Abstract
Currently, network real-time kinematic (NRTK) technology is one of the primary approaches used to achieve real-time dynamic high-precision positioning, and virtual reference station (VRS) technology, with its high accuracy and compatibility, has become the most important type of network RTK solution. The key to its successful implementation lies in correctly fixing integer ambiguities and extracting spatially correlated errors. This paper first introduces real-time data processing flow on the VRS server side. Subsequently, an improved ionosphere-weighted VRS approach is proposed based on single-differenced observations of GPS, GAL, and BDS. With the prerequisite of ensuring estimable integer properties of ambiguities, it directly estimates the single-differenced ionospheric delay and tropospheric delay between reference stations, reducing the double-differenced (DD) observation noise introduced by conventional models and accelerating the system initialization speed. Based on this, we provide an equation for generating virtual observations directly based on single-differenced atmospheric corrections without specifying the pivot satellite. This further simplifies the calculation process and enhances the efficiency of the solution. Using Australian CORS data for testing and analysis, and employing the approach proposed in this paper, the average initialization time on the server side was 40 epochs, and the average number of available satellites reached 23 (with an elevation greater than 20°). Two positioning modes, ‘Continuous’ (CONT) and ‘Instantaneous’ (INST), were employed to evaluate VRS user positioning accuracy, and the distance covered between the user and the master station was between 20 and 50 km. In CONT mode, the average positioning errors in the E/N/U directions were 0.67/0.82/1.98 cm, respectively, with an average success fixed rate of 98.76% (errors in all three directions were within 10 cm). In INST mode, the average positioning errors in the E/N/U directions were 1.29/1.29/2.13 cm, respectively, with an average success fixed rate of 89.56%. The experiments in this study demonstrate that the proposed approach facilitates efficient ambiguity resolution (AR) and atmospheric parameter extraction on the server side, thus enabling users to achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy instantly.
1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of communication technology, cloud servers, and multi-GNSS, a foundation has been established to offer users high-precision positioning services based on extensive GNSS data [1]. The proliferation of applications and devices, such as autonomous driving, unmanned delivery, and consumer-grade drones, has led to the widespread popularity of real-time high-precision positioning services [2]. Rapid, accurate, and stable positioning services have become crucial for realizing these applications. Traditional real-time kinematic (RTK) solutions require users to deploy reference stations, but under such a system, it is difficult to immediately obtain the precise coordinates of reference stations. Additionally, the estimation of spatial distance errors is complex, leading to a noticeable degradation in positioning accuracy as the distance increases [3,4]. Precise point positioning (PPP) technology enables centimeter-level positioning with only a single station, and there is a plethora of research currently being conducted on real-time PPP. However, due to its relatively slow convergence time and the necessity to acquire multiple external services, the implementation of real-time dynamic applications remains challenging [5,6]. PPP–RTK utilizes regional or wide-area reference stations to precisely estimate the necessary products for user positioning, ensuring the swift convergence of positioning results [7,8]. Nevertheless, the user end adopts an algorithm that is self-consistent with the server side, and the protocol has not yet been fully unified, thus making it difficult to ensure compatibility with existing RTK technology users. Network RTK technology effectively overcomes the shortcomings of the aforementioned real-time positioning methods as it features rapid convergence and high precision, and does not require users to set up reference stations themselves, thereby improving operating efficiency and reducing associated costs. As a result, the widespread adoption of this technology is evident across various aspects of modern living [9,10,11].
