Abstract
Building segmentation has extensive research value and application prospects in high-resolution remote sensing image (HRSI) processing. However, complex architectural contexts, varied building morphologies, and non-building occlusions make building segmentation challenging. Compared with traditional methods, deep learning-based methods present certain advantages in terms of accuracy and intelligence. At present, the most popular option is to first apply a single neural network to encode an HRSI, then perform a decoding process through up-sampling or using a transposed convolution operation, and then finally obtain the segmented building image with the help of a loss function. Although effective, this approach not only tends to lead to a loss of detail information, but also fails to fully utilize the contextual features. As an alternative, we propose a novel network called NPSFF-Net. First, using an improved pseudo-Siamese network composed of ResNet-34 and ResNet-50, two sets of deep semantic features of buildings are extracted with the support of transfer learning, and four encoded features at different scales are obtained after fusion. Then, information from the deepest encoded feature is enriched using a feature enhancement module, and the resolutions are recovered via the operations of skip connections and transposed convolutions. Finally, the discriminative features of buildings are obtained using the designed feature fusion algorithm, and the optimal segmentation model is obtained by fitting a cross-entropy loss function. Our method obtained intersection-over-union values of 89.45% for the Aerial Imagery Dataset, 71.88% for the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset, and 68.72% for the Satellite Dataset I.
1. Introduction
Buildings are an imperative part of urban areas, representing their attributes and functions, and thus are a key feature reflecting geographic information [1]. Building segmentation involves the use of image segmentation algorithms to divide remote sensing images into building and non-building areas [2]. This is not only beneficial in helping researchers to grasp the size, location, and layout information of buildings, but also has great significance for the planning and construction of cities, the detection of natural disasters, and the updating of geographic databases [3]. Therefore, realization of the automatic and accurate segmentation of buildings in a large number of HRSIs is a valuable research topic.
In recent years, with the continuous development of remote sensing satellites and image acquisition technology, the volume and resolution of remote sensing images for building segmentation have greatly improved [4]. However, no matter how much the quality of remote sensing images is improved, the characterization of ground objects coexisting with buildings still affects the accuracy of building segmentation. These characteristics can be summarized into three main aspects [5]. The first aspect is the complex background; for example, buildings are usually surrounded by background elements such as trees, roads, and water. These background elements have similarities with buildings, in terms of their color, texture, and shape, which can easily lead to their misclassification as buildings. The second aspect is the diversity of building morphologies; that is, most buildings have different heights, varying lengths and widths, and complex geometrical shapes, which increases the difficulty of building identification. The third aspect is non-building shading; that is, there are often occlusions caused by trees and shadow occlusions caused by lighting conditions, which can lead to the misclassification of some areas of buildings. Furthermore, the season, time, resolution of image acquisition, and accuracy of manual labeling also pose difficulties for building segmentation [6].
To solve the above problems and segment buildings accurately, researchers have carried out many studies and explorations [7]. Before deep learning technology was widely used, researchers mainly relied on four methods to segment buildings: the first is the threshold segmentation method [8], which uses the gray level or color information of HRSIs to separate building areas from non-building areas. This method is simple, intuitive, and fast to compute, but has difficulty in dealing with buildings with complex morphologies and background environments. The second is the region-growing method [9], which starts from a seed pixel and generates regions containing similar pixels through merging neighboring pixels. This method takes the spatial and spectral consistency of pixels into account, to a certain extent, but the effect is unstable for the extraction of building boundaries. The third is the edge detection method [10], which obtains the outline of buildings through extracting edge information in HRSIs. In practical applications, it is often difficult to obtain an ideal segmentation effect using this method, due to the mutual nesting between the main body and the background of the building. The fourth is the morphological segmentation method [11], in which segmentation is carried out after extracting the features of a building through morphological operations, such as open and closed operations. This method can better suppress noise interference and connect neighboring regions, but has greater limitations when segmenting buildings in large-scale and complex scenes. With the development of artificial intelligence technology, the use of deep learning to segment buildings in a large number of HRSIs not only greatly reduces the required labor, but also improves the efficiency of segmentation; therefore, the application of this technology has become more and more widespread.
Among the many available approaches, representative ones for building segmentation include U-Net [12], SegNet [13], DeepLab [14], and so on [15]. Specifically, these models usually have the following characteristics: First, they can automatically learn and extract rich high-level features from HRSIs, including texture, shape, and semantic information, in order to effectively distinguish building and non-building features. Second, they are more adaptable to complex environments and occlusions. They can handle complex scenarios, including light changes, shadow occlusions, and diverse building morphologies, which improves the robustness of building segmentation. Third, they can make full use of the contextual information around building pixels, which improves the accuracy and spatial continuity of pixel classification and makes the results of building segmentation smoother and more accurate. Fourth, they require less human intervention and can automatically learn features based on a large amount of training data. These methods can overcome the limitations of traditional manual methods and have higher segmentation accuracy and robustness for HRSIs. However, due to the simplicity of the model structures, these methods are still unable to fully capture building features or contextual information with complex backgrounds, resulting in limited segmentation accuracy.
Among the various building segmentation frameworks, the encoder–decoder architecture has become the most commonly used architecture, being a popular and effective choice for building segmentation using deep learning techniques [16]. The main idea behind this technique is to use the encoder to gradually extract the deep-level features of a building image, and then map these features to the pixel-level segmentation results via the decoder. Although this type of approach leads to excellent segmentation performance, it also has some drawbacks and challenges [17]. On one hand, the complex background content in HRSIs and the similar spectral and material properties of building and ground objects can cause difficulties in deep-level feature extraction from building images, which can lead to serious semantic confusion problems in the process of segmentation; on the other hand, the single convolutional neural network (CNN) in the encoder usually utilizes successive convolutions and pooling operations to extract the features, making it prone to the loss of small-scale information, ultimately leading to the model’s failure in the semantic segmentation of small buildings and their boundaries.
To effectively minimize the interference of complex building environments, variable building appearances, and non-building obstructions in the segmentation of building images and to overcome the attenuation of building information caused by use of the traditional encoder–decoder structure during feature processing, we have developed an innovative network. This network is designed to reconstruct and enhance the details of building features in the decoding stage, thus effectively preventing semantic confusion of buildings in the segmentation process and significantly improving the accuracy and detail of building segmentation. Specifically, we utilize an improved pseudo-Siamese network to compensate for the information loss of the single CNN when encoding building images, further enrich the details through fusing and decoding the two different scales of features with the corresponding encoded features in a layer-by-layer manner through double-stream branching, and, finally, fuse the decoded features to generate discriminative features. The main contributions of this study are as follows:
- We propose a novel building segmentation network called NPSFF-Net, which enriches and expands upon the traditional encoder–decoder structure.
