Abstract
Modern Multi-Function Radars (MFRs) are sophisticated sensors that are capable of flexibly adapting their control parameters in transmitted pulse sequences. In complex electromagnetic environments, efficiently and accurately recognizing the inter-pulse modulations of non-cooperative radar pulse sequences is a key step for modern Electronic Support (ES) systems. Existing recognition methods focus more on algorithmic designs, such as neural network structure designs, to improve recognition performance. However, in open electromagnetic environments with increased flexibility in radar transmission, these methods would suffer performance degradation due to domain shifts between training and testing datasets. To address this issue, this study proposes a robust radar inter-pulse modulation feature extraction and recognition method based on disentangled representation learning. At first, inspired by the Representation Learning Theory (RLT), the received radar pulse sequences can be disentangled into three explanatory factors related to (i) modulation types, (ii) modulation parameters, and (iii) measurement characteristics, such as measurement noise. Then, an explainable radar pulse sequence disentanglement network is proposed based on auto-encoding variational Bayes. The features extracted through the proposed method can effectively represent the key latent factors related to recognition tasks and maintain performance under domain shift conditions. Experiments on both ideal and non-ideal situations demonstrate the effectiveness, robustness, and superiority of the proposed method in comparison with other methods.
1. Introduction
Modern Multi-Function Radars (MFRs) are capable of performing multiple simultaneous tasks in the radar timeline, with each task being implemented through a sequence of ordered radar pulses [1,2,3,4,5]. In addition, modern radars are equipped with the ability to flexibly select or optimize their control parameters for each individual task based on the sensing of surrounding environments [6,7,8]. These control parameters include the pulse repetition interval (PRI), radio frequency (RF), and pulse width (PW), etc. [9,10,11,12]. Meanwhile, real-world electromagnetic environments are complex, with non-ideal situations related to intercepted pulse sequences such as measurement noise, missing pulses, and spurious pulses. The openness in electromagnetic environments and increased flexibility in radar transmission pose great challenges for modern electronic support (ES) systems. ES systems need to recognize inter-pulse modulations from intercepted radar pulse sequences accurately to support the following processing steps, such as threat assessments or countermeasures [13].
Inter-pulse modulation recognition is a pattern recognition problem, and artificial intelligence (AI) methods have been widely applied to these issues in recent years [14,15,16,17,18]. For instance, recognition methods have been based on the support vector machine (SVM) [19], principal component analysis (PCA) [20], recurrent neural network (RNN) [21], and convolutional neural network (CNN) [10,22]. However, most existing methods focus on supervised learning to recognize inter-pulse modulations [10,23]. The electromagnetic environments are increasingly complex, and the agility and flexibility of advanced radars increase. There would always be new classes of radars or new inter-pulse modulation that need to be recognized. Facing complex real-world electromagnetic environments, existing methods suffer from the following aspects: (i) from the reconnaissance system’s side, it is difficult to obtain a large amount of pulse sequence data for supervised learning; (ii) radar pulse sequences are highly artificial and structured with strong correlations in the time domain, resulting in the lack of a rigorous mathematical theory that adequately explains the performance and reliability of deep neural networks when applied to pulse sequence data; (iii) domain shifts between training and testing pulse sequence datasets always happen in radar applications due to the dynamic environments and software-defined abilities of advanced radars. Moreover, the continuous development of adaptive waveform diversity technologies complicates the recognition process for reconnaissance systems from another perspective [24,25,26,27,28,29]. Traditional methods face severe performance degradation. Specifically, the performance of a well-trained classifier could be degraded or even fail when there is a shift from the training data to the testing data. Thus, there is a vital need for methods with robust feature extraction ability that can tolerate or generalize to domain shift issues and methods with fewer prior knowledge requirements.
Representation learning theory (RLT) is a promising technology for extracting robust and explainable features from data with complex structures and can alleviate the effects of domain shifts [30,31]. In RLT, through the intentional design of latent variable space, a model can extract task-related latent variables that are invariant to some changes in the input [30], i.e., learned latent variables are relatively invariant to other task-irrelevant changes in the domain shift process. Thus, robust feature extraction is achieved. Different datasets and corresponding tasks have different key invariant properties toward various kinds of domain shifts. For instance, in the field of computer vision, a good pattern recognition method is required to extract shift invariant or rotate invariant features [32]. Digging into invariant properties within incoming datasets toward domain shift can help improve recognition performance [33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Specifically, latent variables can be disentangled in the latent space to effectively guide representation learning to separate the informative factors from the complex input data and then achieve recognition tasks based on the extracted informative features [37].
The effectiveness of disentangled representation learning has been verified in the AI domain [32,40]. In the AI community, many studies focus on learning disentangled representations from images or speech data. In recent years, representation learning with latent variable disentanglement has achieved great success for feature extraction in the time series community, such as in speech synthesis tasks [40,41], video generation tasks [42], temperature forecast tasks [43], and radio frequency extraction tasks [44]. In the radar community, the received pulse sequences are composed of intentionally designed variables and unintentionally introduced variables. The intentionally designed variables refer to variables that are related to radar working modes, inter-pulse modulation types, and modulation parameters. Unintentional variables refer to variables introduced in the transmitting-propagation-receiving process, such as measurement noise. Inspired by the disentangled representation technology that can effectively learn task-related features, these variables can be disentangled for effective representation of radar inter-pulse modulation characteristics, and latent variables within different datasets are invariant to different domain shifts. For instance, if there is a shift in the noise mean level in training and testing data, during feature extraction, by removing variables related to the noise, the extracted features are free of this shift. The performance degradation of a trained recognition model after a domain shift would be largely alleviated. Thus, it is important to investigate disentanglement methods for radar pulse sequences.