To improve user positioning accuracy, which is affected by increasing spatial correlation errors due to the growing distances between users and reference stations, ref. [12] proposed utilizing modeled ionospheric delays within a multi-reference station network to rapidly achieve AR for user stations. Based on that research, virtual reference station (VRS) technology was introduced [13]. VRS interpolates atmospheric correction between the master station and the user station according to the user’s location on the server side, and it also generates virtual observations. For users, since it is compatible with conventional RTK solutions, this method is commercially well promoted and currently stands as the most popular network RTK technology [14]. The Flachen Korrektur Parameter (FKP, in German) technology, introduced by Wübbena et al. in 1996 [15], models undifferenced distance-related errors within the network using interpolation algorithms and then transmits parameters to users through one-way communication. In contrast to the FKP, which establishes distance-related models on the server side, master–auxiliary concept (MAC) technology [16] conducts modeling on the user end. However, it involves the broadcasting of a substantial amount of information and is currently only applicable to Leica receivers. At present, due to limitations in communication protocol compatibility and the general applicability of user–receiver positioning algorithms, the popularity of MAC and FKP in practical applications is relatively low. Therefore, the network RTK algorithm proposed in this paper is a development of VRS.
In traditional VRS server-side baseline resolution, the typical procedure involves initially solving DD wide-lane (WL) ambiguities, which can be easily fixed with the wide-lane or Melbourne–Wübbena (MW) combination. Subsequently, the combination of ionosphere-free observables is used to compute tropospheric delay and DD ionosphere-free ambiguities. Finally, the solutions for the raw integer ambiguities are determined [17,18,19,20]. Due to the short wavelength of L1 in the narrow-line (NL) combination, which is unfavorable for fixing raw integer ambiguities, Tang et al. proposed an approach based on the classic three-step method, and this technique obtains the raw integer ambiguities using the linear relationship between WL and NL combinations [21,22,23]. Notably, the method does not require solving equations and offers a fast computation speed. Ionospheric delay is a significant factor affecting rapid AR for medium to long baselines [24,25]. However, the above approaches overlook the potential of ionospheric delay to serve as a constraint for AR. Consequently, investigations turned to using external ionospheric constraints to enhance model strength, thereby accelerating DD wide-lane AR. For NL ambiguities, a partial ambiguity resolution (PAR) method is employed, followed by the subsequent resolution of other parameters. In [26,27], the authors demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in resolving long baseline cases.
It is apparent that the aforementioned methods for AR between reference stations predominantly employ the classical three-step strategy of wide-lane, ionosphere-free, and narrow-lane combinations. Ionospheric delay, a crucial parameter in VRS, is eliminated during the AR process and re-obtained through geometry-free combination after ambiguities are fixed. Unfortunately, they neglected the influence of the ionospheric delay second-order term and introduced combined observation noise, thus to some extent disrupting the physicochemical characteristics of the ionospheric short-term smooth changes. Uncombined single-baseline solutions can, to some extent, address the above issues. In [28,29], the authors pointed out that the DD ionospheric delay within a regional range can be considered as zero. To further account for the uncertainty of ionospheric delay, different prior variances were set for baselines according to different lengths in the stochastic model, and thus, the ionosphere-weighted model was introduced. Experimental results demonstrated that the utilization of the ionosphere-weighted model can reduce convergence time and accelerate the initialization.
The DD observation model can eliminate errors associated with the receiver and satellites. However, the correlation between these observations is troublesome for quality control and identifying the source of outliers, and it may amplify observational noise [30]. Compared to the DD model, the single-differenced (SD) model offers a simpler variance–covariance matrix. Furthermore, due to the retention of receiver errors, the model strength can be enhanced through the analysis of bias characteristics [31,32,33,34]. Processing multi-system GNSS data has become the trend for future development as the combination of multi-GNSS observations allows for a more robust geometric observation structure, thereby significantly reducing the adverse effects of atmospheric errors. The expansion of satellite constellations and observation data is proving beneficial for rapid and accurate AR. Moreover, it facilitates precise modeling of ionospheric and tropospheric delays in local regions, thereby further improving positioning accuracy [35]. Building upon this, a single-differenced ionosphere-weighted RTK method designed for multi-GNSS was proposed [36,37,38,39,40]. By employing this algorithm, the initialization time and positioning accuracy are improved across single-frequency, dual-frequency, and multi-frequency scenarios.
