Abstract
Rivers are crucial pathways for transporting organic carbon from land to ocean, playing a vital role in the global carbon cycle. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) are major components of dissolved organic matter and have significant impacts on maintaining the stability of river ecosystems and driving the global carbon cycle. In this study, the in situ samples of aCDOM(355) and DOC collected along the main stream of the Songhua River were matched with Sentinel-2 imagery. Multiple linear regression and five machine learning models were used to analyze the data. Among these models, XGBoost demonstrated a superior, highly stable performance on the validation set (R2 = 0.85, RMSE = 0.71 m−1). The multiple linear regression results revealed a strong correlation between CDOM and DOC (R2 = 0.73), indicating that CDOM can be used to indirectly estimate DOC concentrations. Significant seasonal variations in the CDOM distribution in the Songhua River were observed: aCDOM(355) in spring (6.23 m−1) was higher than that in summer (5.3 m−1) and autumn (4.74 m−1). The aCDOM(355) values in major urban areas along the Songhua River were generally higher than those in non-urban areas. Using the predicted DOC values and annual flow data at the sites, the annual DOC flux in Harbin was calculated to be approximately 0.2275 Tg C/Yr. Additionally, the spatial variation in annual CDOM was influenced by both natural changes in the watershed and human activities. These findings are pivotal for a deeper understanding of the role of river systems in the global carbon cycle.
1. Introduction
Rivers, as an important constituent of inland water bodies, play a critical role in sustaining human activities, maintaining the Earth’s ecological carbon cycle, as well as being one of the most important channels for transporting organic carbon from land to sea [1]. The storage, supply, circulation, and transformation of organic carbon in rivers reflect the stability and dynamics of river ecosystems; hence, analyzing river carbon cycles is critical for assessing the health of rivers and their watersheds [2]. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is an important component of the organic carbon pool in water bodies. By converting organic carbon from land to water bodies through dissolution, transportation, and transformation, it is also one of the most important intermediates in the global carbon cycle [3]. Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) is the part of DOC that absorbs UV and visible light, reduces the harmful effects of visible blue light and UV radiation on the aquatic environment, and protects the aquatic ecosystems. CDOM and DOC impact the watershed carbon cycle and ecological environment through various pathways. Their effects are also closely related to land use changes caused by human activities and meteorological factors such as temperature and precipitation [4,5]. The absorption coefficient of CDOM, the main colored organic matter in inland waters, is closely related to the concentration of organic matter in the water column. The CDOM absorption characteristics are recognized as a potential proxy for DOC [6]. DOC, as one of the forms of organic carbon present in water, is useful for the in-depth evaluation of the carbon pool in carbon cycle research. The optical activity of CDOM, including light absorption and scattering, affects the optical properties in the water column. The high absorption of UV and visible blue light, decreasing exponentially with increasing wavelength, significantly affects the properties of the water surface. CDOM has a complex composition, mainly including humic-like substances and proteinaceous materials [7]. To facilitate the measurement and standardized representation of CDOM concentration, the absorption coefficient at 355 nm (aCDOM(355)) is typically used [8]. As the primary colored organic matter in inland water bodies, the CDOM absorption coefficient is closely related to the concentration of organic matter in water. The absorption characteristics of CDOM are also considered a potential proxy measurand for DOC. As one of the main sources of organic carbon in water, DOC aids in the in-depth evaluation of carbon cycle pools. The sources of CDOM in rivers are typically divided into allochthonous and autochthonous. Allochthonous CDOM comprises external materials, such as soil organic matter, plant litter, and humic substances, which are introduced into rivers through runoff and rainfall. Autochthonous CDOM, on the other hand, is produced by the metabolism and decomposition activities of aquatic plants, plankton, and microorganisms [9]. The concentration of CDOM is influenced by human activities and climate change. High CDOM concentrations can reduce light transmission and change water color, thereby affecting photosynthetic efficiency and altering concentrations of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, in water. Additionally, elevated CDOM levels may interact with metallic substances in water, forming toxic compounds that adversely impact aquatic ecosystems and human health. The sources and composition of CDOM in rivers are closely related to their surrounding environments. Densely urbanized areas typically exhibit greater intensity of human activities and pollutant emissions, which significantly impact CDOM concentrations [10]. Numerous studies have demonstrated that different land use types can significantly influence CDOM concentrations. For example, the CDOM in rivers of the Yangtze River Basin is affected by land use types and rainfall [11]. Research in the Yellow River Basin shows that the built-up area significantly affects the composition of river CDOM [12]. Additionally, studies on urban rivers in Tianjin indicate that higher proportions of built-up land areas are associated with higher CDOM concentrations [13]. DOC plays a key role in the global carbon cycle and in the study of aquatic ecosystems [14]. As the total of all dissolved organic carbon in water bodies and terrestrial systems, DOC originates from organic matter (e.g., humus and plant decomposition products) in soils and sediments, metabolic and decomposition products of aquatic plants and plankton, as well as anthropogenic activities (e.g., agricultural runoff and industrial discharges), and it is important for regulating organic carbon stocks and carbon fluxes in water bodies [15]. In water bodies, CDOM, as a subset of DOC, is optically active, and this optical property allows CDOM to be identified and quantified by remote sensing inversion. Numerous studies revealed a strong positive correlation between CDOM and DOC, which makes CDOM an important method for indirectly inferring DOC distribution and change [5,16]. By utilizing the optical properties of CDOM, the spatial and temporal dynamics of DOC can be further monitored, thus revealing the cycling process and the changing law of organic carbon in the water system. In addition, CDOM is a key indicator of water quality, biogeochemical status, and nutrient enrichment [17].
In recent years, the use of machine learning, empirical, semi-empirical, and semi-analytical algorithms to estimate water quality has become increasingly popular. Meanwhile, employing remote sensing images such as Sentinel, Landsat, MODIS, and drones to monitor long-term water quality in various inland water bodies has become normal practice [18]. Common water quality indicators include chlorophyll concentration (Chl-a), dissolved oxygen (DO), water turbidity, total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), total suspended solids (TSMs) and CDOM [19]. In recent years, there has been an increase in the remote monitoring of water quality in rivers; nonetheless, the majority of these studies focused on urban and small to medium-sized rivers with little attention paid to large rivers affected by human activities. Sentinel-2 provides high-resolution images (10 m, 20 m, and 60 m) with a short revisit duration (5 days), with worldwide land and ocean coverage. The data encompass 12 spectral radiation bands. The flow velocity and river breadth of the Songhua River are very variable; therefore, Sentinel-2’s excellent spatial resolution and short revisit interval are ideal for the remote sensing picture monitoring of the Songhua River. In recent years, machine learning models have been used in a variety of water color remote sensing studies. Traditional methods for monitoring river CDOM and DOC are time-consuming and labor-intensive, making it difficult to achieve comprehensive spatio-temporal monitoring. However, remote sensing by Sentinel, Landsat, MODIS, and drones for monitoring CDOM and DOC concentrations in various inland water bodies has provided a practical alternative. In recent years, the number of methods available for the remote monitoring of CDOM have increased, with most of them employing machine learning, empirical, semi-empirical, or semi-analytical algorithms. For instance, researchers adopted an empirical model to estimate CDOM and DOC in Tibetan Plateau lakes [20], a machine learning model was used to remotely monitor aCDOM(440) in the Xin’anjiang Reservoir, whereas Ayad et al. (2020) estimated CDOM in the Tijuana River using a quasi-analytical algorithm [21]. Despite the expansion of research on CDOM and DOC monitoring in recent years, most studies have focused on reservoirs and lakes, with little attention given to large rivers significantly affected by human activities. However, using remote sensing to monitor river CDOM is essential. Given the significant variations in the flow velocity and width of the Songhua River, Sentinel-2’s high spatial resolution and short revisit interval make it the ideal choice for the remote monitoring of the Songhua River.
The Songhua River is the third largest inland river in China after the Yangtze River and the Yellow River, flowing through provinces such as Heilongjiang and Jilin. As one of the important water systems in Northeast China, the Songhua River provides drinking, irrigation, and industrial water for tens of millions of people, supporting industrial and agricultural production, maintaining regional ecosystems, and playing a crucial role in economic development and residents’ lives. CDOM is important for the monitoring of river water quality parameters because its content and characteristics are closely related to the source and composition of organic matter in the water body. It can be used to analyze the source and distribution of organic pollutants as well as reflect changes in the aquatic environment. An accurate estimation of CDOM and DOC concentrations in the Songhua River is therefore essential for analyzing the distribution of organic pollution in the river and for determining the effects of anthropogenic and environmental factors in inland waters on organic matter in the water column. CDOM can reveal the sources and distribution of organic pollution, reflect changes in water environment, and expose the main sources and factors influencing dissolved organic matter (DOM) in watersheds, providing a scientific basis for carbon cycling and environmental monitoring. Therefore, accurately estimating the concentrations of CDOM and DOC in the Songhua River is essential for analyzing the distribution of organic pollution and determining the impacts of human and environmental factors on organic matter in inland water bodies. The objectives of this study are (1) to develop a general model for the CDOM absorption coefficient retrieval in the Songhua River; (2) to quantify the relationship between CDOM and DOC to be able to obtain the distribution of DOC indirectly; (3) to understand the spatial and temporal variations in CDOM and DOC in the main stream of the Songhua River; and (4) reveal how the natural factors and human activities contribute to the variations in DOM in the Songhua River.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Area
The Songhua River is the third largest river in China. It originates from the intersection of the Nen River and the Second Songhua River in Changbai Mountain and runs a total length of 2214.3 km with a drainage area of 556,804 km2 [22], passing through Jilin and Heilongjiang provinces. The source area is located in Tianchi, Changbai Mountain, flowing through the four coastal cities of Jilin, Songyuan, Harbin, and Jiamusi, and finally entering Heilongjiang. The Songhua River is the main source of fresh water for industry, agriculture, animal husbandry, and drinking water for residents [23]. The Songhua River Basin is located at a higher latitude in the northeast with vast land and a diverse climate [24]. The continental climate of the Songhua River Basin is significant. The temperature difference is large during the year. The average annual temperature is 3–5 °C, and the annual precipitation is 370–830 mm. Affected by the temperate monsoon climate, the precipitation varies greatly in season. The annual precipitation is mainly in the rainy season (June–September), accounting for 60–80% of the year. The Songhua River Basin is also regarded as one of the three black soil areas in the world. It is famous for its particularly fertile black soil. It is an important agricultural and forestry production base in China [25], with arable land accounting for 20% of the country’s arable land [26]. China’s largest industrial base is located in the Songhua River Basin, which is rich in coal, minerals, and other resources. It discharges about 4.852 billion tons of domestic and industrial wastewater into the basin every year [27].