Auto-encoding variational Bayes-based deep learning models are reasonable model candidates for latent variable disentanglement in radar pulse sequences. The variational auto-encoder (VAE) is a typical auto-encoding variational Bayes model [45,46]. In the VAE, the encoder infers latent variables from input data, and the decoder uses the inferred variables to generate (reconstruct) the input data. The encoder and decoder are bridged by a maximum likelihood problem, and both encoder and decoder can be implemented with the deep neural networks [47,48].
This study considers the radar inter-pulse modulation recognition problem by proposing a disentangled representation learning method for radar pulse sequences. The proposed method can effectively and accurately extract pulse sequence features and alleviate recognition performance degradation in the presence of domain shifts. Firstly, three kinds of latent variables representing the radar modulation types, modulation parameters, and measurement characteristics in radar pulse sequences are introduced to illustrate the radar pulse sequence structure. Then, the latent variables corresponding to modulation types that guide the recognition process are modeled using probabilistic graphical models (PGMs). Finally, a double weight coefficient is designed in accordance with the first two kinds of latent variables to limit the information extracted by each variable based on the information theory. The contributions of this study can be summarized as follows:
- Based on the RLT, a promising paradigm is mathematically designed by decomposing a radar pulse sequence into three informative latent factors: modulation types, modulation parameters, and measurement characteristics (such as measurement noise). Further, the three informative factors can be disentangled through invariant latent variables.
- A novel disentangled representation learning method named Linking Structure to Task via Representation (LiSTaR) for robust radar inter-pulse modulation feature extraction and recognition is proposed. The performance degradation caused by domain shifts between the training and testing datasets is largely alleviated through the proposed method.
- The effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method compared with baseline methods are verified through experiments on both ideal and non-ideal situations.
The remainder of this study is organized as follows. The preliminaries are given in Section 2. Then, a problem formulation for radar inter-pulse modulation recognition and the corresponding disentanglement representation learning methods are presented in Section 3. Finally, verification experiments are described in Section 4, and Section 5 concludes the study.
2. Preliminary
2.1. Radar Inter-Pulse Modulation Principle
The radar inter-pulse modulation type reveals the transition rules and relationships among pulses in pulse sequences and can reflect the radar’s functional purpose and threats [12]. Recognizing the inter-pulse modulation type promotes the radar work mode and task recognition [10,11]. Typical inter-pulse modulation for PRI parameters can be divided into six types, as shown in Figure 1.
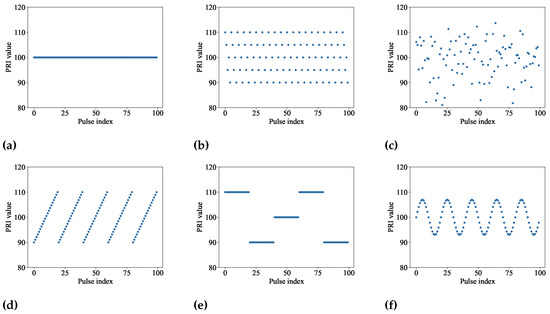
Figure 1.
Different inter-pulse modulation types for PRI. (a) Constant. (b) Stagger. (c) Jittered. (d) Sliding. (e) Dwell and switch. (f) Periodic.
Constant: The variation in PRI values is less than 1% of the whole PRI sequence’s mean value.
Stagger: A certain number of specific PRI values appear in cyclic order.
Jittered: The variation in PRI values reaches about 30% of the whole PRI sequence’s mean value.
Sliding: The continuous pulse values in the PRI sequences monotonically increase or decrease to the maximum or minimum value periodically.
Dwell and Switch (D&S): The pulse values stabilize at a specific value for a short duration, then switch to another value, and remain stable for a while.
Periodic: The pulses appear periodically in a sinusoidal or triangular mode.
2.2. PRI Sequence Structure
Radar PRI sequences are controlled to adopt specific inter-pulse modulation types to address various tasks such as search or tracking. For instance, the stagger modulation type and a set of modulation parameters, such as are adopted for a radar search task. It is critical to figure out the modulation types implicit in the PRI structure to support ES systems’ further decisions. Radar PRI sequences intercepted by an ES system are considered to mainly be composed of three key components [49]. Mathematically, a PRI sequence can be modeled as a three-tuple , wherein and are the variables related to modulation type and corresponding type space, respectively; and are the variables related to modulation parameter and corresponding parameter space, respectively; and represent the variables related to measurement characteristics and corresponding measurement characteristic space , respectively. For instance, a PRI sequence can be represented by if the PRI adopts the constant inter-pulse modulation (i.e., the modulation type M is constant) with a mean value of 100 (i.e., the modulation parameter R is 100), and the variables related to measurement noise (measurement characteristics) follow the Gaussian distribution with zero mean and a variance value of “1", wherein ∼ denotes the distributed according to.
