Application of PlanetScope Imagery for Flood Mapping: A Case Study in South Chickamauga Creek, Chattanooga, Tennessee
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
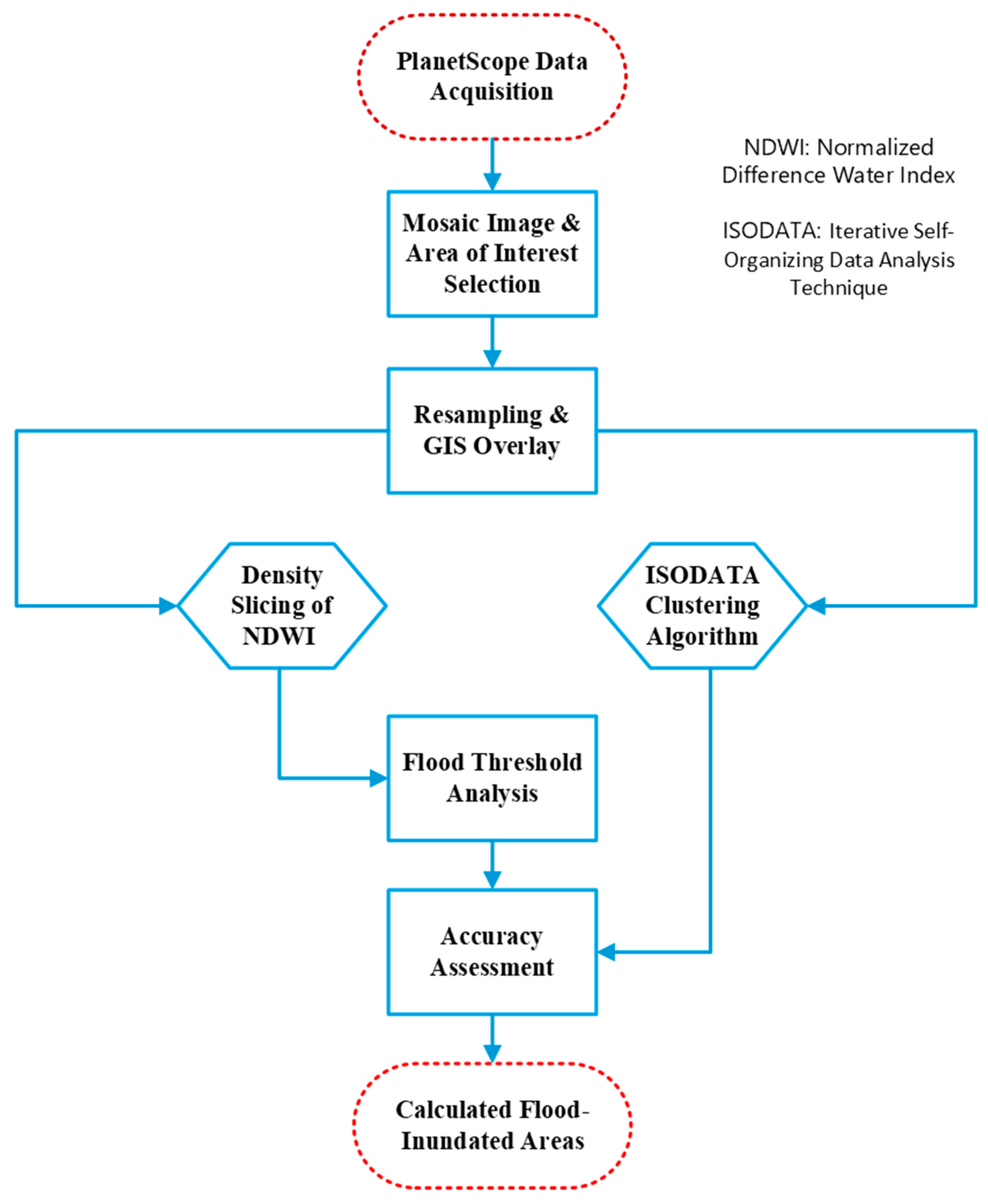
2.2. Work Flow
2.3. Data Acquisition
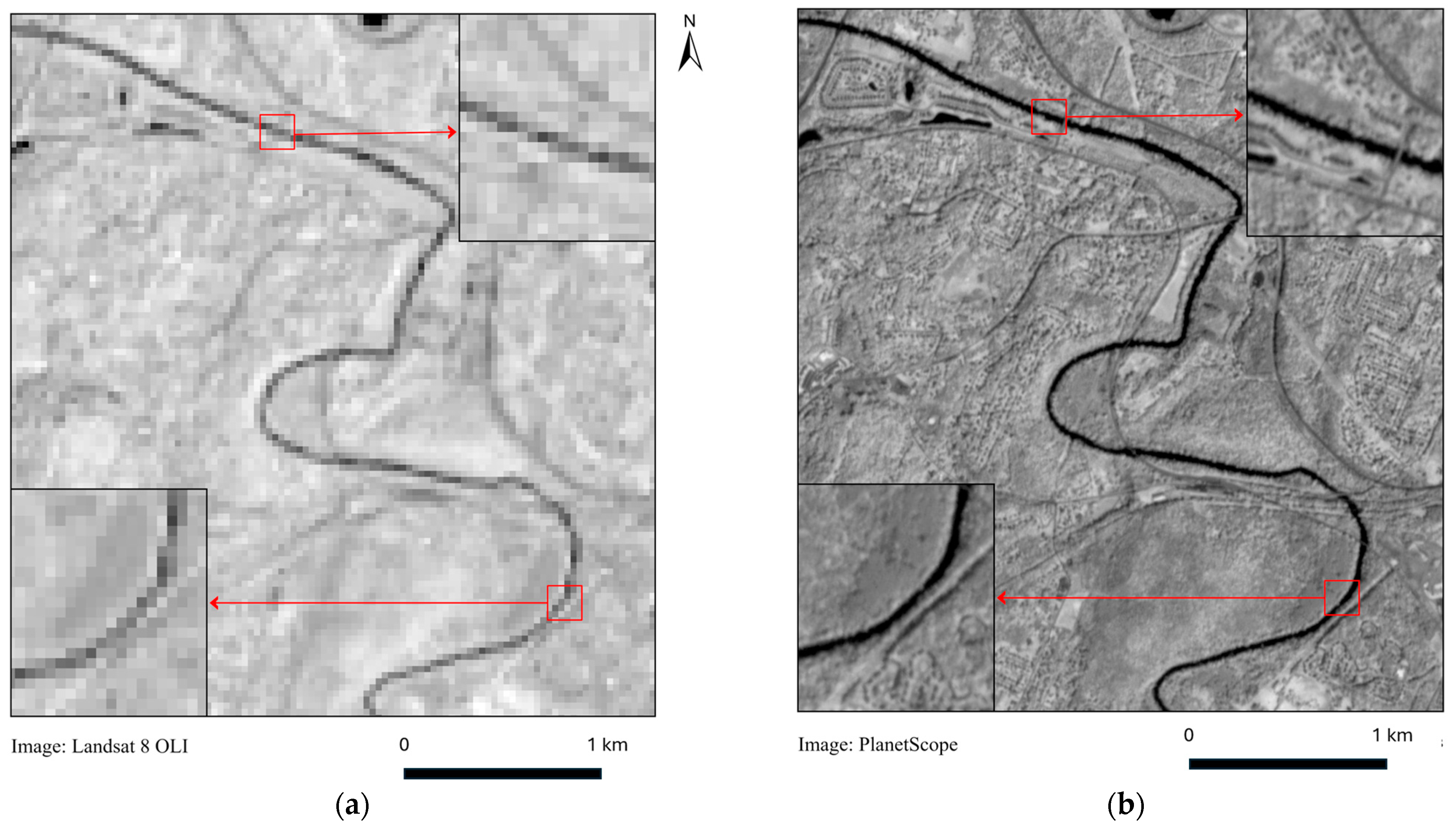
2.4. Image Preprocessing
2.5. Image Processing and Image Classification
2.5.1. Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI)
2.5.2. Density Slicing of NDWI Image
2.5.3. Unsupervised Classification
2.6. Accuracy Assessment
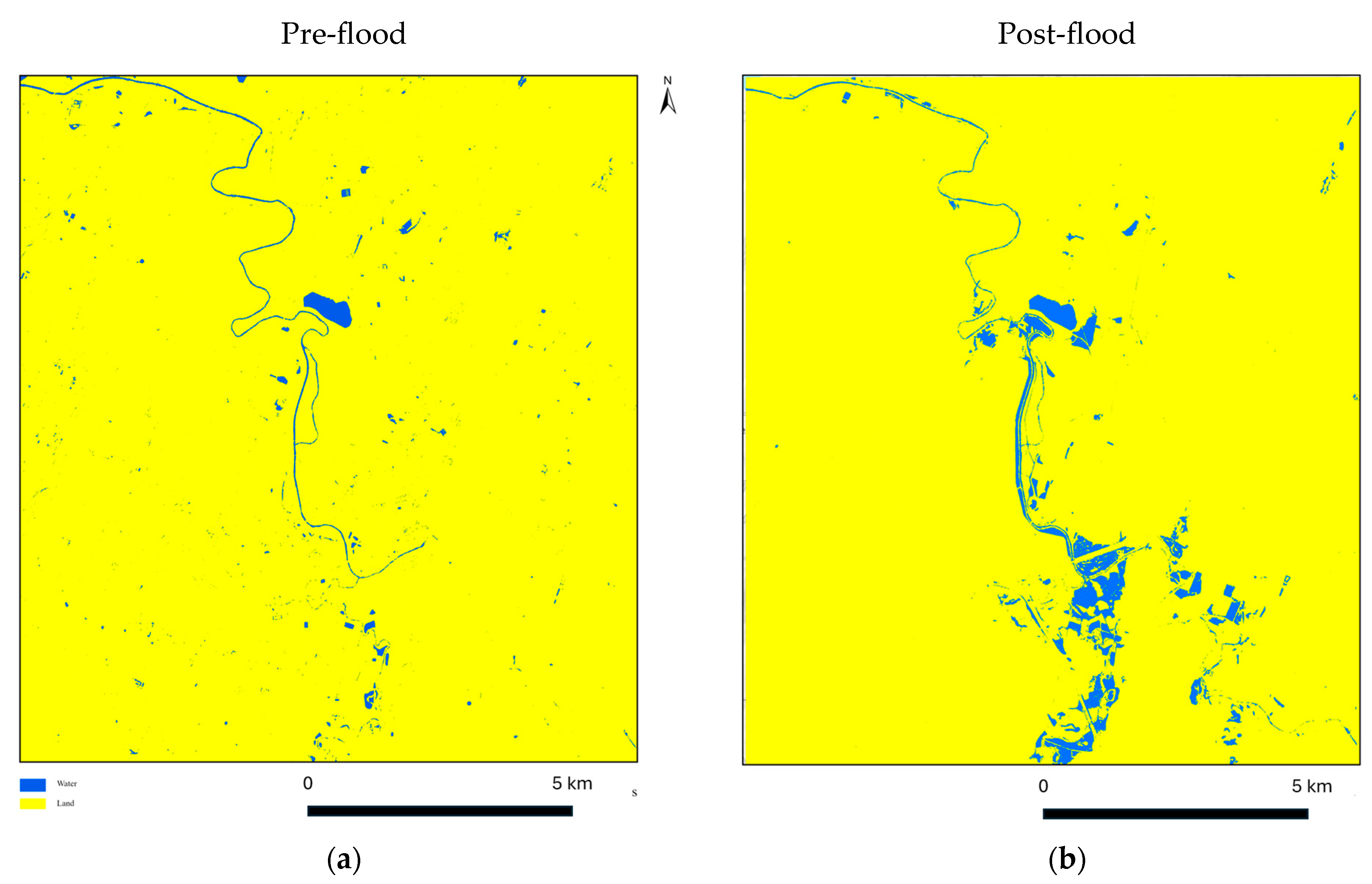
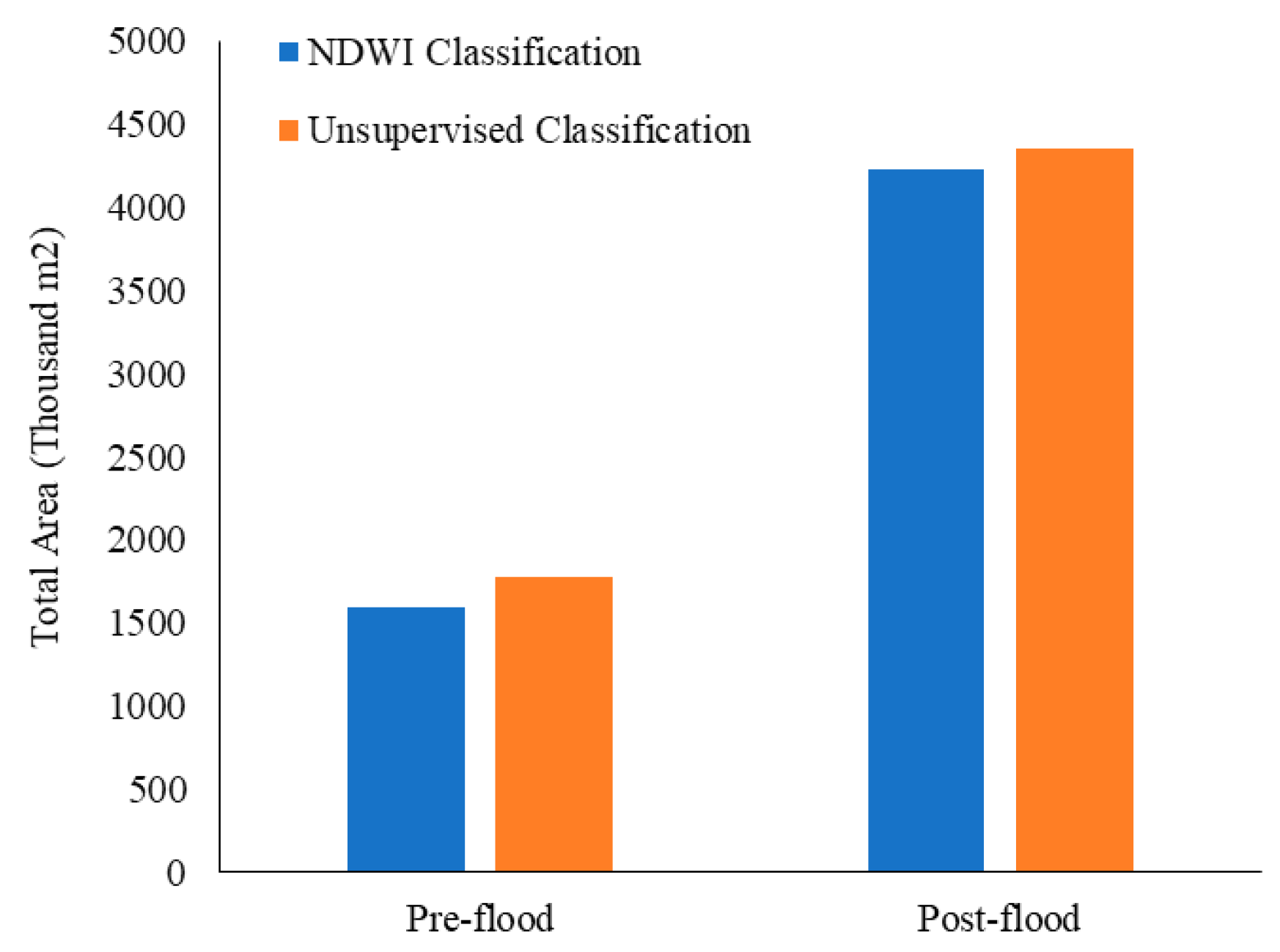
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amen, A.R.M.; Mustafa, A.; Kareem, D.A.; Hameed, H.M.; Mirza, A.A.; Szydłowski, M.; Saleem, B.K.M. Mapping of flood-prone areas utilizing GIS techniques and remote sensing: A case study of Duhok, Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isma’il, M.; Saanyol, I.O. Application of remote sensing (RS) and geographic information systems (GIS) in flood vulnerability mapping: Case study of River Kaduna. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2013, 3, 618–627. [Google Scholar]
- Statista. Economic Damage Caused by Floods and Flash Floods in the United States from 1995 to 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/237420/economic-damage-caused-by-floods-and-flash-floods-in-the-us/#statisticContainer (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Domeneghetti, A.; Schumann, G.J.P.; Tarpanelli, A. Preface: Remote sensing for flood mapping and monitoring of flood dynamics. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Guo, H.; Huth, J.; Leinenkugel, P.; Li, X.; Dech, S. Flood mapping and flood dynamics of the Mekong Delta: ENVISAT-ASAR-WSM based time series analyses. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 687–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xie, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, J. The 1997–1998 warm event in the South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Idowu, D.; Zhou, W. Global Megacities and Frequent Floods: Correlation between Urban Expansion Patterns and Urban Flood Hazards. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Lyu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, Z.; et al. Impact of expansion pattern of built-up land in floodplains on flood vulnerability: A case study in the North China Plain area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Leng, G.; Su, J.; Ren, Y. Comparison of urbanization and climate change impacts on urban flood volumes: Importance of urban planning and drainage adaptation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plate, E.J. Flood risk and flood management. J. Hydrol. 2002, 267, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halounova, L.; Holubec, V. Assessment of flood with regards to land cover changes. