Abstract
Beijing, China’s capital city, has experienced decades of severe land subsidence due to the long-term overexploitation of groundwater. The implementation of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project (SNWDP) and artificial ecological restoration have significantly changed Beijing’s hydro-ecological and geological environment in recent years, leading to a widespread rise in groundwater levels. However, whether the related land subsidence has slowed down or reversed under these measures has not yet been effectively monitored and quantitatively analyzed in terms of time and space. Accordingly, in this study, we proposed using an improved time-series deformation method, which combines persistent scatterers and distributed scatterers, to process Sentinel-1 images from 2015 to 2022 in the Beijing Plain region. We performed a geospatial analysis to gain a better understanding of how the new hydrological conditions changed the pattern of deformation on the Beijing Plain. The results indicated that our combined PS and DS method provided more measurements both in total quantity and spatial density than conventional PSI methods. The land subsidence in the Beijing Plain area has been effectively alleviated from a subsidence region of approximately 1377 km2 in 2015 to only approximately 78 km2 in 2022. Ecological restoration areas in the northeastern part of the Plain have even rebounded over this period, at a maximum of approximately 40 mm in 2022. The overall pattern of ground deformation (subsidence and uplift) is negatively correlated with changes in the groundwater table (decline and rise). Local deformation is controlled by the thickness of the compressible layer and an active fault. The year 2015, when anthropogenic water transfers were eliminated and ecological measures to recharge groundwater were implemented, was the crucial turning point of the change in the deformation trend in the subsidence history of Beijing. Our findings carry significance, not only for China, but also for other areas where large-scale groundwater extractions are causing severe ground subsidence or rebound.
1. Introduction
Land subsidence is one of the most severe geological problems in many megacities worldwide [1,2]. Both natural and anthropogenic processes commonly induce it. Natural subsidence processes include seismicity, volcanic eruption, and sediment compaction [3]. In contrast, human-induced deformation is caused by changes in the extraction of below-ground fluids, mainly groundwater and hydrocarbons, or surface loading by buildings, related infrastructure, reservoirs and other new water bodies, and landfills [4].
Accelerated urbanization in recent decades has led to an increase in subsidence in large cities worldwide. The problem is most urban areas have been overexploited for groundwater. Most megacities with populations of more than 10 million residents, including Tokyo, Shanghai, Mexico City, Cairo, and Jakarta, have experienced land subsidence during the past two decades (Table 1). The damage caused by such subsidence has led governments to implement regulations to reduce groundwater extraction and implement ecologically based recharge measures. In some cases, for example, Delhi and Dhaka, these actions have slowed or even reversed subsidence.

Table 1.
Global megacities experiencing ground subsidence and uplift and the main causes.
Beijing, China’s capital city, has a population of more than 20 million people. The city, which is located on the Beijing Plain, has experienced widespread and severe subsidence for at least 100 years [17,18]. Subsidence in Beijing was first recorded in the 1930s [19] and considerably increased in area and magnitude in the 1960s. The prolonged exploitation of groundwater has been identified as the primary factor contributing to subsidence in the central area of Beijing. Due to the natural water stress (mean annual precipitation less than 500 mm/year) and the growing population, groundwater became the primary source of the water supply in Beijing. Aquifers beneath the Beijing Plain are normally replenished by the inflow from surrounding regions and, to some extent, counter groundwater extraction in the urban area [17]. However, continuing excessive water extraction decreased the volume of water in the aquifers, inducing the expansion and acceleration of land.
Chinese researchers have identified five stages in the evolution of the ground subsidence problem on the Beijing Plain: seed, formation, growth, expansion, and rapid development [20]. The seed stage occurred from around 1935 to 1955 when initial subsidence (of less than 3 mm per year) happened only from Xidan to Dongdan (the inner side of the old imperial Beijing district). The formation stage, from 1955 to 1973, was a period when groundwater extraction was relatively small in scale, and subsidence (several millimeters per year) was limited to the area where the water was extracted (from Balizhuang to Jiuxianqiao and Laiguangying). The growth stage, which started in 1973 and ended in 1983, was a time when groundwater extraction increased rapidly (approximately 2.5 to 2.8 billion cubic meters per year). Ground subsidence increased from 18 to 30 mm/year over a large area in the Changping, Daxing, and Shunyi districts. The expansion stage of subsidence, from 1983 to 1999, was marked by a huge growth in Beijing’s population, urban development, and industrial activity, and resulted in corresponding large increases in water demand. Both the volume of extracted groundwater (approximately 2.6 billion cubic meters per year) and the subsidence rate (approximately 20 mm/year) were relatively stable over this period. Five land subsidence areas became evident in this stage. The rapid development subsidence stage spanned the period from 1999 to 2015 and corresponded to the longest drought in Beijing’s history. Aquifers were severely depleted, with annual withdrawals of approximately 2.36 billion m3, and subsidence rapidly increased. During this period, seven subsidence bowls, with subsidence rates of more than 50 mm/year, formed in the metropolitan area, with a maximum subsidence rate of more than 150 mm/year [21,22].
The year 2015 was the turning point. To protect groundwater supplies and control land subsidence, the government initiated the South-to-North Water Diversion Project (SNWDP) in Beijing, Hebei, Tianjin, and Henan (the northern part of China). The SNWDP Central Route (SNWDP-CR) began to move surface water into Beijing, and the government limited the extraction of groundwater. The water diversion project met approximately 70% of the domestic use in Beijing, and land subsidence moved beyond the rapid development stage [23]. The local government also implemented many related measures, including water conservation and water replenishment projects in river channels. These measures have effectively improved the subsidence problem in Beijing. Groundwater exploitation declined from 2.0 billion m3 in 2014 to 1.35 billion m3 in 2020. The average depth of the water table beneath Beijing has increased for six consecutive years since 2015 and reached approximately 16.39 m at the end of 2022, which is 9.71 m higher than in 2015 [24].
The recovery of groundwater levels over a wide area is certain to change the hydrogeological environment. According to the Terzaghi effective stress principle, an increase in pore water pressure will increase the recovery of elastic, plastic, viscoelastic, and viscoplastic soil components in both aquifers and aquitards. As a result, ground subsidence is likely to decrease and perhaps even reverse [25].
Counterintuitively, however, this recovery might be accompanied by new unexpected problems. Decades of continuous groundwater overexploitation and ground subsidence that are reversed in a short period of time might induce new deformation of the ground, and a rise in the water table might induce the flow of groundwater into deep below-ground infrastructure, for example, subway lines [26]. Thus, an understanding of the dynamic state of the ground in Beijing during the groundwater recovery period is an important topic in China today. In this context, accurate and comprehensive surface deformation monitoring is essential for documenting what is happening in the subsurface and for continued appropriate water management.
