Assessment of Multiple Planetary Boundary Layer Height Retrieval Methods and Their Impact on PM2.5 and Its Chemical Compositions throughout a Year in Nanjing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Methods
2.1. Observation Site and Field Campaign
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Retrieving the PBLH Using the MPL
2.4. Retrieving the PBLH Using the MWR
3. Results and Analysis
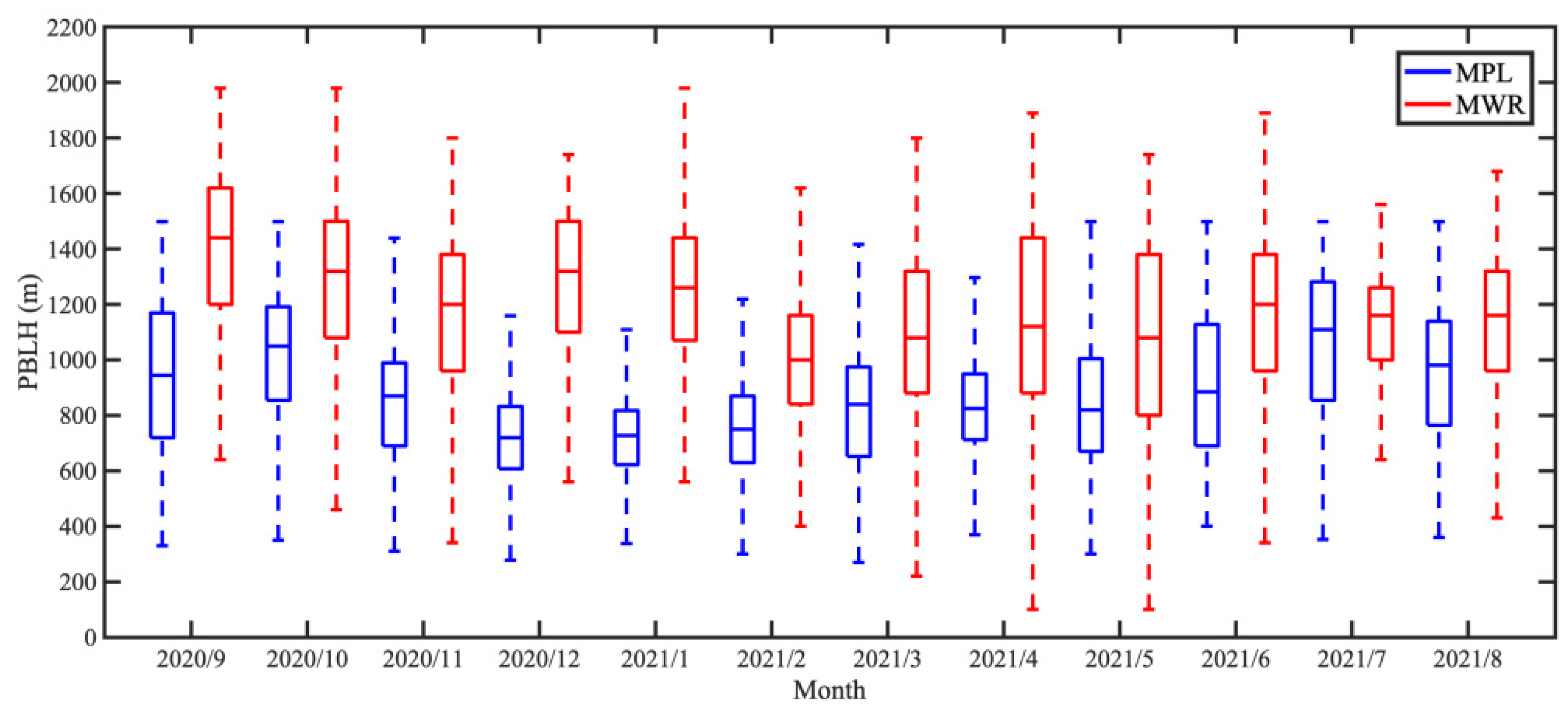