- We use ResNet-34 and ResNet-50 to construct an improved pseudo-Siamese network to learn building features from HRSIs, and combine transfer learning and fusion encoding techniques to achieve efficient encoding of deep semantic features from building images.
- We design a double-stream decoder based on two neighboring deep encoded features and obtain decoded building features through skip connections while cleverly fusing deep and transposed convolutions.
- We conduct sufficient experiments on the Satellite Dataset I, Massachusetts Buildings Dataset, and Aerial Imagery Dataset, and the experimental results prove the effectiveness and advancement of NPSFF-Net.
2. Related Work
2.1. Encoders
An encoder is an important part of a neural network for building segmentation tasks that is mainly responsible for extracting deep-level building features. It usually uses convolutional and pooling layers to continuously reduce the size of HRSIs and, in this way, captures the color, shape, and texture information of buildings. Three main types of encoders are commonly used for building segmentation. The first is based on CNNs [18]. It can effectively extract the texture and shape information of buildings from an HRSI, and can learn to adapt to different building types and background environments through training. However, it has higher computational complexity and requires more computational resources. In addition, it is relatively weak in capturing the global information of buildings. The second is based on the Transformer [19], and is capable of learning a low-dimensional representation of building images and extracting useful features from a large amount of unlabeled data through unsupervised learning. However, it is prone to overfitting during model training, resulting in a poor segmentation of new building images. Moreover, it usually requires a large number of building images for training and has a long training time. The third is based on generative adversarial networks [20], and is able to learn rich building features through the adversarial training of generators and discriminators, allowing it to generate new building images to expand existing datasets. Nevertheless, its training process is usually less stable and careful parameter tuning is required to prevent model crashes. Moreover, it may produce some unrealistic building images, affecting the quality of segmentation. Therefore, we used an improved pseudo-Siamese network based on a CNN with a smaller number of layers as the backbone of the encoder, in order to reduce the computational complexity and enhance the building feature extraction ability.
2.2. Decoders
The decoder is the part corresponding to the encoder in building segmentation, which is mainly responsible for restoring the feature map to the size of the original image. The decoder usually gradually restores the detailed information of the image through up-sampling and convolution operations, making the building segmentation results more accurate. There are three common types of decoders in building segmentation. The first type of decoder is based on transposed convolution [21], which can directly up-sample the feature map with the learned convolution kernel and realize feature fusion at the same time. Although it can better recover the detailed information of HRSIs, it may lead to checkerboard effects in the generated images, which affects the smoothness of the segmentation results. In addition, if the convolution kernel is not properly designed, it may lead to the loss of information or the introduction of noise. The second type is based on up-sampling and convolution [22], which typically uses bilinear interpolation or nearest-neighbor interpolation to up-sample the feature map, then fuses the features and recovers the details with a convolution operation. Despite its high computational efficiency and its ability to avoid the checkerboard effect, to a certain extent, the up-sampling operation cannot completely recover all of the detailed information of HRSIs, resulting in a poor edge segmentation effect. In addition, if the up-sampling multiplier is too large, it may lead to blurring or distortion. The third type is based on skip connections [23]. In this approach, the low-level feature maps in the encoder are fused with the high-level feature maps in the decoder, which helps to recover more detailed information. However, this may increase the computational complexity and memory consumption. Additionally, if the fusion method is not properly designed, it may lead to conflicts between different features and affect the segmentation accuracy. Therefore, in order to avoid the checkerboard effect and recover the building details as much as possible, we fused the advantages of transposed convolution and skip connections to design a double-stream decoder that recovers the detailed information of HRSIs.
2.3. Attention Mechanisms
In building segmentation tasks, the attention mechanism (AM) is a technology that simulates the human visual system to selectively focus on important information associated with building features [24]. This enables the model to adaptively focus on regions that are critical to the segmentation task when processing images, thus improving the accuracy and efficiency of segmentation. The most commonly used AMs are spatial attention [25], the convolutional block attention module (CBAM) [26], and channel attention [27]. An AM can be embedded into different layers in encoder–decoder networks for building segmentation. Through introducing an AM, a network can more accurately recognize the contours, textures, and structures of buildings, thus improving the accuracy and completeness of the segmentation results. However, the AM may also pose some challenges. For instance, the increase in computational complexity may lead to longer training times and a reduced inference speed. In addition, if the AM is not properly designed, it may lead to model overfitting or performance degradation. Therefore, in order to focus on the key information of building features, we designed a feature enhancement module to fuse the encoded features at different scales to ensure that NPSFF-Net performs optimally.
3. Methodology
3.1. The Overall Structure of NPSFF-Net
NPSFF-Net is a new type of segmentation network that is designed to extract building features from HRSIs (see Figure 1). It realizes the segmentation of buildings that are susceptible to background interference in an end-to-end manner through scientifically combining deep convolutional operations and transposed convolutional operations. Through combining different CNNs, it improves the ability to encode building features, which is crucial for understanding the content of building images. In addition, with the support of skip connections and feature fusion, the decoding ability is improved when using features at the original scale in combination with the deeper encoded features adjacent to buildings. The overall structure of NPSFF-Net consists of four main parts: data pre-processing, pseudo-Siamese feature fusion encoding, double-stream feature fusion decoding, and building feature generation and prediction.
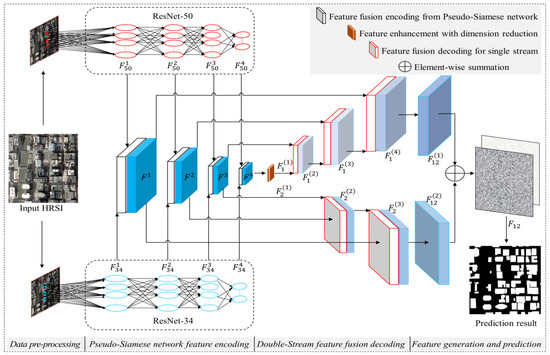
Figure 1.
The overall structure of NPSFF-Net.