Advanced Satellite Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) technology provides accurate surface deformation information with millimeter accuracy on a two-week cycle. It offers complete spatial coverage of an area of interest, in contrast to the much more limited coverage of traditional ground discrete point measurement techniques (leveling, borehole extensometer, and GNSS). Multi-temporal InSAR algorithms and applications have been rapidly developed and applied with the global coverage provided by radar satellites such as Sentinel-1.
Many previous InSAR studies of land subsidence in Beijing have been completed (Table 2). Using conventional methods, such as Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) and Small Baseline Subset (SBAS), these studies have documented the main evolution and characteristics of the evolving land subsidence problem in Beijing. However, conventional PSI and SBAS methods mainly extract persistent scatterers with high coherence. They cannot precisely detect low-coherence pixels in vegetation and bare soil regions, resulting in a reduced density of relevant data [27].

Table 2.
Previous InSAR studies of land subsidence in Beijing.
In this study, we thus applied a new technique to document the spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and development patterns of Beijing’s ground deformation under the remedial 2015 water policies instituted by the Chinese and municipal governments. Our objectives in this paper were to (1) improve the existing MT-InSAR methods by combining both PS and DS points using a two-layer network and thus provide a denser coverage of deformation measurements in Beijing; (2) clarify the temporal and spatial evolution of ground deformation in Beijing under the new water situation; (3) quantitatively evaluate the relationship between land deformation and its main cause (groundwater extraction) using geospatial statistics; and (4) corroborate the hypothesis that the marked reduction in groundwater extraction in 2015 caused a decrease and local reversal of subsidence on the Beijing Plain. Following this introduction, we describe the study area and our datasets in Section 2. The improved InSAR method and data processing are described in Section 3. The InSAR-derived deformation results, including subsidence and uplift patterns, are shown and discussed in Section 4. Finally, we provide conclusions and recommendations for further work in Section 5.
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Geography and Hydrogeology of the Study Area
Beijing (115°25′–117°35′E, 39°28′–41°05′N) is located in the extreme northern part of the North China Plain (Figure 1). It has a typical continental monsoon climate, with annual average precipitation, temperature, and evapotranspiration of 580 mm, 10–12 °C, and 1800 mm, respectively. The city has an average elevation of 43.5 m above sea level and is characterized by higher elevations in the northwest and lower elevations in the southeast. The northern and western regions of the metropolitan area are surrounded by Yanshan, Jundu, and Xi Mountains. Our study mainly focused on the Beijing Plain (BJP) in the south, which has an area of approximately 6300 km2 and consists of the alluvial deposits of Yongding, Chaobai, Daqing, Beiyun, and Jiyun rivers. The study area comprises all of Chaoyang, Haidian, Core Area, Tongzhou, Daxing districts, and parts of the Fengtai, Pinggu, Miyun, Huairou, Changping, Mentougou, and Fangshan districts.
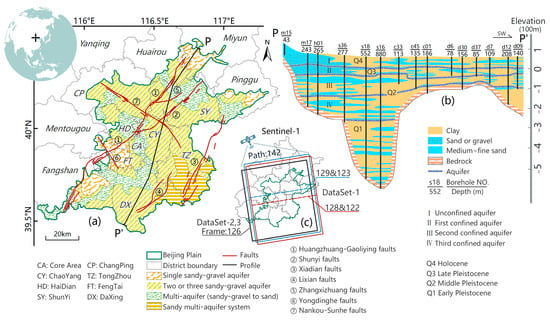
Figure 1.
Overview of the study area. (a) Geographical location and hydrogeological setting of the study area. The black cross is the location of Beijing in the world. (b) one typical hydrogeological profile P-P′ (location is shown in (a)). (c) SAR datasets were used in this study.
There are seven major active high-angle normal faults and four main aquifers in the BJP (Figure 1). The faults, which are key in controlling the geological development of rift basins and depressions in the BJP, are the ① Huangzhuang-Gaoliying fault, ② Shunyi fault, ③ Xiadian fault, ④ Lixian fault, ⑤ Zhangxizhuang fault, ⑥ Yongdinghe fault, and ⑦ Nankou-Sunhe fault. The first five strike in a NW-SE direction, whereas the last two strike NE-SW. Quaternary alluvial sediments underlie the BJP, but differ considerably in thickness and lithology, from gravel to clay. Aquifers range from a single sandy gravel layer to multi-layer interbedded sand and clay. Researchers have identified four main aquifer groups (an unconfined aquifer and three underlying confined aquifer) based on groundwater depth, drainage, genesis, and extraction level [20] (Figure 1b).
2.2. Background of SNWDP and Beijing’s New Water Management Strategy
The South-to-North Water Transfer Project is one of the largest and most complex water diversion projects worldwide (Figure 2). It addresses the issue of the uneven water distribution in the northern and southern parts of China. The project was first proposed in the 1950s and gained momentum in the early 2000s when the Chinese government recognized the urgent need to alleviate water scarcity in the north. The SNWTP consists of three main routes: Eastern, Central, and Western. The terminus of the Eastern route is Tianjin, and the Western route has not yet been constructed. Here, we focus on the Central route of SNWTP. The Central Route (CR), which is approximately 1267 km in length and diverts water from the Danjiangkou Reservoir on the Han River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, to the Yellow and Huai River Basin. It supplies water to Henan, Hubei, Tianjin, and Beijing.
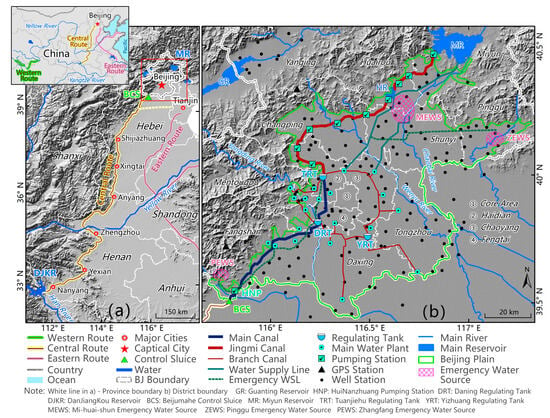
Figure 2.
The China South-to-North Water Diversion Project. (a) South-to-North Water Diversion Project Central Route from Danjiangkou Reservoir (DJKR) to Beijing. (b) Beijing South-to-North Water Diversion Project area with supporting infrastructure.
