Detection of the Infection Stage of Pine Wilt Disease and Spread Distance Using Monthly UAV-Based Imagery and a Deep Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
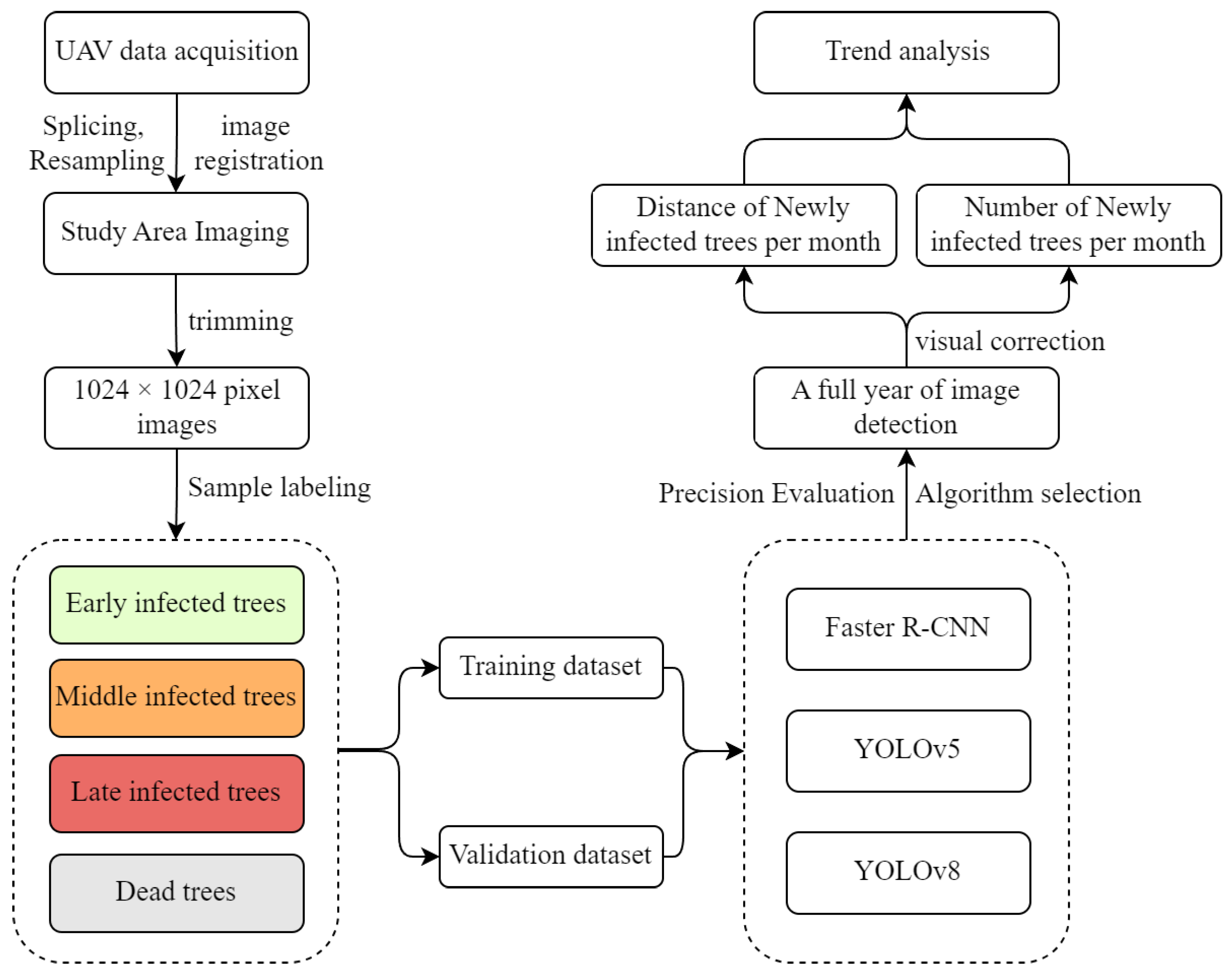
2.2. Dataset Collection and Preprocessing
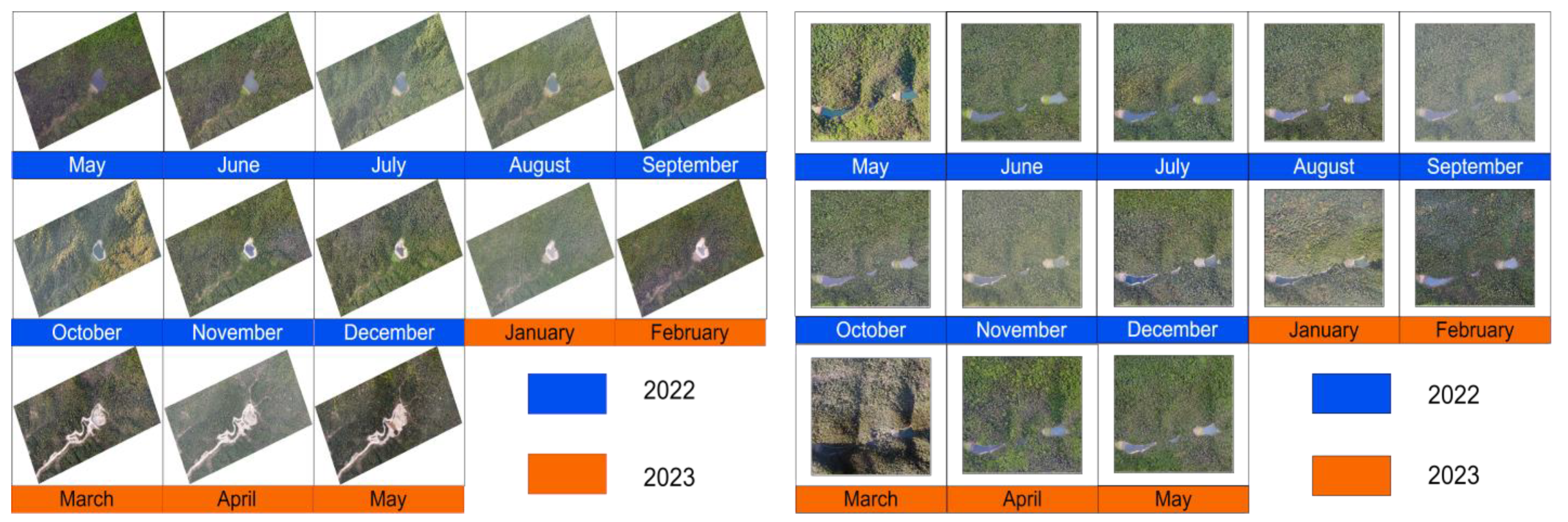
2.2.1. UAV-Based Imagery Acquisition
2.2.2. UAV-Based Imagery Preprocessing
2.2.3. Land Cover Classification
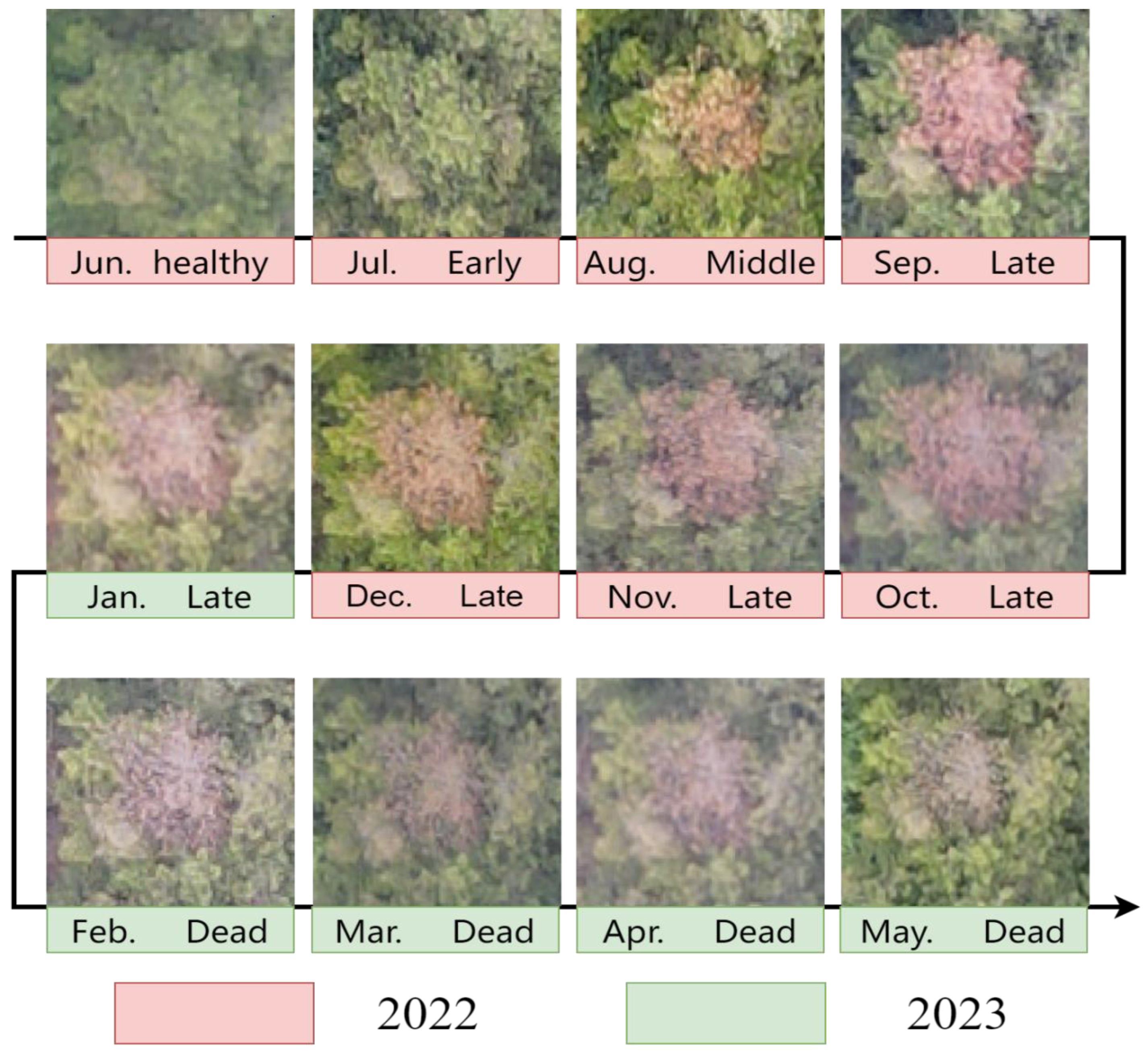
2.2.4. Image Labeling
2.3. Deep Learning Algorithms
2.4. Accuracy Assessment Metric
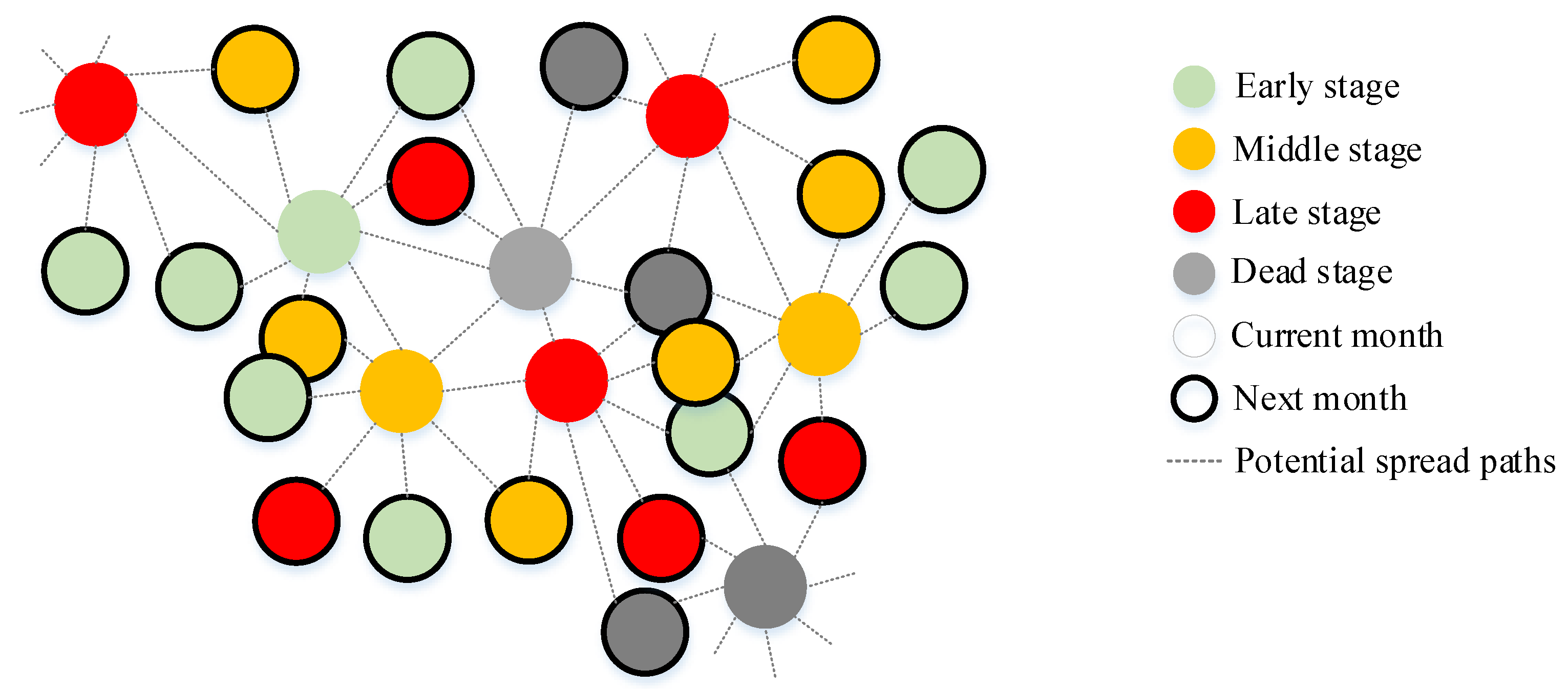
2.5. The Number of Newly Infected Trees and Spread Distance in Different Months
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy of Land Cover Classification Using UAV-Based Imagery
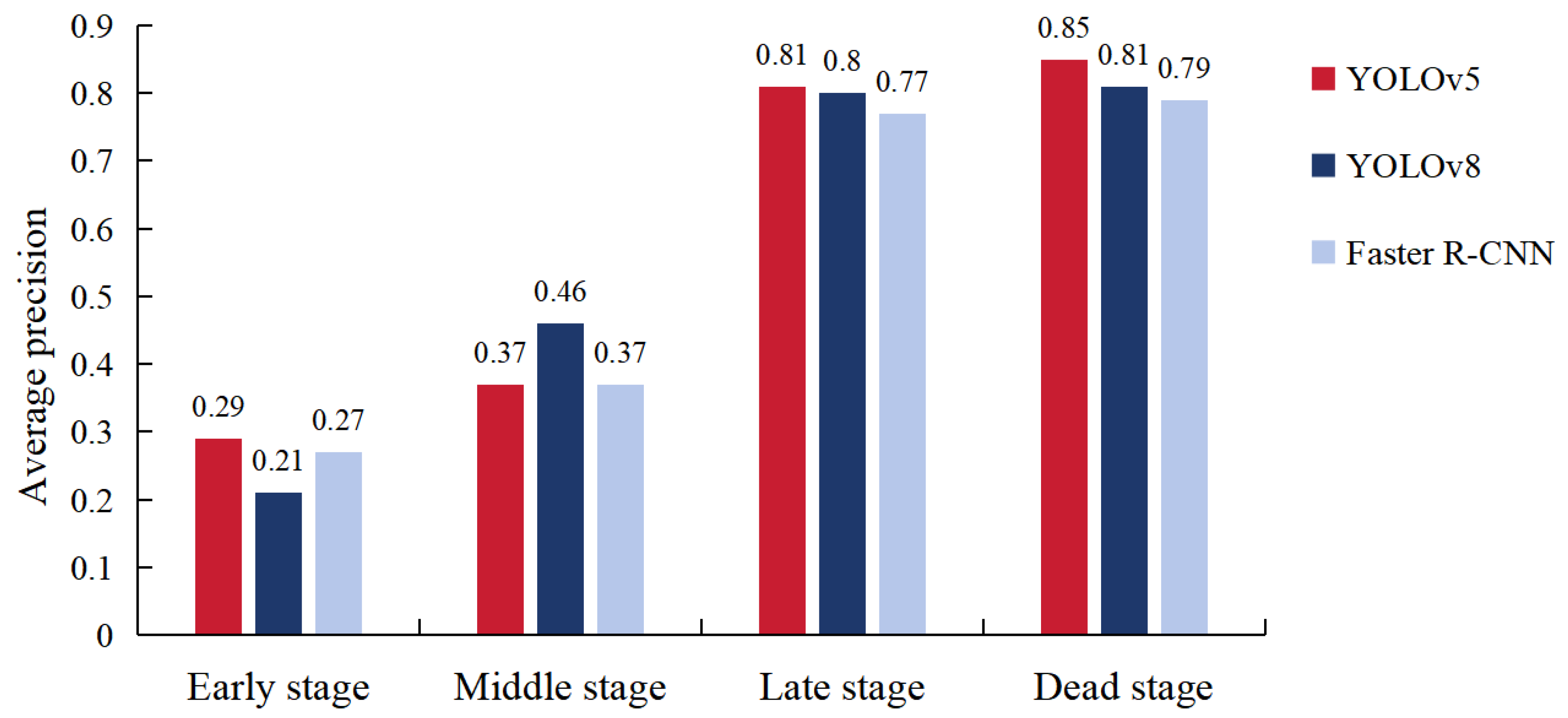
3.2. Accuracy of Tree Infection Stage Prediction with Deep Learning
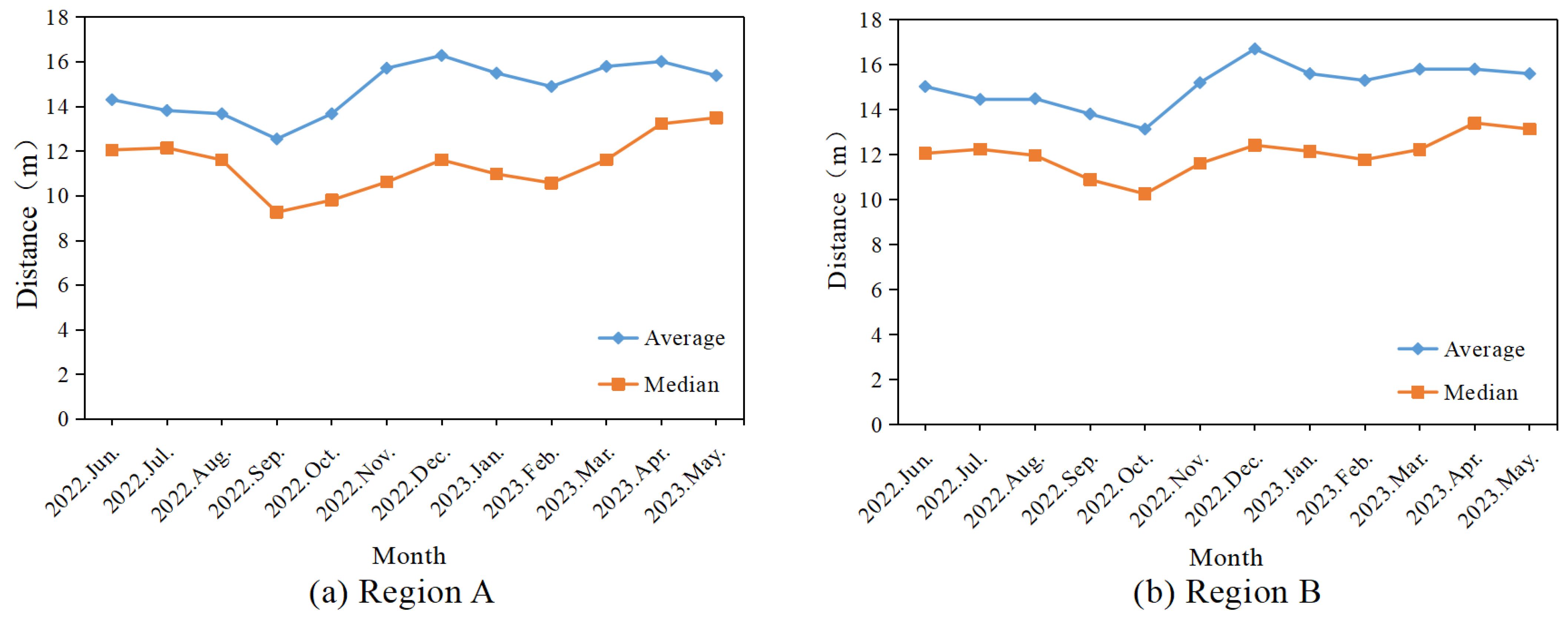
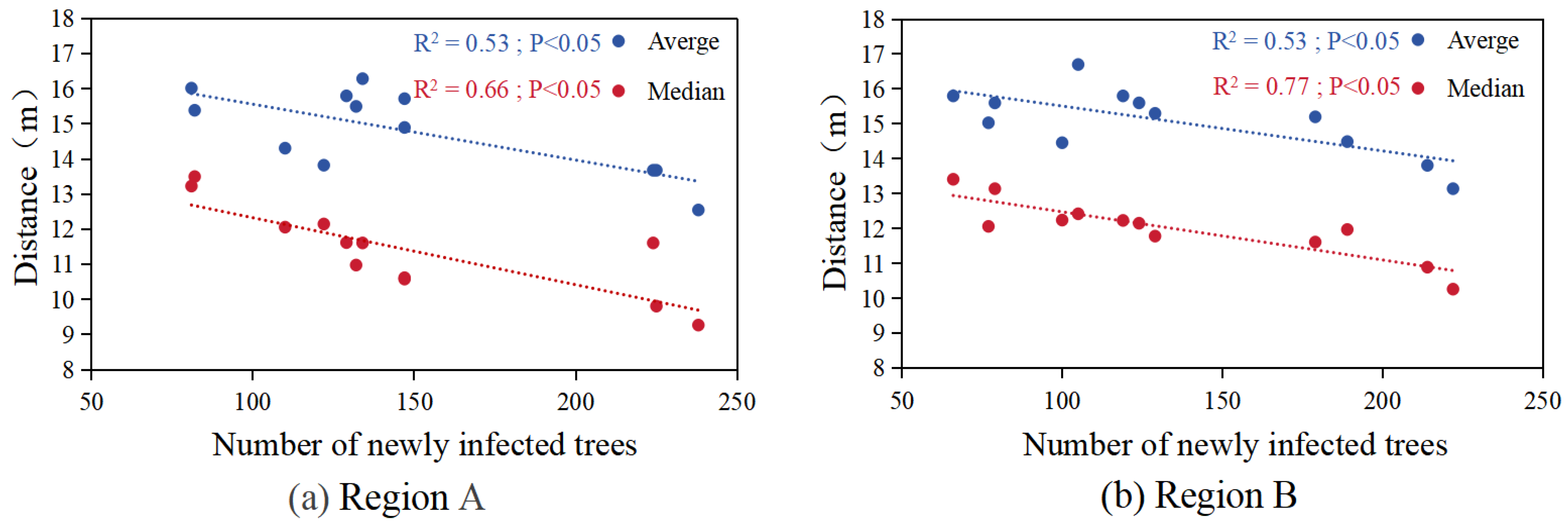
3.3. Trends in the Number of Newly Infected Trees and Spread Distance at the Monthly Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Q.; He, G.; Liu, X.; Peng, W.; Cai, Y. Impacts of climate change on pine wilt disease outbreaks and associated carbon stock losses. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 334, 109426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Lao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhou, H. Pine pest detection using remote sensing satellite images combined with a multi-scale attention-UNet model. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-N.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Cho, B.-K.; Kim, Y.-H.; Min, J. A short review of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2020, 12, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Epidemic status of pine wilt disease in China and its prevention and control techniques and counter measures. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2019, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, A.; Nakamura, K.; Nakao, K.; Kominami, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Ohashi, H.; Takano, K.T.; Takeuchi, W.; Matsui, T. Potential distribution of pine wilt disease under future climate change scenarios. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhong, Y. Detecting pine wilt disease at the pixel level from high spatial and spectral resolution UAV-borne imagery in complex forest landscapes using deep one-class classification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, R.; Shi, W.; Yu, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, X. Automatic Detection and Classification of Dead Nematode-Infested Pine Wood in Stages Based on YOLO v4 and GoogLeNet. Forests 2023, 14, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Fang, G. A multi-point aggregation trend of the outbreak of pine wilt disease in China over the past 20 years. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 505, 119890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; LI, X. National Occurrence of Major Forestry Pests in 2022 and Trend Forecast in 2023. For. Pest Dis. 2023, 42, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oide, A.H.; Nagasaka, Y.; Tanaka, K. Performance of machine learning algorithms for detecting pine wilt disease infection using visible color imagery by UAV remote sensing. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 28, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Ding, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. The Detection of Pine Wilt Disease: A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.; Borralho, N.; Cabral, P.; Caetano, M. Recent Advances in Forest Insect Pests and Diseases Monitoring Using UAV-Based Data: A Systematic Review. Forests 2022, 13, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Dennison, P.E.; Zhao, F.; Shendryk, I.; Rickert, A.; Hanavan, R.P.; Cook, B.D.; Serbin, S.P. Mapping canopy defoliation by herbivorous insects at the individual tree level using bi-temporal airborne imaging spectroscopy and LiDAR measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onojeghuo, A.O.; Onojeghuo, A.R. Object-based habitat mapping using very high spatial resolution multispectral and hyperspectral imagery with LiDAR data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 59, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W. Individual tree segmentation and tree species classification in subtropical broadleaf forests using UAV-based LiDAR, hyperspectral, and ultrahigh-resolution RGB data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Xie, Y.; Chen, E.; Zhang, X. Discriminative feature constraints via supervised contrastive learning for few-shot forest tree species classification using airborne hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, M.S.; Poblete, T.; de Silva, D.; Estarija, H.J.C.; Hartley, R.J.L.; Leonardo, E.M.C.; Massam, P.; Buddenbaum, H.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J. Prediction of the severity of Dothistroma needle blight in radiata pine using plant based traits and narrow band indices derived from UAV hyperspectral imagery. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 330, 109294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, J.; Xu, H.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H. Evaluating the potential of airborne hyperspectral LiDAR for assessing forest insects and diseases with 3D Radiative Transfer Modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 297, 113759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswidiyanto, L.W.; Wang, P.; Noh, H.-H.; Jung, H.-Y.; Jung, D.-H.; Han, X. Airborne hyperspectral imaging for early diagnosis of kimchi cabbage downy mildew using 3D-ResNet and leaf segmentation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 214, 108312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smigaj, M.; Gaulton, R.; Suárez, J.C.; Barr, S.L. Combined use of spectral and structural characteristics for improved red band needle blight detection in pine plantation stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 434, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Gao, R.; Zhao, F.; Huang, C.; Sun, R.; Lv, Z.; Huang, Z. Landsat-based monitoring of southern pine beetle infestation severity and severity change in a temperate mixed forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.M.; Chapman, W.K.; Prescott, C.E.; Nijland, W. Using excess greenness and green chromatic coordinate colour indices from aerial images to assess lodgepole pine vigour, mortality and disease occurrence. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 374, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Williams, P.J.; Hoffman, L.C. An overview of pre-processing methods available for hyperspectral imaging applications. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, G.; Rani, R.; Mangotra, H.; Sharma, A. Integration of hyperspectral imaging and autoencoders: Benefits, applications, hyperparameter tunning and challenges. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2023, 50, 100584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Guo, P.; Zhang, B.; Yan, J.; He, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J. Spatial-spectral attention-enhanced Res-3D-OctConv for corn and weed identification utilizing hyperspectral imaging and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastaranta, M.; Kantola, T.; Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, P.; Holopainen, M.; Kankare, V.; Wulder, M.A.; Hyyppä, J.; Hyyppä, H. Area-Based Mapping of Defoliation of Scots Pine Stands Using Airborne Scanning LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalagnol, R.; Phillips, O.L.; Gloor, E.; Galvão, L.S.; Wagner, F.H.; Locks, C.J.; Aragão, L.E.O.C. Quantifying Canopy Tree Loss and Gap Recovery in Tropical Forests under Low-Intensity Logging Using VHR Satellite Imagery and Airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Zhang, X. A new method of equiangular sectorial voxelization of single-scan terrestrial laser scanning data and its applications in forest defoliation estimation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, B.C.; Hudak, A.T.; McGaughey, R.; Andersen, H.-E.; Negrón, J. Predicting live and dead tree basal area of bark beetle affected forests from discrete-return lidar. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 39, S99–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, B.C.; Hudak, A.T.; Kennedy, R.E.; Meddens, A.J. Landsat time series and lidar as predictors of live and dead basal area across five bark beetle-affected forests. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3440–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Ren, L. A machine learning algorithm to detect pine wilt disease using UAV-based hyperspectral imagery and LiDAR data at the tree level. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 101, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, X.C.; Yu, A.Z.; Zhang, P.Q.; Wan, G. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery based on recurrent neural networks. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.L.; Park, W.Y.; Park, H.C.; Choi, S.K.; Choi, J.W.; Im, H.R. Dimensionality Reduction Methods Analysis of Hyperspectral Imagery for Unsupervised Change Detection of Multi-sensor Images. J. Korean Assoc. Geogr. Inf. Stud. 2019, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Park, J.K. Comparison of UAV Image and UAV LiDAR for Construction of 3D Geospatial Information. Sens. Mater. 2019, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; He, X.; Yao, H.; Liang, Y.; Deng, T.; He, H.; Fan, D.; Lan, G.; He, W. Comparison of RFE-DL and stacking ensemble learning algorithms for classifying mangrove species on UAV multispectral images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osco, L.P.; Arruda, M.d.S.d.; Marcato Junior, J.; da Silva, N.B.; Ramos, A.P.M.; Moryia, É.A.S.; Imai, N.N.; Pereira, D.R.; Creste, J.E.; Matsubara, E.T.; et al. A convolutional neural network approach for counting and geolocating citrus-trees in UAV multispectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 160, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eon-taek, L.; Do, M. Pine Wilt Disease Detection Based on Deep Learning Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. KSCE J. Civ. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 41, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangruirui, Z.; Youjie, Y.; Kim, B.; Sun, J.; Lee, J. Searching the Damaged Pine Trees from Wilt Disease Based on Deep Learning. Smart Media J. 2020, 9, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Ren, L. Early detection of pine wilt disease using deep learning algorithms and UAV-based multispectral imagery. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 497, 119493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, H. Identifying Pine Wood Nematode Disease Using UAV Images and Deep Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Rao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Fang, Y.; Gao, X. Identification of Pine Wilt Disease Infected Wood Using UAV RGB Imagery and Improved YOLOv5 Models Integrated with Attention Mechanisms. Forests 2023, 14, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Sun, F.; Shen, W.; Dong, B.; Ma, S.; Huo, X.; Lan, P. Deep Learning-Based Pine Nematode Trees’ Identification Using Multispectral and Visible UAV Imagery. Drones 2023, 7, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Tong, Z.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Z. Detection and Location of Dead Trees with Pine Wilt Disease Based on Deep Learning and UAV Remote Sensing. AgriEngineering 2020, 2, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, D.; Huang, J. A GA and SVM Classification Model for Pine Wilt Disease Detection Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imagery. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.; Baek, G.; Kim, H.; Wook, L.C. Detection of Damaged Pine Tree by the Pine Wilt Disease Using UAV Image. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2019, 35, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Bi, H.; Chen, R.; Zong, S.; Luo, Y. A Detection Method for Individual Infected Pine Trees with Pine Wilt Disease Based on Deep Learning. Forests 2022, 13, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Huo, L.; Zhang, X. Classification of pine wilt disease at different infection stages by diagnostic hyperspectral bands. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, D.; Tan, W.; Yao, Q.; Liu, J. YOLO5Face: Why Reinventing a Face Detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.M.; Yang, X.T. Pine wilt disease detection in UAV-CAPTURED images. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2022, 37, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, E.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, G.; Mo, D. An efficient approach to monitoring pine wilt disease severity based on random sampling plots and UAV imagery. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Yao, P.; Wan, M.; Bao, W.; Zeng, W. Detection and classification of diseased pine trees with different levels of severity from UAV remote sensing images. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ibrayim, M.; Hamdulla, A. Detection of Pine Wilt Nematode from Drone Images Using UAV. Sensors 2022, 22, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Chang, Q.; Lyu, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Feng, W. Detection Method of Infected Wood on Digital Orthophoto Map–Digital Surface Model Fusion Network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4295. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Huang, H.; Yu, L.; Ren, L. Three-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network Model for Early Detection of Pine Wilt Disease Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liang, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, T.; Zou, Z.; Yang, D.; Tang, W.; Li, J.; Su, J. Application of conventional UAV-based high-throughput object detection to the early diagnosis of pine wilt disease by deep learning. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 486, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Early detection of pine wilt disease in Pinus tabuliformis in North China using a field portable spectrometer and UAV-based hyperspectral imagery. For. Ecosyst. 2021, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, A.; Yang, D.; Cheng, H.; Ye, J. Preliminary Study on Early Diagnosis and Rehabilitation Treatment of Pine Wood Nematode Disease Based on Partial Symptoms. Forests 2023, 14, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Hu, J.; Pan, M.; Shen, L.; Ye, J.; Tan, J. Early Diagnosis of Pine Wilt Disease in Pinus thunbergii Based on Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters. Forests 2023, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Fang, G. Accurate Identification of Pine Wood Nematode Disease with a Deep Convolution Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liming, H.; Yixiang, W.; Qi, X.; Qinghua, L. Recognition of abnormally discolored trees caused by pine wilt disease using YOLO algorithm and UAV images. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Wook, K.K.; Hyun, K.J. A Study on Orthogonal Image Detection Precision Improvement Using Data of Dead Pine Trees Extracted by Period Based on U-Net model. J. Korean Soc. Surv. Geod. Photogramm. Cartogr. 2022, 40, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Wook, K.K. Orthophoto Imagery Comparison Analysis of U-NET Model and Mask R-CNN Model for Pine Wilt Disease Detection. J. Korean Soc. Cadastre 2022, 38, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Yu, L.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Detection of the Monitoring Window for Pine Wilt Disease Using Multi-Temporal UAV-Based Multispectral Imagery and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-M.; Yoon, S.; Hwang, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, W.-H. Analysis of the spread distance of pine wilt disease based on a high volume of spatiotemporal data recording of infected trees. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 553, 121612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, R.; Hu, X.; Liang, G.; Huang, S.; Lian, C.; Zhang, F.; Wu, S. Landscapes drive the dispersal of Monochamus alternatus, vector of the pinewood nematode, revealed by whole-genome resequencing. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 529, 120682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liang, J.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X. Effect of Plant Diversity on the Occurrence of Diplodia Tip Blight in Natural Secondary Japanese Red Pine Forests. Forests 2021, 12, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Chung, Y.-J.; Moon, Y.-S. Hazard ratings of pine forests to a pine wilt disease at two spatial scales (individual trees and stands) using self-organizing map and random forest. Ecol. Inform. 2013, 13, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, N.N.; Vanhellemont, M.; Baeten, L.; Dillen, M.; Verheyen, K. The effects of local neighbourhood diversity on pest and disease damage of trees in a young experimental forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 334, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Weight | 0.57 kg |
| Pixels | 8000 × 6000 |
| Aperture | f/2.8 |
| Flight altitude | 300 m |
| Flight speed | 9 m/s |
| Viewing angle | −90° |
| Across-track overlap | 80% |
| Along-track overlap | 80% |
| Region | Region A | Region B |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Accuracy (OA) | 89.95% | 92.44% |