Before training the building segmentation model, an HRSI that contains building and non-building features is first pre-processed, such that NPSFF-Net is able to read and process these image data. This part mainly includes three important steps. The first step involves cropping the building images and building labels in the network to a size of 512 × 512 and forming an image dataset and a label dataset, respectively, such that they satisfy the requirements of the network and the training platform regarding the size of the input images. The second step involves converting the image and label data to be inputted in a tensor format that can be understood by the neural network. The third step consists of converting the input data in tensor format into a floating-point data type and scaling the values between 0 and 1, in order to eliminate the differences in intensity between different input data and reduce the complexity of the subsequent operations.
We remark that, in the feature fusion encoding stage, it may be difficult for a single network to capture the detailed information of a building, and it may even be easy to lose the information of small targets. Therefore, we opted to draw on the design characteristics of a pseudo-Siamese network and innovatively propose the utilization of the convolutional features extracted from two different CNNs as the seed features for building feature encoding, instead of directly adopting the convolutional features extracted from the networks. For the feature decoding stage, we drew on the method of residual networks and designed a deep semantic feature fusion decoding algorithm to reduce the loss of details in the decoding process. In the building feature generation and prediction stage, our network generates discriminative features through fusing double-stream decoded features originating from different sizes, then realizes the accurate segmentation of buildings through the use of a cross-entropy loss function.
3.2. Pseudo-Siamese Feature Fusion Encoding
Most existing building segmentation methods have used a single neural network in the feature encoding stage to extract the deeper building features [28]. These encoding methods usually have a single structure including input, hidden, and output layers. Although computationally efficient, they may lose or even blur some small building targets or detail information when extracting features due to the use of a pooling layer. As shown in Figure 2, a Siamese network is obtained through splicing two networks with the same structure and shared weights, using two samples as inputs [29]. Pseudo-Siamese networks borrow some ideas from Siamese networks, in that they allow the use of different network structures for the inputs in order to better extract different features of the same data [30]. The different network structures allow them to acquire different information when the buildings are encoded. Inspired by this architecture, we designed a building image encoding network in the style of a pseudo-Siamese network in order to enable NPSFF-Net to segment more complex building images and to be able to apply it to a variety of new and unseen HRSIs.
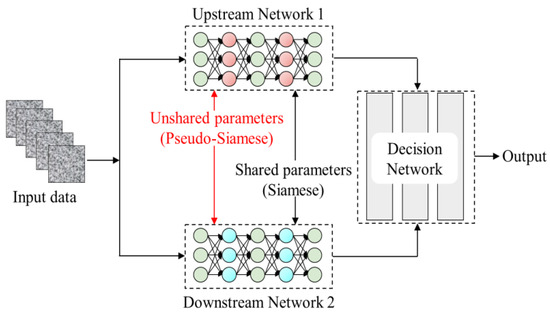
Figure 2.
Examples of Siamese and pseudo-Siamese architectures.
To reduce the computational complexity and improve the computational efficiency of NPSFF-Net while retaining the key features and local information of the building features in HRSIs as much as possible, we chose two classical CNNs: ResNet-34 and ResNet-50. The residual neural network (ResNet) architecture has excellent feature extraction capabilities, and its core idea is to solve the problems of gradient vanishing and gradient explosion that arise in deep networks through introducing the residual learning technique, as shown in Figure 3 [31]. In order to help NPSFF-Net converge with better segmentation performance faster, we adopted the transfer learning technique [32] to migrate the knowledge from the two pre-trained models for the extraction of building features, and obtained the convolutional features , , , and for the upstream part of ResNet-34 and , , , and for the downstream part of ResNet-50.
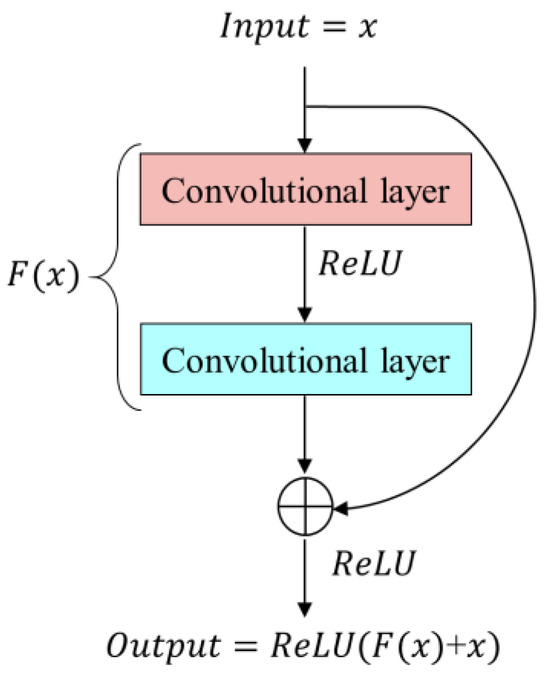
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of residual learning.
During the process of encoding the features extracted from the pseudo-Siamese network, we designed a fusion encoding algorithm, as shown in Figure 4. First, the convolutional features and (n = 1, 2, 3, 4), corresponding to the two networks, are spliced according to the channel dimensions, using the concatenation function to obtain the encoded feature . Then, after padding both sides of the matrix with 0 values, a 3 × 3 convolutional kernel is used to perform a convolution operation, which reduces the number the channels to that of . To avoid gradient loss, another convolution operation is then similarly performed; however, the number of channels is not adjusted. Specifically, after each convolution operation, batch normalization [33] and linear correction processes [34] are sequentially performed to prevent gradient explosion. Finally, the four encoded features , , , and are obtained.
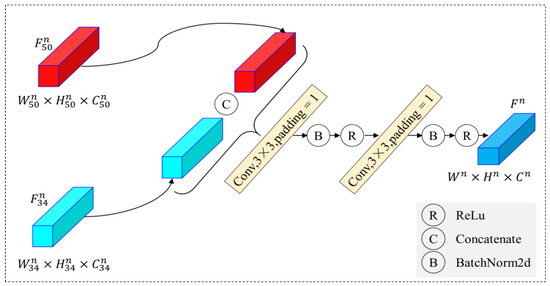
Figure 4.
Framework of feature fusion encoding.
3.3. Double-Stream Feature Fusion Decoding
To improve the decoding capability of NPSFF-Net for building features in HRSIs, we designed a feature enhancement module (FEM) containing a dimensionality reduction module and a layer-by-layer fusion decoding module for double-stream features at different scales.
