Improvement of Coal Mining-Induced Subsidence-Affected (MISA) Zone Irregular Boundary Delineation by MT-InSAR Techniques, UAV Photogrammetry, and Field Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
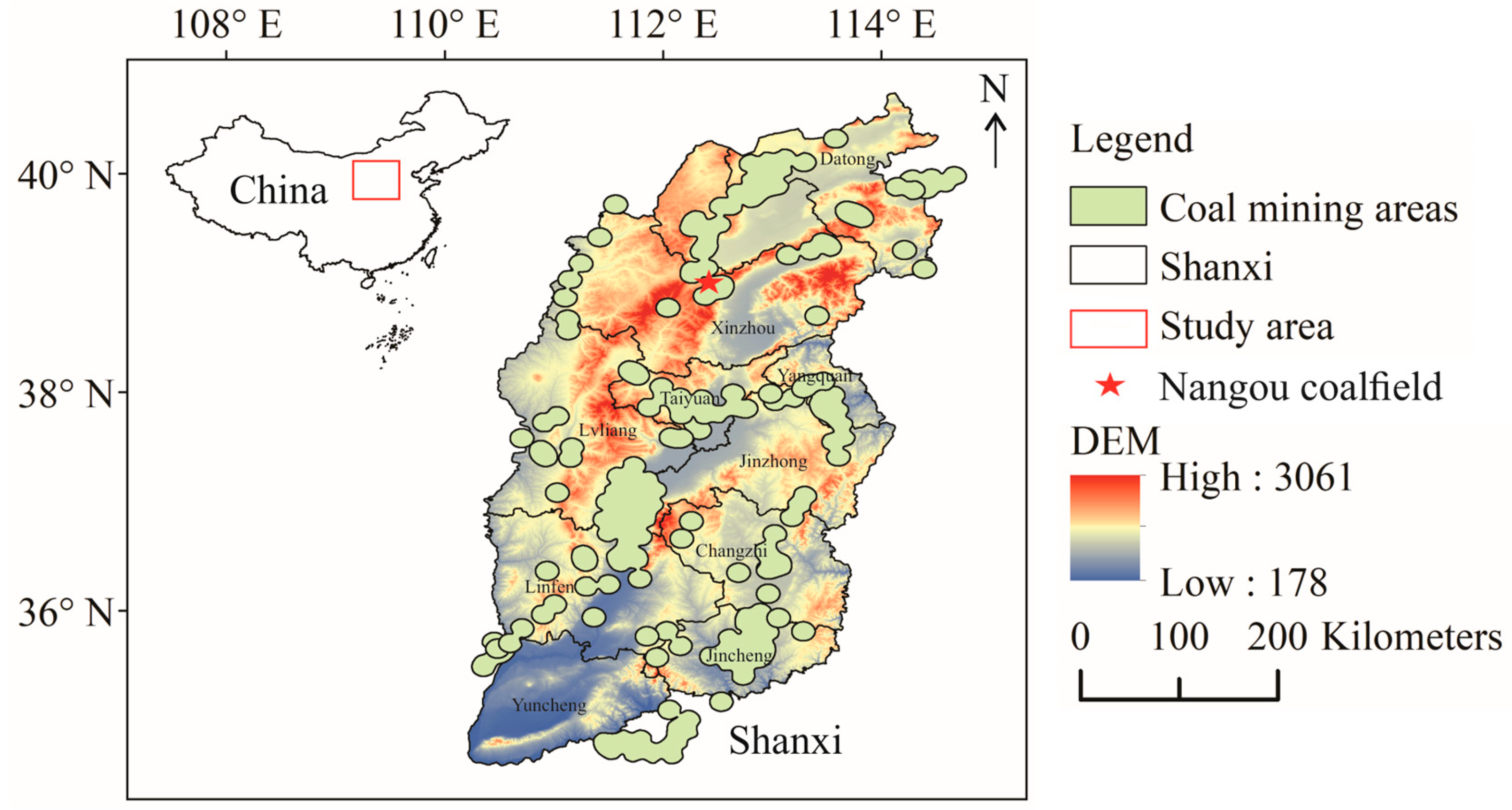
2. Study Area
3. Methodology
3.1. Field Investigation
3.2. UAV Photogrammetry
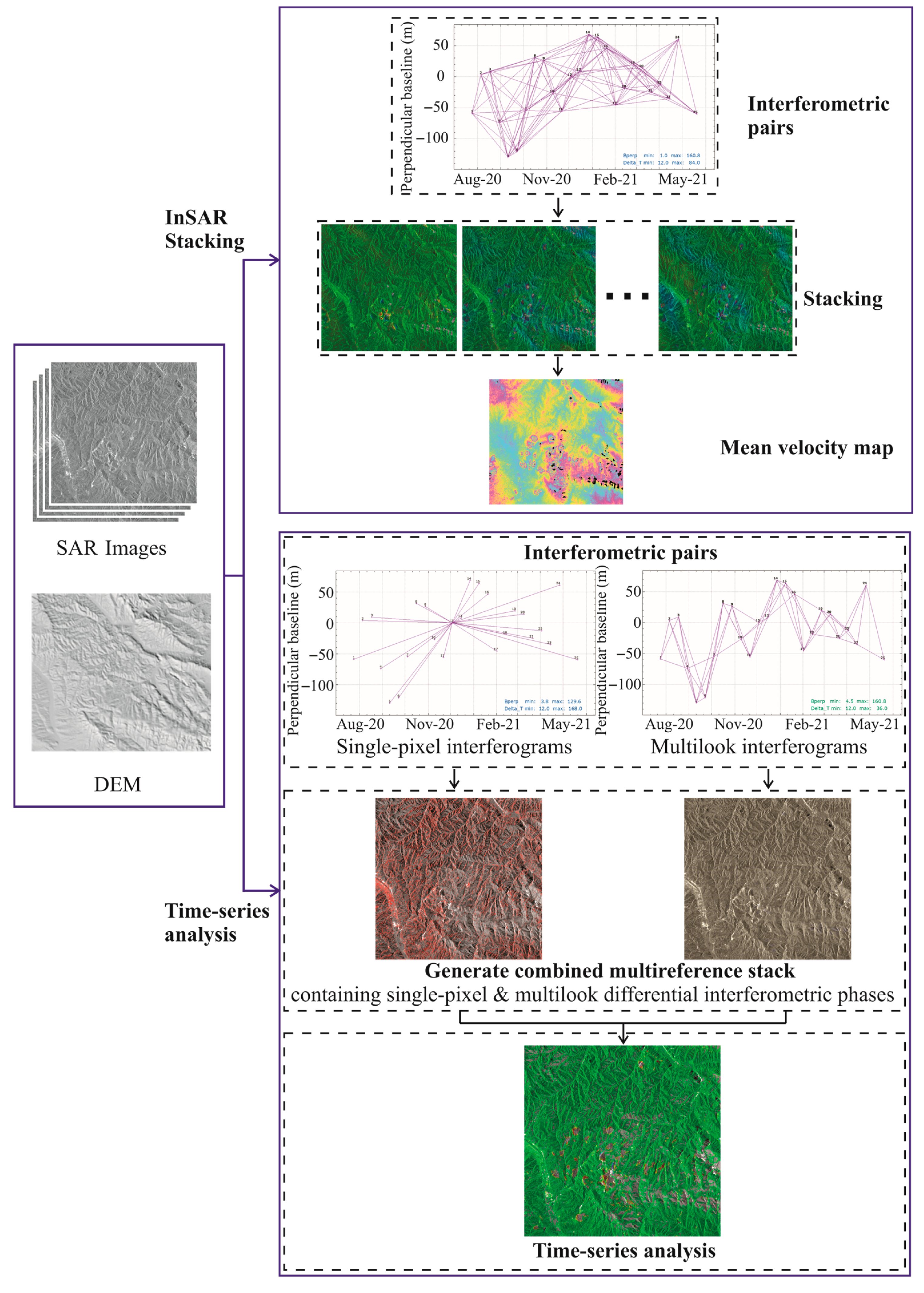
3.3. InSAR Processing
3.3.1. Dataset Collection
3.3.2. DInSAR
3.3.3. InSAR Stacking
3.3.4. IPTA Time-Series Analysis
3.3.5. SAR Dataset Processing
4. Results
4.1. Mining History Reconstruction
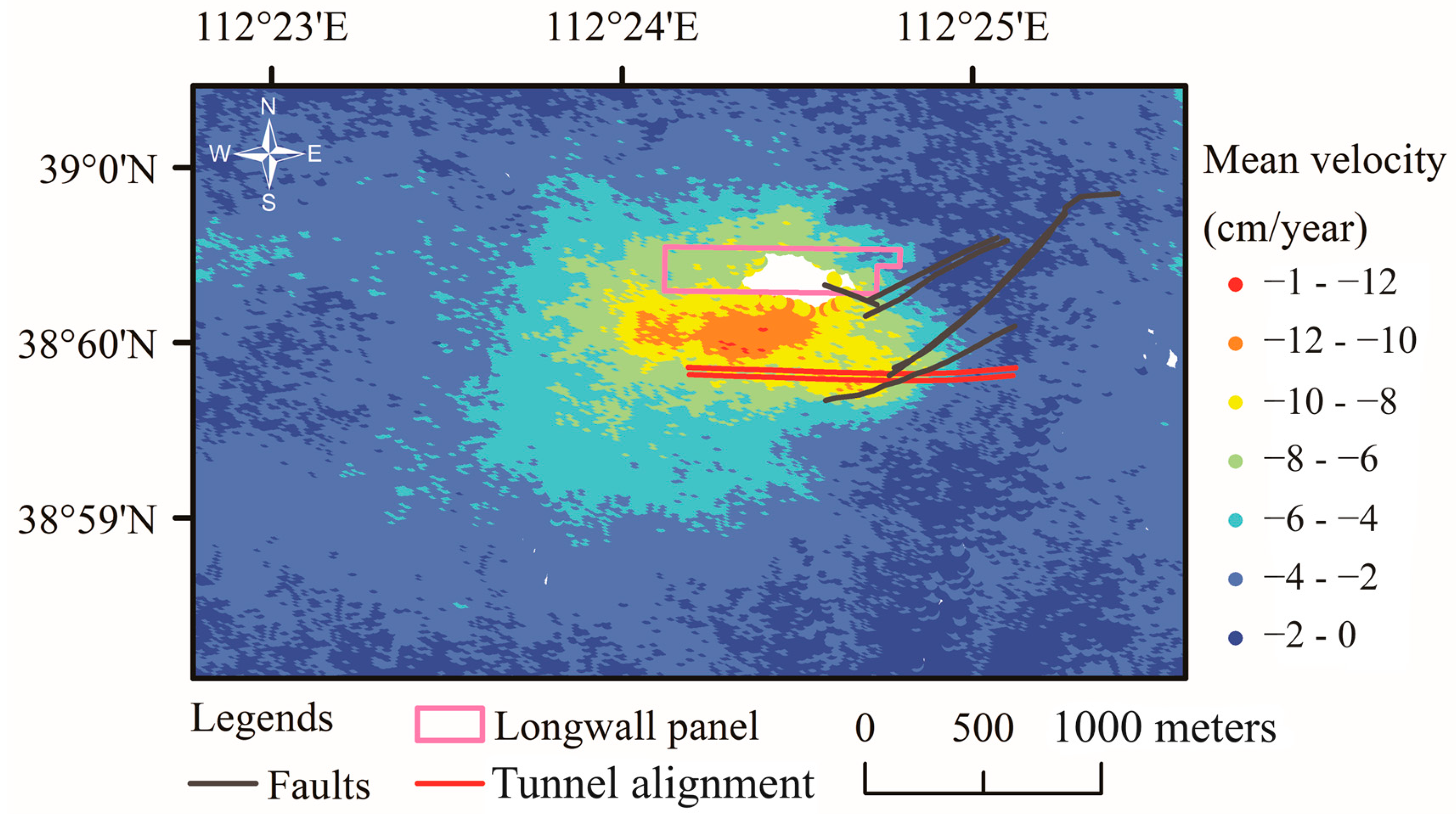
4.2. Mean LOS Velocity of Mining-Induced Ground Subsidence/Surface Mean Velocity Fields
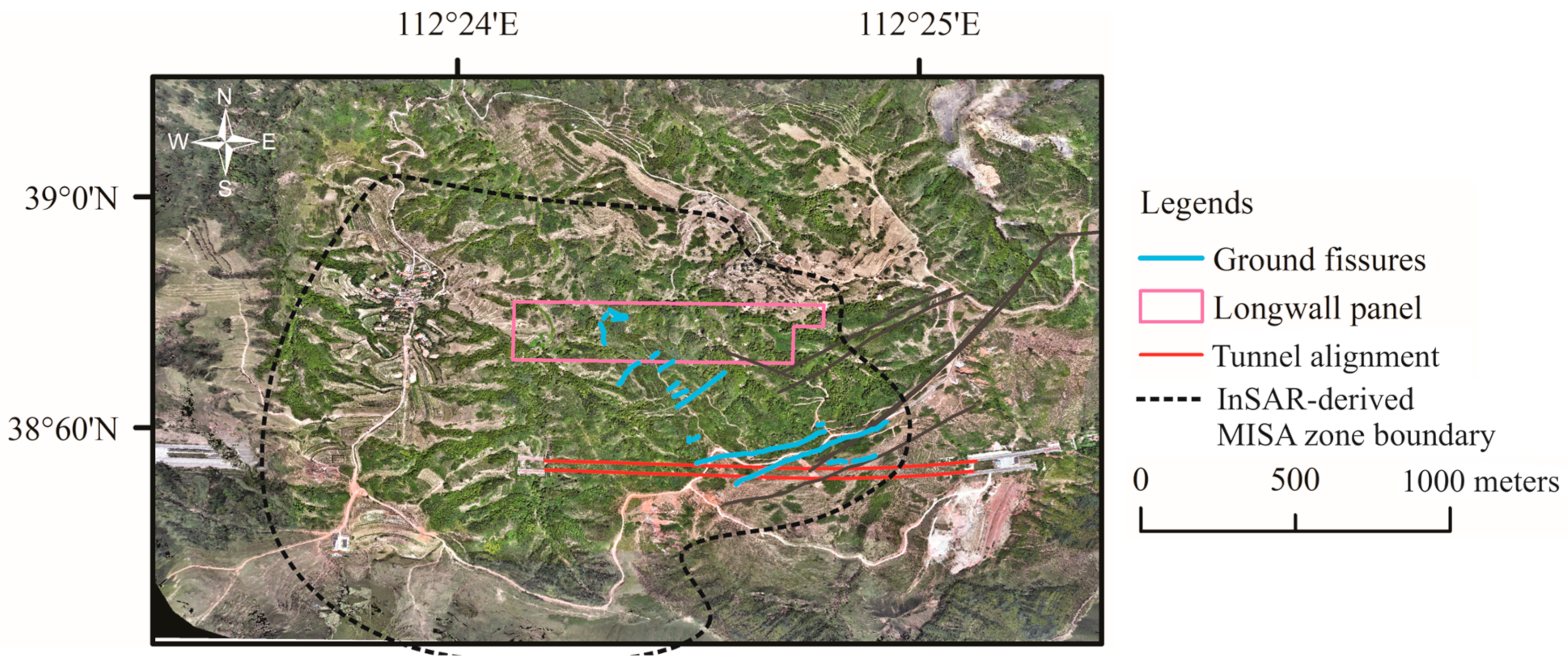
4.3. Ground Fissures Derived from Field Investigation and UAV Measurements
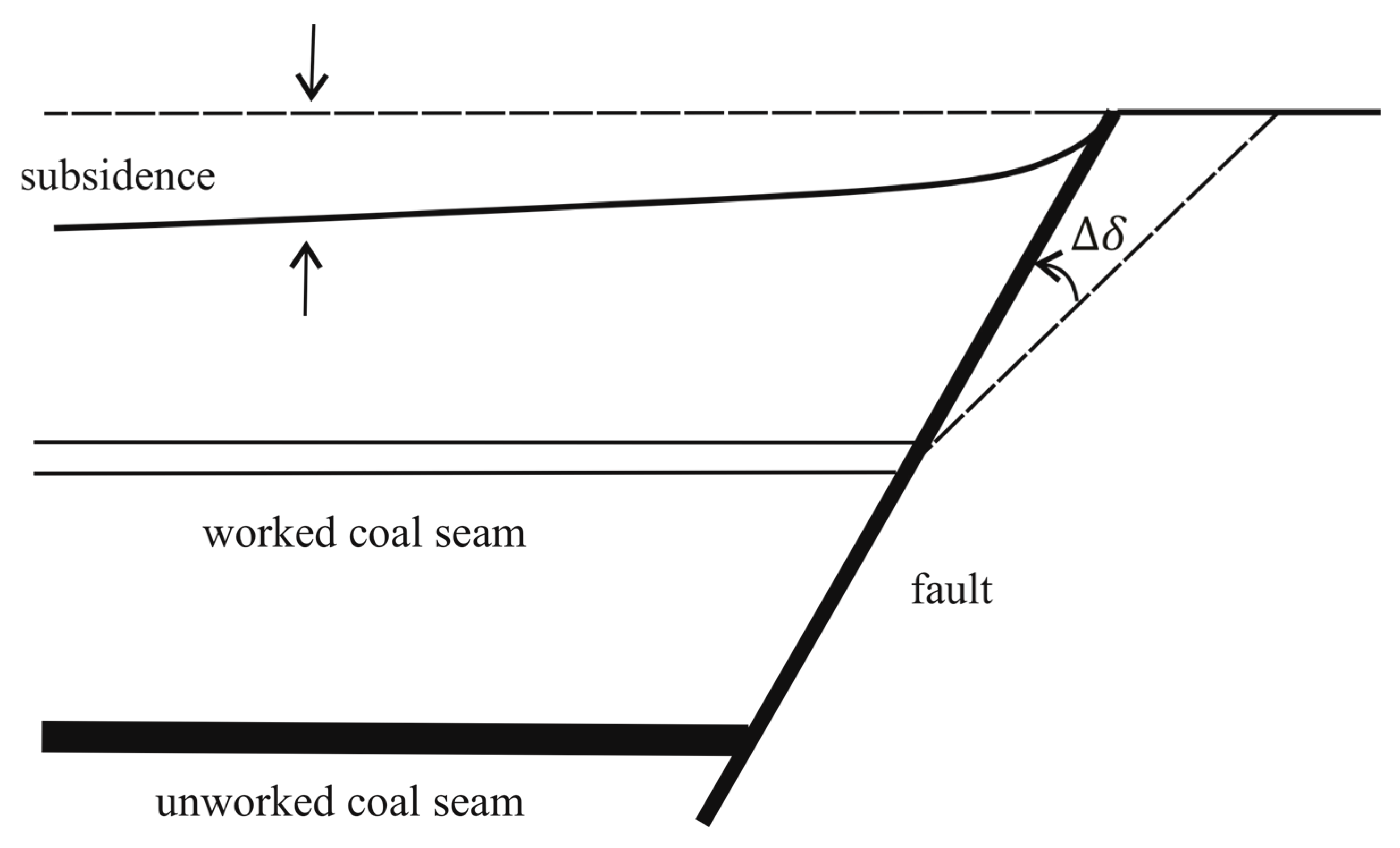
4.4. Angles of Draw of Unevenly Distributed Ground Movements
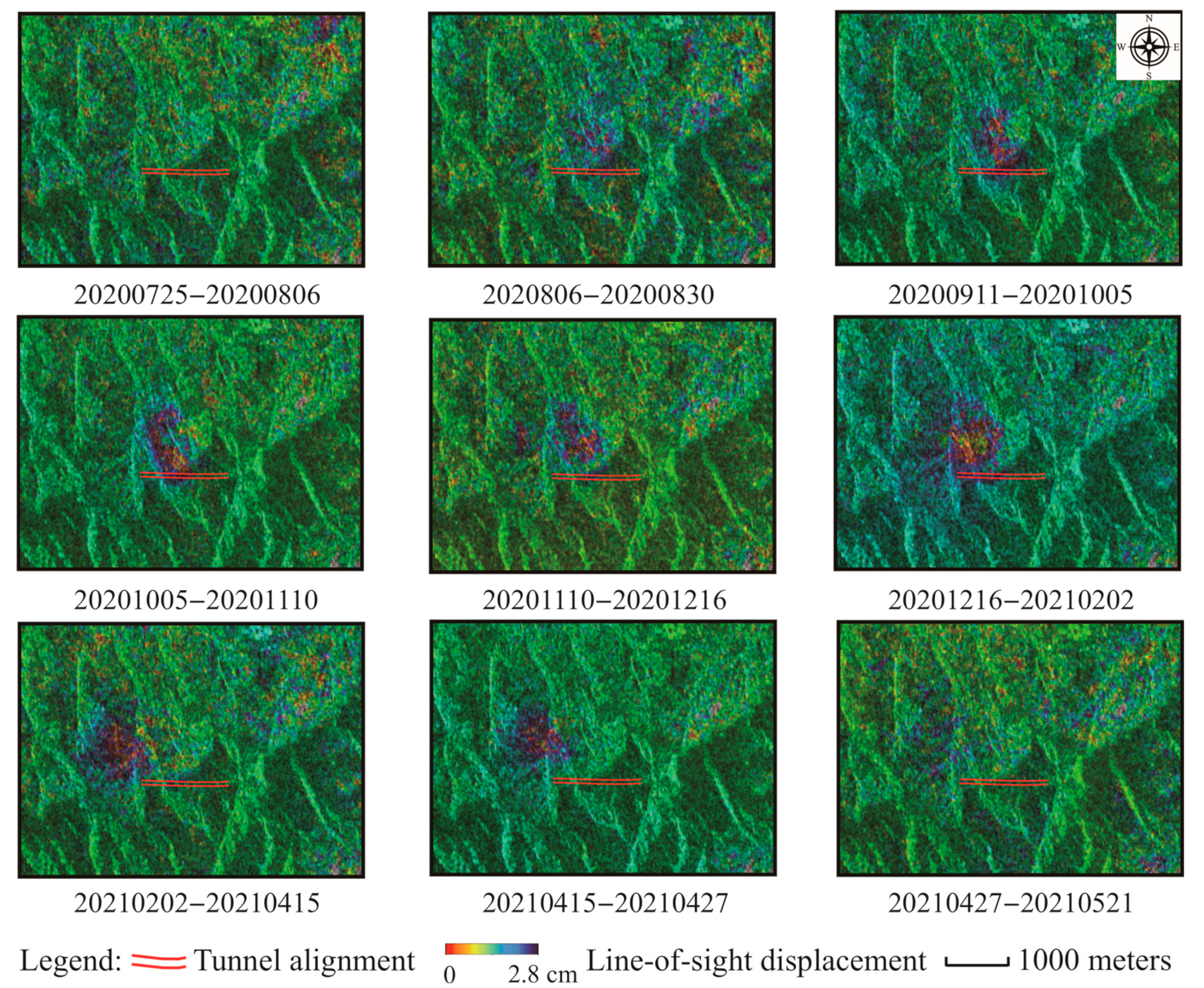
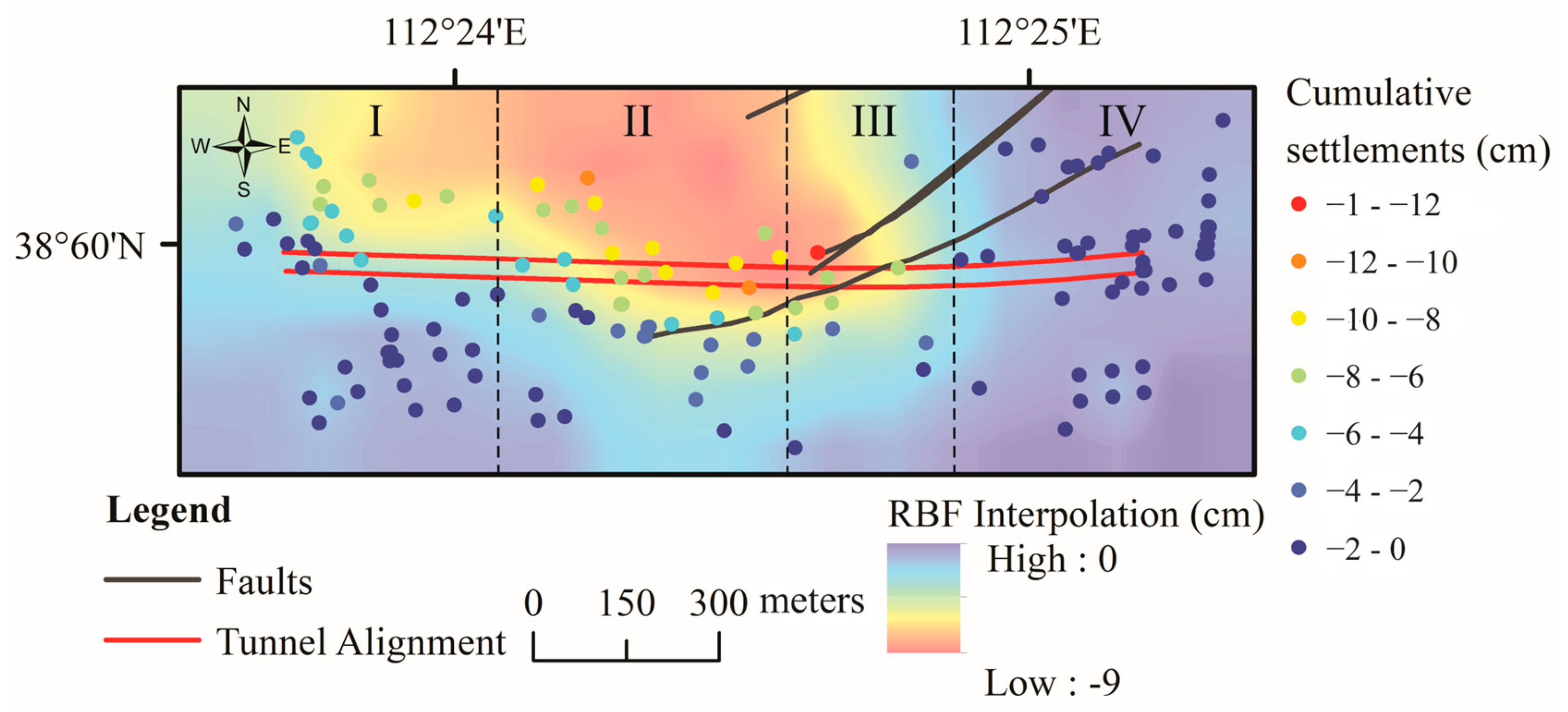
4.5. Time-Series Measurements Around Tunnel Alignments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, M. Mine Subsidence, Society of Mining Engineers; AIME: Littleton, CO, USA, 1986; p. 73-1. [Google Scholar]
- Guéguen, Y.; Deffontaines, B.; Fruneau, B.; Al Heib, M.; de Michele, M.; Raucoules, D.; Guise, Y.; Planchenault, J. Monitoring residual mining subsidence of Nord/Pas-de-Calais coal basin from differential and Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (Northern France). J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzsch, H. Mining Subsidence Engineering; Fleming, R.F.S., Translator; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, B.N.; Reddish, D.J. Subsidence-Occurrence, Prediction and Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, R.; Yang, J. Identifying the cause of abnormal building damage in mining subsidence areas using InSAR technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 172296–172304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modeste, G.; Doubre, C.; Masson, F. Time evolution of mining-related residual subsidence monitored over a 24-year period using InSAR in southern Alsace, France. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Coal Board (NCB). Subsidence Engineer’s Handbook; NCB Mining Department: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Holla, L.; Barclay, E. Mine Subsidence on the Southern Coalfield New South Wales; New South Wales Department of Mineral Resources: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2000; Volume 118. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Li, J. A study of angle of draw in mining subsidence using numerical modeling techniques. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2008, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shao, F. Boundary demarcation of the damaged cultivated land caused by coal mining subsidence. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2014, 73, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.L.; Whittaker, B.N.; Reddish, D.J. Influence of overburden mass behavioural properties on subsidence limit characteristics. Min. Sci. Technol. 1991, 13, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.B.; Singh, T.N. Ground movements over longwall workings in the Kamptee coalfield, India. Eng. Geol. 1998, 50, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Chen, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cai, L. Theoretical analysis of mining induced overburden subsidence boundary with the horizontal coal seam mining. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6657738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, K.; Zhou, W.; Gutierrez, M. Mapping Urban Excavation Induced Deformation in 3D via Multiplatform InSAR Time-Series. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyłucka, M.; Kowalski, Z.; Perski, Z. Twenty years of coal mining-induced subsidence in the Upper Silesia in Poland identified using InSAR. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, K.; Zhou, W.; Gutierrez, M. Tunneling- and dewatering-induced rapid differential ground rebound and delayed subsidence measured by InSAR in an urban environment. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 024512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowski, J.; Jirankova, E.; Lazecký, M.; Kadlečík, P.; Milczarek, W. Application of satellite radar interferometry (PSInSAR) in analysis of secondary surface deformations in mining areas. Case studies from Czech Republic and Poland. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2018, 15, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, W.; Gutierrez, M. Mapping Tunneling-Induced Uneven Ground Subsidence Using Sentinel-1 SAR Interferometry: A Twin-Tunnel Case Study of Downtown Los Angeles, USA. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Holzer, T.; Vadon, H. Land subsidence caused by the East Mesa geothermal field, California, observed using SAR interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, R.J.; Wright, P. Mining subsidence land survey by SAR interferometry. In ESA SP (Print); ESA Publications Division: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Perski, Z. Applicability of ERS-1 and ERS-2 InSAR for land subsidence monitoring in the Silesian coal mining region, Poland. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1998, 32, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Wempen, J.M. Application of DInSAR for short period monitoring of initial subsidence due to longwall mining in the mountain west United States. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lowry, B.; Wnuk, K.; Liu, L.; Gutierrez, M. InSAR and Its Applications in Geo-engineering: Case Studies with Different Platforms and Sensors. In Information Technology in Geo-Engineering, Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Information Technology in Geo-Engineering, Golden, CO, USA, 5–8 August 2024; Gutierrez, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, L.C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Integration of DInSAR and SBAS Techniques to determine mining-related deformations using sentinel-1 data: The case study of Rydułtowy mine in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. SAR monitoring of progressive and seasonal ground deformation using the Permanent Scatterers technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1685–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Sunar, F.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E. Time series analysis of InSAR data: Methods and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piter, A.; Haghighi, M.H.; Motagh, M. Evaluation of pixel selection methods for traffic infrastructure monitoring using Sentinel-1 InSAR. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 43, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmüller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Interferometric point target analysis for deformation mapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’03, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 1, pp. 221–223. [Google Scholar]
- Teatini, P.; Ferronato, M.; Gambolati, G.; Bertoni, W.; Gonella, M. A century of land subsidence in Ravenna, Italy. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Strozzi, T.; Tosi, L.; Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C.; Carbognin, L. Assessing short-and long-time displacements in the Venice coastland by synthetic aperture radar interferometric point target analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Tao, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, F. Accuracy verification and correction of D-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR in monitoring mining surface subsidence. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parwata, I.N.S.; Shimizu, N.; Zeka, S.; Gruji, B.; Vrkljan, I. Application of DInSAR for monitoring the subsidence induced by salt mining in Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina. In Proceedings of the ISRM International Symposium-Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ISRM-ARMS10), Singapore, 29 October–3 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, B.S.; Wempen, J.M. Quantifying relationships between subsidence and longwall face advance using DInSAR. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Wegmuller, U.; Werner, C.; Wiesmann, A. Measurement of slow uniform surface displacement with mm/year accuracy. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37120), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; Volume 5, pp. 2239–2241. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, T.; Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y. Research on the applicability of DInSAR, stacking-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR for mining region subsidence detection in the datong coalfield. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Jiang, M.; He, X. InSAR stacking with atmospheric correction for rapid geohazard detection: Applications to ground subsidence and landslides in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, J.; Smith, A. UAV & satellite synergies for optical remote sensing applications: A literature review. J. Remote Sens. Technol. 2023, 12, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Doe, J.; Lee, B. Identification of mining induced ground fissures using UAV and infrared thermal imager: Temperature variation and fissure evolution. J. Geospat. Technol. 2023, 15, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Trippi, M.H.; Belkin, H.E.; Dai, S.; Tewalt, S.J.; Chou, C.J. USGS Compilation of Geographic Information System (GIS) Data Representing Coal Mines and Coal-Bearing Areas in China (No. 2014-1219); US Geological Survey: Reston, VI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ESA (European Space Agency). SENTINEL-1, ESA’s Radar Observatory Mission for GMES Operational Services; ESA SP-1322/1; ESA: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- NASA JPL. NASADEM Merged DEM Global 1 Arc Second V001. Distributed by OpenTopography. 2021. Available online: https://portal.opentopography.org/datasetMetadata?otCollectionID=OT.032021.4326.2 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Ge, L.; Cheng, E.; Li, X.; Rizos, C. Quantitative subsidence monitoring: The integrated InSAR, GPS and GIS approach. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Satellite Navigation Technology Including Mobil Positioning & Location Services, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 22–25 July 2003; Volume 87. [Google Scholar]
- Raucoules, D.; Parcharidis, I.; Feurer, D.; Novalli, F.; Ferretti, A.; Carnec, C. Ground deformation detection of the greater area of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece) using radar interferometry techniques. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lin, H.; Ma, J.; Kong, B.; Wang, Y. Potential of small-baseline SAR interferometry for monitoring land subsidence related to underground coal fires: Wuda (Northern China) case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, Y.; Tan, K. Coal mining deformation monitoring using SBAS-InSAR and offset tracking: A case study of Yu County, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6077–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, L.J.; Culshaw, M.G.; Bell, F.G. Longwall mining-induced fault reactivation and delayed subsidence ground movement in British coalfields. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2008, 41, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

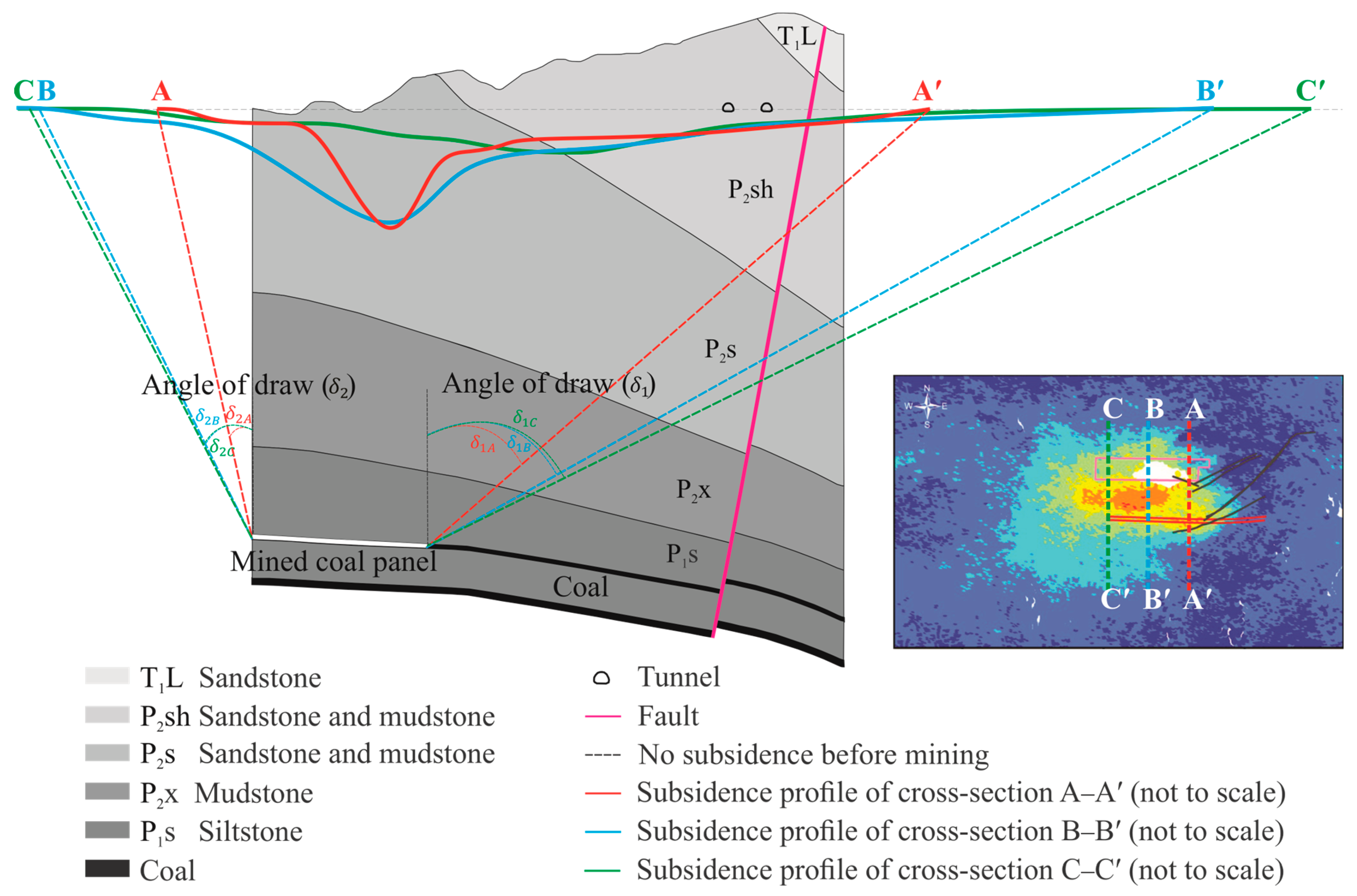
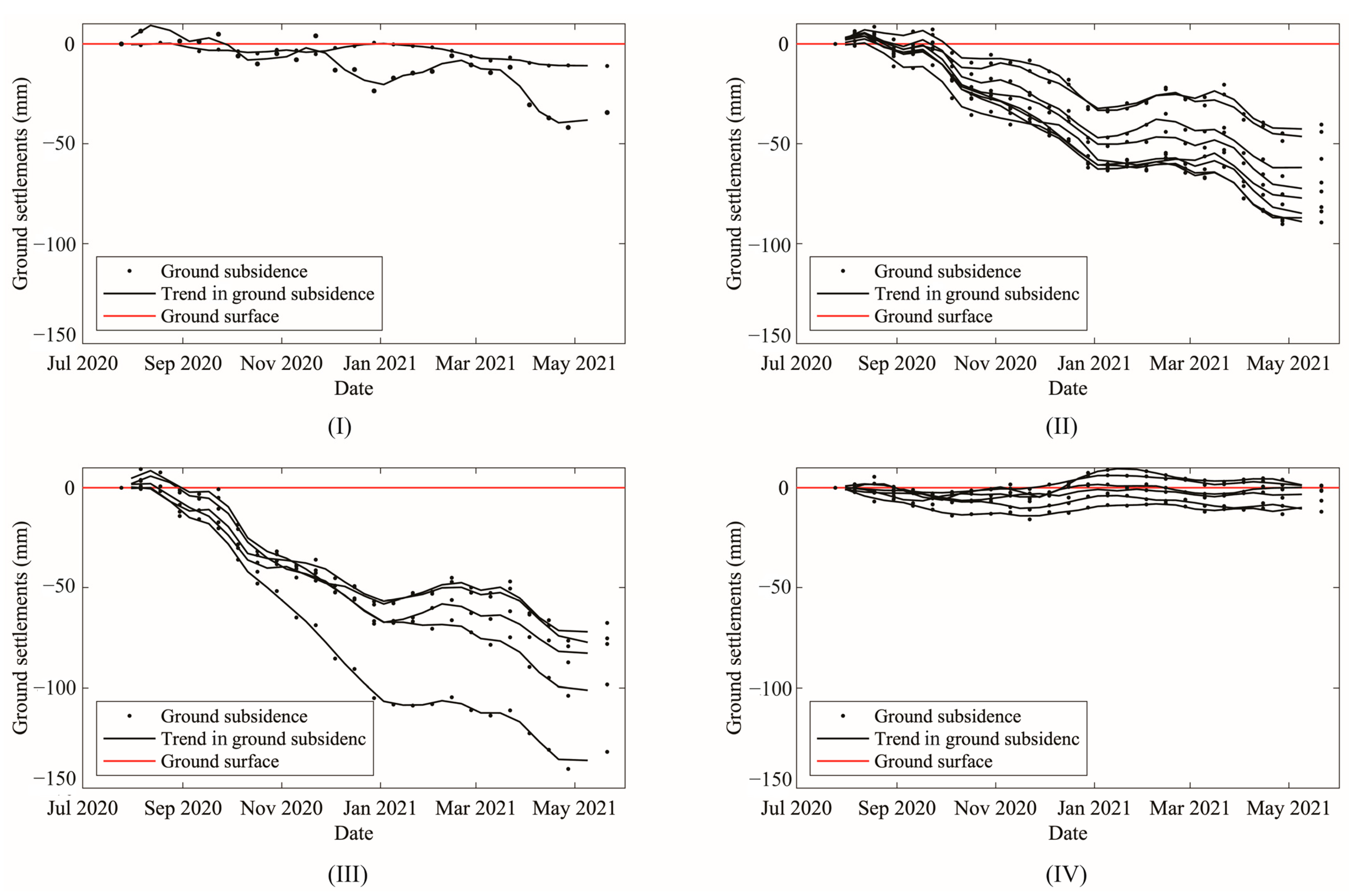
| Profile A–A’ ) | Profile B–B’ ) | Profile C–C’ ) | Profile A–A’ ) | Profile B–B’ ) | Profile C–C’ ) | |
| Values in degrees | 61 | 64 | 77 | 41 | 29 | 26 |
| Methodology | Objectives | Measurement Accuracy | Interferograms |