2.2. Field Sampling and Laboratory Measurements
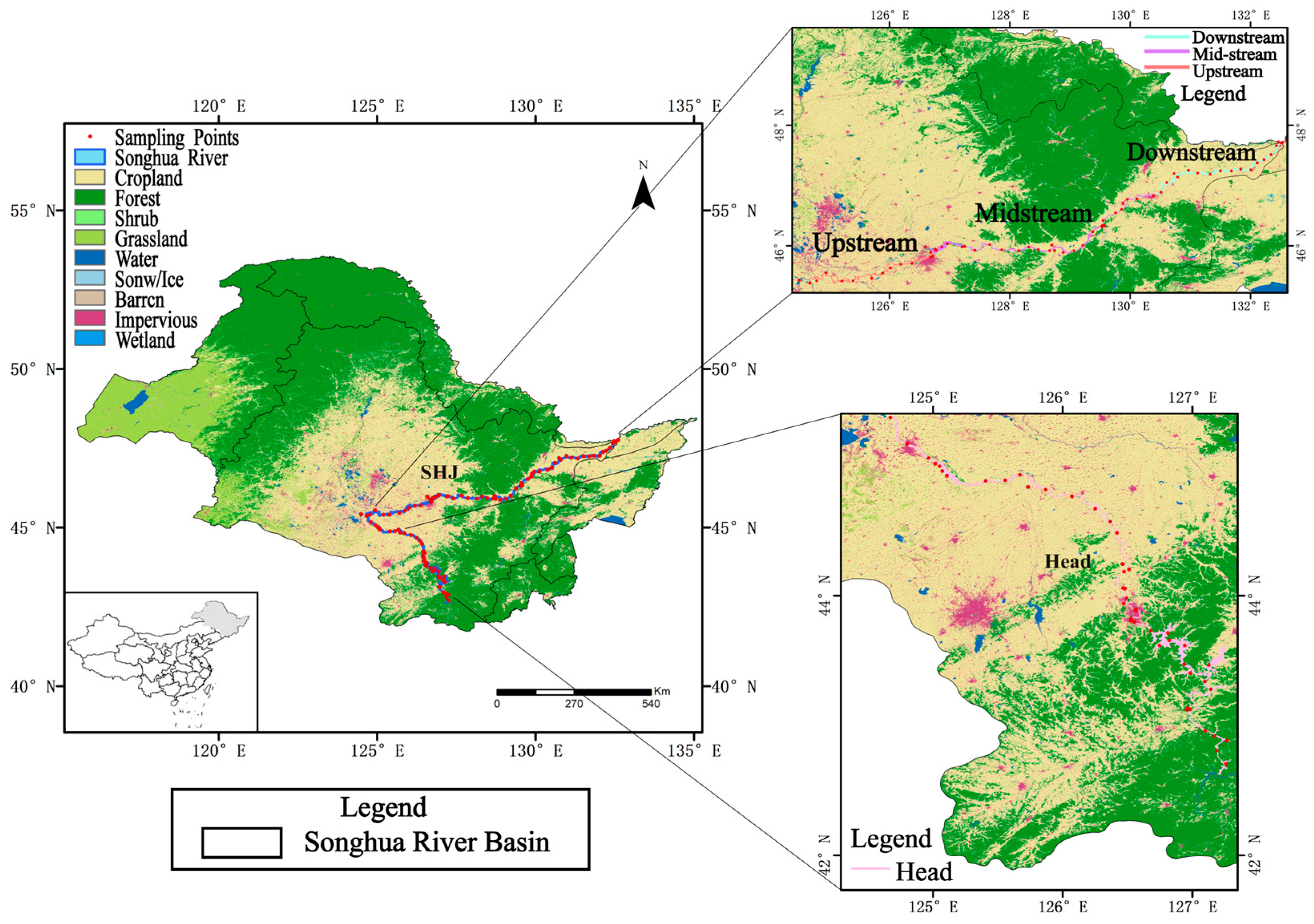
The Songhua River was sampled in the time periods of August–September 2021 and July–December 2022, with surface water samples collected from 69 sites in 2021 and 99 sites in 2022, for a total of 168 active sampling sites (Figure 1). Temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), salinity, turbidity, chlorophyll, etc., were measured at each sampling point using a YSI multi-parameter water quality meter (YSI EXO2) in the field. The location and elevation of each sampling point were recorded using a hand-held GPS. Water samples were collected approximately 0.2 m below the surface of the water layer at each sampling point. A 3 L water sample was collected in a clean PET plastic bottle. On the same day, water samples were filtered using a hybrid fiber peninsula (0.45 μm) and stored in a portable refrigerator at 4 °C.
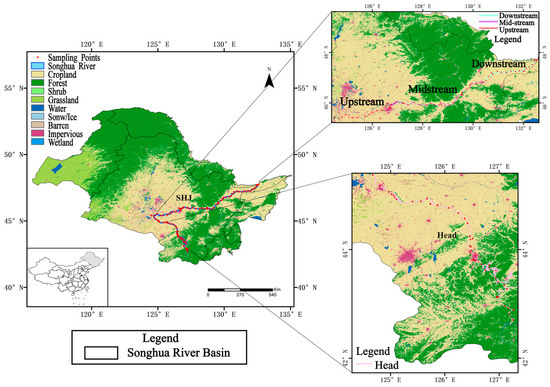
Figure 1.
Location of sampling points along Songhua River. All experimental sampling points are set in the main stream of the Songhua River, excluding small headwaters and tributaries within the watershed. The sampling points are distributed according to the Songhua River basin and divided into the following areas: “Head” represents the source of the Songhua River, “Upstream” represents the upper reaches of the main stream of the Songhua River, “Midstream” represents the middle reaches of the main stream of the Songhua River, and “Downstream” represents the lower reaches of the main stream of the Songhua River.
Total organic carbon DOC concentrations in filtered water samples were measured in the lab using a TOC-VCPN (Shimadzu, Japan) total organic carbon analyzer. To obtain a CDOM test water sample, the first filtered water sample must be filtered again using a 0.22 μm polycarbon dioxide chemical microporous filter membrane to find the absorption coefficient of CDOM. Using a Shimadzu Visible Spectrophotometer (UV2660) to measure the absorbance of the CDOM test water sample in the 200–800 nm wavelength range and a Milli-Q pure water as a reference, the absorption coefficient of CDOM was computed using the following formula:
where L is the optical path length (1 cm), and () the measured absorption density. CDOM absorbs light most strongly in the ultraviolet to blue wavelength bands, decreasing to near zero in the red wavelength band as the wavelength increases [28]; the absorption coefficient at 355 nm (aCDOM(355)) was used in this study to express the content of CDOM. The aromaticity of CDOM can be expressed by SUVA 254, and the SUVA 254 (Specific UV absorbance) can be calculated by dividing the absorption coefficient of CDOM at 254 nm by the concentration of DOC [29].
2.3. Model Calibration and Validation
The Sentinel-2A series of satellites are capable of providing images with a spatial resolution of 10 m, with a global revisit frequency of 5 days and containing 12 spectral bands. Sentinel 2 images were used in this study. Surface reflectance is the ratio between the amount of radiation reflected from a surface and the amount of incident solar radiation, reflecting the surface ability to reflect solar radiation. The Sentinel-2 datasets are the bottom-of-atmosphere reflectance generated by processing the Sentinel-2 Level-1C raw image data using the Sen2Cor application [30]. Using the GEE platform, cloud-free imagery was selected on the same day or within a week, and rocker reflectance was extracted from the sampling sites using the Arcgis 10.7 software.
The in situ CDOM coefficient of aCDOM(355) was matched with the corresponding Sentinel-2 remote sensing reflectance from the GEE platform. Two-thirds of datasets were used to test the established model, and one-third of the data for model validation. CDOM absorbs the blue band strongly; thus, bands B1–B5 with the highest correlation with CDOM were selected as input variables of the model, encompassing the wavelengths from 443 nm to 704 nm. The calibration, validation, and error analysis were performed using remote sensing bands, and a batch inversion of images was performed after the model was complete. To build a suitable CDOM identification model for the Songhua River, a correlation analysis between distant remote sensing bands and absorption coefficients was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26. The remote sensing bands included a single band, band ratios, and multi-band combinations.
This study employs five advanced machine learning techniques to establish the CDOM estimation model. The models include the Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT), which enhances accuracy and robustness by sequentially building decision trees that correct the errors of their predecessors [31]; eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), a scalable implementation of gradient boosting that incorporates regularization to prevent overfitting and effectively handle large-scale datasets [32]; Support Vector Regression (SVR), which captures complex data relationships by finding a function that deviates from actual observations by no more than a specified margin [33]; the Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN), which uses the back propagation algorithm to iteratively adjust weights and capture non-linear patterns through its multi-layer architecture [34]; and the Random Forest (RF), an ensemble method that constructs numerous decision trees during training and aggregates their predictions to improve generalization and reduce the risk of over fitting [35]. This comprehensive analysis elucidated the strengths and limitations of each technique in the context of CDOM estimation from satellite images.
2.4. Other Datasets
To analyze the impact of human activities and environmental factors on colored CDOM and DOC in the Songhua River, we compiled several key datasets. These include land use raster data, meteorological data (precipitation, temperature, wind speed), population raster data, and flow data from major stations along the Songhua River. The land use datasets were sourced from the 1990–2019 annual 30 m land cover datasets of China [36]. The temperature and wind speed data were obtained from the China Meteorological Elements Monthly Spatial Interpolation Datasets, published by the Resource and Environmental Science Data Registration and Publishing System (http://www.resdc.cn/DOI), 2022. DOI:10.12078/2022090901 (accessed on 1 December 2023). Population data were derived from the 10 m resolution raster datasets developed by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory of the U.S. Department of Energy (https://landscan.ornl.gov/LandScan) (accessed on 1 December 2023). Precipitation data were sourced from the high-quality, high spatial-temporal resolution precipitation datasets for Asia, published by the National Tibetan Plateau Data Center [37]. Additionally, the monthly average flow of the Songhua River in 2022 was compiled and analyzed based on real-time flow data from major rivers across the country, as published by the Ministry of Water Resources Information Center (http://xxzx.mwr.gov.cn) (accessed on 1 December 2023). Finally, for the model establishment, the Songhua River was segmented into urban and non-urban sections within the municipalities of Jilin, Songyuan, Harbin and Jiamusi, based on the delineation of urban areas and townships defined by the respective municipal authorities. These datasets provide a solid foundation for analyzing the sources and distribution of CDOM and DOC in the Songhua River. This segmentation was based on the delineation of urban areas and townships as defined by the respective municipal authorities.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
This article utilizes the correlation coefficient (R) and root mean square error (RMSE) as metrics to determine and analyze the accuracy and predictive ability of the constructed machine learning models. The R measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between predicted and actual values. The RMSE quantifies the extent of prediction errors, calculated as the square root of the average of the squared differences between predicted and actual values. A lower RMSE indicates better model performance, showing smaller deviations between predicted and actual values. Together, the correlation coefficient and RMSE provide a comprehensive assessment of model performance. These metrics are used to evaluate and compare the accuracy and predictive capabilities of different machine learning models in predicting CDOM concentrations.
To analyze the factors influencing CDOM in the Songhua River, we organized raster datasets for meteorological, population, and land use data from May to October, corresponding to the ice-free period. We calculated the annual averages for these monthly data. Using a nine-level basin division method from a referenced article, we partitioned the Songhua River into 108 sub-basins. Within each sub-basin, we conducted a statistical analysis of land use types and various driving factors. The annual average CDOM values for the different sub-basins were treated as dependent variables. To assess the significance of natural and anthropogenic driving factors on CDOM values, we performed an ANOVA using a multiple linear regression model in R. Finally, we determined the contribution rates of different factors based on standardized regression coefficients and regression equations.