In addressing the limitations of the previously mentioned approach, this paper proposes the SD ionosphere-weighted VRS server-side method based on GPS, GAL, and BDS observations. The approach utilizes SD uncombined observations and applies rank deficiency theory to guarantee the estimable integer properties of ambiguities, while directly estimating the SD ionospheric delay and the relative zenith tropospheric wet delay between receivers. By directly obtaining the SD atmospheric correction required for spatial error interpolation, it effectively reduces DD observation noise and renders it unnecessary to specify the pivot satellite, thus further simplifying the calculation process and improving the solution efficiency. Therefore, the method is more conducive to real-time processing.
This paper begins with a concise overview of the network RTK server-side algorithm workflow, detailing the construction of the ionosphere-weighted full-rank equation, the establishment of the stochastic model, and the validation of ambiguity resolution. Subsequently, we propose the single-differenced virtual observation generation equation, which eliminates the need for selecting a pivot satellite. Finally, we evaluate both the server-side service performance and the user-side positioning performance using data from the AUSCORS network.
2. Materials and Methods
This section will focus on the ionosphere-weighted network RTK (VRS) server-side method based on single-differenced observations of GPS, GAL, and BDS. We will present the mathematical model, stochastic model, and data processing strategy for estimating DD ambiguity, SD ionospheric delay, and undifferenced (UD) relative wet tropospheric delay between reference stations.
2.1. Brief Review of VRS Technology Principles and Server-Side Data Processing Flows
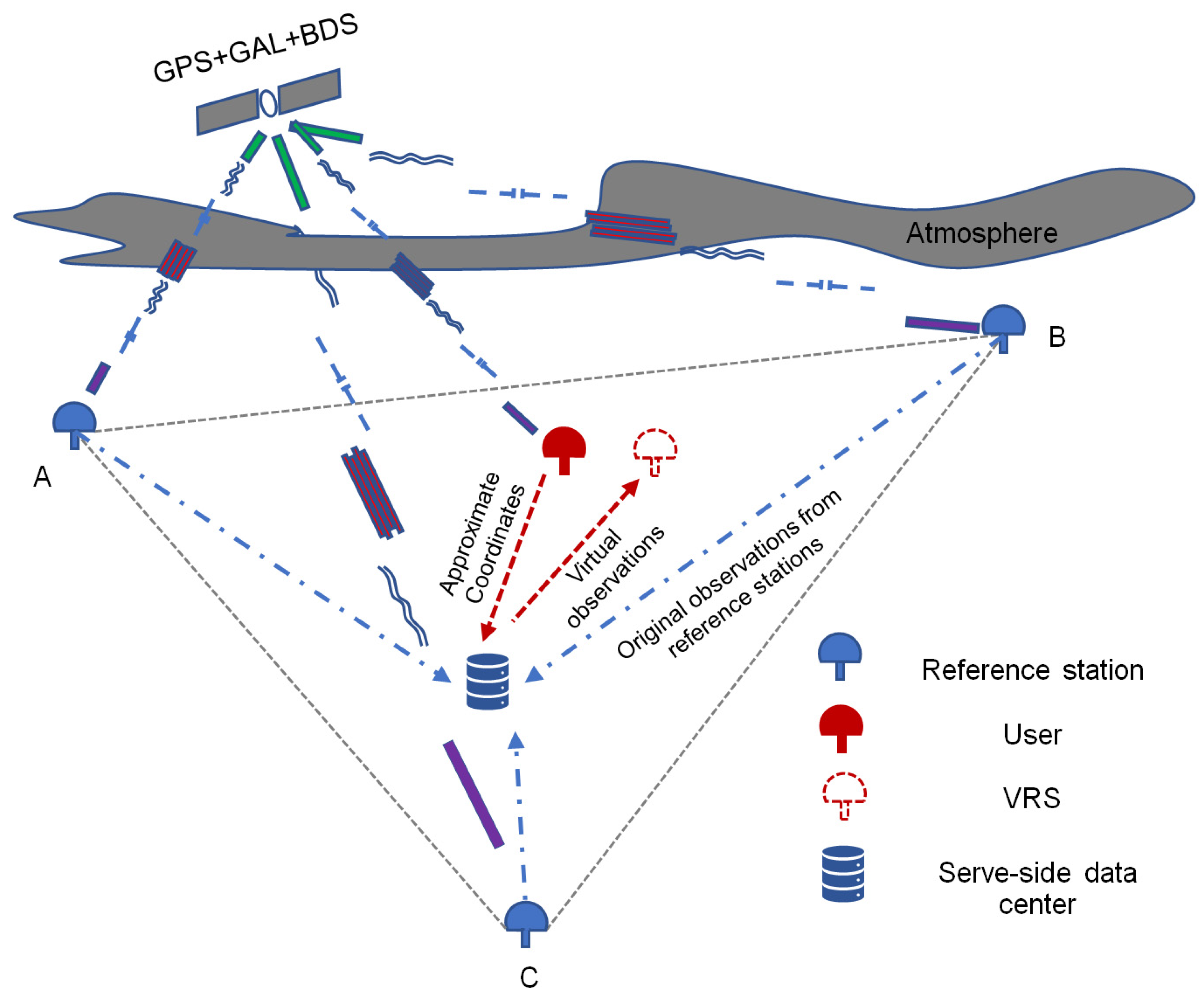
As illustrated in Figure 1, the fundamental principle of VRS can be succinctly summarized: the server side collects the original observation data from each reference station in the regional area and resolves the baselines. Upon receiving the user’s positioning request and approximate coordinates, the server generates virtual observations and transmits them to the user. Finally, the user can obtain coordinates by processing a short baseline RTK, thereby achieving rapid and reliable high-precision positioning [13].