To illustrate the modulation types, it is necessary to predefine the dynamic characteristics within them. Specifically, dynamic characteristics show the rules of transition dynamics between adjacent pulses [49], and the transition dynamics can be explicitly modeled through PGMs, such as the first-order Markov chain, high-order Markov chain, infinite-order Markov chain, and hidden Markov model [50]. In addition, probabilistic temporal neural networks can be used to model complex dynamic characteristics over long time horizons, with non-linear relationships. Then, pulse sequences with different modulation types can be distinguished through different dynamic characteristics. This study takes measurement noise as an example of measurement characteristics. Modulation parameters and measurement noise are the specific state values and corresponding noise given modulation types. Thus, the dynamic characteristics are unique for different inter-pulse modulations, and they are key explanatory invariant features within a specific modulation type for robust inter-pulse modulation recognition.
2.3. Auto-Encoder Architecture
An auto-encoder (AE) is a neural network architecture that has been widely applied to reconstruct input data by abstracting high-dimensional complex data to a low-dimensional spatial structure [51]. An AE model consists of an encoder that provides the low-dimensional latent representation (i.e., the features or latent variables) of the input data , followed by a decoder that tries to reconstruct the original data from learned features . Then, the reconstructed data are denoted as . The AE model aims to obtain an appropriate latent representation that considers both the latent space structure and reconstruction performance. This effective representation framework can extract key features hidden within data to guide tasks, including de-noise, classification, and recognition [33,35,40].
3. Methodology
In this section, we first introduce the overall LiSTaR method, which aims to disentangle the latent variable representations that contain modulation information to support the inter-pulse modulation recognition task. Next, a PRI sequence disentanglement process is described based on the VAE model. Finally, we present the optimization objective and the corresponding training methods in detail.
3.1. Overall Disentanglement Procedure
As shown in Figure 2, the proposed disentanglement method consists of three modules: the inter-pulse modulation recognition task module, the PRI sequence structure description module, and the PRI sequence representation module. The latter two modules provide support for the task module from different perspectives. Specifically, extracting robust and explanatory features from the PRI sequence is critical for guiding the radar inter-pulse modulation recognition task. From the aspect of the PRI sequence structure, the intercepted PRI sequences consist of measurement noise and ideal PRI sequences. Furthermore, considering that the modulation type contains vital information for recognition, we need to disentangle the modulation type and modulation parameter from the ideal PRI sequence to obtain the object modulation type information. In terms of the disentangled representation module, according to the above PRI structure, two explanatory variables that represent the modulation types and modulation parameters are learned through the VAE technology.
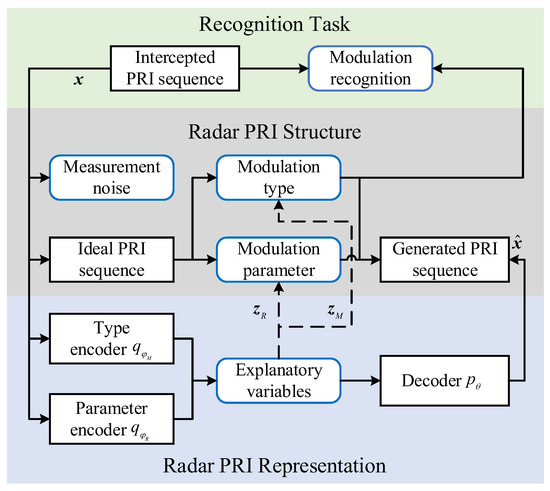
Figure 2.
The procedure of radar PRI sequence disentanglement through the LiSTaR method.
A good representation can effectively disentangle latent invariant variables from complex data. Specifically, disentangling latent variables from the latent space can effectively guide representation learning to separate informative factors from the complex input data and then achieve the recognition tasks based on the extracted informative features. As depicted on the level of the PRI sequence structure, PRI sequences can be represented by three kinds of variables related to modulation types, modulation parameters, and measurement noise, respectively. The modulation type variables are invariant in the presence of changes in variables related to modulation parameters and measurement noise. In terms of the target of disentanglement representation, we are concerned with disentangling variables related to modulation types from the PRI sequence, which is equal to extracting type features that are invariant from shifts for modulation parameters and measurement noise. As for the radar PRI sequence representation process, a type encoder and parameter encoder are jointly adopted to learn two different explanatory variables related to modulation types and parameters, respectively.
3.2. Feature Representation Learning
We consider a set of J intercepted PRI sequences , where denotes the jth PRI sequence with length L. We aim to build a model that disentangles a PRI sequence into two latent representations for two generative explanatory variables, i.e., the modulation type variable with size N and the modulation parameter variable with size H. Then, the relationship between the PRI sequence and its underlying latent variables is modeled with the VAE.
According to the VAE model structure and the composition of the latent variables considered within the PRI sequences, the distributions of the modulation type and modulation parameter representations are modeled using two encoders, which are, respectively, denoted as and , wherein and are trainable parameters of the corresponding encoder. Correspondingly, the decoder models the PRI sequences conditioned on learned latent modulation type variables and modulation parameter variables . The decoder is denoted as , wherein is a set of parameters to be trained in the decoder. The parameters , and are jointly estimated during the training process.
