf exchanges in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean: Numerical simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 7949–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acha, E.M.; Mianzan, H.W.; Guerrero, R.A.; Favero, M.; Bava, J. Marine fronts at the continental shelves of austral South America: Physical and ecological processes. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 44, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.A.; Ramirez, N.; Pizarro, O.; Piola, A.R. The role of the Magellan Strait on the southwest South Atlantic shelf. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 237, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorioso, P.D. Temperature distribution related to shelf-sea fronts on the Patagonian shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1987, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.D.; Matano, R.P.; Tonini, M.H.; Martos, P.; Combes, V. Dynamical analysis of the oceanic circulation in the Gulf of San Jorge, Argentina. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 203, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, V.; Matano, R.P. The Patagonian shelf circulation: Drivers and variability. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, A.R.; Campos, E.J.D.; Möller, O.O., Jr.; Charo, M.; Martinez, C. Subtropical shelf front off eastern South America. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2000, 105, 6566–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, A.R.; Möller, O.O., Jr.; Guerrero, R.A.; Campos, E.J.D. Variability of the subtropical shelf front off eastern South America: Winter 2003 and summer 2004. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muelbert, J.H.; Acha, M.; Mianzan, H.; Guerrero, R.; Reta, R.; Braga, E.S.; Garcia, V.M.T.; Berasategui, A.; Gomez-Erache, M.; Ramírez, F. Biological, physical and chemical properties at the Subtropical Shelf Front Zone in the SW Atlantic Continental Shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.D.; Matano, R.P. A numerical study of the Magellan Plume. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, C05041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guihou, K.; Piola, A.R.; Palma, E.D.; Chidichimo, M.P. Dynamical connections between large marine ecosystems of austral South America based on numerical simulations. Ocean Sci. 2020, 16, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.; Beighley, E.; Laraque, A.; Lee, H.; Tshimanga, R.; O’Loughlin, F.; Mahé, G.; Dinga, B.; Moukandi, G.; Spencer, R.G. Opportunities for hydrologic research in the Congo Basin. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 378–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denamiel, C.; Budgell, W.P.; Toumi, R. The Congo River plume: Impact of the forcing on the far-field and near-field dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 964–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vic, C.; Berger, H.; Tréguier, A.M.; Couvelard, X. Dynamics of an equatorial river plume: Theory and numerical experiments applied to the Congo plume case. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshimanga, R.M.; Moukandi N’kaya, G.D.; Alsdorf, D. (Eds.) Congo Basin Hydrology, Climate, and Biogeochemistry: A Foundation for the Future; American Geophysical Union, Geophysical Monograph Series; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; Volume 269, 592p. [Google Scholar]
- Sorí, R.; Nieto, R.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. A Lagrangian perspective of the hydrological cycle in the Congo River basin. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2017, 8, 653–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzimi, Y.A.; Hansen, M.C.; Asante, K.O. Estimating daily streamflow in the Congo Basin using satellite-derived data and a semi-distributed hydrological model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, L.; Toumi, R. Assimilation of satellite salinity for modelling the Congo River plume. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laraque, A.; Moukandi N’kaya, G.D.; Orange, D.; Tshimanga, R.; Tshitenge, J.M.; Mahé, G.; Nguimalet, C.R.; Trigg, M.A.; Yepez, S.; Gulemvuga, G. Recent budget of hydroclimatology and hydrosedimentology of the Congo River in Central Africa. Water 2020, 12, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarugula, S.; McPhaden, M.J. Indian Ocean Dipole affects eastern tropical Atlantic salinity through Congo River Basin hydrology. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchuig, S.; Kitambo, B.; Papa, F.; Paris, A.; Fleischmann, A.S.; Gal, L.; Boucharel, J.; Paiva, R.; Oliveira, R.J.; Tshimanga, R.M.; et al. Improved modeling of Congo’s hydrology for floods and droughts analysis and ENSO teleconnections. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, L.V.; Agenbag, J.J.; Buys, M.E.L. Large- and mesoscale features of the Angola-Benguela front. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1987, 5, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, H.U.; Schmidt, M.; Mohrholz, V.; Nausch, G. Hydrographic and current measurements in the area of the Angola–Benguela front. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2000, 30, 2589–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrholz, V.; Schmidt, M.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; John, H.C. Space–time behaviour of the Angola–Benguela Frontal Zone during the Benguela Niño of April 1999. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizy, E.K.; Cook, K.H.; Sun, X. Decadal change of the South Atlantic Ocean Angola-Benguela frontal zone since 1980. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 3251–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, W.R.H.; Hutchings, L. Upwelling in the southern Benguela Current. Prog. Oceanogr. 1980, 9, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, L.; Van der Lingen, C.D.; Shannon, L.J.; Crawford, R.J.M.; Verheye, H.M.S.; Bartholomae, C.H.; Van der Plas, A.K.; Louw, D.; Kreiner, A.; Ostrowski, M.; et al. The Benguela Current: An ecosystem of four components. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 83, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, L.; Armstrong, B.A.; Mitchell-Innes, D.A. The frontal zone in the southern Benguela Current. In Marine Interfaces Eco-Hydrodynamics, Proceedings of the 17th International Liege Colloquium on Ocean Hydrodynamics, Liege, Belgium, 13–17 May 1985; Nihoul, J.C.J., Ed.; Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; Volume 42, pp. 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.A.; Mitchell-Innes, B.A.; Verheye-Dua, F.; Waldron, H.; Hutchings, L. Physical and biological features across an upwelling front in the southern Benguela. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1987, 5, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, I.M.; Cornillon, P.C.; Sherman, K. Fronts in Large Marine Ecosystems. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 81, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncombe Rae, C.M. A demonstration of the hydrographic partition of the Benguela upwelling ecosystem at 26°40′S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 27, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.A.; Mohrholz, V.; Schmidt, M. The circulation dynamics associated with a northern Benguela upwelling filament during October 2010. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 63, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, I.M.; Gordon, A.L. Southern Ocean fronts from the Greenwich meridian to Tasmania. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 3675–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smythe-Wright, D.; Chapman, P.; Duncombe Rae, C.; Shannon, L.V.; Boswell, S.M. Characteristics of the South Atlantic subtropical frontal zone between 15°W and 5°E. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 1998, 45, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, M.F.; Alves, M.L. The Atlantic subtropical front/current systems of Azores and St. Helena. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2007, 37, 2573–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, M.L.; Menezes, V.V. Double-celled subtropical gyre in the South Atlantic Ocean: Means, trends, and interannual changes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C03024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, M. On the Subtropical Front in the South Atlantic Ocean. Master’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009; 82p. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11427/6473 (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Peterson, R.G.; Stramma, L. Upper-level circulation in the South Atlantic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 1991, 26, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS mission: New tool for monitoring key elements of the global water cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, E.; González-Haro, C.; Hoareau, N.; Umbert, M.; González-Gambau, V.; Martínez, J.; Gabarró, C.; Turiel, A. Nine years of SMOS sea surface salinity global maps at the Barcelona Expert Center. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 857–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, I.M.; O’Reilly, J.E. An algorithm for oceanic front detection in chlorophyll and SST satellite imagery. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, I.M. Remote sensing of ocean fronts in marine ecology and fisheries. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, N.C.; Wise, G.L. A theoretical analysis of the properties of median filters. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1981, 29, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.R.; Petersen, G.W. Texture transforms of remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1981, 11, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currant-Everett, D. Explorations in statistics: The log transformation. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2018, 42, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 4th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E.; Eddins, S.L. Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB®, 3rd ed.; Gatesmark Publishing: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.W. The lognormal distribution as a model for bio-optical variability in the sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 13237–13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, W.W.; Casey, N.W. Global and regional evaluation of the SeaWiFS chlorophyll data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; McKinna, L.I.W.; Boss, E.; Ackleson, S.G.; Craig, S.E.; Gregg, W.W.; Lee, Z.P.; Maritorena, S.; Roesler, C.S.; Rousseaux, C.S.; et al. An overview of approaches and challenges for retrieving marine inherent optical properties from ocean color remote sensing. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.F.; Hu, J.Y.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.Z. Summertime sea surface temperature and salinity fronts in the southern Taiwan Strait. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4452–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramma, L.; Peterson, R.G. The South Atlantic Current. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, I.M. Frontal structure of the South Atlantic. In Pelagic Ecosystems of the Southern Ocean; Voronina, N.M., Ed.; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1993; pp. 40–53. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziejczyk, N.; Hernandez, O.; Boutin, J.; Reverdin, G. SMOS salinity in the subtropical North Atlantic salinity maximum: 2. Two-dimensional horizontal thermohaline variability. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 972–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.L.; Giulivi, C.F.; Busecke, J.; Bingham, F.M. Differences among subtropical surface salinity patterns. Oceanography 2015, 28, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.G.; Whitworth, T., III. The Subantarctic and Polar Fronts in relation to deep water masses through the southwestern Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1989, 94, 10817–10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubriot, L.; Zabaleta, B.; Bordet, F.; Sienra, D.; Risso, J.; Achkar, M.; Somma, A. Assessing the origin of a massive cyanobacterial bloom in the Río de la Plata (2019): Towards an early warning system. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, C.; Martínez, A.; de la Escalera, G.M.; Trinchin, R.; Manta, G.; Segura, A.M.; Piccini, C.; Brena, B.; Yannicelli, B.; Fabiano, G.; et al. Rapid freshwater discharge on the coastal ocean as a mean of long distance spreading of an unprecedented toxic cyanobacteria bloom. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, A.R.; Romero, S.I. Space-time variability of the Plata River Plume. Gayana (Concepción) 2004, 68, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta-Almeida, M.; Dalbosco, A.; Franco, D.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M. Dynamics of river plumes in the South Brazilian Bight and South Brazil. Ocean Dyn. 2021, 71, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, P.M.; Figueroa, D.; Müller, M. Freshwater input into the coastal ocean and its relation with the salinity distribution off austral Chile (35–55°S). Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekau, W.; Verheye, H.M. Influence of oceanographic fronts and low oxygen on the distribution of ichthyoplankton in the Benguela and southern Angola currents. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 27, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammelsrød, T.; Bartholomae, C.H.; Boyer, D.C.; Filipe, V.L.L.; O’Toole, M.J. Intrusion of warm surface water along the Angolan-Namibian coast in February–March 1995: The 1995 Benguela Nino. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 19, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bodungen, B.; John, H.C.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Mohrholz, V.; Veitch, J. Hydrographic and biological patterns across the Angola–Benguela Frontal Zone under undisturbed conditions. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubone, N.; Palma, E.D.; Piola, A.R. The surface salinity maximum of the South Atlantic. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 191, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Variable | Period | Sensor/Mission | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allega et al., 2021 [16] | SST | 1985–2019 | AVHRR, MODIS | Patagonian Shelf |
