GNSS and Sentinel-1 InSAR Integrated Long-Term Subsidence Monitoring in Quetta and Mastung Districts, Balochistan, Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Using the SBAS-InSAR technique, 7 years of time series analysis was performed to measure land subsidence in the Quetta and Mastung districts using Sentinel-1 SAR images. The temporal range of the InSAR analysis ranges from December 2015 to December 2022.
- Up to 16 years (2006–2022) of campaign and continuous GNSS data were collected and processed over Quetta city from five GNSS stations.
- Groundwater depletion data from 1988 to 2020 were collected to assess the decline rate in the aquifer system from 37 monitoring wells operated by the Balochistan Irrigation Department (BID).
- The GNSS and InSAR measurements including the Ascending and Descending values are cross-validated in this study.
- The causes of LS are revealed by cross-correlation among GWL and InSAR measurements in addition to subsurface lithology. Moreover, the groundwater decline is correlated with the population growth over time.
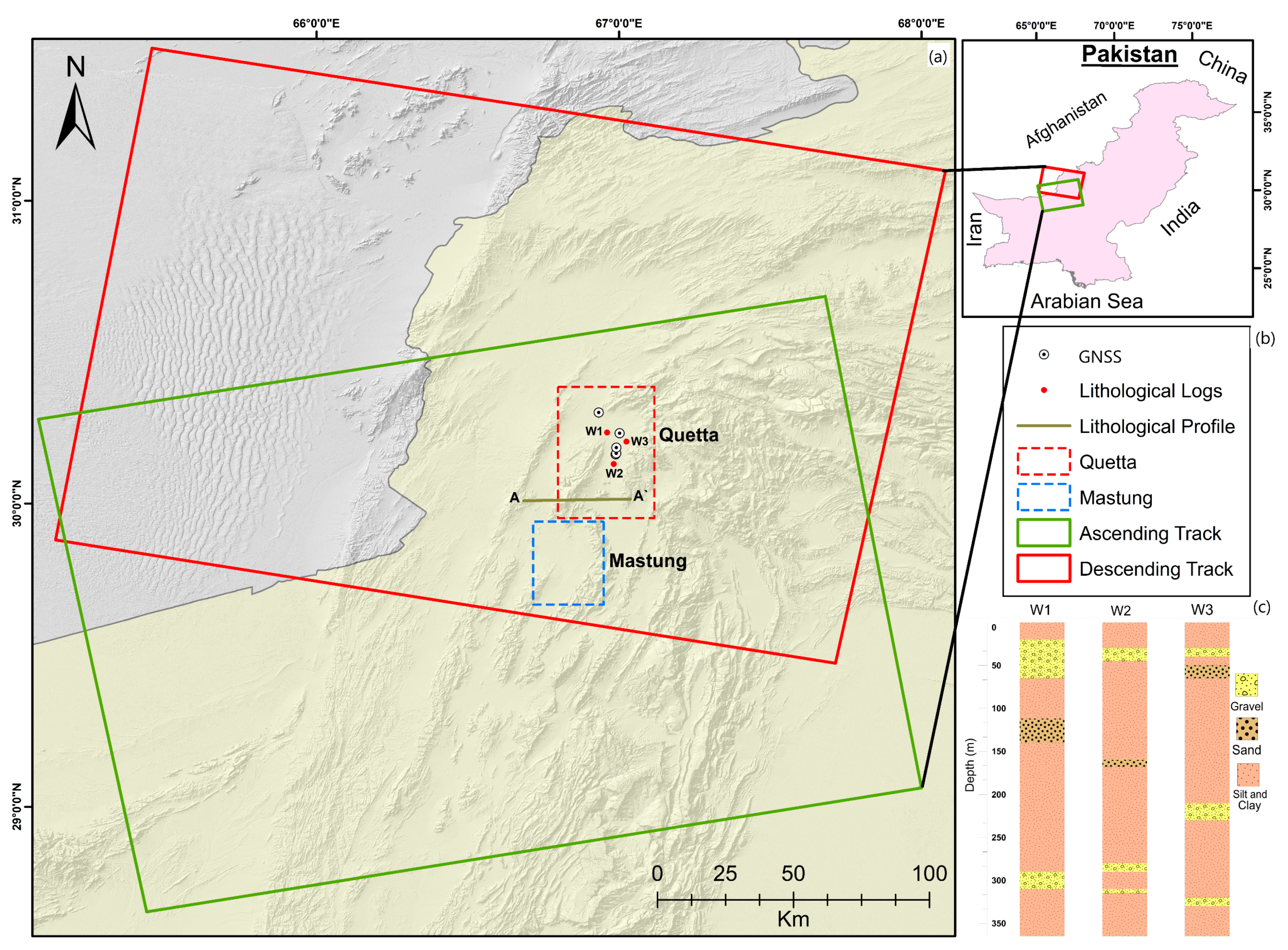
2. Study Area
2.1. Climate and Population
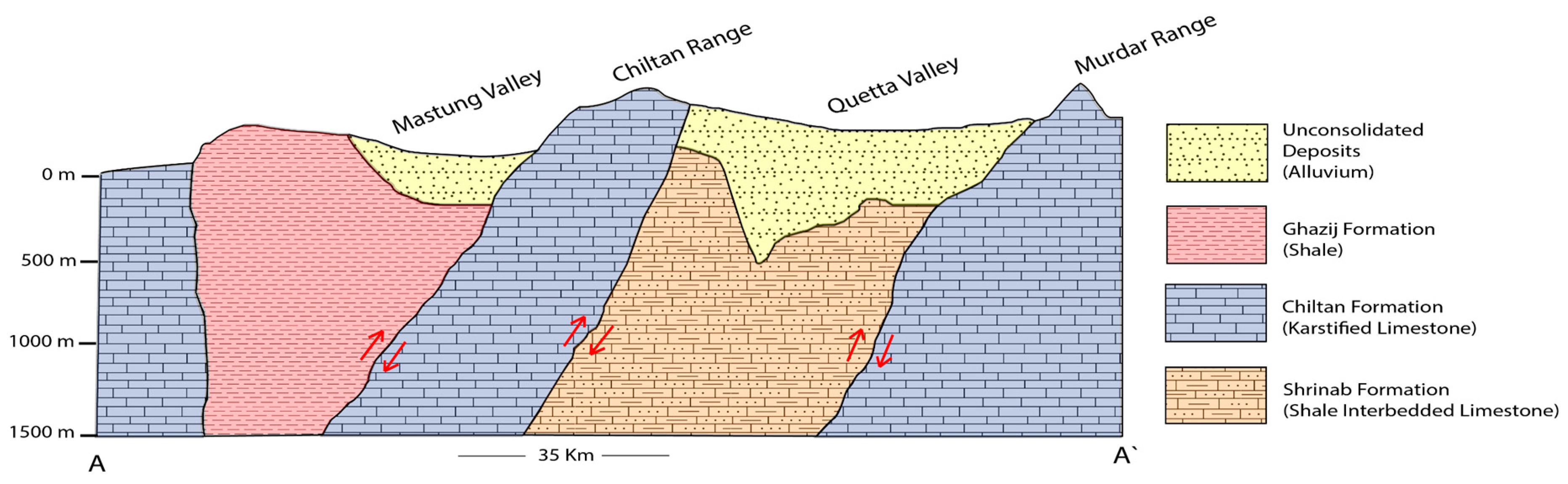
2.2. Geological Settings