In order to encourage the latent variables and to capture the key PRI generation information through the disentanglement procedure, we need to define the prior distribution of latent variables to control the bottleneck of the captured latent information. The VAE model parameterized the probabilistic latent variables with a multi-layer perception, which greatly improves the representation ability of the latent variables. Specifically, the features within the input data (i.e., the intercepted PRI sequence in this study) are represented by Gaussian random variables that are parametrized by their mean and variance. We define the prior distributions of and as multivariate Gaussian distributions such that , and . In summary, the set explanatory factor priors and the designed encoders and jointly create a disentanglement network.
3.3. Optimization Principle
From the perspective of reconnaissance, the disentanglement representation method is expected to disentangle the generative latent variables that can generate the input data. Thus, the problem’s objective is to maximize the marginal likelihood of the intercepted PRI sequences over the distribution of latent variables and as follows:
For the given intercepted PRI sequence , the disentanglement representation process aims to capture the generative latent variables through the learned posterior distributions and . In addition, in order to control the capacity of captured information bottleneck and embody the expectation of statistical independence for different generative variables [47], we introduce two constraints for matching the learned latent variables to corresponding priors and . The formula for adding constraints to the original generative objective is given by:
wherein and are constraint strengths that constrain the similarity of the encoded type and parameter latent variable distributions to their prior distributions, respectively. In addition, the Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence in the constraints encourages the latent variables to tend to be independent. According to Karush–Kuhn–Tucker (KKT) conditions [52,53], the above formula can be rewritten as Lagrangian. The Lagrangian reformulation of the original disentanglement representation problem is derived as follows:
wherein and are Lagrange multipliers for controlling the captured information through the latent variables and , respectively. We suppose that and . The above formula in (3) is also the final loss of the disentanglement representation problem. Since the , , and are all non-negative, the above Lagrangian reformulation can be rewritten into a form similar to the -VAE formulation [47] as follows:
Note, that the evidence lower bound (ELBO) for the designed disentanglement method is given by in (4), which consists of a reconstruction term and two regularization terms. To further analyze the regularization terms that control the trade-off between reconstruction quality and the disentanglement representation performance, we break down the regularization terms into two parts, and we take the type regularization term as an example:
wherein is the data distribution of , is the mutual information (MI) between and the latent type variable under , and the joint distribution is typically approximated to [47]. The larger the MI value , the stronger the mutual dependence between and . The KL term pushes the learned distribution toward the prior distribution . Similarly, the decomposition of the parameter regularization term is given by:
The MI shows the information captured by latent variables from the input data. Then, coefficients and of the regularization terms in (3) act as the gates for controlling the information of going through and . Thus, properly selecting and is equal to constraining the features extracted by latent variables and affecting the degree of disentangled representation. On the one hand, the absolute values of coefficients and can jointly control the information bottleneck. On the other hand, the type variable and parameter variable are desired to capture information at different granularities in the PRI sequences through the proposed disentanglement representation method. From the aspect of the latent variables inference in LiSTaR, each feature is expected to be represented by a latent variable. Thus, in addition to the absolute values of latent variable coefficients and , the relative values between the two coefficients deserve attention.
3.4. Model Structure
The encoders and and the decoder are parameterized using neural networks for their non-Markovian and non-linear dependency representation ability. The network structures in LiSTaR are shown in Figure 3. The encoder backbones are composed of three linear layers with 512, 64, and 32 hidden units each, and the rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation function is used. Similarly, the decoder is equipped with a structure that is symmetrical to that of the encoder, that is, the decoder is composed of three linear layers with 32, 64, and 512 hidden units each, and the ReLU activation function is used. In addition, the variables related to the modulation type and modulation parameters are the same size.
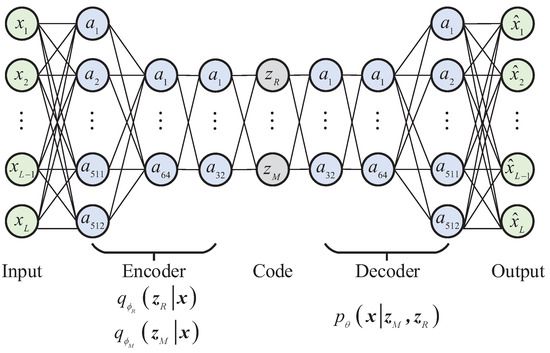
Figure 3.
Network structure in LiSTaR.
4. Experiments
The experimental setup, including the data description, baseline methods, evaluation metrics, and implementation details, is described in Section 4.1. The disentangled results for ideal and non-ideal experiments are shown in Section 4.2 and Section 4.3, respectively. Section 4.4 provides the time complexity and real-time performance analysis.
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Data Description
PRI sequences are used for disentanglement representation [12]. We perform experiments on both the ideal and non-ideal situations for the comprehensive validation of our method. In both situations, five typical PRI modulation types were adopted: periodic, constant, sliding, D&S, and stagger [9].
The learned latent features within pulse sequences are desired to maintain robustness when a data domain shift occurs. Thus, the training datasets and testing datasets were set to show differences from the perspective of modulation parameter scenarios. We define one training dataset and three testing datasets with different modulation parameter values as scenarios for the evaluation of the robustness of the methods, as shown in Table 1. It is expected that the method with good robustness will not suffer significant performance degradation when trained and tested separately on different datasets (scenarios) with domain shifts.

