Water–Ecological Health Assessment Considering Water Supply–Demand Balance and Water Supply Security: A Case Study in Xinjiang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
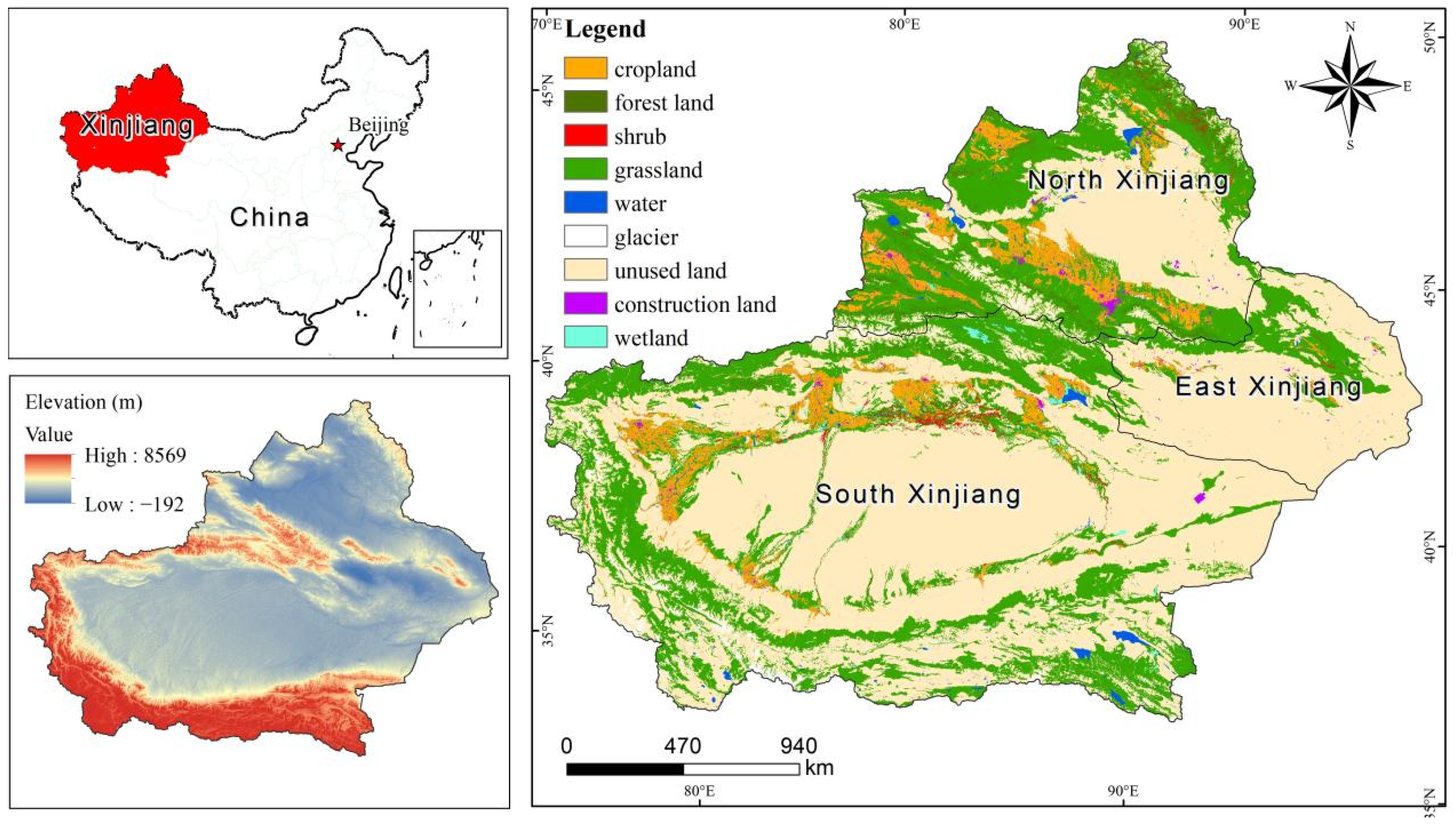
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Framework for Assessing the State of Water–Ecological Safety and Health
2.3.1. Water Supply–Demand Ratio
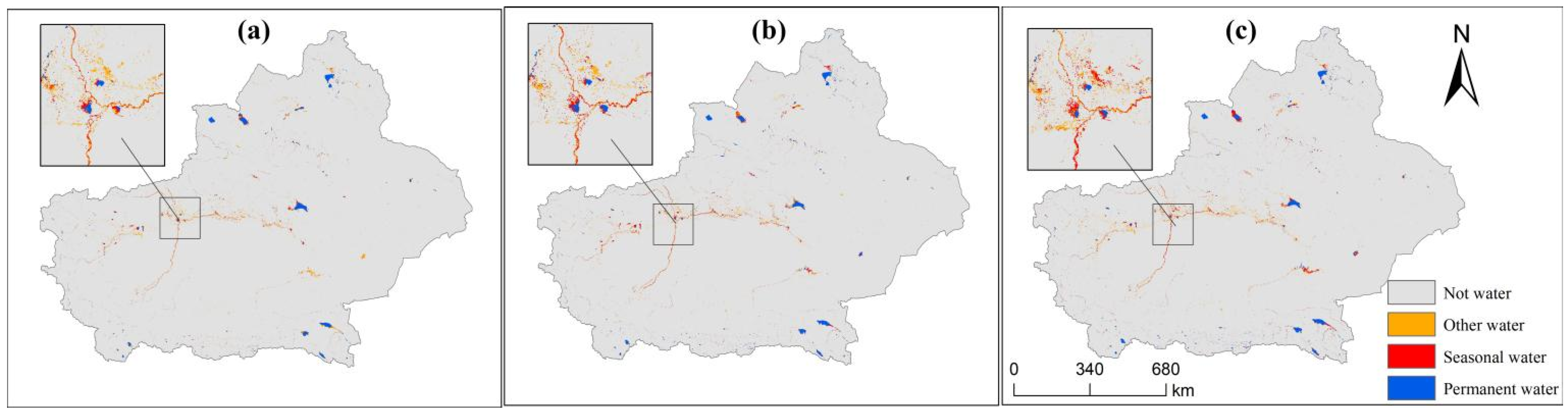
2.3.2. Water Supply Security
2.3.3. Ecological Resilience
2.4. Aridity Index
2.5. Rate of Change
3. Results
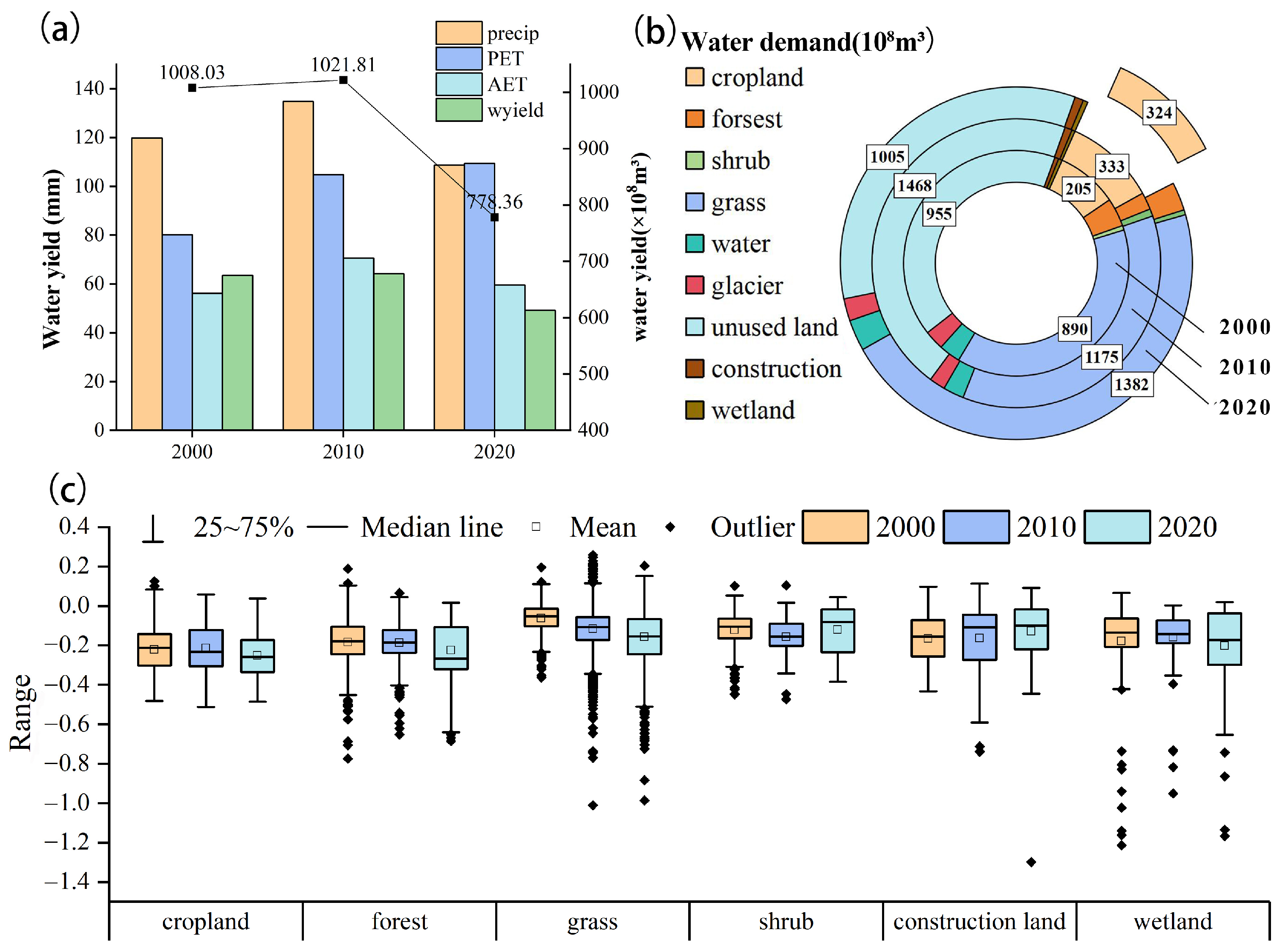
3.1. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Variations in WSDR
3.2. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Variations in WSC
3.3. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Changes in ER
3.4. Evaluation of the WESHI
3.5. Indicator Response to AI
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Health Assessment and Changes in the WESHI
4.2. Impact of Human Activity on Ecological Health
4.3. Recommendations for Optimal Allocation of Water Resources
4.4. Impact of Warming and Humidification Processes on the WESHI
4.5. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Description | Lucode | Root_depth | Kc | LULC_veg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 1 | 2000 | 0.65 | 1 |
| Forest | 2 | 5000 | 1 | 1 |
| Shrub | 3 | 3500 | 0.93 | 1 |
| Grass | 4 | 2000 | 0.75 | 1 |
| Water | 5 | 100 | 1 | 0 |
| Glacier | 6 | 100 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Unused land | 7 | 300 | 0.2 | 0 |
| Construction | 8 | 100 | 0.2 | 0 |
| Wetland | 9 | 1000 | 0.8 | 1 |

References
- Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, J. Ecological Vulnerability Assessment of the Qaidam Basin Based on SRP Model. J. Salt Lake Res. 2024, 32, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Lu, H.; Li, W.Y.; Gong, P. Natural lakes dominate global water storage variability. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1016–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Yang, P.; Zhou, H.; Xu, H. Water Conversion and Strategy of Ecological Water Conveyance in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River. Arid Zone Res. 2017, 34, 717–726. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Cai, H.; Zhang, X.; She, Y.; Peng, S. Driving Factors and Evolution of Supply and Demand of Water Conservation Services in Raohe River Basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 389–399, 464. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Xiao, F.; Sun, J.; Song, D. The current status of ecosystem health and its assessment. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2004, 12, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, J. Assessment of ecosystem health--concept framework and indicator selection. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 12, 627–629. [Google Scholar]
- Rapport, D.J.; Costanza, R.; McMichael, A.J. Assessing ecosystem health. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Progress of Ecosystem Health Assessment Study. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2002, 15, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, T.; Sun, M.; Hao, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y. Development of Ecosystem Health Assessment (EHA) and Application Method: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Zhong, X.; Yu, G.; He, G. The concept and methods of assessment for regional ecosystem influence of human development and decision. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2005, 39, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Tian, B.; Gu, S.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y. The Influence of Vegetation Coverage on the Dynamic Evolution of Ecological Vulnerability: A Case Study of Zhangjiakou, Hebei Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 310–320. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yu, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, X. Post-Restoration Monitoring of Wetland Restored from Farmland Indicated That Its Effectiveness Barely Measured Up. Water 2024, 16, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Tao, Y.; Pang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yu, X. Ecological health assessment and main influencing factors of Lake Taihu Basin based on PSR model. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2024, 14, 846–855. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Huang, X. Research on the geometric weighting-coupling degree method for the urban ecological environment vulnerability index. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Ao, Z.; Jiang, Y. Assessment of ecological environment vulnerability in Tianshui city based on the CRITIC objective weighting method. J. Desert Res. 2024, 44, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Q.; Heal, K.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Yao, X. The Performance of the Construction of a Water Ecological Civilization City: International Assessment and Comparison. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Bose, S. Comparative study on remote sensing-based indices for urban ecology assessment: A case study of 12 urban centers in the metropolitan area of eastern India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 133, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Mo, J.; Liu, X. Assessment of ecosystem health based on landscape pattern in ecologically fragile regions at different spatial scales: A case study of Dianchi Lake basin, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1076344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, W.; He, Z.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J. Ecological health assessment of Tibetan alpine grasslands in Gannan using remote sensed ecological indicators. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Qiao, B.; Yu, H.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Q. Ecological health assessment of the alpine wetland landscape in the Heihe River source area based on vigor, organization, and resilience. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 41, 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Liang, Q.; Song, H.; Liu, S. Assessing the Landscape Ecological Health (LEH) of Wetlands: Research Content and Evaluation Methods (2000–2022). Water 2023, 15, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, H.; Xia, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, J. Assessing ecological health in a semi-arid basin: A case study of the Wei River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 21687–21708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, D.; Lu, H. Identification of key indicators of water ecological health and establishment of comprehensive evaluation system of the Sunan Canal. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 407–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kaghazchi, M.E.; Soleimani, M. Changes in ecological and health risk assessment indices of potentially toxic elements associated with ambient air particulate matters (PM2.5) in response to source, land use and temporal variation in Isfahan city, Iran. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C. Ecological health assessment of the Qinghe River Basin: Analysis and recommendations. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.C.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.Z.; Hu, M.X.; Tian, J.J.; Zhao, H.Z.; Ren, H.Z. Analysis of the spatial and temporal evolution of water and soil resource carrying capacity in arid region of northwest China. Water Supply 2022, 22, 8813–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhao, X.; Fan, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Assessing spatio-temporal characteristics and their driving factors of ecological vulnerability in the northwestern region of Liaoning Province (China). Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Ren, Z.; Zi, Y. Analysis on evolution of carrying state of water and soil resources in artificial oases in arid areas. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2023, 41, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gao, K.; Luo, N.; Mei, P.; Zhang, Z. Establishment and Application of the Index System for River Ecosystem Health Assessment. Environ. Monit. China 2023, 39, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Feng, Q.; Lyu, M. Tradeoffs of ecosystem services and their influencing factors: A case study of the Shanxi Section of the Yellow River Basin. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 41, 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Legesse, D.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Gasse, F. Analysis of the hydrological response of a tropical terminal lake, Lake Abiyata (Main Ethiopian Rift Valley) to changes in climate and human activities. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Barek, S.A.; Bouslihim, Y.; Rochdi, A.; Miftah, A. Effect of LULC data resolution on hydrological and erosion modeling using SWAT model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Wu, M.; Jia, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Spatiotemporal variation of water yield in the upstream regions of the Shule River Basin using the InVEST Model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 6418–6429. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yin, Z.; Liu, T.; Xin, Q. Modeling and analyzing supply-demand relationships of water resources in Xinjiang from a perspective of ecosystem services. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Feng, S.; Jiang, D.; Jiang, F. Characteristics and estimation of vegetation ecological water demand in the Mara River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 7523–7535. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Deng, C.; Zhao, K.; Jin, Y.; Chen, D. Supply-Demand Balance of Ecosystem Services in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Based on Land Use Change. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; OuYang, H.; Fu, B.; Niu, H. Forest Ecosystem Health Assessment Indicators and Application in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 805–809. [Google Scholar]