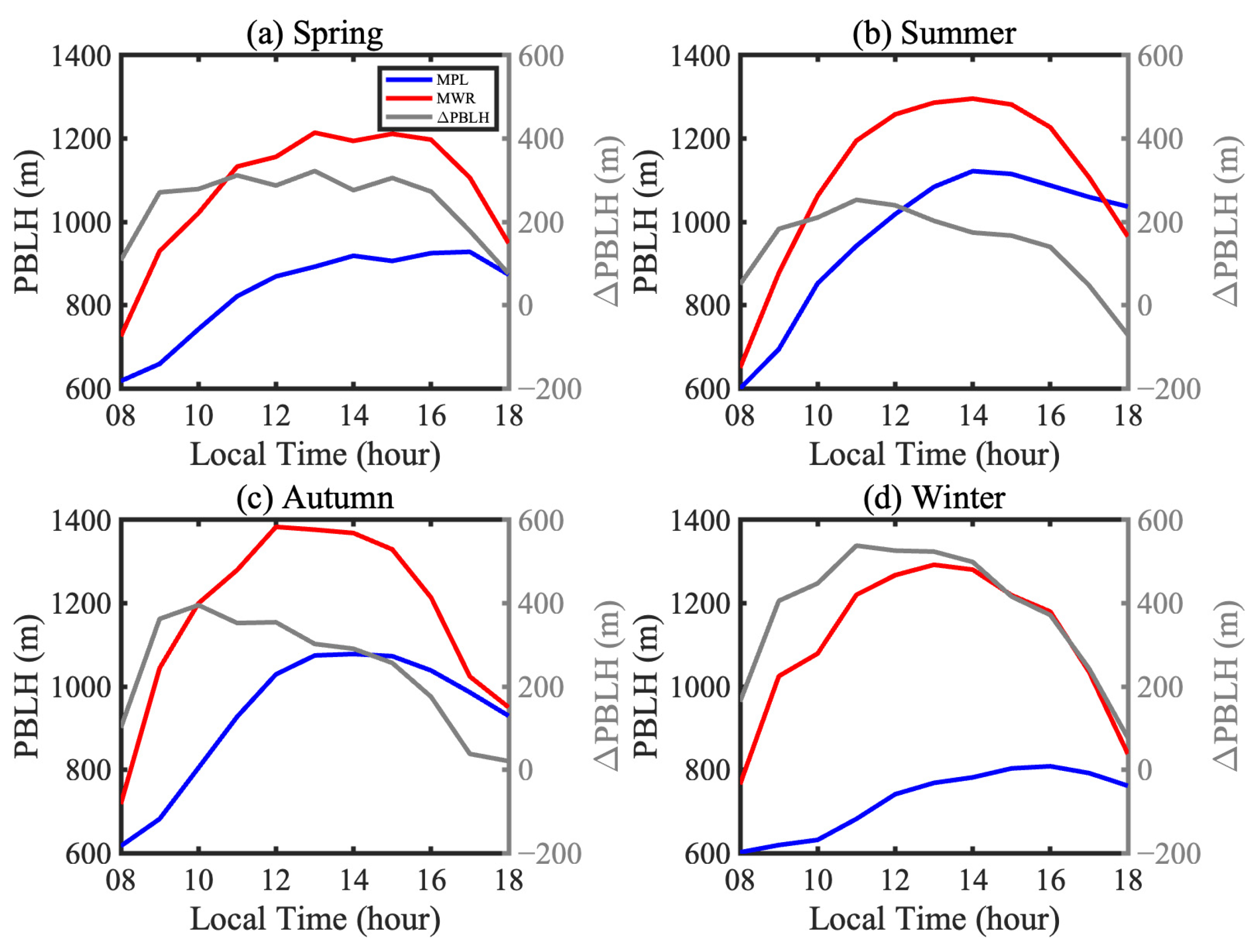
3.1. Comparison of PBLHs Retrieved by Different Instruments and Methods
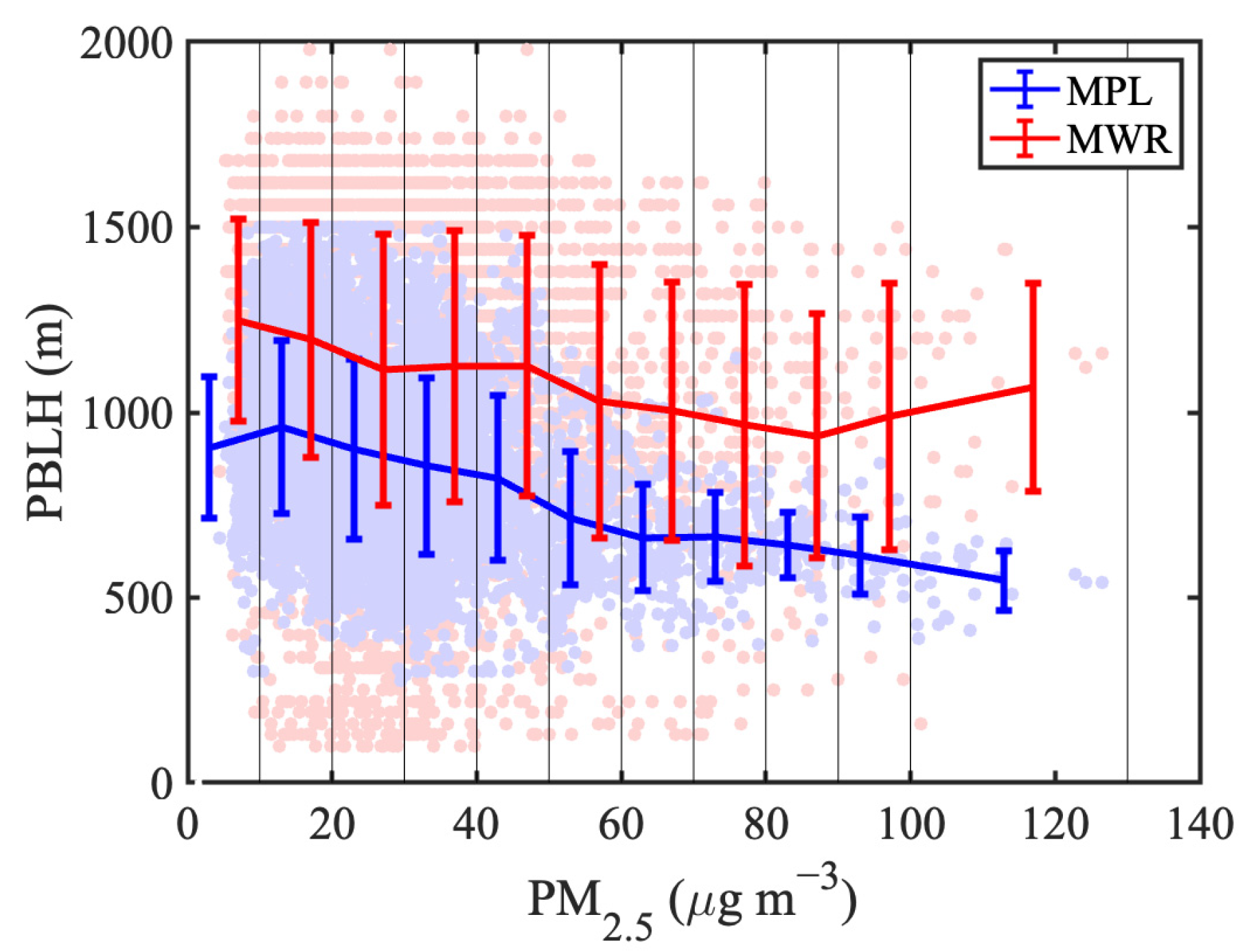
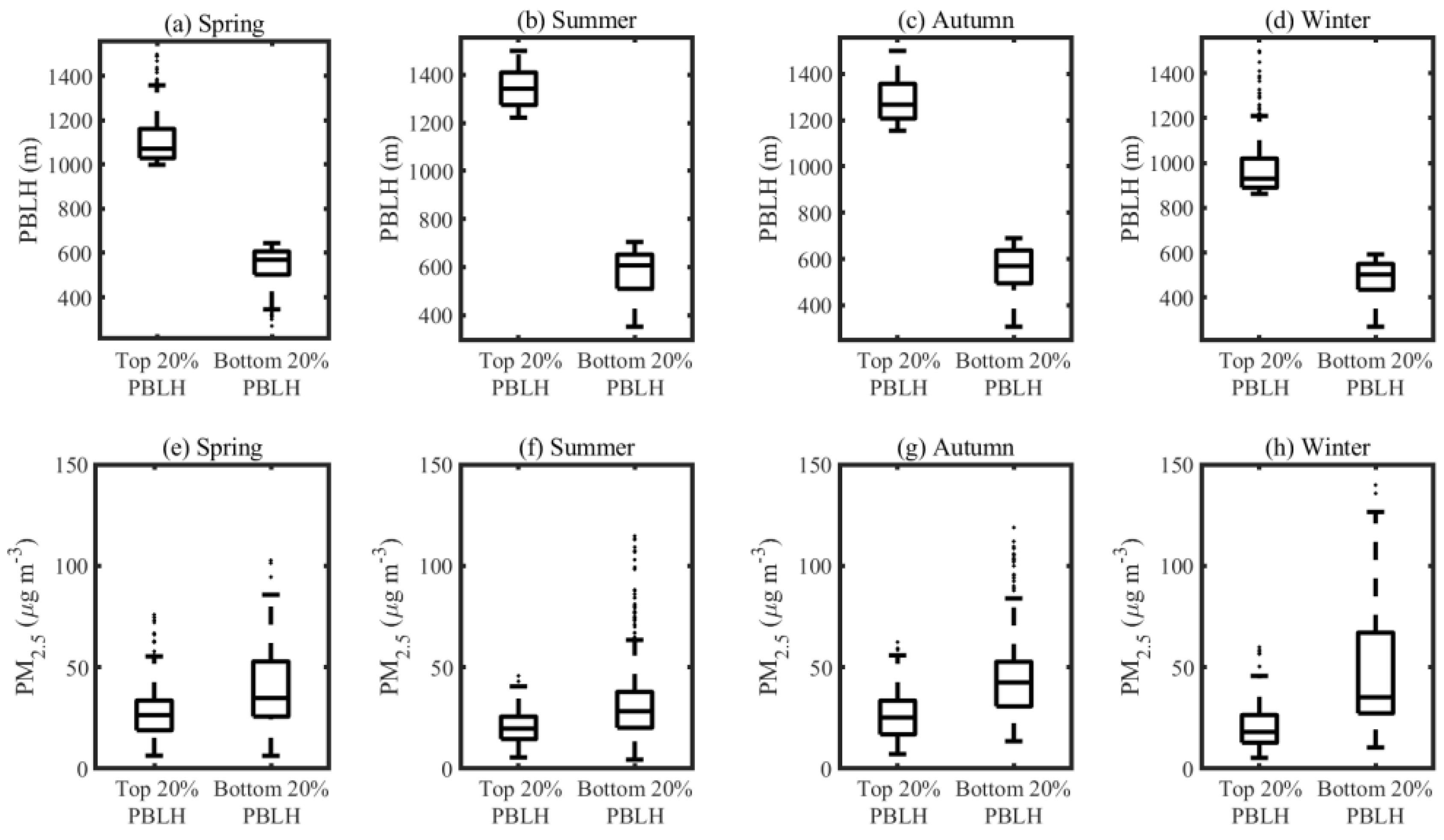
3.2. Relationships between the PBLH and PM2.5
