Abstract
Vision–language tracking presents a crucial challenge in multimodal object tracking. Integrating language features and visual features can enhance target localization and improve the stability and accuracy of the tracking process. However, most existing fusion models in vision–language trackers simply concatenate visual and linguistic features without considering their semantic relationships. Such methods fail to distinguish the target’s appearance features from the background, particularly when the target changes dramatically. To address these limitations, we introduce an innovative technique known as multimodal features alignment (MFA) for vision–language tracking. In contrast to basic concatenation methods, our approach employs a factorized bilinear pooling method that conducts squeezing and expanding operations to create a unified feature representation from visual and linguistic features. Moreover, we integrate the co-attention mechanism twice to derive varied weights for the search region, ensuring that higher weights are placed on the aligned visual and linguistic features. Subsequently, the fused feature map with diverse distributed weights serves as the search region during the tracking phase, facilitating anchor-free grounding to predict the target’s location. Extensive experiments are conducted on multiple public datasets, and our proposed tracker obtains a success score of 0.654/0.553/0.447 and a precision score of 0.872/0.556/0.513 on OTB-LANG/LaSOT/TNL2K. These results are satisfying compared with those of recent state-of-the-art vision–language trackers.
1. Introduction
As one of the most fundamental tasks in computer vision, visual object tracking (VOT) aims to locate objects, initialized by a bounding box in the first frame of a video sequence. It has been widely used in many applications such as video surveillance, robotics, and autonomous driving. From a model-based perspective, tracking algorithms have evolved from classical correlation-filter-based models to deep neural networks due to their powerful feature representation [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In the last few years, transformer-based trackers have shown improved performances due to the development of an attention mechanism that enables the modeling of complex feature interactions [7,8,9]. However, existing single-model trackers do not perform as well in practice as they have done during testing with publicly available datasets, especially in challenging scenarios such as , , and , as shown in Figure 1; here, poor feature representations and model drifting often lead to tracking failures. Although many attempts have been made to optimize the tracking paradigm for better accuracy and robustness [10,11], trackers based only on RGB images are still becoming closer to the upper bound. Another viable approach for addressing the aforementioned problem is incorporating natural language descriptions as an auxiliary modality to enhance the informativeness of features in the tracking process [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Unlike visual features that can be easily influenced, natural language features, describing the target with color, motion, position, and category information, are less sensitive to variations in appearance [18,19,20,21].
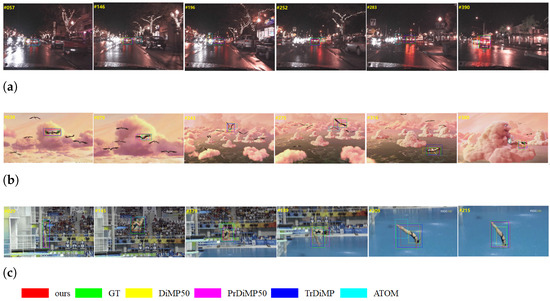
Figure 1.
Tracking results on OTB-LANG and LaSOT sequences. Language descriptions are provided under each group of frames. (a) Natural language description: car in front with two lights. (b) Natural language description: body of a bird on the top right. (c) Natural language description: diver on a diving board.
Vision–language tracking is a new research topic [12,13,14,15,16,17] following it being first proposed by Li [22]. Previous researchers have made attempts to model fusion methods for combining linguistic features and visual features. These approaches include the simple concatenation of visual and linguistic features, employing self-attention within each modality to enhance their interaction, or using cross-attention to promote the interactions between the two modalities [12,13,14,15,17]. Specifically, linguistic features are typically embedded using natural language processing (NLP) models [12] and then concatenated with visual features extracted from CNN models. However, simple concatenation may ignore the relationship between visual and linguistic features during the fusion process. Fused features consist of visual features and linguistic features; however, fused features lack the semantic similarity relation that exists between visual and linguistic features, resulting in less informative feature representation. In fact, there are certain unexplored challenges within the vision–language tracking field. This study aims to establish a coherent connection between visual and linguistic features without diminishing the inherent feature strengths of each individual modality.
We are inspired by the intrinsic reflections of the human brain. Given an image annotated with a natural language description, a human brain can quickly attend to the nouns inferred by the adjectives and adverbs [23]. This inspiration led us to seek a novel fusion feature representation that assigns higher weights to regions where visual and linguistic features exhibit semantic similarity. Simultaneously, it aims to suppress irrelevant regions to enhance the distinguishability of the target.
A novel feature fusion method is proposed in this paper, termed multimodal features alignment (MFA), to merge visual and linguistic features, aiming to minimize cross-modality differences and enhance the target’s feature representation in tracking tasks. In our proposed method, extracted visual features, X, and embedding linguistic features, Q, are fed into a bilinear pooling (BP) [24] model to obtain a joint expression of multimodal features. Given that a single sentence annotates a set of video frames in public tracking datasets, and considering the density of visual features and the sparsity of linguistic features, we integrate a factorization machine within BP to regulate the sparse weight matrices of these two features [18,19]. To mitigate cross-modality discrepancies, we employ soft attention mechanisms twice during the feature fusion phase. The first soft attention is utilized to ascertain the weight of each word in the natural language description, while the second soft attention generates the distribution of visual–spatial grid weights. The linguistic weights map is combined with the original linguistic feature to derive the linguistic attentional feature . Subsequently, acts as a “” to fuse with the visual feature through a factorized bilinear pooling model, followed by additional soft attention layers to generate the distribution of visual–spatial grid weights.