3. Datasets and Methodology
3.1. InSAR Datasets
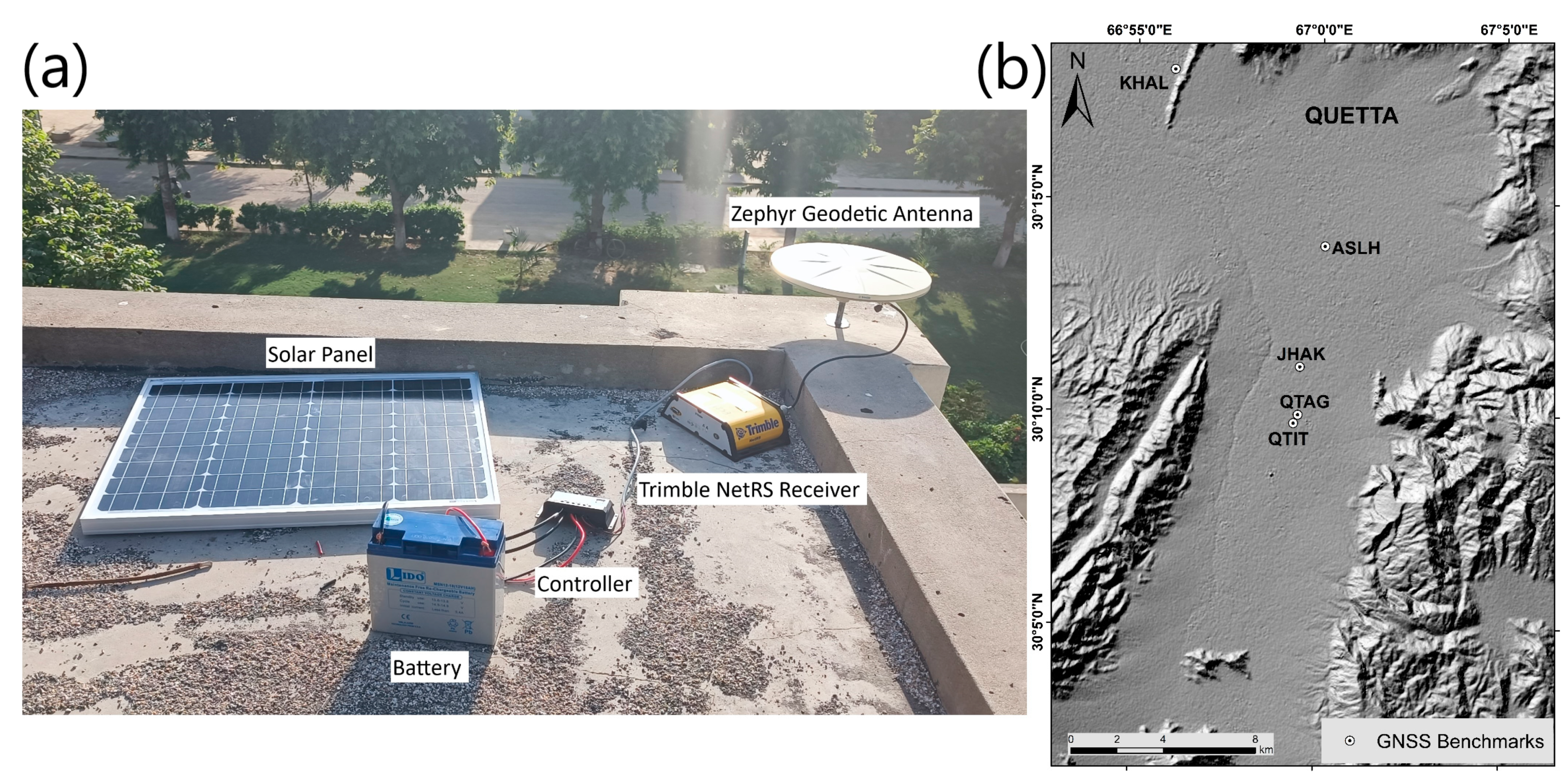
3.2. GNSS Measurements and Methodology
3.3. Groundwater Level
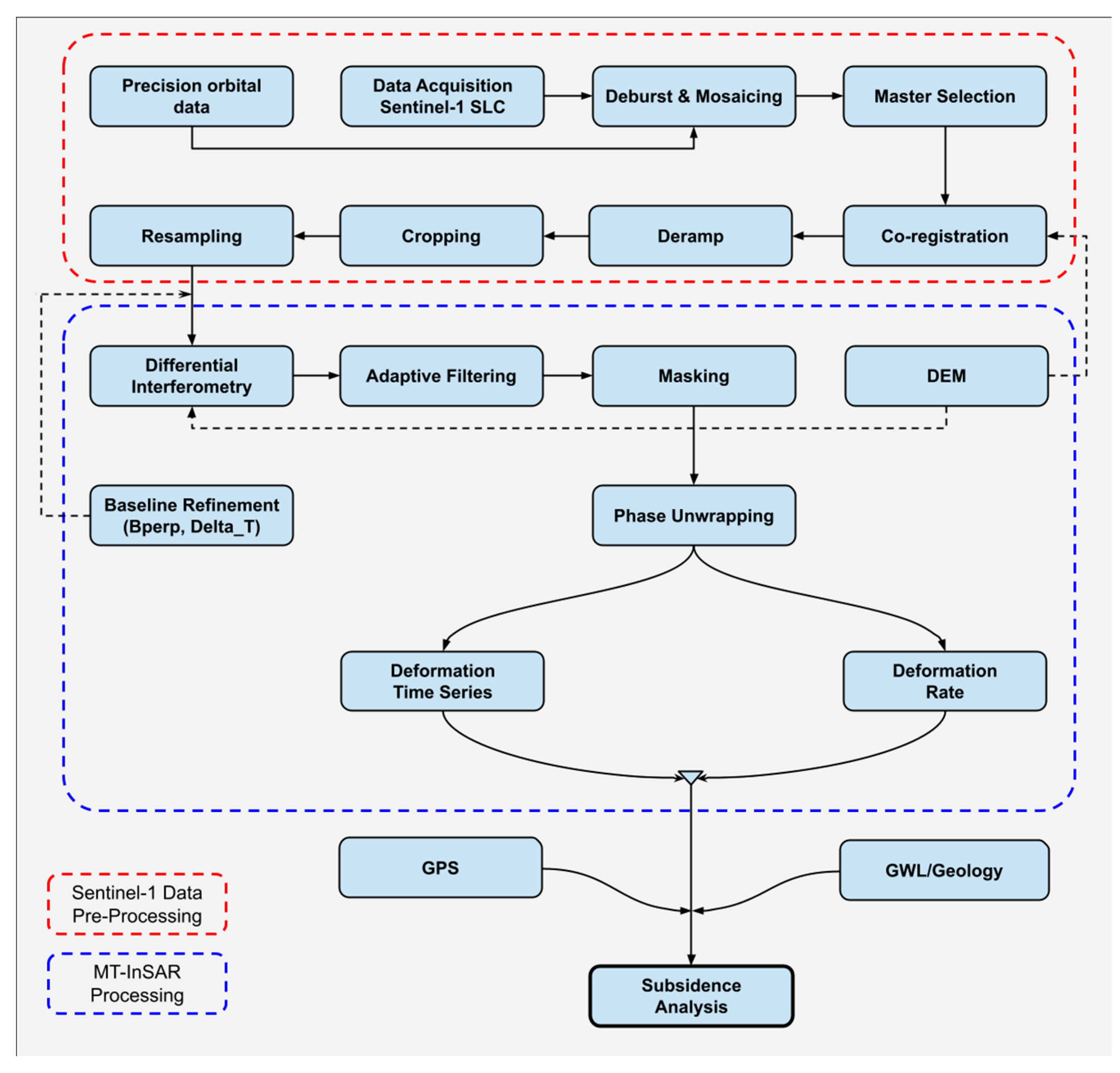
3.4. InSAR Methodology
4. Results
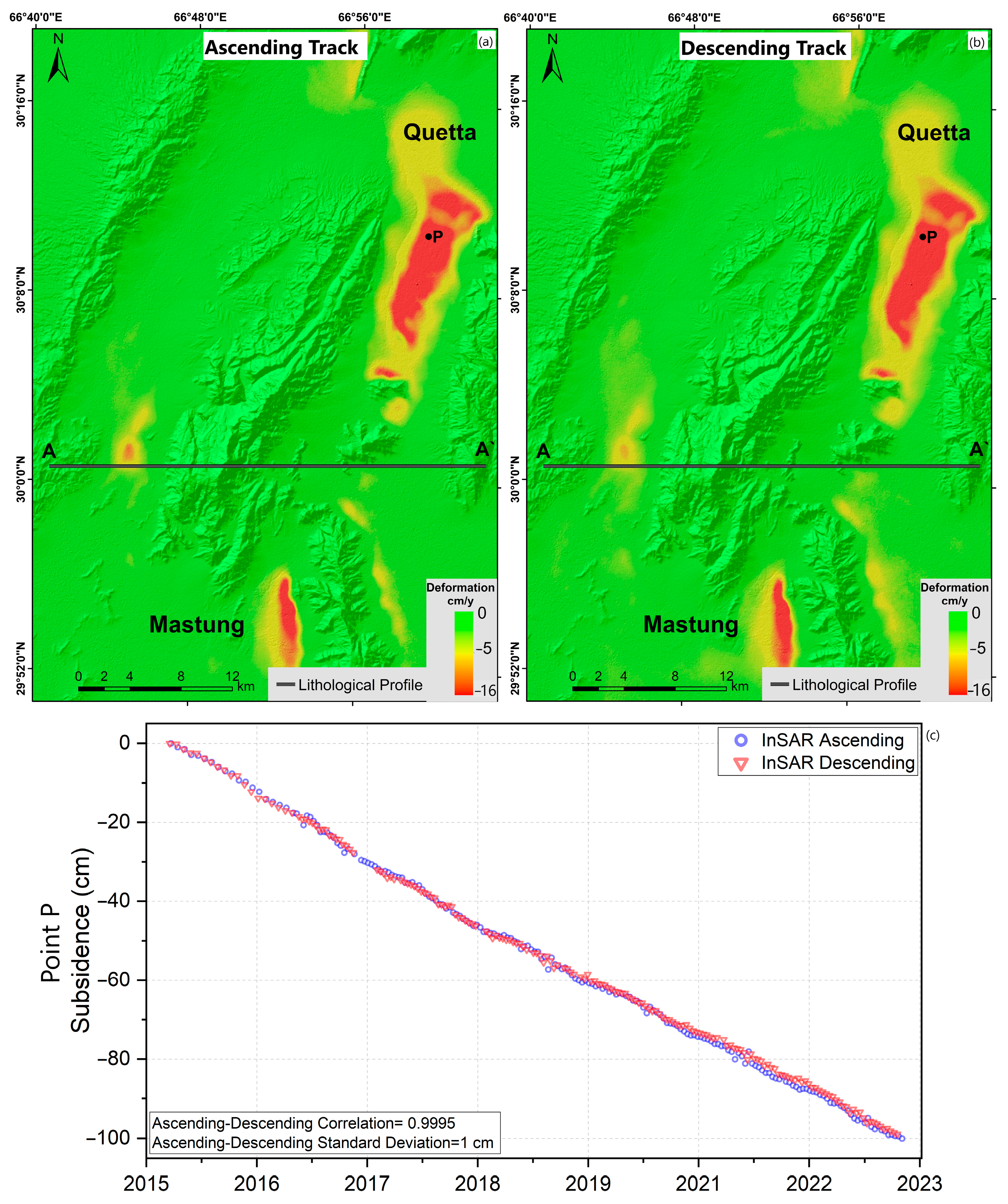
4.1. InSAR Ascending vs. Descending Deformation
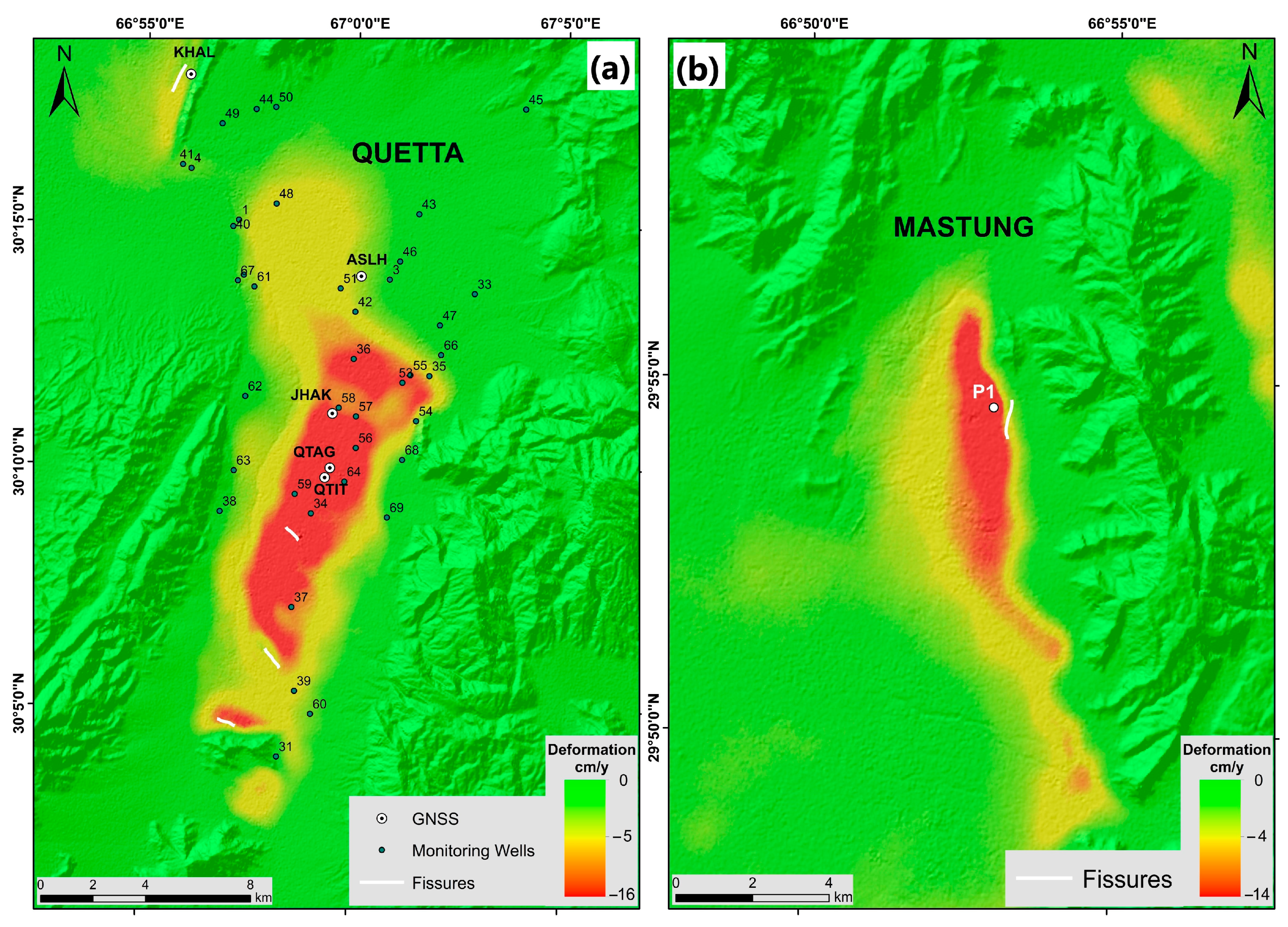
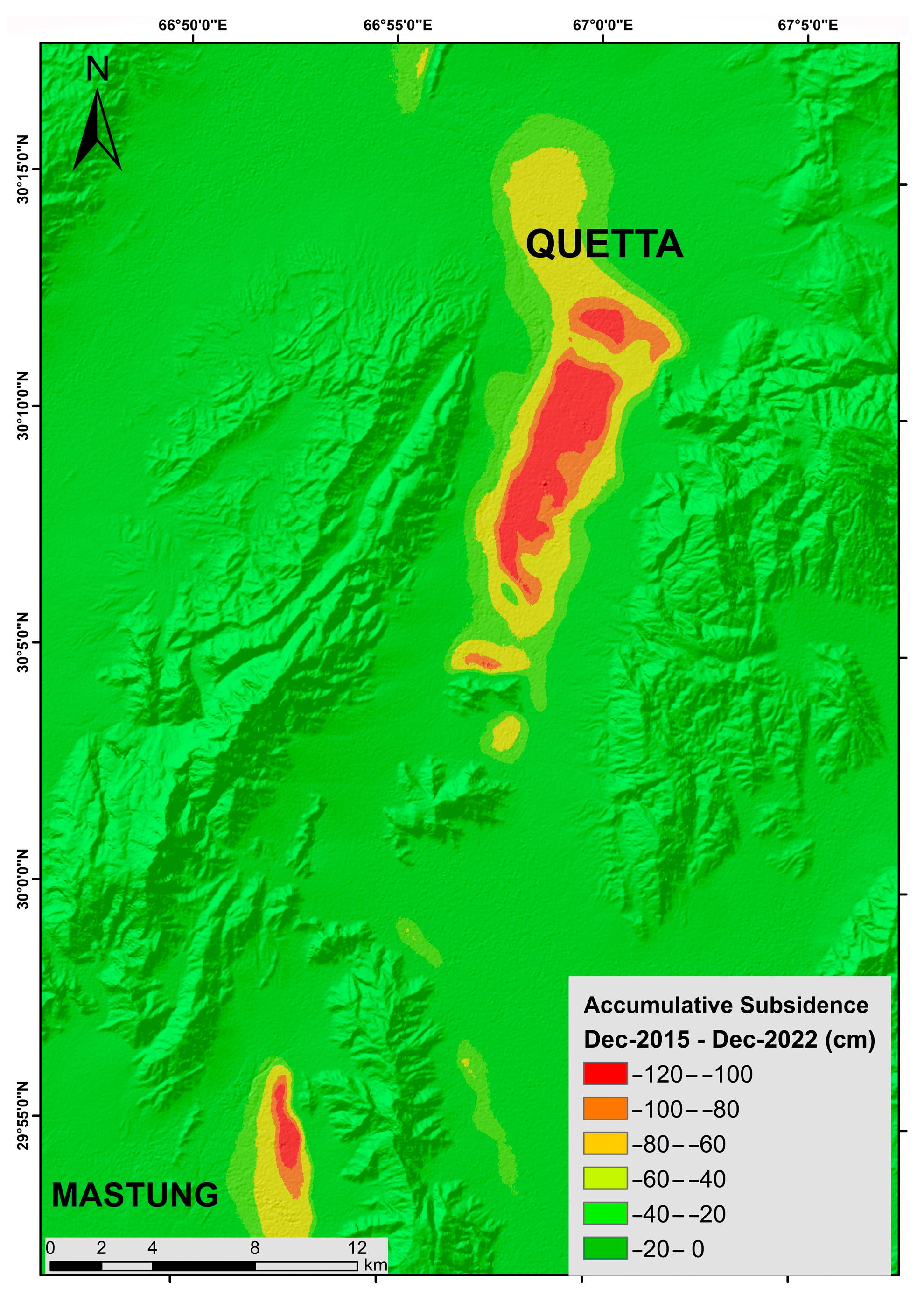
4.2. Land Subsidence Distribution and Time Series
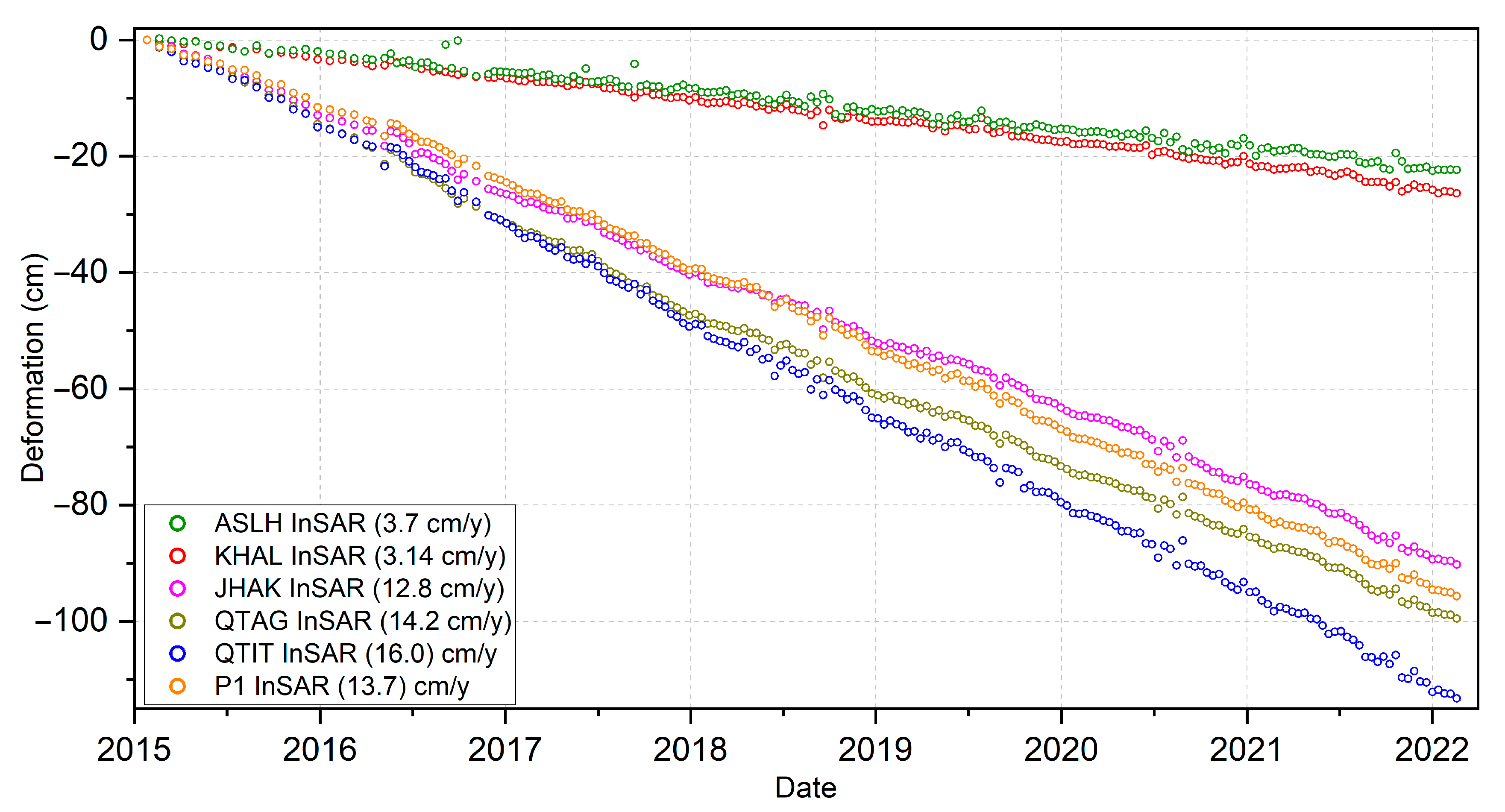
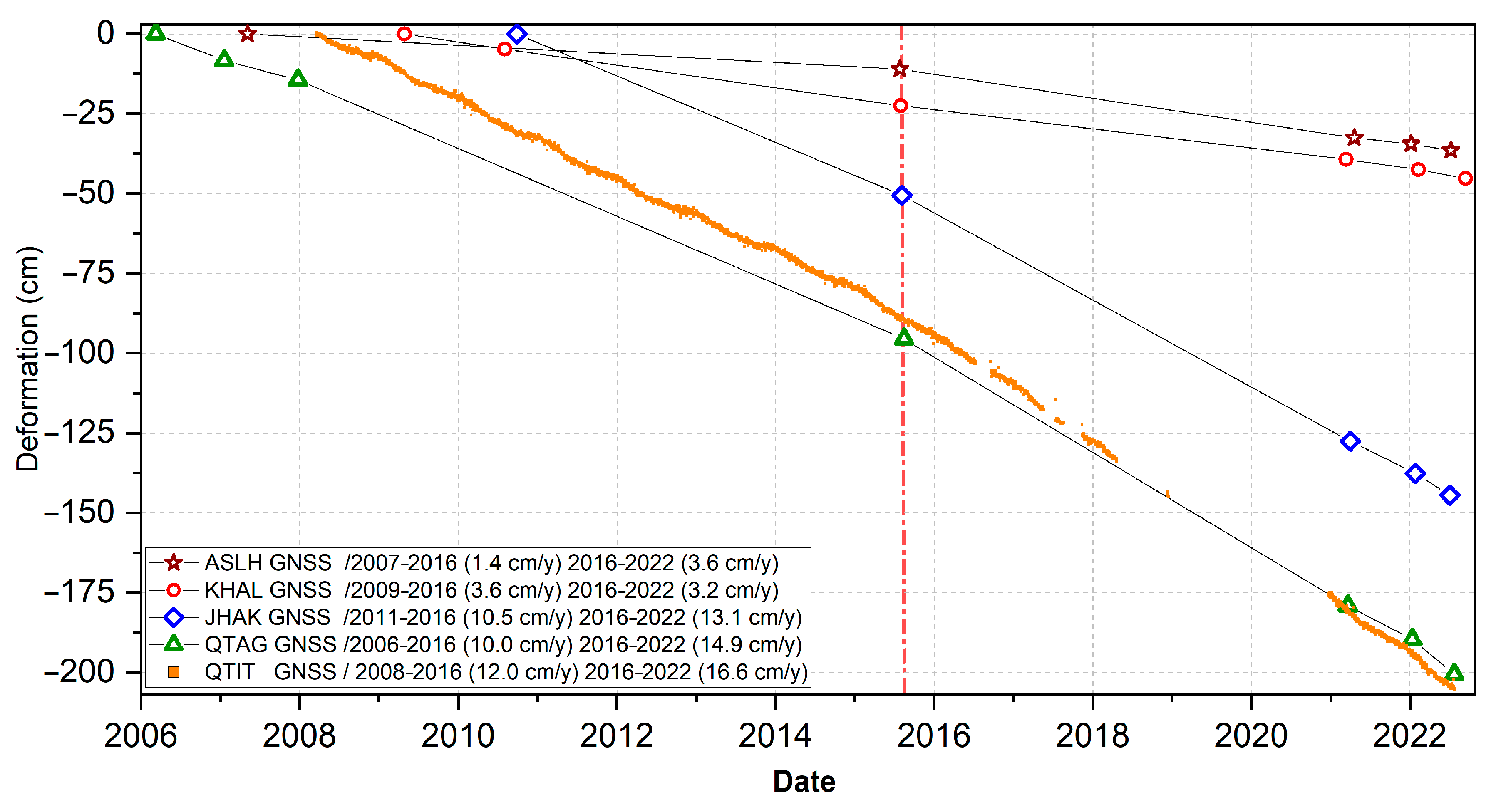
4.3. GNSS Results
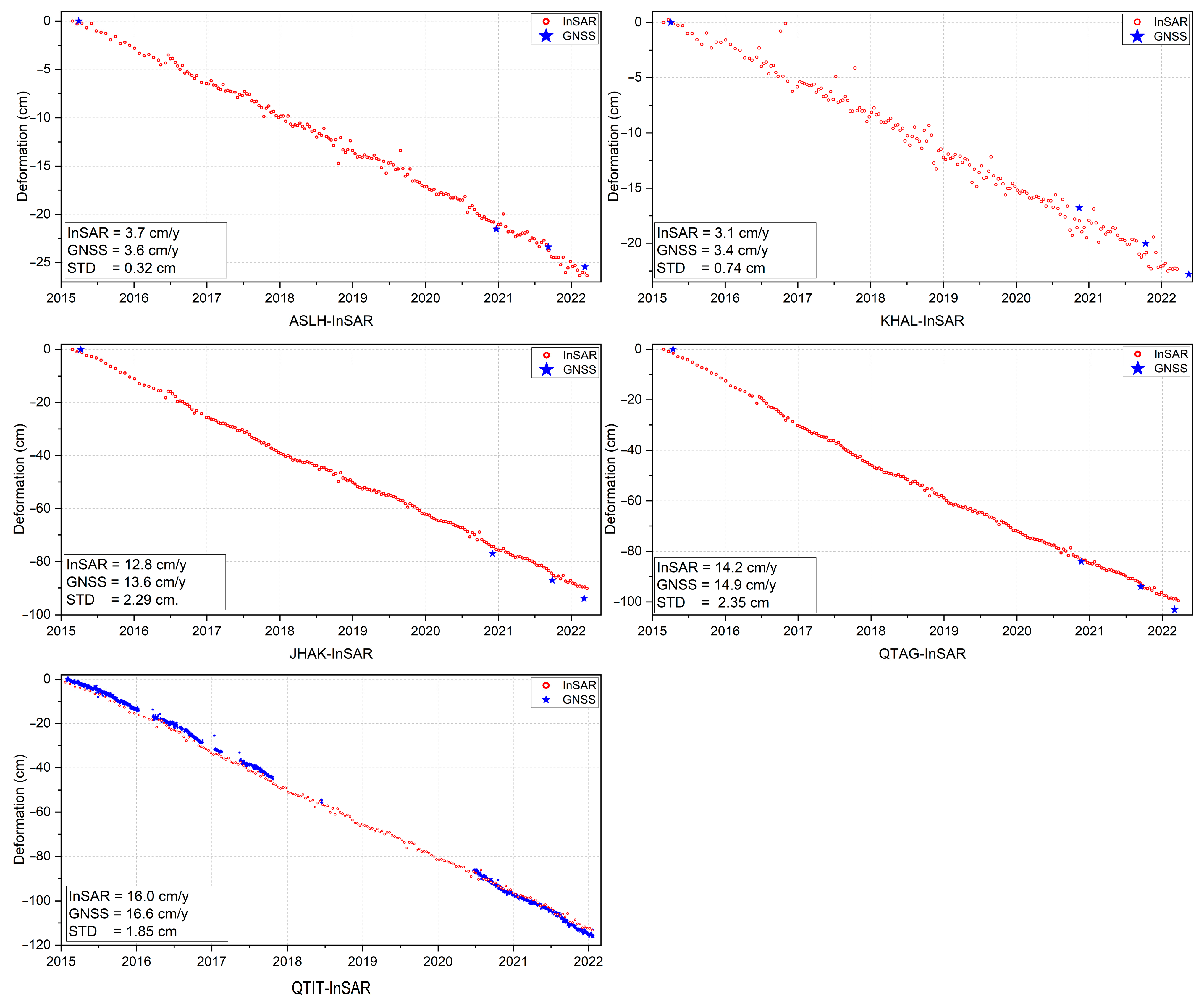
4.4. GNSS-InSAR Correlation
