Investigating Prior-Level Fusion Approaches for Enriched Semantic Segmentation of Urban LiDAR Point Clouds
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Designing three prior-level fusion scenarios for 3D semantic segmentation that fuse PCs, aerial images, and prior knowledge into the DL pipeline;
- Evaluating the performance of each scenario in terms of enhancing DL techniques’ knowledge;
- Enhancing semantic segmentation richness by detecting a maximum number of urban classes more efficiently and accurately;
2. Related Works
2.1. Prior-Level Fusion Approaches
2.2. Point-Level Fusion Approaches
2.3. Feature-Level Fusion Approaches
2.4. Decision-Level Fusion Approaches
2.5. Summary
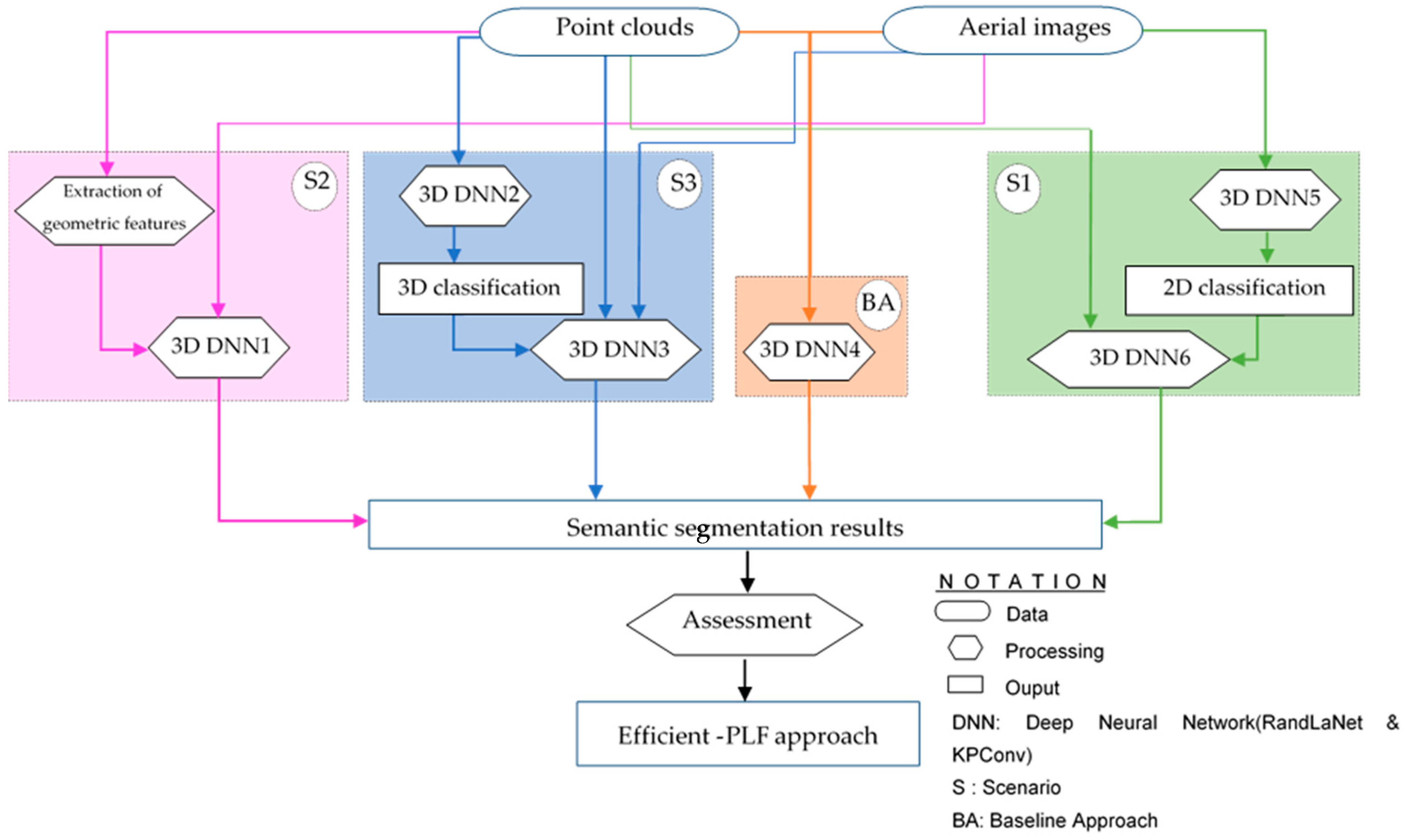
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Methodology
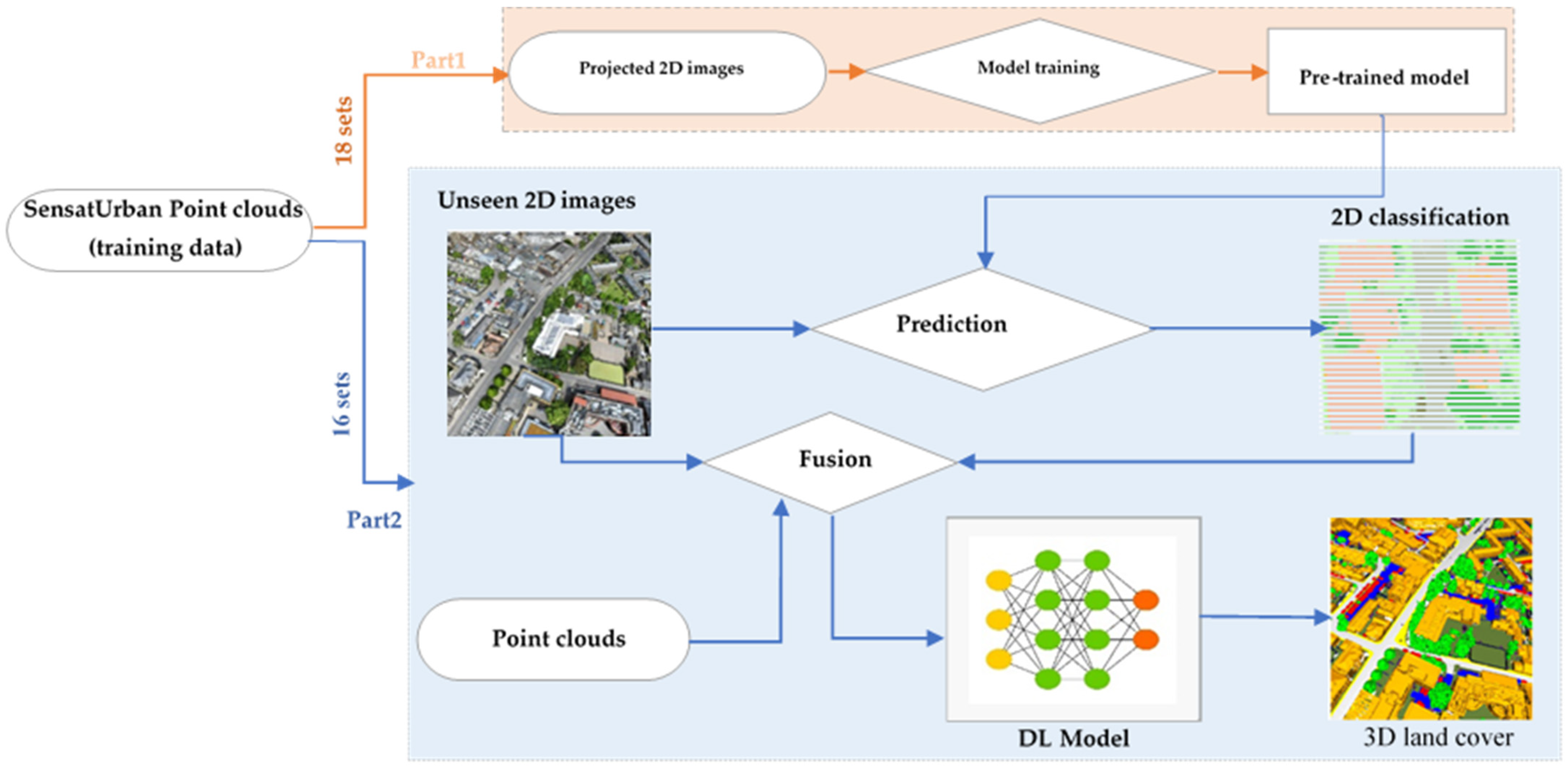
3.2.1. Classified Images and PC-Based Scenario (S1)
3.2.2. Geometric Features, PC, and Aerial Images-Based Scenario (S2)
- (A)
- Selection of the appropriate geometric features
- (B)
- Data Training and Semantic Segmentation Using RandLaNet and KPConv Techniques
3.2.3. Classified XYZ PC, PC, and Optical Images-Based Scenario (S3)
3.2.4. Baseline Approach
4. Experiments and Results Analysis
4.1. Implementation
4.2. Results
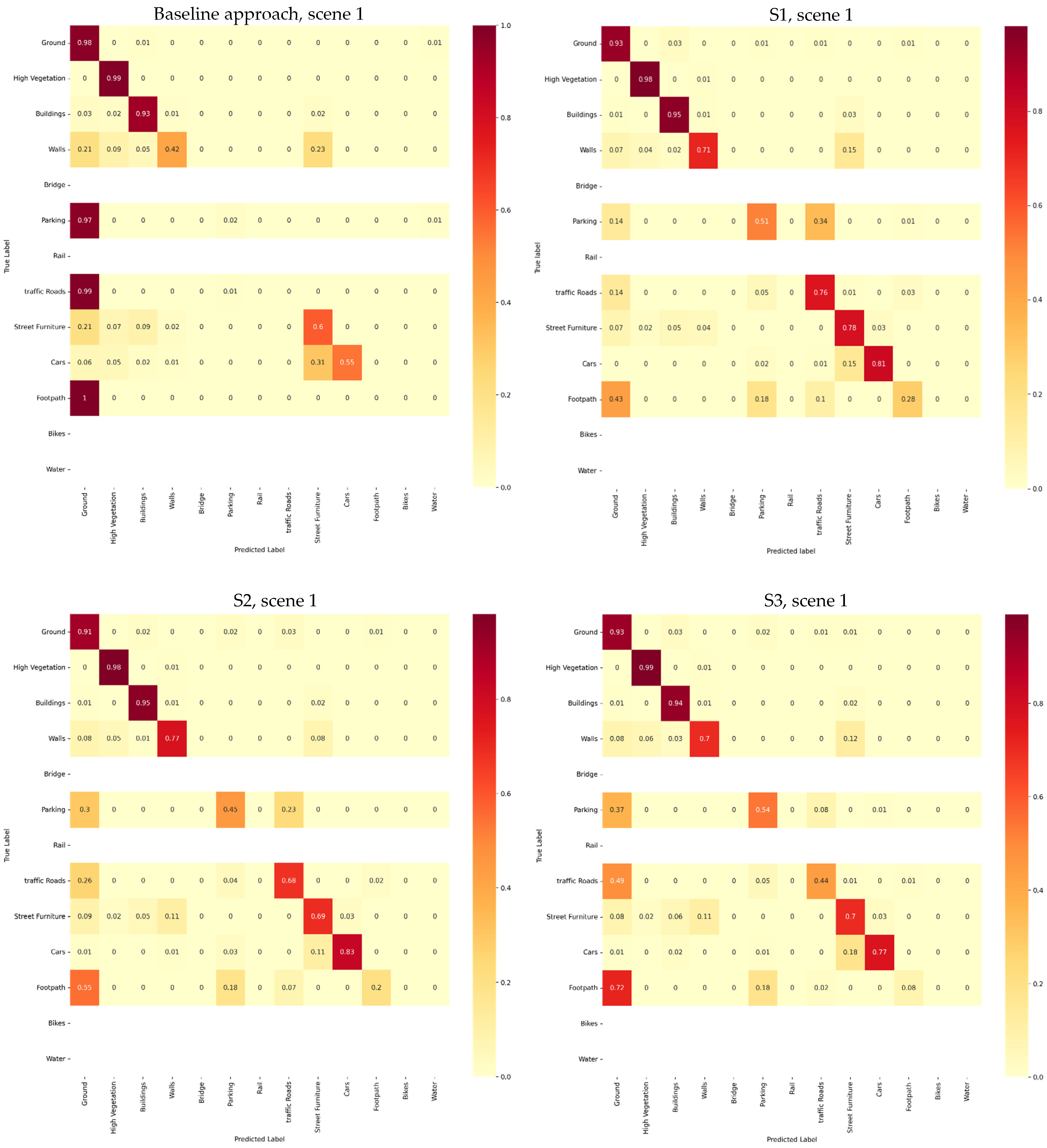
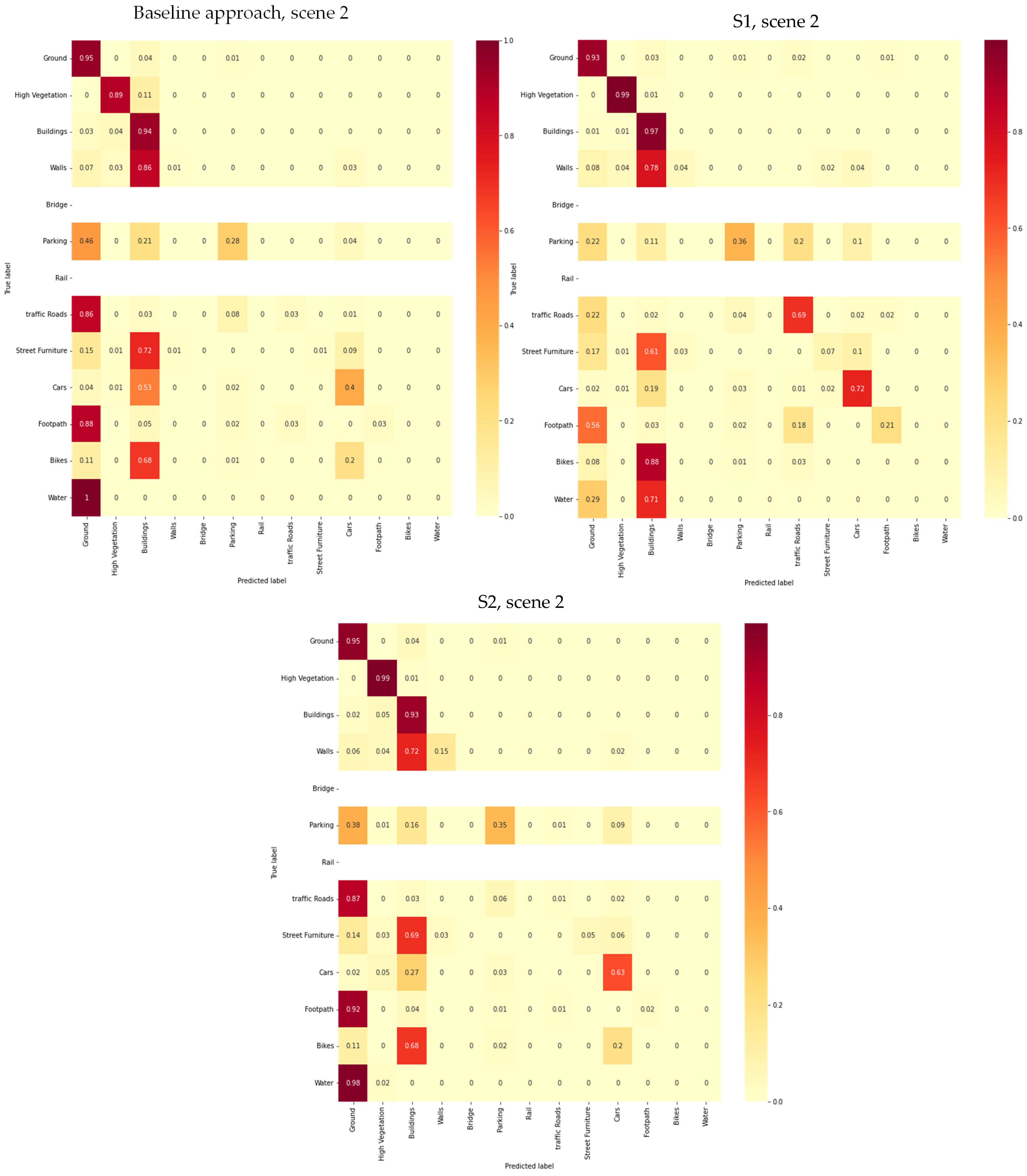
4.2.1. Primary Semantic Segmentation Results Using RandLaNet
- (A)
- Quantitative Assessments
| Urban | Processes | F1-Score | Recall | Precision | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scene 1 | Baseline approach | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.63 |
| S1 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.80 | |
| S2 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.77 | |
| S3 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.75 | |