Table 1.
Settings for the training and testing datasets.
In addition, there is usually more than one variable modulation parameter within a specific modulation type. For instance, the mean PRI values and deviation of the average PRI of the periodic modulation type can be distributed in different value ranges. Details of various radar modulation parameter definitions can be found by referring to [9]. In this study, two kinds of modulation parameter shifts, namely, shifts in the PRI value (such as mean PRI values, candidate PRI values, and initial PRI values) and the other specific PRI differential shifts toward certain modulation types (such as the deviation of the average PRI in periodic modulation, and the max-min ratio in sliding modulation) were considered. The specific datasets that reflect the domain shifts are shown in Table 1; scenario 1 and scenario 2 involve PRI value shifts and other specific PRI differential shifts relative to the corresponding training datasets, respectively, and scenario 3 combines the shifts in scenario 1 and scenario 2.
4.1.2. Baseline Methods and Evaluation Metrics
We compare the proposed LiSTaR method with three generative feature extraction methods:
AE: This method learns the latent variables through feature extraction and dimension reduction technologies [51].
VAE: This method combines the AE model and the approximate posterior inference model to represent the latent variables, and it uses a variational Bayesian (VB) approach to solve the posterior approximation problem [45].
Long short-term memory auto-encoder (LSTMAE): An LSTM-based auto-encoder framework that considers the underlying features and the temporal data correlations for automatic anomaly detection in time series data was developed [54].
The performance of the proposed method and baseline methods was evaluated with three metrics: the t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (T−SNE) visualization [55], radar inter-pulse modulation recognition performance, and the feature distinction performance. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) can be used to bridge the extracted features to recognition results, and the modulation recognition accuracy is given by:
wherein is the sample numbers of the mth modulation type, and is the indicator function that quantifies the match situation between the estimated data label and the corresponding true data label ; it is given by:
To evaluate the performance of the extracted feature discrimination, the Davies–Bouldin index (DBI) [56] was utilized. The DBI metric measures both the intra-cluster variance and the distance among clusters. Unlike the classical DBI, we replace the cluster labels with known true labels to demonstrate the distinction degree for the feature extraction, that is, the smaller the DBI value, the better the feature extraction performance. The DBI metric is defined as follows:
where and represent the mean values of the extracted features for the ith and jth modulation types, respectively. is the distance between two elements and . and are the average distance between the extracted ith and jth modulation feature’s centers and all of their elements, respectively. Taking as an example, it is defined as follows:
4.1.3. Implementation Details
There were 60 pulses in one PRI sequence sample for all five modulation types, i.e., . For the LiSTaR method, the learning rate in the Adam optimizer was set to 1 × 10−3. Coefficients and for and are set as 1 × 10−1 and 1 × 10−9, respectively. The sizes of type-related variables and parameter-related variables were both set to 5, i.e., and . The batch size was 256.
4.2. Experimental Results in Ideal Situations
We first tested the proposed LiSTaR method and comparison methods in an ideal situation from two aspects: qualitative evaluation and quantitative evaluation. We simulated training samples and 5000 for testing samples for all modulation types. In the training datasets, samples were used for qualitative evaluation, and samples were used for quantitative evaluation.
4.2.1. Qualitative Evaluation
Firstly, we visualized the feature extraction performance for all methods from the qualitative perspective. Specifically, we selected some PRI values for all modulation types from the interval [100, 300] and fixed the other specific PRI differential shifts to test the representation results. Figure 4 shows that compared to other methods, the LiSTaR was able to effectively represent the explanatory underlying features that were able to discriminate different radar modulation types when facing the PRI modulation parameter shifts. However, none of the other three comparison methods was able to learn the explanatory feature information that distinguishes different radar modulation types.
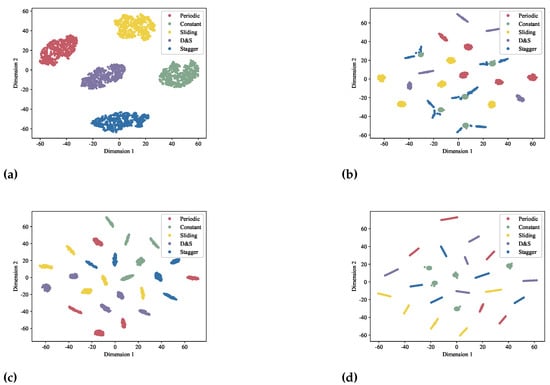
Figure 4.
T-SNE visualization of learned representations for four methods. (a) LiSTaR. (b) AE. (c) VAE. (d) LSTMAE.
4.2.2. Quantitative Evaluation
Then, we quantitatively analyze the performance of all methods. When a domain shift occurs between a training dataset and a testing dataset, a robust model with smaller accuracy degradation is expected. Table 2 illustrates the accuracy in the three testing scenarios for all four methods. The results in Table 2 show that the LiSTaR method was more robust to domain shifts in the modulation parameter than the other methods, especially for PRI value shifts (scenario 1). The LiSTaR method showed significantly better performance with an accuracy exceeding 90%, while other methods lost performance by up to about 10%–70% compared with LiSTaR. However, all methods presented relatively greater accuracy degradation when facing the other specific PRI differential shifts and the combined scenario in comparison with their performance in the PRI value shift scenario. LiSTaR achieved better performance and maintained an accuracy of over 74%. Note, that the accuracy for the VAE was about 15% higher than that for the AE in scenario 1, but there was a relatively small difference between them in scenario 2 and scenario 3. Also, the results showed that the LSTMAE method was not suitable for the task of PRI disentangled representation. In addition, DBI values presented that the LiSTaR method was able to extract more informative and effective underlying features than the other methods in all domain shift scenarios.

