SGR: An Improved Point-Based Method for Remote Sensing Object Detection via Dual-Domain Alignment Saliency-Guided RepPoints
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To enhance the accuracy of feature representation, we propose Saliency-Guided RepPoints, a method that utilizes information within bounding boxes to guide the learning of distribution patterns for DCN offsets.
- To alleviate the potential misalignment between the spatial and feature domains caused by model-guiding, we have designed a dynamic dual-domain alignment training strategy, which mitigates the optimization difficulties.
- We propose an interpretable visualization method to assist in validating the effectiveness of our proposed SGR.
2. Related Work
2.1. Remote Sensing Object Detection
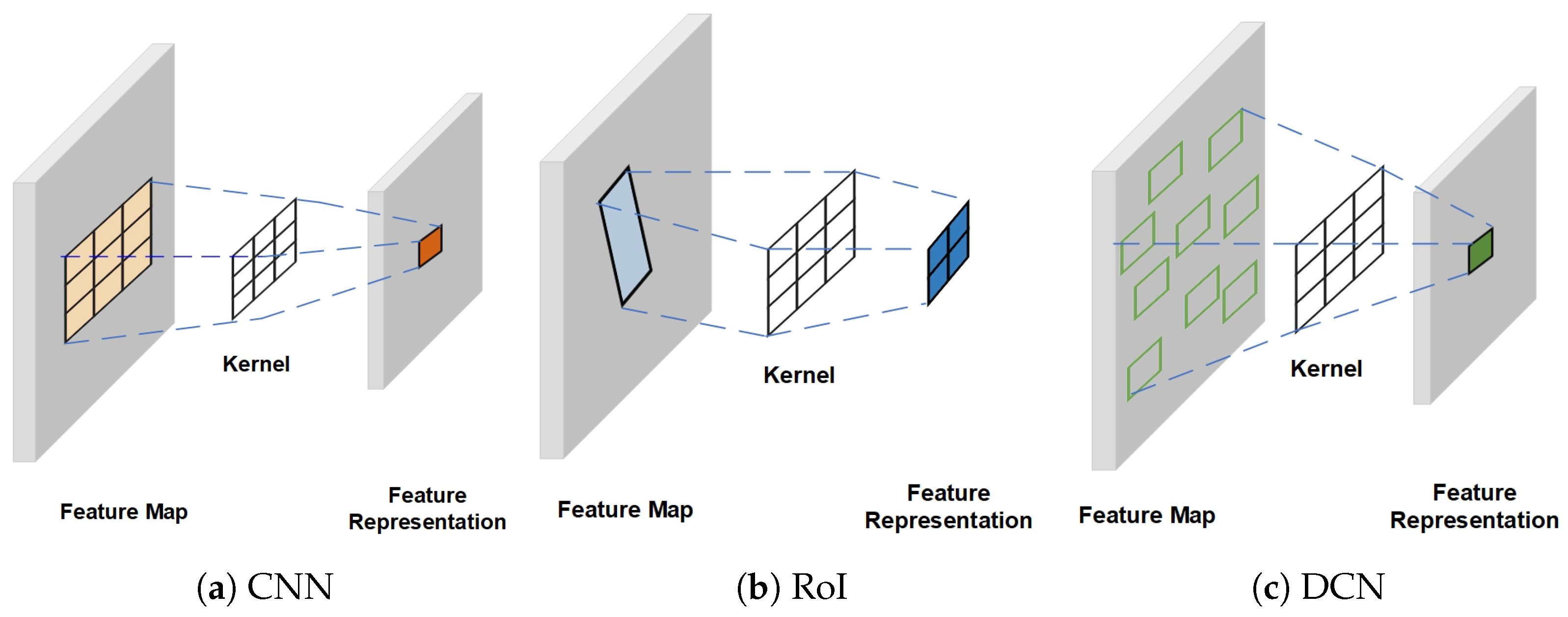
2.2. Feature Representation of Objects
2.3. Dynamic Assignment Strategies
3. Method
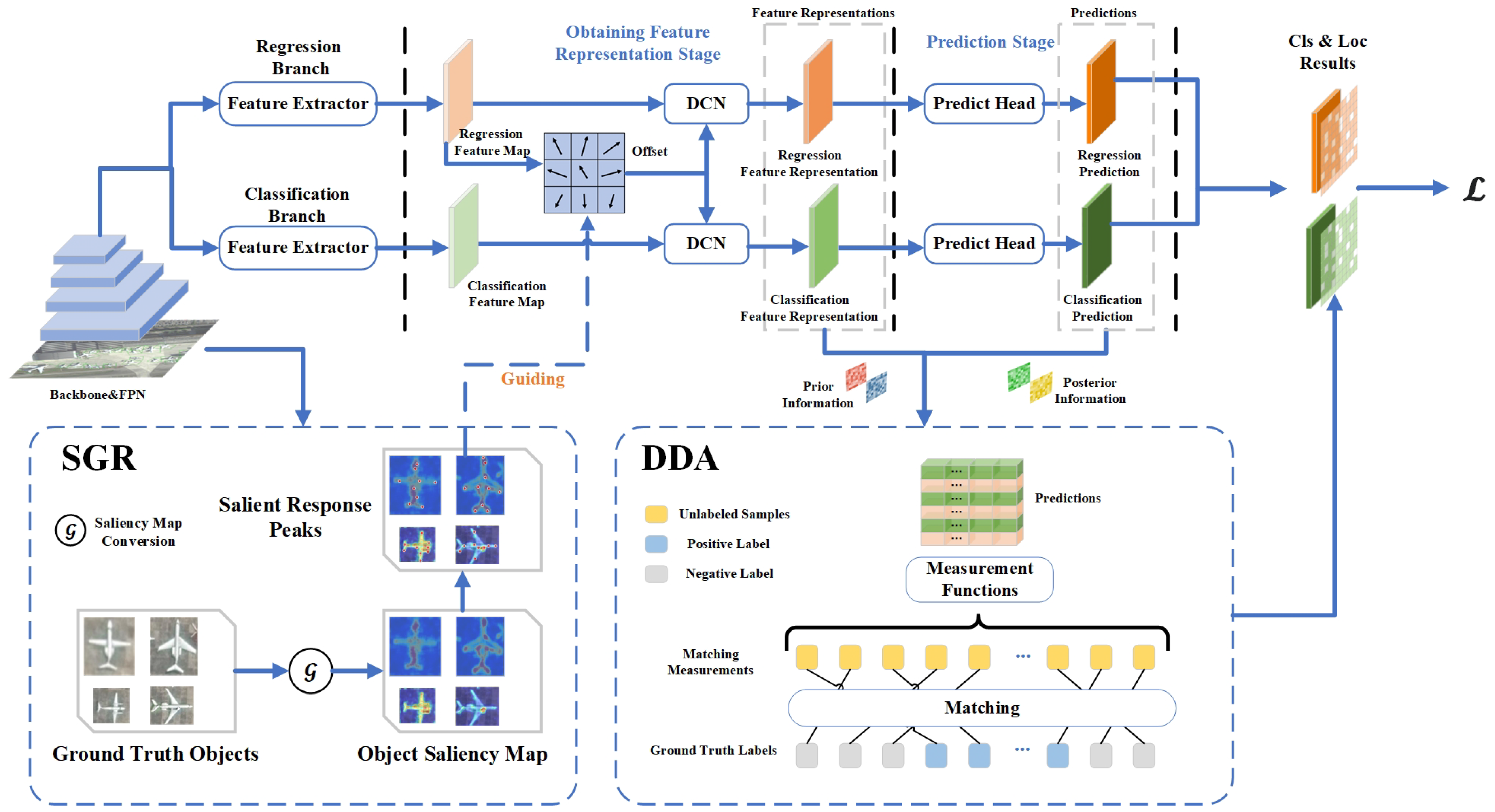
3.1. Overview of Proposed Method
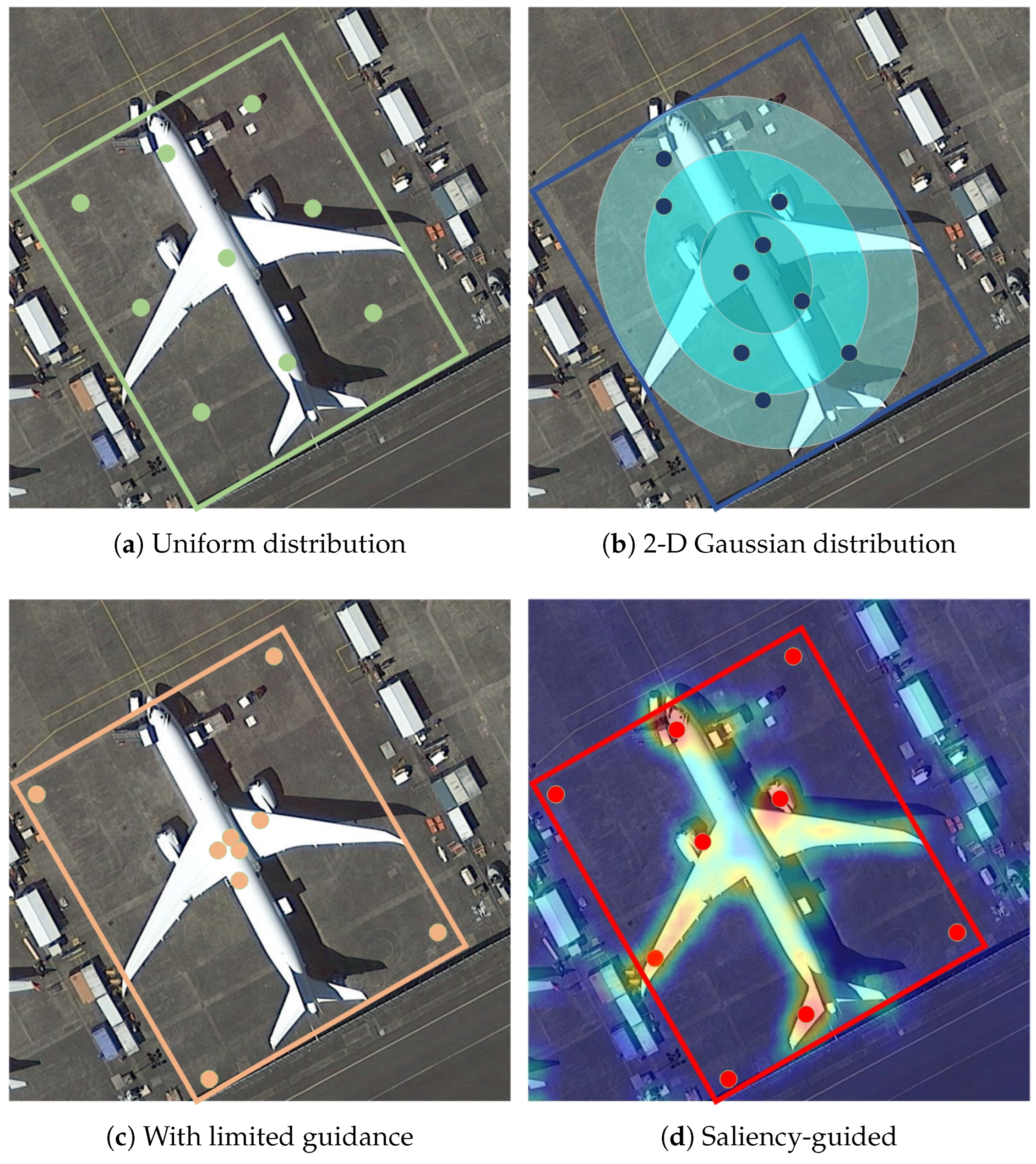
3.2. Sampling Points Distribution Pattern
3.3. Saliency-Guided RepPoints (SGR)
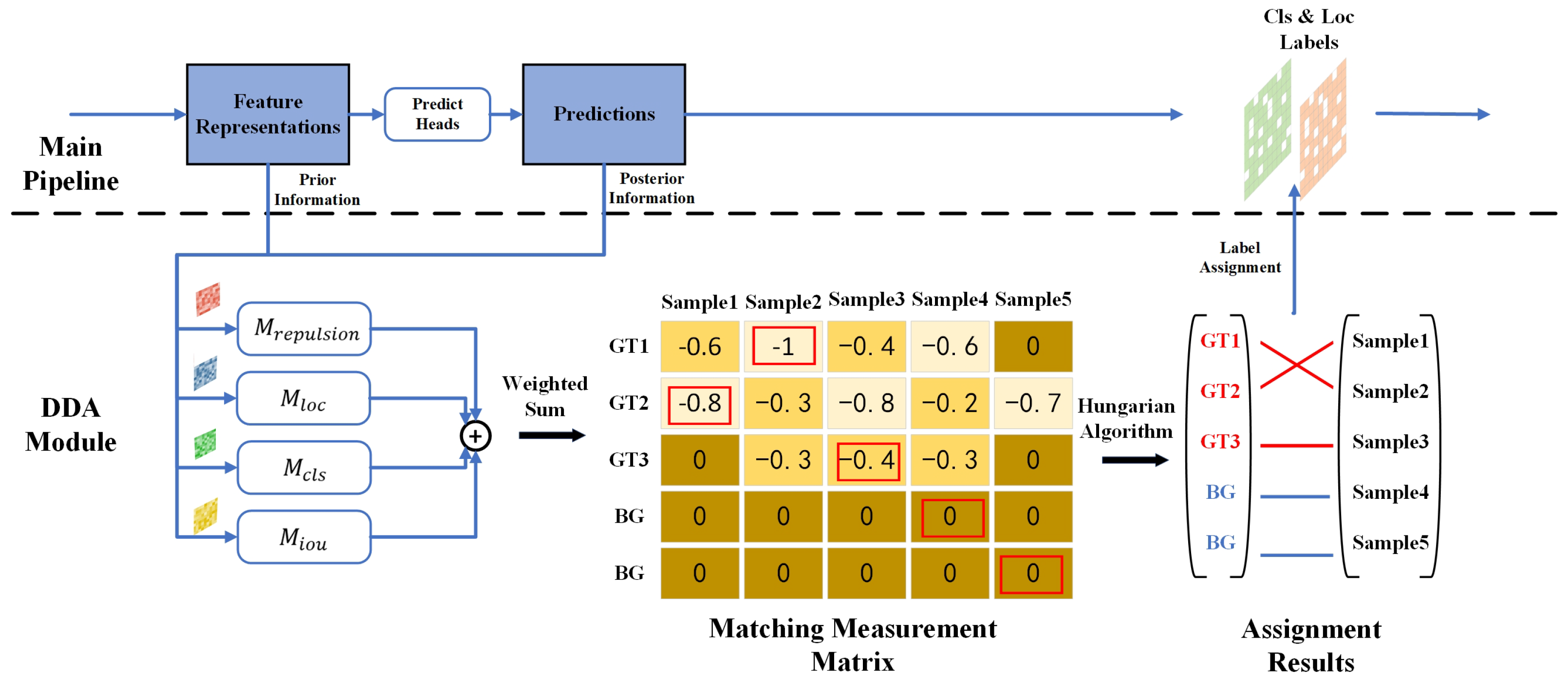
3.4. Dynamic Dual-Domain Alignment (DDA) Assignment
3.5. Point Local Interpretable Map
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparing Methods and Results
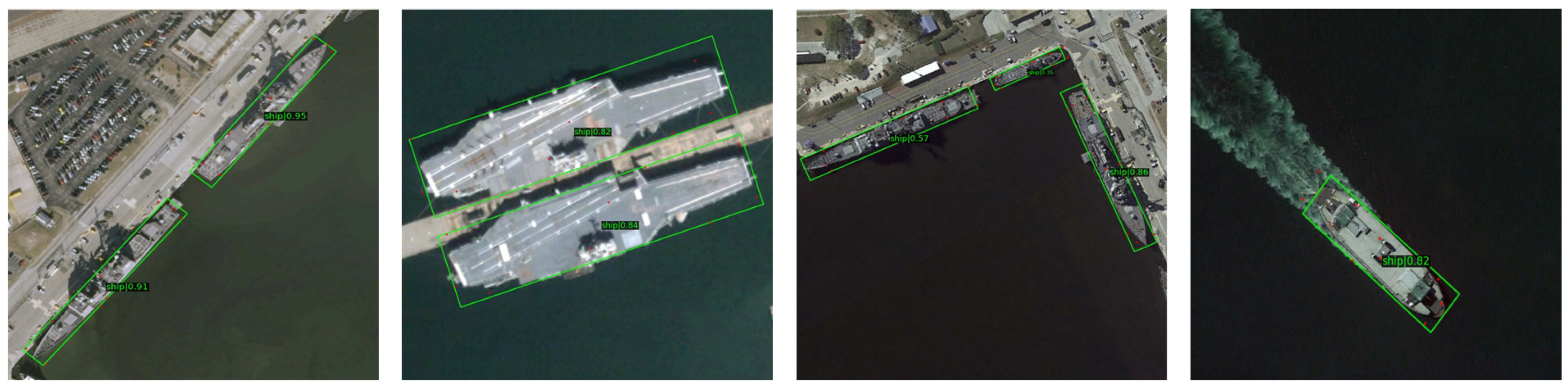
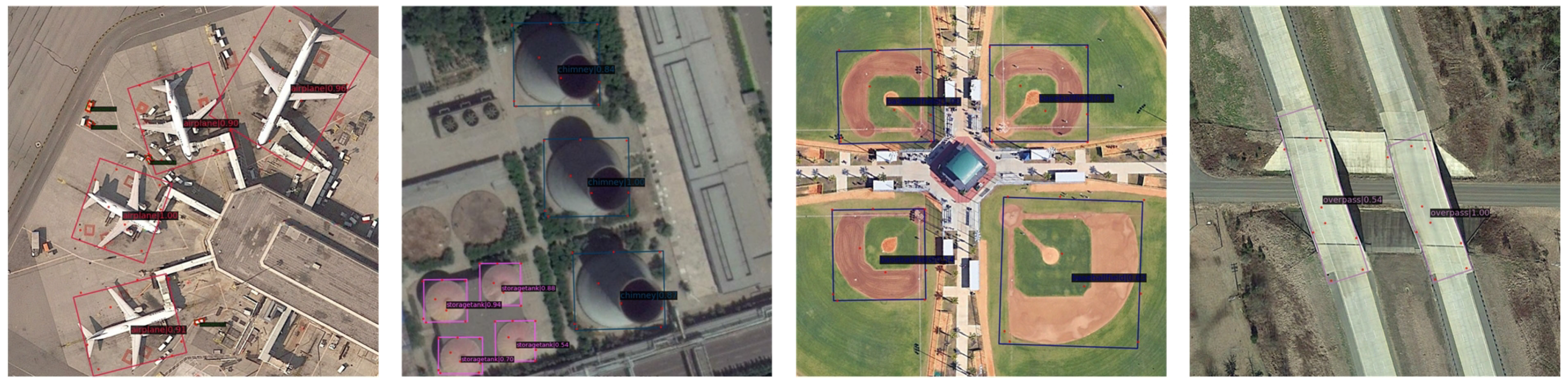
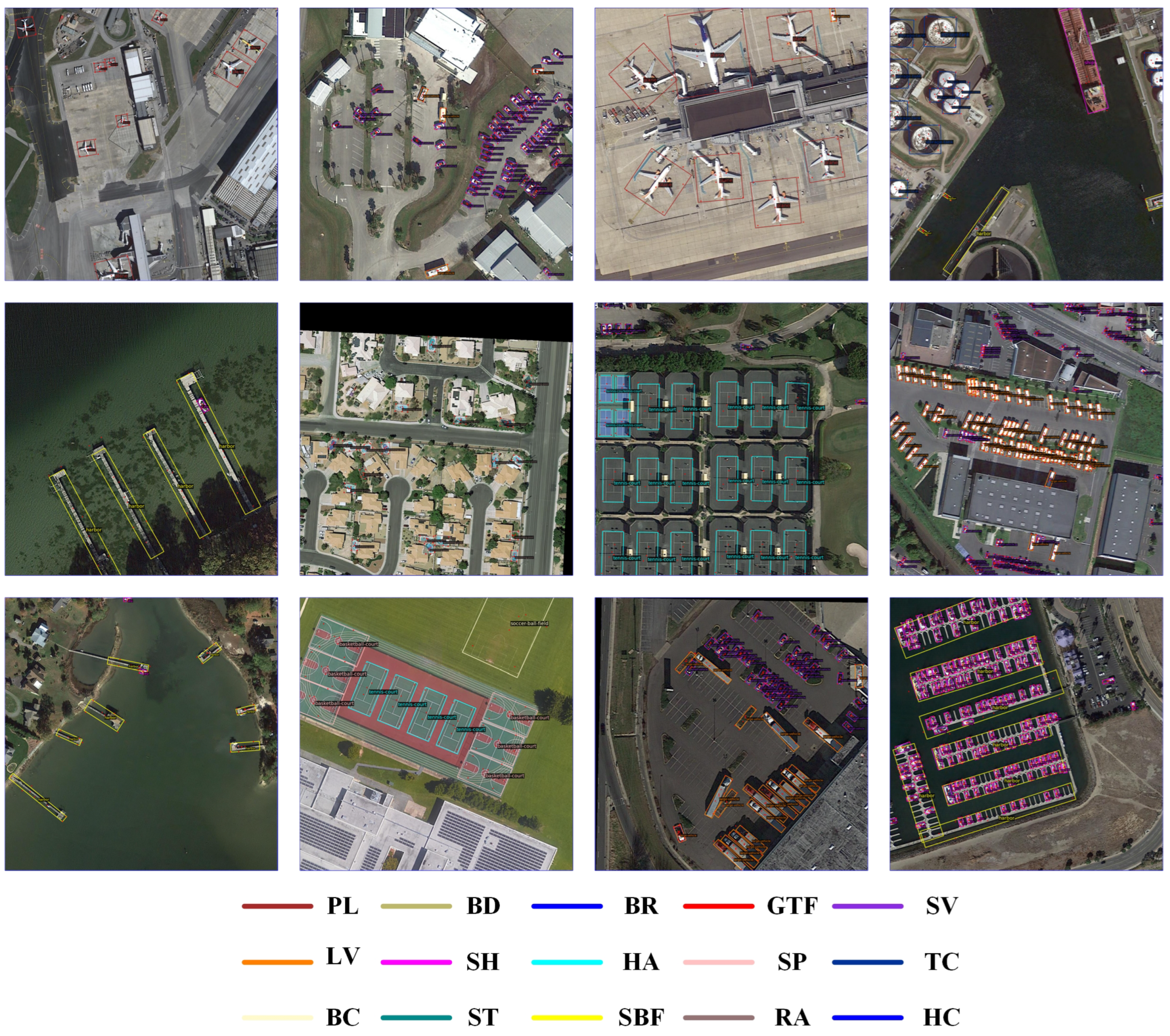
4.4. Main Visualization of Results
4.5. Visualization of Results on Different Datasets
5. Discussion
5.1. Effectiveness of Saliency-Guided Methods
5.2. Assessing The Impact of SGR and DDA on Model Performance
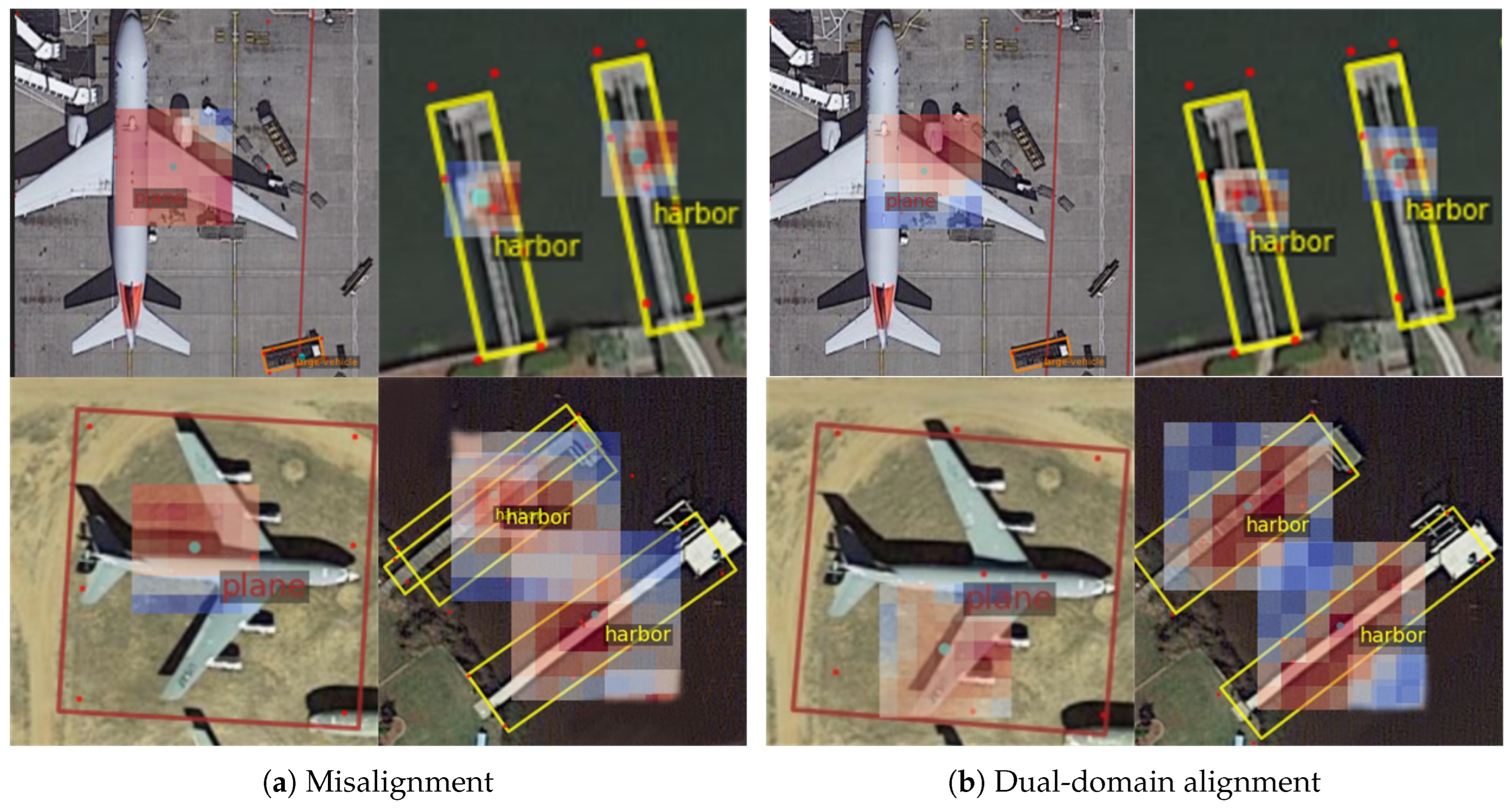
5.3. Visual Interpretability Analysis of Alignment
5.4. Effectiveness of Hyperparameters
5.5. Future Directions Based on SGR
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DCN | Deformable Convolutional Network |
| SGR | Saliency-Guided RepPoints |
| DDA | Dynamic Dual-domain Alignment |
| FPN | Feature Pyramid Network |
| RoI | Region of Interest |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| mAP | Mean Average Precision |
| AP | Average Precision |
References
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–15 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.t.; Wu, X. Object detection with deep learning: A review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bashir, S.M.A.; Khan, M.; Ullah, Q.; Wang, R.; Song, Y.L.; Guo, Z.; Niu, Y.L. Remote sensing image super-resolution and object detection: Benchmark and state of the art. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 197, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xu, W. Multi-oriented object detection in high-resolution remote sensing imagery based on convolutional neural networks with adaptive object orientation features. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–15 December 2015; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.B.; Yao, X.W.; Han, J.W. Oriented R-CNN for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), New York, NY, USA, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3500–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, S.; Dai, J.F.; Soc, I.C. Deformable ConvNets v2: More Deformable, Better Results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New York, NY, USA, 27–28 March 2019; pp. 9300–9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align Deep Features for Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Wei, Y.; Shi, H.; Feris, R.; Xiong, J.; Huang, T. Revisiting rcnn: On awakening the classification power of faster rcnn. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 453–468. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Long, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q.K.; Soc, I.C. Learning RoI Transformer for Oriented Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2844–2853. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Yu, C.H. Point RCNN: An Angle-Free Framework for Rotated Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.P.; Lu, K.; Xue, J.; Li, Y.Q.; Assoc Advancement Artificial, I. Shape-Adaptive Selection and Measurement for Oriented Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/34th Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence/12th Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 23–25 January 2022; pp. 923–932. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, X.; Zhuang, L.; Dong, X.; Sha, J.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, K. AFRE-Net: Adaptive Feature Representation Enhancement for Arbitrary Oriented Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.P.; Lu, K.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.Q.; Xue, J. G-Rep: Gaussian Representation for Arbitrary-Oriented Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Yu, H.; Yu, L.; Xia, G.S. Dynamic Coarse-to-Fine Learning for Oriented Tiny Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7318–7328. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, S.H.