Water sourced from the south began to enter Beijing on 27 December 2014. From that date up to 27 December 2022, Beijing has received 8.408 billion m3 of water from SNWDP (approximately 1.0 billion m3/yr). In order to make the precious southern water better serve the people of the capital, Beijing has constructed many regulating tanks, water transmission pipes, new and renovated water plants, and other infrastructure to deliver the southern water. The new water is used mainly for three purposes after entering Beijing: domestic water use, storage, and aquifer recharge. To meet the domestic water needs of Beijing’s citizens, the city has constructed a system of water supply ring pipelines that connect the primary water plants in the urban area. Water is also pumped into and stored in reservoirs surrounding the city (Miyun, Huairou, and Daning reservoirs). Third, groundwater should be recharged in the emergency water source. Implementing ecological water replenishment in rivers is achieved by coordinating multiple water sources, which is mainly targeted at the emergency water sources region. At the same time, implementing the new water use policies in Beijing, such as gradually shutting down self-owned wells and prohibiting groundwater extraction, has extensively conserved groundwater in the Beijing Plain area.
2.3. Datasets
2.3.1. SAR Images
Ground movements over BJP have been measured using multi-frame (Path: 142; Frame: 122, 126, 128) SAR Satellite Sentinel-1 image acquisitions from July 2015 to December 2022 with a biweekly revisit period. The C-band Sentinel-1 satellites of the European Space Agency (ESA) acquire Terrain Observation by Progressive Scan (TOPS) data in Interferometric Wide Swath (IWS) mode. We downloaded the Sentinel-1 images in Single Look Complex (SLC) format from the Alaska Satellite Facility Vertex online database system (https://search.asf.alaska.edu/#/, accessed on 22 April 2024). The detailed parameters of Sentinel-1 SAR imagery are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
The parameters of SAR data.
2.3.2. Auxiliary Datasets
The external DEM data used in InSAR data processing are 30 m resolution SRTM data provided by NASA from http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/srtmdata/, accessed on 22 April 2024. Precise Orbit Ephemerides (POD) data, which we used for SAR image registration and the removal of the orbit phase in InSAR time image analysis, were provided by ESA from https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/, accessed on 22 April 2024. The China Earthquake Networks Center provided continuously monitored Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data in the study area. In situ groundwater level (GWL) data in the confined aquifer system were recorded yearly in 52 monitoring wells around BJP from 2015 to 2022 by Beijing Water Authority (BWA) https://swj.beijing.gov.cn/, accessed on 22 April 2024. High-resolution optical time-series satellite images over groundwater ecological recharge regions were downloaded from Google Earth.
3. Methods and Data Processing
3.1. SAR Data Preprocessing and Interferogram Generation
Accurate co-registration of SAR image pairs is a key factor influencing the coherence of interferograms. For Sentinel-1 TOPS data, which require extremely precise co-registration (approximately one thousandth of a pixel) in the azimuth direction [40], we first employed deburst and merging using GAMMA software 2022 to make a wide-area SLC product. We then used offset_pwr and the spectral diversity method to refine the interferometric phase of the burst overlap region.
Due to the length of the period of deformation measurement (2015 to 2022), a single reference image method must be used with caution. We used multi-interval acquisition interferometry and multi-index optimization to select the main reference image. First, all the SAR acquisitions were divided into three datasets for the periods 2015–2017, 2018–2020, and 2021–2022. Interference processing and time-series analysis were performed independently for each dataset. Secondly, we applied the joint correlation index (JCI) [21] to select the optimized reference image in each dataset.
where is the JCI value when image is selected as the reference image. , , and represent the perpendicular baseline , the temporal baseline and the Doppler Centroid Difference (DCD) , respectively, between the images k and m. Then, we selected the maximum JCI image as the reference image in each dataset (Figure 3).
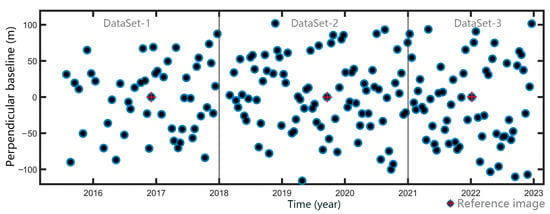
Figure 3.
Temporal and perpendicular baselines of interferograms. The blue points are SAR images, and the red cross points are the reference images in each dataset. Every image is paired with the reference image in each dataset to prepare interferograms.
3.2. Data Processing Flowchart of Joint Detection of PS and DS
We used the open-source software Generic Mapping Tools Synthetic Aperture Radar (GMTSAR) 6.2 [41] to perform the time-series InSAR analyses (Figure 4). The SRTM DEM was employed to remove the terrain phase contribution. After removing the terrain phase contribution, the sum of the interferometric phase can be expressed as follows:
where is the ground deformation in the satellite line of sight (LOS) direction, is the atmosphere delay, is the residual phase from the orbit inaccuracies, is the look angle error, and is the noise term that might result, for example from thermal noise and co-registration errors. In this study, we used spatiotemporal filtering to remove the atmosphere delay phase.
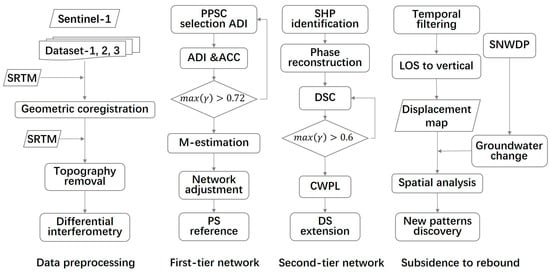
Figure 4.
Flowchart of SAR data processing and analysis used in this study. ADI is amplitude dispersion index, ACC is average coherence coefficient, and CWPL is coherence-weighted phase-linking.
We selected the most reliable primary PS candidates (PPSCs) based on the amplitude dispersion index (ADI) (Equation (3)) and average coherence coefficient (ACC):
where and are the standard deviations and mean of the series amplitude values, respectively.
where is the number of interferometric pairs; is the unwrapping interferometric phase; are the deformation, atmospheric, and orbit phases that are correlated in space; and is the estimated topographic phase. The M-estimator was used to recalculate the relative estimate using the unwrapped phase [42]. For C-band Sentinel-1 interferometric measurements, we set the threshold at 0.72 and ADI at 0.56 as the simultaneous conditions to choose the most reliable PS points as the reference.
Moreover, in this study, we also consider the DS pixels by the Anderson–Darling test to identify and cluster statistically homogeneous pixels (SHPs) as the regional extension of the reference PS pixels [43]. A complex coherence matrix (CCM) was created for neighboring pixels using normalized complex scattering vectors Z(x′) and the weight d(x, x′) of a potential DS candidate:
where is the estimated weight of CCM, SHP families are , is the pixel-wise production operation, and is the complex value of the interferogram of each two images. A more effective coherence-weighted phase-linking (CWPL) method was used to obtain the phase optimization [44]. In this study, we used a value of 0.6 for temporal coherence in DS selection.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. InSAR-Derived Deformation Results and Validation
We processed the datasets in three periods (2015–2017, 2018–2020, and 2021–2022) using conventional PSI and the improved-PS-DS method described above. The LOS direction deformation was transformed to the vertical direction using the 3D solution formula [45]. As all the InSAR-derived deformation measurements are relative displacement changes, we calculated the deformation relative to a reference point in Tiananmen Square, which is assumed to be the most stable and central location in Beijing. The final vertical mean deformation rate results for three time periods calculated using the improved-PS-DS method are presented in Figure 5.