| Scene 2 | Baseline approach | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.75 |
| S1 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.88 | |
| S2 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.86 | |
| S3 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.85 | |
| Scene 3 | Baseline approach | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.67 |
| S1 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.79 | |
| S2 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.77 | |
| S3 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.76 | |
| Scene 4 | Baseline approach | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.58 | 0.50 |
| S1 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.84 | 0.68 | |
| S2 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.67 | |
| S3 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.57 |
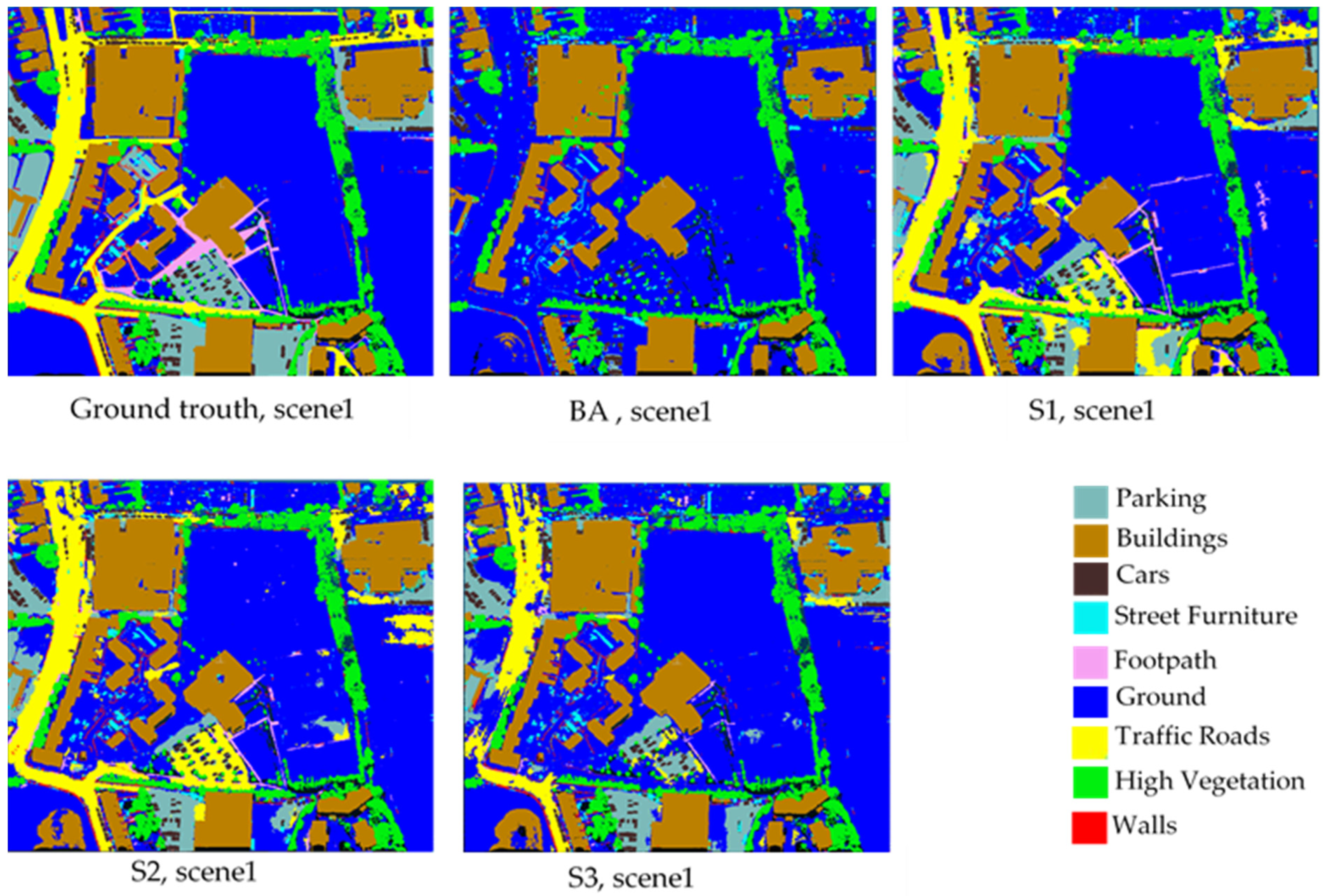
- (B)
- Qualitative Assessments
4.2.2. Results Confirmation with KPConv
4.2.3. Comparison of Efficient-PLF Approach with DL Techniques from the Literature
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahat, E.; Hyun, C.T.; Yeom, C. City Digital Twin Potentials: A Review and Research Agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruohomäki, T.; Airaksinen, E.; Huuska, P.; Kesäniemi, O.; Martikka, M.; Suomisto, J. Smart City Platform Enabling Digital Twin. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), Funchal, Portugal, 25–27 September 2018; pp. 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- White, G.; Zink, A.; Codecá, L.; Clarke, S. A Digital Twin Smart City for Citizen Feedback. Cities 2021, 110, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Z. A Review of Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation for Point Cloud. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179118–179133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Rosa, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. RandLA-Net: Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11105–11114. [Google Scholar]
- Landrieu, L.; Simonovsky, M. Large-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation with Superpoint Graphs. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4558–4567. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Jin, W.; Meng, X. Deep-Learning-Based Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation: A Survey. Electronics 2023, 12, 3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.-E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. KPConv: Flexible and Deformable Convolution for Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6411–6420. [Google Scholar]
- Ballouch, Z.; Hajji, R.; Ettarid, M. Toward a Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Semantic Segmentation of 3D Lidar Point Clouds in Urban Areas. In Geospatial Intelligence: Applications and Future Trends; Barramou, F., El Brirchi, E.H., Mansouri, K., Dehbi, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 67–77. ISBN 978-3-030-80458-9. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann, M.; Weinmann, M. Fusion of hyperspectral, multispectral, color and 3D point cloud information for the semantic interpretation of urban environments. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W13, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Khalid, S.; Xiao, W.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Towards Semantic Segmentation of Urban-Scale 3D Point Clouds: A Dataset, Benchmarks and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4977–4987. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Nan, L.; Boom, B.; Ledoux, H. SUM: A Benchmark Dataset of Semantic Urban Meshes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 179, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, T.; Savinov, N.; Ladicky, L.; Wegner, J.D.; Schindler, K.; Pollefeys, M. Semantic3D.Net: A New Large-Scale Point Cloud Classification Benchmark. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.03847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, D.; Zhang, W. Integrating UAV Photogrammetry and Terrestrial Laser Scanning for Three-Dimensional Geometrical Modeling of Post-Earthquake County of Beichuan. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering; Toledo Santos, E., Scheer, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1086–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.-I.; Kang, H.-B. Object Detection and Classification by Decision-Level Fusion for Intelligent Vehicle Systems. Sensors 2017, 17, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wan, S. Three-Dimensional Urban Land Cover Classification by Prior-Level Fusion of LiDAR Point Cloud and Optical Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Li, M.; Wang, L. Fusion of Images and Point Clouds for the Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale 3D Scenes Based on Deep Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 143, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballouch, Z.; Hajji, R.; Poux, F.; Kharroubi, A.; Billen, R. A Prior Level Fusion Approach for the Semantic Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds Using Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliyapram, V.; Wang, W.; Nakamura, R. A Point-Wise LiDAR and Image Multimodal Fusion Network (PMNet) for Aerial Point Cloud 3D Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Pan, H.; Yu, X.; Gao, H. A