| Kappa Coefficient | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| Land Cover Types | PA (%) | UA (%) | CE (%) | OE (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region A | Region B | Region A | Region B | Region A | Region B | Region A | Region B | |
| Bare ground | 91.37 | 96.19 | 92.47 | 91.89 | 7.53 | 8.11 | 8.63 | 3.81 |
| Water | 96.99 | 99.40 | 98.05 | 99.71 | 1.95 | 0.29 | 3.01 | 0.60 |
| Needleleaf trees | 86.91 | 87.14 | 85.78 | 87.48 | 14.22 | 12.52 | 13.09 | 12.86 |
| Broadleaf trees | 90.06 | 91.32 | 91.39 | 95.16 | 8.61 | 4.84 | 9.94 | 8.68 |
| Models | YOLOv5 | YOLOv8 | Faster R-CNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.68 | 0.64 | 0.63 |
| R | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.54 |
| F1 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.58 |
| mAP | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.55 |
| Params/M | 14.46 | 22.04 | 100.1 |
| Training time/h | 6.62 | 7.83 | 13.42 |
| Testing time/s | 15.6 | 22.1 | 177.7 |
| Land Cover Types | Early Stage | Middle Stage | Late Stage | Dead Stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region A | Region B | Region A | Region B | Region A | Region B | Region A | Region B | |
| YOLOv5 | 1023 | 801 | 761 | 604 | 789 | 636 | 631 | 562 |
| Manual labeling | 219 | 275 | 292 | 274 | 685 | 554 | 575 | 500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, C.; Lin, Q.; Du, H.; Chen, C.; Hu, M.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Y. Detection of the Infection Stage of Pine Wilt Disease and Spread Distance Using Monthly UAV-Based Imagery and a Deep Learning Approach. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020364
Tan C, Lin Q, Du H, Chen C, Hu M, Chen J, Huang Z, Xu Y. Detection of the Infection Stage of Pine Wilt Disease and Spread Distance Using Monthly UAV-Based Imagery and a Deep Learning Approach. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020364
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Cheng, Qinan Lin, Huaqiang Du, Chao Chen, Mengchen Hu, Jinjin Chen, Zihao Huang, and Yanxin Xu. 2024. "Detection of the Infection Stage of Pine Wilt Disease and Spread Distance Using Monthly UAV-Based Imagery and a Deep Learning Approach" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020364
APA StyleTan, C., Lin, Q., Du, H., Chen, C., Hu, M., Chen, J., Huang, Z., & Xu, Y. (2024). Detection of the Infection Stage of Pine Wilt Disease and Spread Distance Using Monthly UAV-Based Imagery and a Deep Learning Approach. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020364