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, S. RepPoints: Point Set Representation for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), New York, NY, USA, 27–28 March 2019; pp. 9656–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Lin, S.; Hu, H. Reppoints v2: Verification meets regression for object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 5621–5631. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.T.; Chen, Y.J.; Hu, K.X.; Zhu, J.K. Oriented RepPoints for Aerial Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, I. Artificial intelligence, values, and alignment. Minds Mach. 2020, 30, 411–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Yao, Y.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Dual-aligned oriented detector. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yuan, L.; Weng, L.; Yang, Y. A high resolution optical satellite image dataset for ship recognition and some new baselines. In International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods; SciTePress: Setúbal, Portugal, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Xie, X.; Lang, C.; Yao, Y.; Han, J. Anchor-free oriented proposal generator for object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, X.; Dai, W.; Fu, K.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J. Orientation robust object detection in aerial images using deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 3735–3739. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Ye, F.; Jiang, T. Reppoints-Based Multi-Scale Task Enhancement Network and Sample Assignment Method For Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 6009305. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.V.; Van, H.N.N.; Bui, D.C.; Vo, P.; Vo, N.D.; Nguyen, K. Empirical study of reppoints representation for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Ninth International Conference on Communications and Electronics (ICCE), Nha Trang, Vietnam, 27–29 July 2022; pp. 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Su, H.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Yan, W.; Li, J. Feature Aligned Ship Detection Based on RepPoints in SAR Images. In International Forum on Digital TV and Wireless Multimedia Communications; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Momanyi, B.M. Center-Ness and Repulsion: Constraints to Improve Remote Sensing Object Detection via RepPoints. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J. Arbitrary-oriented object detection with circular smooth label. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Proceedings, Part VIII 16, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 677–694. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Ran, B.; Meng, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, Z. OPD-Net: Prow detection based on feature enhancement and improved regression model in optical remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 6121–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Ming, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q. Rethinking rotated object detection with gaussian wasserstein distance loss. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11830–11841. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Hou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, J. Dense label encoding for boundary discontinuity free rotation detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 15819–15829. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Da, F. Phase-shifting coder: Predicting accurate orientation in oriented object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13354–13363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9759–9768. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Miao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, L. Dynamic anchor learning for arbitrary-oriented object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 35, pp. 2355–2363. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Song, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Sun, J.; Zheng, N. End-to-end object detection with fully convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 15849–15858. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Q.; Miao, L.J.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Yang, X.; Dong, Y.P. Optimization for Arbitrary-Oriented Object Detection via Representation Invariance Loss. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, W.; Luo, P.; Chen, K. Dense Distinct Query for End-to-End Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7329–7338. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, R.; Netto, S.L.; Da Silva, E.A. A survey on performance metrics for object-detection algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), Niteroi, Brazil, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Yang, X.; Peng, S.; Yan, J.; Guo, Y. Learning modulated loss for rotated object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Aartificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 35, pp. 2458–2466. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.C.; Feng, Z.M.; He, T. R3Det: Refined Single-Stage Detector with Feature Refinement for Rotating Object. In Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/33rd Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence/11th Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 23–25 January 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3163–3171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Lu, S.; Zhang, W. CAD-Net: A context-aware detection network for objects in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10015–10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Fu, K. Scrdet: Towards more robust detection for small, cluttered and rotated objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international Conference on Computer Vision, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8232–8241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xu, C.; Cui, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J. Feature-attentioned object detection in remote sensing imagery. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE international Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 3886–3890. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xia, G.S.; Bai, X. Gliding vertex on the horizontal bounding box for multi-oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Guo, H.; Cheng, W.; Pan, T.; Yang, W. Mask OBB: A semantic attention-based mask oriented bounding box representation for multi-category object detection in aerial images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Li, H.C.; Zhang, H.; Xia, G.S. Learning center probability map for detecting objects in aerial images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4307–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Xia, G.S. Redet: A rotation-equivariant detector for aerial object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2786–2795. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Krähenbühl, P. Objects as points. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07850. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, K.; Lin, W.; See, J.; Yu, H.; Ke, Y.; Yang, C. Piou loss: Towards accurate oriented object detection in complex environments. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part V 16. pp. 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, X. Oriented objects as pairs of middle lines. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, K. Stacked hourglass network for robust facial landmark localisation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Ren, Y.; Sheng, K.; Dong, W.; Yuan, H.; Guo, X.; Ma, C.; Xu, C. Dynamic refinement network for oriented and densely packed object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11207–11216. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, J.; Ji, X.; Ye, Q. Beyond bounding-box: Convex-hull feature adaptation for oriented and densely packed object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8792–8801. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Xia, X.G.; Tao, R. A general Gaussian heatmap label assignment for arbitrary-oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 1895–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]






| Method | Backbone | PL | BD | BR | GTF | SV | LV | SH | TC | BC | ST | SBF | RA | HA | SP | HC | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| single-stage | |||||||||||||||||
| RetinaNet-O [43] | R-50-FPN | 88.67 | 77.62 | 41.81 | 58.17 | 74.58 | 71.64 | 79.11 | 90.29 | 82.18 | 74.32 | 54.75 | 60.60 | 62.57 | 69.67 | 60.64 | 68.43 |
| DAL [37] | R-101-FPN | 88.61 | 79.69 | 46.27 | 70.37 | 65.89 | 76.10 | 78.53 | 90.84 | 79.98 | 78.41 | 58.71 | 62.02 | 69.23 | 71.32 | 60.65 | 71.78 |
| RSDet [44] | R-152-FPN | 90.10 | 82.00 | 53.80 | 68.50 | 70.20 | 78.70 | 73.60 | 91.20 | 87.10 | 84.70 | 64.30 | 68.20 | 66.10 | 69.30 | 63.70 | 74.10 |
| R3Det [45] | R-152-FPN | 89.49 | 81.17 | 50.53 | 66.10 | 70.92 | 78.66 | 78.21 | 90.81 | 85.26 | 84.23 | 61.81 | 63.77 | 68.16 | 69.83 | 67.17 | 73.74 |
| S2A-Net [10] | R-50-FPN | 89.11 | 82.84 | 48.37 | 71.11 | 78.11 | 78.39 | 87.25 | 90.83 | 84.90 | 85.64 | 60.36 | 62.60 | 65.26 | 69.13 | 57.94 | 74.12 |
| R3Det-DCL [34] | R-152-FPN | 89.78 | 83.95 | 52.63 | 69.70 | 76.84 | 81.26 | 87.30 | 90.81 | 84.67 | 85.27 | 63.50 | 64.16 | 68.96 | 68.79 | 65.45 | 75.54 |
| AFRE-Net [15] | R-101-FPN | 89.34 | 85.74 | 53.23 | 75.96 | 79.22 | 81.03 | 87.88 | 90.86 | 83.82 | 87.08 | 65.95 | 67.33 | 76.52 | 73.06 | 64.52 | 77.44 |
| two-stage | |||||||||||||||||
| Faster-RCNN-O [2] | R-50-FPN | 88.44 | 73.06 | 44.86 | 59.09 | 73.25 | 71.49 | 77.11 | 90.84 | 78.94 | 83.90 | 48.59 | 62.95 | 62.18 | 64.91 | 56.18 | 69.05 |
| CAD-Net [46] | R-101-FPN | 87.80 | 82.40 | 49.40 | 73.50 | 71.10 | 63.50 | 76.60 | 90.90 | 79.20 | 73.30 | 48.40 | 60.90 | 62.00 | 67.00 | 62.20 | 69.90 |
| SCRDet [47] | R-101-FPN | 89.98 | 80.65 | 52.09 | 68.36 | 68.36 | 60.32 | 72.41 | 90.85 | 87.94 | 86.86 | 65.02 | 66.68 | 66.25 | 68.24 | 65.21 | 72.61 |