In the final steps, the visual weights map is combined with the original visual feature to produce the visual attentional feature . and are input into a second factorized bilinear pooling process to generate the fused feature . Our approach employs a Siamese-based network as the backbone, similar to many tracking models, with tracking inference involving a classification head and a regression head [25,26]. In most tracking-by-detection models, the effectiveness of the classification and positive/negative ratio in the dataset significantly impacts the classification and regression outcomes, potentially leading to ambiguous results. In our cases, the fused feature map acts as the search region instead of a resized image, thereby modifying the anchor-based tracking paradigm to predict the target’s location.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- A novelty multimodal features alignment network (MFA) for vision–language visual tracking is proposed, which is used in modeling a semantic relationship between visual features and annotated language descriptions to generate fusion features. Experiments are conducted on three natural-language-annotated datasets, and our tracker exhibits a good performance compared to that of a state-of-the-art tracker.
- Weighted fusion features are used as input to the tracking procedure instead of traditional resized images. The fused feature map is divided into multiple grids with distributed weights. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to use fusion feature maps instead of traditional search images for a tracking network.
- The proposed loss function minimizes the cross-modality discrepancy between visual and natural language features, reflecting the effectiveness of the fusion in the tracking procedure.
2. Related Work
In this section, we present relevant research in the fields of visual object tracking, vision–language fusion modules, and vision–language object tracking, respectively.
2.1. Visual Object Tracking
Correlation-filter-based tracking models aim to design a filter that can be applied on a target when the response is maximized; they are most commonly used in visual object tracking in early stages [27]. Siamese-based trackers have received increasing attention from researchers due to their deep neural networks, which have powerful capabilities in feature representation. SiameseFC [3] was the first model of this kind to be proposed, and SiameseRPN [1] was proposed, bringing a region proposal network into tracking and being used in developing tracking-by-detection methods. Subsequently, several improved versions have been developed to enhance different aspects. SiameseRPN++ [2] and SiamDW [28] aim to improve feature representation with deeper and wider networks. ATOM [29], DiMP [30], and PrDiMP [13] are proposed to enable targets to be more easily discriminated from their backgrounds. Recently, transformer-based trackers have outperformed CNN-based models in many benchmarks [8,31,32,33,34]. Their advantage lies in their ability to model long-range dependencies and capture complex relations in sequential data. From the scenario attribute, Dai [35] proposed a meta-updater (LTMU) model for learning geometric cues, appearance cues, and easily discriminated cues, adaptively, in long-term tracking. Moreover, many strategic adjustments [10,11] are conducted to optimize tracking models for faster and more robust performance. It can be concluded that two-stream paradigm trackers still play an important role in tracking models, and a representative feature, particularly in challenging cases, is critical for successful tracking.
2.2. Vision–Language Fusion Model
Before being applied in visual tracking, vision–language fusion models have commonly been used in audio–visual speech recognition (AVSR) applications [36] and image retrieval [37] and video question-answering tasks [38]. In recent years, transformer-based models have become the preferred architecture for multimodal pretraining due to their excellent capacity for use in modeling global dependencies [9]. Lu [39] propose ViLBERT for use in inputting linguistic features and visual features into transformer encoders; they adopted a common attention mechanism to fuse heterogeneous information. However, they ignored feature distribution within the single modality itself, as well as the interaction between multiple modalities. Similarly, Visual BERT [40] and Unicoder-VL [41] also implement BERT and transformer networks for feature extraction and integration purposes. Kim [42] encoded images and language through an image encoder and a language encoder, respectively, and then integrated visual and linguistic features through a multimodal encoder by cross-model attention. RoBERTa [43] is designed for pretraining natural language processing (NLP) systems, improving on Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, i.e., BERT. However, the visual encoders mentioned above are often limited by annotation information such as category labels or bounding boxes for specific tasks, which hinders the generalization performance of the models. Moreover, language embedding models require pretraining on large datasets; then, they must be fine-tuned for different downstream tasks using smaller test datasets. In comparison, vision–language tracking annotated descriptions are relatively small. This may lead to a misalignment between visual and linguistic features. Furthermore, such a paradigm is both time-consuming and expensive in computational costs; this is due to the huge number of learnable parameters.
In tracking tasks, visual features change between different frames, while linguistic features remain unchanged. Methods to reduce the cross-modality discrepancy of visual and linguistic features at the semantic level deserves further exploration.