Spatially Enhanced Network with Camera-Lidar Fusion for 3D Semantic Segmentation. Neurocomputing 2022, 484, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, C.; Xi, X.; Zeng, H.; Li, D.; Xia, S.; Wang, P. Fusion of Airborne Discrete-Return LiDAR and Hyperspectral Data for Land Cover Classification. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzapour, F.; Ghassemian, H. Improving Hyperspectral Image Classification by Combining Spectral, Texture, and Shape Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1070–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Liu, C.; Ren, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Su, Y. Object Classification via Feature Fusion Based Marginalized Kernels. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chi, M. Mask-R-FCN: A Deep Fusion Network for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 155753–155765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabib Mahmoudi, F.; Samadzadegan, F.; Reinartz, P. Object Recognition Based on the Context Aware Decision-Level Fusion in Multiviews Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Candra, S.A.; Vetter, K.; Zakhor, A. Sensor Fusion for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1850–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Bennamoun, M. Deep Learning for 3D Point Clouds: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4338–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzeczkowicz, G.; Vallet, B. Semantic Segmentation of Urban Textured Meshes through Point Sampling. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhan, L.; Min, W.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wen, C. Semantic Segmentation of Point Cloud With Novel Neural Radiation Field Convolution. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Vosselman, G.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y. Local and Global Encoder Network for Semantic Segmentation of Airborne Laser Scanning Point Clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 176, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Jo, K.; Cho, J.; Son, Y.; Kim, C.; Han, K. A Training Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Point Cloud Map for Intelligent Vehicles. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 187, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atik, M.E.; Duran, Z.; Seker, D.Z. Machine Learning-Based Supervised Classification of Point Clouds Using Multiscale Geometric Features. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, E.; Remondino, F. Classification of aerial point clouds with deep learning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W13, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarchenko, M.; Park, J.; Koltun, V.; Zhou, Q.-Y. Tangent Convolutions for Dense Prediction in 3D. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3887–3896. [Google Scholar]




| Semantic Segmentation Performance | Baseline Approach | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground | Precision | 0.746 | 0.952 | 0.917 | 0.907 |
| Recall | 0.990 | 0.921 | 0.927 | 0.917 | |
| F1-score | 0.851 | 0.936 | 0.922 | 0.912 | |
| High Vegetation | Precision | 0.937 | 0.997 | 0.995 | 0.995 |
| Recall | 0.998 | 0.992 | 0.995 | 0.993 | |
| F1-score | 0.967 | 0.994 | 0.995 | 0.994 | |
| Buildings | Precision | 0.985 | 0.982 | 0.987 | 0.976 |
| Recall | 0.909 | 0.955 | 0.938 | 0.951 | |
| F1-score | 0.946 | 0.968 | 0.962 | 0.963 | |
| Walls | Precision | 0.790 | 0.769 | 0.766 | 0.725 |
| Recall | 0.677 | 0.690 | 0.776 | 0.639 | |
| F1-score | 0.729 | 0.727 | 0.771 | 0.680 | |