| Artana et al., 2018 [17] | SST, SSH | 2007–2016 | Multisensor; Altimeters | SW Atlantic |
| Barre et al., 2006 [18] | SST, color | 2002–2004 | MODIS, SeaWiFS | Brazil-Malvinas Confluence |
| Belkin & Shen 2024 (this study) | SSS | 2011–2019 | SMOS | South Atlantic (0–60°S) |
| Billany et al., 2010 [19] | SSH | 1993–2007 | Altimeters | Greenwich Meridian |
| Bouali et al., 2017 [20] | SST | 2003–2014 | MODIS | South Atlantic (0–60°S) |
| Burls & Reason 2006 [21] | SST | 2002–2005 | TRMM, AMSR-E | South Atlantic (25–55°S) |
| Castellanos et al., 2019 [22] | SSS | 2011–2015 | SMOS | SW Atlantic; SE Atlantic; 12mos |
| Chao et al., 2015 [23] | SSS | 2011–2013 | Aquarius | Congo River plume |
| Chen et al., 2019 [24] | SST | 2002–2016 | MODIS | SE Brazil; Shelf fronts |
| Da Silveira et al., 2023 [25] | SST SSH | 2002–2020 1993–2020 | Multi-sensor Altimeters | Brazil Current, 22–23°S |
| Dencausse et al., 2011 [26] | SSH | 1992–2007 | Altimeters | SE Atlantic (5°W–35°E) |
| Dong et al., 2006 [27] | SST | 2002–2005 | AMSR-E | Polar Front |
| Franco et al., 2008 [28] | SST | 1985–2002 | AVHRR | Patagonian Shelf; SBF (39–44°S) |
| Franco et al., 2022 [29] | SST SSH CHL | 1993–2019 1993–2019 2002–2020 | Multi-sensor Altimeters MODIS | Patagonian Shelf |
| Freeman & Lovenduski 2016 [30] | SST | 2002–2014 | Microwave radiometers | Polar Front |
| Graham & de Boer 2013 [31] | SST SSH | 1999–2009 1999–2009 | AVHRR Altimeters | Subtropical Front |
| Guerrero et al., 2014 [32] | SSS | 2010–2013 2011–2013 | SMOS Aquarius | SW Atlantic |
| Hopkins et al., 2013 [33] | SST SSS CHL SSH | 2010 | AVHRR, AMSR SMOS MODIS, MERIS Altimeters | Congo River plume |
| Hösen et al., 2016 [34] | SST | 2006–2011 2011–2014 | AMSR-E/MODIS 9 km MODIS 4 km | Benguela Upwelling filaments |
| Houndegnonto et al., 2021 [35] | SSS | 2010–2017 | SMOS | Congo River plume |
| Kim & Orsi 2014 [36] | SSH | 1992–2011 | Altimeters | ACC fronts |
| Legeckis & Gordon 1982 [37] | SST | 1975–1978 | VHRR | Brazil-Malvinas Confluence |
| Lorenzzetti et al., 2009 [38] | SST | 2000–2002 | AVHRR | Brazil Current |
| Luko et al., 2021 [39] | Velocity | 1993–2018 | Altimeters | South Equatorial Current |
| Lutjeharms & Meeuwis 1987 [40] | SST | 1982–1985 | AVHRR | SE Atlantic; Benguela Upwelling |
| Lutjeharms et al., 1993 [41] | SST | 1988 | AVHRR | Subtropical Front |
| Martins & Stammer 2022 [42] | SSS | 2010–2020 | SMOS, Aquarius, SMAP | Congo River plume |
| Meeuwis & Lutjeharms 1990 [43] | SST | 1982–1985 | AVHRR | Angola-Benguela Current |
| Melnichenko et al., 2016 [10] | SSS | 2011–2015 | Aquarius | Global |
| Meeuwis 1991 [44] | SST | 1982–1985 | AVHRR | South Atlantic and South Indian |
| Moore et al., 1997 [45] | SST | 1987–1988 | AVHRR | Polar Front, 90°W–20°W |
| Moore et al., 1999 [46] | SST | 1987–1993 | AVHRR | Polar Front, Circumpolar |
| Olson et al., 1988 [47] | SST | 1981–1987 | AVHRR | Brazil-Malvinas Confluence |
| Piola et al., 2008a [48] | CHL | 1998–2005 | SeaWiFS | Rio de la Plata plume |
| Reul et al., 2014 [2] | SSS | 2010–2012 | SMOS | Congo River plume |
| Rivas 2010 [49] | SST | 1985–2002 | AVHRR | Southwest Atlantic |
| Rivas & Pisoni 2010 [50] | SST | 1985–2002 | AVHRR | Patagonian Shelf |
| Ruiz-Etcheverry & Saraceno 2020 [51] | SSH | 1993–2017 | Altimeters | South Atlantic (36–55°S) |
| Saraceno et al., 2004 [52] | SST | 1987–1995 | AVHRR | Brazil-Malvinas Confluence |
| Saraceno et al., 2005 [53] | SST CHL | 1998–2003 1998–2003 | AVHRR, AMSR-E SeaWiFS | Southwest Atlantic |
| Veitch et al., 2006 [54] | SST | 1982–1999 | AVHRR | Angola-Benguela Front |
| Wang et al., 2021 [55] | SST CHL | 2004–2019 2007–2019 | Multi-sensor MODIS | SW Atlantic |
| Wang et al., 2023 [56] | SST SSH | 2010–2018 2010–2018 | AVHRR Altimeters | SW Atlantic |
| Yu et al., 2015 [9] | SSS | 2012–2013 | Aquarius | Tropical Atlantic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belkin, I.M.; Shen, X.-T. Salinity Fronts in the South Atlantic. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091578
Belkin IM, Shen X-T. Salinity Fronts in the South Atlantic. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(9):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091578
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelkin, Igor M., and Xin-Tang Shen. 2024. "Salinity Fronts in the South Atlantic" Remote Sensing 16, no. 9: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091578
APA StyleBelkin, I. M., & Shen, X.-T. (2024). Salinity Fronts in the South Atlantic. Remote Sensing, 16(9), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091578