Generally, the safest way to improve network performance is to increase the width and depth; however, this can lead to negative side effects. A deeper and wider network will often imply a huge number of parameters and, when the amount of data is very small, the trained network is easily overfitted. When a network is very deep, the phenomenon of gradient vanishing can easily occur. Additionally, among the four encoded features we obtained in the previous step, has the largest perceptual field and captures the richest semantic information of the building images. Accordingly, we constructed a feature enhancement module, the architecture of which is shown in Figure 5. The core objective of this module is to promote the expansion of the depth and width of NPSFF-Net, not only to significantly enhance the accuracy of the feature decoding process, but also to optimize the computational process in order to effectively reduce the computational complexity of NPSFF-Net and the consumption of resources.
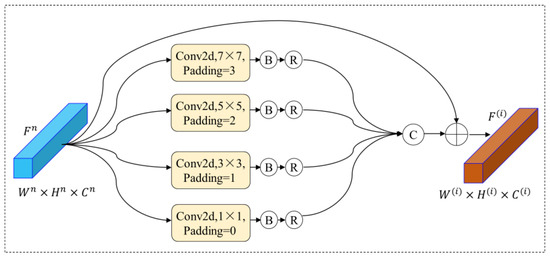
Figure 5.
Feature enhancement with dimension reduction.
First, the channel dimension of is reduced to one-quarter of the original size using four 1 × 1 convolutions, following which four filters of different sizes are used to perform a convolution operation, with padding of the corresponding boundaries. The four new features obtained with the same dimensions are concatenated in turn, according to the channel dimensions after the normalization and regularization process. Finally, the concatenated feature is summed with in an element-wise manner to obtain the enhanced encoded feature :
where denotes the concatenation function, denotes the ReLU function, denotes the batch normalization process, denotes the nth convolution operation, and denotes the element-wise summation of the feature maps.
The traditional methods for building feature decoding generally use up-sampling or transposed convolution and utilize only the highest layer of the encoded features at the beginning. Although such methods can achieve certain results, they also inevitably cause key information to be lost through the layer-wise decoding process. Therefore, we designed a double-stream feature fusion decoding module, as shown in Figure 6. First, the encoded feature is computed using transposed convolution to obtain with a doubled feature map size, and then is obtained by doubling the channel dimension of through two convolution layers:
where denotes the transposed convolution operation.
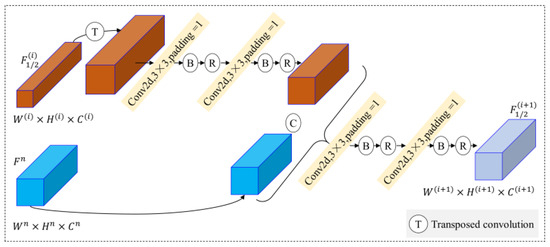
Figure 6.
Feature fusion decoding for a single stream.
Then, the features are concatenated with the encoded feature in the channel direction, and the fused decoded features are obtained by doubling the channel dimensions using two convolution layers. The amount of computation is reduced and gradient explosion is prevented through the inclusion of normalization and regularization processes after each convolution.
Finally, two decoded features are obtained, and , with the same size and dimensions.
3.4. Building Feature Generation and Prediction
This module was mainly designed to generate discriminative features of the input building images and predict the building features from these input images.
As shown in Figure 7, first, the channel dimension of the upstream decoded feature is reduced to one-quarter of the original size. Then, the size is augmented to double that of the original using transposed convolution, and, finally, the channel dimension is restored using 1 × 1 convolution to obtain . In a similar way, the feature is obtained from . Then, the features and are fused via element-wise summation to obtain the new feature . The dimension of the feature is reduced to half that of the original after transposed convolution in order to enlarge the dimension by a factor of one. Finally, after reducing the channel dimension twice using 1 × 1 convolution, it is inputted into the sigmoid function to generate the discriminative feature of the building image.
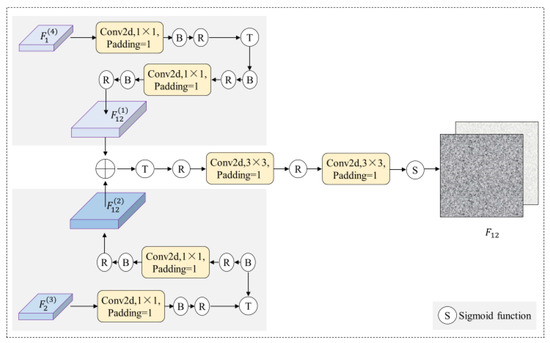
Figure 7.
Framework of discriminative feature generation.
For the prediction phase, we chose to employ the cross-entropy loss function [35] to quantify the inconsistency between the discriminated features and the ground truth. This function computes the cross-entropy value between the categorical probability distribution of each predicted pixel point and the true label, thus obtaining a loss function value that reflects the overall prediction error. This loss function value is then used to guide the training process of NPSFF-Net, namely, to minimize the prediction error.
where denotes the cross-entropy value, denotes building and non-building categories, denotes the predicted probability distribution, and denotes the distribution of true labels after one-hot coding.
In order to efficiently optimize the loss value, we employed adaptive moment estimation (Adam) [36]. The Adam algorithm combines the ideas of momentum and the root-mean-square propagation algorithm to accelerate convergence and dampen oscillations through dynamically adjusting the learning rate of each parameter, which enabled us to find the combination of parameters that would minimize the value in a more stable and faster way.
Through continuous iterative training, we gradually reduced the difference between the discriminative features and the true labels until NPSFF-Net reached a convergent state. Eventually, we obtained an optimal model that could accurately segment building regions, demonstrating excellent performance on the test dataset.
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Datasets
To validate the effectiveness and sophistication of NPSFF-Net for building segmentation in HRSIs, we selected two building segmentation datasets that have been widely used in existing research for segmentation and ablation experiments.
4.1.1. Satellite Dataset I
These data were collected from a variety of satellite sensors, such as QuickBird and the Worldview series [37]. The imagery covers cities in several regions of the world, showing mainly urban structures—ranging from high-rise buildings to small houses—in different geographic regions and climates. After manual labeling by the researchers, the final number of images used for this dataset was 204, each with a size of 512 × 512 and a resolution ranging from 0.3 to 2.5 m. As shown in Figure 8, to ensure that the model was not overfitted during training and to allow us to accurately assess the model’s performance on new data, we used the traditional division method of utilizing 70% of the data for training, 10% for validation, and 20% for testing.

Figure 8.
Examples from the Satellite Dataset I.