3. Results
3.1. In Situ Measurement of CDOM and DOC in Songhua River
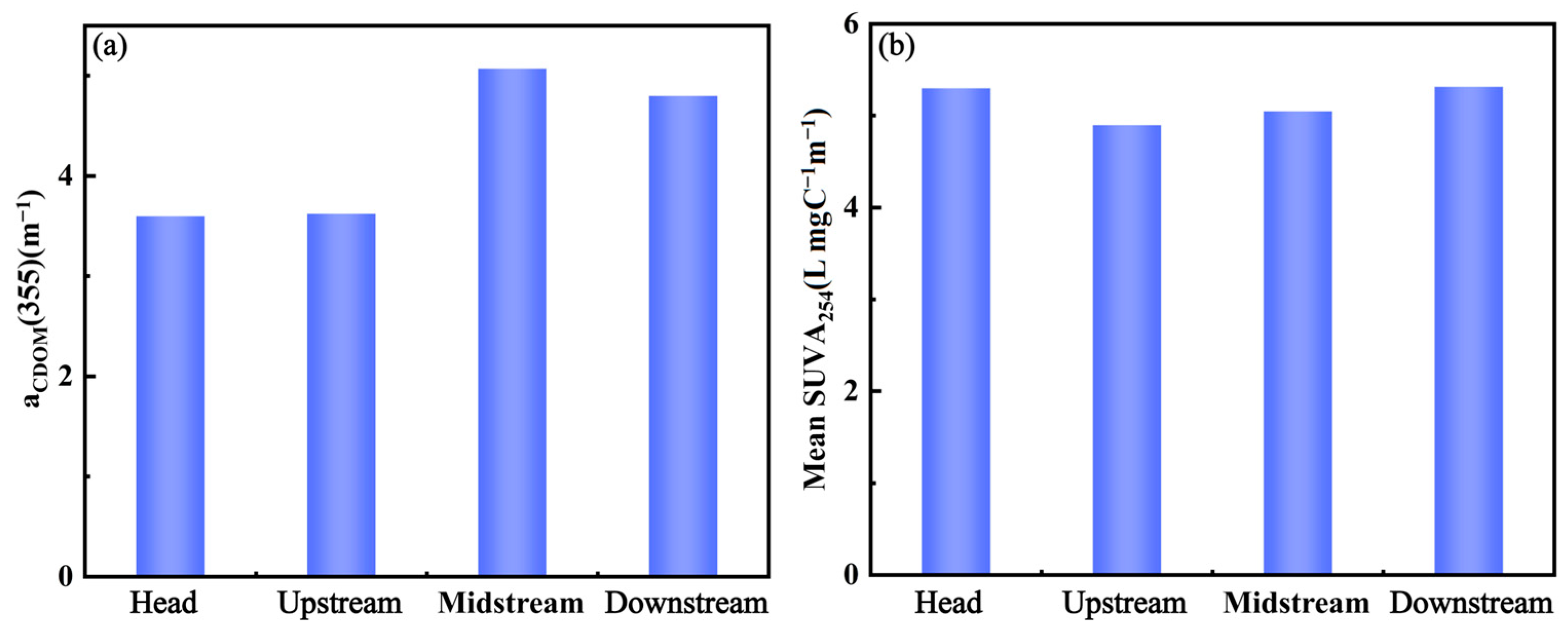
The range of in situ measured aCDOM(355) of the river main stream was 1.34 to 7.55 m−1. The mean concentrations of CDOM and in the Songhua River are shown in Figure 2. The downstream trend of aCDOM(355) from the source showed first an increase and then a decrease, with the lowest concentration at the annual average source concentration (3.60 ± 1.47 m−1) and the highest concentration in the annual average midstream concentration (5.08 ± 1.06 m−1). The overall trend was consistent with the aCDOM(355) concentrations from the remote sensing images. As shown in Figure 2, the average concentrations ranged from 4.99 to 5.47 L·mg−1m−1, with the maximum concentration at the source (5.47 ± 1.99 L·mg−1m−1) and the lowest in the upstream (4.99 ± 0.89 L·mg−1m−1). The concentration increased monotonically from upstream to downstream.
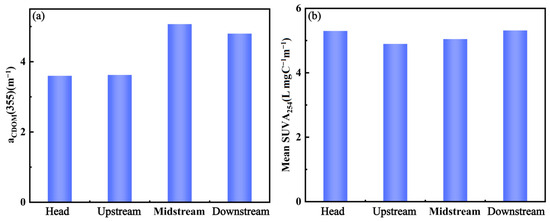
Figure 2.
Distribution of aCDOM(355) (a) and SUVA254 (b) along Songhua River.
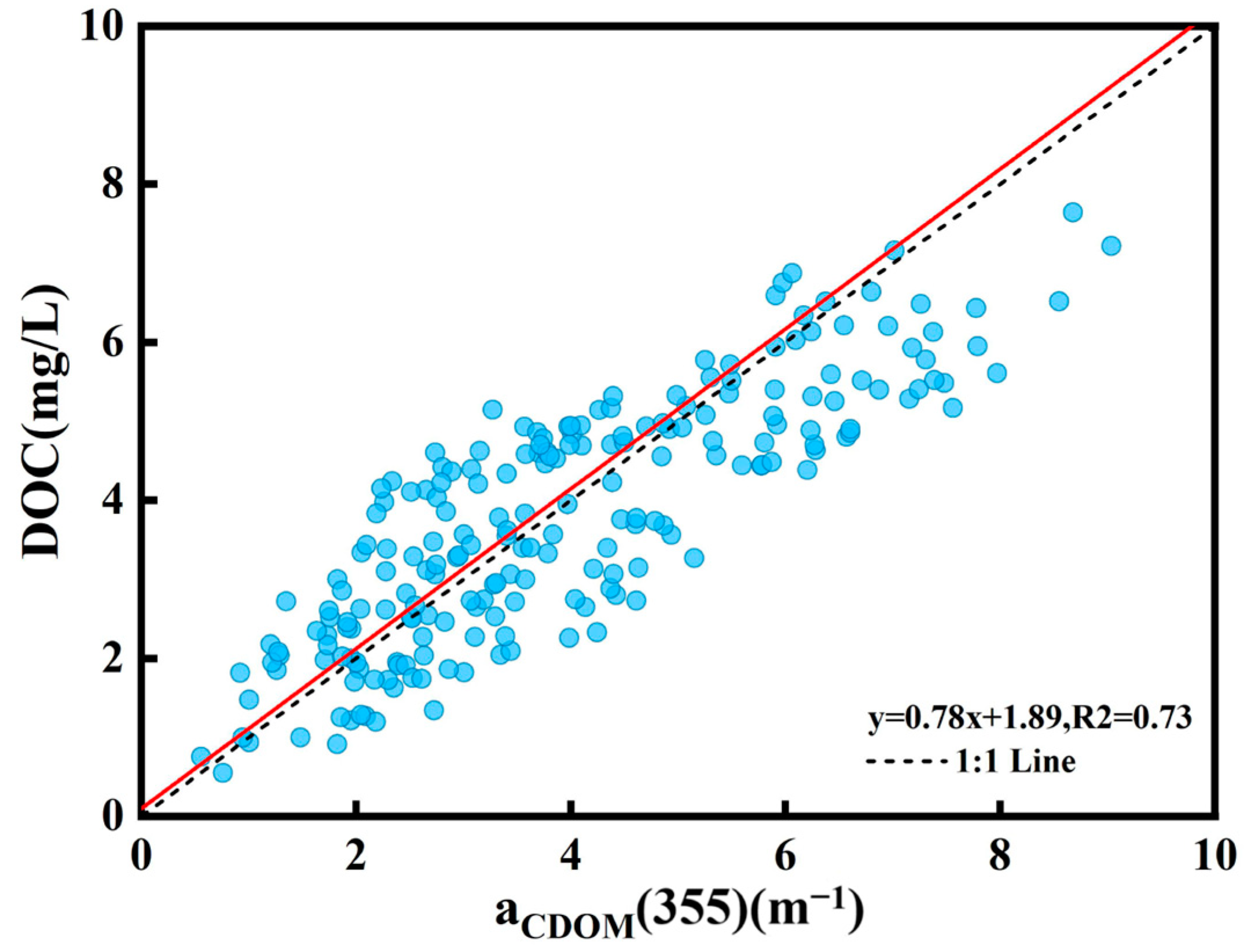
Based on the laboratory analysis of field samples, the mean DOC concentration in the Songhua River was 4.12 ± 1.57 mg/L, with a range of 0.55 to 7.15 mg/L. There was a substantial linear association between the aCDOM(355) absorbance and DOC concentration at the 355 nm wavelength, and the linear model precision was good and consistent with earlier research. Based on the strong correlation between the absorption coefficient of colored dissolved organic matter at 355 nm (aCDOM(355)) and the concentration of DOC observed in field collections (R2 = 0.73, p < 0.01), an empirical linear model was developed to estimate the concentration of DOC. The empirical model is shown in Figure 3:
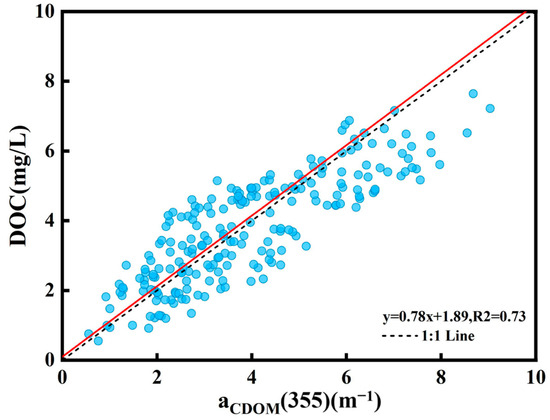
Figure 3.
Linear relationship between DOC and aCDOM(355) in main stream of Songhua River.
