Multipath-Closure Calibration of Stereo Camera and 3D LiDAR Combined with Multiple Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
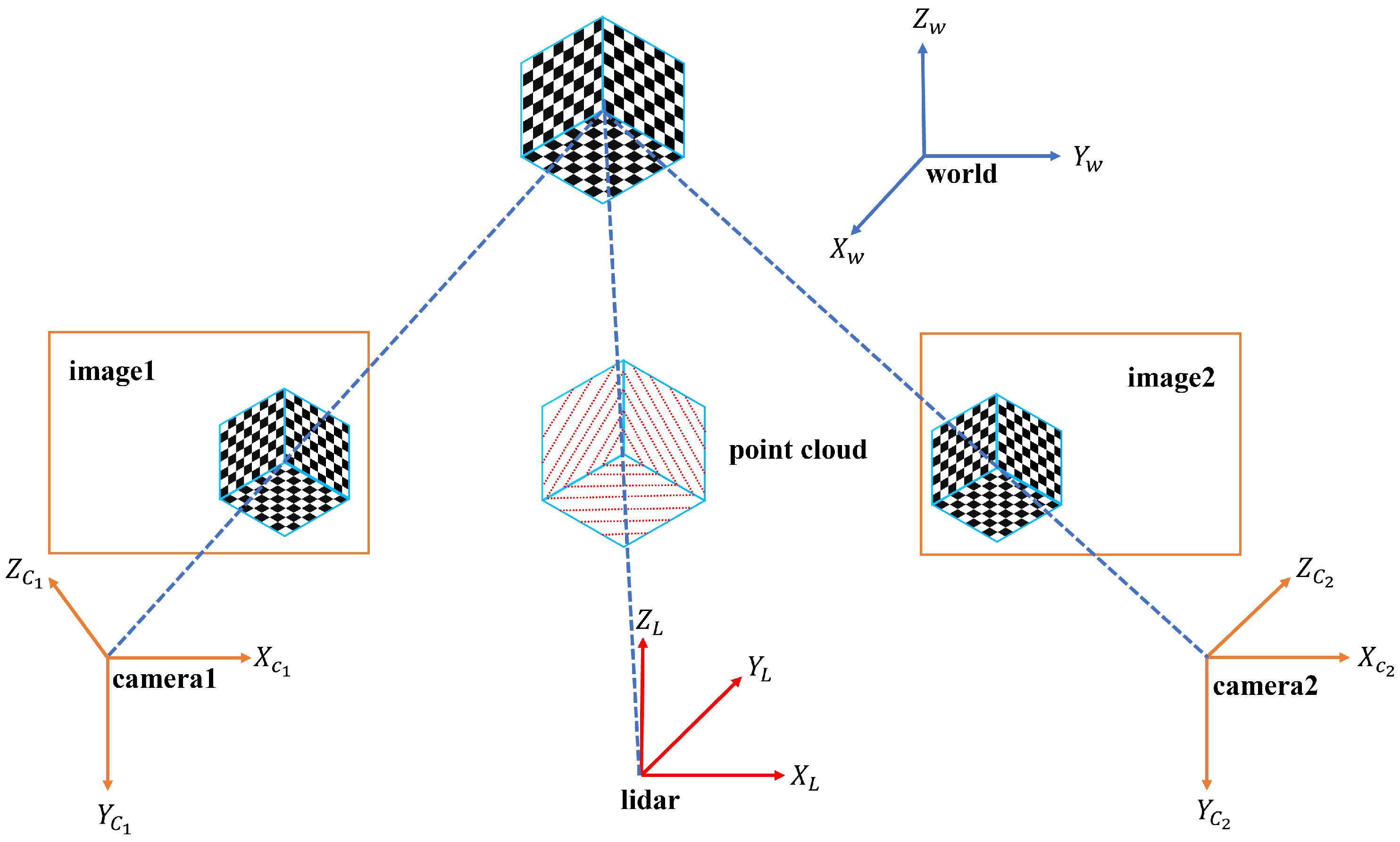
2.1. Problem Definition
2.2. The Multipath-Closure Calibration Method with Multiple Constraints
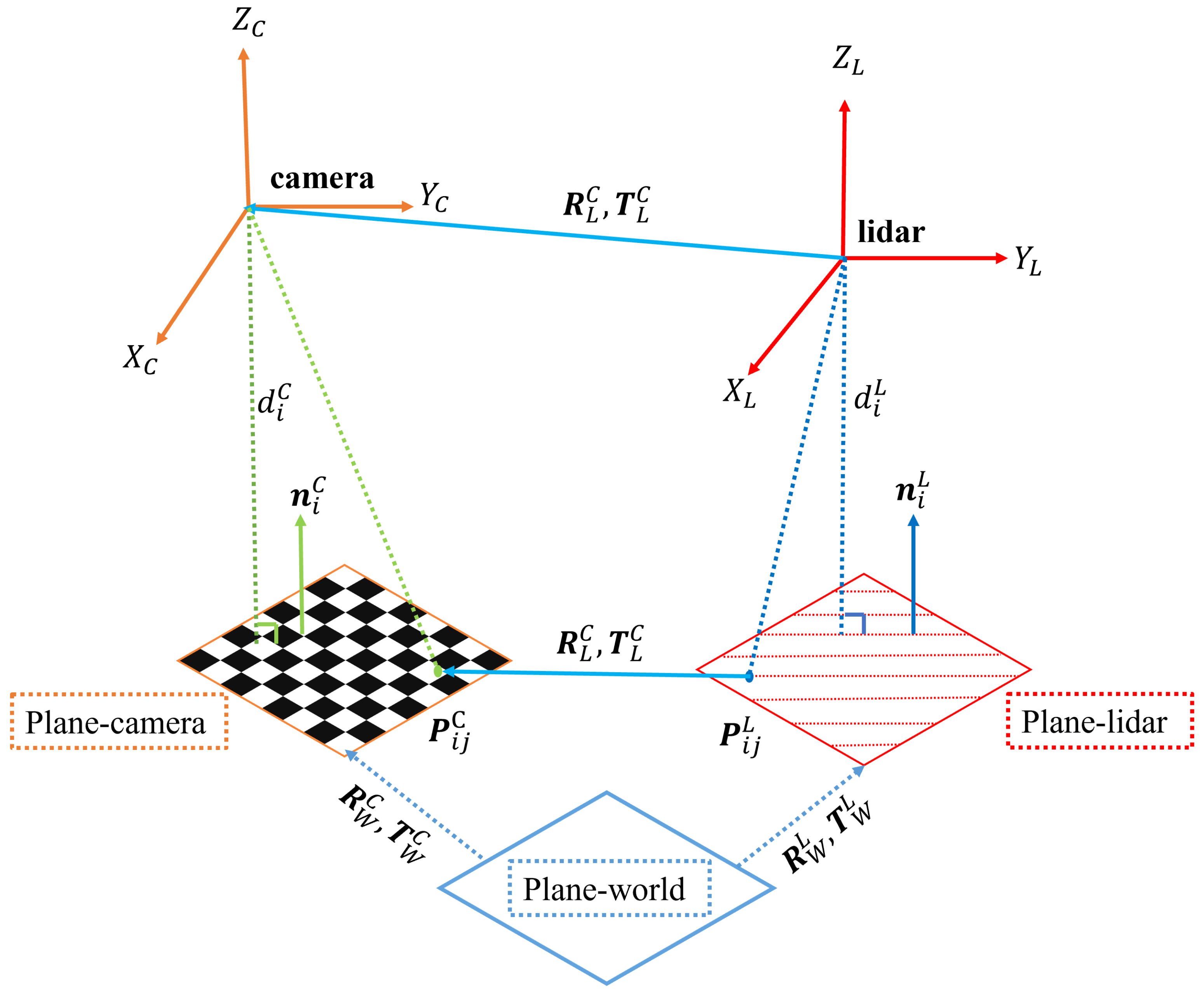
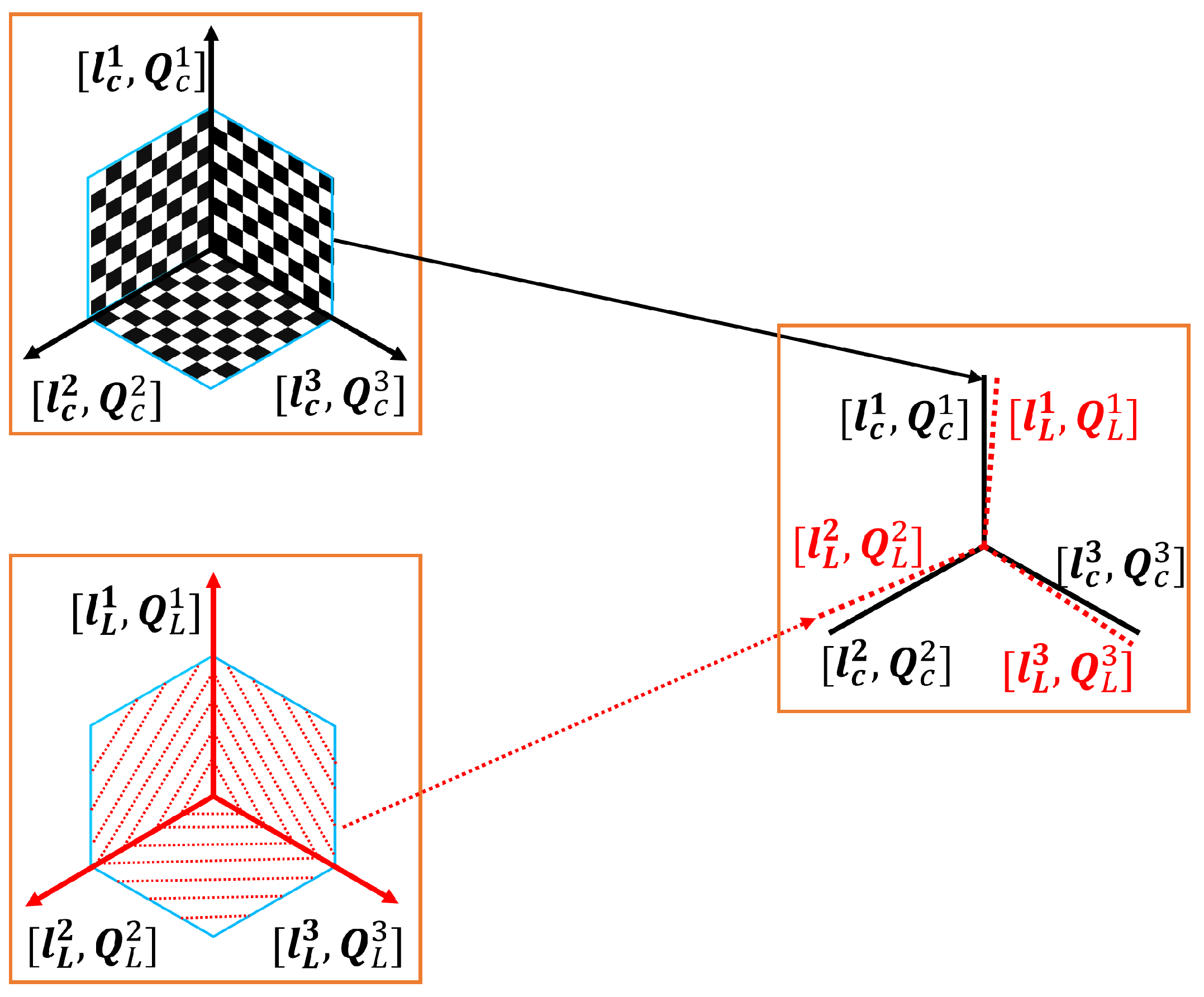
2.2.1. Geometric Constraint Relationships Established by Trihedron Calibration Object
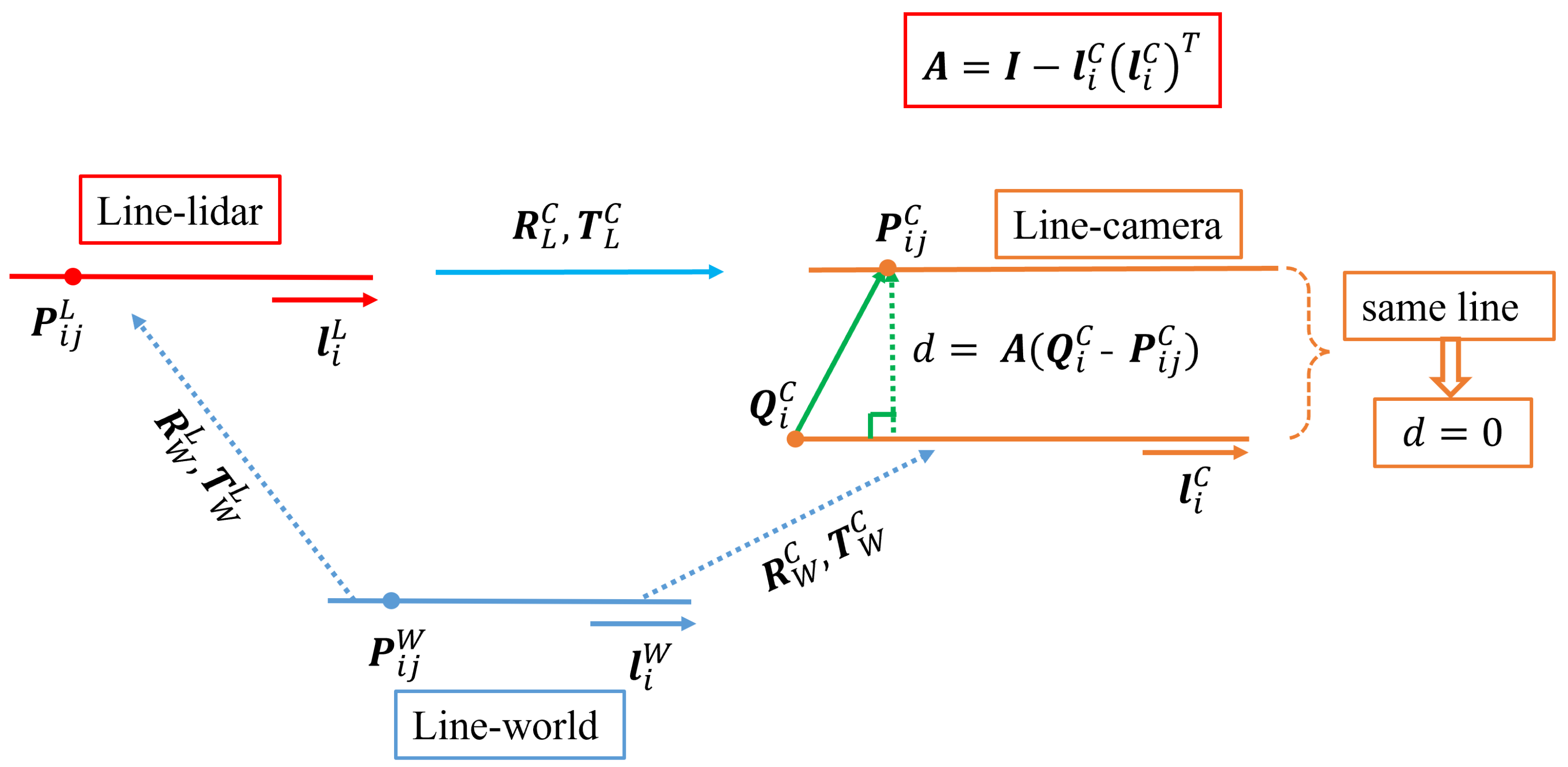
2.2.2. Geometric Information Extraction of Trihedron Calibration Object
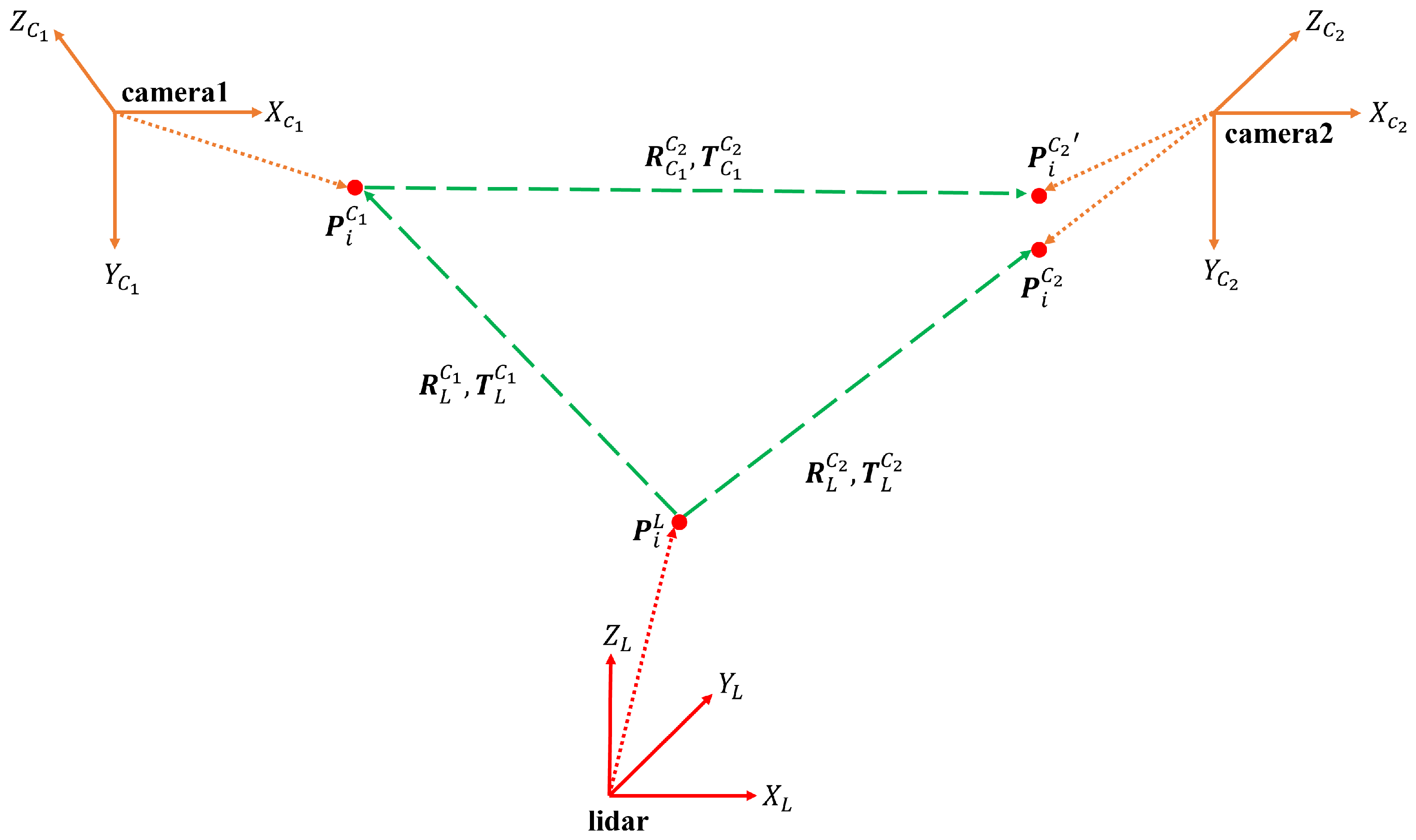
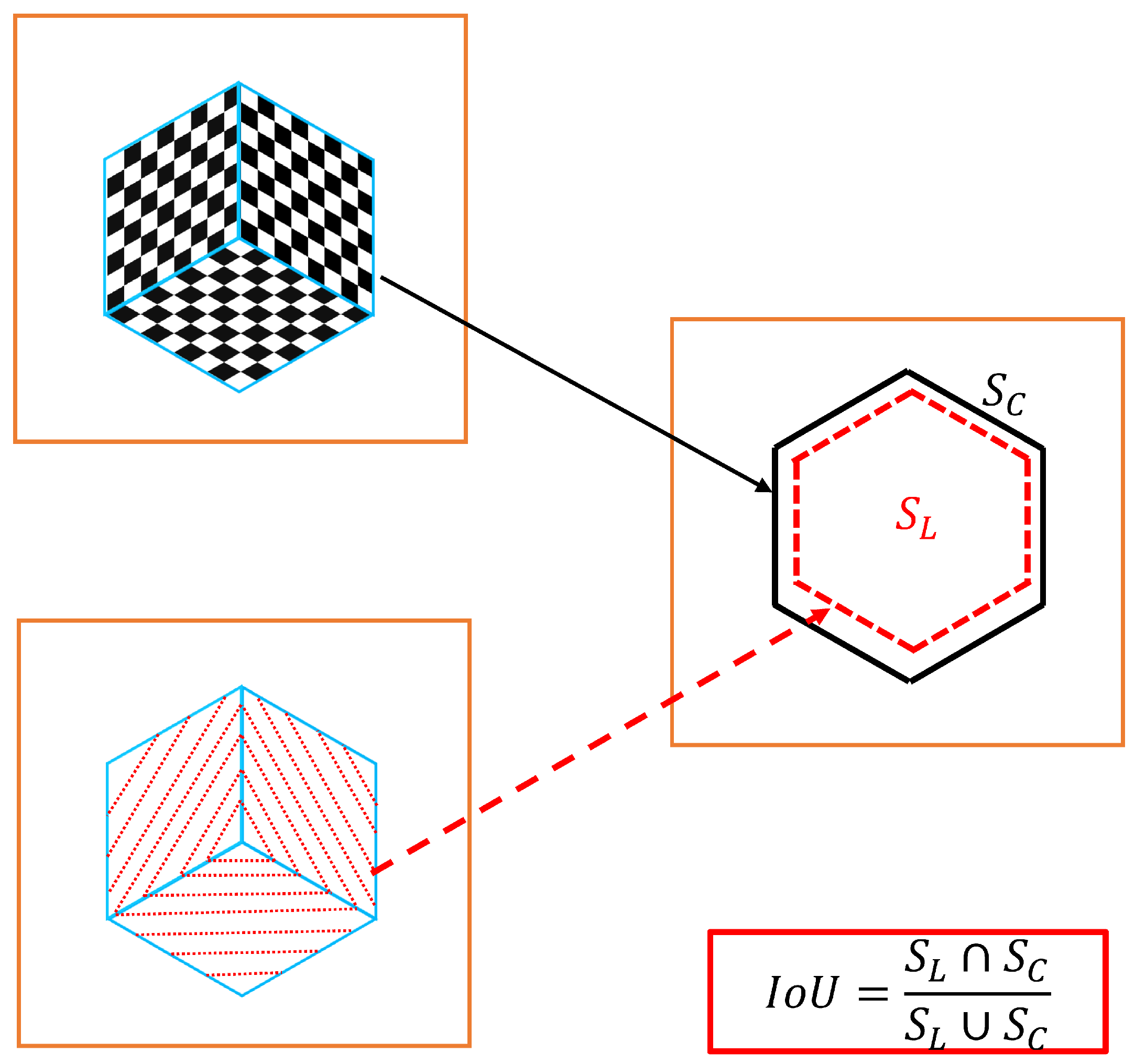
2.2.3. Multipath-Closure Constraint between Sensors
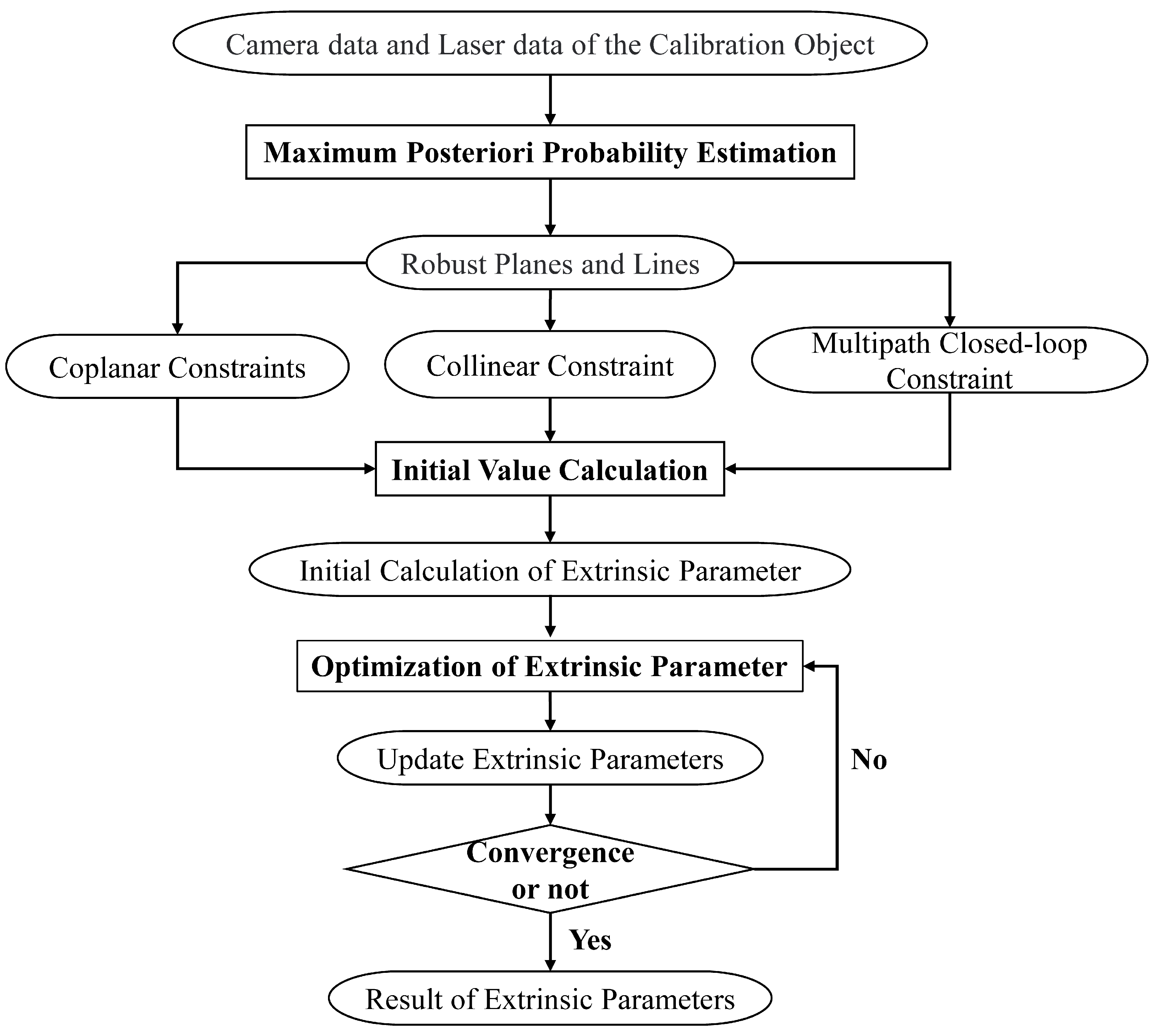
2.3. Multipath-Closure Calibration Process
2.3.1. Initial Calculation of Extrinsic Parameters
2.3.2. Optimization of Extrinsic Parameters
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
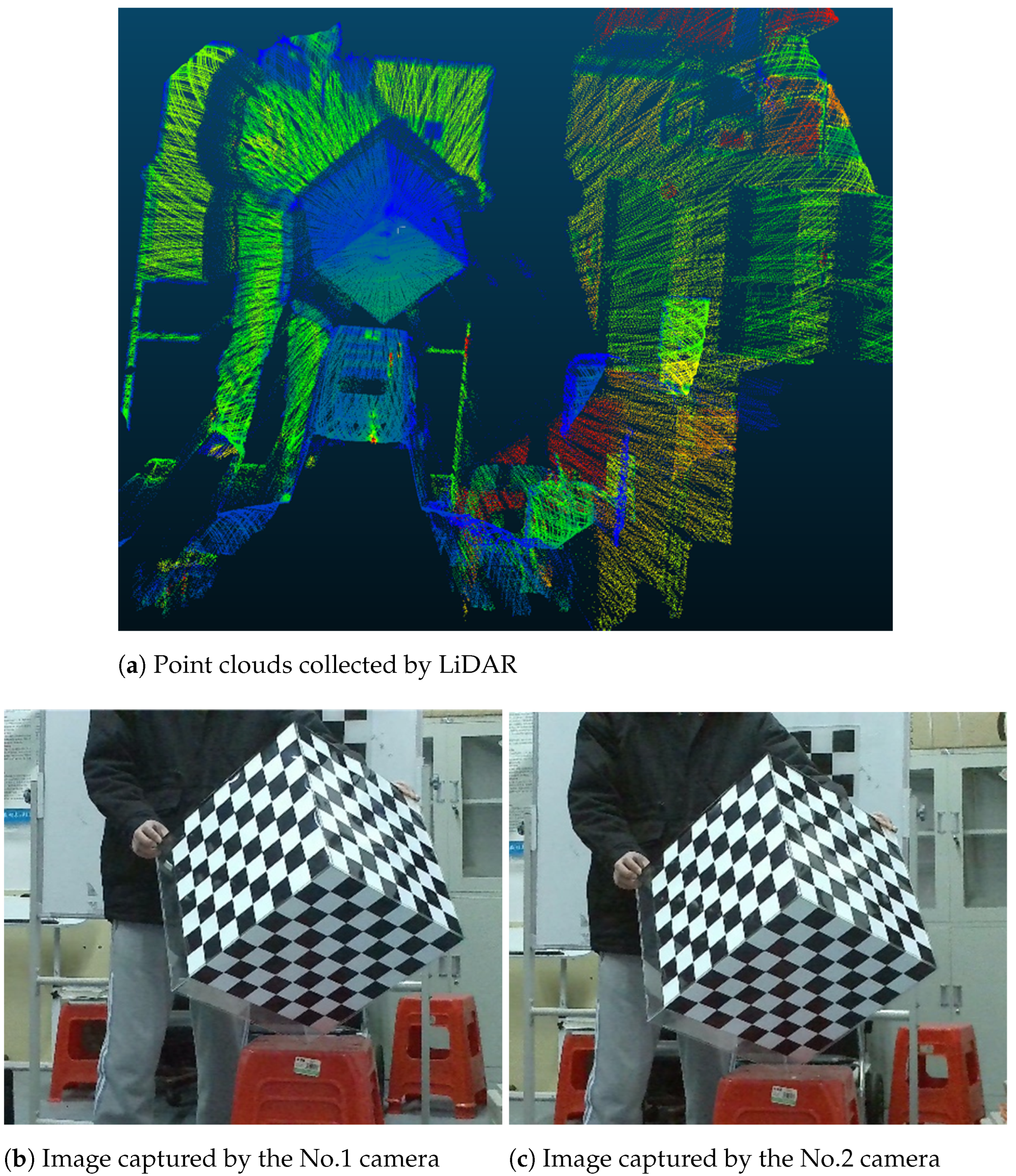
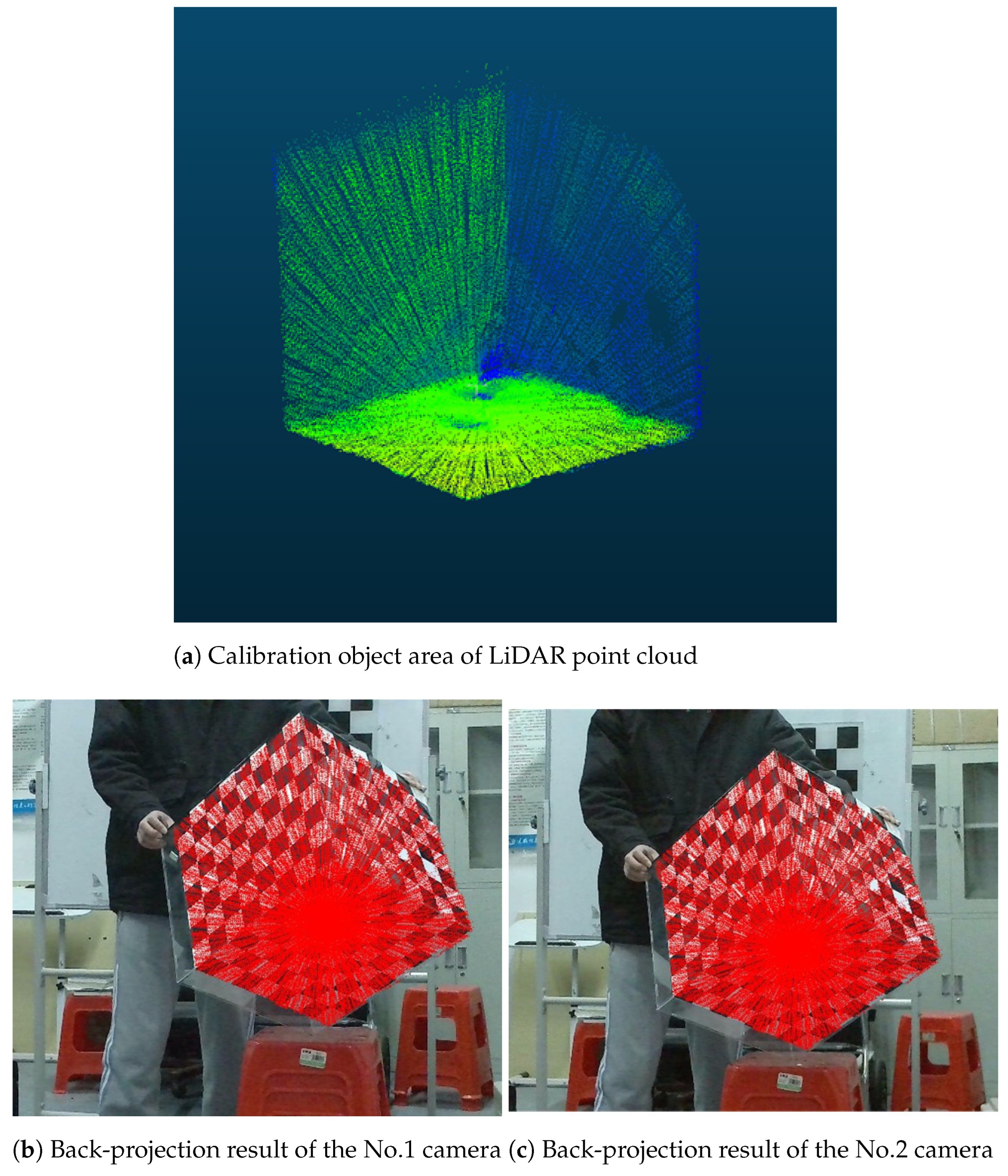
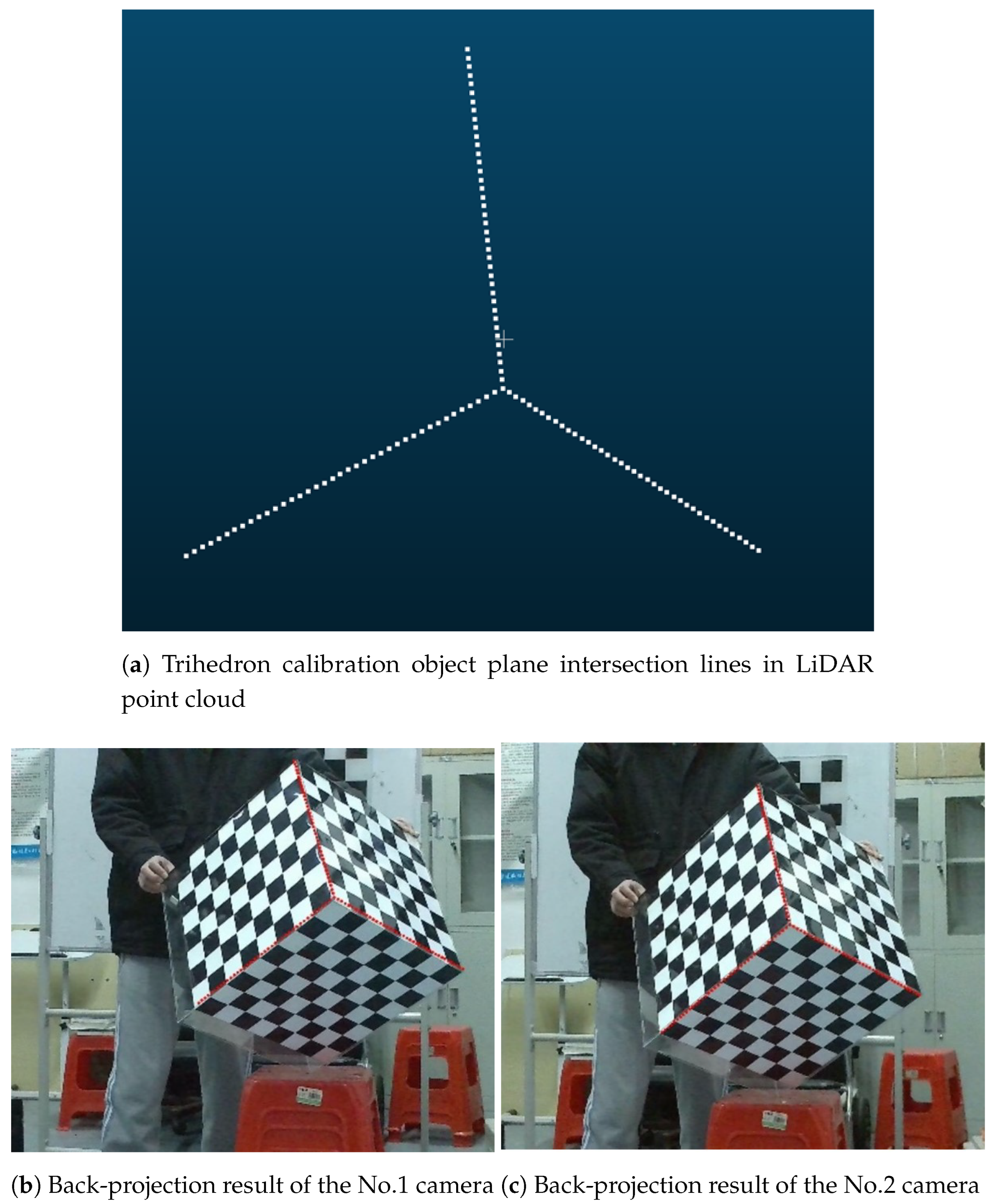
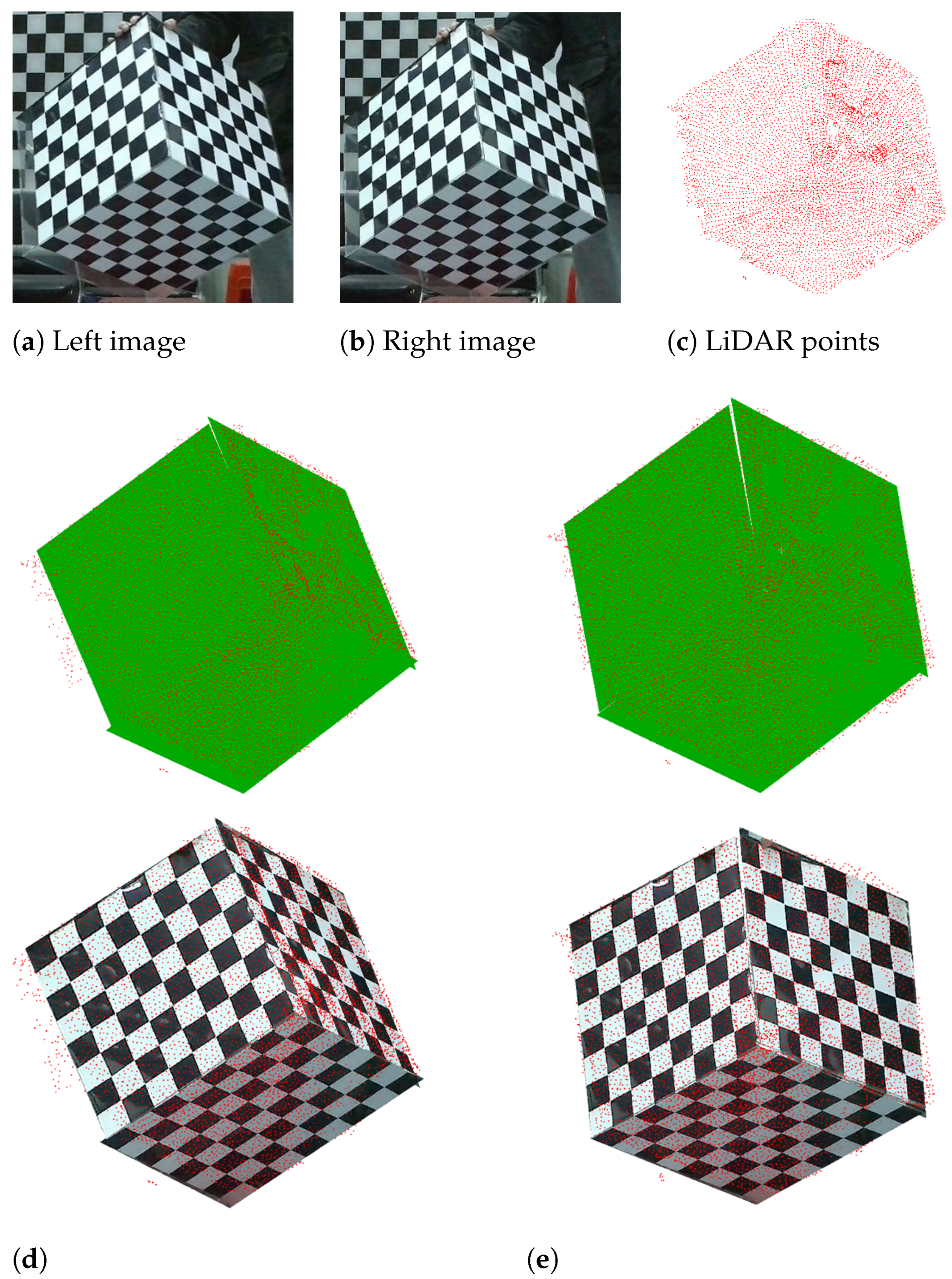
3.1. Real Experiments
3.1.1. Accuracy Verification of Algorithms in Real Scenarios
3.1.2. Influence of Point Cloud Noise Estimation Methods on the Calibration Results
3.1.3. Influence of Different Constraints on Calibration Results
3.1.4. Data Fusion Results Using the Calibration Results
3.2. Simulation Experiments