4.1.2. Massachusetts Buildings Dataset
This dataset was publicly released by the University of Toronto in 2013 and covers a total of 340 square kilometers of Boston, containing a variety of buildings in its urban area and suburbs [38]. It has 137 images for training, 4 for validation, and 10 for testing, each of which has a size of 1500 × 1500 and a resolution of 1 m. To facilitate comparison of the experimental results with those of other state-of-the-art algorithms, we directly adopted the original configuration ratio of the data. Furthermore, we set the overlap coefficient between images to 72 pixels within the allowable range of GPU memory and cropped the size to 512 × 512 in order to adapt to the model’s required image size and to increase the segmentation accuracy of the edge pixels. Example images from this dataset are shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9.
Examples from the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
We used five commonly used evaluation metrics to evaluate the performance of NPSFF-Net, which were calculated as follows.
4.2.1. IoU
4.2.2. Accuracy
4.2.3. Precision
4.2.4. Recall
4.2.5. F1-Score
In the equations above, TP denotes the number of pixels of buildings in all images that are correctly categorized as buildings, FP denotes the number of pixels that are incorrectly categorized as buildings, FN denotes the number of pixels that are incorrectly categorized as non-buildings, and TN denotes the number of pixels that are correctly categorized as non-buildings.
4.3. Experimental Conditions
4.3.1. Computing Environment
We developed the NPSFF-Net framework using the Python language within the PyTorch framework, and optimized the structure of the network using a combination of scientific computing tools such as Numpy and OpenCV. Iterative training was performed on the Windows 10 operating system for the two datasets, and a graphics card was utilized to accelerate the computation. Finally, the trained model was utilized to segment the test data. Table 1 describes the basic platform and key parameters of the experiments in detail.

Table 1.
Specific computing environment.
4.3.2. Hyperparameter Settings
Hyperparameters are parameters that need to be set and adjusted by human beings before or during the training of a model. Usually, reasonable setting of hyperparameters can improve the performance and effectiveness of a deep learning model. The batch size is the number of samples selected for each gradient update. A small batch size saves memory but leads to slow convergence, while a large batch size speeds up training but consumes memory. According to the model, dataset, and computational resources, we set 16 images as the input. In order to fully learn the data features and improve the performance, we set the number of training epochs to 100.
As the Adam algorithm has the advantages of adaptively adjusting the learning rate, being computationally efficient, and having a small memory requirement, we chose it to guide the model towards minimizing the loss function during training. The learning rate controls how much a model updates the weights in each iteration. A learning rate that is too large may cause the model to be unstable, while a learning rate that is too small may cause the model to converge too slowly. Therefore, we empirically set the learning rate to 0.0001 in order to help the model converge better. In addition, the weight decay factor also plays a crucial role in model training, and we empirically set the weight decay factor to 0.0005 to prevent overfitting while improving training stability.
4.4. Experimental Results
4.4.1. Satellite Dataset I
To demonstrate that NPSFF-Net has a certain degree of effectiveness and advancement in building segmentation, we selected eight existing algorithms (both traditional and advanced) to learn the data under the same conditions, and evaluated the evaluation metrics of the various methods on the test dataset, as shown in Table 2. It can be seen that the NPSFF-Net method had higher IoU, Accuracy, Recall, and F1-Score values than the eight comparative segmentation methods. This demonstrates that NPSFF-Net was able to segment building features more accurately than similar methods on a small-sample dataset. In addition, although the Precision obtained by NPSFF-Net was smaller than that obtained by methods (c) and (g), the Recall and F1-Score that it obtained were the highest values. This demonstrates that NPSFF-Net has better stability regarding building segmentation in HRSI datasets with fewer samples.

Table 2.
Results of different methods on Satellite Dataset I (%).
To graphically demonstrate the segmentation results, we selected five more typical images in the test dataset of Satellite Dataset I and utilized the models obtained with the nine different algorithms to segment the images; the results are shown in Figure 10. It can be seen that the nine methods had different degrees of error in the segmentation of buildings and non-buildings. The segmentation maps obtained with methods (b) and (f) had more red pixels, indicating that these methods recognized many real building features as non-building features. The plots obtained with methods (a), (d), (e), (g), and (h) had more green pixels, indicating that these methods recognized many non-building features as building features. The segmentation maps obtained with NPSFF-Net had a relatively small number of red or green pixels, although some were present. In addition, as we reduced the loss of building features in the encoding stage and enriched the detailed features of the buildings as much as possible in the decoding stage, our method showed better segmentation results than those of the state-of-the-art methods for all types of building layouts in the Satellite Dataset I. This illustrates the superiority of NPSFF-Net for segmenting buildings in small samples of HRSIs, from the point of view of a qualitative evaluation.
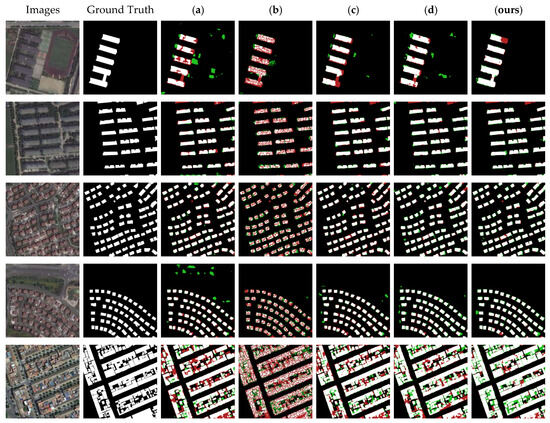
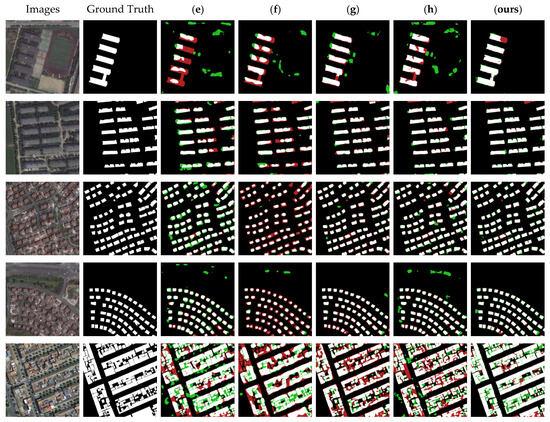
Figure 10.
Partial segmentation results for typical buildings with different methods on the Satellite Dataset I: (a) UNet, (b) SegNet, (c) DeepLabV3-Plus, (d) CE-Net, (e) SSFC-Net, (f) CFENet, (g) MaResU-Net, (h) MAFF-HRNet, and (ours) NPSFF-Net.
