Abstract
When a synthetic aperture sonar (SAS) system operates under low-frequency broadband conditions, the azimuth range coupling of the point target reference spectrum (PTRS) is severe, and the high-resolution imaging range is limited. To solve the above issue, we first convert multi-receivers’ signal into the equivalent monostatic signal and then divide the equivalent monostatic signal into range subblocks and the range frequency subbands within each range subblock in order. The azimuth range coupling terms are converted into linear terms based on piece-wise linear approximation (PLA), and the phase error of the PTRS within each subband is less than π/4. Then, we use the chirp-z transform (CZT) to correct range cell migration (RCM) to obtain low-resolution results for different subbands. After RCM correction, the subbands’ signals are coherently summed in the range frequency domain to obtain a high-resolution image. Finally, different subblocks are concatenated in the range time domain to obtain the final result of the whole swath. The processing of different subblocks and different subbands can be implemented in parallel. Computer simulation experiments and field data have verified the superiority of the proposed method over existing methods.
1. Introduction
Synthetic aperture sonar (SAS) has high resolution by coherently receiving sideboard echo data along the azimuth direction [1,2,3,4,5] and its azimuth resolution is independent of range [4,6,7,8,9]. Therefore, SAS is widely used to detect high-value targets such as mines [10,11,12,13,14], buried objects [15,16], or seabed remote sensing [17,18,19,20]. The low-speed nature of sound in seawater [21,22] results in two issues for the SAS system. The first issue is the contradiction between the maximum detection range and the minimum azimuth sampling frequency. The maximum detection range of SAS is determined by pulse repetition frequency (PRF), and the SAS system with low PRF is generally used to obtain a larger swath. At the same time, SAS samples along the azimuth direction at a fixed PRF. If the PRF is too low, it may be smaller than the Doppler bandwidth, resulting in frequency aliasing and ghost targets in the azimuth direction [23]. To solve the above contradiction, in practice, SAS systems use single-transmit/multi-receive configuration [24,25], where multiple receivers sample the echo signal synchronously. This type of SAS is also known as the multi-receiver SAS. The multi-receiver SAS’s configuration improves the actual sampling frequency in the azimuth direction when PRF remains unchanged, overcoming the first issue. The second issue is that the low speed of underwater sound causes the along-track motion of the SAS platform between signal transmission and reception. SAS imaging algorithms must adopt a complex non-stop–hop–stop (NSHS) assumption [26] instead of stop–hop–stop assumption widely used in SAR [27,28], and the platform’s along-track motion between signal transmission and reception must be considered.
The phase center approximation (PCA) method [29] for multi-receiver SAS is based on NSHS assumption and uses the distance from the effective phase center (EPC) to the target as the round-trip range history. The beam center approximation (BCA) used in the PCA method leads to an increase in range history error with the rise in beamwidth [30], which cannot achieve high-resolution imaging (range history error < ). Zhang et al. [31] proposed a new range history for the multi-receiver SAS based on the method of reversion (MSR) [32,33,34,35,36], which also adopts BCA and is inefficient due to the receiver-by-receiver processing. The LBF method [7,20,37,38,39,40] can acquire a more accurate point target reference spectrum (PTRS), also called the two-dimensional frequency spectrum, and obtain results only through one imaging, but BCA and the assumption that the transmitter and receiver equally contribute to the azimuth modulation are used. The azimuth range coupling of the PTRS is caused by range cell migration (RCM) [33,41] and has not been carefully considered yet due to the insignificance of azimuth range coupling of the PTRS in side-looking view, narrowband, and narrow beamwidth conditions.
However, high-order terms (azimuth range coupling) cannot be ignored under broadband and wide beam conditions. The most accurate method is to use omega-KA [42,43] (OKA) to directly compensate for the azimuth range coupling term without any approximation, but the Stolt interpolation is time-consuming. The range-Doppler algorithm (RDA) [7,44,45] also requires time domain interpolation processing to perform RCM Correction (RCMC) and is not efficient. The chirp scaling algorithms (CSA) [46,47,48,49] use fast Fourier transform (FFT) and phase multiplication in the RCMC to avoid interpolation and significantly improve computational efficiency. The original CSA does not consider the spatially variant range in the secondary range compression (SRC), resulting in the limited high-resolution imaging range. To increase the high-resolution imaging range, the non-linear CSA (NCSA) [50,51,52] solves the problem of range spatial variation in SRC by using a range-variant non-linear scaling equation to make the chirp rate linearly change with range. However, like CSA, it requires that the transmitted signal must be a chirp signal. Loffeld et al. [53] proposed the scaled Fourier transform (SCFT) to perform range migration correction, eliminating the azimuth range coupling caused by RCM in the PTRS, avoiding interpolation, and the impact of truncation interpolation [54]. However, the influence of SRC was not considered in [53]. Wu et al. [55] considered the influence of SRC and applied SCFT to the squint mode’s SAR imaging, but also did not solve the problem of range variation in SRC. Although SCFT has one more FFT operation than CS, it can be applied to non-chirp signals [53] and can be achieved by the chirp-z transform (CZT) [56,57,58] in the digital system. Franceschetti et al. [59] divided the range into several subblocks continuously to decrease the range spatial variance of the SRC in squint mode SAR imaging. Zhang et al. [60] proposed a range-subblock processing method to decrease the PTRS error and residual quadratic coupling error for a multi-receiver SAS system with a wide-bandwidth signal. Residual coupling error will be small when the blocks are very dense, but the computational efficiency will not be high when azimuth range coupling is severe.
This paper proposes a CZT algorithm for multi-receiver synthetic aperture sonar based on range frequency division. First, the exact analytical PTRS based on the range history shifting (RHS) is obtained without any approximation in azimuth FFT. The above PTRS is expanded into a series of the range frequency and kept to the quadratic term. Then, the processed PTRS is divided into subblocks, and Taylor expansion is used in the coefficients of the range frequency at the center of each subblock. Residual RCM and SRC terms are obtained by performing high-order phase compensation and bulk phase compensation. In each range subblock, we divide the PTRS into subbands in the range frequency domain to ensure that the error of the PTRS is less than π/4. The residual SRC term can be merged into the residual RCM term by the piece-wise linear approximation (PLA), which means that the square term of range frequency is divided into many small linear frequency segments, and then the residual RCM term can be corrected through CZT to obtain low-resolution results of different subbands. The high-resolution result is obtained by coherent superposition of low-resolution resolution results, and then all range subblocks are concatenated in the range time domain to obtain the focusing image of the whole swath.