3.2. Model Calibration and Validation of CDOM and DOC
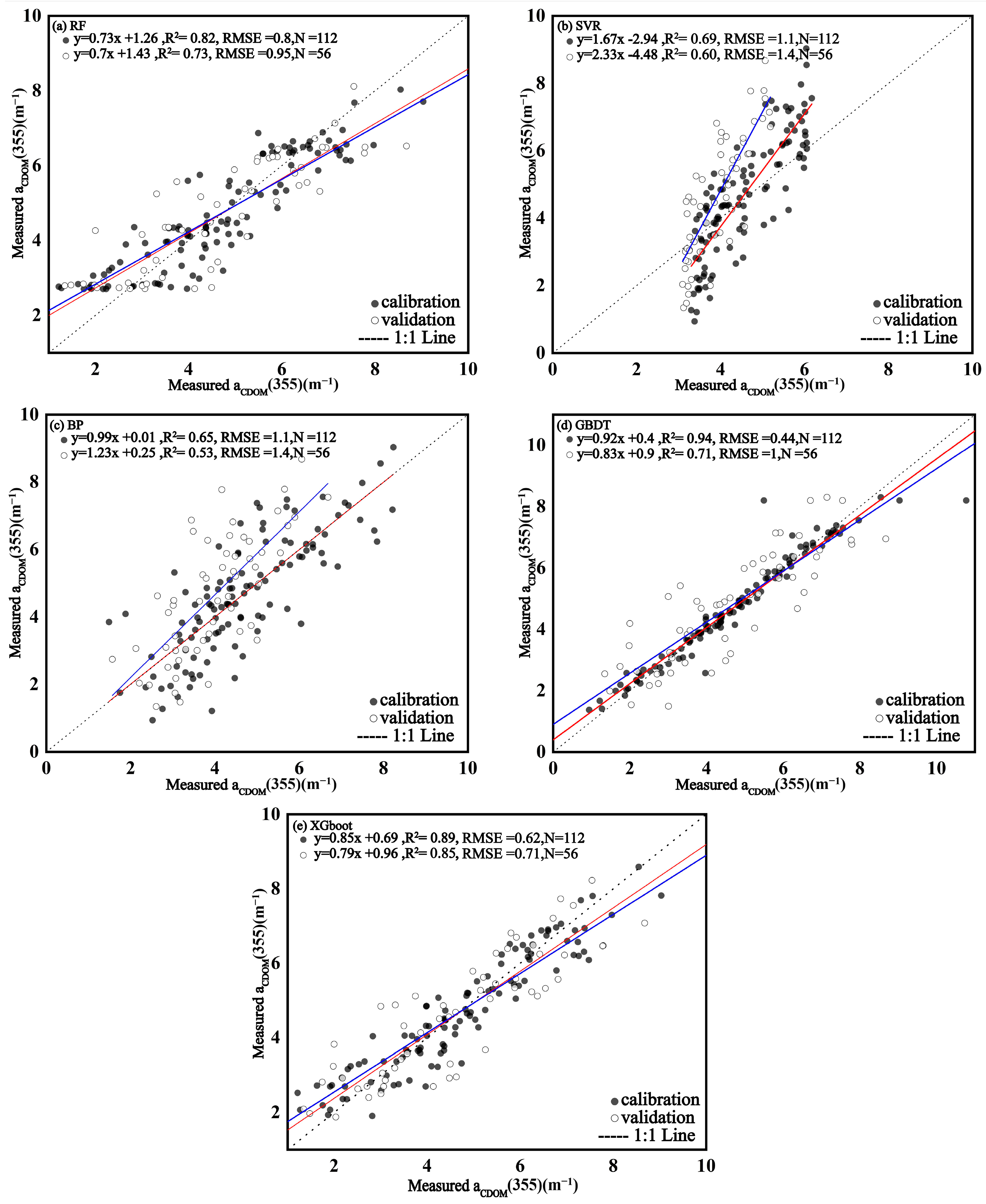
We used the Matlab 2022 software to fit the relationship between the CDOM absorption coefficient aCDOM(355) and the reflectance bands of Sentinel 2, selecting the remote sensing bands B1–B5 with high correlation among them or various band combinations to build a model for aCDOM (355) using the R studio software https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/. It was found that the band combinations [(B1 × B2)/((B3 + B2) + (B4 × B1))] had the highest correlation (R2 = 0.74). By comparing the linear models (Table 1) trained using a band combination and a single band into the machine learning model (Table 2), it was found that the machine learning results had higher correlation and stability than the linear model; thus, the machine learning models were preferred. The XGBoost model training and validation had (R2 = 0.89) and (R2 = 0.85), respectively, and outperformed the remaining machine learning models (as shown in Figure 4). Therefore, the XGBoost machine learning model was adopted for aCDOM(355) mapping to CDOM concentrations in the Songhua River.

Table 1.
This study examines the performance of different Sentinel-2 band combinations in the Songhua River.

Table 2.
Accuracy assessment of modeling and validation of machine learning algorithms.
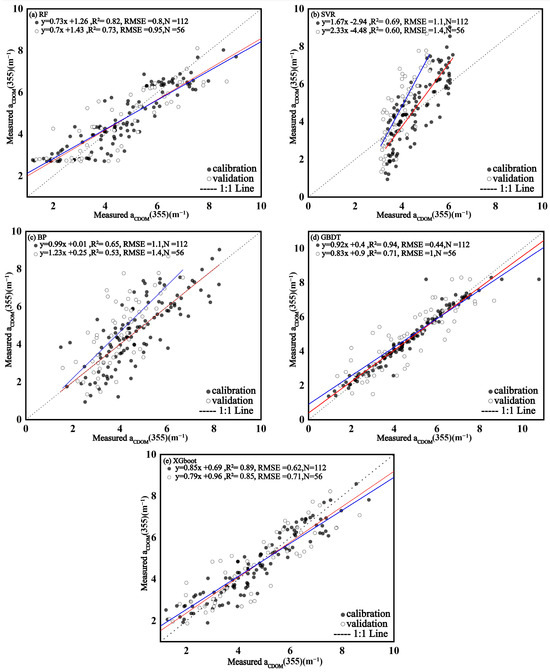
Figure 4.
Calibration and validation of different algorithm models for aCDOM(355) in the Songhua River: (a) Random Forest (RF); (b) Support Vector Regression (SVR); (c) Back Propagation Neural Network (BP); (d) Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT); and (e) eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost).
3.3. The Spatial and Temporal Distribution of CDOM in Songhua River
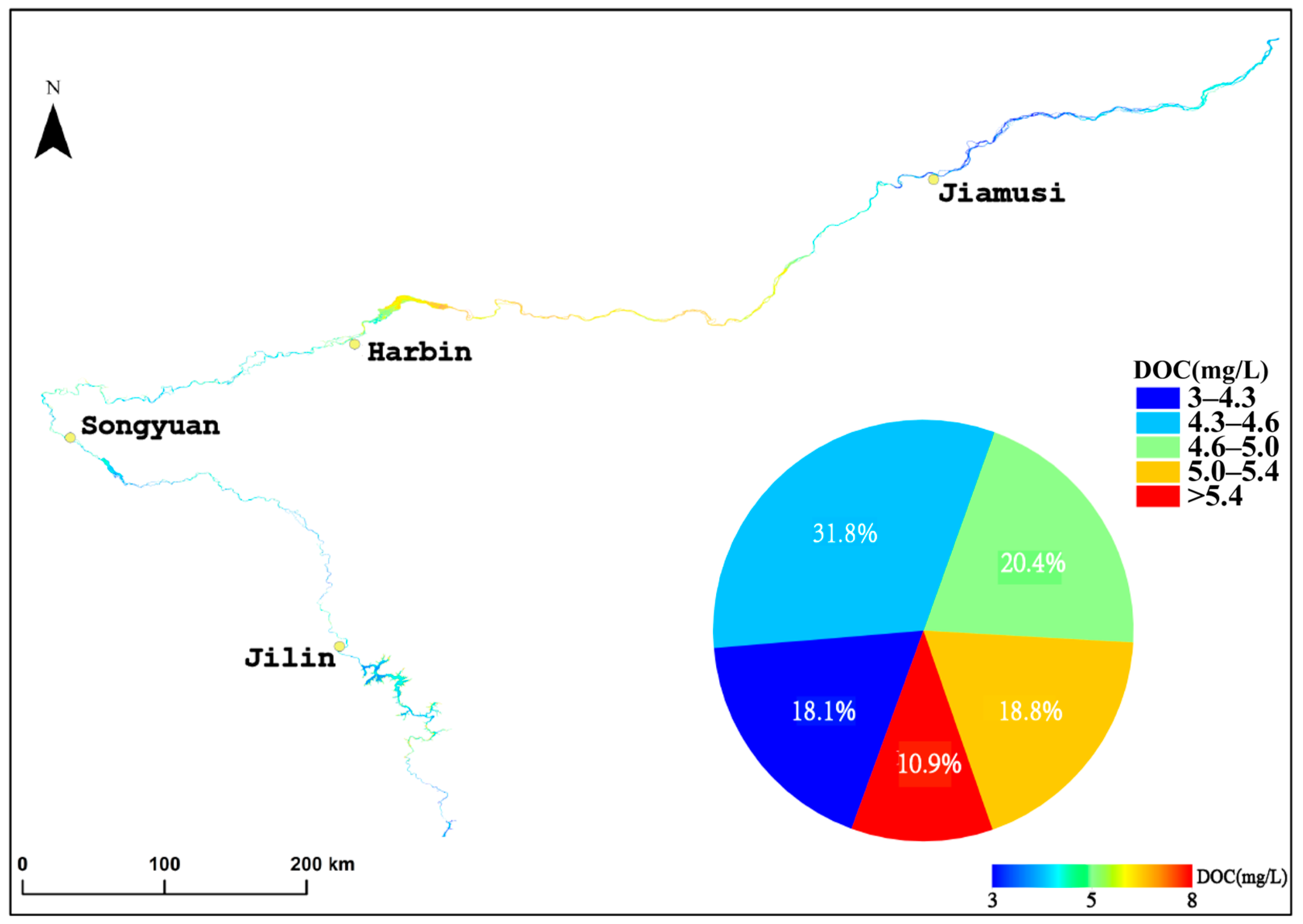
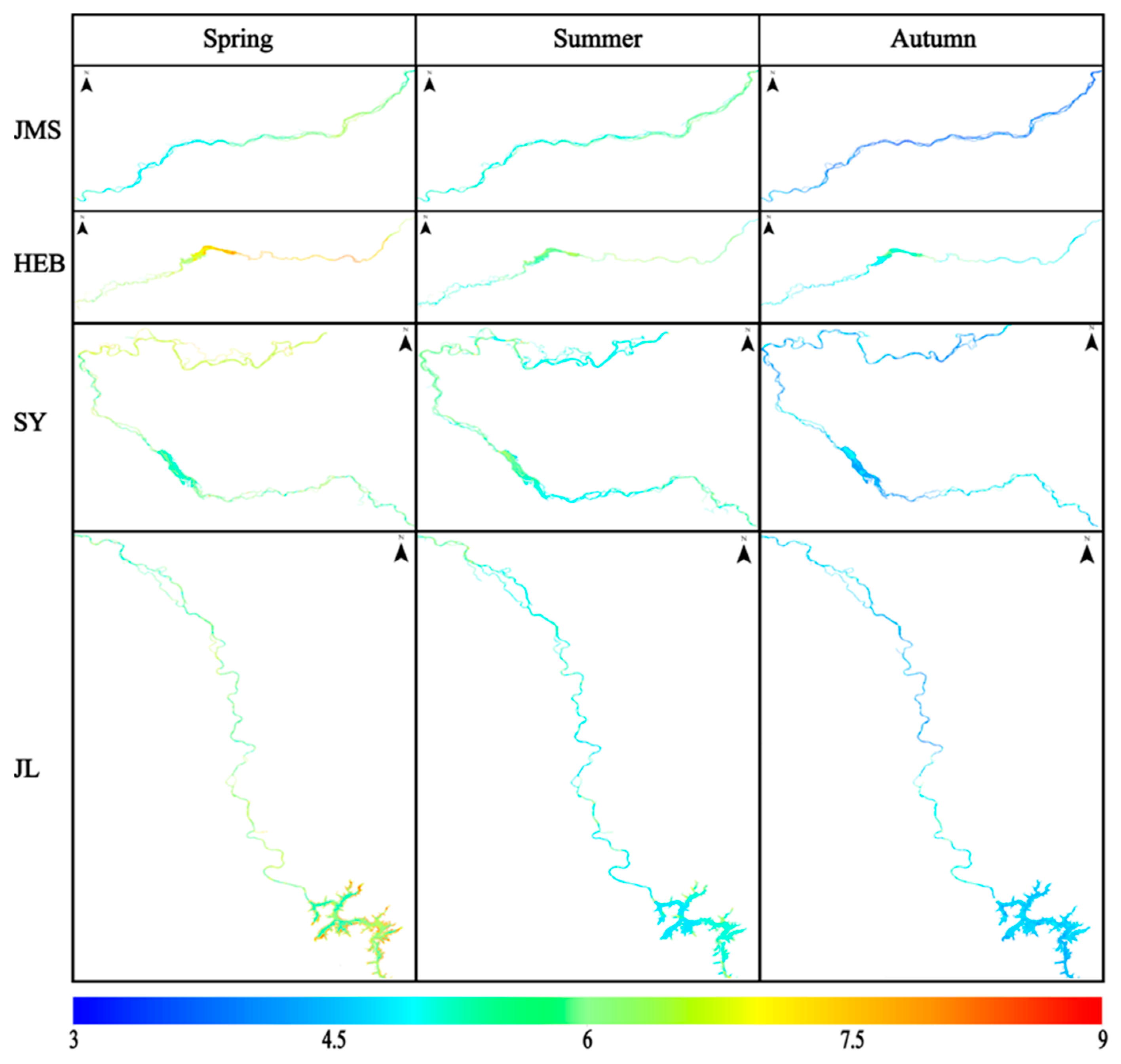
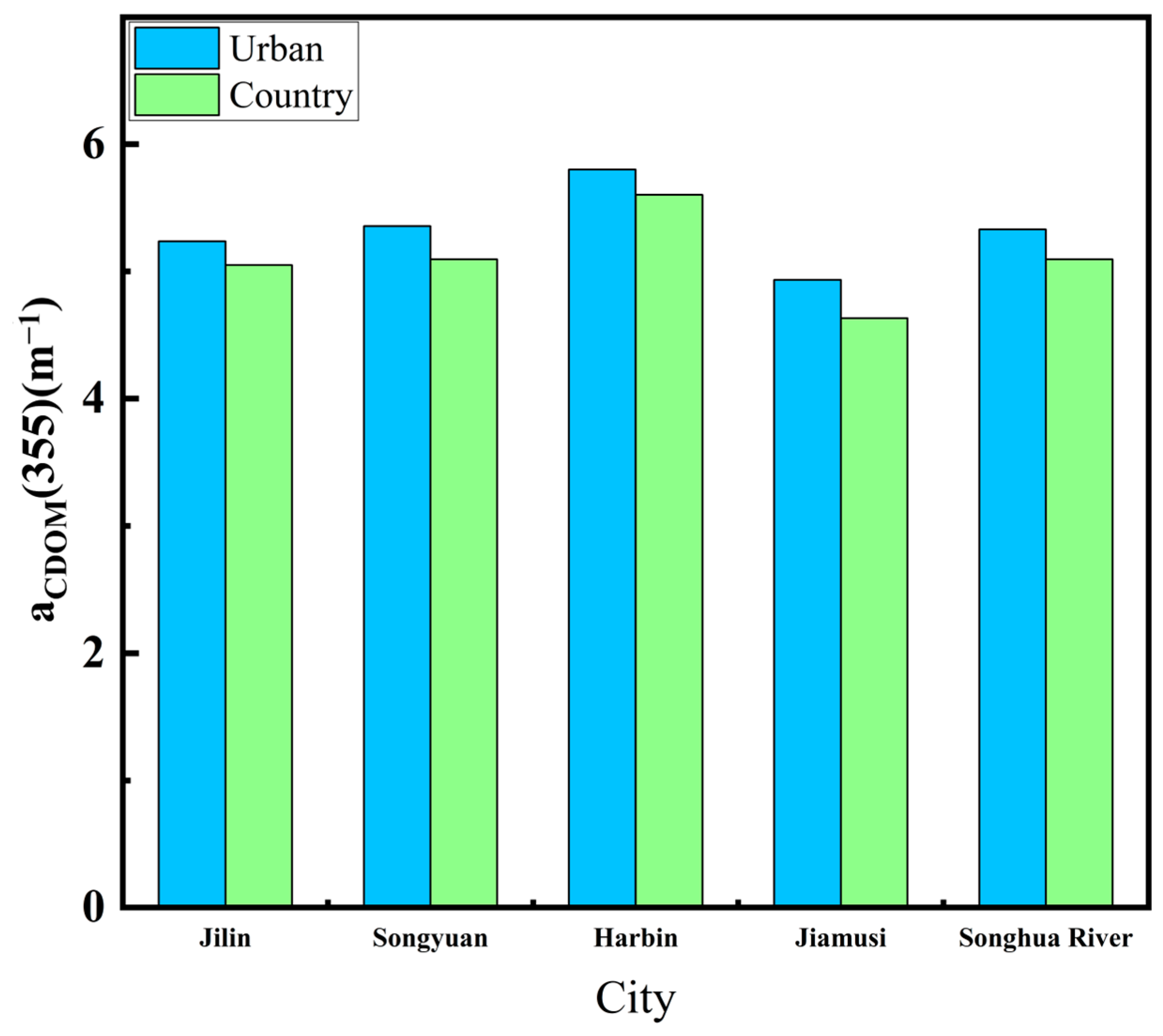
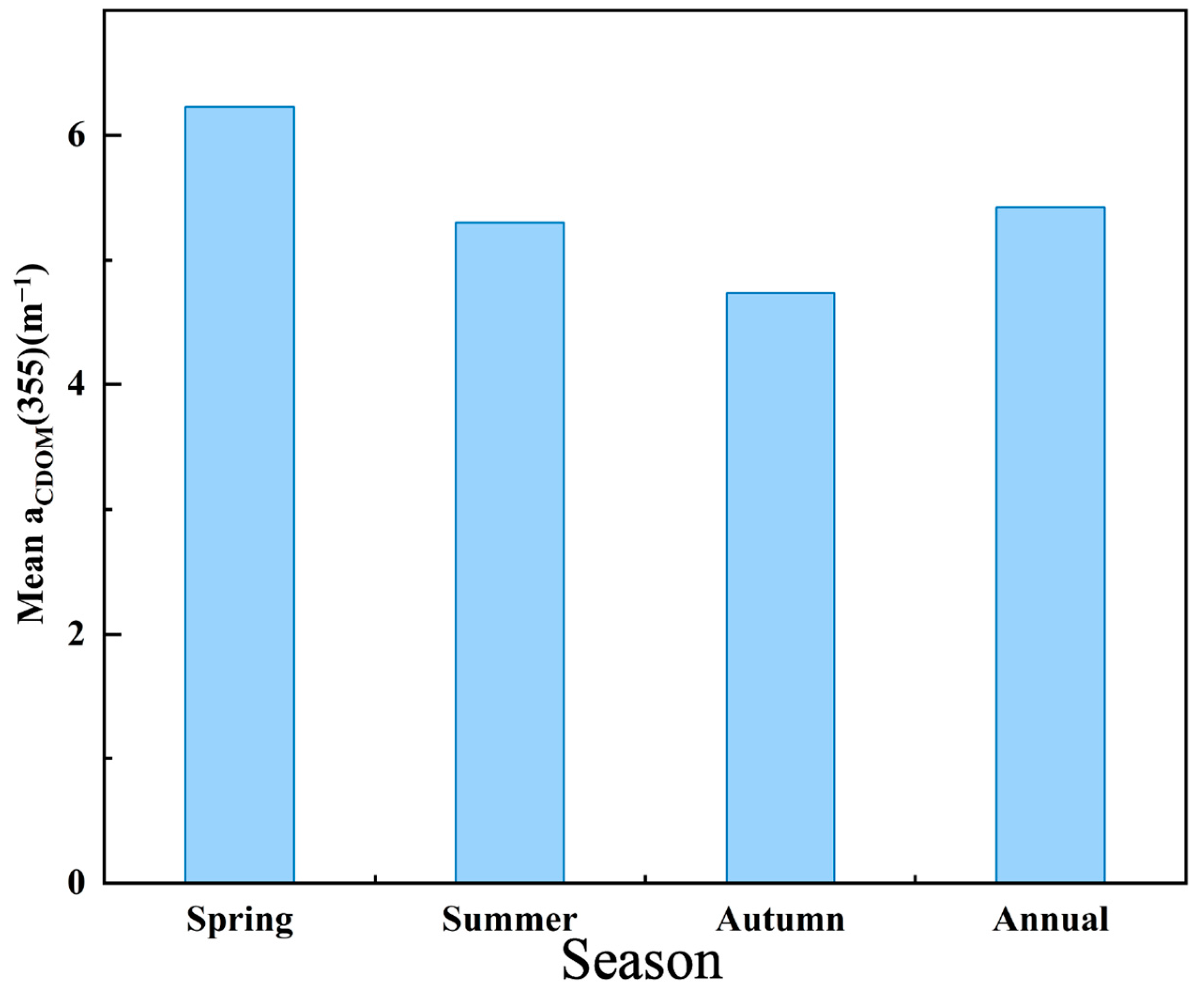