4.4.2. Massachusetts Buildings Dataset
Similarly, we recorded the evaluation metrics obtained with the eight different algorithms trained on the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset under the same experimental conditions and compared them with those of our method, as shown in Table 3. The Accuracy, IoU, Recall, and F1-Score obtained with NPSFF-Net were higher than those obtained with both the traditional and advanced methods. This quantitatively illustrates that NPSFF-Net was able to segment more accurate building features on the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset. In addition, although the Precision obtained by NPSFF-Net was relatively low, the Recall and F1-Score were higher. This indicates that NPSFF-Net also had high stability in terms of building segmentation on the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset.

Table 3.
Results of different methods on the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset.
Figure 11 shows the segmentation effect for five typical images in the test dataset. It can be seen that the nine methods still inevitably presented segmentation errors. There were relatively more red pixels in the maps obtained with methods (a), (b), (f), (g), and (h), which indicated that these methods recognized many real building features as non-building features. Meanwhile, the relatively large number of green pixels in the plots obtained with methods (c), (d), and (e) indicated that they recognized many non-building features as building features. The segmentation maps obtained with NPSFF-Net had a relatively small number of red and green pixels, although they were still present. As can be seen from the figure below, for both dense and sparse building clusters in HRSIs, our method obtained better segmentation results than other state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, for building targets of different sizes in the HRSIs, our segmentation results were also better than those of other methods. This also illustrates the superiority of segmenting buildings in the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset using our algorithm.
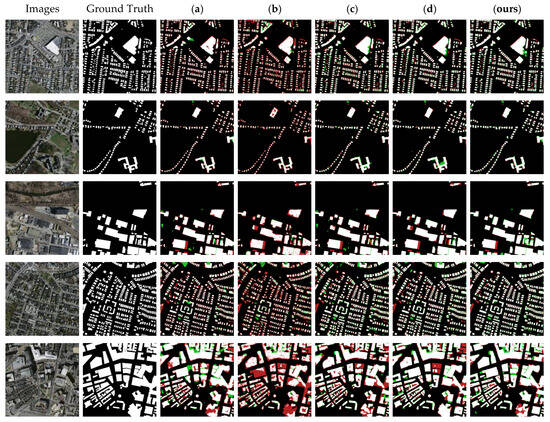
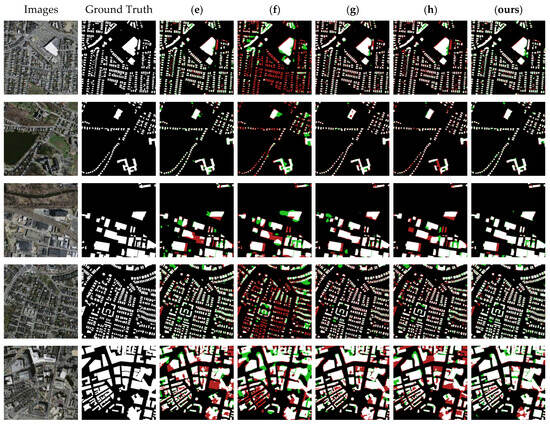
Figure 11.
Partial segmentation results for typical buildings with different methods on the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset: (a) UNet, (b) SegNet, (c) DeepLabV3-Plus, (d) CE-Net, (e) SSFC-Net, (f) CFENet, (g) MaResU-Net, (h) MAFF-HRNet, and (ours) NPSFF-Net.
4.5. Ablation Experiments
4.5.1. Encoding Networks
To further analyze the effectiveness of NPSFF-Net, in terms of the selection of encoding network, we chose three networks that are commonly used for building feature coding—namely MobileNet [46], ResNet-34, and ResNet-50—as the encoding networks of NPSFF-Net. In addition, no fusion algorithm was used for all three backbones in the process of coding the buildings, in order to highlight the advantages of our proposed fusion method in terms of its segmentation effect. The other structures were kept maximally unchanged. We obtained evaluation metrics for the test data under the same platform and training conditions, as shown in Figure 12. It can be seen that ResNet played a more significant role than MobileNet in the segmentation task. When fusing ResNet-34 and ResNet-50 as the backbone networks, the IoU and F1-Score values were higher than those of the individual networks alone. This indicates that our backbone network was superior in improving the accuracy of building segmentation, and our model was more stable in predicting the buildings.
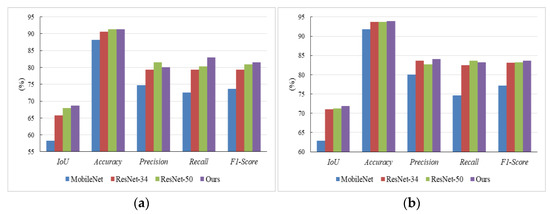
Figure 12.
The evaluation indices obtained using the different encoding networks on (a) the Satellite Dataset I and (b) the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset.
4.5.2. Attention Mechanisms
To further analyze the role of the feature enhancement module, we conducted comparative experiments in three aspects. The first related to whether it enhanced the segmentation performance. We removed the feature enhancement module from NPSFF-Net and obtained evaluation metrics for the test data with the trained model under the same conditions. Second, in order to determine whether it is more appropriate than the commonly used attention mechanism, we chose the CBAM as a state-of-the-art alternative to replace the FEM and obtained the evaluation metrics. Third, to discover whether it can improve the performance of downstream feature fusion decoding, we obtained the evaluation metrics after adding the FEM behind the downstream branch of NPSFF-Net. The results of the comparison are listed in Table 4, which reveals that the values obtained using the FEM were higher than those achieved without it; that is, the IoU, Accuracy, Recall, and F1-Score obtained when using the CBAM were lower than those obtained when using the FEM. Meanwhile, the use of the FEM for the two streams enhanced the segmentation performance, while the upstream enhancement lead to better segmentation.

Table 4.
The evaluation indices obtained with different attention mechanisms (%).
4.5.3. Decoding Patterns
To further verify the effectiveness and sophistication of NPSFF-Net’s double-stream design and the generation of discriminative features in the fusion decoding process, we designed two groups of comparative experiments.
In the first group, we obtained the evaluation metrics under single-stream fusion decoding in the test data. Specifically, the downstream feature fusion decoding part of NPSFF-Net was removed, and only the upstream part was used. The second group involved obtaining discriminative features through concatenation; that is, we used concatenation to replace the element-wise summation in NPSFF-Net for the generation of discriminative features. The results of the comparison are presented in Table 5, from which it can be seen that the values obtained with the double-stream design were higher than those achieved with the single-stream design in terms of the IoU, Recall, and F1-Score. In addition, the approach of generating discriminative features through element-wise summation outperformed the concatenation approach in terms of the IoU, Accuracy, Recall, and F1-Score. The results illustrate the effectiveness and sophistication of our decoding patterns.