| FAOD [48] | R-101-FPN | 90.21 | 79.58 | 45.49 | 76.41 | 73.18 | 68.27 | 79.56 | 90.83 | 83.40 | 84.68 | 53.40 | 65.42 | 74.17 | 69.69 | 64.86 | 73.28 |
| RoI-Trans. [12] | R-101-FPN | 88.65 | 82.60 | 52.53 | 70.87 | 77.93 | 76.67 | 86.87 | 90.71 | 83.83 | 82.51 | 53.95 | 67.61 | 74.67 | 68.75 | 61.03 | 74.61 |
| Gliding-Vertex [49] | R-101-FPN | 89.64 | 85.00 | 52.26 | 77.34 | 73.01 | 73.14 | 86.82 | 90.74 | 79.02 | 86.81 | 59.55 | 70.91 | 72.94 | 70.86 | 57.32 | 75.02 |
| MaskOBB [50] | R-50-FPN | 89.61 | 85.09 | 51.85 | 72.90 | 75.28 | 73.23 | 85.57 | 90.37 | 82.08 | 85.05 | 55.73 | 68.39 | 71.61 | 69.87 | 66.33 | 74.86 |
| CenterMap [51] | R-50-FPN | 88.88 | 81.24 | 53.15 | 60.65 | 78.62 | 66.55 | 78.10 | 88.83 | 77.80 | 83.61 | 49.36 | 66.19 | 72.10 | 72.36 | 58.70 | 71.74 |
| ReDet [52] | ReR-50-ReFPN [52] | 88.79 | 82.64 | 53.97 | 74.00 | 78.13 | 84.06 | 88.04 | 90.89 | 87.78 | 85.75 | 61.76 | 60.39 | 75.96 | 68.07 | 63.59 | 76.25 |
| Oriented R-CNN [7] | R-101-FPN | 88.86 | 83.48 | 55.27 | 76.92 | 74.27 | 82.10 | 87.52 | 90.90 | 85.56 | 85.33 | 65.51 | 66.82 | 74.36 | 70.15 | 57.28 | 76.28 |
| anchor-free | |||||||||||||||||
| CenterNet-O [53] | DLA-34 [53] | 81.00 | 64.00 | 22.60 | 56.60 | 38.60 | 64.00 | 64.90 | 90.80 | 78.00 | 72.50 | 44.00 | 41.10 | 55.50 | 55.00 | 57.40 | 59.10 |
| PIoU [54] | DLA-34 | 80.90 | 69.70 | 24.10 | 60.20 | 38.30 | 64.40 | 64.80 | 90.90 | 77.20 | 70.40 | 46.50 | 37.10 | 57.10 | 61.90 | 64.00 | 60.50 |
| O2-DNet [55] | H-104 [56] | 89.31 | 82.14 | 47.33 | 61.21 | 71.32 | 74.03 | 78.62 | 90.76 | 82.23 | 81.36 | 60.93 | 60.17 | 58.21 | 66.98 | 61.03 | 71.04 |
| DRN [57] | H-104 | 89.71 | 82.34 | 47.22 | 64.10 | 76.22 | 74.43 | 85.84 | 90.57 | 86.18 | 84.89 | 57.65 | 61.93 | 69.30 | 69.63 | 58.48 | 73.23 |
| CFA [58] | R-101-FPN | 89.26 | 81.72 | 51.81 | 67.17 | 79.99 | 78.25 | 84.46 | 90.77 | 83.40 | 85.54 | 54.86 | 67.75 | 73.04 | 70.24 | 64.96 | 75.05 |
| G-Rep. [16] | R-50-FPN | 87.76 | 81.29 | 52.64 | 70.53 | 80.34 | 80.56 | 87.47 | 90.74 | 82.91 | 85.01 | 61.48 | 68.51 | 67.53 | 73.02 | 63.54 | 75.56 |
| Oriented Rep. [20] | R-101-FPN | 89.53 | 84.07 | 59.86 | 71.76 | 79.95 | 80.03 | 87.33 | 90.84 | 87.54 | 85.23 | 59.15 | 66.37 | 75.23 | 73.75 | 57.23 | 76.52 |
| SGR(Ours) | R-50-FPN | 87.53 | 84.64 | 57.78 | 73.78 | 79.40 | 77.61 | 86.58 | 90.91 | 85.49 | 85.30 | 63.52 | 71.05 | 73.61 | 69.50 | 66.59 | 76.88 |
| SGR(Ours) | R-101-FPN | 87.52 | 85.10 | 57.92 | 74.67 | 79.78 | 78.21 | 87.31 | 91.67 | 86.16 | 85.87 | 63.01 | 70.90 | 76.08 | 69.87 | 67.41 | 77.55 |