We selected the non-glacial (May to October), cloud-free, or less than 10% cloudy images of the Songhua River taken in 2022. The images were fused and spliced, the NDVI algorithm was used to produce the raster vectors of the Songhua River in the images. Then, the raster vectors of the Songhua River were extracted by cropping out the sections of the Songhua River. The XGBoost model established previously was finally used to process images for each monthly mean. The aCDOM(355) values obtained from the images were then fused with the monthly inverted images, and the Songhua River DOC was inverted using the empirical model mentioned in Section 3.1 (Figure 3) to establish the DOC values for the whole year of 2022 (Figure 5). Figure 6 shows the inversion results for each city section (Jilin, Songyuan, Harbin, and Jiamusi) of the Songhua River in 2022. Figure 7 shows that the lowest annual aCDOM(355) absorption coefficients were, respectively, 4.935 m−1 and 4.633 m−1 for the urban and non-urban sections of the Songhua River in Jiamusi, whereas the highest were 5.802 m−1 and 5.603 m−1 in Harbin, with aCDOM(355) absorption coefficients of 5.332 m−1 and 5.096 m−1 for the urban and non-urban sections of the Songhua River, respectively. The non-glacial period (May to October) of the Songhua River was divided into three seasons, spring, summer, and fall, with spring in May, summer in June, July, and August, and fall in September and October. The inverted aCDOM(355) value images for each month were statistically processed using mean fusion to find out the changes in the mean value of aCDOM(355) between different seasons as shown in Figure 8. The mean value in spring (6.23 m−1) was the largest, followed by summer (5.30 m−1) and autumn (4.74 m−1). The mean annual value of aCDOM(355) was 5.40 m−1.
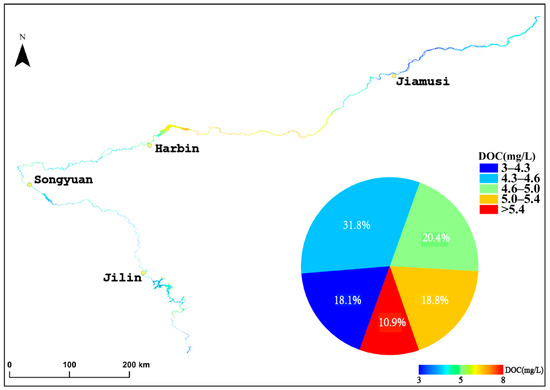
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of the annual average dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration in the Songhua River Basin in 2022.