| Parking | Precision | 0.605 | 0.428 | 0.417 | 0.408 |
| Recall | 0.123 | 0.757 | 0.727 | 0.722 | |
| F1-score | 0.205 | 0.547 | 0.530 | 0.522 | |
| Traffic Roads | Precision | 0.000 | 0.840 | 0.828 | 0.803 |
| Recall | 0.000 | 0.726 | 0.629 | 0.498 | |
| F1-score | 0.000 | 0.779 | 0.715 | 0.614 | |
| Street Furniture | Precision | 0.325 | 0.250 | 0.259 | 0.230 |
| Recall | 0.518 | 0.828 | 0.779 | 0.698 | |
| F1-score | 0.399 | 0.384 | 0.389 | 0.346 | |
| Cars | Precision | 0.929 | 0.909 | 0.904 | 0.862 |
| Recall | 0.721 | 0.937 | 0.956 | 0.935 | |
| F1-score | 0.812 | 0.922 | 0.929 | 0.897 | |
| Footpath | Precision | 0.000 | 0.655 | 0.601 | 0.530 |
| Recall | 0.000 | 0.664 | 0.557 | 0.530 | |
| F1-score | 0.000 | 0.660 | 0.578 | 0.530 |
| Semantic Segmentation Performance | BA | S1 | S2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground | Precision | 0.762 | 0.880 | 0.767 |
| Recall | 0.946 | 0.931 | 0.949 | |
| F1-score | 0.844 | 0.905 | 0.849 | |
| High Vegetation | Precision | 0.961 | 0.989 | 0.948 |
| Recall | 0.889 | 0.986 | 0.987 | |
| F1-score | 0.924 | 0.987 | 0.967 | |
| Buildings | Precision | 0.766 | 0.882 | 0.871 |
| Recall | 0.936 | 0.975 | 0.926 | |
| F1-score | 0.843 | 0.926 | 0.903 | |
| Walls | Precision | 0.456 | 0.540 | 0.760 |
| Recall | 0.008 | 0.043 | 0.148 | |
| F1-score | 0.016 | 0.080 | 0.257 | |
| Parking | Precision | 0.373 | 0.534 | 0.462 |
| Recall | 0.280 | 0.357 | 0.352 | |
| F1-score | 0.320 | 0.428 | 0.400 | |
| Traffic Roads | Precision | 0.475 | 0.727 | 0.558 |
| Recall | 0.025 | 0.691 | 0.014 | |
| F1-score | 0.048 | 0.709 | 0.028 | |
| Street Furniture | Precision | 0.334 | 0.344 | 0.606 |
| Recall | 0.012 | 0.074 | 0.055 | |
| F1-score | 0.023 | 0.122 | 0.093 | |
| Cars | Precision | 0.735 | 0.761 | 0.751 |