Table 5.
The evaluation indices obtained with different decoding patterns (%).
4.5.4. Loss Functions
To further prove that the chosen loss function has a certain degree of sophistication, we chose three other commonly used loss functions to conduct comparative experiments.
Focal Loss introduces hyperparameters on the basis of the cross-entropy loss function, and is capable of increasing the weight of samples with fewer categories [47]. The dice coefficients of the SoftDiceLoss function [48] are insensitive to imbalances in category size. Meanwhile, the parameters α and β of the Tversky Loss function [49] can flexibly adjust the weights of the Precision and Recall. Thus, all three loss functions can effectively deal with the problem of imbalance in the number of pixels in the foreground and background. Therefore, we replaced the cross-entropy loss function with Focal Loss, SoftDiceLoss, or TverskyLoss, and utilized the trained models to segment and evaluate the test data. Figure 13 shows the obtained evaluation results, from which it can be seen that cross-entropy and SoftDiceLoss had relative advantages in terms of the IoU and Accuracy, but cross-entropy had a higher F1-Score. This indicates that the cross-entropy loss function is more suitable for NPSFF-Net in terms of segmentation accuracy and prediction stability.
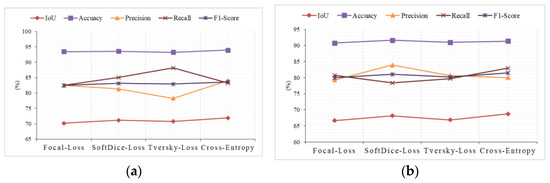
Figure 13.
The evaluation indices obtained with different loss functions on (a) the Satellite Dataset I and (b) the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset.
5. Discussion
5.1. Applicability
To investigate the applicability of NPSFF-Net, we validated its segmentation performance on a larger dataset. The Aerial Imagery Dataset [37] was publicly released by Wuhan University in 2018 and, as shown in Figure 14, its images contain not only dense building areas in urban centers but also buildings on the edges of urban areas, in suburbs, and even in rural areas, with a total of 4736 training images, 1036 validation images, and 2416 test images. The size of each image was 512 × 512. We did not change the training ratio of the data, in order to facilitate comparisons with other methods.
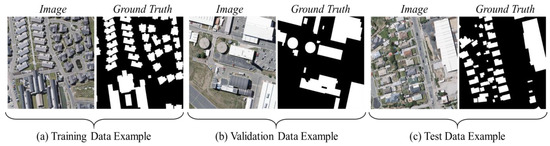
Figure 14.
Examples of the Aerial Imagery Dataset.
We list the evaluation metrics obtained with the different algorithms under the same experimental conditions in Table 6. Compared with the eight state-of-the-art methods, NPSFF-Net presented the highest IoU, Accuracy, and F1-Score. This revealed that our method has good segmentation performance even on datasets with a large number of samples.

Table 6.
Results of different methods on the Aerial Imagery Dataset (%).
Similarly, we show the segmentation results for five typical images from the test data in Figure 15. It can be seen that the segmentation performance was usually better when the amount of training data and the resolution of the remote sensing images were sufficiently large. All eight methods were able to segment most of the building features in the images, achieving results that were almost similar to the ground truth. Especially for methods (a) and (d), although the values of Precision and Recall were higher than those of NPSFF-Net, it can be seen from the actual segmentation that, for different building sizes and different building densities in HRSIs, the segmentation results of our method were slightly better.
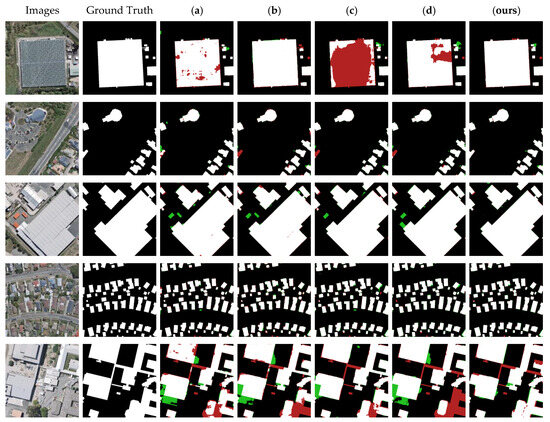
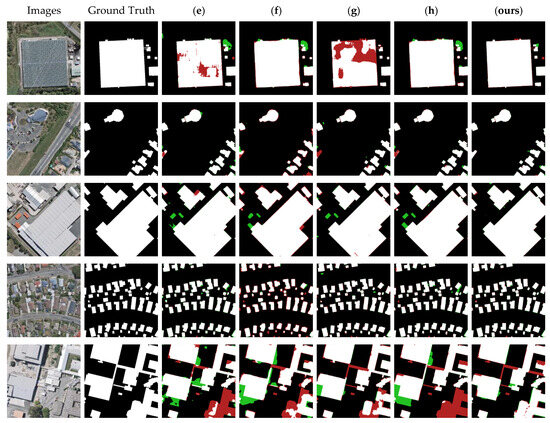
Figure 15.
Partial segmentation results for typical buildings with different methods on the Aerial Imagery Dataset: (a) UNet, (b) SegNet, (c) DeepLabV3-Plus, (d) CE-Net, (e) SSFC-Net, (f) CFENet, (g) MaResU-Net, (h) MAFF-HRNet, and (ours) NPSFF-Net.
5.2. Limitations
Despite NPSFF-Net obtaining IoU, Accuracy, and F1-Score values on three typical datasets that were consistently in the leading position, there was still a small gap between the values it obtained for Precision and Recall and those obtained with the state-of-the-art algorithms. This could mean that our method incorrectly predicts many pixels that are not in the building class as being in the building category and, at the same time, may not correctly identify many pixels that are in the building category. This problem is related to the model’s design and data class imbalances, among other things. When the numbers of building and non-building pixels in the training data are severely imbalanced, the model may be biased towards predicting classes with a high number of pixels, resulting in lower Precision and Recall for classes with a low number of pixels [50]. In the future, we plan to collect more high-resolution building data, as well as further optimizing the structure of the model, in an effort to improve the predictive values of all evaluation indicators.