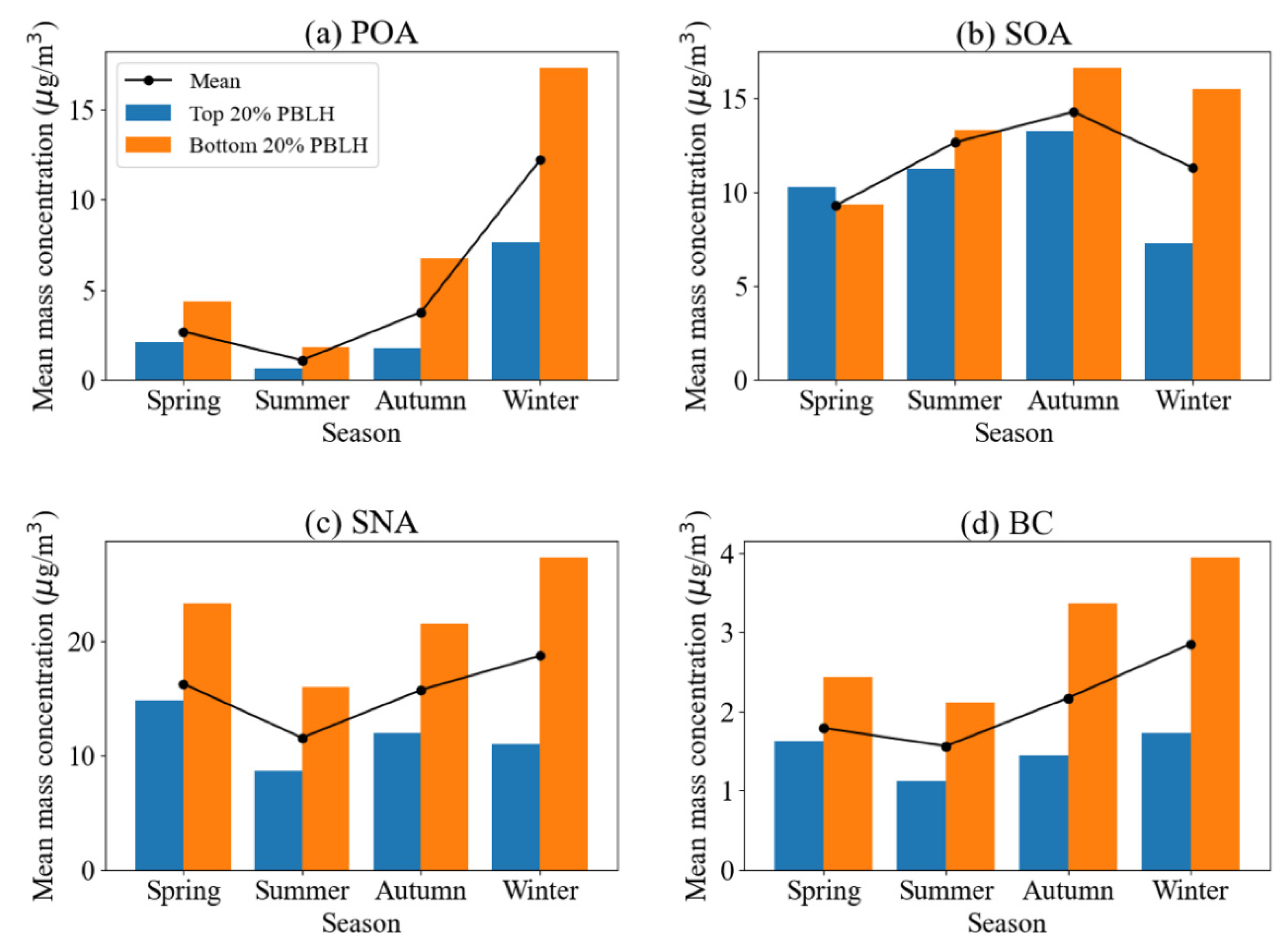
3.3. Impact of the PBLH on PM2.5 Chemical Components
4. Summary
- (1)
- This study compares the long-term PBLH retrieval results between a micro-pulse lidar (MPL) and a microwave radiometer (MWR), encompassing seasonal and daily variations, highlighting notable PBLH differences retrieved by these two instruments. The MPL consistently provides more consistent and reliable PBLH measurements compared to the MWR.