Table 2.
Radar PRI modulation recognition and representation performance under ideal situation for four methods.
The confusion matrices of the four methods for all scenarios in Table 1 are shown in Figure 5. The LiSTaR method was able to maintain robust recognition performance for most modulation types when facing the PRI value shifts. However, the other methods have recognition difficulties in one or more kinds of modulation types. All methods suffered from recognition confusion when specific PRI differential shifts happened, the proposed method is about 10% better than the other methods.
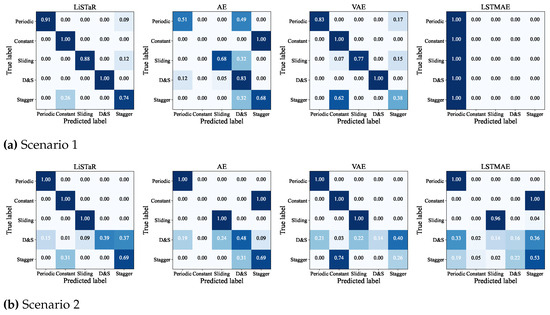
Figure 5.
Confusion matrix of the recognition performance for four methods in three different data domain shift scenarios.
4.3. Experimental Results in Non-Ideal Situations
To further explore the effectiveness and robustness of all methods, we considered four typical non-ideal conditions: measurement noise, missing pulse, spurious pulse, and hybrid scene. Specifically, the measurement noise level values were represented by a Gaussian white noise distribution with a standard deviation, and we selected five noise levels at equal intervals from 0.5 to 2.5. Then, due to the PRI sequences being the first-order differences of radar time of arrival (TOA) sequences, missing pulses and spurious pulses would affect the first-order difference values. Missing pulses will lead to a large PRI value that combines the current and previous PRI values. Inversely, spurious pulses would produce two adjacent small PRI values by splitting the current PRI into two parts [49]. To alleviate the impact of outliers generated by non-ideal situations on the verification of the method, we detect outliers and substitute them with medians [57]. The missing pulse ratios and spurious pulse ratios were both set from 3% to 15% with five equally spaced levels. The missing pulse ratios and spurious pulse ratios were both set from 1.5% to 7.5% with five equally spaced levels in the hybrid non-ideal situations, and the noise level within the hybrid non-ideal situations was set to 0.5. For each non-ideal condition, we simulated testing datasets that covered five modulation types. To provide comprehensive non-ideal experimental results, all data shift scenarios in Table 1 were evaluated under four non-ideal conditions.
The radar inter-pulse modulation recognition results under different types and degrees of non-ideal conditions are shown in Figure 6. From the aspect of the effects of all non-ideal conditions, firstly, we noted that all methods were able to effectively cope with the measurement noise issues, which demonstrated the advantages of generative models against noise. The recognition accuracy of the LiSTaR method was better than the other methods in general, and there were small performance fluctuations across different scenarios for all methods. Then, all methods were more robust to missing pulses that produced large PRI values than they were to spurious pulses that resulted in small pulse values overall. In addition, the accuracy under spurious conditions dropped faster than that under missing conditions. A reasonable explanation for these results is that for the same non-ideal ratio, a spurious pulse produces twice as many abnormal PRI values as a missing pulse. As we expected, the performance of all methods in hybrid scenes generally fell between missing pulses and spurious pulses due to the balanced hybrid. Also, the recognition accuracy of the LiSTaR method was higher than that of the other methods in most conditions, especially under weak non-ideal conditions.
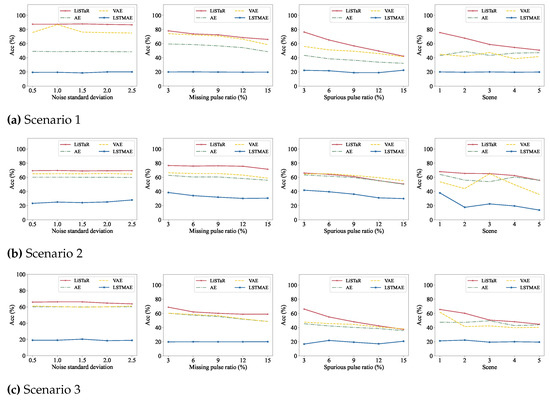
Figure 6.
Radar PRI modulation recognition performance in non-ideal situations for four methods.
In terms of different data shift scenarios, as in the ideal situation, the LiSTaR and VAE methods performed better in scenario 1 and scenario 2 than in scenario 3. The AE and LSTMAE methods tended to be more robust to scenarios 2 & 3 and to scenarios 3, respectively. As the degree of non-idealness increases, there were no significant differences in performance degradation in the three scenarios. In summary, the proposed LiSTaR method was more able to cope with some degree of non-ideal situations than comparative methods.