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 18, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeu-wei, I.T.; Blackburn, G.A. Applications of open-access remotely sensed data for flood modelling and mapping in developing regions. Hydrology 2018, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opolot, E. Application of remote sensing and geographical information systems in flood management: A review. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 6, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H. A review on applications of remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS) in water resources and flood risk management. Water 2018, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.V.; Pham, Q.B.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bogireddy, C.; Yadav, S.M. Advancements in drought using remote sensing: Assessing progress, overcoming challenges, and exploring future opportunities. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 4251–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.R.; Faruk, O.; Chanda, M.; Falak, A.A.; Akter, A. Groundwater Table Variation in Rangunia Upazila Using GIS Application: A Case Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Planning, Architecture, & Civil Engineering (ICPACE), Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 9–11 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tanguy, M.; Chokmani, K.; Bernier, M.; Poulin, J.; Raymond, S. River flood mapping in urban areas combining Radarsat-2 data and flood return period data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.D.; Liou, Y.A. Object-based flood mapping and affected rice field estimation with Landsat 8 OLI and MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5077–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Giordan, D.; Caló, F.; Pepe, A.; Zucca, F.; Galve, J.P. Potential and limitations of open satellite data for flood mapping. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.K.; Agrawal, S. Mapping and assessment of flood risk in Prayagraj district, India: A GIS and remote sensing study. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2020, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.S.; Bala, S.K.; Haque, M.A. Flood inundation map of Bangladesh using MODIS time-series images. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2010, 3, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormanski, J.; Okruszko, T.; Ignar, S.; Batelaan, O.; Rebel, K.T.; Wassen, M.J. Flood mapping with remote sensing and hydrochemistry: A new method to distinguish the origin of flood water during floods. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.A.; Colombo, R.; Maggi, M.; Tomasoni, R. Integration of remote sensing data and GIS for accurate mapping of flooded areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 23, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, U.L.; Matori, A.N.; Hashim, A.M.; Chandio, I.A.; Sabri, S.; Balogun, A.L.; Abba, H.A. Geographic information system and remote sensing applications in flood hazards management: A review. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 3, 933–947. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, E.; Shan, J. Mapping major floods with optical and SAR satellite images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Munasinghe, D.; Cohen, S.; Huang, Y.F.; Tsang, Y.P.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Z. Intercomparison of satellite remote sensing-based flood inundation mapping techniques. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 54, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, R.; Akhtar, Z.; Imran, M.; Ofli, F. Integrating remote sensing and social sensing for flood mapping. Remote Sens. Appl. 2022, 25, 100697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syifa, M.; Park, S.J.; Achmad, A.R.; Lee, C.W.; Eom, J. Flood mapping using remote sensing imagery and artificial intelligence techniques: A case study in Brumadinho, Brazil. J Coast Res. 2019, 90, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafitlhile, T.M.; Li, Z. Applicability of ε-support vector machine and artificial neural network for flood forecasting in humid, semi-humid and semi-arid basins in China. Water 2019, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, H.; Najafzadeh, M. Flood risk mapping by remote sensing data and random forest technique. Water 2021, 13, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Ghaderi, K.; Omidvar, E.; Al-Ansari, N.; Clague, J.J.; Geertsema, M.; Khosravi, K.; Amini, A.; Bahrami, S.; et al. Flood detection and susceptibility mapping using sentinel-1 remote sensing data and a machine learning approach: Hybrid intelligence of bagging ensemble based on k-nearest neighbor classifier. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, J.; Gong, J. Urban flood mapping based on unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing and random forest classifier—A case of Yuyao, China. Water 2015, 7, 1437–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabameri, A.; Saha, S.; Mukherjee, K.; Blaschke, T.; Chen, W.; Ngo, P.T.T.; Band, S.S. Modeling spatial flood using novel ensemble artificial intelligence approaches in northern Iran. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A.; Meyer, F.J. Operational flood mapping using multi-temporal Sentinel-1 SAR images: A case study from Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, J.; Lu, X.X. Application of remote sensing in flood management with special reference to monsoon Asia: A review. Nat. Hazards 2004, 33, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, H.; Guan, Z.; Qian, Z.; Yang, A. Multiple kernel learning with maximum inundation extent from MODIS imagery for spatial prediction of flood susceptibility. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jin, S. Rapid flood mapping and evaluation with a supervised classifier and change detection in Shouguang using Sentinel-1 SAR and Sentinel-2 optical data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, D. Blending MODIS and Landsat images for urban flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayne, J.V.; Bolten, J.D.; Doyle, C.S.; Fuhrmann, S.; Rice, M.T.; Houser, P.R.; Lakshmi, V. Flood mapping in the lower Mekong River Basin using daily MODIS observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1737–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Fahrner, D.; Arribas-Bel, D.; Rowe, F. A reproducible notebook to acquire, process and analyze satellite imagery: Exploring long-term urban changes. Region 2020, 7, R15–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpanelli, A.; Mondini, A.C.; Camici, S. Effectiveness of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 for flood detection assessment in Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 2473–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Huang, H.; Houborg, R.; Martins, V.S. A global analysis of the temporal availability of PlanetScope high spatial resolution multi-spectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Team. Planet Imagery Product Specifications; Planet Labs Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018; Volume 91, p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- Tunca, E.; Köksal, E.S.; Taner, S.Ç. Silage maize yield estimation by using PlanetScope, sentinel-2A and Landsat 8 OLI satellite images. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 4, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Tokumoto, Y.; Shin, N.; Shimizu, K.K.; Pungga, R.A.S.; Ichie, T. Utility of commercial high-resolution satellite imagery for monitoring general flowering in Sarawak, Borneo. Ecol. Res. 2023, 38, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faxon, A. Studying Suspended Sediment Concentrations in the South Chickamauga Creek of Chattanooga, TN Using Satellite Imagery, Digital Image Processing, and Numeric Modeling. Honors Thesis, The University of Tennessee at Chattanooga, Chattanooga, TN, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L.; Gege, P. Physics-based bathymetry and water quality retrieval using planetscope imagery: Impacts of 2020 COVID-19 lockdown and 2019 extreme flood in the Venice Lagoon. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhrachy, I. Flash flood hazard mapping using satellite images and GIS tools: A case study of Najran City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P. Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis in Hydrological Modeling: A Case Study of South Chickamauga Creek Watershed Using BASINS/HSPF. Master’s Thesis, The University of Tennessee at Chattanooga, Chattanooga, TN, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- South Chickamauga Creek near Chickamauga, TN. USGS Water Data for the Nation. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/monitoring-location/03567500/#parameterCode=00065&period=P7D&showMedian=false (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Rain Causes Flooding at South Chickamauga Creek. 2021. Available online: https://www.local3news.com/rain-causes-flooding-at-south-chickamauga-creek/article_4f40c589-060a-5b91-8299-1f1b6fd75db7.html (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Record Flooding of May 2003 Across East Tennessee. 2003. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/mrx/may03flood#:~:text=Heavy%20rains%20across%20the%20South,feet%20observed%20in%20February%201990 (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Flood Damage up to $17 Million as 480 Structures Affected. Available online: https://www.chattanoogan.com/2003/5/8/36201/Flood-Damage-Up-To-17-Million-As-480.aspx (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A. Potential flood hazard zonation and flood shelter suitability mapping for disaster risk mitigation in Bangladesh using geospatial technology. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2021, 11, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veh, G.; Lützow, N.; Tamm, J.; Luna, L.V.; Hugonnet, R.; Vogel, K.; Geertsema, M.; Clague, J.J.; Korup, O. Less extreme and earlier outbursts of ice-dammed lakes since 1900. Nature 2023, 614, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.E.; Hemingway, B.L. A technical review of planet smallsat data: Practical considerations for processing and using planetscope imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aati, S.; Avouac, J.P.; Rupnik, E.; Deseilligny, M.P. Potential and limitation of planetscope images for 2-D and 3-D earth surface monitoring with example of applications to glaciers and earthquakes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, H.; Conway, C.; Perera, D. Mapping of flood areas using landsat with google earth engine cloud platform. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogashawara, I.; Curtarelli, M.P.; Ferreira, C.M. The use of optical remote sensing for mapping flooded areas. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2013, 3, 1956–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Dash, J.; Asamoah, M.; Sheffield, J.; Dzodzomenyo, M.; Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Anghileri, D.; Wright, J. Increased flooded area and exposure in the White Volta river basin in Western Africa, identified from multi-source remote sensing data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.K.M.A.; Jia, Y.; Chao, X. Estimation of Manning’s roughness coefficient distribution for hydrodynamic model using remotely sensed land cover features. In Proceedings of the IEEE 17th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Fairfax, VA, USA, 12–14 August 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.; Hossain, A.K.M.A. Mapping urbanization and evaluating its possible impacts on stream water quality in Chattanooga, Tennessee, using GIS and remote sensing. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.K.M.A.; Easson, G. Mapping small reservoirs in semi-arid region using optical and microwave remote sensing. In Proceedings of the ASPRS 2007 Annual Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 7–11 May 2007; pp. 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.B. Introduction to Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: Abingdon, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Enderle, D.I.; Weih, R.C., Jr. Integrating supervised and unsupervised classification methods to develop a more accurate land cover classification. J. Ark. Acad. Sci. 2005, 59, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.R.; Thakur, P.K. Detecting, mapping and analysing of flood water propagation using synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite data and GIS: A case study from the Kendrapara District of Orissa State of India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2018, 21, S37–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasmadi, M.; Pakhriazad, H.Z.; Shahrin, M.F. Evaluating supervised and unsupervised techniques for land cover mapping using remote sensing data. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2009, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Akter, T.; Gazi, M.Y.; Mia, M.B. Assessment of land cover dynamics, land surface temperature, and heat island growth in northwestern Bangladesh using satellite imagery. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 661–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Du, Z.; Zhang, F.; Huang, F.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Guo, Z. Landslide susceptibility prediction based on remote sensing images and GIS: Comparisons of supervised and unsupervised machine learning models. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbarte, N.; Nagpure, A.; Sanodiya, B.; Sevatkar, H.; Balamwar, S. Knowledge Based Classifier and Pattern Recognition Technique for Satellite Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd Global Conference for Advancement in Technology (GCAT), Bangalore, India, 7–9 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Anusha, N.; Bharathi, B. Flood detection and flood mapping using multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar and optical data. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitrano, D.; Di Martino, G.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Unsupervised rapid flood mapping using Sentinel-1 GRD SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landuyt, L.; Verhoest, N.E.; Van Coillie, F.M. Flood mapping in vegetated areas using an unsupervised clustering approach on sentinel-1 and-2 imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overview of Image Classification. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/help/analysis/image-analyst/overview-of-image-classification.htm#:~:text=Unsupervised%20classification%20is%20where%20you,class%20categories%20within%20your%20schema (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Eroğlu, H.; Çakır, G.; Sivrikaya, F.; Akay, A.E. Using high resolution images and elevation data in classifying erosion risks of bare soil areas in the Hatila Valley Natural Protected Area, Turkey. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2010, 24, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, R.; Hossain, A.K.M.A. Mapping the recovery process of vegetation growth in the Copper Basin, Tennessee using remote sensing technology. GeoHazards 2020, 1, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, R.; Pham, Q.B.; Sharifi, E.; Linh, N.T.T.; Abba, S.I.; Vojtek, M.; Vojteková, J.; Nhi, P.T.T.; Khoi, D.N. Flash-flood susceptibility assessment using multi-criteria decision making and machine learning supported by remote sensing and GIS techniques. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, M.; Dobrinić, D.; Medak, D. Urban vegetation detection based on the land-cover classification of PlanetScope, RapidEye and worldview-2 satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the 18th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geo-Conference SGEM2018, Albena, Bulgaria, 2–8 July 2018; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. Explaining the unsuitability of the kappa coefficient in the assessment and comparison of the accuracy of thematic maps obtained by image classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; McCarty, G.W.; Zhang, X.; Lang, M.W.; Vanderhoof, M.K.; Li, X.; Huang, C.; Lee, S.; Zou, Z. Mapping forested wetland inundation in the Delmarva Peninsula, USA using deep convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Wylie, B. Analysis of dynamic thresholds for the normalized difference water index. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, S.; Gácsi, Z.; Balazs, B. Specific features of NDVI, NDWI and MNDWI as reflected in land cover categories. Landsc. Environ. 2016, 10, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, T.; Chakraborty, D.; Pal, R.; Sarkar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Roy, N.; Karforma, S. A hybrid approach for water body identification from satellite images using NDWI mapping and histogram of gradients. Innov. Syst. Softw. Eng. 2024, 20, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, P.; Peng, J.; Ye, C. A physical explanation of the variation in threshold for delineating terrestrial water surfaces from multi-temporal images: Effects of radiometric correction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5862–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, V.B.; Hassan, Q.K.; He, J. Development of flow forecasting models in the Bow River at Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Water 2014, 7, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.S.G.; Siam, Z.S.; Kabir, I.; Kabir, Z.; Ahmed, M.R.; Hassan, Q.K.; Rahman, R.M.; Dewan, A. A novel framework for addressing uncertainties in machine learning-based geospatial approaches for flood prediction. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, E.H.; Hassan, Q.K. Use of remote sensing data in comprehending an extremely unusual flooding event over southwest Bangladesh. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 1805–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belvederesi, C.; Dominic, J.A.; Hassan, Q.K.; Gupta, A.; Achari, G. Predicting River flow using an AI-based sequential adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Water 2020, 12, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, H.; Esmaeily, A.; Najafzadeh, M. Flood monitoring by integration of Remote Sensing technique and Multi-Criteria Decision Making method. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 160, 105045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Using Landsat 7 TM data acquired days after a flood event to delineate the maximum flood extent on a coastal floodplain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| ID | Class | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | Water | Water bodies—small water storage areas, retention ponds, lakes, and rivers. |
| 02 | Land | Surfaces without water bodies—bridges, buildings, crops, forests, industries, natural grass, pastures, roads, rocks, shrubs, and soils. |
| Reference Pixels | NDWI Classified Pixels | Unsupervised Classified Pixels | Total Pixels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Land | Water | Land | ||
| Water | 58 | 2 | 55 | 5 | 60 |
| Land | 6 | 54 | 7 | 53 | 60 |
| Total | 64 | 56 | 62 | 58 | 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chanda, M.; Hossain, A. Application of PlanetScope Imagery for Flood Mapping: A Case Study in South Chickamauga Creek, Chattanooga, Tennessee. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234437
Chanda M, Hossain A. Application of PlanetScope Imagery for Flood Mapping: A Case Study in South Chickamauga Creek, Chattanooga, Tennessee. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(23):4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234437
Chicago/Turabian StyleChanda, Mithu, and Azad Hossain. 2024. "Application of PlanetScope Imagery for Flood Mapping: A Case Study in South Chickamauga Creek, Chattanooga, Tennessee" Remote Sensing 16, no. 23: 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234437
APA StyleChanda, M., & Hossain, A. (2024). Application of PlanetScope Imagery for Flood Mapping: A Case Study in South Chickamauga Creek, Chattanooga, Tennessee. Remote Sensing, 16(23), 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234437