The remaining parts of the article are as follows: In Section II, we establish multi-receiver SAS’s model based on RHS and finally derive the accurate PTRS of each receiver. In Section III, the multi-receiver SAS’s data is converted into the monostatic equivalent signal by monostatic conversion, and the PTRS is divided into subblocks in the range time domain and subbands in the range frequency domain. The low-resolution results of the range subbands are obtained through the CZT algorithm, and the whole image can be obtained by concatenating low-resolution results in the range time domain after coherent superposition. In Section IV, simulation and field data results are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Section V serves as a summary.
2. The Multi-Receiver SAS’s Model
2.1. The Accurate Range History
The geometric schematic diagram of the multi-receiver SAS operating in side-looking mode is shown in Figure 1. The SAS platform consists of one transmitter and uniformly arranged receivers, numbered . Receivers are represented in yellow, and red represents the transmitter.
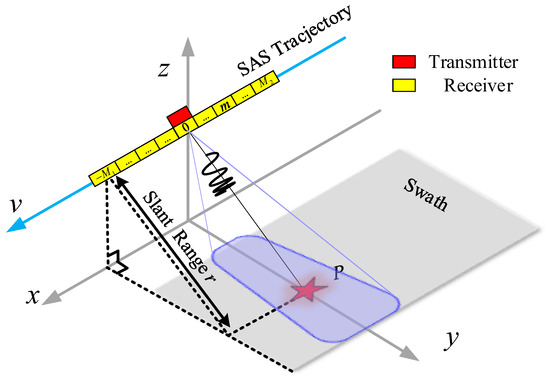
Figure 1.
Geometric model of the multi-receiver SAS in the side-looking mode.
To facilitate the understanding of the imaging process, we draw an imaging geometric diagram of the slant range plane, as shown in Figure 2. We take the trajectory direction as the x-axis called the azimuth direction, also known as the along-track direction, and the direction perpendicular to the trajectory is the r-axis, which is called the range direction, also known as the cross-track direction. is the distance from the m-th receiver to the reference receiver, and the position of the reference receiver coincides with that of the transmitter. The SAS platform insonifies the ideal scattering point represented as a red pentagram by moving in a uniform straight line at a speed v along the azimuth direction.
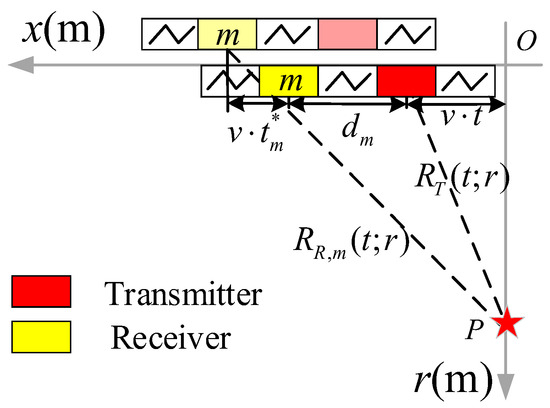
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram in the slant plane.
The SAS platform emits chirp signals in a fixed PRF while moving along the azimuth direction. At time t, the position of the transmitter is , represented as the solid red. Based on geometric relationships, the distance from the transmitter to the point target can be expressed as
At time t, the position of the m-th receiver is , represented as the solid yellow. Considering the NSHS time during signal propagation , the azimuth movement of the SAS platform during this time is . It should be noted that Figure 2 is only a schematic diagram, and is very small in reality. The true position of the m-th receiver receiving the signal is , represented as the light yellow, so the distance from the point target to the m-th receiver can be expressed as
According to (1) and (2), the round-trip range history of the m-th receiver considering NSHS time can be expressed as
Meanwhile, during the NSHS time , the distance traveled by sound waves from emission to reception by the m-th receiver can be expressed as
where c is a constant speed of sound. The distance derived from geometric relationships and the propagation distance of sound waves is equal, so (3) and (4) can be combined, and the exact round-trip NSHS time can be obtained as
where A, B, and C are represented as follows:
Substituting (5) and (6) into (4), we can obtain the accurate range history.
2.2. The Range History Shifting Method
However, the accurate range history is too complex to be conducive to subsequent processing. We use the receiver numbered 0 as the reference receiver where . Substituting into (4) and the accurate range history of the reference receiver is shown in the red curve in Figure 3 and can be expressed as
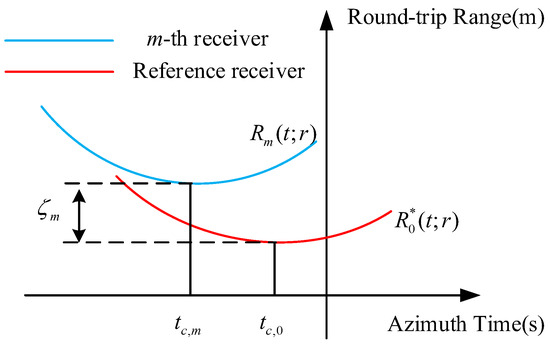
Figure 3.
Range migration curves of different receivers.
Let and ; then, (7) can be expressed as
The beam center’s time is the time when the slant range history is minimum. Let we can obtain the beam center’s time as follows:
The sampling interval between the m-th receiver and the reference receiver is [61]. When the reference receiver samples at , the equivalent sampling time of the m-th receiver is . If the curvature’s difference of the RCM curves of different receivers is ignored, then the RCM curve of the m-th receiver is regarded as the translation of the reference receiver in the slant plane, with the translation amounts on the t-axis and r-axis being and , respectively, as shown by the blue curve in Figure 3. Based on the geometric relationship, can be expressed as
According to (4), (5), (6), and (8), the analytical expressions of can be expressed as
The round-trip range history can be obtained by substituting into (10), and the complex accurate range history is transformed into the SSR form with the linear term and constant term, which facilitates the subsequent derivation of PTRS. Since is obtained by shifting reference range history, we call range history shifting (RHS) method. The error compared with the accurate range history is . Figure 4 shows in whole swath using the parameters shown in Table 1.