4.4. Time Complexity and Real-Time Performance Analysis
The time complexity and real-time performance of adopting deep neural networks-based methods to address the radar inter-pulse modulation recognition problems need to be paid attention to. The backbones of LiSTaR, AE, and VAE methods are fully connected neural networks and L denotes the number of network layers for the above methods. The time complexity of each fully connected neural network layer is , where and are the hidden units for layer and the corresponding previous layer , respectively. For the LSTMAE method, the time complexity of each LSTM layer is , where T is the pulse sequence length and d is the representation dimension. The specific time complexity for the proposed and baseline methods is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Time complexity and real-time performance for four methods.
Furthermore, Table 3 describes the testing time of four methods for 5000 testing sample data averaged on 100 times Monte-Carlo test. The execution environment is Intel Core i9-10850K CPU and NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 GPU. The results show that there were no obvious differences among LiSTaR, AE, and VAE methods in terms of time complexity and real-time performance due to the similar backbones. Compared with the other two methods, the proposed LiSTaR method achieved robust feature extraction through the disentangling representation network that introduces a small amount of time complexity. The LSTMAE method does not have advantages due to its high complexity and long testing time. Such a conclusion verified that the proposed method is suitable for practical applications and has the potential to handle high-density pulse streams.
5. Conclusions
This study considered the disentanglement of different latent variables from intercepted pulse sequences for robust radar inter-pulse modulation recognition. Firstly, we illustrated the radar inter-pulse modulation structure, followed by an introduction to the designed LiSTaR method, which effectively codes the latent variables with two informative encoders. Then, the latent variable inference process was derived to constrain the grains of the captured information. Finally, verification experiments showed the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed method in comparison with other methods.
Future works could investigate robust recognition in electronic support applications. For instance, in terms of method expansion, other latent variables related to more explanatory features can be added for other recognition tasks. From the aspect of applications, this disentangled representation method can also be used for radar waveform recognition or RF fingerprint recognition tasks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z.; Methodology, L.Z.; Software, L.Z.; Validation, L.Z.; Data curation, L.Z.; Writing—original draft, L.Z.; Writing—review & editing, M.Z. and Y.L.; Visualization, L.Z. and Z.Z.; Supervision, Y.L.; Funding acquisition, M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under grant number 62301031.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Haykin, S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2006, 23, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, S.Z.; Griffiths, H.D.; Charlish, A.; Rangaswamy, M.; Greco, M.S.; Bell, K. An Overview of Cognitive Radar: Past, Present, and Future. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2019, 34, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlish, A.; Hoffmann, F.; Degen, C.; Schlangen, I. The Development From Adaptive to Cognitive Radar Resource Management. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2020, 35, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaratnam, I.; Haykin, S.; Kirubarajan, T.; Dilkes, F. Tracking the Mode of Operation of Multi-Function Radars. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, IEEE, Verona, NY, USA, 24–27 April 2006; pp. 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Visnevski, N.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Haykin, S.; Currie, B.; Dilkes, F.; Lavoie, P. Multi-function radar emitter modelling: A stochastic discrete event system approach. In Proceedings of the 42nd IEEE International Conference on Decision and Control, Maui, HI, USA, 9–12 December 2003; Volume 6, pp. 6295–6300. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, C.E.; Buehrer, R.M.; Dhillon, H.S.; Martone, A.F. Universal Learning Waveform Selection Strategies for Adaptive Target Tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 5798–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, E.; Buehrer, R.M.; Martone, A.; Sherbondy, K. Reinforcement Learning for Adaptable Bandwidth Tracking Radars. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 3904–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S.; Xue, Y.; Setoodeh, P. Cognitive Radar: Step Toward Bridging the Gap Between Neuroscience and Engineering. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 3102–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, J.P.; Martikainen, K.; Ruotsalainen, U. Hierarchical classification of dynamically varying radar pulse repetition interval modulation patterns. Neural Netw. 2010, 23, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zhong, P.; Cai, X.; Bi, D.; Jing, A. Robust Bayesian attention belief network for radar work mode recognition. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 133, 103874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. A novel segmentation approach for work mode boundary detection in MFR pulse sequence. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 126, 103462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Model-Based Representation and Deinterleaving of Mixed Radar Pulse Sequences with Neural Machine Translation Network. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 1733–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, J. Specific emitter identification. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Radar Symposium (IRS), Wroclaw, Poland, 21–23 May 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; He, X.; Cai, X.; Bi, D. Balanced Neural Architecture Search and Its Application in Specific Emitter Identification. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 5051–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordanov, I.; Petrov, N.; Petrozziello, A. Supervised radar signal classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 1464–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z. Attention-Based Radar PRI Modulation Recognition with Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 57426–57436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J. Work modes recognition and boundary identification of MFR pulse sequences with a hierarchical seq2seq LSTM. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Qu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Liang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. Self-Attention Bi-LSTM Networks for Radar Signal Modulation Recognition. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 5160–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jin, W.; Hu, L. Radar emitter signal recognition based on support vector machines. In Proceedings of the ICARCV 2004 8th Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision Conference, Kunming, China, 6–9 December 2004; Volume 2, pp. 826–831. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, X.; Ono, Y.; Peng, L.; Xu, Y. Unsupervised Learning Discriminative MIG Detectors in Nonhomogeneous Clutter. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4107–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Yu, P.S. Classification, Denoising, and Deinterleaving of Pulse Streams with Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 1624–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, T. Toward Convolutional Neural Networks on Pulse Repetition Interval Modulation Recognition. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 2286–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, F.; Guo, X.; Zhou, F. Shipborne Multi-Function Radar Working Mode Recognition Based on DP-ATCN. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; De Maio, A.; Piezzo, M.; Farina, A.; Wicks, M. Cognitive design of the transmitted phase code and receive filter in reverberating environment. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Waveform Diversity & Design Conference (WDD), Kauai, HI, USA, 22–27 January 2012; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Tuck, J.; Stoica, P. Polyphase Waveform Design for MIMO Radar Space Time Adaptive Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, P.; Babu, P.; Stoica, P. Low-PAPR OFDM Waveform Design for Radar and Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Radar Syst. 2023, 1, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; De Maio, A.; Piezzo, M.; Naghsh, M.M.; Soltanalian, M.; Stoica, P. Cognitive radar waveform design for spectral coexistence in signal-dependent interference. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2014; pp. 0474–0478. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Stoica, P. Information-theoretic waveform design for MIMO radar detection in range-spread clutter. Signal Process. 2021, 182, 107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Aubry, A.; De Maio, A.; Yu, X.; Cui, G.; Iommelli, S. Constant Modulus Discrete Phase Radar Waveforms Design Subject to Multi-Spectral Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace, Pisa, Italy, 22–24 June 2020; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, I.; Amos, D.; Pfau, D.; Racaniere, S.; Matthey, L.; Rezende, D.; Lerchner, A. Towards a Definition of Disentangled Representations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.02230. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z.; Shen, X.; Hao, J.; Wang, J. CausalVAE: Disentangled Representation Learning via Neural Structural Causal Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9593–9602. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, G.; Liu, C.; Sahoo, D.; Kumar, A.; Hoi, S. CoST: Contrastive Learning of Disentangled Seasonal-Trend Representations for Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.01575. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchacourt, D.; Tomioka, R.; Nowozin, S. Multi-Level Variational Autoencoder: Learning Disentangled Representations From Grouped Observations. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zha, D.; Du, M.; Ni, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H.; Hu, X. Towards Learning Disentangled Representations for Time Series. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 August 2022; pp. 3270–3278. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Trajcevski, G.; Zhong, T.; Zhou, F. Learning Latent Seasonal-Trend Representations for Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 35, pp. 38775–38787. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Huang, T.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, D. Radar Signal Intrapulse Modulation Recognition Based on a Denoising-Guided Disentangled Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Gan, F.; Cao, X.; Liu, W.; Li, P. Radar Intra–Pulse Signal Modulation Classification with Contrastive Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H. Time–Frequency Feature Enhancement of Moving Target Based on Adaptive Short-Time Sparse Representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.N.; Zhang, Y.; Weiss, R.J.; Chung, Y.A.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Glass, J. Disentangling Correlated Speaker and Noise for Speech Synthesis via Data Augmentation and Adversarial Factorization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 5901–5905. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Ni, J.; Lai, C.I.; Cox, D.; Hasegawa-Johnson, M.; Chang, S. ContentVec: An Improved Self-Supervised Speech Representation by Disentangling Speakers. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; pp. 18003–18017. [Google Scholar]
- Vowels, M.J.; Camgoz, N.C.; Bowden, R. VDSM: Unsupervised Video Disentanglement with State-Space Modeling and Deep Mixtures of Experts. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8176–8186. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Jianxing, Z. Feature disentanglement learning model for ocean temperature field forecast. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 117, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Hu, A.; Ng, D.W.K.; Swindlehurst, A.L. Disentangled Representation Learning for RF Fingerprint Extraction Under Unknown Channel Statistics. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 3946–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Girin, L.; Leglaive, S.; Bie, X.; Diard, J.; Hueber, T.; Alameda-Pineda, X. Dynamical Variational Autoencoders: A Comprehensive Review. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2021, 15, 1–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, I.; Matthey, L.; Pal, A.; Burgess, C.; Glorot, X.; Botvinick, M.; Mohamed, S.; Lerchner, A. beta-VAE: Learning Basic Visual Concepts with a Constrained Variational Framework. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Mnih, A. Disentangling by Factorising. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2649–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, S. Bayesian Nonparametric Hidden Markov Model for Agile Radar Pulse Sequences Streaming Analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2024, 71, 3968–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.M. Stochastic Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, H.W.; Tucker, A.W. Nonlinear programming. In 2nd Berkeley Symposium; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1951; pp. 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Karush, W. Minima of Functions of Several Variables with Inequalities as Side Constraints. Master’s Thesis, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA, 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Provotar, O.I.; Linder, Y.M.; Veres, M.M. Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in Time Series Using LSTM-Based Autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Trends in Information Theory (ATIT), Kyiv, Ukraine, 18–20 December 2019; pp. 513–517. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing Data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, D.L.; Bouldin, D.W. A Cluster Separation Measure. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1979, PAMI-1, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revillon, G.; Mohammad-Djafari, A.; Enderli, C. Radar emitters classification and clustering with a scale mixture of normal distributions. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 13, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).