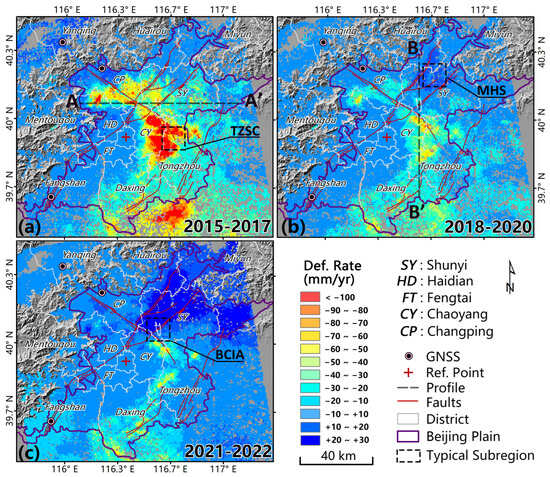
Figure 5.
Mean vertical deformation rates for three periods ((a) 2015–2017, (b) 2018–2020, and (c) 2021–2022). The red cross is the reference point; the rectangles are typical sub-regions used to compare different InSAR methods; black broken lines are the typical profiles (AA′ and BB′) for further time-series deformation analysis (Section 4.3); the background image is the DEM with a hill shade effect.
All three datasets measured by the improved PS and DS method, as summarized in Figure 5, covered nearly the entire Beijing Plain. Deformation rates ranged from −156 to +13 mm/yr, −77 to +18 mm/yr, and −85 to +39 mm/yr over the periods 2015–2017, 2018–2020, and 2021–2022, respectively. To better compare the deformation details, we normalized the color bar of these three deformation rate fields into the same range from −100 to 30 mm/yr, which was divided into 12 intervals with 12 different colors (Figure 5).
The InSAR-derived results indicate that, overall, the land subsidence pattern in the Beijing Plain changed markedly from 2015 to 2022. First, subsidence diminished abruptly, both in time and space, after 2015. Second, the northeast region rose after 2015. Third, the spatial heterogeneity of surface movements is evident across the whole region. The central district (the reference point location) and west side of BJP remained stable (−10 to 10 mm/yr) from 2015 to 2022. The areas with the highest rates of subsidence (>100 mm/yr from 2015 to 2017; red color region in Figure 5a) experienced a marked change in 2018. The subsidence rates in this area decreased to <80 mm/yr, and the rebound phenomenon happened in the Miyun–Huairou–Shunyi region for the first time on record of BJP deformation (Figure 5b). By 2021, this region almost ceased to subside, and uplift at a rate of more than 30 mm/yr happened in the northern part of BJP from 2021 to 2022 (Figure 5c). Details and analyses of two typical profiles, AA′ in an east–west direction, BB′ in a north–south direction, and three typical sub-regions (TZSC, MHS, and BCIA) are discussed in the following sections.
Both the number and density of deformation measurements derived using the improved PS and DS InSAR method exceeded by more than ten times those generated by the conventional PSI method (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparison of conventional PSI and improved PS and DS methods in BJP region.
The InSAR-derived deformation results were evaluated by in situ continuous Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) station measurements (Figure 6). The GNSS stations are located northwest (BJSH and BJYQ) and southwest (BJFS) of Beijing (Figure 5). A comparison of the InSAR and GNSS results (Figure 6a) indicates that the vertical land level changes in both cases for both methods are generally less than 15 mm. Additionally, the seasonal variations in both datasets are consistent. Displacement values derived by InSAR and GNSS cluster near a linear 1:1 line (Figure 6b), which indicates the high level of consistency of the two techniques. Therefore, the ground GNSS measurement data effectively validated the accuracy of the improved methods in obtaining surface deformation, demonstrating a high level of precision.
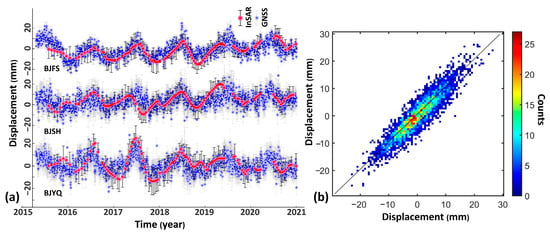
Figure 6.
Validation of InSAR-derived results with ground GNSS measurements. (a) Time series of GNSS stations BJFS, BJSH, and BJYQ (locations shown in Figure 5) and InSAR-derived displacement, with 1-sigma confidence intervals (black vertical bars). (b) Cumulative displacement comparisons between InSAR and the three GNSS stations. The different colors show the count density in different displacement ranges.
4.2. Comparison between Improved PS-DS to Conventional PSI Methods
To gain a better understanding of the improvement provided by our improved PS-DS method, we selected three typical sub-regions for further analysis (Figure 5 and Figure 7): the boundary of Tongzhou subsidence bowl, the Mi-Huai-Shun recharge region, and Beijing Capital International Airport. Comparisons of the PS-DS InSAR results with those obtained using the conventional PSI method show marked differences. The spatial density of deformation pixels is much higher using the PS-DS method, and more details of uneven deformation are evident near the boundaries of subsidence or uplift regions (Figure 7(a2,b2)). In particular, the differences in deformation along the north and south sides of the Tongzhou fault in the Beijing Capital International Airport area, which is one of the most critical infrastructure elements in Beijing [46], are evident in Figure 7(c2), but not in Figure 7(c1). The number of data pixels yielded by the improved PS-DS method was 3 to 7 times that provided by the traditional PSI method.
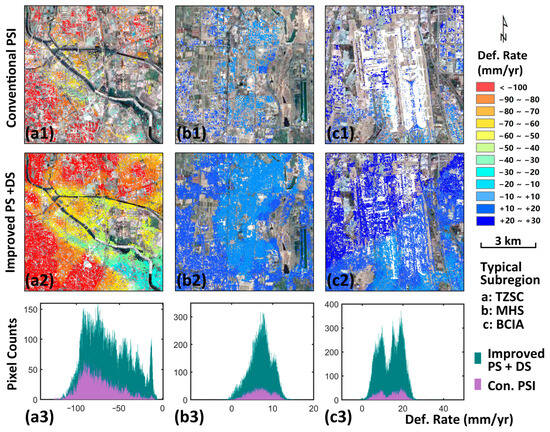
Figure 7.