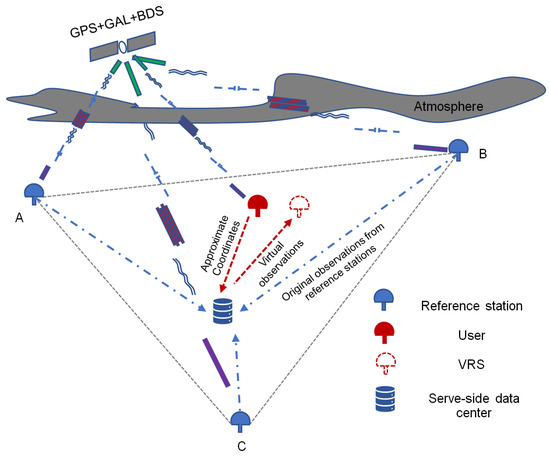
Figure 1.
Principle of network RTK algorithm based on real-time data stream.
2.2. GNSS Observation Equations
The reference station is a continuously operating station equipped with a stable antenna, offering favorable observation conditions and long-term high-quality observation data. Its precise coordinates can be obtained from PPP/PPP-AR. Consequently, coordinate estimation becomes unnecessary during the baseline solving process on the server side. Assuming receiver tracks satellite at frequency with carrier phase and code observations at the same time, where , , and represent the number of receivers, observed satellites, and the frequency, respectively, the undifferenced observed-minus-computed observation equations of GNSS can be expressed as [37,41]:
In Table 1, we have provided a clearer and more intuitive explanation of the symbol system.

Table 1.
Symbol systems and definitions.
2.3. Full-Rank Single-Differenced Ionosphere-Weighted Functional Model
Utilizing the SD operation between receivers eliminates errors associated with satellites, such as residual orbit errors, satellite clock errors, and satellite phase and code biases. However, the equations become rank deficient after the SD operation (as shown in Equation (2)), and the rank deficiency is equal to the number of linear combinations of column vectors in the design matrix that produce a zero vector [42].
In Equation (2), subscripts represent two reference stations, where 1 indicates the reference receiver in this paper. The term represent the receiver clock bias between stations for each system, denotes the zenith relative wet tropospheric delay, represents the ionospheric slant delay between receivers on the first frequency of each system, and are the relative code/phase biases. represents the SD ambiguity. In Equation (2), there are three types of rank deficiency. By applying the S-basis theory [36,37] and introducing pseudo-observations, the rank-deficient parameters in the equation can be eliminated, resulting in a full-rank functional model.