5. Discussion
5.1. Ground Fissures
5.2. Geological Relationship
5.3. InSAR–GWL Correlation
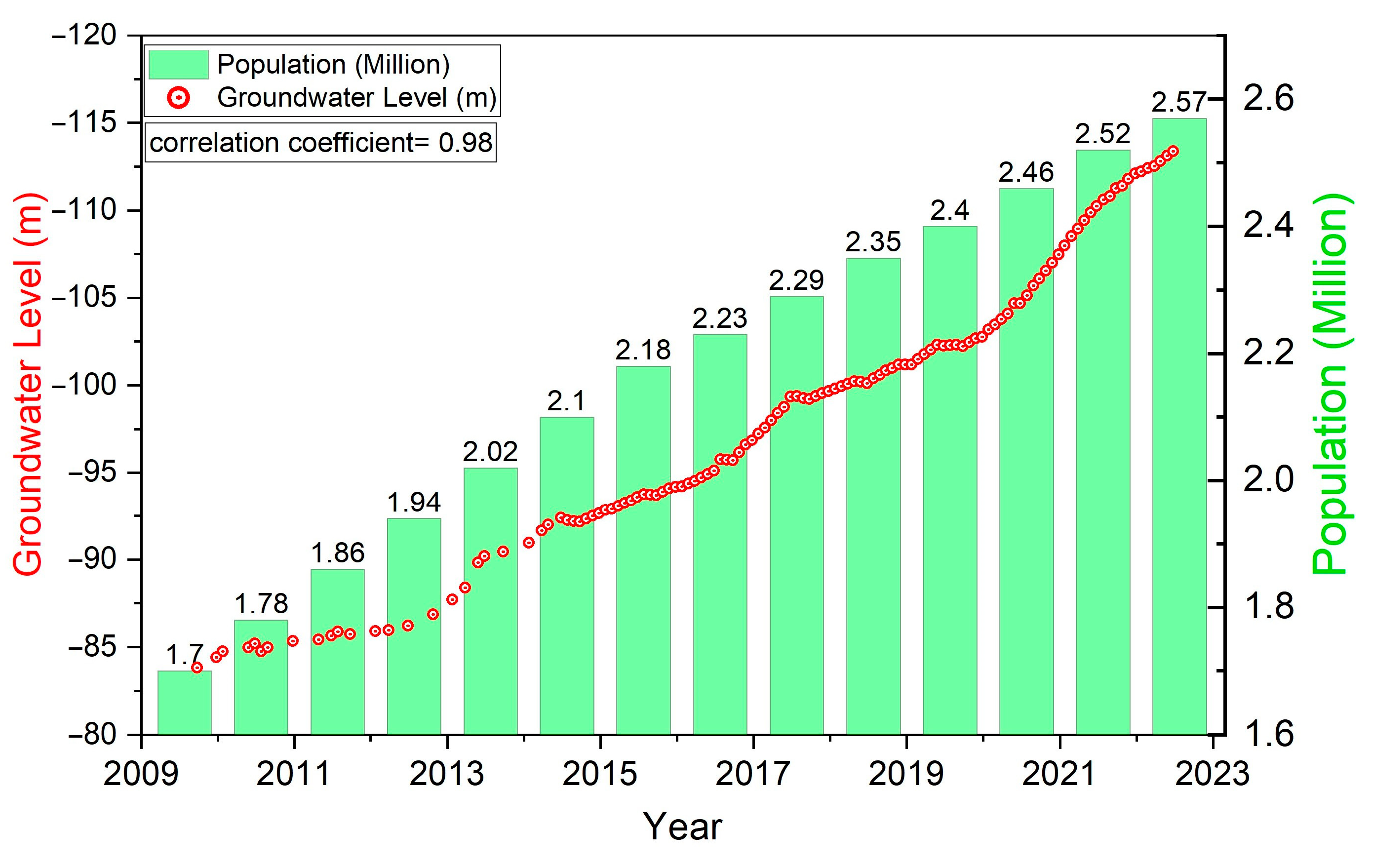
5.4. Population–GWL Association
6. Conclusion and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrera-García, G.; Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; López-Vinielles, J.; Rossi, M.; Mateos, R.M.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Lambert, J.; Teatini, P.; et al. Mapping the Global Threat of Land Subsidence. Science 2021, 371, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shi, M. Wuhan Surface Subsidence Analysis in 2015–2016 Based on Sentinel-1A Data by SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T.; Befus, K.; Jasechko, S.; Luijendijk, E.; Cardenas, M. The Global Volume and Distribution of Modern Groundwater. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 9, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A. Groundwater Governance in Pakistan: From Colossal Development to Neglected Management. Water 2020, 12, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumra, D.-K.; Mumtaz, M.; Khan, K. National Water Policy of Pakistan: A Critical Analysis. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 14, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, J.; Su, C.; Rashid, A.; Yang, N.; Baloch, M.Y.J.; Talpur, S.A.; Ullah, Z.; Rahman, G.; Rahman, N.U.; Earjh, E.; et al. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater and Suitability Analysis for Domestic and Agricultural Utility in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, R.D. Records of Geological Survey of India; Forgotten Book: Calcutta, India, 1892. [Google Scholar]
- WAPDA Groundwater Level during 1967–1988 in Quetta Valley. Hydrogeology Project, Quetta, Basic Data Release No. 1; Kalat Publishers: Quetta, Pakistan, 1988; p. 96.