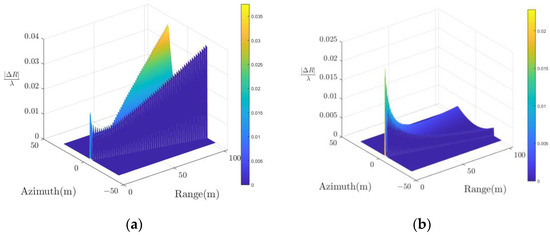
Figure 4.
Range history errors. (a) Range history error of the PCA method. (b) Range history error of the RHS.

Table 1.
SAS’s system parameters.
From Figure 4, it can be seen that although the range history errors of RHS and PCA methods have not exceeded , the range history error of the RHS method does not widen with the beam, and the RHS method has a wider range of applications.
2.3. Derivation of the PTRS
The baseband form of the echo signal of target P received by the m-th receiver can be represented as
To obtain the phase of the PTRS of the echo signal, we perform range FFT on (12), and obtain the expression of the range spectrum as
The phase in the integral expression of (13) is
According to the principle of stationary phase [62] (PSP), let , the stationary phase time in the range direction can be obtained as
Bringing into , we can obtain
Based on (16), the range spectrum can be rewritten as
where .
The PTRS can be obtained by performing azimuth FFT, and the PTRS is expressed as
Substituting (17) into (18), the phase in the integral is
Using PSP, let , and the azimuth phase stationary time can be expressed as
where is the range migration factor, expressed as
Bringing into (18), we can obtain the analytical expression of the PTRS, expressed as
where is the envelope of Doppler frequency. is the transmitter size, and is the receiver size. Perform Taylor expansion on (22) at and preserve it to the quadratic term, we can obtain
where represents the coefficient of range compression, represents the azimuth compression term, represents the coefficient of the RCM term, and represents the coefficient of the SRC term, represents the higher order phase (HOP), which cannot be ignored in severe azimuth range coupling. The above coefficients can be expressed as follows:
where , and are expressed as follows:
3. The Subblock–Subband CZT Algorithm
3.1. Monostatic Conversion
According to the first exponential term in (23), it can be seen that will cause envelope offset and phase error, and the phase compensation function is
Assuming the transmitter is located in the middle of the array, the curves of changing with r are shown in Figure 5 based on the parameters in Table 1. From Figure 5, it can be seen that the variation of exceeds one range resolution unit, so range subblocks processing or interpolation [60] is needed to ensure that the variation of in each range subblock is less than one range resolution unit. Therefore, for the n-th subblock, is the center of the subblock, and can be used to perform envelope offset (delay) compensation. The corresponding compensation function is
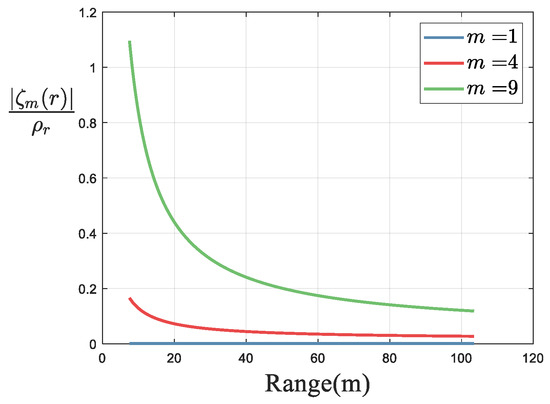
Figure 5.
Curves of changing with r.
The second exponential term in (23) is the bistatic deformation term, which is due to the different positions of the transmit/receive arrays in multi-receiver SAS. According to the time shifting property of FFT, this term will cause the data of the m-th receiver to shift in the azimuth axis by an amount of . Therefore, we can offset the impact of this term by rearranging the data in the time domain at intervals of , which is equivalent to compensating for the bistatic deformation term.
After compensating for the receiver-dependent terms, the monostatic conversion has been completed, and the converted signal is represented as
3.2. Range Time Domain Subblocks
Firstly, perform range compression with a compensation filter of , and the range compressed signal is
If is discarded, it is equivalent to ignoring azimuth range coupling terms. The high-order phase error increases with the increase of range. When the HOP term is equal to , the corresponding range is the maximum allowable imaging range, also known as the high-resolution imaging range (relative to the starting point of the swath). The larger the relative bandwidth, the smaller the high-resolution imaging range. In low-frequency broadband signals, the azimuth range coupling is very severe, severely limiting the high-resolution imaging range. If the HOP term at the center of the swath is compensated, then the high-order phase at the center of the swath is zero, which can be fully focused. The maximum allowable imaging range is transformed into the maximum permissible imaging range relative to the center of the swath, which is half the swath. However, the HOP terms at both edges of the swath may still exceed . To solve the above problem, we divide the range into many subblocks in the time domain, and the center of each subblock is used as a reference range to compensate for the HOP, ensuring that the HOP terms at both edges of each range subblock are less than .
The total number of sampling points in the time domain is . If the range is uniformly divided into P subblocks in the time domain, and the number of points in each block is , then the total number of sampling points in the time domain is expressed as
where p is the range time domain subblock subscript, and p can be expressed as
Assuming the center reference range of the p-th subblock is , the range within the p-th subblock can be discretized as
where is range sampling frequency and represents the range time domain sampling point in the p-th subblock and can be expressed as
The HOP compensation is applied to the p-th subblock’s center, and the expression for the HOP compensation is
The PTRS after the HOP compensation is
where represents the residual HOP error after HOP compensation, expressed as
As the higher order Taylor expands, becomes smaller but the expression becomes more complex. It can be seen that , which means at the reference range , the residual HOP is zero, and the image at the reference range can be completely focused. The , and are expanded at and kept as first-order terms for subsequent CZT processing. This is equivalent to the azimuth-frequency range decoupling (ARD), and the phase expression is obtained as follows:
where is the high-order phase term of the Taylor expansion at for , , and , and can be expressed as
Perform bulk compensation on (37) by removing range-independent terms from the first and second order coefficients of , so that the RCM and SRC terms at the center of each subblock are zero, and the remaining terms are the residual range variant RCM and SRC terms. The phase multiplication factor is
After the above bulk compensation, the compensated PTRS is expressed as
At the center of each subblock, the RCM term and SRC term are zero, and and increase with range relative to . It is only necessary to ensure that there is always in each subblock for high-resolution imaging. However, it is difficult to meet the requirements of high-resolution imaging solely through range time domain subblocks, as the azimuth range coupling is more pronounced in the range frequency domain, and changes rapidly with . Therefore, we need to divide the range frequency into subbands in each range time domain subblock.