2.3. Vision–Language Object Tracking
As a new topic in computer vision, vision–language visual tracking has attracted a lot of attention from researchers in recent years especially [7,12,13,14,15,16,22], along with the rapid development of natural language processing. Li [22] was the first to apply the fusion of vision–language features in a tracking task. In addition, the OTB-99LANG dataset was released, which is the first vision–language tracking dataset. Wang [17] proposed a structure-aware graph convolutional neural network, using graph nodes representing samples and edges modeling the spatiotemporal relationships between samples. However, the heterogeneity of the two modalities was not considered, and the added features were not used in the final candidate proposal. Wang also proposed [13] a vision–language tracker based on AdaSwitch model to avoid BBox drifting away. Visual grounding is introduced to the tracking procedure, and the linguistic feature was used to initialize the target instead of BBox. A large natural-language-annotated object tracking dataset, TNL2K, has been published. Feng [16] presented a track-by-detection route that identified the most likely image region given the NL description. He then proposed a Siamese natural language RPN++ tracker named SNLT [14]. The correlation process can be duplicated three times and the correlation results are aggregated dynamically by using joint conditional probabilities between the language network and the vision network. Guo [44] proposed a ModaMixer and asymmetrical networks to learn a unified-adaptive vision–language representation. Zhao [7] presented a transformer-based tracking network, using a proxy token to guide the cross-modal attention. The proxy token is used to modulate word embeddings and make them attend to visual features. Yet, the language token has not been attended to by visual features. JointNLT [45] unifies the cross-modality relation and the cross-temporal relation among natural language and image, which can be implemented in both grounding tasks and tracking tasks.
Previous works have illustrated that language descriptions, acting as auxiliary modality information, enable improvements to be made in the tracking performance, if they are exploited correctly. However, the fusion approach has more possibilities beyond simple concatenation. In this paper, we learn a fused feature representation by aligning a target-relevant linguistic feature and a visual feature, achieving better results.
3. Methods
In this section, we introduce the details of our new vision–language tracking framework, as shown in Figure 2. Specifically, we first describe the multimodal features alignment module for generating a vision–language feature representation with factorized bilinear pooling and a co-attention mechanism. Then, the fused features act as search regions, to be fed into the Siamese-based network for tracking. The definitions of the variables are listed in Table 1.
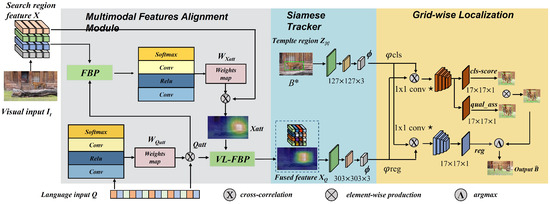
Figure 2.
An overview of the Siamese tracking network with a multimodal features alignment (MFA) framework, including a vision–language features factorized bilinear fusion model and tracking inference. The green frame represents bilinear pooling model.

Table 1.
Definitions of variables.
3.1. Vision–Language Feature Factorized Bilinear Module
In our proposed method, visual features and linguistic features are first projected in a latent space to obtain a joint representation by implementing factorized bilinear pooling.
Consider and as pairwise features; a common linear transformation can be represented as:
where is a projection matrix and is the output of the bilinear model as shown in Figure 3. The bias term is omitted here since it is implicit in W [24]. Equation (1) can be rewritten as:
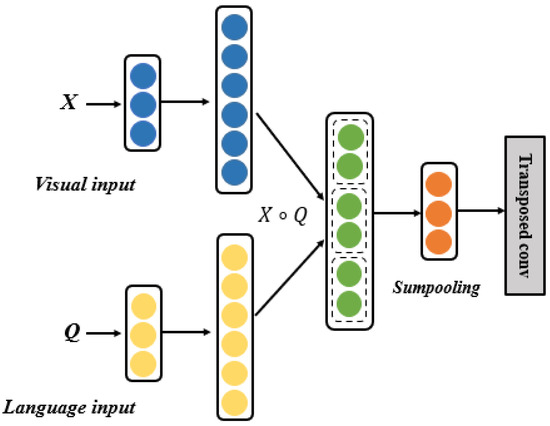
Figure 3.
Vision–language multimodal features alignment module. represents visual input and represents linguistic input; ∘ denotes Hadamard product. A convolution layer is followed by Sumpooling.
Specifically, to obtain a o-dimensional output, F, we need to learn . Although the bilinear pooling is capable of capturing pairwise interactions, it also embraces a quadratic number of parameters in the projection matrix, .
Due to the matrix factorization tricks for uni-modal data, the projection matrix in Equation (2) can be factorized as two low-rank matrices, as follows:
where , k is the factor or the latent dimensionality of the factorized matrices and , ∘ is the Hadamard product or the element-wise multiplication of two vectors.