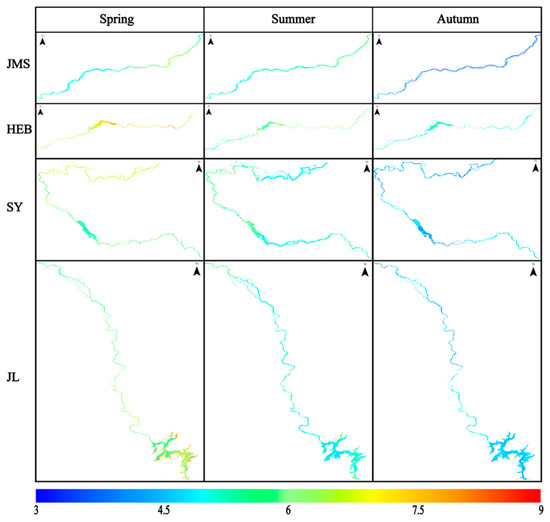
Figure 6.
Spatio-temporal distribution of aCDOM(355) in the main stream of the Songhua River. (Note: JMS represents the Jiamusi section of the Songhua River; HEB denotes the Harbin section; SY refers to the Songyuan section; and JL indicates the Jilin section.)
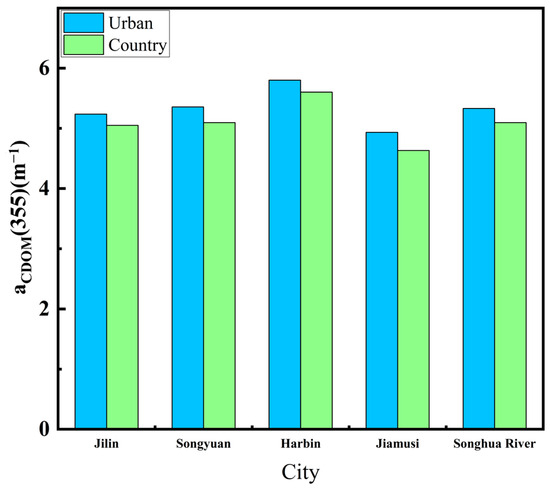
Figure 7.
Annual mean values of aCDOM(355) in urban and non-urban sections of Songhua River flowing through each city.
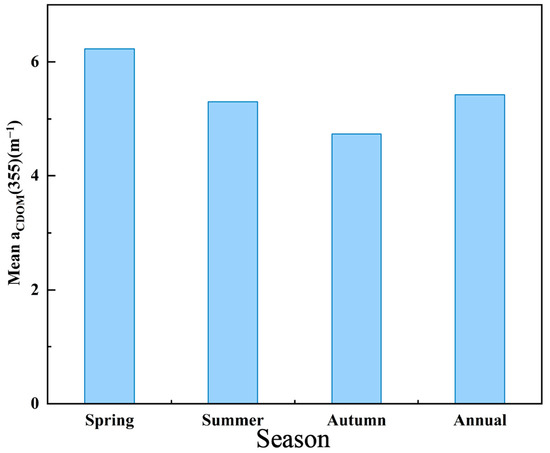
Figure 8.
Mean values of aCDOM(355) in main stream of Songhua River during non-glacial periods (spring, summer, autumn) and throughout entire year (annual).
3.4. The Factors Contributed to CDOM of Songhua River
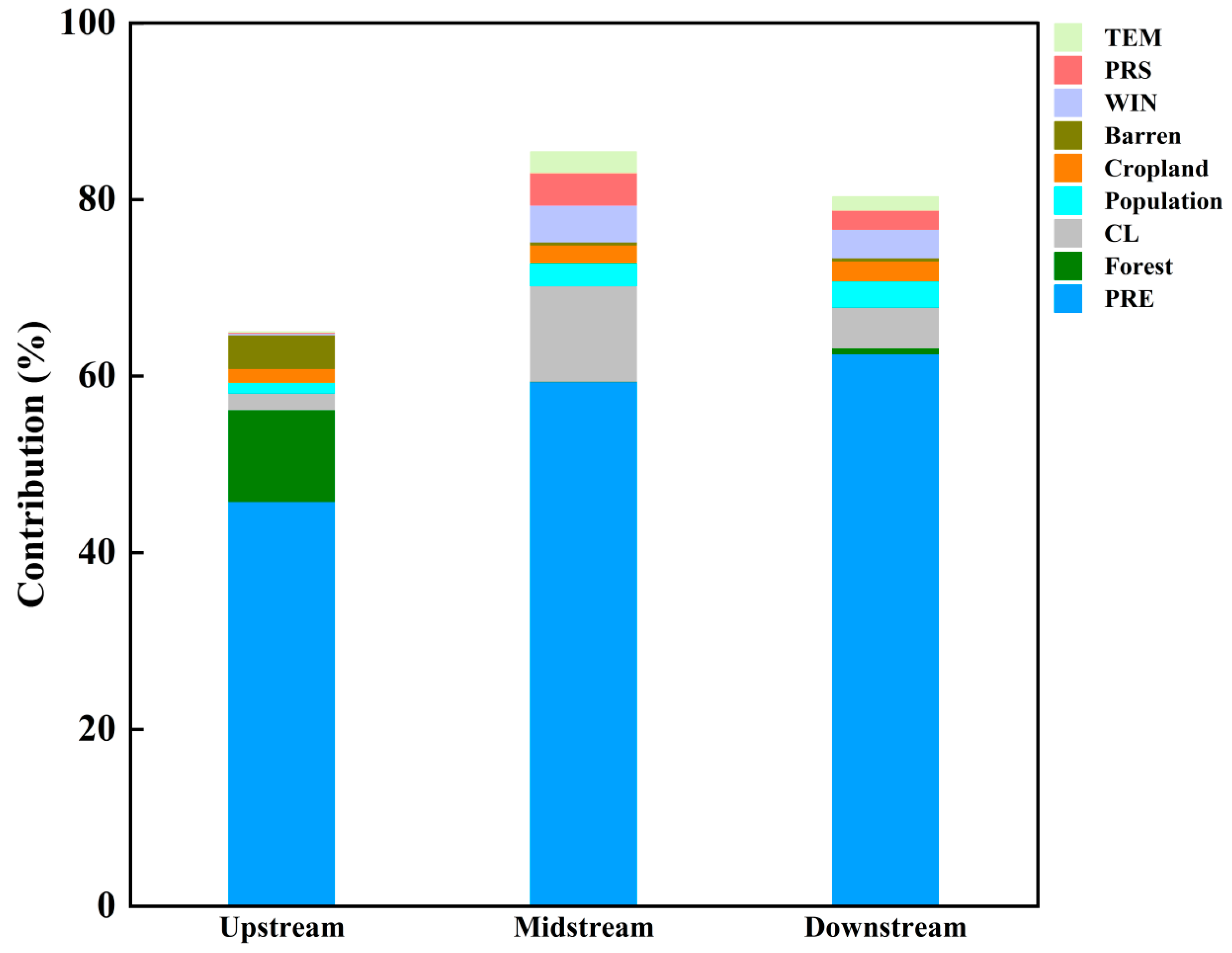
aCDOM(355) absorption was influenced by a variety of factors. The Songhua River basin was divided into 108 sub-basins based on a nine-level watershed system, and the analysis considered the impact of land use, population, and natural factors on the aCDOM(355) absorption. The results of the factor contribution analysis are shown in Table 3 and Figure 9. The upstream influencing factors contributed 66.03% to aCDOM(355), while the midstream and downstream factors contributed 85.43% and 80.32%, respectively. The top three upstream contributors were rainfall, forest, and wasteland lands, contributing 45.77%, 10.41%, and 3.81%, respectively. The top three midstream contributions were rainfall, built-up land, and wind speed, contributing 59.38%, 10.85%, and 4.16%, respectively. Finally, the top three downstream contributions were rainfall, construction lands, and wind speed. They contributed 62.53%, 4.66%, and 3.26%, respectively.

Table 3.
The contribution percentage of various driving factors to aCDOM(355) in the Songhua River.
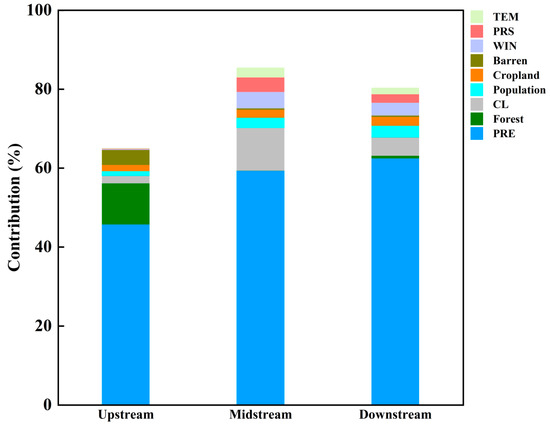
Figure 9.
Contributions of various factors to CDOM in main stream of Songhua River (driving factors: PRE (precipitation); forest; CL (construction land); population; cropland; barren (land without vegetation); WIN (wind); PRS (pressure); and TEM (temperature)).
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages and Disadvantages of the Model
The XGBoost is an enhanced algorithm based on gradient boosted trees that incorporates a more efficient tree generation process as well as regularization techniques to improve the model accuracy and generalization [38]. CDOM is the colored part of the organic matter in the water body that absorbs light to produce a brown or yellow color, whereas DOC is the concentration of organic carbon dissolved in water, which is a type of organic carbon [39]. It accounts for all dissolved organic carbon compounds, including CDOM, and numerous studies have demonstrated that using the link between CDOM and DOC can be adopted for determining indirectly the spatial distribution of DOC concentration [40,41,42]. The CDOM absorption decays exponentially with the wavelength, and the blue band is the ideal band for CDOM estimation. However, the aerosol in the atmosphere scatters and absorbs more of the blue light, resulting in a larger error. On the other hand, the optical properties of the red band are less affected by water [43]. As a result, the addition of the red band can reduce the atmospheric error. The green band light has a greater penetration depth in water, which can compensate for the absorption of the blue band on phytoplankton and non-algae particles. Using the blue, red, and green bands will help to establish a more accurate model [44].
Most of the recently developed algorithms for estimating river CDOM from remote sensing are not only machine learning algorithms but also empirical or semi-empirical modeling algorithms [45]. These algorithms have noticeable shortcomings, such as large computational efforts, complex model construction, and the need for a large number of measured intrinsic optical properties for model construction. On the other hand, the machine learning algorithms utilizing a band ratio are simple, fast, and can partially eliminate the influence of the atmosphere. The disadvantage is that these models are data-driven and do not explain the physical mechanisms behind the relationship between the image radiance bands and the CDOM [46,47]. The model is mainly based on statistical relationships of field sampling data and can only perform inversions for a specific region with limited applicability, and their generalization to other regions or seasons of the year cannot be guaranteed. On the other hand, the XGBoost algorithm used in this study to estimate the CDOM of the Songhua River randomly sampled only 168 points, which will have an impact on the algorithm accuracy due to the small number of samples. Thus, the number of random samples should be increased in future trials, and an updated band ratio should be employed to reduce the influence of the atmosphere, producing a more accurate CDOM remote sensing identification and DOC estimation model.