Statistical and spatial distributions of pixels in the typical sub-region a, b, and c (Figure 5) by conventional PSI and improved PS and DS methods. The conventional PSI deformation results at the boundary of Tongzhou subsidence bowl (TZSB) (a1), Mi-Huai-Shun recharge region (MHS) (b1), and Capital International Airport (BCIA) (c1); the improved PS and DS deformation results at the boundary of TZSB (a2), MHS (b2), and BCIA (c2). Pixel counts difference between conventional PSI and improved methods results in TZSC (a3), MHS (b3), and BCIA (c3).
4.3. Annual Deformation Trends in the Beijing Plain
The inter-annual changes in deformation demonstrate a periodicity, and the annual average deformation results illustrate the spatiotemporal evolution pattern of surface deformation in the Beijing Plain Area in the years following the inception of the SNWDP. Through spatial analysis of deformation results over three time periods, we obtained the deformation variables that control inter-annual changes (Figure 8 and Figure 9).
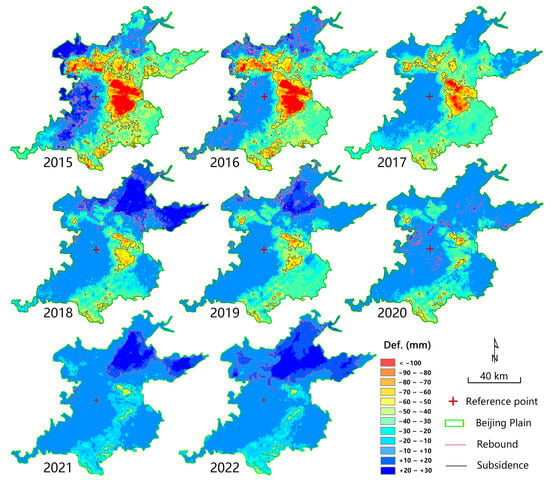
Figure 8.
Annual deformation changes in the study area from 2015 to 2022.
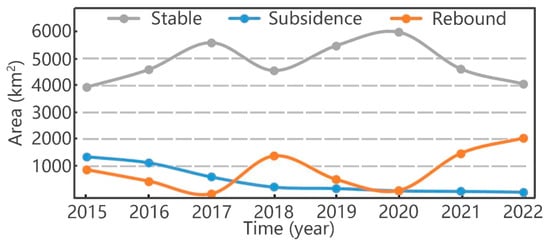
Figure 9.
Changes in the areal extent of stable, subsiding, and uplifting areas on the Beijing Plain.
We assumed that an annual deformation rate of −30 mm sets the boundaries of subsidence areas [21]. There are no existing standards for defining uplift phenomena, but considering that uplift was observed on a large scale in Beijing for the first time, we defined regions with annual deformation greater than +10 mm as uplift areas [44]. We calculated statistics for subsidence and uplift for different years based on these assumptions to document the patterns of deformation from 2015 to 2022. In summary, subsidence in the Beijing Plain area gradually diminished over time, the variability in uplift increased, and the size of stable regions initially grew and then decreased.
Considering subsidence, we found that the most severe subsidence of approximately 150 mm occurred around Chaoyang and Tongzhou in 2015, but gradually decreased to 50 mm in 2022. The total area affected by subsidence decreased from 1377 km2 in 2015 (22.1% of the entire plain area) to 78 km2 in 2022 (1.3% of the plain area). Thus, both the magnitude and areal extent of subsidence have been effectively controlled.
In contrast, uplift spatially shifted from the western foothill regions to the upstream area of Chaobai River in the northeastern BJP by 2022. In 2015, water from the SNWDP mainly accumulated in Beijing’s Tuancheng Lake, which experienced uplift. In 2016, sporadic rebound was observed only in the northwest and northern foothill regions. In 2017 and 2020, there was almost no rebound in the plain area; large areas of subsidence transformed into stable areas. In 2018, 2019, 2021, and 2022, the northeast part of the plain was generally rising, although at different rates and magnitudes.
In the recharge area in the upper and middle reaches of the Chaobai River, the maximum annual uplift rate reached approximately 30 mm per year. The data indicate that the current centralized water supply and river recharge measures, water supply spatial allocation, and replacement of self-contained wells after the southern water was transferred into Beijing by the SNWDP are conducive to groundwater level recovery and surface rebound. Overall, the Beijing plain area has transitioned from being dominated by land subsidence to surface uplift.
We selected two typical cross-sections to further depict the spatiotemporal patterns of vertical deformation: an east–west profile (AA′, Figure 5a) and a north–south profile (BB′, Figure 5b). The two profiles intersect at a significant infrastructure element (BCIA, also the location of the Shunyi fault).
The time-series cumulative subsidence curves reveal that there are four distinct zones along the east–west profile where the deformation is concentrated (located 10 km, 30 km, 42 km, and 65 km from point A in Figure 10a). The zones at 30 km and 42 km are within or near active faults, indicating a significant tectonic control over ground deformation related to changes in the water table. The subsidence data from point A to 30 km show mitigation of the amount of subsidence after 2018. Uplift occurs east of the Huangzhuang–Gaoliying faults (30 km), with most areas returning to the deformation level of 2015. The section of the profile 75 km from point A has experienced a cumulative uplift exceeding approximately 40 mm since 2015.
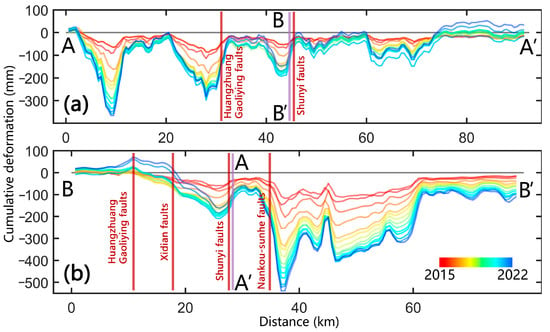
Figure 10.
Time-series deformation changes along typical profiles AA′ and BB′ from 2015 to 2022. (a) Profile AA′ and (b) Profile BB′. (Locations of typical AA′ and BB′ are shown in Figure 5a,b, respectively).
There are two marked zones of deformation concentration along the north–south profile BB′ (Figure 10b), one located north of the Shunyi fault and the other south of the Nankou–Sunhe fault. Presumably, these structures have played a significant role in groundwater-induced ground surface deformation. North of the Nankou–Sunhe fault, there is evidence of an uplift totaling approximately 65 mm. South of this fault, the subsidence rate significantly slowed in 2017.
