The Characteristics of Precipitation with and without Bright Band in Summer Tibetan Plateau and Central-Eastern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
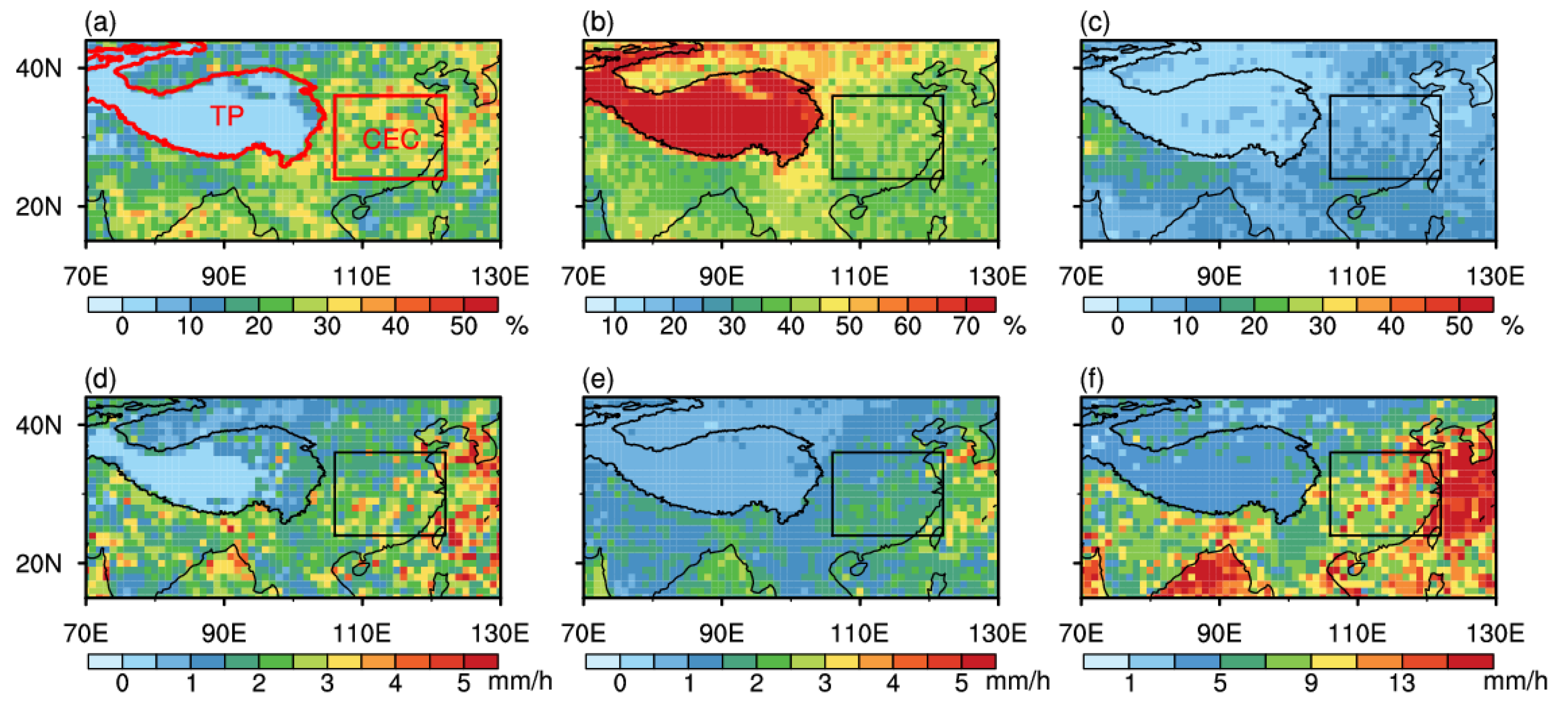
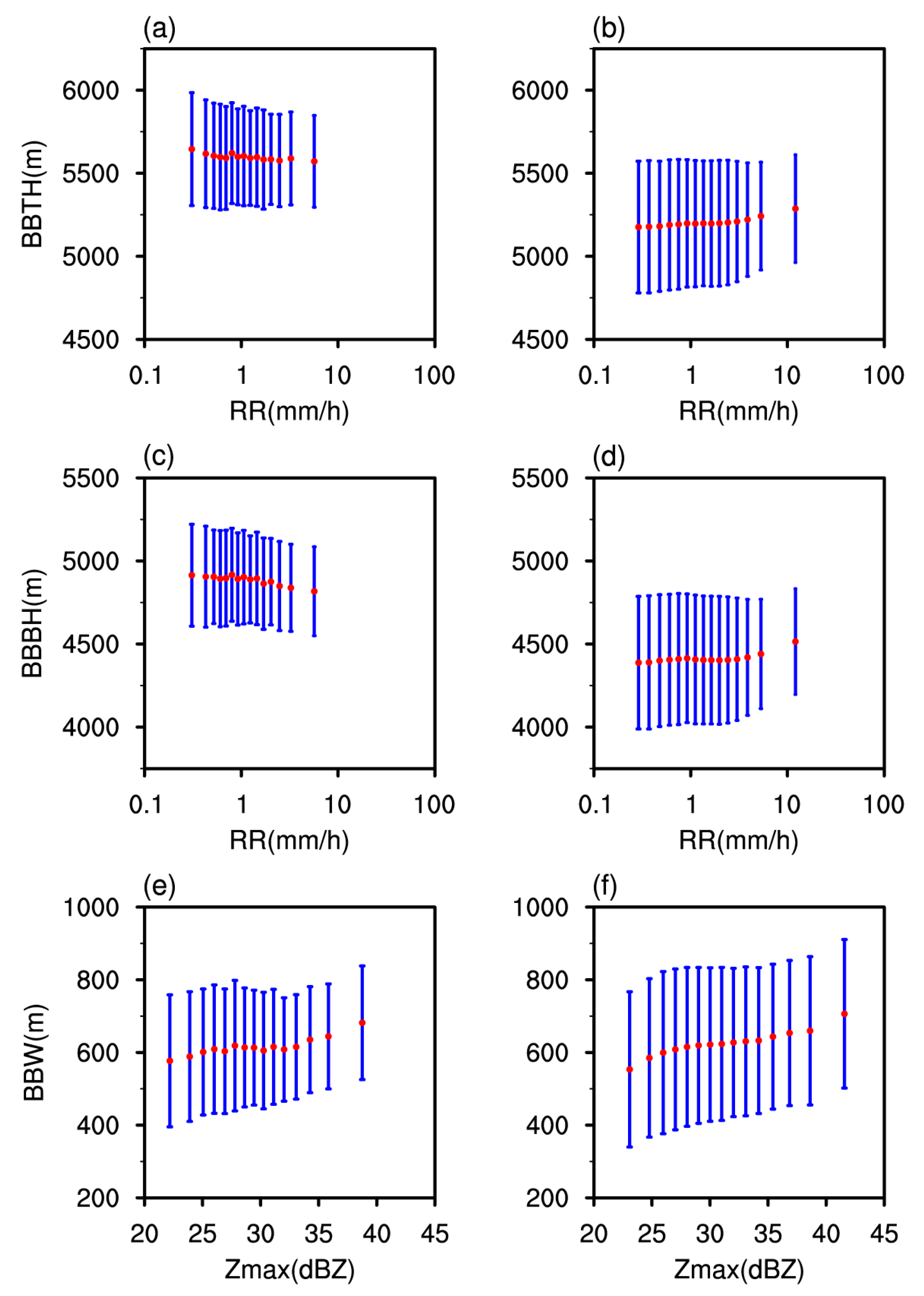
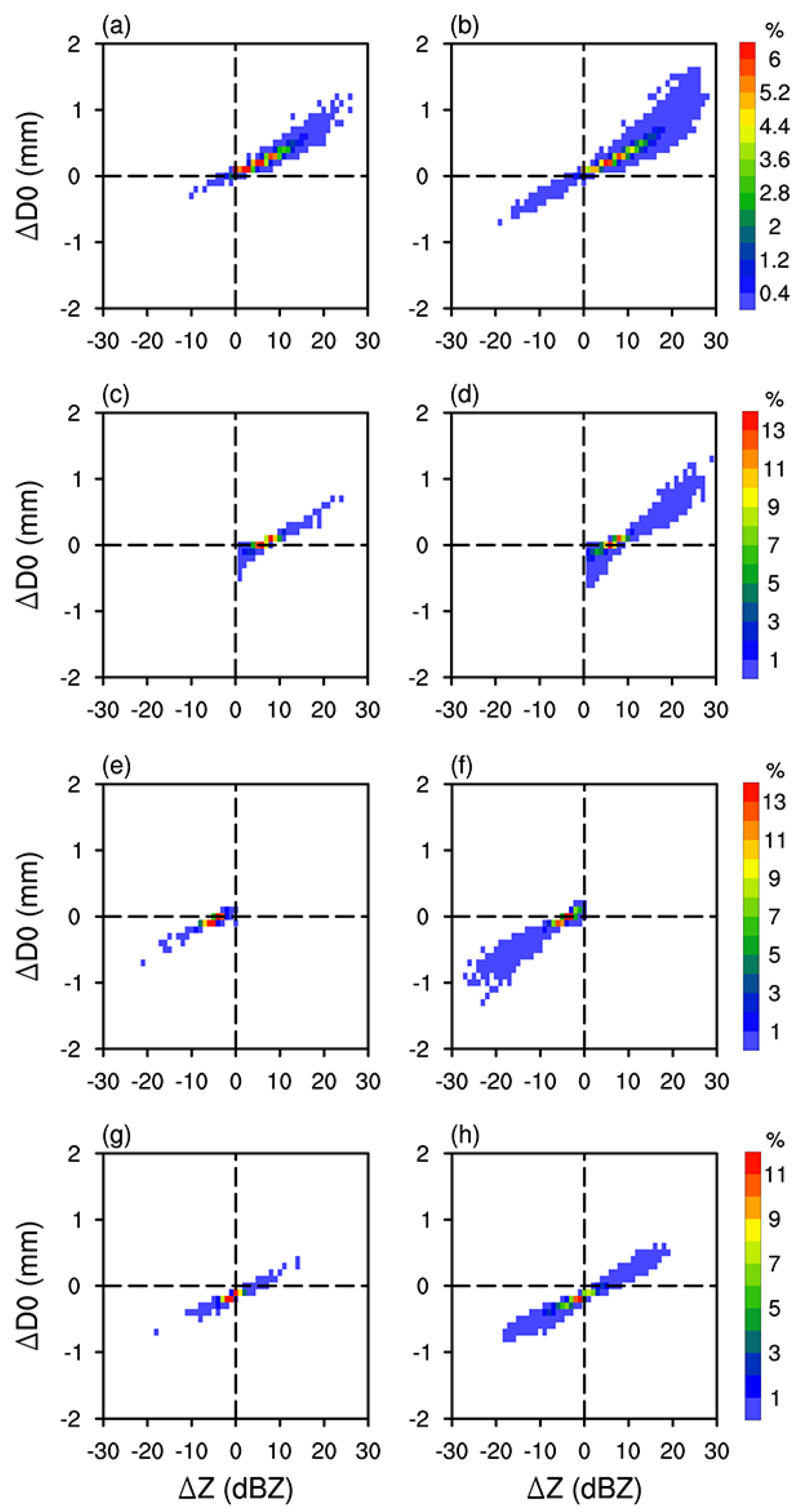
3.1. Characteristics of Precipitation Parameters and BB Parameters
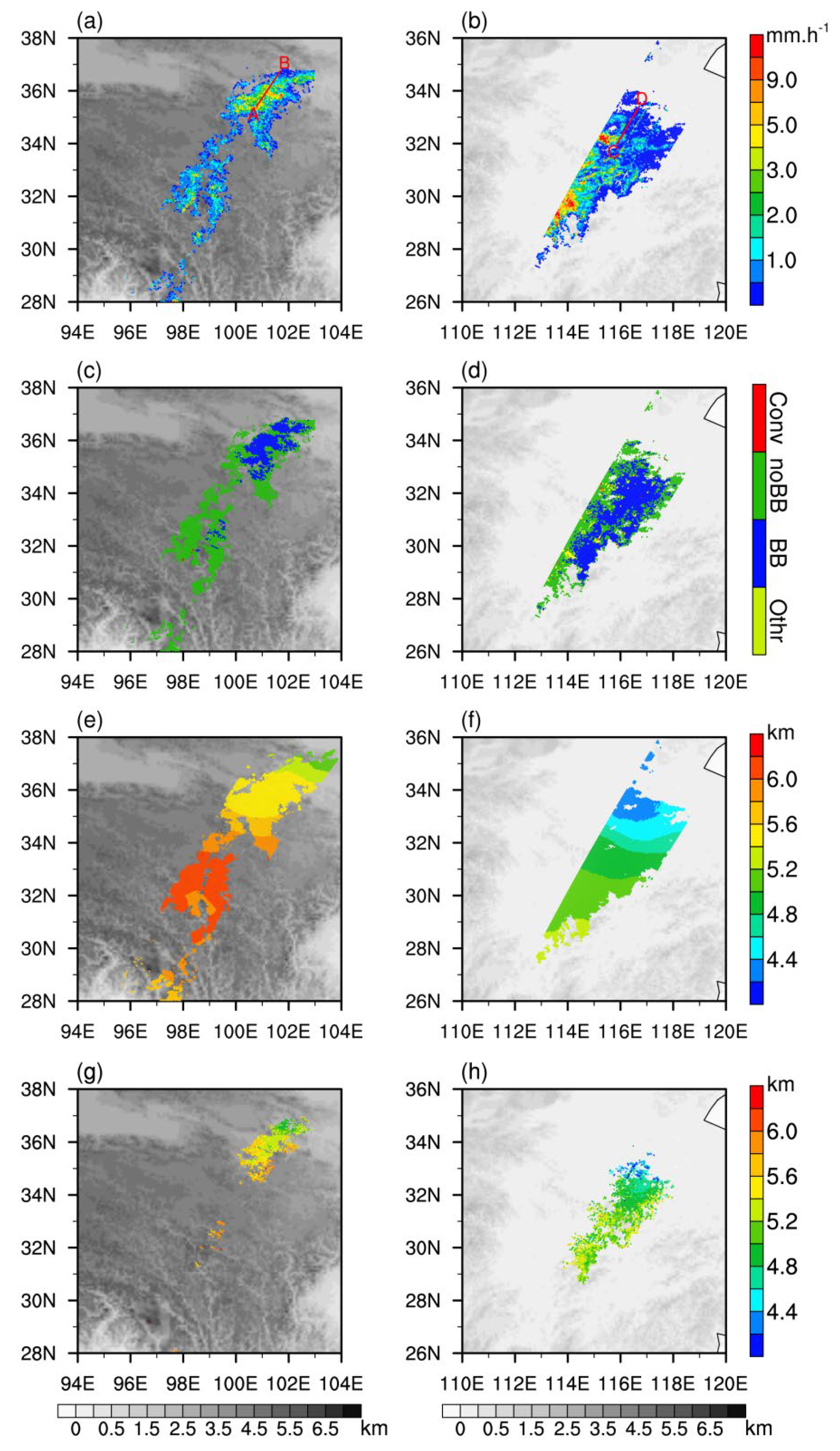
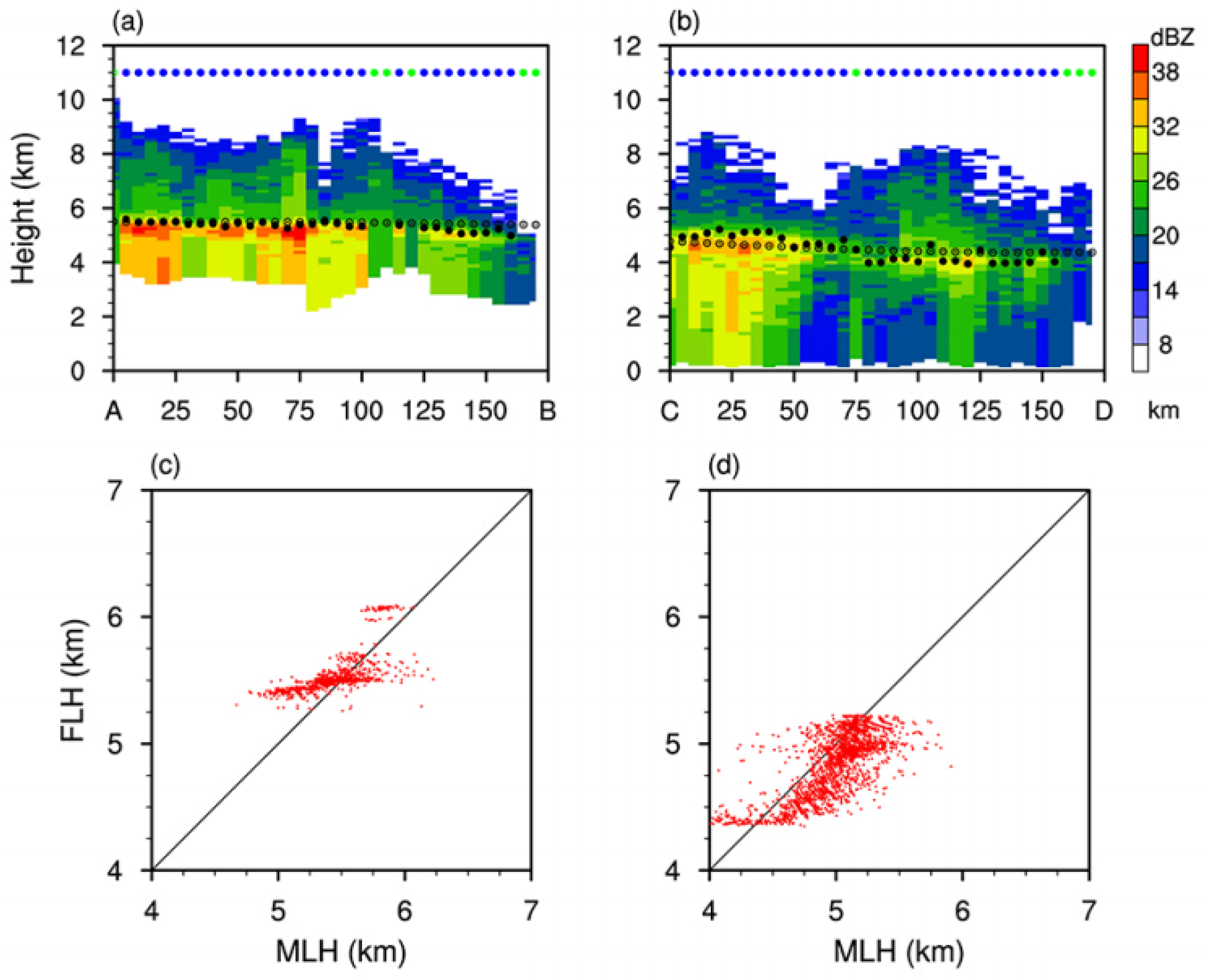
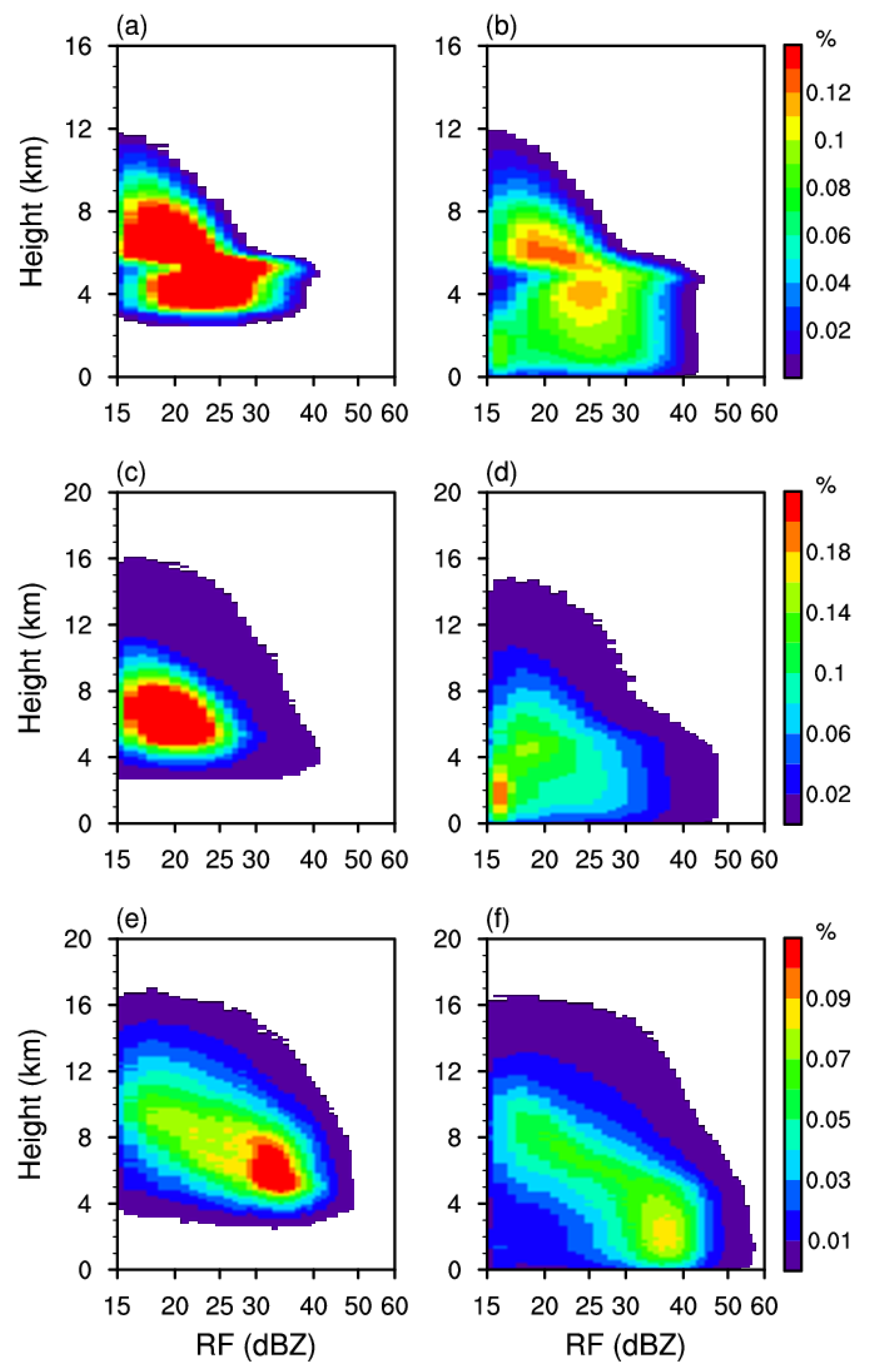
3.2. Characteristics of Vertical Structure for Different Types of Precipitation
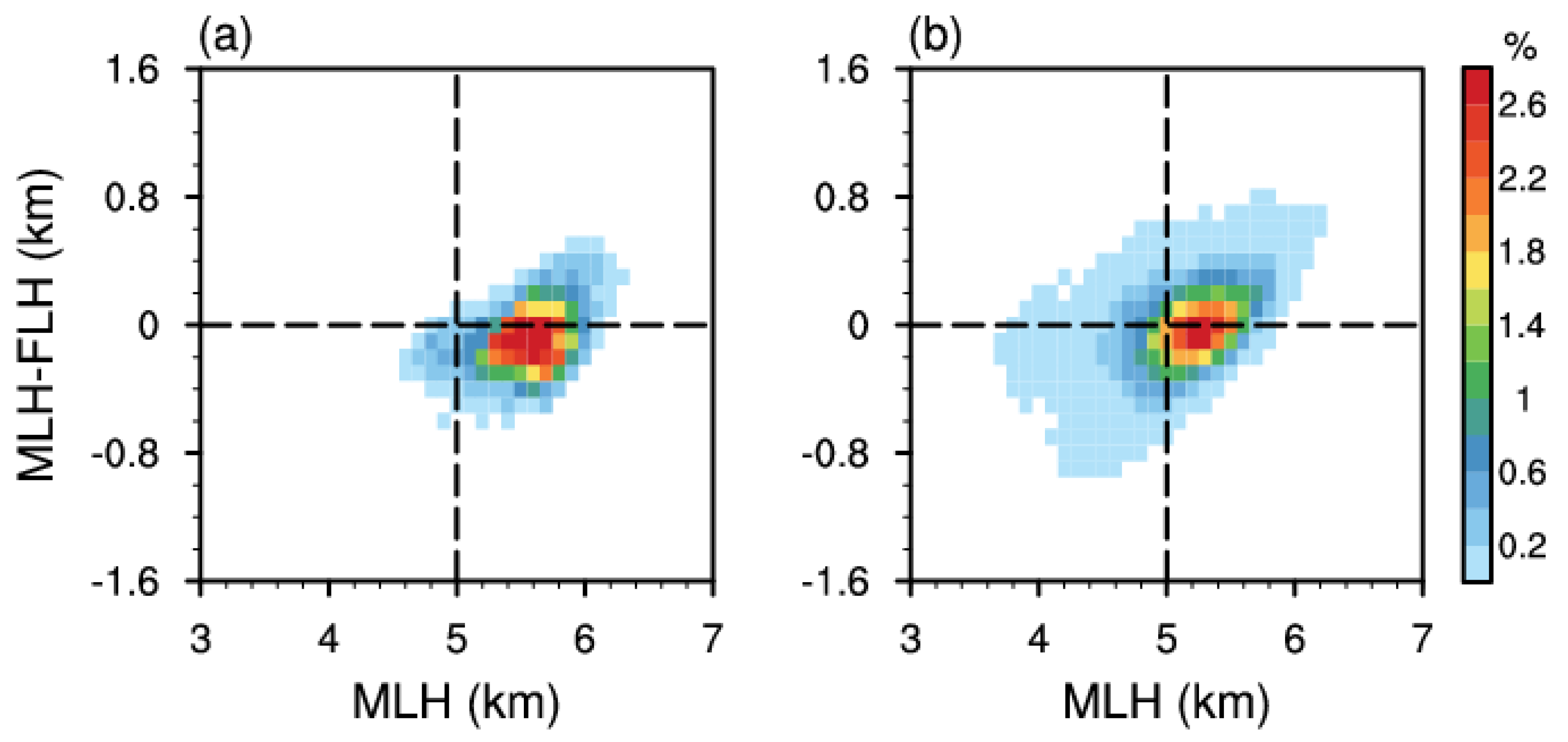
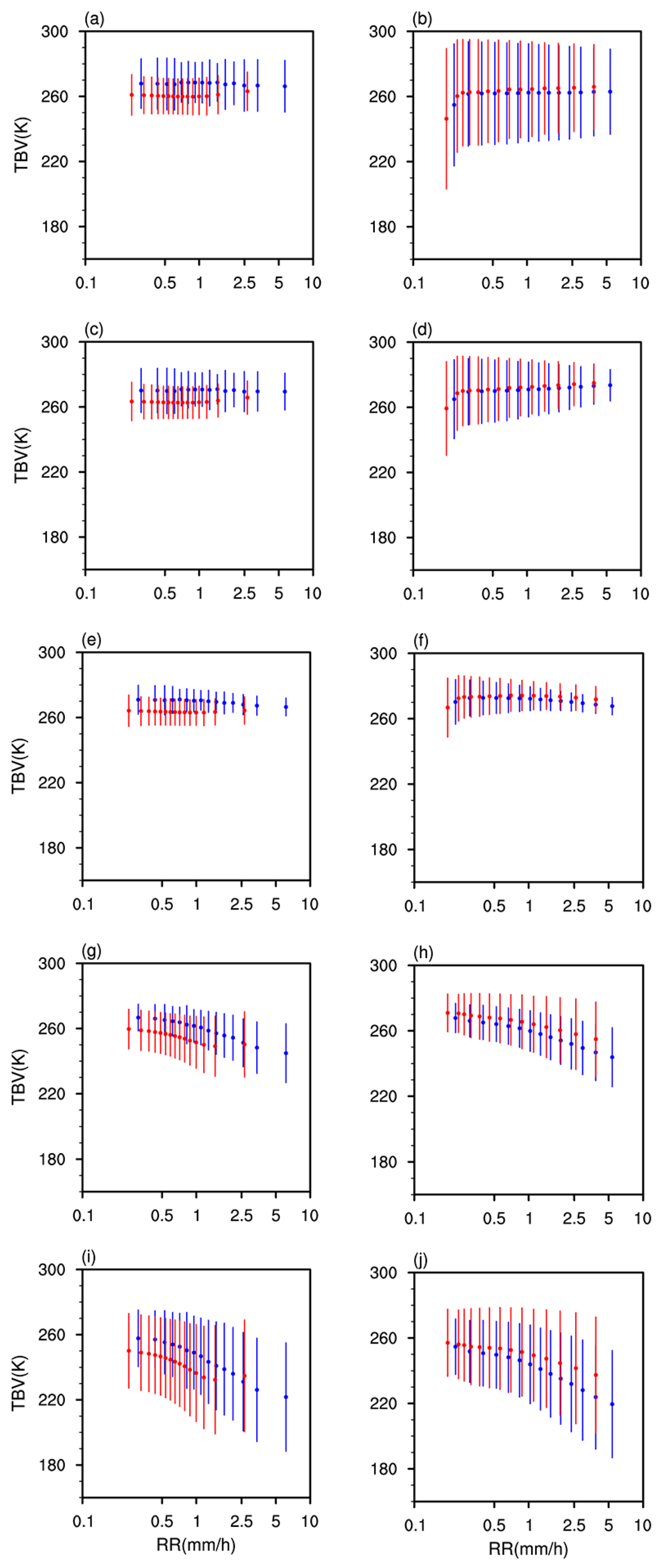
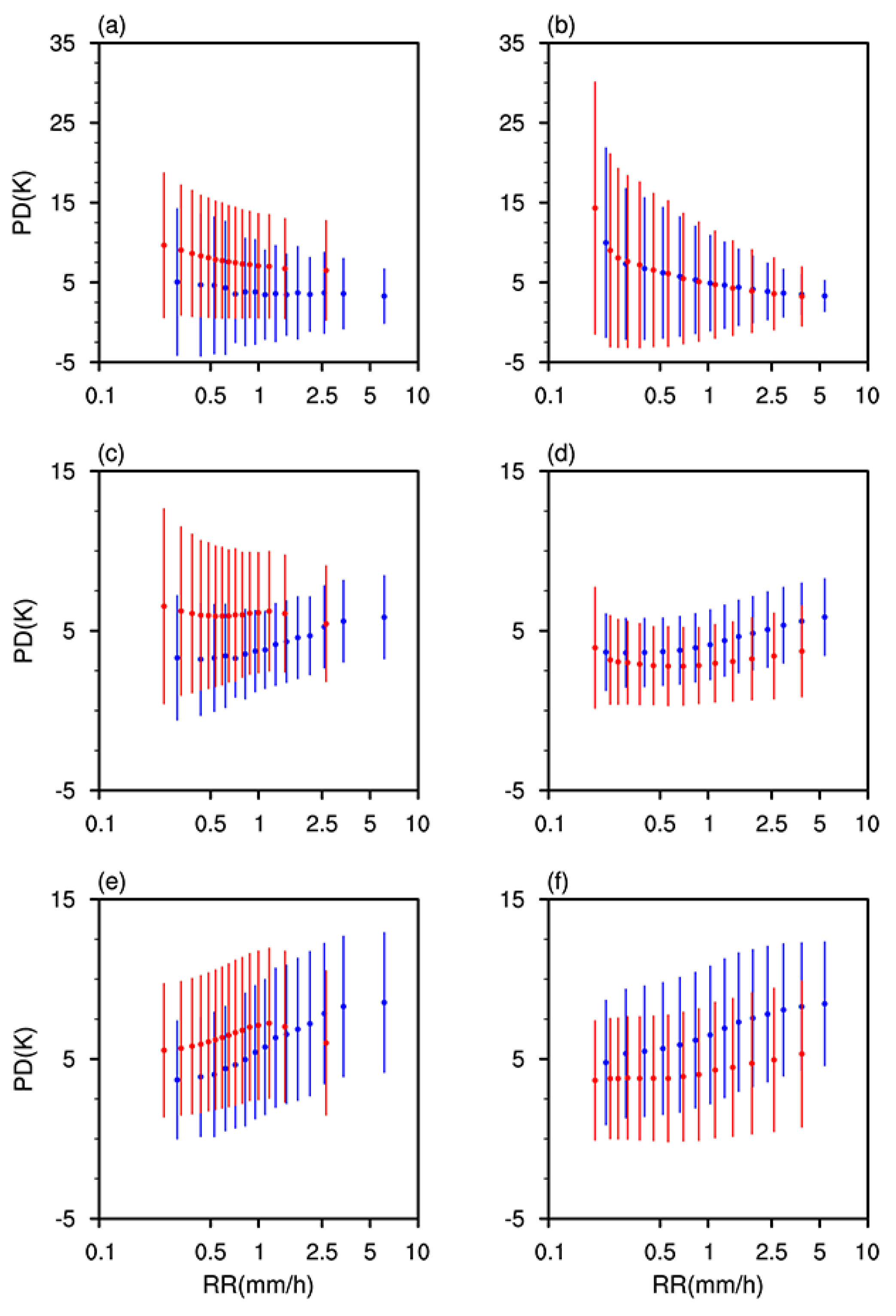
3.3. The Influence of BB on Passive Microwave Observations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Houze, R.; Robert, A. Cloud Dynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; p. 577. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.R.; Ecklund, W.L.; Gage, K.S. Classification of precipitating clouds in the tropics using 915 MHz wind profilers. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 996–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickman, T.S. Glossary of Meteorology, 2nd ed.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; 855p. [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzki, I.; Szyrmer, W.; Bell, C.; Fabry, F. Modeling of the melting layer. Part III: The density effect. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 3705–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwar, M.; Maheskumar, R.S.; Das, S.K.; Morwal, S.B. Nature of light rain during presence and absence of bright band. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 121, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Gatlin, P.N.; Bringi, V.N. Separating stratiform and convective rain types based on the drop size distribution characteristics using 2D video disdrometer data. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaka, J.; Iguchi, T.; Kumagai, H.; Okamoto, K. Rain Type Classification algorithm for TRMM precipitation radar. In Proceedings of the IGARSS’97—1997 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Singapore, 3–8 August 1997; Volume 4, pp. 1633–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Awaka, J.; Le, M.; Chandrasekar, V.; Yoshida, N.; Higashiuwatoko, T.; Kubota, T.; Iguchi, T. Rain Type Classification Algorithm Module for GPM Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J. The reduction of errors caused by bright bands in quantitative rainfall measurements made using radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1986, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qi, Y.C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.F.; Cao, Q. VPR correction of bright band effects in radar QPEs using polarimetric radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 3627–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Kramer, S. Classification and correction of the bright band using an operational C-band polarimetric radar. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 531, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Su, D.B.; Fan, X.G.; Chen, H.B. Evaluating the algorithm for correction of the bright band effects in QPEs with S-, C- and X-Band dual-polarized radars. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabry, F.; Zawadzki, I. Long-term radar observations of the melting layer of precipitation and their interpretation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Moisseev, D. Melting layer attenuation at Ka- and W-bands as derived from multi-frequency radar Doppler spectra observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 9520–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, B.; Chandrasekar, V. Global study of bright band structure as observed from spaceborne precipitation radar. Microw. Remote Sens. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 5654, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Thurai, M.; Iguchi, T. Rain height information from TRMM precipitation radar. Electron. Lett. 2000, 36, 1059–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Iguchi, T.; Kozu, T.; Eastment, J.D.; Wilson, C.L.; Ong, J.T. Radar observations in Singapore and their implications for the TRMM precipitation radar retrieval algorithms. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Maitra, A.; Shukla, A.K. Melting layer characteristics at different climatic conditions in the Indian region: Ground based measurements and satellite observations. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Sasaki, H.; Deguchi, E.; Thurai, M. Bright Band height statistics observed by the TRMM precipitation radar. In Proceedings of the 2nd TRMM International Science Conference, Nara, Japan, 6–10 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sumesh, R.K.; Resmi, E.A.; Unnikrishnan, C.K.; Jash, D.; Sreekanth, T.S.; Resmi, M.M.; Rajeevan, K.; Nita, S.; Ramachandran, K.K. Microphysical aspects of tropical rainfall during Bright Band events at mid and high-altitude regions over Southern Western Ghats, India. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martner, B.; Yuter, S.; White, A.B.; Matrosov, S.; Kingsmill, D.; Ralph, F. Raindrop Size Distributions and Rain Characteristics in California Coastal Rainfall for Periods with and without a Radar Bright Band. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Bansemer, A.; Poellot, M.R.; Wood, N. Observations of ice microphysics through the melting layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 2902–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Lu, G.P.; Fu, Y.F. Microphysical characteristics of precipitation within convective overshooting over East China observed by GPM DPR and ERA5. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 7123–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, W.S.; Bauer, P.; Kummerow, C.D.; Hong, Y.; Tao, W.K. A melting-layer model for passive/active microwave remote sensing applications. Part II: Simulation of TRMM observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.T.; Olson, W.S.; Skofronick-Jackson, G. The microwave properties of simulated melting precipitation particles: Sensitivity to initial melting. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, A.; Kummerow, C.; Shin, D.B.; Williams, C. Constraining microwave brightness temperatures by radar bright band observations. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2003, 20, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galligani, V.S.; Prigent, C.; Defer, E.; Jimenez, C.; Eriksson, P. The impact of the melting layer on the passive microwave cloud scattering signal observed from satellites: A study using TRMM microwave passive and active measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5667–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, S.; Hu, R.; et al. The influence of complex terrain on cloud and precipitation on the foot and slope of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2024, 62, 3143–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.F.; Liu, Y.M. Vertical structures of convective and stratiform clouds in boreal summer over the Tibetan Plateau and its neighboring regions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulies, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, M. Temporal and spatial variations of convection, clouds and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau from recent satellite observations. Part II: Precipitation climatology derived from global precipitation measurement mission. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 4858–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, T.; Seto, S.; Meneghini, R.; Yoshida, N.; Awaka, J.; Le, M.; Chandrasekar, V.; Brodzik, S.; Kubota, T. GPM/DPR Level-2 Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Le, M.; Chandrasekar, V. Precipitation type classification method for Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) onboard the GPM. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wu, D.L. Microphysical Properties of Frozen Particles Inferred from Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Microwave Imager (GMI) Polarimetric Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2741–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zeng, X.; Wu, D.L.; Munchak, S.J.; Li, X.; Kneifel, S.; Liao, L.; Barahona, D. Linkage among Ice Crystal Microphysics, 480 Mesoscale Dynamics and Cloud and Precipitation Structures Revealed by Collocated Microwave Radiometer and Multi-frequency Radar Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12633–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Günther, G.; Li, D.; Stein, O.; Wu, X.; Griessbach, S.; Heng, Y.; Konopka, P.; Müller, R.; Vogel, B.; et al. From ERA-interim to ERA5: The considerable impact of ECMWF’s next-generation reanalysis on Lagrangian transport simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3097–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, T.; Homeyer, C.R. Global tropopause altitudes in radiosondes and reanalyses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5661–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.F.; Liu, G.S. Possible misidentification of rain type by TRMM PR over Tibetan Plateau. J. App. Meteor. 2007, 46, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, P.; Gu, S.Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, N. A New Algorithm of Rain Type Classification for GPM Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar in Summer Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.Q.; Ai, W.H.; Hu, X.; Hu, S.S.; Du, X.Y. Characteristics of Melting Layer in Cyclones Over the Western North Pacific Detected by the GPM Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2021EA001967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.H.; Zhao, P. Characteristics of the summer atmospheric boundary layer height over the Tibetan Plateau and influential factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5253–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.F.; Liu, Y.M.; Lu, J.H. Cloud vertical structure, precipitation, and cloud radiative effects over Tibetan Plateau and its neighboring regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5864–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, J.T.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Estimation of melting-layer cooling rate from dual-polarization radar: Spectral bin model simulations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 1485–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Sun, N.; Ma, M.; Cui, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y. The Characteristics of Precipitation with and without Bright Band in Summer Tibetan Plateau and Central-Eastern China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193703
Yang L, Sun N, Ma M, Cui C, Wang B, Wang X, Fu Y. The Characteristics of Precipitation with and without Bright Band in Summer Tibetan Plateau and Central-Eastern China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(19):3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193703
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Liu, Nan Sun, Ming Ma, Chunguang Cui, Bin Wang, Xiaofang Wang, and Yunfei Fu. 2024. "The Characteristics of Precipitation with and without Bright Band in Summer Tibetan Plateau and Central-Eastern China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 19: 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193703
APA StyleYang, L., Sun, N., Ma, M., Cui, C., Wang, B., Wang, X., & Fu, Y. (2024). The Characteristics of Precipitation with and without Bright Band in Summer Tibetan Plateau and Central-Eastern China. Remote Sensing, 16(19), 3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193703