4.2. The Influencing Factors of CDOM Changes in the Songhua River
This study revealed that CDOM and DOC had significantly non-homogeneous temporal and spatial distributions, which were primarily influenced by the synergistic effects of human activities and natural factors (Figure 9), such as natural rainfall, temperature, wind speed, farmland, and forest coverage, as well as wastewater discharges from the urban construction lands and material transportation and conversion [48]. The correlations between CDOM concentrations in the Songhua River and rainfall, construction land, forests, wasteland, and agricultural land areas were strong. In terms of different parts of the Songhua River, rainfall had the biggest influence on CDOM in both the upper and lower flows. Specifically, the Songhua River is located at a high latitude with a long ice cover period, and the annual release of snow melt and rainfall during the thawing period transports a large amount of organic matter from the land to the river [49]. High-intensity precipitation also leads to the inflow of water into the river, increasing the river flow rate and accelerating aquatic metabolic processes. Hence, the river organic matter staining is diluted, and the organic matter is more likely to come into contact with microorganisms and oxygen in water, which accelerates its degradation. The degradation of organic matter will in turn accelerate the microbial life cycles, which will then consume large amounts of organic matter and reduce the concentration of CDOM. In addition to rainfall, forests had a stronger influence on the upper Songhua River. The areas surrounding the upper Songhua River are heavily forested, which stabilizes soil, intercepts rainfall water flowing into the river, reduces soil and organic loads carried in runoff, and lowers the content of suspended particles and organic matter in the water, all of which affect the concentration of CDOM in the upper reaches. The middle and lower reaches showed a combination of rainfall, residential land use, farmland, temperature, wind speed, and pressure, mainly because the middle and lower reaches pass through Jiamusi and Harbin with substantial heavy industry on both sides, and high levels of human activities and annual discharges of industrial and domestic wastewater are released into the river [50]. Industrial activities and domestic wastewater are important sources of CDOM, particularly substances containing aromatic compounds and humic matters contributing to the high levels of CDOM in rivers [51]. The exposed farmland soil is susceptible to rainfall carrying soil particles and organic matter into the river, with the temperature accelerating the degradation of organic matter in the soil and changes to the CDOM impacting factors. Strong winds will stir up waves on the river surface, so that the organic matter at the bottom of the river will become suspended. Changes in atmospheric pressure will release air bubbles from water, creating turbulence, which will stir and suspend the riverbed sediment. Furthermore, the higher levels of CDOM in urban areas compared to rural ones are well known [13,50].
4.3. Seasonal Analysis of DOC Flux in the Songhua River
Seasonal variations in the Songhua River DOC concentration were also observed. During spring, the Songhua River average total DOC concentration reached its peak of 5.35 mg/L. The average total DOC concentration exhibited significant seasonal variations: spring > summer > autumn. The long freezing period of the river located at a high altitude limits the decomposition of organic matter. During the snow melting period, DOC migration from land to aquatic ecosystems occurs; thus, the DOC concentration in rivers in most high latitudes reaches a peak during snow melting [52]. The freezing period around the Songhua River lasted from November 2021 to April 2022, and snow and ice melted in May. Organic substances were released into the river with the melting of ice and snow, which was the reason for the highest concentration of DOC in the Songhua River in spring. The rising temperature in summer increases precipitation, the river flow rate increases, and the rainfall dilutes the DOC concentration [53]. In addition to the organic matter directly released by snow melt, it is also possible that the snow water carries organic matter, such as plant materials, soil organic carbon, and other pollutants accumulated during the freezing period. The release of these organic materials may lead to an increase in DOC concentration in rivers during the snow melt period [54]. Furthermore, warmer summer temperatures enhance microbial activity in water that degrade DOC. All these factors decrease summer DOC concentration. The sudden drop in water temperature in the fall slowed down the rate of microbial metabolism in the river, resulting in the lowest DOC content. Harbin, located in the middle reaches of the Songhua River, is a heavy industrial city in China. It hosts the largest reservoir on the main stream of the Songhua River, which serves multiple purposes, including aquaculture, irrigation, power generation, and soil and water conservation. From the urban area of Harbin to the Datongzi Mountain Reservoir, the river’s width dramatically increases from 280 to 850 m to 340–7100 m, and the riverbed slope also becomes steeper. Due to the widening of the river and the increased slope, this section has continuously accumulated a large amount of industrial wastewater and domestic sewage. These wastewaters introduce significant amounts of organic matter into the river, resulting in markedly elevated levels of DOC and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). DOC inhibits the organic PAH degradation, and residue accumulates [55]. Significant industrial activity, such as the burning of coal for heating and human activities along the Songhua River, is the main cause of high levels of PAHs in the surface layer of the river [56]. Elevated levels of organic matter can lead to a large increase in DOC concentrations in the river. Therefore, the high concentration of DOC in the middle reaches of the Songhua River is most likely because of a large amount of organic substances and DOC from the industrial wastewater produced by the numerous heavy industry plants located in the middle reaches that were imported into the river. Furthermore, the middle reaches pass through the urban areas with a lot of human activity. The gradient of the middle reaches of the river steepens, leading to a sizeable DOC accumulation in the vicinity of the reservoirs. This is an important factor behind the highest DOC concentration in the middle reaches of the river as well.
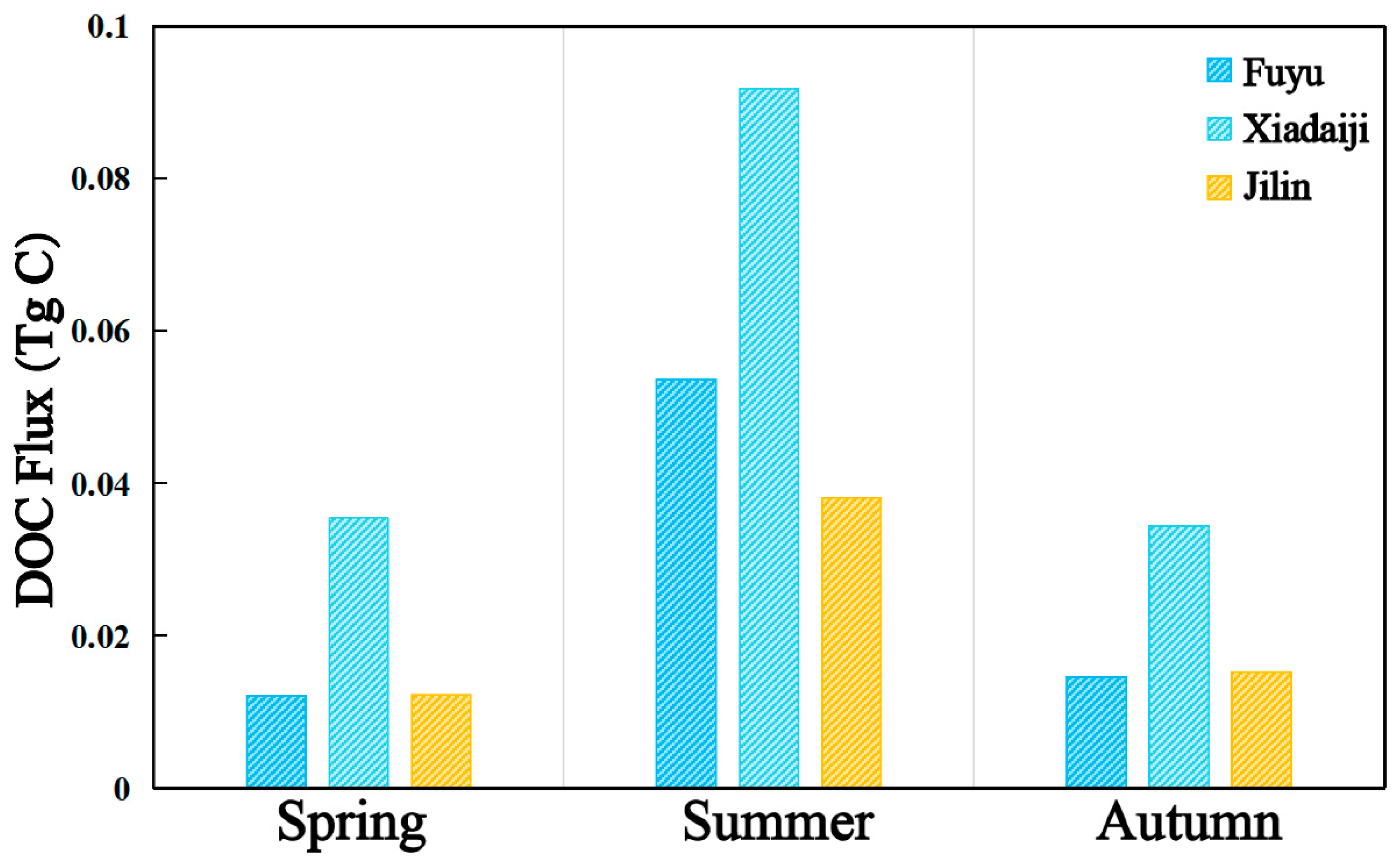
In this study, the DOC fluxes in different seasons at three stations (Fuyu, Xiaodaiji, and Jilin) on the main stream of the Songhua River, as well as the annual DOC fluxes at the Harbin station, were estimated using large river flow data released by the Information Center of the Ministry of Water Resources of China (MWRC). The DOC concentration fluxes are shown in Figure 10, where a significant variability in fluxes in different seasons can be observed, with the highest DOC fluxes at the Lower Daiji station in summer (0.0918 Tg C), followed by spring (0.0355 Tg C) and fall (0.0345 Tg C), DOC fluxes at the Fuyu station in summer (0.0536 Tg C), followed by fall (0.0145 Tg C) and spring (0.0122 Tg C), and DOC fluxes at the Jilin station (0.0381 Tg C), followed by fall (0.0152 Tg C) and spring (0.0123 Tg C). DOC fluxes were much higher at all the different sites during the summer than during the other seasons, and there was a significant negative linear relationship between flow and DOC concentration (R = −0.63) [57]. Organic carbon transported by rivers is mainly in the form of DOC, which can help in assessing the sources of organic carbon and carbon balance. Riverine organic carbon transport not only records the natural variability of a watershed, but also reflects the impacts of anthropogenic activities within the watershed. Rainfall, land use, human activity, and temperature are all factors that influence DOC concentrations in rivers. Harbin is located in the middle reaches of the Songhua River. The annual flux of DOC at the Harbin Station of the Songhua River is 0.2275 Tg C/Yr, which is higher than that of other cities. As the largest provincial capital city in Northeast China, Harbin’s industrial pollution emissions, urban emissions, and land use changes due to urbanization lead to the input of organic matter and nutrients, which affected the river carbon fluxes and ecological environment. These changes altered the content and distribution of organic matter in the Songhua River water bodies, affecting the future accuracy of carbon content estimation and carbon cycle process analysis. The correct understanding and consideration of these changes is necessary for accurate carbon flux estimation, and carbon cycle process analysis and the estimation of DOC fluxes based on stream classification will be undertaken in the future.
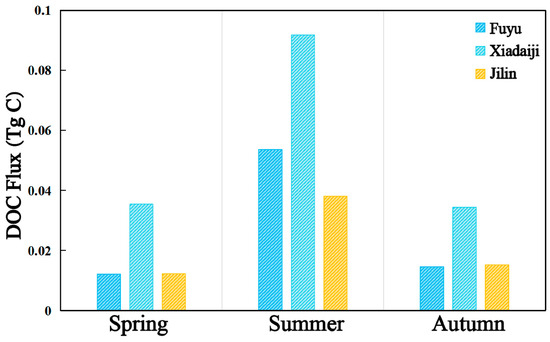
Figure 10.