Given a video sequence, is the search region at frame t. A visual feature, , is extracted through the CNNs model; at the same time, a natural language description is embedded through GloVe, followed by a two-layer LSTM, to generate the linguistic feature, . The soft attention mechanism is conducted for the visual feature and the linguistic feature, respectively, to obtain their inner modality possibility distribution. Specifically, for linguistic feature , we apply two convolutional layers and the softmax function to predict each word’s attention weight, . Then, we take a weighted sum of the linguistic feature and create an attentional map to output the linguistic attentional feature, . On the other hand, the visual feature is merged with the linguistic attentional feature using factorized bilinear pooling; this is followed by two convolutional layers and softmax normalization to obtain an attention distribution over the search region, , as shown in Equation (3). Without the loss of generality, we can reformulate U and V as the 2D matrices and , respectively, with simple reshape operations, as shown in Equation (3). Accordingly, and can be formulated as follows:
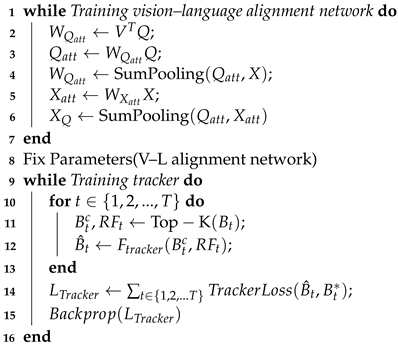
Here, we conduct linguistic attentional feature as “” to bridge the linguistic feature and the visual feature, and pinpoint the highly relevant region in search image. The visual weights vectors for each grid represent the attention distribution brought about by the natural language descriptions. Finally, we take the weighted sums of the visual feature vectors and the visual weights to generate the attended visual feature, , conditioned by Q. The training algorithm is shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: Curriculum training for the tracker. |
 |
3.2. Vision–Language Feature Co-Attention Module
We employ the co-attention method to align the visual feature and the linguistic feature. It can be specified into two steps, self-attention for a natural language description of target embedding and the description conditioned attention for a visual embedding.
The attention mechanism uses an attention probability distribution over the G grid space. is defined as:
where ; the softmax function applies to each row vector of . The bias terms are omitted for simplicity. The weight matrix of the visual attentional feature, , is a linear combination of with coefficients . Each attention probability distribution is for a glimpse, g. For , is the concatenation of each glimpse vector, as follows:
After that, the linguistic attention feature and the visual attention feature, , are fed into another factorized bilinear pooling module to generate a joint feature representation, .
3.3. Prediction Head
In the tracking procedure, we take the Siamese-based two-stream network as the tracking backbone, and invoke a grid-wise target localization strategy, as performed in [46]. The fused feature, , generated by MFA, is reshaped by transposed convolution, then fed into the tracking network as the search region; is the visual template region. The inference algorithm is shown in Algorithm 2. Both branches share parameters through the backbone network, which applies the same transformation to embed and into a shared feature space.
where is feature extractor; is for the and tasks. The feature maps are fine-tuned by two convolutional layers between and .
| Algorithm 2: Inference of the proposed tracker. |
 |
The classification head takes as input. If on the feature map, then is regarded as a positive sample when its corresponding position on the input image is within the BBox. Here, q is the step size of the backbone. The regression head takes as input, and the output offsets to optimize the prediction of the bounding box position. For each positive sample, , the last layer of the regression head predicts the distance to the ground truth and obtains :
where and represent the top left and the bottom right, respectively, and q represents the backbone step size.
It is assumed that the feature pixels around the center of the target have better estimation quality than other pixels. A convolution layer is added in parallel with the classification head for quality estimation. This output is used to estimate the prior spatial score; this is defined as follows:
3.4. Loss Function
We detail the training objective function following the recently proposed anchor-free tracking methods [46]. For classification, the sub-task focal loss approach is employed.
For quality assessment, BCE loss is selected, since we consider it to be a binary classification.
For the regression sub-task, the loss is employed for the bounding box:
where 1 is the indicator function that takes 1 to if is considered as a positive sample, and is 0 is considered as a negative sample.
Finally, the overall loss is defined as:
4. Experiments
In this section, we first describe the datasets, metrics, and implementation details of our experiments. Then, we compare our tracker with other state-of-the art visual object trackers and past NL trackers and conduct a comprehensive set of ablation studies to show the effectiveness of our proposed method.
4.1. Datasets and Metrics
4.1.1. Datasets
Our backbone ResNet model was pretrained on ImageNet [47]. For training the vision–language alignment model and the Siamese tracking model, we used images and phrases from VisualGenome [48], together with images and natural language descriptions from the training portions of LaSOT [49] and OTB-LANG [22]. With the vision–language tracking step, there are three publicly available tracking benchmarks that are annotated with natural language for targets: OTB-LANG [22], LaSOT [49], and TNL2K [13].
4.1.2. Metrics
We perform the One Pass Evaluation (OPE) protocol and measure the success and precision of the tracker, following the original publication on the testing split from the mentioned datasets [49]. The success is measured as the Intersection over Union (IOU) of the pixels between the ground truth bounding boxes () and predicted bounding boxes (). The precision P is usually measured as the distance in pixels between the centers of the ground truth () and the center of the predicted bounding box (). It is important to consider the sensitivity of the resolution of the image and the size of the bounding boxes. Precision, P, is usually normalized over the size of the ground truth bounding box. All the measurement metrics can be calculated as follows:
4.2. Implementation Details
We initialize the model with pretrained weights, following the original work [13]. We freeze stages 1 and 2, fine-tune stages 3 and 4; we augment the base learning rate to , and multiply the learning rate of the parameters by 0.1 with regard to the global learning rate. We reduced the number of image pairs per epoch to 150 k, and the total epoch is 20 (5 for warming up and 15 for training). The step size, q, as in Equation (9), is 8. Visual features are extracted by a bottom–up attention model pretrained on ResNet-101 [50], through leveraging the object and attribute annotations from the VisualGenome. The input image is resized to , and the image representation utilizes 2048-D features. Language descriptions are tokenized into words and then converted into one-hot feature vectors with a maximum length of L. The feature vector is subsequently passed through an embedding layer and fed into a two-layer LSTM network with 1024 hidden units [51]. The last word feature of each layer is extracted to form 2048-D linguistic features. The fused feature, , is transferred to the input image size through the transposed convolution layers.