| SGR(Ours) | Swin-T-FPN | 87.58 | 86.67 | 61.04 | 74.53 | 79.99 | 79.10 | 87.13 | 90.85 | 84.48 | 87.04 | 62.51 | 75.00 | 80.80 | 74.70 | 65.37 | 78.45 |
| Methods | Backbone | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|
| RoI-Trans. [12] | R-101-FPN | 86.20 |
| Gliding Vertex [49] | R-101-FPN | 88.20 |
| RetinaNet-O [43] | R-101-FPN | 89.18 |
| R3Det [45] | R-101-FPN | 89.26 |
| DAL [37] | R-101-FPN | 89.77 |
| GWD [33] | R-101-FPN | 89.85 |
| S2A-Net [10] | R-101-FPN | 90.17 |
| AOPG [25] | R-50-FPN | 90.34 |
| Oriented Rep. [20] | R-50-FPN | 90.38 |
| Oriented R-CNN [7] | R-101-FPN | 90.50 |
| SGR(Ours) | R-50-FPN | 90.67 |
| Method | RetinaNet-O [43] | FR-OBB [2] | RoI-Trans. [12] | AOPG [25] |
| mAP (%) | 57.55 | 59.54 | 63.87 | 64.41 |
| Method | GGHL [59] | Oriented Rep. [20] | DCFL [17] | SGR (Ours) |
| mAP (%) | 66.48 | 66.71 | 66.80 | 67.28 |
| Methods | Car (%) | Plane (%) | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3-O [60] | 74.63 | 89.52 | 82.08 |
| RetinaNet-O [43] | 84.64 | 90.51 | 87.57 |
| RoI Trans. [12] | 87.99 | 89.90 | 88.95 |
| RIDet-O [39] | 88.88 | 90.35 | 89.62 |
| DAL [37] | 89.25 | 90.49 | 89.87 |
| Oriented Rep. [20] | 89.51 | 90.70 | 90.11 |
| G-Rep. [16] | 89.64 | 90.67 | 90.16 |
| SGR (Ours) | 88.72 |
| SGR | DDA | mAP (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✕ | ✕ | 75.97 | 0 |
| ✕ | ✕ | 76.05 | +0.08 |
| ✓ | ✕ | 76.24 | +0.27 |
| ✓ | ✓ | 76.88 | +0.91 |
| mAP (%) | |
|---|---|
| 0.10 | 75.93 |
| 0.15 | 76.74 |
| 0.20 | 76.88 |
| 0.25 | 76.18 |
| 0.30 | 75.66 |
| 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | |
| mAP (%) | 76.45 | 76.48 | 76.88 | 76.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mai, S.; You, Y.; Feng, Y. SGR: An Improved Point-Based Method for Remote Sensing Object Detection via Dual-Domain Alignment Saliency-Guided RepPoints. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020250
Mai S, You Y, Feng Y. SGR: An Improved Point-Based Method for Remote Sensing Object Detection via Dual-Domain Alignment Saliency-Guided RepPoints. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020250
Chicago/Turabian StyleMai, Shuhua, Yanan You, and Yunxiang Feng. 2024. "SGR: An Improved Point-Based Method for Remote Sensing Object Detection via Dual-Domain Alignment Saliency-Guided RepPoints" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020250
APA StyleMai, S., You, Y., & Feng, Y. (2024). SGR: An Improved Point-Based Method for Remote Sensing Object Detection via Dual-Domain Alignment Saliency-Guided RepPoints. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020250