DOC fluxes at different stations of Songhua River in different seasons in 2022.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a model for CDOM concentrations during the ice-free period of the Songhua River in 2022 was developed from field samples and remote sensing images from the Sentinel 2 series satellites using the XGBoost machine learning algorithm. The monthly mean and annual mean aCDOM(355) values in the main stream of the Songhua River from May through October were retrieved. It was demonstrated that the Sentinel-2 images enabled CDOM estimation by using machine learning processing and a band ratio as the input. The spatial distribution of CDOM concentration in the Songhua River revealed that urban areas had slightly higher concentrations compared to non-urban areas. This difference was likely due to human activities and the discharge of industrial wastewater. In terms of temporal trends, changes in the CDOM concentration in the Songhua River exhibited seasonal variations, which were related to the Songhua River long freezing period, the large amount of organic matter entering the river with runoff from snow melting, and the large amount of rain and flooding in summer. The reliability of CDOM was demonstrated, and the concentration distribution of DOC was inverted using the strong correlation between CDOM and DOC. Based on the river flow data from the Ministry of Water Resources of China, the seasonal DOC flux at each hydrological station and the annual carbon flux at the Harbin station were estimated. This paper provides valuable insights and ideas on the sources and distribution of organic matter in the river, as well as ideas for future inversion studies of the river to characterize the spatial distribution of organic matter and carbon sources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: P.F.; methodology: P.F.; formal analysis: P.F.; investigation: Y.S., X.Y., Z.W. and H.T.; data curation: P.F.; resources: Y.S., X.Y., Z.W. and H.T.; project administration: K.S.; roles/writing—original draft: P.F.; writing—review and editing: Y.S.; visualization: P.F.; supervision: Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42371390, 42471358, 42101366), the Jilin Provincial Department of Ecology and Environment (2024-01), the Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program (2021FY100406), Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences of China granted for Yingxin Shang, the Jilin Changbai Talent Program granted for Yingxin Shang, the Staying Postdoctoral Researcher Support Program of Jilin Province granted for Yingxin Shang (2024), the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, China (20220508017RC), the National funded postdoctoral researcher program (GZC20232638) and the Young Scientist Group Project of the Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, China (2023QNXZ01). The authors thank all staff and students for their persistent assistance with both field sampling and laboratory analysis. We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to European Space Agency (ESA) and GEE for the Sentinel-2 data. Thanks to Jie Yang and Xin Huang for providing the 30 m annual land cover dataset in China. Thanks to the Resource and Environmental Science Data Registration and Publishing System for providing the China Meteorological Elements Spatial Interpolation Datasets on temperature and wind speed. Thanks to the Oak Ridge National Laboratory of the U.S. Department of Energy for providing the population raster datasets. Thanks to the National Tibetan Plateau Scientific Data Center for providing the precipitation datasets for Asia. We also acknowledge the data support from the Ministry of Water Resources Information Center.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gao, Y.; Jia, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Carbon transportation, transformation, and sedimentation processes at the land-river-estuary continuum. Fundam. Res. 2022, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D. Role of Rivers in the Carbon Cycle and the Impact of Anthropogenic Activities. In Rivers of India: Past, Present and Future; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 173–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, S.; Schubotz, F.; Kaiser, K.; Hallmann, C.; Waska, H.; Rossel, P.E.; Hansman, R.; Elvert, M.; Middelburg, J.J.; Engel, A.; et al. Soothsaying DOM: A current perspective on the future of oceanic dissolved organic carbon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yao, X.; Shi, K.; Jeppesen, E.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, W. Chromophoric dissolved organic matter in inland waters: Present knowledge and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Song, K.; Liu, G.; Lyu, L.; Shang, Y.; Fang, C.; Du, J. Characterizing DOC sources in China’s Haihe River basin using spectroscopy and stable carbon isotopes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Jin, H.Y. Absorption features of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) and tracing implication for dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in Changjiang Estuary, China. Biogeosciences Discuss. 2013, 10, 12217–12250. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Cui, Z.; Ding, D.; Hong, C.; Cui, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Qu, K. The characteristics of CDOM structural composition and the effect on indirect photodegradation of sulfamerazine. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pan, B.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, G.; Han, X. CDOM in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China: Optical properties, possible sources, and their relationships with environmental variables. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32856–32873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Z.; Chen, J.; Feng, C. Characterization and spacial distribution variability of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Shao, T.; Zheng, K. Characteristics, sources and driving factors of riverine CDOM in a severe erosion basin on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, H.; Zhu, G. Influence of land use and rainfall on the optical properties of dissolved organic matter in a key drinking water reservoir in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Shao, T.; Ning, J.; Zhuang, D.; Liang, X. Water quality, basin characteristics, and discharge greatly affect CDOM in highly turbid rivers in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 404, 136995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yue, F. Seasonal variations of dissolved organic matter in urban rivers of Northern China. Land 2023, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichot, C.G.; Tzortziou, M.; Mannino, A. Remote sensing of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) stocks, fluxes and transformations along the land-ocean aquatic continuum: Advances, challenges, and opportunities. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 242, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Luyssaert, S.; Kaplan, L.A.; Aufdenkampe, A.K.; Richter, A.; Tranvik, L.J. The boundless carbon cycle. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.J.; Li, S. Riverine dissolved organic matter (DOM) as affected by urbanization gradient. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzortziou, M.; Zeri, C.; Dimitriou, E.; Ding, Y.; Jaffé, R.; Anagnostou, E.; Pitta, E.; Mentzafou, A. Colored dissolved organic matter dynamics and anthropogenic influences in a major transboundary river and its coastal wetland. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1222–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Fu, R.; Li, D.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Jia, K.; Hicks, B.J. Remote sensing big data for water environment monitoring: Current status, challenges, and future prospects. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Jian, H.; Su, R.; Yao, Q.; Shi, X. New approach for rapid assessment of trophic status of Yellow Sea and East China Sea using easy-to-measure parameters. J. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 16, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, S.; Song, K.; Wang, X.; Wen, Z.; Kutser, T.; Andrew Jacinthe, P.; Shang, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Fang, C.; et al. Remote sensing of CDOM and DOC in alpine lakes across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using Sentinel-2A imagery data. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.; Li, J.; Holt, B.; Lee, C. Analysis and classification of stormwater and wastewater runoff from the Tijuana River using remote sensing imagery. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 599030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.; Tian, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, X.; Mustavich, L.F.; Li, B. Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liu, S.; Su, M.; Wang, C.; Ying, Z.; Huo, M.; Lin, Y.; Yang, W. Spatial distribution and potential sources of microplastics in the Songhua River flowing through urban centers in Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J. Assessing climate change impacts on water resources in the Songhua River basin. Water 2016, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Li, S. Streamflow changes and its influencing factors in the mainstream of the Songhua River basin, Northeast China over the past 50 years. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Wang, H.; Tong, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J. Spatial–temporal pattern of cultivated land productivity based on net primary productivity and analysis of influencing factors in the Songhua River basin. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, C.; Yan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, W.; Chu, Z.; Chang, Y.; Ling, Y. Seasonal distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of phthalate esters in surface sediment of Songhua River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markager, S.; Vincent, W.F. Spectral light attenuation and the absorption of UV and blue light in natural waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Jin, M.; Yu, X.; Yu, J.; Zheng, R. Spatiotemporal variations in chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in a mixed land-use river: Implications for surface water restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for Sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIII, Warsaw, Poland, 4 October 2017; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics. 2001, 29(5), 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, H.; Burges, C.J.; Kaufman, L.; Smola, A.; Vapnik, V. Support vector regression machines. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1996, 9, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.Z. 1-km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for China (1901–2022); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentéjac, C.; Csörgő, A.; Martínez-Muñoz, G. A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 1937–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Huan, Y.; Mao, Z.; He, Y. Remote sensing estimation of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) from GOCI measurements in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 6872–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Tian, Y.Q.; Boutt, D.F. Effects of landcover, soil property, and temperature on covariations of DOC and CDOM in inland waters. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2018, 123, 1352–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, Z.; Fang, C.; Shang, Y. A systematic examination of the relationships between CDOM and DOC in inland waters in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5127–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcântara, E.; Bernardo, N.; Rodrigues, T.; Watanabe, F. Modeling the spatio-temporal dissolved organic carbon concentration in Barra Bonita reservoir using OLI/Landsat-8 images. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Lyu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, B. Characterization of CDOM absorption of reservoirs with its linkage of regions and ages across China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16009–16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churilova, T.; Moiseeva, N.; Skorokhod, E.; Efimova, T.; Buchelnikov, A.; Artemiev, V.; Salyuk, P. Parameterization of Light Absorption of Phytoplankton, Non-Algal Particles and Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter in the Atlantic Region of the Southern Ocean (Austral Summer of 2020). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.I.; Frey, K.E. Assessment of empirical and semi-analytical algorithms using MODIS-aqua for representing in-situ chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the bering, chukchi, and Western Beaufort seas of the Pacific Arctic region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Han, K.-S. Comparison of Two Semi-Empirical BRDF algorithms using SPOT/VGT. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2013, 29, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Betancur-Turizo, S.P.; González-Silvera, A.; Santamaría-del-Ángel, E.; Tan, J.; Frouin, R. Evaluation of Semi-Analytical Algorithms to Retrieve Particulate and Dissolved Absorption Coefficients in Gulf of California Optically Complex Waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Cui, S.; Zhang, F.; Hough, R.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; An, L. Concentrations, possible sources and health risk of heavy metals in multi-media environment of the Songhua River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Heim, B.; Foerster, S.; Brosinsky, A.; De Araújo, J.C. In situ and satellite observation of CDOM and chlorophyll-a dynamics in small water surface reservoirs in the brazilian semiarid region. Water 2017, 9, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, F.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Xue, H. The Taxon-Specific Species Sensitivity and Aquatic Ecological Risk Assessment of Three Heavy Metals in Songhua River Water, China. Water 2023, 15, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Song, K.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Wen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lyu, L.; Fang, C.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Zhang, N. Fluorescence spectroscopy of CDOM in urbanized waters across gradients of development/industrialization of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, J.; Neff, J.; Zimov, S.; Davydova, A.; Davydov, S. Snowmelt dominance of dissolved organic carbon in high-latitude watersheds: Implications for characterization and flux of river DOC. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, C.; Fernandes, C.V.S.; Braga, S.M.; do Prado, L.L.; Froehner, S.; Hilgert, S. Water quality dynamic during rainfall episodes: Integrated approach to assess diffuse pollution using automatic sampling. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, T.; Sponseller, R.A.; Laudon, H. Extreme climate effects on dissolved organic carbon concentrations during snowmelt. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2018, 123, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, D.; Ghosh, S.; Dutta, T.K.; Ahn, Y. Current state of knowledge in microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Dong, W.; Yan, G. PAHs and PAEs in the surface sediments from Nenjiang River and the Second Songhua River, China: Distribution, composition and risk assessment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 178, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Tao, B.; Pan, D.; Chen, C.T.A.; Gong, C. Satellite estimation of particulate organic carbon flux from Changjiang River to the estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).