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Trackers
We compare our proposed tracker with state-of-the-art trackers on three public language-assisted datasets: OTB-LANG [22], LaSOT [49], and TNL2K [13]. Detailed comparison results are presented in Table 2. It is worth noting that the compared state-of-the-art tracking algorithms are divided into two groups: RGB-only trackers and vision–language trackers. RGB-only trackers are initialized with a bounding box, while the vision–language trackers are initialized with a natural language description or a bounding box with a natural language description.

Table 2.
Comparisons on three language-assisted benchmarks. Note: ‘-’ indicates that the code is unavailable or cannot be reproduced. The best three results compared with vision–language trackers are shown in red, blue, and green fonts, respectively.
OTB-99LANG [22] contains 51 training videos and 48 testing videos from OTB100, with the target in each video annotated by natural language description. We use OTB-99LANG as our training and testing dataset. Our tracker achieves a success score of 0.654 and the third-best precision score of 0.872, as shown in Figure 4. Notably, our tracker outperforms Li’s [1] tracker, which achieves a success score of 0.553 and a precision score of 0.724, as well as Feng’s [16] tracker, which scores a success score of 0.608 and a precision score of 0.794. When compared with the latest VL trackers, our tracker can achieve a competitive performance with SNLT [14] and TNL2K [13].
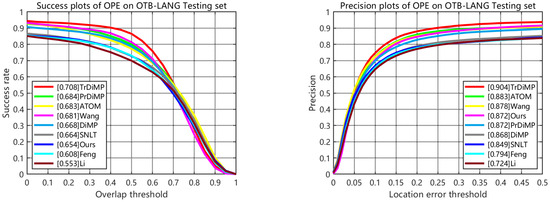
Figure 4.
Evaluation results of the proposed tracker compared with SOTA trackers on OTB-LANG testing set.
LaSOT [49] is a large-scale single-object tracking benchmark with natural language descriptions, containing 1400 sequences and a total of 3.52 million frames. We also employ LaSOT as our training and testing dataset. Our MFA tracker achieves a success score of 0.553, as shown in Figure 5 and Table 2, an improvement of 1.4/3.5 percentage points over SNLT/TNL2K. Additionally, it achieves a precision score of 0.556, which is competitive with SNLT’s precision score of 0.558. Furthermore, our tracker demonstrates an impressive running efficiency of 37 frames per second (fps).
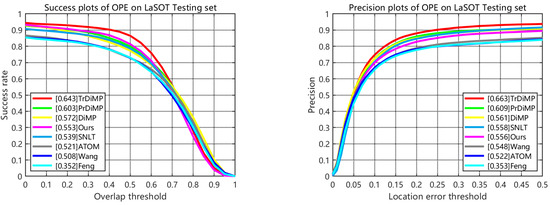
Figure 5.
Evaluation results of the proposed tracker compared with with SOTA trackers on LaSOT testing set.
TNL2K [13] is a recently released multimodal object tracking dataset, which contains 2000 video sequences. Each sequence is annotated with a natural language description. The annotated natural language description indicates the attribute, category, spatial position, and relative location with other objects of the target in first frame. Considering the diverse and complicated sequences in TNL2K, we use it as a testing dataset, as shown in Figure 6. The sixth column in Table 2 shows that our tracker obtains the third-best success score, 0.447, and the best precision score, 0.513. Our proposed tracker outperforms SNLT and TNL2K by a large margin, especially improving the SNLT 0.197/0.177 for the success score and the precision score, respectively.
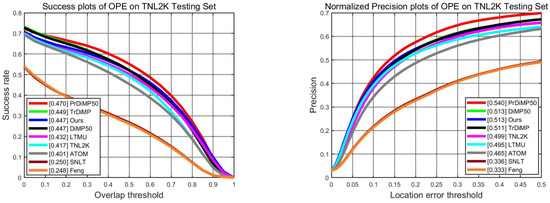
Figure 6.
Evaluation results of the proposed tracker compared with SOTA trackers on TNL2K testing set.
From Table 2, it can be inferred that our tracker demonstrates a competitive performance compared to current vision–language trackers, although it still shows a narrow gap when compared to cutting-edge RGB single-modality trackers. There are two possible reasons for this. First, typically, a tracker initialized with a natural language description may yield a less optimal performance as opposed to the same baseline algorithm. This is due to the dynamic nature of target changes within a video sequence, whereas the target annotation remains static despite the target’s motion. Conversely, initializing the target with both a natural language description and a bounding box leads to an outperforming of the baseline algorithm. The inclusion of a bounding box allows the tracker to ground the target more precisely. Secondly, vision–language trackers predominantly employ Siamese-based networks, while state-of-the-art RGB-only trackers are either based on correlation filters (ATOM [29], DiMP [30], or PrDiMP [52]) or transformer-based networks (STARK [31], OSTrack [33], or TransInMo [34]). The ability to extract features and the ability to model the relationship between different networks are different abilities. There is still little margin between the two structures. It is worth noting that, even though a greater amount of information can be handled compared to conventional methods involving visual and linguistic features, our approach maintains computational efficiency, resulting in a tracker that operates at approximately 37 fps on a single GPU. Our trackers maintain an advantage in terms of both accuracy and real-time performance compared with [13,14]. Visualization results of the tracking are shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
Tracking results on OTB-LANG and LaSOT sequences. Language descriptions are listed under each group of frames.