3.3. Range Frequency Domain Subbands
If the number of sampling points is , then the range frequency in the p-th subblock can be discretized as
where the range frequency domain full sampling points can be expressed as
Based on (32) and (41), can be discretized as
where and are expressed as
Next, the range frequency domain fully sampling point k is divided into subbands in the p-th subblock. The number of fully frequency sampled points is and the range frequency is uniformly divided into Q subbands. The size of each subband is , and k can be expressed as
where the subband subscript is , and the frequency point in the q-th subband is . After dividing k into subbands, in (43) can be linearly approximated in each subband, which we refer to as piece-wise linear approximation (PLA). For each segment, the tangent at the center of the frequency subband is taken as the approximate value of the subband, so that the center can be fully compensated and there is no phase jump at the edge, as shown in Figure 6. The approximate expressions for is expressed as follows:
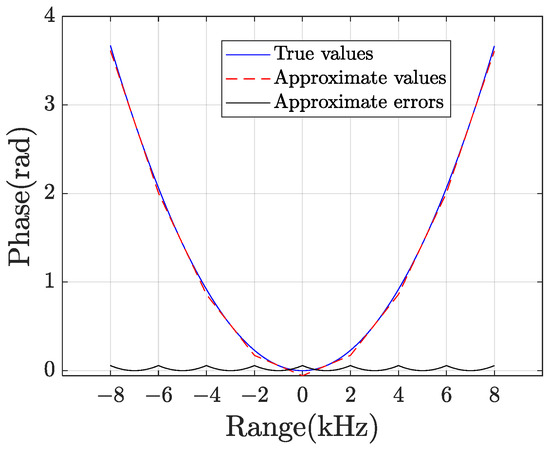
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of PLA.
After PLA, the PTRS corresponding to the q-th frequency domain subband in the p-th time domain subblock can be expressed as
where is the phase error caused by PLA, and it can be expressed as
Combining with and , the cumulative error is
Now, it is necessary to ensure that there is within each frequency domain subband. is zero at of the p-th subblock (corresponding sampling point ), and the maximum value at the edge of the subblock is . For the PTRS at , PTRS is divided into Q subbands. If , reaches its maximum value in the q-th subband when the minimum range frequency and the maximum azimuth frequency are taken. If , reaches its maximum value in the q-th subband when the range frequency and azimuth frequency are both maximized. It can be seen that the errors in different subbands within the p-th subblock are only related to and . According to (45), Q subbands are traversed in the p-th subblock to obtain the maximum phase error, which can be expressed as
where is the range frequency sampling point corresponding to the maximum value of .
Next, according to (30), P subblocks are traversed to obtain the maximum phase error over the entire swath, which can be expressed as
where represents the range sampling point when reaches its maximum value. The maximum error value is only related to and , while is only associated with and is only related to . Based on and , the curves of changing with P and Q can be obtained. Based on the parameters in Table 1, we obtain for different P and Q, as shown in Figure 7. It can be seen that the higher the PTRS is expanded, the smaller the number of time domain subblocks required. However, if the expanding order is too high, it will increase the algorithm complexity in program execution. If range frequency division is not performed (Q = 1), P needs to be large enough to meet , which will cause a sharp increase in computational complexity. If P is fixed, will decrease with the growth of Q, but it cannot be infinitely reduced. Considering the computational complexity, we expand the PTRS to the quadratic phase term and take P = 16 and Q = 6 as the required division parameters for the SAS shown in Table 1.
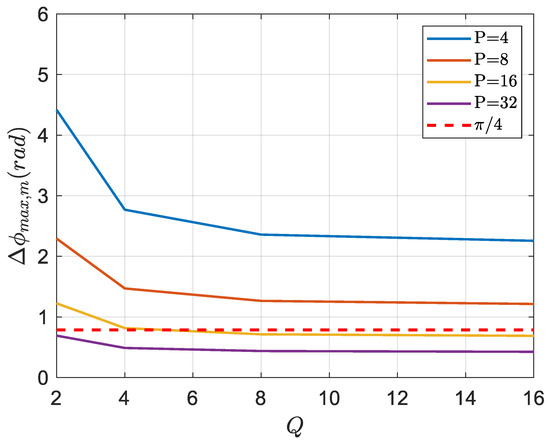
Figure 7.
Curves of changing with P and Q.
3.4. The CZT Algorithm
After the above subblock–subband processing and PLA, if in each subband, the error shown in can be ignored, and the focusing process in each subband meets the requirements of high-resolution imaging. From here, it can be seen that there are no longer quadratic terms of range frequency, and the first-order term for range frequency can be corrected through RCMC. Therefore, the PLA process is equivalent to converting the residual SRC term to RCM terms. SCFT is used to avoid time-consuming interpolation operations in RCMC and efficiently implemented in digital systems through CZT, which can effectively handle first-order spatially range cell migration [63]. After CZT processing, the RD domain data of the q-th frequency domain subband under the p-th time domain subblock is expressed as
According to Bluestein’s equation [64,65]
we can rewrite (52) as
where and are, respectively, represented as
Equation (54) is equivalent to multiplied by , then multiplied by , and finally convolved with . To achieve higher computational efficiency, frequency domain convolution can generally be achieved through time domain multiplication, and finally multiplied by to obtain the result after RCMC and SRC. The quick implementation of CZT is shown in Figure 8.