|---|---|---|---|
| DInSAR | Mining history reconstruction | Centimeter | 9 |
| InSAR stacking | Surface mean velocity fields; | Centimeter | 146 |
| Time-series analysis | High-resolution time-series analysis of ground movement above the existing tunnel and around the boundary of the mining-impacted area | Millimeter | 24 single reference 68 multireference |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Xu, N.; Zhou, W.; Qin, Y.; Luan, S. Improvement of Coal Mining-Induced Subsidence-Affected (MISA) Zone Irregular Boundary Delineation by MT-InSAR Techniques, UAV Photogrammetry, and Field Investigation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224221
Liu L, Xu N, Zhou W, Qin Y, Luan S. Improvement of Coal Mining-Induced Subsidence-Affected (MISA) Zone Irregular Boundary Delineation by MT-InSAR Techniques, UAV Photogrammetry, and Field Investigation. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(22):4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224221
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Linan, Nengxiong Xu, Wendy Zhou, Yan Qin, and Shilong Luan. 2024. "Improvement of Coal Mining-Induced Subsidence-Affected (MISA) Zone Irregular Boundary Delineation by MT-InSAR Techniques, UAV Photogrammetry, and Field Investigation" Remote Sensing 16, no. 22: 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224221
APA StyleLiu, L., Xu, N., Zhou, W., Qin, Y., & Luan, S. (2024). Improvement of Coal Mining-Induced Subsidence-Affected (MISA) Zone Irregular Boundary Delineation by MT-InSAR Techniques, UAV Photogrammetry, and Field Investigation. Remote Sensing, 16(22), 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224221