4.4. Different Time-Series Patterns in Typical Regions
The cumulative deformation variable over time is a crucial indicator that reveals the unique spatiotemporal evolution pattern of the entire Beijing Plain after the operation of the SNWDP. By comprehensively superimposing the deformation results from three time periods, we obtained the cumulative deformation results for the plain area from 2015 to 2022 (Figure 11). We selected multiple typical locations for temporal deformation analysis.
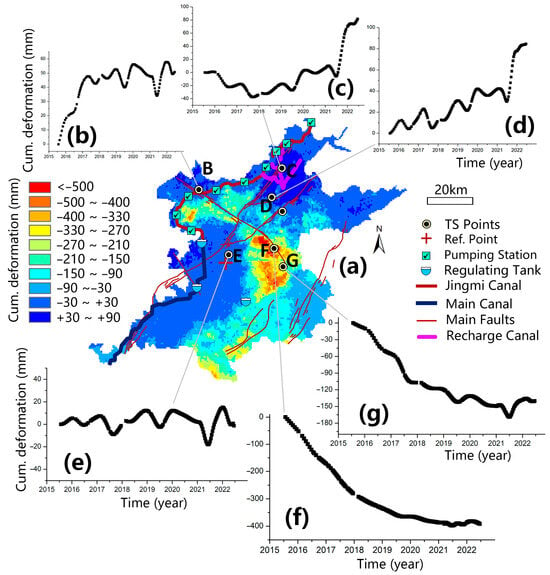
Figure 11.
Typical examples of long time-series deformation patterns in the Beijing Plain. (a) Mean deformation in the BJP from 2015 to 2022. (b–g) Time-series deformation from typical points B to G, respectively.
In general, surface deformation on the Beijing Plain follows three major patterns over the eight-year period: (1) coexistence of subsidence and uplift with noticeable differences in the two; (2) a gradual reduction of land subsidence rates, with subsidence gradually ceasing; and (3) uplift dominating, mainly in the northeast recharge area, with a significant increase in rates and amplitude.
Cumulative subsidence of the Beijing Plain is manifested in three subsidence regions: northwest, central-east, and central-south. However, this subsidence does not reflect the specific temporal evolution process. In reality, the most severely subsided area, the center of the subsidence zone at the point indicated in Figure 11g, has experienced almost no subsidence since 2020. The subsidence rate at the point indicated in Figure 11f has decreased yearly from 2015 to 2020. In summary, the years from 2015 to 2020 mark a period of minor subsidence in Beijing.
There has been a notable uplift in the vicinity of the SNWDP water conveyance channel on the Beijing Plain. Tuan Cheng Lake serves as the first storage site for the diverted water, and there has been significant uplift in its vicinity. A portion of the water stored in Tuan Cheng Lake is used for residents in six districts, but most of the water is transported to Mayan Reservoir via the Jigme Diversion Canal using a pumping system. Uplift has occurred in some mountainous areas along this route, with the point indicated in Figure 11b experiencing a rapid rebound from 2015 to 2017. The central core area of the Beijing Plain shows general stability, although there are minor seasonal fluctuations (Figure 11e).
There is a significant uplift phenomenon in the northeast ecological replenishment area, which serves as an emergency water source for Miyun and Huairou. Excessive groundwater extraction occurred for several consecutive years, leading to a continuous decline in groundwater levels before 2015.
Groundwater levels in most areas have risen after 2015 with the implementation of effective measures, including water replenishment and the closure of private wells. The deformation turning point at the point indicated in Figure 11c occurred in 2018. This area experienced slow fluctuating subsidence (approximately 15 mm/yr) from 2015 to 2018, but then entered a fluctuating uplift period (uplift rate of approximately 13 mm/yr) in 2018, with an increase in uplift from 2021 (approximately 40 mm/yr during 2021–2022). Typical points experienced a fluctuating slow uplift from 2015 to 2021 (at a rate of approximately 7 mm/yr), followed by a sudden increase in uplift in the second half of 2021 (at a rebound rate of approximately 60 mm/yr) (Figure 11d).
4.5. The Relationship between Surface Deformation and Groundwater Change
The most significant cause of land subsidence in Beijing is long-term excessive groundwater extraction, as documented in several previous studies [21,47]. As mentioned previously, the lowering of the water table in sediment results in a reduction of effective stress between soil particles, leading to the consolidation and other changes in the structure of the sediment. These changes cause the ground surface to subside.
After 2015, with the reduction in groundwater extraction accompanied by a new supply of surface water from the south and coupled with several years of increased rainfall, the water table in the Beijing Plain area has risen. In this new hydrological environment, there remain questions about future ground surface subsidence and uplift. There is still insufficient analysis and discussion as to whether areas with rising groundwater levels will experience a slowdown in ground subsidence or, alternatively, uplift. Additionally, the extent to which the general rise in the water table contributes to the mitigation of ground deformation has yet to be effectively analyzed or discussed.
Therefore, this section of the paper considers the spatial relationship between changes in groundwater levels and surface deformation by compiling data over the entire area of the Beijing Plain. First, we use our improved InSAR method to obtain a continuous surface deformation field over the entire plain. Second, contoured groundwater level data from all stations on the plain were contoured based on Kriging spatial interpolation. Finally, we calculated and examined the correlation between groundwater level changes and deformation variables at different locations through raster resampling. Scatter plots of groundwater levels and deformation variables were distributed in four quadrants: Q1 (rising water level—surface uplift), Q2 (rising water level—ground subsidence), Q3 (falling water level—ground subsidence), and Q4 (falling water level—surface uplift). The spatial distribution of these four characteristic points is mapped in Figure 12c.
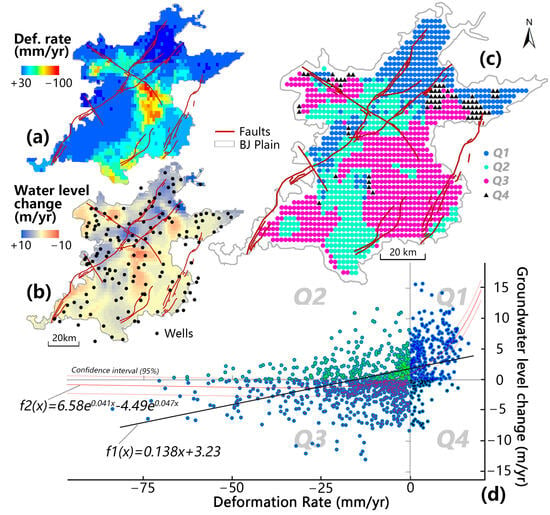
Figure 12.
Spatial relationship between surface deformation and changes in groundwater levels on the Beijing Plain. (a) Deformation rate map from 2015 to 2022. (b) Rate of groundwater level change from 2015 to 2022. (c) Spatial distribution of four (Q1 to Q4) patterns between groundwater level changes and deformation rates. (d) Plot and best fits between groundwater level changes and deformation rate.