- Lobser, S.E.; Cohen, W.B. MODIS tasselled cap: Land cover characteristics expressed through transformed MODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5079–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiao, L.; Lai, F.; Zhang, N. Evaluation of ecological changes based on a remote sensing ecological index in a Manas Lake wetland, Xinjiang. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Li, B.; Kong, F.; He, T. Spatial-temporal variation, driving mechanism and management zoning of ecological resilience based on RSEI in a coastal metropolitan area. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, B. Greater increases in China’s dryland ecosystem vulnerability in drier conditions than in wetter conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 291, 112689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gui, D.; Xue, D.; Liu, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Lei, J. Analysis of the Expansion Characteristics and Carrying Capacity of Oasis Farmland in Northwestern China in Recent 40 Years. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Jim, C.-Y.; Chan, N.W.; Johnson, V.C.; Liu, C.; Duan, P.; Bahtebay, J. Spatio-temporal variations and drivers of ecological carrying capacity in a typical mountain-oasis-desert area, Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 180, 106672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Hou, Y.; Bo, Y. Analysis on Evolution of Ecological Vulnerability of Shanxi Province based on the Remote Sensing and GIS Technique. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2024, 39, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Luo, J.; Cui, C. Oasis agriculture sustainable development in Xinjiang. J. Arid Land. Res. Environ. 2011, 25, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Jiao, D. Regional supply-demand balance and carrying capacity of water resources for Linze Oasis in the middle of Hexi Corridor. Arid Land Geogr. 2018, 41, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, K. Evaluation of water resource carrying capacity of Qitai Oasis in Xinjiang by entropy method. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2012, 20, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. A review of social-ecological system vulnerability in desertified regions: Assessment, simulation, and sustainable management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y. Livelihood Vulnerability and Adaptation for Households Engaged in Forestry in Ecological Restoration Areas of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 849–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Li, M.; Dilinuer, T.; Chen, J.; Mao, W. The assessment on “warming-wetting” trend in Xinjiang at multi-scale during 1961–2019. Arid Zone Res. 2022, 39, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Wu, Y.; Chi, H.; Zheng, S.; Yan, J.; Ren, Y.; Sun, Z. Detecting Spatiotemporal Changes of Freshwater in Northwest China under a Warm-Wetting Climate using Remote Sensing. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2023, 25, 1842–1854. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Mao, W.; Chen, J.; Dilinuer, T. Signal and impact of wet-to-dry shift over Xinjiang, China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, P.; Xue, T.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, P. Regional Responses to Global Climate Change: Progress and Prospects for Trend, Causes, and Projection of Climatic Warming-Wetting in Northwest China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2023, 38, 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Wang, X.; Miao, H. Ecosystem services analyses and valuation of China terrestrial surface water system. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2004, 24, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.P. Reservoir ecology and limnology in China: A retrospective comment. Sci. Limnol. Sin. 2010, 22, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, G.; Huang, L.; Kong, L.; Suo, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. Environmental changes and cladoceran community responses during the past 200 years in an alpine lake of Wodi Co, Northwest Yunnan. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 2170–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, L. Change Features and Influencing Factors of Trophic States of the Caotang River in Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 29, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar]








| Classification | Data Name | Resolution | Time Range | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate | Monthly average temperature (°C) | 1 km | 2000–2020 | The National Scientific Data Center on the Tibetan Plateau (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn) (accessed on 6 May 2024) |
| Monthly total precipitation (mm) | 1 km | 2000–2020 | ||
| Monthly actual evapotranspiration volume (mm) | 1 km | 2000–2020 | ||
| Monthly potential evapotranspiration volume (mm) | 1 km | 2000–2020 | ||
| Soil humidity | 1 km | 2000–2020 | The National Data Center for Earth System Sciences (https://auth.geodata.cn/) (accessed on 7 May 2024) | |
| Landform | Altitude (m) | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn) (accessed on 7 May 2024) | |
| Soil | Type | 1 km | Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn) (accessed on 8 May 2024) | |
| Land use | Land use type | 30 m | 2000, 2010, 2020 | |
| Water supply guarantee | Water frequency | 30 m | 2000, 2010, 2020 | Google Earth Engine Platform (JRC, MOD09A1, MOD13A1, MOD11A2) (https://earthengine.google.com/) (accessed on 12 May 2024) |
| Ecological resilience | NDVI, WET, LST, NDBSI, EVI, LAI | 500 m | 2000, 2010, 2020 | |
| Water resource data | Surface water resources and production, water system number | 2001–2020 | Xinjiang Water Resources Department (http://slt.xinjiang.gov.cn) (accessed on 14 May 2024) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Lai, X.; Long, A.; Zhang, P.; Deng, X.; Deng, M.; Ren, C.; Xiao, Y. Water–Ecological Health Assessment Considering Water Supply–Demand Balance and Water Supply Security: A Case Study in Xinjiang. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203834
Zhang J, Lai X, Long A, Zhang P, Deng X, Deng M, Ren C, Xiao Y. Water–Ecological Health Assessment Considering Water Supply–Demand Balance and Water Supply Security: A Case Study in Xinjiang. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(20):3834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203834
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ji, Xiaoying Lai, Aihua Long, Pei Zhang, Xiaoya Deng, Mingjiang Deng, Cai Ren, and Yi Xiao. 2024. "Water–Ecological Health Assessment Considering Water Supply–Demand Balance and Water Supply Security: A Case Study in Xinjiang" Remote Sensing 16, no. 20: 3834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203834
APA StyleZhang, J., Lai, X., Long, A., Zhang, P., Deng, X., Deng, M., Ren, C., & Xiao, Y. (2024). Water–Ecological Health Assessment Considering Water Supply–Demand Balance and Water Supply Security: A Case Study in Xinjiang. Remote Sensing, 16(20), 3834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203834