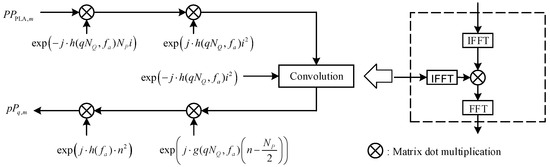
Figure 8.
Quick implementation of CZT.
The bandwidth of each subband is one-Nth of the total range chirp bandwidth, so the range resolution is only one-Nth of the original signal. Therefore, the result obtained in this step is called a low-resolution result. Coherently summing Q low-resolution results can obtain a high-resolution result.
Concatenating data along the range axis in the RD domain to obtain data of the whole swath, the expression of the concatenated signal is
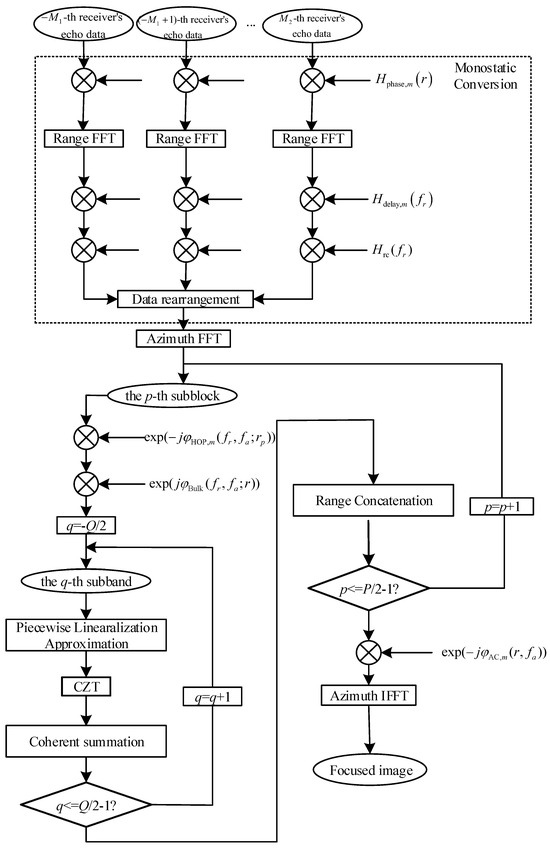
Figure 9.
The flowchart of the proposed method.
4. Simulation and Experimental Results
4.1. Computer Simulation
To verify the proposed method’s superiority, we conducted computer simulation. The imaging geometry is shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, and the SAS system parameters are shown in Table 1. Point targets represented as the red dots are located as shown in Figure 10. The computer CPU used in the simulation experiment is Intel i7-10700@2.90 GHz, RAM is 32 GB, and MATLAB version is R2020A. We used the BPA [66,67] as the evaluation criterion and compared the range time domain subblocks CZT algorithm based on the RHS, called the subblock CZT method [60], and the range time domain subblocks/frequency domain subbands algorithm based on the RHS, called the subblock–subband CZT method. The imaging results of different methods are shown in Figure 11. To display the differences of different methods more clearly, range and azimuth cross-sections of P1 (0 m, 20 m), P2 (0 m, 50 m), and P3 (0 m, 80 m) are shown in Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14 without any windowing processing [68]. From range and azimuth cross-sections, the point target imaging result of the proposed method is similar to that of BPA, both of which are superior to the subblock CZT method that only uses subblock processing. The quantitative analysis can be found in the following text.
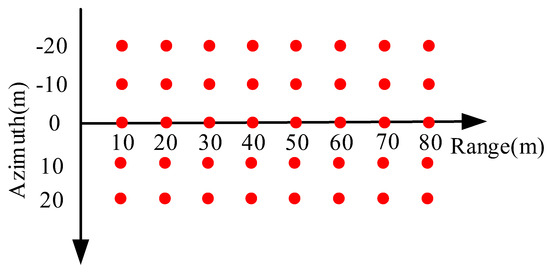
Figure 10.
Location of simulation point targets.
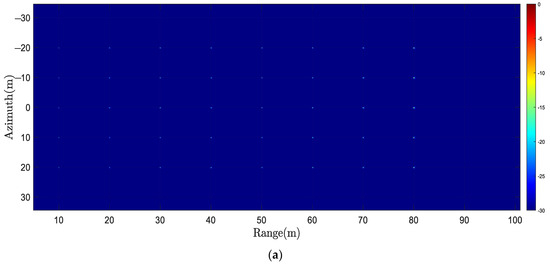
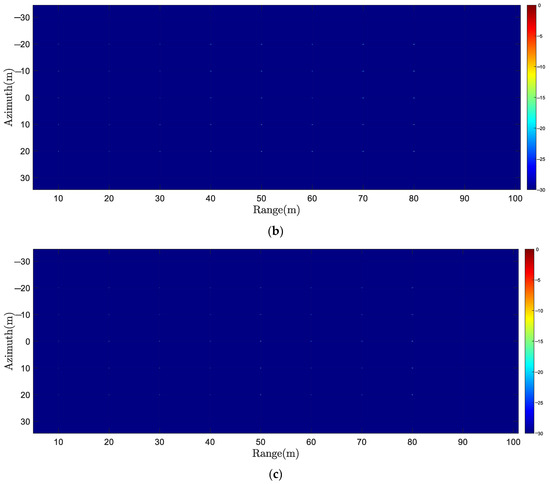
Figure 11.
The imaging results of different methods. (a) The subblock CZT method. (b) The subblock–subband CZT method. (c) BPA.
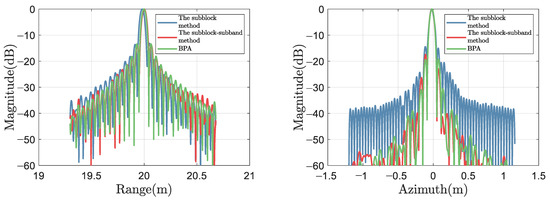
Figure 12.
Cross-sections of the point target P1.