The results indicated a specific linear correlation (R2 = 0.56) between surface deformation and changes in groundwater levels as a whole, although numerous data points did not conform to this pattern. Regions where the water level is rising and the surface is rising are mainly located in the western foothills and the northeast groundwater recharge area. The apparent rise in water levels and rise in the land surface along the Huangzhuang–Gaoliying fault is an exciting discovery warranting further study. In the southeastern part of the plain, the water table is still dropping, and subsidence is continuing, but areas such as Chaoyang and Tongzhou are experiencing rising groundwater levels and ongoing subsidence.
Instances of a fall in groundwater levels accompanied by uplift are relatively rare but occur sporadically in the northeast foothill areas. Overall, the statistical results demonstrated a positive correlation between groundwater levels and ground deformation, indicating that subsidence occurs with a lowering water table, while rebound occurs with a rising water table.
An area that clearly demonstrates an uplift in the Beijing Plain is the groundwater replenishment area in the upper reaches of the Chaobai River. To better understand the impact of the replenishment on ground deformation, we selected a representative point (Gaoliying station, as shown in Figure 11d) at the groundwater replenishment area for a long-term analysis of water level changes and deformation from 2005 to 2022 (Figure 13).
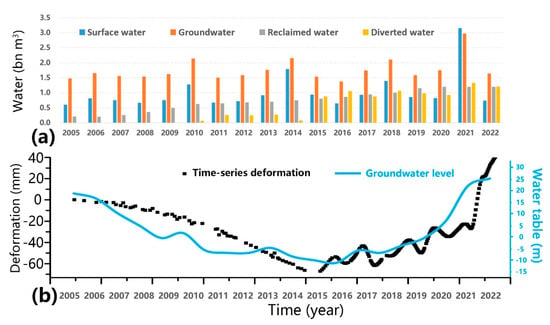
Figure 13.
Groundwater level change and surface deformation turning point in the Mihuaishun recharge area from 2005 to 2022. (a) Water resource change from 2005 to 2022 in Beijing. (b) Time-series deformation and groundwater level change from 2005 to 2022 at typical point in recharge area. Time-series deformation from 2005 to 2014 derived from ASAR and RadarSAT-2 acquisitions using the PSI method [21].
This analysis was complemented by a comparative study of the changes in the quantity of various water sources in the Beijing region over this period. The main conclusions are as follows: In 2015, there was a turning point in surface deformation in response to emergency water recharge at Mihuaishun. Before 2015, Beijing experienced a decade-long drought and low water levels, with groundwater levels continuously declining. There were only slight increases in the water table in 2009 and 2013. Over this period, the ground continuously subsided. After 2015, with the increased transfer of surface and recycled water, groundwater levels and the land surface in the region markedly rose. In 2019, an increase in surface water recharge to 31 billion m3, which was nearly three times the amount in previous years, rapidly increased the groundwater levels. The trend of surface rebound closely matched the trend of rising water levels, with a delay of approximately three months.
5. Conclusions
In the context of prolonged and severe land subsidence in the Beijing Plain area, amidst the backdrop of the SNWDP and artificial ecological recharge, there has been a certain degree of groundwater level rebound. The new hydrogeological environment is bound to have a series of impacts on Beijing’s land subsidence. This study utilized satellite radar imagery and, for the first time, applied an improved method combining PS and DS to monitor ground surface deformation in the Beijing Plain area. This approach provided a more detailed and better understanding of the ground surface deformation process. By integrating GIS spatial-temporal analysis and groundwater changes, the study further documented the spatiotemporal evolution and the main influencing factors of land subsidence and rebound phenomena under the new hydrological conditions. The following paragraphs outline the main findings of this study.
Compared to the traditional PSI deformation calculation method, the approach proposed in this paper considers both PS and DS pixels, thus effectively increasing the number and density of deformation points in the Beijing Plain area and allowing more precise monitoring of surface deformation. It significantly enhances the extraction of detailed information from satellite radar imagery and provides essential technical support for monitoring surface deformation processes in Beijing and its surroundings.
In the context of the SNWDP and artificial ecological recharge, satellite remote sensing has captured, for the first time, a significant reversal of widespread subsidence disappearance and surface rebound of the Beijing Plain. The rise in the water table beneath the plain has been accompanied by a rapid decline in the rate of subsidence, followed in some areas by a rebound-driven rise in the land surface. The spatial-temporal evolution patterns of the overall subsidence trend slowing down and fluctuation-induced rebound being captured are of great significance for understanding the evolution and management of ground deformation phenomena, especially the new ground rebound process.
Our study employed geographic spatial statistical methods to comprehensively summarize the relationship between changes in groundwater levels and surface deformation. With the rise in groundwater levels across the Beijing Plain, we found a specific linear correlation between the overall spatial changes in surface deformation and changes in groundwater levels. Additionally, surface deformation in some areas was influenced by major active faults.
The reversal reason for the long-term severe land subsidence trend is the change in water resource structure in the Beijing Plain area. By combining historical subsidence time-series deformation records with post-SNWDP deformation monitoring results, we found a significant deformation reversal process in the Mi-Huai-Shun region of the Beijing Plain in 2015. The corresponding significant changes in water resource structure involved inter-basin water transfer and the fluctuating growth of surface water resources. In summary, increased rainfall and human interventions, such as the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, have allowed groundwater recharge in the Beijing Plain area since 2015. This further triggered a transition in the trend of surface deformation from subsidence to uplift.
Author Contributions
C.Z. performed experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the original draft. Q.T. provided crucial guidance and support through the research. Y.Z., T.A.W., H.L. and J.J.C. provided essential suggestions and language improvements. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a project funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2022M723124), grants from the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System, and the Key Laboratory of Detection and Application of Space Effect in South-west Sichuan at Leshan Normal University, Education Department of Sichuan Province (No. ZDXM202301003).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The Sentinel-1 images are copyrighted by the European Space Agency (ESA) and were downloaded from the Alaska Satellite Facility, Distributed Active Archive Center. The GNSS data were provided by the China Earthquake Networks Center, National Earthquake Data Center. NASA provided the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) DEM. The Beijing Water Authority provided groundwater data. We thank these institutions for their support. We also thank the anonymous reviewers and journal editors for their help and valuable suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Herrera-García, G.; Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; López-Vinielles, J.; Rossi, M.; Mateos, R.M.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Lambert, J.; Teatini, P.; et al. Mapping the global threat of land subsidence. Science 2021, 371, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashrafi, S. Land subsidence: A global challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Jones, D.R.; Ingebritsen, S.E. Land Subsidence in the United States; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999; Volume 1182.