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Attribute Analysis
TNL2K dataset contains 17 attributes in tracking scenarios listed in Table 3, and the corresponding AUC overlap plots are shown in Figure 8. We surprisingly observed that evaluation under diverse challenging factors on the TNL2K testing set shows promising results.

Table 3.
Description of 17 attributes in the TNL2K dataset.
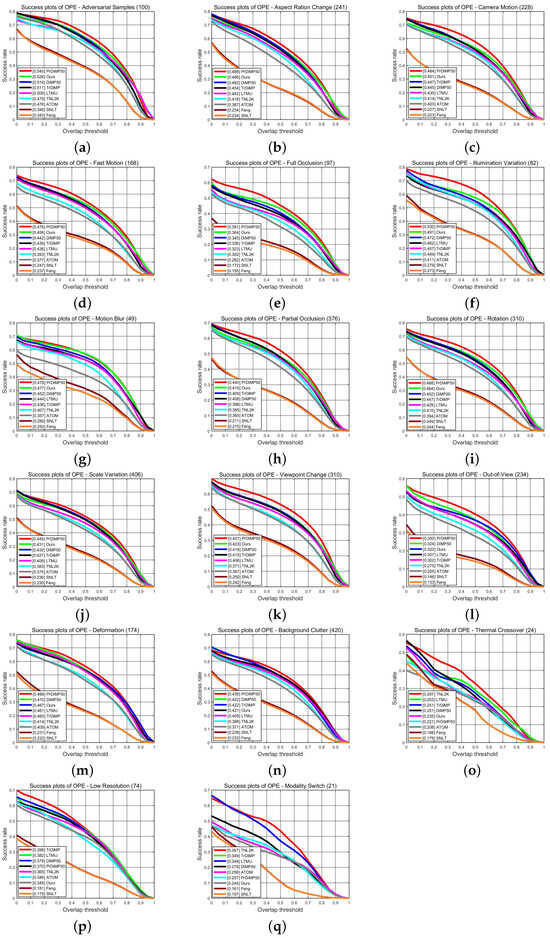
Figure 8.
Success plots on the attribute subset in TNL2K: (a) AS; (b) ARC; (c) CM; (d) FM; (e) FOC; (f) IV; (g) MB; (h) POC; (i) ROT; (j) SV; (k) VC; (l) OV; (m) DEF; (n) BC; (o) TC; (p) LR; (q) MS. Best viewed in color and magnified.
The experiment results show that our proposed MFA vision–language tracker obtains 11 of the best results and 3 of the third-best results when compared with those of other vision–language models. In practical scenarios, such as rotation, aspect ratio change, motion blur, illumination variation, fast motion, and out of view, our method obtains favorable results compared to the state-of-the-art RGB-based tracker PrDiMP and transformer-based trackers; it also outperforms existing vision–language trackers; though, in some cases, the results are sub-optimal, such as in the background clutter scenario. Although we pay attention to the grid-wise cross-correlation of the template region and the fusion search feature map, the distinction between the foreground and the background is not good enough. There are also some practical scenarios in which our tracker performs poorly, such as in the modality switch, low resolution, and thermal crossover scenarios, since the target cannot be distinguished using the natural language description in the low-resolution frame or the thermal image. In the modality switch and thermal crossover sequences, when the light changes from visible to thermal, the color description of the target immediately becomes infeasible. All the experimental results on the attribute subsets show the advantages and disadvantages of our method. The failure cases inspire us to focus on improving the tracker’s generalization in future work.
4.4.2. Component-Wise Ablation Analysis
We conduct series ablation experiments to illustrate each component’s contribution in our proposed tracker. Table 4 shows the results of the ablation study. Figure 9 shows an activation map of the fusion process.

Table 4.
Ablation experiments results on the LaSOT test dataset. ✓ denotes the component is performed in the model.

Figure 9.
Visualization for component contribution; “” denotes visual attentional feature map; “” denotes simple concatanation; “” denotes visual attentional feature merged with linguistic attentional feature with factorized bilinear pooling.
Note the comparison between ➀ and ➃. The tracker is initialized only by natural language without BBox. The last column in Figure 9 shows that greater weights are put on the target and vicinity area in the fused feature. The surrounding salient regions distinguish the target from the background, acting as target spatial information during the cross-correlation with the template region. Fusion feature maps are used as the search regions, and the second row in Table 4 shows that the tracker obtained a success score of 0.519 and a precision score of 0.517. When natural language annotation does not uniquely describe the target, leading the model to drift away, the tracking performance drops slightly.