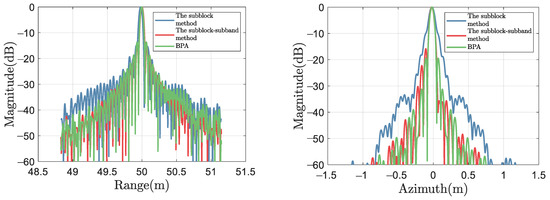
Figure 13.
Cross-sections of the point target P2.
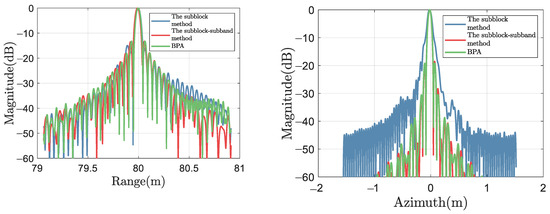
Figure 14.
Cross-sections of the point target P3.
For quantitative analysis, PSLRs, ISLRs, and IRWs of P1, P2 and P3 are measured, and the results are shown in Table 2. For the measurement results in the range direction, since the range envelope after pulse compression is a standard sinc function, the theoretical values of PSLR and ISLR in the range direction are −13.26 dB and −9.73 dB, respectively, and the IRW’s theoretical value (−4 dB) is 4.69 cm. Due to the main-lobe’s widening and the fusion of the first side-lobe into the main lobe [41], PSLRs may exceed the theoretical value, causing that the PSLR and ISLR of the second side lobe were actually measured. In addition, unaliased frequency recovery is achieved by the Nyquist sampling frequency, but to attain undistorted amplitude recovery, a higher frequency than the Nyquist sampling frequency is required [69]. Due to the limited sampling frequency, there may be distortion in the envelope amplitude, resulting in a gap between PSLR and theoretical values. However, IRW does not experience distortion. Therefore, we mainly use IRW as the evaluation indicator for the focusing effect. For the azimuth measurement results, since the azimuth envelope after pulse compression is the product of two sinc functions and then a weighted average of multiple receivers’ direction maps. The theoretical values of PSLR and ISLR are challenging to acquire, and we directly use the PSLR and ISLR of BPA’s results as the evaluation criterion.

Table 2.
Measured values of different point targets.
The theoretical value of azimuth IRW is 5.10 cm, related to the SAS’s transmitter size. Indicators that cannot truly reflect image quality due to main-lobe broadening or amplitude distortion are represented by underlined numbers, while black numbers represent superior results except for BPA’s results. From Table 2, it can be seen that for range cross-sections, the subblock CZT method has poor IRWs on all targets, while the subblock–subband CZT method has improved IRWs, which is related to theoretical values. This is due to the subband processing. For azimuth cross-sections, the ISLR of the subblock–subband CZT method is 5.84 dB lower than that of the subblock method for the P1 target, resulting in a reduction in the possibility of azimuth ghosting targets. For P2 and P3, due to azimuthal IRW broadening, the measured values of PSLR and ISLR of the subblock CZT method are distorted. However, the measured values of the subblock–subband CZT method are close to theoretical values. Therefore, simulation results can demonstrate the superiority of the proposed subband processing method.
4.2. Real Data Processing
To further validate the effectiveness of this method, we presented the measured data collected in 2019 by Wuhan Huanda Electronics Co., Ltd. at Zhanghe Reservoir in Jingmen City, Hubei Province, China. The sonar parameters used in the experiment are the same as the parameters used in simulation. The subblock CZT method [60], the proposed subblock–subband CZT method, and BPA [66] were used to focus the measured data, and the results are shown in Figure 15. From the red dashed rectangular box, it can be seen that without subband processing, the subblock CZT method yields the worst results, making it difficult to distinguish the focusing result from the background. The use of subband processing can improve the quality of imaging. The imaging quality of the proposed subblock–subband CZT method is comparable to that of BPA, and contour information can be clearly seen.
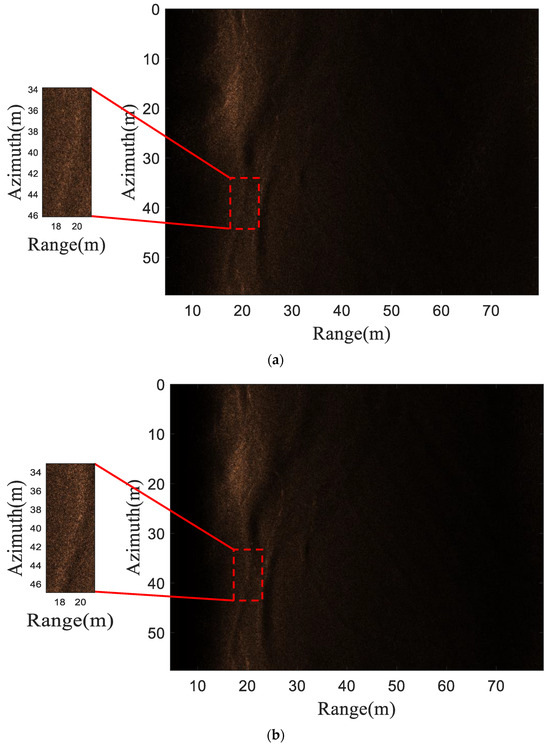
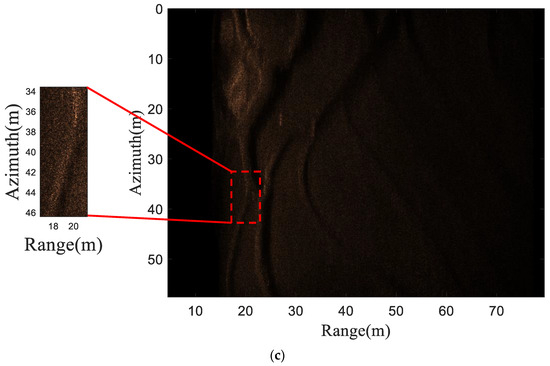
Figure 15.