3.2.1. Simulation Experiments under Different LiDAR Noise
3.2.2. Influence of Point Cloud Noise Estimation Methods on Algorithm Accuracy
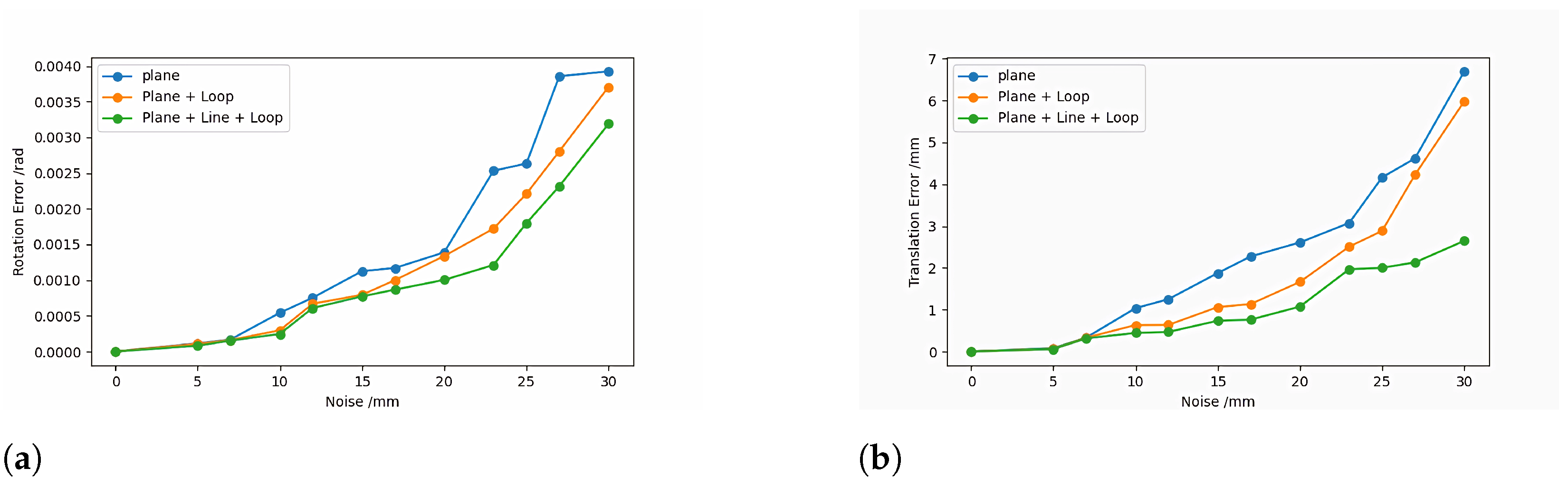
3.2.3. Influence of Coplanar Constraint and Multipath-Closure Constraint on Algorithm’s Accuracy
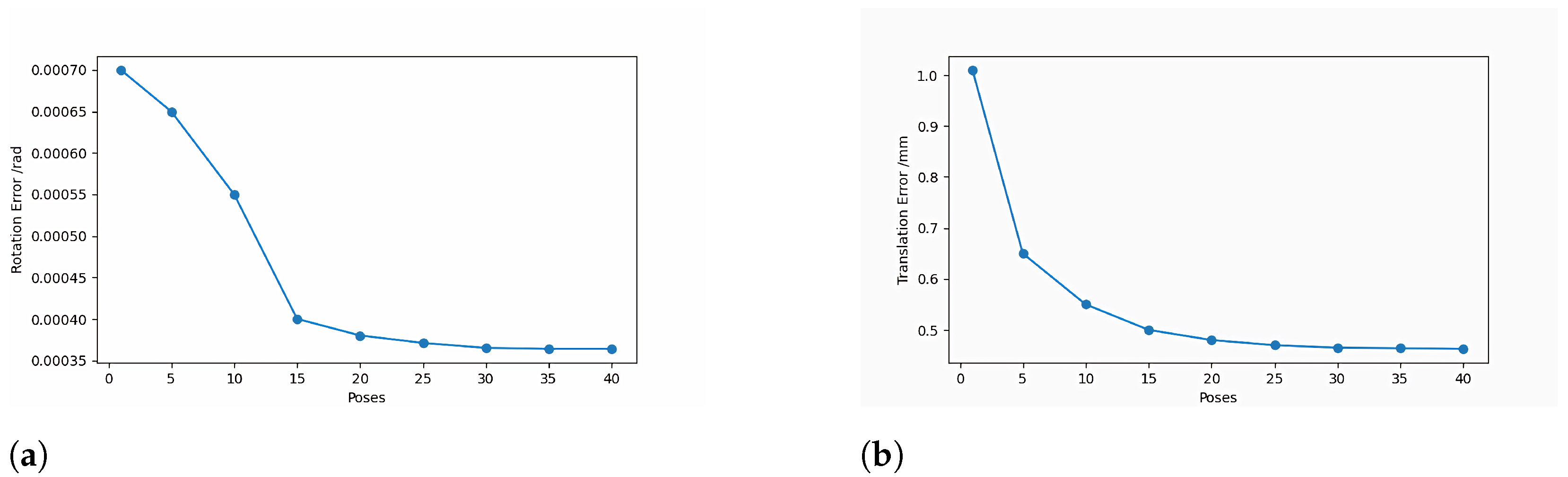
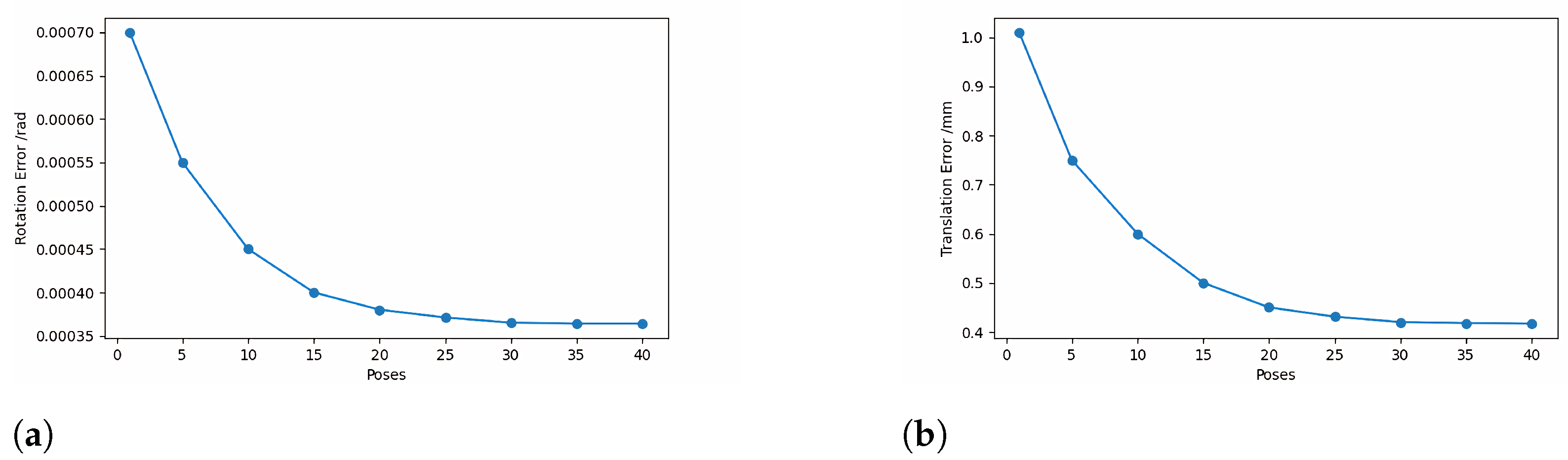
3.2.4. Influence of The Trihedron Calibration Object Poses Number on The Algorithm’s Accuracy
4. Discussion
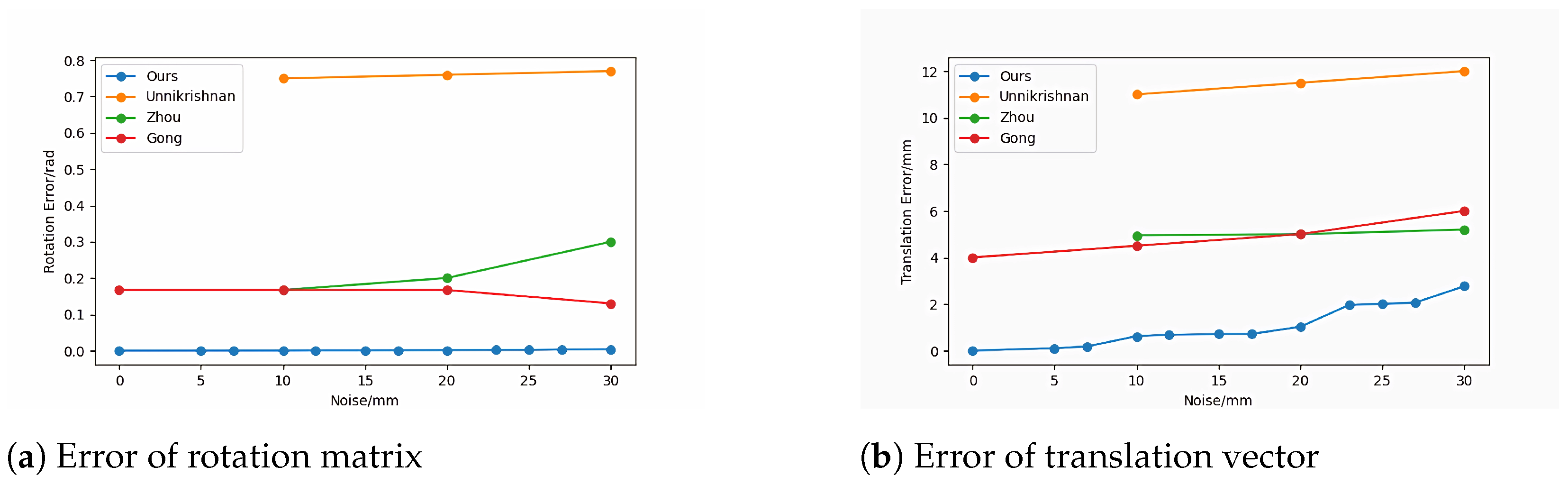
4.1. Accuracy Comparison between the Proposed Method and the Current Mainstream Methods
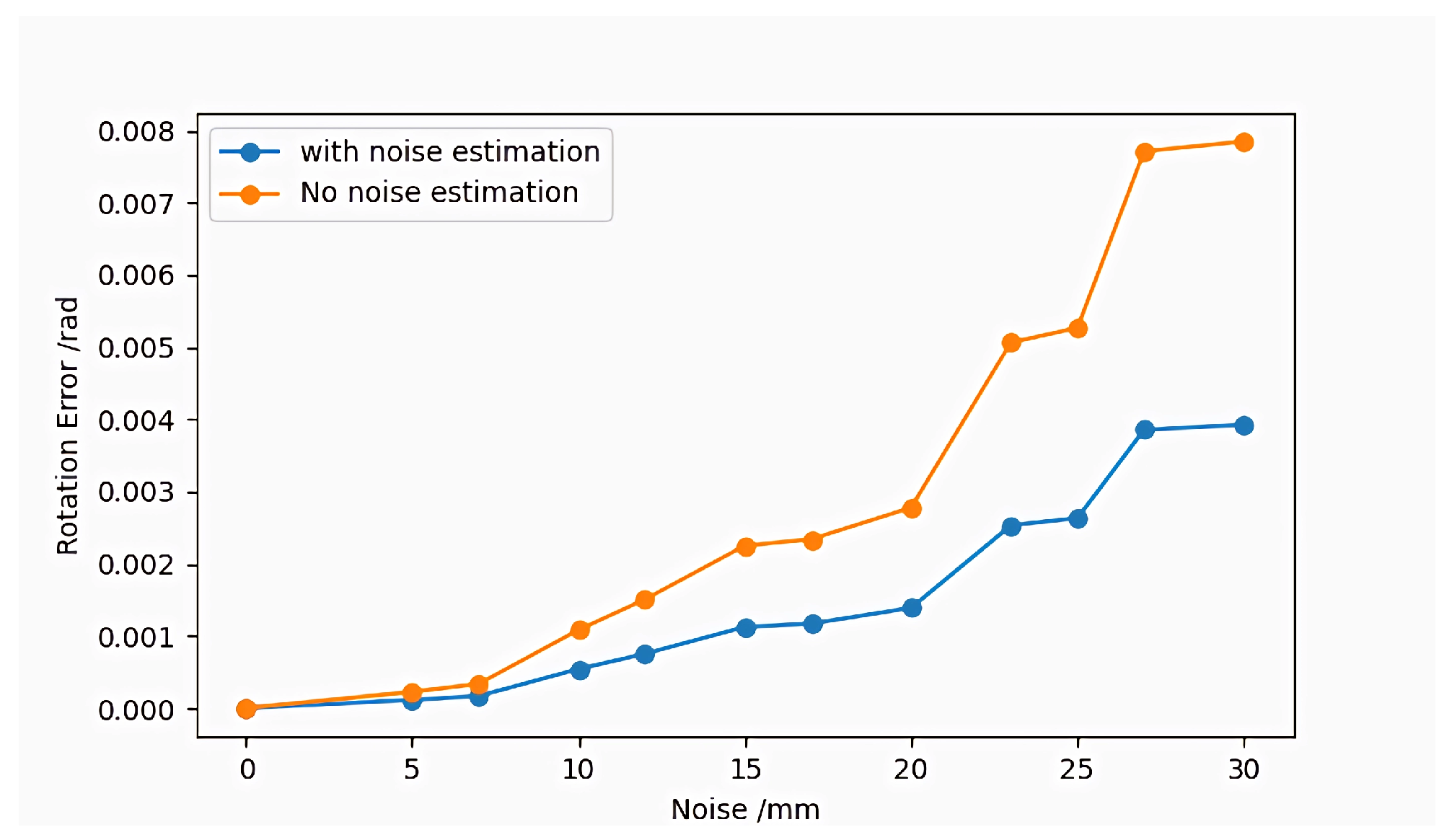
4.2. Influence of Point Cloud Noise Estimation Methods on the Calibration Results
4.3. Influence of Different Constraints on Calibration Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alismail, H.; Browning, B. Automatic calibration of spinning actuated lidar internal parameters. J. Field Robot. 2015, 32, 723–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R. Sensors for robotic perception. Part two: Positional and environmental awareness. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2015, 42, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, T.; Dai, X. Robot kinematic parameters compensation by measuring distance error using laser tracker system. Infrared Laser Eng. 2015, 44, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Xu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, S. An automatic calibration algorithm for laser vision sensor in robotic autonomous welding system. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Application of sensing technology in intelligent robotic arc welding: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 79, 854–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Actuators and sensors for application in agricultural robots: A review. Machines 2022, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, C. Accurate fruit localisation using high resolution LiDAR-camera fusion and instance segmentation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Luo, D.; Yan, F.; Zhuang, Y. A novel lidar-assisted monocular visual SLAM framework for mobile robots in outdoor environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fanyu, L.Y.D.; Yan, X. Map-building approach based on laser and depth visual sensor fusion SLAM. Appl. Res. Comput. 2016, 33, 2970–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Lenac, K.; Kitanov, A.; Cupec, R.; Petrović, I. Fast planar surface 3D SLAM using LIDAR. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 92, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, B. Object detection and tracking using multi-layer laser for autonomous urban driving. In Proceedings of the 19th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Droeschel, D.; Schwarz, M.; Behnke, S. Continuous mapping and localization for autonomous navigation in rough terrain using a 3D laser scanner. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 88, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, S.; Burke, J.; Pak, A.; Rentschler, T. Camera calibration as machine learning problem using dense phase shifting pattern, checkerboards, and different cameras. Opt. Data Sci. IV 2023, 12438, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- ElSheikh, A.; Abu-Nabah, B.A.; Hamdan, M.O.; Tian, G.-Y. Infrared Camera Geometric Calibration: A Review and a Precise Thermal Radiation Checkerboard Target. Sensors 2023, 23, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, C. Automatic checkerboard detection for robust camera calibration. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shenzhen, China, 5–9 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yu, J. A self-identifying checkerboard-like pattern for camera calibration. In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yu, J. A novel camera calibration pattern robust to incomplete pattern projection. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 10051–10060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Salazar, R.; Diaz-Ramirez, V.H. Flexible camera-projector calibration using superposed color checkerboards. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 120, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, R.; Hebert, M. Fast Extrinsic Calibration of a Laser Rangefinder to a Camera (Tech. Report); CMU-RI-TR-05-09; Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, G.; McBride, J.; Savarese, S.; Eustice, R. Extrinsic calibration of a 3D laser scanner and an omnidirectional camera. Fac Proc. Vol. 2010, 43, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, F.M.; Kottas, D.G.; Roumeliotis, S.I. 3D LIDAR–camera intrinsic and extrinsic calibration: Identifiability and analytical least-squares-based initialization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J. Extrinsic calibration of a 3D LIDAR and a camera using a trihedron. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravian, A.; Chin, T.; Reid, I. A branch-and-bound algorithm for checkerboard extraction in camera-laser calibration. arXiv Prepr. 2017, arXiv:1704.00887. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Deng, Z. Extrinsic calibration of a camera and a lidar based on decoupling the rotation from the translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Madrid, Spain, 3–7 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zou, Z. Accurate Calibration of a Large Field of View Camera with Coplanar Constraint for Large-Scale Specular Three-Dimensional Profile Measurement. Sensors 2023, 23, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhai, C. Fast and practical method for underwater stereo vision calibration based on ray-tracing. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, X.; Tan, Z.; Wang, H. A RANSAC based phase noise filtering method for the camera-projector calibration system. Optoelectron. Lett. 2022, 18, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Kaess, M. Automatic extrinsic calibration of a camera and a 3D lidar using line and plane correspondences. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Liu, H.; Dong, M. Easy pose-error calibration for articulated serial robot based on three-closed-loop transformations. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ding, H. An enhanced kinematic model for calibration of robotic machining systems with parallelogram mechanisms. Robot. -Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2019, 59, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kana, S.; Gurnani, J.; Ramanathan, V.; Turlapati, S.H.; Ariffin, M.Z.; Campolo, D. Fast kinematic re-calibration for industrial robot arms. Sensors 2022, 22, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domhof, J.; Kooij, J.F.P.; Gavrila, D.M. An extrinsic calibration tool for radar, camera and lidar. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.V.; Ng, A.Y. Joint calibration of multiple sensors. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ruichek, Y.; Cappelle, C. 3D triangulation based extrinsic calibration between a stereo vision system and a LIDAR. In Proceedings of the 2011 14th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ruichek, Y.; Cappelle, C. Extrinsic calibration between a stereoscopic system and a LIDAR with sensor noise models. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), Hamburg, Germany, 13–15 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Domhof, J.; Kooij, J.F.P.; Gavrila, D.M. A joint extrinsic calibration tool for radar, camera and lidar. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2021, 6, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, Y. Closed-loop kinematic calibration of robots using a six-point measuring device. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.; Sock, J.; Kwak, K. Indirect correspondence-based robust extrinsic calibration of LiDAR and camera. Sensors 2016, 16, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Ma, Y. The extrinsic calibration of area-scan camera and 2D laser rangefinder (LRF) using checkerboard trihedron. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 36166–36179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. Acm 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, K.S.; Huang, T.S.; Blostein, S.D. Least-squares fitting of two 3-D point sets. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, 5, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, T.; Pusztai, Z.; Hajder, L. Automatic LiDAR-camera calibration of extrinsic parameters using a spherical target. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020. [Google Scholar]







| Vertical Field of View | 90 degrees |
| Vertical Angle Resolution | 1 degree |
| Horizontal Field of View | 270 degrees |
| Horizontal Angle Resolution | 0.5 degrees |
| Constraints Condition | Overlap Ratio | Line Distance |
|---|---|---|
| Literature [14] | 0.67 | 9.33 |
| Coplanar | 0.85 | 2.31 |
| Coplanar + Collinear | 0.88 | 1.04 |
| Coplanar + Multipath-closure + Collinear | 0.93 | 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, X.; Yang, H. Multipath-Closure Calibration of Stereo Camera and 3D LiDAR Combined with Multiple Constraints. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020258
Duan J, Huang Y, Wang Y, Ye X, Yang H. Multipath-Closure Calibration of Stereo Camera and 3D LiDAR Combined with Multiple Constraints. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020258
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Jianqiao, Yuchun Huang, Yuyan Wang, Xi Ye, and He Yang. 2024. "Multipath-Closure Calibration of Stereo Camera and 3D LiDAR Combined with Multiple Constraints" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020258
APA StyleDuan, J., Huang, Y., Wang, Y., Ye, X., & Yang, H. (2024). Multipath-Closure Calibration of Stereo Camera and 3D LiDAR Combined with Multiple Constraints. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020258