The first type of rank deficiency arises from the relationships among receiver clock bias , code bias , and phase bias , with a rank deficiency of 1. The code bias on the first frequency of each system is selected as the datum.
The second type of rank deficiency can be identified when the matrix columns for the between-receiver phase bias and ambiguity parameters are considered, with a rank deficiency of . The between-receiver ambiguity of the first (or pivot) satellite at each frequency is chosen as the datum.
The last type of rank deficiency arises from the relationships between-receiver clock bias, code/phase bias, and ionospheric delays. The rank deficiency can be eliminated by introducing additional ionospheric pseudo-observations.
Through the resolution of rank deficiency using the three aforementioned steps, the full-rank single-differenced ionosphere-weighted model can be expressed as:
In Equation (3), there have been changes in the estimable form of unknown parameters, and their detailed expression is provided in Table 2. Since the estimated ambiguity parameters are still in DD form, the integer properties of ambiguities have been preserved.

Table 2.
Estimable form of ionosphere-weighted model.
2.4. Stochastic Model
In addition to the functional model, the stochastic model plays a crucial role in the least square adjustment process of GNSS. This model describes the statistical characteristics of the variance–covariance form of observations, and a reasonable selection of the stochastic model is a prerequisite for high-precision parameter estimation. In this subsection, we introduce the stochastic model used in this paper. According to the law of error propagation, the variance–covariance matrix of single-system SD code/phase observations is given first, as shown in Equation (4).
Within Equation (4), represents the variance–covariance (VCV) matrix of single-system SD observations, and are the VCV matrix of the original code and undifferenced phase observations in the zenith direction, where and are the a priori code and phase standard deviations (STD) of the undifferenced observations. The ratio of STD between the pseudo-range and carrier phase observations for the same GNSS system are considered to be 1:100. In this paper, we assume that GPS, Galileo, and BeiDou (MEO) observations have the same measurement accuracy, and the STDs are set to 0.3 m and 3 mm, respectively, with a scale factor . For BeiDou’s IGSO and GEO satellites, the a priori STD scale factors are set to 1.5 and 2 [43,44], respectively. is the between-receiver difference matrix with a dimension of . represents the VCV matrix of the observations based on the weighted function of elevation and can be expressed in the form of Equation (5), where is the elevation corresponding to satellite in system :
The variance–covariance matrix of the single-system ionospheric pseudo-observations can be expressed as:
where is the prior empirical standard deviation of the ionosphere, set to in this paper, and represents the ionospheric variance–covariance matrix based on the weighted function of elevation and distance, as shown in Equation (7), where represents the baseline length in kilometers.
Therefore, the statistical model of the single-system ionospheric weighted RTK method can be expressed as , and the variance–covariance matrix of the ionospheric weighted model for combined GPS, GAL, and BDS is , as shown in Equation (8):
2.5. Ambiguity Closure Check
In this paper, a single-baseline solution mode is employed at the server-side. To ensure the correctness of parameter estimation, an ambiguity closure check is implemented. Following the completion of AR, in addition to passing the bootstrapped success rate and ratio test, each baseline necessitates that the DD ambiguity closure be zero for any closed reference station network composed of three or more connected reference stations. The expression is shown in Equation (9).
2.6. Virtual Observation Generation
Within our approach, the generated Delaunay triangles serve as the minimum solving units. After the closure check confirms the validity of DD ambiguities, the process of interpolation of spatial correlated errors begins. Considering that the distance between receivers in network RTK solutions typically does not exceed 200 km, and the maximum ranging error when using broadcast ephemeris for relative positioning does not surpass 5 cm [20], along with the availability of ultra-rapid ephemeris, interpolation is generally applied just for ionospheric delay and tropospheric delay in scenarios with small inter-station distances. Commonly employed methods including the linear interpolation model (LIM) [13], the linear combination model (LCM) [45], the distance-based linear interpolation model (DIM) [17], and the modified combined bias interpolation (MCBI) [23,46]. The performance distinctions among these methods are negligible. In the experiments conducted in this paper, the LIM method was selected for interpolation.