6. Conclusions
This study discusses several challenges related to the task of building segmentation in HRSIs, including complex building backgrounds, diverse building morphologies, and non-building occlusions. Accordingly, we analyzed the advantages and limitations of traditional and deep learning techniques in the context of building segmentation. In particular, focusing on the shortcomings of the CNN-based encoder–decoder architecture—which tends to lose building details during feature processing and fails to adequately integrate contextual information in the decoding phase—we proposed a novel encoder–decoder network. First, we constructed an improved pseudo-Siamese network using ResNet-34 and ResNet-50, which allowed for the realization of building encoding through fusion encoding and reducing the information loss. Second, the multi-scale information of the deepest coded feature was enriched using the newly designed feature enhancement module. Then, a double-stream fusion decoding algorithm was designed, using skip connections and transposed convolutions to decode the building features and obtain discriminative features. Finally, the optimal model was obtained through calculating the cross-entropy loss and updating the gradient via backpropagation using the Adam optimizer. We conducted experiments on the Satellite Dataset I, the Massachusetts Buildings Dataset, and the Aerial Imagery Dataset, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of NPSFF-Net in various aspects. Next, we intend to consider the incorporation of a Transformer architecture, with the aim of further minimizing the information loss that may occur during the building feature extraction process, thus further enhancing the expressiveness of the model.
Author Contributions
N.G. and M.J.: methodology, software, and writing—original draft preparation; X.H., Z.S., W.Z., R.L. and J.L.: validation and investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Internal Parenting Program (grant number: 145AXL250004000X).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used for this study are publicly available. The Satellite Dataset I and the Aerial Imagery Dataset can be downloaded at https://study.rsgis.whu.edu.cn/pages/download/building_dataset.html (accessed on 5 April 2024). The Massachusetts Buildings Dataset can be downloaded at https://tianchi.aliyun.com/dataset/93425/ (accessed on 5 April 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, X.; Wen, D.; Li, J.; Qin, R. Multi-level monitoring of subtle urban changes for the megacities of China using high-resolution multi-view satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanjani, S.M.; Fathi, A.; Moradkhani, K. Grsnet: Gated residual supervision network for pixel-wise building segmentation in remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 4872–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Sui, H.; Hua, L.; Xu, C.; Ma, G.; Huang, W. Building extraction from VHR remote sensing imagery by combining an improved deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture and historical land use vector map. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 6595–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chanussot, J.; Hong, D.; Yao, J.; Gao, L. Progress and challenges in intelligent remote sensing satellite systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Matsushita, B.; Zhang, H. Improving building rooftop segmentation accuracy through the optimization of UNet basic elements and image foreground-background balance. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 201, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Kou, R.; Huang, F.; Yang, B.; Yang, T.; Gao, M. Techniques and Challenges of Image Segmentation: A Review. Electronics 2023, 12, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, H.; Deng, R.; Zhuang, S. A Comprehensive Survey of Optical Remote Sensing Image Segmentation Methods. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 46, 501–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargavi, K.; Jyothi, S. A survey on threshold based segmentation technique in image processing. Int. J. Innov. Res. Dev. 2014, 3, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, J. Improved region growing method for image segmentation of three-phase materials. Powder Technol. 2020, 368, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, R.; Radha, M. Edge detection techniques for image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2011, 3, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, X.; Ruan, K.; Hu, Z. Improved image segmentation method based on morphological reconstruction. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 19781–19793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, G. Deep Learning Segmentation and Classification for Urban Village Using a Worldview Satellite Image Based on U-Net. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atik, S.O.; Atik, M.E.; Ipbuker, C. Comparative research on different backbone architectures of DeepLabV3+ for building segmentation. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2022, 16, 024510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.D.; Alarabi, L.; Basalamah, S. An Encoder–Decoder Deep Learning Framework for Building Footprints Extraction from Aerial Imagery. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 48, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, P.; Yan, X. Deep Learning-Based Building Extraction from Remote Sensing Images: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2021, 14, 7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M. CNN-based encoder-decoder networks for salient object detection: A comprehensive review and recent advances. Inf. Sci. 2020, 546, 835–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fang, S.; Meng, X.; Li, R. Building extraction with vision transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Lv, W.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Huang, J. GAN-Based virtual-to-real image translation for urban scene semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 2020, 394, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Z.; Ji, S. Pixel transposed convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sediqi, K.M.; Lee, H.J. A Novel Upsampling and Context Convolution for Image Semantic Segmentation. Sensors 2021, 21, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Quan, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhu, D.; Yang, W. SED: Searching Enhanced Decoder with switchable skip connection for semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 149, 110196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Semantic Segmentation with Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas, A.A.; Tang, H. Channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 0–0. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Tu, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. A review of building detection from very high resolution optical remote sensing images. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1199–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D. Siamese neural networks: An overview. Artif. Neural Netw. 2021, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, K.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, G. Pseudo-Siamese Capsule Network for Aerial Remote Sensing Images Change Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, S.T.; Kalluri, H.K. Deep learning and transfer learning approaches for image classification. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 7, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Santurkar, S.; Tsipras, D.; Ilyas, A.; Madry, A. How does batch normalization help optimization? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, P.; Gribonval, R. An Embedding of ReLU Networks and an Analysis of Their Identifiability. Constr. Approx. 2022, 57, 853–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sabuncu, M. Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14126980. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully Convolutional Networks for Multisource Building Extraction from an Open Aerial and Satellite Imagery Data Set. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V. Machine Learning for Aerial Image Labeling. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J. CE-Net: Context Encoder Network for 2D Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, Q.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Z. Superpixel segmentation with fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13964–13973. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yan, X. A Context Feature Enhancement Network for Building Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Duan, C.; Su, J.; Zhang, C. Multistage attention ResU-Net for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Shen, L.; Huo, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Bi, F. MAFF-HRNet: Multi-Attention Feature Fusion HRNet for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:04861.2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhoti, J.; Kulharia, V.; Sanyal, A.; Golodetz, S.; Torr, P.; Dokania, P. Calibrating deep neural networks using focal loss. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 15288–15299. [Google Scholar]
- Nordström, M.; Hult, H.; Maki, A.; Löfman, F. Noisy Image Segmentation with Soft-Dice. arXiv 2023, arXiv:00801.2023. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, S.S.M.; Erdogmus, D.; Gholipour, A. Tversky loss function for image segmentation using 3D fully convolutional deep networks. In Machine Learning in Medical Imaging; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Qi, Q. Full Convolutional Neural Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion for the Class Imbalance Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).