- Konak, H.; Küreç Nehbit, P.; Karaöz Fendoğlu, A.; Cerit, F. Interpreting Deformation Results of Geodetic Network Points Using the Strain Models Based on Different Estimation Methods. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2020, 5, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuşat, E.; Ozyuksel, F. Comparison of GPS Satellite Coordinates Computed from Broadcast and IGS Final Ephemerides. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2018, 3, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalvaç, S. Validating InSAR-SBAS Results by Means of Different GNSS Analysis Techniques in Medium- and High-Grade Deformation Areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping Small Elevation Changes over Large Areas: Differential Radar Interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.R.; Li, F.K.; Madsen, S.; Rodriguez, E.; Goldstein, R.M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Tofani, V.; Agostini, A.; Tanteri, L.; Tacconi Stefanelli, C.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Subsidence Mapping at Regional Scale Using Persistent Scatters Interferometry (PSI): The Case of Tuscany Region (Italy). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, F.; Galloway, D.; Bell, J.; Zebker, H.; Laczniak, R. Sensing the Ups and Downs of Las Vegas: InSAR Reveals Structural Control of Land Subsidence and Aquifer-System Deformation. Geology 1999, 27, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawden, G.; Stein, R.; Hudnut, K.; Peltzer, G. Tectonic Contraction across Los Angeles after Removal of Groundwater Pumping Effects. Nature 2001, 412, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauknes, T.R. Rockslide Mapping in Norway by Means of Interferometric SAR Time Series Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, G.; Schattner, U.; Wachs, D.; Sandwell, D.; Wdowinski, S.; Frydman, S. The Lowest Place on Earth Is Subsiding—An InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) Perspective. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2002, 114, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.; Hudnut, K.; Ingebritsen, S.; Phillips, S.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P. Detection of Aquifer System Compaction and Land Subsidence Using Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Galloway, D.; Zebker, H. Inverse Modeling of Interbed Storage Parameters Using Land Subsidence Observations, Antelope Valley, California. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, SBH 5-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorqui, J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A Small Baseline Approach for Investigating Deformation on Full Resolution Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoglu, B.; Dixon, T.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Jiang, Y. Mexico City Subsidence Observed with Persistent Scatterer InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.; An, J.; Zhou, C.; Ma, Y. Time-Series Analysis of Subsidence in Nanning, China, Based on Sentinel-1A Data by the SBAS InSAR Method. PFG J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2020, 88, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Esquivel, R.; Tapete, D. Accuracy of Sentinel-1 PSI and SBAS InSAR Displacement Velocities against GNSS and Geodetic Leveling Monitoring Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R. Radar Interferometry Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 2, ISBN 978-0-7923-6945-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Ding, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z. Mitigating Ionospheric Artifacts in Coseismic Interferogram Based on Offset Field Derived from ALOS-PALSAR Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Shamshiri, R.; Haghshenas Haghighi, M.; Wetzel, H.-U.; Akbari, B.; Nahavandchi, H.; Roessner, S.; Arabi, S. Quantifying Groundwater Exploitation Induced Subsidence in the Rafsanjan Plain, Southeastern Iran, Using InSAR Time-Series and in Situ Measurements. Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Samsonov, S.; Yin, H.; Ye, S.; Cao, Y. Time-Series Analysis of Subsidence Associated with Rapid Urbanization in Shanghai, China Measured with SBAS InSAR Method. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 72, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Land Subsidence and Ground Fissures in Xi’an, China 2005–2012 Revealed by Multi-Band InSAR Time-Series Analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.A.; Overeem, I.; Steckler, M.S.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Seeber, L.; Akhter, S.H. InSAR Measurements of Compaction and Subsidence in the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, Bangladesh. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Arroyo Domínguez, N.; Martel, R.; Calderhead, A.; Normand, J.; Garfias, J.; Rivera, A. Land Subsidence in Major Cities of Central Mexico: Interpreting InSAR-Derived Land Subsidence Mapping with Hydrogeological Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 47, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land Subsidence in Central Mexico Detected by ALOS InSAR Time-Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.Z.; Hong, S.-H. Sinking Cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR Detects Rapid Subsidence due to Groundwater and Gas Extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bozzano, F.; Marra, F.; Wegmuller, U.; Cinti, F.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M. Subsidence Induced by Urbanisation in the City of Rome Detected by Advanced InSAR Technique and Geotechnical Investigations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Kakar, D. Land Subsidence and Declining Water Resources in Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2719–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, N.; Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Kakar, D. Land Subsidence Caused by Groundwater Exploitation in Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2016, 7, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.; Kim, D. Detection of Land Subsidence and Its Relationship with Land Cover Types Using ESA Sentinel Satellite Data: A Case Study of Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 9572–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, I.H.; Adnan, S.; Ahmad, M.; Khair, S.M.; Kakar, E. Observed Long-Term Climatic Variability and Its Impacts on the Ground Water Level of Quetta Alluvial. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 2018, 42, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, I.; Adnan, S.; Aftab, S.M. Historical and Future Climatological Drought Projections over Quetta Valley, Balochistan, Pakistan. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 414, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, I.; Adnan, S.; Aftab, S.M. Daily Climate Extremes of Temperature and Precipitation over Quetta Valley, Pakistan during 1961–2019. Int. J. Environ. 2021, 10, 20–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asian Development Bank. Quetta Water Supply and Environmental Improvement Project; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong City, Philippines, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Home|Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://www.pbs.gov.pk/ (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Hunting, S.C. Hunting Survey Corporation. Reconnaissance Geology of Part of West Pakistan, Balochistan, a Colombo Plan Cooperative Project; Photographic survey corporation limited: Toronto, ON, Canda, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, A.; Reza, S.Q. Water Supply of Quetta Basin, Balochistan, Pakistan. Geol. Surv. Pak. Rec. 1970, 20, 97–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, S. Geohydrology of Quetta Valley; Hydrogeology Directorate, Reclamation Division, Water and Power Development Authority: Quetta, Pakistan, 1973; Volume 72. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, A. Geology of Ziarat-Kach-Zardalu Area of Balochistan. DIC Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 1955. Volume 157. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, A.H.; Hamza, A. The Bibai and Gogai Nappes in the Kach-Ziarat Area of Northeastern Baluchistan; Geodynamics of Pakistan. Geological Survey of Pakistan: Quetta, Pakistan, 1979; pp. 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Sagintayev, Z.; Sultan, M.; Khan, S.D.; Khan, S.A.; Mahmood, K.; Yan, E.; Milewski, A.; Marsala, P. A Remote Sensing Contribution to Hydrologic Modelling in Arid and Inaccessible Watersheds, Pishin Lora Basin, Pakistan. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilham, R.; Kakar, N.U.; Kakar, D.M.; Wang, K.; Bürgmann, R.; Barnhart, W.D. The 1892 Chaman, Pakistan, Earthquake. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2019, 90, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeliga, W.; Bilham, R.; Schelling, D.; Din, M.; Kakar, D.; Lodi, S. Fold and Thrust Partitioning in a Contracting Fold Belt: Insights from the 1931 Mach Earthquake in Baluchistan. Tectonics 2009, 28, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Ahmad, N. Determination of Aquifer Geometry through Geophysical Methods: A Case Study from Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Acta Geophys. 2014, 62, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Khan, S.; Ghulam, A.; Crupa, W.; Abir, I.; Khan, A.; Kakar, D.; Kasi, A.; Kakar, N. Study of Subsidence and Earthquake Swarms in the Western Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASF Data Search. Available online: https://search.asf.alaska.edu/#/ (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- De Zan, F.; Monti Guarnieri, A. TOPSAR: Terrain Observation by Progressive Scans. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegnüller, U.; Werner, C.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A.; Frey, O.; Santoro, M. Sentinel-1 Support in the GAMMA Software. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GipsyX/RTGx, a New Tool Set for Space Geodetic Operations and Research. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 469–489. [CrossRef]
- Characterisation and Mapping of Land Subsidence Based on Geodetic Observations in Lagos, Nigeria. Geod. Geodyn. 2020, 11, 151–162. [CrossRef]
- Dawood, F.; Akhtar, M.M.; Ehsan, M. Evaluating Urbanization Impact on Stressed Aquifer of Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 222, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Kassi, A.M.; Aftab, S.M.; Zahir, M. Decline of Static Water Level in Quetta Sub-Basin, Balochistan, Pakistan. J. Geogr. Soc. Sci. 2021, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.F.K.; Nawaz, M. Karez Irrigation in Pakistan. GeoJournal 1995, 37, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planning & Monitoring Wing Water Resources PD&M Directorate Irrigation Department Quetta “Quarterly Report on Groundwater Monitoring of Quetta Sub-Basin”. “Irrigation Quetta”; Kalat Publishers: Quetta, Pakistan, 2011.
- Peng, M.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z. Research on Spatiotemporal Land Deformation (2012–2018) over Xi’an, China, with Multi-Sensor SAR Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.B.; Rucker, M.L.; Fergason, K.C. Modeling of Earth Fissures Caused by Land Subsidence due to Groundwater Withdrawal. Proc. IAHS 2015, 372, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, T.; Inkenbrandt, P.; Lund, W.; Lowe, M.; Bowman, S. Investigation of Land Subsidence and Earth Fissures in Cedar Valley, Iron County, Utah; Natural Resources Map & Bookstore; North Temple: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Chen, G.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W.; Chong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence and Rebound over Xi’an in Western China Revealed by SBAS-InSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, F.; Liu, R.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C. Ground Deformation and Fissure Activity of the Yuncheng Basin (China) Revealed by Multiband Time Series InSAR. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahdary, M. Shrinking Aquifers and Land Subsidence in Iran. Science 2022, 376, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunori, C.A.; Bignami, C.; Albano, M.; Zucca, F.; Samsonov, S.; Groppelli, G.; Norini, G.; Saroli, M.; Stramondo, S. Land Subsidence, Ground Fissures and Buried Faults: InSAR Monitoring of Ciudad Guzmán (Jalisco, Mexico). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8610–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlown, M.A.; Tahir, M.A.; Hifza, R. Fifth Monitoring Report (2005–2006) (No. 133–2007), National Water Quality Monitoring Programme. [WWW Document]; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR): Lahore, Pakistan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Perveen, S. Amar-Ul-Haque Drinking Water Quality Monitoring, Assessment and Management in Pakistan: A Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G. Structure, Crystal Chemistry, and Origin of the Phyllosilicate Minerals Common in Soil Clays. In Soil Colloids and Their Associations in Aggregates; De Boodt, M.F., Hayes, M.H.B., Herbillon, A., De Strooper, E.B.A., Tuck, J.J., Eds.; NATO ASI Series; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 7–38. ISBN 978-1-4899-2611-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ojha, C.; Shirzaei, M.; Werth, S.; Argus, D.F.; Farr, T.G. Sustained Groundwater Loss in California’s Central Valley Exacerbated by Intense Drought Periods. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 4449–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneed, M.; Brandt, J. Mitigating Land Subsidence in the Coachella Valley, California, USA: An Emerging Success Story. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 382, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Jones, D.R.; Ingebritsen, S.E. (Eds.) Land Subsidence in the United States; U.S. Geological Survey Circular; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-607-92696-5.
- Leake, S.A. Land Subsidence From Ground Water Pumping. Available online: http://www.savethesantacruzaquifer.info/land%20subsidence.htm (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- The Incredible Sinking Quetta. Available online: http://www.thefridaytimes.com/2018/02/23/the-incredible-sinking-quetta/ (accessed on 14 March 2024).





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kakar, N.; Zhao, C.; Li, G.; Zhao, H. GNSS and Sentinel-1 InSAR Integrated Long-Term Subsidence Monitoring in Quetta and Mastung Districts, Balochistan, Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091521
Kakar N, Zhao C, Li G, Zhao H. GNSS and Sentinel-1 InSAR Integrated Long-Term Subsidence Monitoring in Quetta and Mastung Districts, Balochistan, Pakistan. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(9):1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091521
Chicago/Turabian StyleKakar, Najeebullah, Chaoying Zhao, Guangrong Li, and Haolin Zhao. 2024. "GNSS and Sentinel-1 InSAR Integrated Long-Term Subsidence Monitoring in Quetta and Mastung Districts, Balochistan, Pakistan" Remote Sensing 16, no. 9: 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091521
APA StyleKakar, N., Zhao, C., Li, G., & Zhao, H. (2024). GNSS and Sentinel-1 InSAR Integrated Long-Term Subsidence Monitoring in Quetta and Mastung Districts, Balochistan, Pakistan. Remote Sensing, 16(9), 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091521