- Shirzaei, M.; Freymueller, J.; Törnqvist, T.E.; Galloway, D.L.; Dura, T.; Minderhoud, P.S.J. Measuring, modelling and projecting coastal land subsidence. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 2, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, C.; Haga, M.; Nishino, J. Land subsidence and groundwater management in Tokyo. Int. Rev. Environ. Strateg. 2006, 6, 403–424. [Google Scholar]
- Aimaiti, Y.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W. Multi-sensor InSAR analysis of progressive land subsidence over the Coastal City of Urayasu, Japan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Kumar, D.; Perissin, D. Assessment of subsidence in Delhi NCR due to groundwater depletion using TerraSAR-X and persistent scatterers interferometry. Imaging Sci. J. 2018, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Kumar, A.; Gee, D.; Grebby, S.; Gomes, R.L.; Marsh, S. Comparative Study of Groundwater-Induced Subsidence for London and Delhi Using PSInSAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Kumar, D.; Perissin, D.; Pradhan, B. Estimation of ground subsidence of New Delhi, India using PS-InSAR technique and Multi-sensor Radar data. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 1863–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, B.; Sandwell, D. Satellite Interferometric Investigations of Subsidence Events Associated with Groundwater Extraction in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Int. J. Geol. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Urban growth and land subsidence: Multi-decadal investigation using human settlement data and satellite InSAR in Morelia, Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.; Becker, M. New estimation of Nile Delta subsidence rates from InSAR and GPS analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 78, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateb, A.; Abotalib, A.Z. Inferencing the land subsidence in the Nile Delta using Sentinel-1 satellites and GPS between 2015 and 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, S.A.; Overeem, I.; Steckler, M.S.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Seeber, L.; Akhter, S.H. InSAR measurements of compaction and subsidence in the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, Bangladesh. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enamul Haque, D.M.; Hayat, T.; Tasnim, S. Time Series Analysis of Subsidence in Dhaka City, Bangladesh Using Insar. Malays. J. Geosci. 2019, 3, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tomás, R.; Li, Z.; Motagh, M.; Li, T.; Hu, L.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Gong, X. Imaging Land Subsidence Induced by Groundwater Extraction in Beijing (China) Using Satellite Radar Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKirdy, E. That Sinking Feeling: Beijing Dropping by up to 4 Inches a Year, Study Shows. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2016/06/26/asia/beijing-sinking-study/index.html (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Ji, Y. A preliminary discussion of the genesis of land subsidence in the city preper and outskirts of Beijing. Geol. Beijing 1996, 15–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lei, K.; Ma, F.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Cui, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, F.; Sha, T. Characteristics of land-subsidence evolution and soil deformation before and after the Water Diversion Project in Beijing, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 1111–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Warner, T.A.; Wang, C. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Subsidence in the Beijing Plain 2003–2015 Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) with Multi-Source SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.A.; Kang, Y.; Zhu, C. Ground Subsidence in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region from 1992 to 2014 Revealed by Multiple SAR Stacks. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jiang, S.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Han, X. The Temporal Evolution of Physical Water Consumption and Virtual Water Flow in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- News, B.J. Seven Years Rise 9.71 Meters, Beijing Groundwater Increase behind. Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1751522688018893553&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Lade, P.; De Boer, R. The concept of effective stress for soil, concrete and rock. Geotechnique 1997, 47, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Lin, Q.; Gong, Q. Numerical simulation and analysis on the mechanical responses of the urban existing subway tunnel during the rising groundwater. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 98, 103297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lu, Z.; Yan, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhou, M.; et al. SAR interferometry on full scatterers: Mapping ground deformation with ultra-high density from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Lei, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Gu, Z.; Dang, Y. Spatial-temporal characteristics of land subsidence corresponding to dynamic groundwater funnel in Beijing Municipality, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.L.; Gong, H.L.; Chen, B.B.; Zhou, C.F.; Liu, K.S.; Shi, M. Mapping and characterization of land subsidence in Beijing Plain caused by groundwater pumping using the Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) InSAR technique. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y. Beijing subway tunnelings and high-speed railway subsidence monitoring with PSInSAR and TerraSAR-X data. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 6883–6886. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Xiaojing, L.; Li, L. Mapping land subsidence over the eastern Beijing city using satellite radar interferometry. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 11, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Dai, K.; Xing, C.; Li, Z.; Tomás, R.; Clark, B.; Shi, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, Q.; et al. Land subsidence in Beijing and its relationship with geological faults revealed by Sentinel-1 InSAR observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 82, 101886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lan, H.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Warner, T.A.; Clague, J.J.; Wu, Y. Reduced rate of land subsidence since 2016 in Beijing, China: Evidence from Tomo-PSInSAR using RadarSAT-2 and Sentinel-1 datasets. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 41, 1259–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Ke, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Gong, H.; Constantinos, C. Change in regional land subsidence in Beijing after south-to-north water diversion project observed using satellite radar interferometry. GISci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Lei, K.; Zhu, L.; Duan, L.; Zhao, X. Land subsidence and its relation with groundwater aquifers in Beijing Plain of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Lian, X.; Zhu, Q.; Horgan, F.G.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of the impact of the South-to-North water diversion project on water balance and land subsidence in Beijing, China between 2007 and 2020. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Balz, T. Beijing Land Subsidence Revealed Using PS-InSAR with Long Time Series TerraSAR-X SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Fan, Q.; Si, J.; Zhu, W.; Song, M. Interpretation of the Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Land Deformation in Beijing during 2003–2020 Using Sentinel, ENVISAT, and Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Chen, P.; Li, S.; Su, Y. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ground Subsidence in the Beijing Plain Area Using Long Time Series Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yague-Martinez, N.; Zan, F.D.; Prats-Iraola, P. Coregistration of Interferometric Stacks of Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.; Mellors, R.; Tong, X.; Wei, M.; Wessel, P. GMTSAR: An InSAR Processing System Based on Generic Mapping Tools; UC San Diego: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P.J. Robust Estimation of a Location Parameter. In Breakthroughs in Statistics: Methodology and Distribution; Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 492–518. [Google Scholar]
- Parizzi, A.; Brcic, R. Adaptive InSAR stack multilooking exploiting amplitude statistics: A comparison between different techniques and practical results. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 8, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lan, H.; Bürgmann, R.; Warner, T.A.; Clague, J.J.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J. Application of an improved multi-temporal InSAR method and forward geophysical model to document subsidence and rebound of the Chinese Loess Plateau following land reclamation in the Yan’an New District. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 279, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Peng, Y.; Ma, X.; Huang, M. Long-Term SAR Data Analysis for Subsidence Monitoring and Correlation Study at Beijing Capital Airport. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, B.; Dai, Z.; Teatini, P. Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in the northern Beijing plain, China. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).