Image results of the field data. (a) The subblock CZT method. (b) The subblock–subband- CZT method. (c) BPA.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes a range subblock–subband CZT algorithm, and we divide the echo data into the range frequency subbands within each range subblock compared to the traditional range subblocks method. The azimuth range coupling terms are converted into linear terms based on PLA. Then, we use the CZT to correct the RCM to obtain low-resolution results for different subbands. After RCM correction, the subbands’ signals are coherently summed in the range frequency domain to obtain a high-resolution image. Finally, different subblocks are concatenated in the range time domain to obtain the final result of the whole swath. The processing of different subblocks and different subbands can be implemented in parallel and can efficiently deploy on hardware with parallel processors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N. and J.T.; methodology, M.N.; software, H.Z.; validation, M.M. and P.Z.; formal analysis, H.W.; investigation, H.W. and J.Z.; resources, H.Z.; data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N.; writing—review and editing, M.N. and J.T.; visualization, J.Z.; supervision, J.T.; project administration, H.Z.; funding acquisition, H.Z., M.M. and P.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 42176187 and 62301592 and the Science Foundation of the National University of Defense Technology under Grant ZK21-30.
Data Availability Statement
The real data presented in this paper is not readily available due to technical limitations and copyright issues of Huanda Electronics Co., Ltd.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all reviewers and editors for their comments on this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Putney, A.; Chang, E.; Chatham, R.; Marx, D.; Nelson, M.; Warman, L.K. Synthetic aperture sonar-the modern method of underwater remote sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Big Sky, MT, USA, 10–17 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, D.; Nelson, M.; Chang, E.; Gillespie, W.; Putney, A.; Warman, K. An introduction to synthetic aperture sonar. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing, Manor, PA, USA, 14–16 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Tang, J.-S.; Zhang, C.-H. Multi-aperture Synthetic Aperture Sonar lmaging Algorithm. Signal Process. 2003, 19, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, M.P. A processing requirement and resolution capability comparison of side-scan and synthetic-aperture sonars. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1992, 17, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Yang, P.-X. Synthetic aperture imagery for high-resolution imaging sonar. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1049761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-F.; Cheng, G.-L.; Tang, J.-S.; Xie, Z.-M.; Wu, H.-R. A Novel Imaging Algorithm for Wide-Beam Multiple-Receiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar Systems. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Wang, Y.-M.; Shen, W.-Y.; Yang, J.-C.; Wang, J.-F.; Ye, K.; Zhou, M.-Z.; Sun, H.-X. A Novel Multireceiver SAS RD Processor. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4203611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-R.; Zhou, F.-Y.; Xie, Z.-M.; Tang, J.-S.; Zhong, H.-P.; Zhang, J.-F. Two-Dimensional Space-Variant Motion Compensation Algorithm for Multi-Hydrophone Synthetic Aperture Sonar Based on Sub-Beam Compensation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B. An efficient method for the simulation of multireceiver SAS raw signal. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 37351–37368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlicht, D.D.; Femandez, J.E.; Holtzapple, R.; Kucik, D.P.; Montgomery, T.C.; Loeffler, C.M. Advanced sonar technologies for autonomous mine countermeasures. In Proceedings of the OCEANS’11 MTS/IEEE KONA, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 19–22 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fossum, T.G.; Sæbø, T.O.; Langli, B.; Callow, H.; Hansen, R.E. HISAS 1030—High resolution interferometric synthetic aperture sonar. In Proceedings of the Canadian Hydrographic Conference and National Surveyors Conference, Victoria, BC, Canada, 6–7 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, J.-S.; Zhong, H.-P.; Ning, M.-Q.; Liu, D.-D.; Wu, K. Self-Trained Target Detection of Radar and Sonar Images Using Automatic Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4701914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, P.E.; Hansen, R.; Fossum, T.; Langli, B. Development of High-Resolution Synthetic Aperture Sonar for Demanding AUV Applications. In Proceedings of the 9th Unmanned Underwater Vehicle Showcase, Southampton, UK, 26–27 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, X.; Yang, B. Fast imaging algorithm for the multiple receiver synthetic aperture sonars. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, J.E.; Commander, K.W.; Thorsos, E.I.; Williams, K.L. Detection of buried targets using a synthetic aperture sonar. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2002, 27, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.J.; Wilby, A.; Stewart, C. Deep ocean survey and search using synthetic aperture sonar. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Washington, DC, USA, 20–23 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chatillon, J.; Adams, A.E.; Lawlor, M.A.; Zakharia, M.E. SAMI: A low-frequency prototype for mapping and imaging of the seabed by means of synthetic aperture. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1999, 24, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.A.; Rodrigues, G.P.; Alvarenga, I.D. Seabed Mapping with HISAS Sonar For Decommissioning Projects High-Resolution Surveying for Decom Planning. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:49237309 (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Charlot, D.; Couade, M.; Marty, B.; Fabre, M.N.; Alain, P.; Delbecke, J.; Laquet, T.; Chemisky, B.; Mosca, F.; Bouhier, M.E.; et al. The Synthetic Aperture Mapping Sonar SAMS150 onboard UlyX AUV 6000m: An advanced solution for simultaneous detection and identification of deep-sea features. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2023, Limerick, Ireland, 5–8 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Sun, M. Experiment results of a novel sub-bottom profiler using synthetic aperture technique. Curr. Sci. 2022, 122, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Yu, Y.-X. Overview of deep water acoustics. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W. Research on the Characteristics of Underwater Acoustic Channels and the Propagation Characteristics of Signals in Them. Ship Electron. Eng. 2023, 43, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. Communication in the Presence of Noise. Proc. Proc. IRE 1949, 37, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Nannini, M.; Martín-del-Campo-Becerra, G.D.; Pardini, M.; Papathanassiou, K.; Reigber, A. Spaceborne Multi-Baseline Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Tan, C.; Ying, W.-W. Imaging Algorithm for Multireceiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2019, 14, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Chen, X.-H.; Wu, Q. Influence of the stop-and-hop assumption on synthetic aperture sonar imagery. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Chengdu, China, 27–30 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Fu, X.; Lv, X. New Channel Errors Estimation Method for Multichannel SAR Based on Virtual Calibration Source. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.-N.; Shang, M.-Y.; Zhong, L.-H.; Qiu, X.-L.; Ding, C.-B. A Novel Imaging Scheme of Squint Multichannel SAR: First Result of GF-3 Satellite. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-L.; Zhang, S.; Tang, J.