- (2)
- The relationships between the two different PBLH retrievals and PM2.5 are explored and compared. Surprisingly, the PBLH derived from the MWR does not exhibit the same negative correlation with PM2.5 as observed with the MPL, particularly in cases of severe pollution.
- (3)
- This research delves into the effects of the PBLH on different PM2.5 chemical components, observing substantial variations depending on the season and the specific component. Notably, the study finds that the PBLH has the most pronounced impact on primary aerosols, with its effect being most prominent during winter. Conversely, the PBLH appears to have a relatively minimal impact on secondary aerosols, especially secondary organic aerosols during spring.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived fromradiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, J.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L. Classification and estimation of unfavourable boundary-layer meteorological conditions in Beijing for PM2.5 concentration changes using vertical meteorological profiles. Atmos. Res. 2023, 293, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Chen, W.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, C. Exploration of the downward transport mechanisms of biomass burning emissions from Indochina at the low boundary layer in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 314, 120117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilitinkevich, S.S.; Tyuryakov, S.A.; Troitskaya, Y.I.; Mareev, E.A. Theoretical models of the height of the atmospheric boundary layer and turbulent entrainment at its upper boundary. Izvestiya. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2012, 48, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Sarawade, P.; Adhikary, B. Transport of black carbon from planetary boundary layer to free troposphere during the summer monsoon over South Asia. Atmos. Res. 2020, 235, 104761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yu, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, P.; Lin, H.; Shui, L.; Tang, M.; et al. Residential greenness, air pollution and incident neurodegenerative disease: A cohort study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siming, Y.; Lingli, X.; Peng, D.; Zhaohui, Q.; Qianqian, Z.; Tuanjie, Z. The impact of air pollution on corporate environmental information disclosure–Evidence from heavy pollution industries in China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 59, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, Cloud Microphysics, and Fractional Cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. Pollution and the Planetary Albedo. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Jung, Y.; Lee, Y.G. Spectral dependence on the correction factor of erythemal UV for cloud, aerosol, total ozone, and surface properties: A modeling study. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Lu, K.; Song, H.; Mu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. A critical review of sulfate aerosol formation mechanisms during winter polluted periods. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Kim, S. Estimating the transboundary budget of sulfate aerosols in Northeast Asia with NASA MERRA aerosol reanalysis data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Deng, J.; Xie, M. Investigations on direct and indirect effect of nitrate on temperature and precipitation in China using a regional climate chemistry modeling system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D00K19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Natesan, S. Richardson extrapolation technique for singularly perturbed system of parabolic partial differential equations with exponential boundary layers. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 333, 254–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T. Experimental investigation of particle dynamics in particle-laden turbulent boundary layer. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 263, 108757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; Heald, R.C.; Lenschow, D.H.; Stankov, B.B.; Troen, I.B. An observational study of the structure of the nocturnal boundary layer. Bound. -Layer Meteor. 1979, 17, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Cai, X.; Fan, S.; Song, Y.; Hu, F.; Che, H.; Quan, J.; Kang, L.; et al. Research Progress on Estimation of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xin, J.; Gong, C.; Quan, J.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, T. The formation mechanism of air pollution episodes in Beijing city: Insights into the measured feedback between aerosol radiative forcing and the atmospheric boundary layer stability. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam, M.V.; Santhi, Y.D.; Rajeevan, M.; Rao, S.V.B. Diurnal variability of stability indices observed using radiosonde observations over a tropical station: Comparison with microwave radiometer measurements. Atmos. Res. 2013, 124, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temimi, M.; Fonseca, R.M.; Nelli, N.R.; Valappil, V.K.; Weston, M.J.; Thota, M.S.; Wehbe, Y.; Yousef, L. On the analysis of ground-based microwave radiometer data during fog conditions. Atmos. Res. 2020, 231, 104652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhao, D.; Jia, D.; Tang, G.; Quan, J.; Wang, M.; Dai, L. Analysis of differences between thermodynamic and material boundary layer structure: Comparison of detection by ceilometer and microwave radiometer. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, G.D.A.; Oliveira, A.P.D.; Sánchez, M.P.; Codato, G.; Lopes, F.J.D.S.; Landulfo, E.; Filho, E.P.M. Performance assessment of aerosol-lidar remote sensing skills to retrieve the time evolution of the urban boundary layer height in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo City, Brazil. Atmos. Res. 2022, 277, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.T.; Simpas, J.B.; Sorooshian, A.; Betito, G.; Cambaliza, M.O.L.; Collado, J.T.; Eloranta, E.W.; Holz, R.; Topacio, X.G.V.; Del Socorro, J.; et al. Impacts of regional wind circulations on aerosol pollution and planetary boundary layer structure in Metro Manila, Philippines. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 293, 119455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Xia, X.; Ren, G.; An, D.; Ayikan, M.; Zhong, Y. Characteristics of atmospheric boundary layer and its relation with PM2.5 during winter in Shihezi, an Oasis city in Northwest China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xin, Y. Impact of thermal structure of planetary boundary layer on aerosol pollution over urban regions in Northeast China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Li, Z.; Wong, M.S.; Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, W.M.; Zhao, F. Aerosol single scattering albedo estimated across China from a combination of ground and satellite measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Y. Assessment of carbonaceous aerosols in suburban Nanjing under air pollution control measures: Insights from long-term measurements. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, B.; Ren, R.; An, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. The Impacts of Dust Storms with Different Transport Pathways on Aerosol Chemical Compositions and Optical Hygroscopicity of Fine Particles in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2023JD039679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Croteau, P.; Williams, L.; Canagaratna, M.; Onasch, T.; Cross, E.; Zhang, X.; Robinson, W.; Worsnop, D.; Jayne, J. Laboratory characterization of an aerosol chemical speciation monitor with PM2.5 measurement capability. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Yan, P.; Cribb, M.; Li, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wu, H.; Wu, T.; et al. Enhancement of secondary aerosol formation by reduced anthropogenic emissions during Spring Festival 2019 and enlightenment for regional PM2.5 control in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Farley, R.N.; Li, L.; Srivastava, D.; Niedek, C.R.; Li, J.; Wang, N.; Cappa, C.D.; Pusede, S.E.; Yu, Z.; et al. PM2.5 composition and sources in the San Joaquin Valley of California: A long-term study using ToF-ACSM with the capture vaporizer. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabakhsh, S.; Poulain, L.; Chen, G.; Canonaco, F.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Pöhlker, M.; Wiedensohler, A.; Herrmann, H. A 1-year aerosol chemical speciation monitor (ACSM) source analysis of organic aerosol particle contributions from anthropogenic sources after long-range transport at the TROPOS research station Melpitz. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 6963–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Shi, H.; Bian, Y.; Han, Y.; et al. Aerosol chemistry and particle growth events at an urban downwind site in North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14637–14651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamant, C.; Pelon, J.; Flamant, P.H.; Durand, P. Lidar determination of the entrainment zone thickness at the top of the unstable marine atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteor. 1997, 83, 247–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennemuth, B.; Lammert, A. Determination of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height from Radiosonde and Lidar Backscatter. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 120, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.M.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T. Evaluation of retrieval methods of daytime convective boundary layer height based on lidar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4578–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.J.; Gamage, N.; Hagelberg, C.R.; Kiemle, C.; Lenschow, D.H.; Sullivan, P.P. An Objective Method for Deriving Atmospheric Structure from Airborne Lidar Observations. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2000, 17, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzworth, C.G. Estimates of mean maximum mixing depths in the contiguous United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 1964, 92, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaud Coen, M.; Praz, C.; Haefele, A.; Ruffieux, D.; Kaufmann, P.; Calpini, B. Determination and climatology of the planetary boundary layer height above the Swiss plateau by in situ and remote sensing measurements as well as by the COSMO-2 model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13205–13221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arruda Moreira, G.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Róman, R.; Bedoya-Velásquez, A.E.; Landulfo, E.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Study of the planetary boundary layer by microwave radiometer, elastic lidar and Doppler lidar estimations in Southern Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, J. A comprehensive evaluation of planetary boundary layer height retrieval techniques using lidar data under different pollution scenarios. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X.; Cao, J.; Han, S.; Meng, J.; Chen, P.; Zhao, D. Evolution of planetary boundary layer under different weather conditions, and its impact on aerosol concentrations. Particuology 2013, 11, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ni, C.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Q. Effects of aerosols on the atmospheric boundary layer temperature inversion over the Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Fan, R.; Gong, W. The relationship between atmospheric boundary layer and temperature inversion layer and their aerosol capture capabilities. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, P.; Wang, T. Study of PBLH and Its Correlation with Particulate Matter from One-Year Observation over Nanjing, Southeast China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y. Contrasting the effect of aerosol properties on the planetary boundary layer height in Beijing and Nanjing. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 308, 119861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Huang, S.; Yan, Y.; Lou, M. Unraveling the relationships between boundary layer height and PM2.5 pollution in China based on four-year radiosonde measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blay-Carreras, E.; Pino, D.; Vilà-Guerau De Arellano, J.; van de Boer, A.; De Coster, O.; Darbieu, C.; Hartogensis, O.; Lohou, F.; Lothon, M.; Pietersen, H. Role of the residual layer and large-scale subsidence on the development and evolution of the convective boundary layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4515–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, W.; Zhang, F.; Tan, H.; Xu, H.; Fan, T.; Jin, X.; Fan, X.; et al. Characterization of aerosol hygroscopicity, mixing state, and CCN activity at a suburban site in the central North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11739–11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Sun, Y.; Cribb, M.; Ren, R.; Lv, M.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; et al. Contrasting aerosol growth potential in the northern and central-southern regions of the North China Plain: Implications for combating regional pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 267, 118723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q.; Xie, M. Sensitivity of PM2.5 and O3 pollution episodes to meteorological factors over the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J.; Du, Z.; Liang, L.; Geng, G.; Ma, W.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. Secondary inorganic aerosol during heating season in a megacity in Northeast China: Evidence for heterogeneous chemistry in severe cold climate region. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Shang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhan, P.; Song, X.; Lv, M.; Yang, Y. Assessment of Multiple Planetary Boundary Layer Height Retrieval Methods and Their Impact on PM2.5 and Its Chemical Compositions throughout a Year in Nanjing. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183464
Han Z, Wang Y, Xu J, Shang Y, Li Z, Lu C, Zhan P, Song X, Lv M, Yang Y. Assessment of Multiple Planetary Boundary Layer Height Retrieval Methods and Their Impact on PM2.5 and Its Chemical Compositions throughout a Year in Nanjing. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(18):3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183464
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Zhanghanshu, Yuying Wang, Jialu Xu, Yi Shang, Zhanqing Li, Chunsong Lu, Puning Zhan, Xiaorui Song, Min Lv, and Yinshan Yang. 2024. "Assessment of Multiple Planetary Boundary Layer Height Retrieval Methods and Their Impact on PM2.5 and Its Chemical Compositions throughout a Year in Nanjing" Remote Sensing 16, no. 18: 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183464
APA StyleHan, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Shang, Y., Li, Z., Lu, C., Zhan, P., Song, X., Lv, M., & Yang, Y. (2024). Assessment of Multiple Planetary Boundary Layer Height Retrieval Methods and Their Impact on PM2.5 and Its Chemical Compositions throughout a Year in Nanjing. Remote Sensing, 16(18), 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16183464