In contrast to the traditional approach of using corrections in DD form to generate VRS virtual observations, this study adopted a novel approach by directly utilizing corrections in SD form. It eliminates the necessity to select the pivot satellite, further simplifying the calculation process and improving the solution efficiency. The expression is given by Equation (10).
In Equation (10), the master reference station is denoted as , and the virtual reference station (VRS) is denoted as . and represent the interpolated ionospheric delay and tropospheric delay, respectively. denotes orbit errors, and the meanings of other terms are specified in Equation (10).
3. Results
In this section, tests and analyses were conducted separately on the network RTK solution at the server side and user end. Firstly, the experiment setup was as described previously. Subsequently, we performed a statistical analysis on receiver-related biases, ADOP/PDOP/VDOP, the initialization time, and the available number of satellites for each subnet on the server side. Finally, an analysis of the user-end solution was carried out, including the ionospheric interpolation accuracy and the user positioning accuracy.
3.1. GNSS Data Collection and Processing Strategy
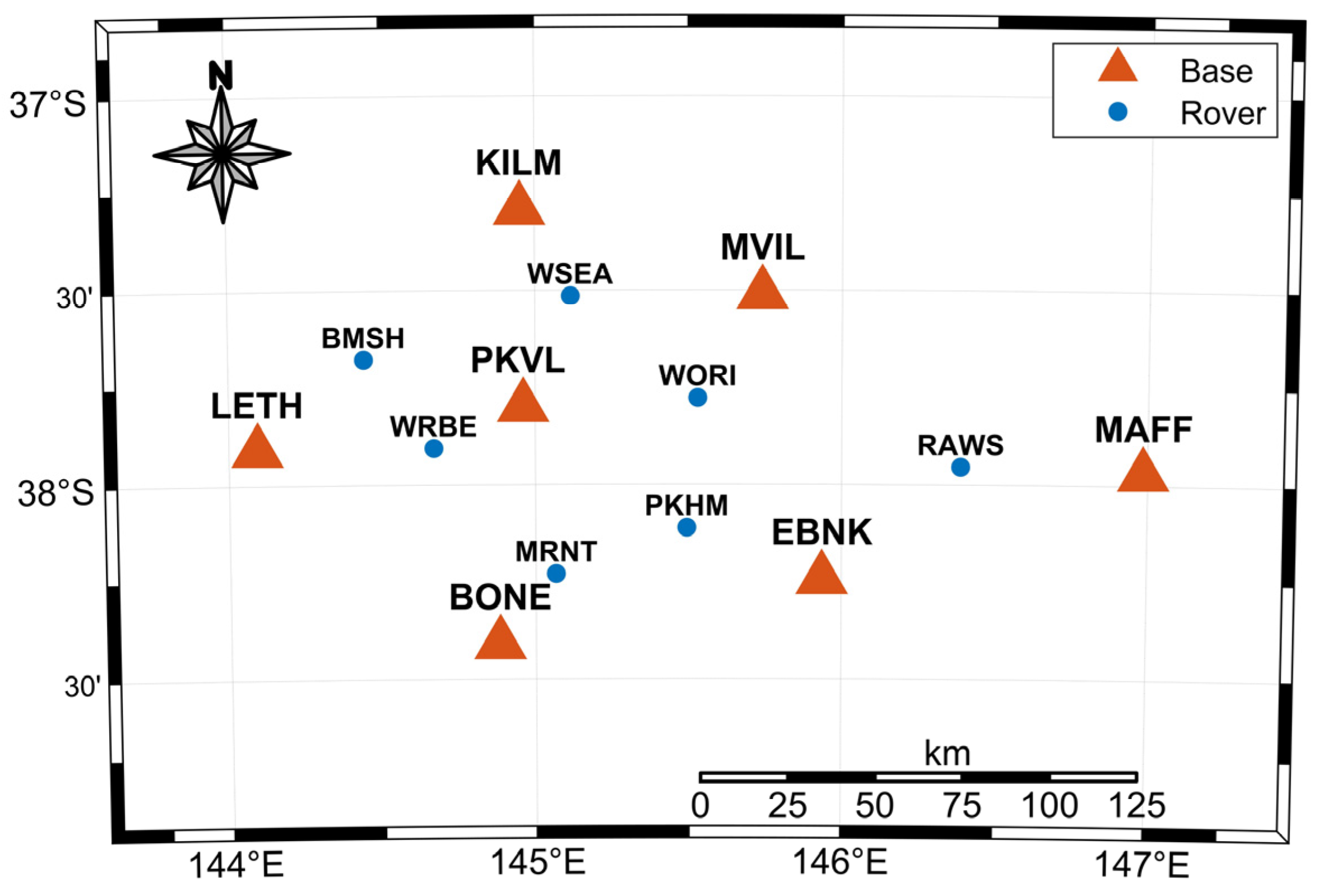
To validate the correctness and applicability of the algorithm proposed in this paper, CORS data from Australia on DOY 339, 2023 (5 December 2023), were chosen. A total of 14 continuously operating reference stations were selected, with seven stations serving as reference stations to estimate various parameters in the regional area and provide VRS services. In addition, seven other stations were used as user stations for positioning tests. The reference network comprised 12 baselines, with lengths ranging from 50 to 120 km and an average inter-station spacing of 82.32 km. The baseline information is detailed in Table 3, and the distribution of reference stations is depicted in Figure 2, where red triangles represent reference stations and blue dots represent user stations.