-S. Study on Simulation of Multiple-receiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar Imagery Based on Wide Swath. J. Syst. Simul. 2011, 23, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Deng, X.-Y. Influence of Phase Centre Approximation Error on SAS Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Chengdu, China, 23–26 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Tang, J.-S.; Zhang, S.; Bai, S.-X.; Zhong, H.-P. Four-order Polynomial Based Range-Doppler Algorithm for Multi-receiver Synhetic Aperture Sonar. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2014, 36, 1592–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, Y.L.; Wong, F.; Cumming, I.G. A Two-Dimensional Spectrum for Bistatic SAR Processing Using Series Reversion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-R.; Jin-Song, T.; Zhong, H.-P.; Yi-Shuo, T. Multi-aperture range-Doppler imaging algorithm based on spectrumofseries reversion. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 46, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Ying, W.-W.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Deng, X.-Y. Processing Multireceiver SAS Data Based on the PTRS Linearization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Sun, H.-X. Frequency-domain multireceiver synthetic aperture sonar imagery with Chebyshev polynomials. Electron. Lett. 2022, 58, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Dai, X.-T. Focusing Multireceiver SAS Data Based on the Fourth-Order Legendre Expansion. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 2607–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Loffeld, O.; Ul-Ann, Q.; Nies, H.; Ortiz, A.M.; Samarah, A. A Bistatic Point Target Reference Spectrum for General Bistatic SAR Processing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Wu, H.-R.; Sun, H.-X.; Ying, W.-W. Multireceiver SAS Imagery Based on Monostatic Conversion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10835–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J.; Li, Z.-Y.; Huang, Y.-L.; Yang, J.-Y.; Liu, Q.-H. An Omega-K Algorithm for Translational Invariant Bistatic SAR Based on Generalized Loffeld’s Bistatic Formula. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6699–6714. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Wang, Y.-M.; Shen, W.-Y.; Yang, J.-C.; Ye, K.; Zhou, M.-Z.; Sun, H.-X. LBF-Based CS Algorithm for Multireceiver SAS. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1502505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic ApertureRadar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Artech House Inc.: Norwood, OH, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Sun, H.-X. An omega-k algorithm for multireceiver synthetic aperture sonar. Electron. Lett. 2023, 13, e12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Sun, M. A Novel Sub-Bottom Profiler and Signal Processor. Sensors 2019, 19, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, J.-C.; Shen, W.-Y.; Sun, H.-X. Range-Doppler Imaging Algorithm for Multireceiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2022, 44, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-H.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, N.; Song, Y.-P.; Han, S.-D.; Liu, W.-J.; Huang, X.-T. Delay-Doppler Map Shaping through Oversampled Complementary Sets for High-Speed Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, H.; Bamler, R. A Novel High Precision SAR Focussing Algorithm Based On Chirp Scaling. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 26–29 May 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Raney, R.K.; Runge, H.; Bamler, R.; Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Precision SAR processing using chirp scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-B.; Tang, J.-S.; Zhong, H.-P.; Wu, H.-R. Multireceiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar Chirp Scaling Algorithm Considering Intrapulse Doppler Shift. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 47, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-X. An imaging algorithm for high-resolution imaging sonar system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 31957–31973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, G.W.; Cumming, I.G.; Ito, M.R. A chirp scaling approach for processing squint mode SAR data. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1996, 32, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X.; Feng, X.; Sun, H.-X. Efficient imaging method for multireceiver SAS. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2022, 16, 1470–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y.-K. Focus Improvement of Airborne High-Squint Bistatic SAR Data Using Modified Azimuth NLCS Algorithm Based on Lagrange Inversion Theorem. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffeld, O.; Hein, A.; Schneider, F. SAR focusing: Scaled inverse Fourier transformation and chirp scaling. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–10 July 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Wu, D. Wavenumber Domain Algorithm Based on the Principle of Chirp Scaling for SAR Imaging. J. Radars 2020, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-J.; Huang, Y. Inverse Scaled Fourier Transformation Algorithmfor Squint Mode SAR lmaging. Signal Process. 2010, 26, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.-B.; Tang, J.-S.; Wu, H.-R.; Zhang, P.; Ning, M.-Q. CZT Algorithm for the Doppler Scale Signal Model of Multireceiver SAS Based on Shear Theorem. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5201412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-B.; Jin-Song, T.; Zhong, H.-P. CZT Algorithm for Multiple-Receiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1902–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-B.; Jin-Song, T.; Zhong, H.-P.; Tian, Z. CZT Algorithm for Multiple-receiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 47, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Lanari, R.; Marzouk, E.S. A new two-dimensional squint mode SAR processor. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1996, 32, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X. An Improved Imaging Algorithm for Multi-Receiver SAS System with Wide-Bandwidth Signal. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jin-Song, T.; Ming, C.; Sheng-Xiang, B. Development and sea trial of interferometric synthetic aperture sonar. Tech. Acoust. 2012, 31, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K. A New And Fundamental Fourier Transform Pair. In Proceedings of the IGARSS ‘92 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 26–29 May 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-L. Study on Signal Modeling and Imaging Algorithm for Airborne/Spaceborne SAR with Nonlinear Trajectory. Ph.D. Thesis, Xidian University, Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.R.; Schafer, R.W.; Rader, C.M. The chirp z-transform algorithm and its application. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1969, 48, 1249–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestein, L. A linear filtering approach to the computation of discrete Fourier transform. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1970, 18, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Tang, J.-S.; Wang, F.; Bai, S.-X.; Liu, D.-D. Accurate back projection imaging algorithm for multi-receiverSAS in engineering application. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2014, 26, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Yang, P.-X. Back Projection Algorithm for Multi-Receiver Synthetic Aperture Sonar Based on Two Interpolators. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-H.; Song, Y.-p.; Jiang, N.; Xie, Z.; Fan, C.-Y.; Huang, X.-T. Enhanced Doppler Resolution and Sidelobe Suppression Performance for Golay Complementary Waveforms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-C.; Yu, S.-X. The Analysis of the Error in Sampling. Pet. Instrum. 1995, 9, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).