Note the comparison between ➁ and ➃. In our proposed multimodal feature alignment module, factorized bilinear pooling has been operated twice. Here, we replaced the second FBP between the language attentional feature and the visual attentional feature by simply concatenating them. The third column in Figure 9 shows the feature activation map. Compared with the fourth column, the target and the vicinity area have drifted away, illustrating the fact that factorized bilinear pooling was only once followed by concatenation with the linguistic attentional feature easily leading to an ambiguous target region. The activation map in the first row, fourth column, shows that the concatenation gives larger attention to the “person” rather than the “skateboard”. The results in Table 4 show that the tracker obtains a success score of only 0.483 and a precision score of only 0.506. Without expansion and squeezing of the visual attentional feature and the visual attentional feature, the learned feature representation has been weakened, resulting in poor tracking performance.
Note the comparison between ➂ and ➃. The language weights map is used to generate the visual attentional feature as usual. Differently to the MFA, the visual attentional features are then merged with the original linguistic features by second factorized bilinear pooling. Table 4 shows that the fusion effect is weakened without the co-attention module. The activation map in the second column in Figure 9 shows the visual grid attention weights distribution, and in the forth column, it shows the activation region in the fused feature. The ablation results show that our co-attention module enhances the weights of the semantically similar patches from the visual and linguistic representations, reflecting the benefits of the linguistic attention features for tracking purposes.
4.4.3. Limitations
Although our proposed MFA tracker achieves quite competitive succession scores and meets real-time requirements, it is still not the absolute best-performing among the state-of-the-art RGB-based trackers and vision–language trackers. One possible reason for this performance difference is that natural language descriptions may not fully characterize the target in some video sequences. For example, sequences like airplane-6 and airplane-10 are annotated with the same sentence, i.e., “airplane flying in the air”; meanwhile, airplane-2 and “airplane-16” are annotated with the same sentence, i.e., “brown airplane flying in the air”. Similarly, airplane-5 is annotated as “airplane flying among other airplanes”. These descriptions do not provide sufficient specific information to distinguish similar targets. Another underlying reason is that long-term video sequences, typically consisting of more than 2000 frames per sequence, are annotated with a single sentence from the first frame to the last frame. As the target undergoes motion throughout the sequence, it cannot always be precisely described by the initial annotation.
5. Conclusions
We present a novel multimodal features alignment (MFA) approach for vision–language object tracking. Unlike prior attempts, we adopt factorized bilinear pooling and an attention mechanism to align visual features and linguistic features by constraining them based on semantic similarities. The weighted fusion feature map takes cross-correlation with the template region in grid-wise level, avoiding ambiguity from anchor boxes. Experiments on public datasets demonstrate that our Siamese MFA tracker achieves competitive results compared with other state-of-the-art vision–language trackers using standard evaluation metrics. When appearance dramatically changes—i.e., through rotation, aspect ratio change, and fast motion scenarios or there is a complex context, i.e., in illumination variation or out of view scenarios—our proposed tracker attains a satisfactory performance even compared with other state-of-the-art RGB trackers. The outstanding performance shows that our multimodal feature alignment is effective in vision–language tracking. Over all, we expect that our method will be useful in enhancing the performance of vision–language fusion trackers. In future works, we will focus on the particular information of visual features and linguistic features, especially for the modeling relationship of inter-modality and inner-modality.
Author Contributions
P.Y.: conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing; G.X.: supervision, reviewing, editing, funding acquisition, project administration; J.L.: visualization and investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61673270, No. 61973212), the Artificial Intelligence Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province under Grant 2022RZY02.
Data Availability Statement
The OTB-LANG dataset utilized in this work is openly available at https://github.com/QUVA-Lab/lang-tracker?tab=readme-ov-file, accessed on 17 May 2018. The LaSOT dataset utilized in this work is openly available at https://github.com/HengLan/LaSOT_Evaluation_Toolkit, accessed on 27 March 2023. The TNL2K dataset utilized in this work is openly available at https://github.com/wangxiao5791509/TNL2K_evaluation_toolkit, accessed on 13 October 2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, B.; Yan, J.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X. High Performance Visual Tracking with Siamese Region Proposal Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8971–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xing, J.; Yan, J. SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese Visual Tracking with Very Deep Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4277–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H.S. Fully-Convolutional Siamese Networks for Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the ECCV Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10 and 15–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. ECO: Efficient Convolution Operators for Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6931–6939. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Guo, S.; Luo, H.; Yao, Y.; Cui, G. A Robust Target Tracking Method for Crowded Indoor Environments Using mmWave Radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Su, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kwong, S. Multi-Stage Visual Tracking with Siamese Anchor-Free Proposal Network. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Ruan, X. Transformer vision-language tracking via proxy token guided cross-modal fusion. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 168, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Li, H. Transformer Meets Tracker: Exploiting Temporal Context for Robust Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribano, C.; Sapienza, D.; Franchini, G.; Verucchi, M.; Bertogna, M. All You Can Embed: Natural Language based Vehicle Retrieval with Spatio-Temporal Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4248–4257. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, W.; Shao, L.; Ling, H.; Porikli, F. Dynamical Hyperparameter Optimization via Deep Reinforcement Learning in Tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Shen, J.; Porikli, F.; Luo, J.; Shao, L. Adaptive Siamese Tracking with a Compact Latent Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 8049–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Yang, R.; Zhang, T.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. Describe and attend to track: Learning natural language guided structural representation and visual attention for object tracking. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.10014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, F. Towards More Flexible and Accurate Object Tracking with Natural Language: Algorithms and Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13763–13773. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Ablavsky, V.; Bai, Q.; Sclaroff, S. Siamese Natural Language Tracker: Tracking by Natural Language Descriptions with Siamese Trackers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 5851–5860. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Kumar, T.; Chen, T.; Su, J.; Luo, J. Grounding-Tracking-Integration. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 3433–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Ablavsky, V.; Bai, Q.; Li, G.; Sclaroff, S. Real-time Visual Object Tracking with Natural Language Description. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2019; pp. 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Ablavsky, V.; Bai, Q.; Sclaroff, S. Robust Visual Object Tracking with Natural Language Region Proposal Network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.02048. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; He, J.; Li, P.; Zhong, S.; Li, H.; He, G. Unified Transformer with Cross-Modal Mixture Experts for Remote-Sensing Visual Question Answering. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Xiang, C.; Fan, J.; Tao, D. Beyond Bilinear: Generalized Multimodal Factorized High-Order Pooling for Visual Question Answering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 29, 5947–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Tian, Q.; Qu, H. ACTNet: A Dual-Attention Adapter with a CNN-Transformer Network for the Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Zhao, W.; Ran, C. DMRFNet: Deep Multimodal Reasoning and Fusion for Visual Question Answering and explanation generation. Inf. Fusion 2021, 72, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tao, R.; Gavves, E.; Snoek, C.G.; Smeulders, A.W. Tracking by natural language specification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6495–6503. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Multimodal Learning via Exploring Deep Semantic Similarity. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15–19 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Fan, J.; Tao, D. Multi-modal Factorized Bilinear Pooling with Co-attention Learning for Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1839–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Fu, C.; Ye, J.; Li, B.; Li, Y. SiamAPN++: Siamese Attentional Aggregation Network for Real-Time UAV Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 3086–3092. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnovik, I.; Moskalev, A.; Smeulders, A.W.M. Scale Equivariance Improves Siamese Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 2764–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Wan, G.; Zhang, W.; Guo, N.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cong, D.; Jia, Y.; Wei, Z. An Integrated Detection and Multi-Object Tracking Pipeline for Satellite Video Analysis of Maritime and Aerial Objects. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, H. Deeper and Wider Siamese Networks for Real-Time Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4586–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. ATOM: Accurate Tracking by Overlap Maximization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4655–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.; Danelljan, M.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Learning Discriminative Model Prediction for Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6181–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Peng, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, D.; Lu, H. Learning Spatio-Temporal Transformer for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10428–10437. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yan, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Lu, H. Transformer Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8122–8131. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, B.; Chang, H.; Ma, B.; Shan, S. Joint Feature Learning and Relation Modeling for Tracking: A One-Stream Framework. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, H.; Jing, L.; Lyu, Y.; Li, B.; Hu, W. Learning target-aware representation for visual tracking via informative interactions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.02526. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, X. High-Performance Long-Term Tracking with Meta-Updater. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6297–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Ahuja, C.; Morency, L.P. Multimodal Machine Learning: A Survey and Taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Li, Y.; Jian, T.; Tian, P.; Roy Chowdhury, K.; Ioannidis, S. Multi-modality Sensing and Data Fusion for Multi-vehicle Detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 2280–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Hazan, T. High-Order Attention Models for Visual Question Answering. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.04323. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. ViLBERT: Pretraining Task-Agnostic Visiolinguistic Representations for Vision-and-Language Tasks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.H.; Yatskar, M.; Yin, D.; Hsieh, C.J.; Chang, K.W. VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.03557. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Duan, N.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, M. Unicoder-VL: A Universal Encoder for Vision and Language by Cross-modal pretraining. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 29–31 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Park, S. AOBERT: All-modalities-in-One BERT for multimodal sentiment analysis. Inf. Fusion 2022, 92, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, H.; Jing, L. Divert more attention to vision-language tracking. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 4446–4460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, K.; He, Z. Joint Visual Grounding and Tracking with Natural Language Specification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 23151–23160. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Ye, Y.; Yu, G. SiamFC++: Towards Robust and Accurate Visual Tracking with Target Estimation Guidelines. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.06188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, R.; Zhu, Y.; Groth, O.; Johnson, J.; Hata, K.; Kravitz, J.; Chen, S.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, L.J.; Shamma, D.A.; et al. Visual Genome: Connecting Language and Vision Using Crowdsourced Dense Image Annotations. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2016, 123, 32–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Lin, L.; Yang, F.; Chu, P.; Deng, G.; Yu, S.; Bai, H.; Xu, Y.; Liao, C.; Ling, H. LaSOT: A High-Quality Benchmark for Large-Scale Single Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5369–5378. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, A.; Park, D.H.; Yang, D.; Rohrbach, A.; Darrell, T.; Rohrbach, M. Multimodal Compact Bilinear Pooling for Visual Question Answering and Visual Grounding. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; He, X.; Buehler, C.; Teney, D.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S.; Zhang, L. Bottom-Up and Top-Down Attention for Image Captioning and Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6077–6086. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Probabilistic Regression for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 7181–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).