| Recall | 0.399 | 0.719 | 0.634 | |
| F1-score | 0.517 | 0.739 | 0.681 | |
| Footpath | Precision | 0.512 | 0.574 | 0.584 |
| Recall | 0.028 | 0.208 | 0.023 | |
| F1-score | 0.053 | 0.305 | 0.043 |
| Ground | High Vegetation | Buildings | Walls | Parking | Traffic Roads | Street Furniture | Cars | Footpath | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet [35] | 67.96 | 89.52 | 80.05 | 0.00 | 3.95 | 31.55 | 0.00 | 35.14 | 0.00 |
| PointNet++ [36] | 72.46 | 94.24 | 84.77 | 2.72 | 25.79 | 31.54 | 11.42 | 38.84 | 7.12 |
| TagentConv [37] | 71.54 | 91.38 | 75.90 | 35.22 | 45.34 | 26.69 | 19.24 | 67.58 | 0.01 |
| SPGraph [6] | 69.93 | 94.55 | 88.87 | 32.83 | 15.77 | 30.63 | 22.96 | 56.42 | 0.54 |
| RandLaNet adopted to our Efficient-PLF approach | 85.42 | 97.33 | 90.81 | 49.22 | 42.06 | 56.00 | 35.00 | 77.97 | 19.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ballouch, Z.; Hajji, R.; Kharroubi, A.; Poux, F.; Billen, R. Investigating Prior-Level Fusion Approaches for Enriched Semantic Segmentation of Urban LiDAR Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020329
Ballouch Z, Hajji R, Kharroubi A, Poux F, Billen R. Investigating Prior-Level Fusion Approaches for Enriched Semantic Segmentation of Urban LiDAR Point Clouds. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleBallouch, Zouhair, Rafika Hajji, Abderrazzaq Kharroubi, Florent Poux, and Roland Billen. 2024. "Investigating Prior-Level Fusion Approaches for Enriched Semantic Segmentation of Urban LiDAR Point Clouds" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020329
APA StyleBallouch, Z., Hajji, R., Kharroubi, A., Poux, F., & Billen, R. (2024). Investigating Prior-Level Fusion Approaches for Enriched Semantic Segmentation of Urban LiDAR Point Clouds. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020329