Table 3.
Baseline information.
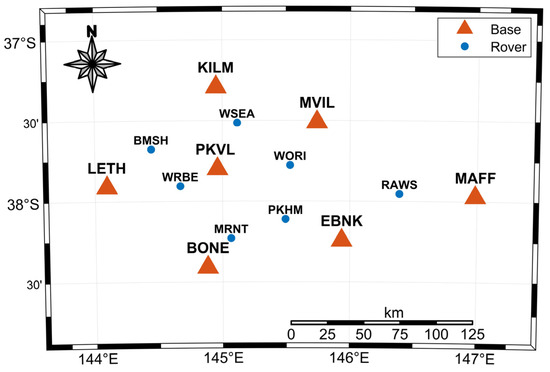
Figure 2.
The distribution map of stations. Red triangles indicate reference stations; blue dots represent user stations.
In Table 4, we present the processing strategies for both the server side and user end. Throughout the processing, a Kalman filter serves as the parameter estimator. A bootstrapped success rate threshold of 99.99% is employed to filter float solutions of ambiguities. Furthermore, the least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment (LAMBDA) method is utilized to achieve integer ambiguity resolution (IAR). It is crucial, during partial ambiguity resolution, to successfully fix a sufficient number of ambiguities (over 60% of float ambiguities in the current epoch) to ensure correct parameter estimation [47], thus guaranteeing the accuracy of user positioning solutions. Additionally, triangles are taken as the minimum computation unit during the solution processing. Interpolation and virtual observation generation for the respective satellites are performed only when passing the closure test, as shown in Equation (9).

Table 4.
Data processing strategy used in the study.
3.2. Server-Side Test Results and Analysis
Ambiguity dilution of precision (ADOP) is an index that represents the strength of the ambiguity resolution model, proposed by Teunissen [48], and has been widely adopted. ADOP can describe the intrinsic precision characteristics of ambiguity parameters [49] and is also a measure of the volume of the ambiguity confidence ellipsoid [50]. The formula is given by Equation (11):
where is the dimension of the ambiguity, is the variance–covariance matrix of the ambiguity in cycles, and represents the determinant of the matrix. Since ADOP is a measure of the ambiguity search space, a smaller ADOP value indicates a higher success rate and reliability of ambiguities. Typically, it is considered that when ADOP is less than 0.12 cycles, the corresponding ambiguity success rate is greater than 99.9% [49].
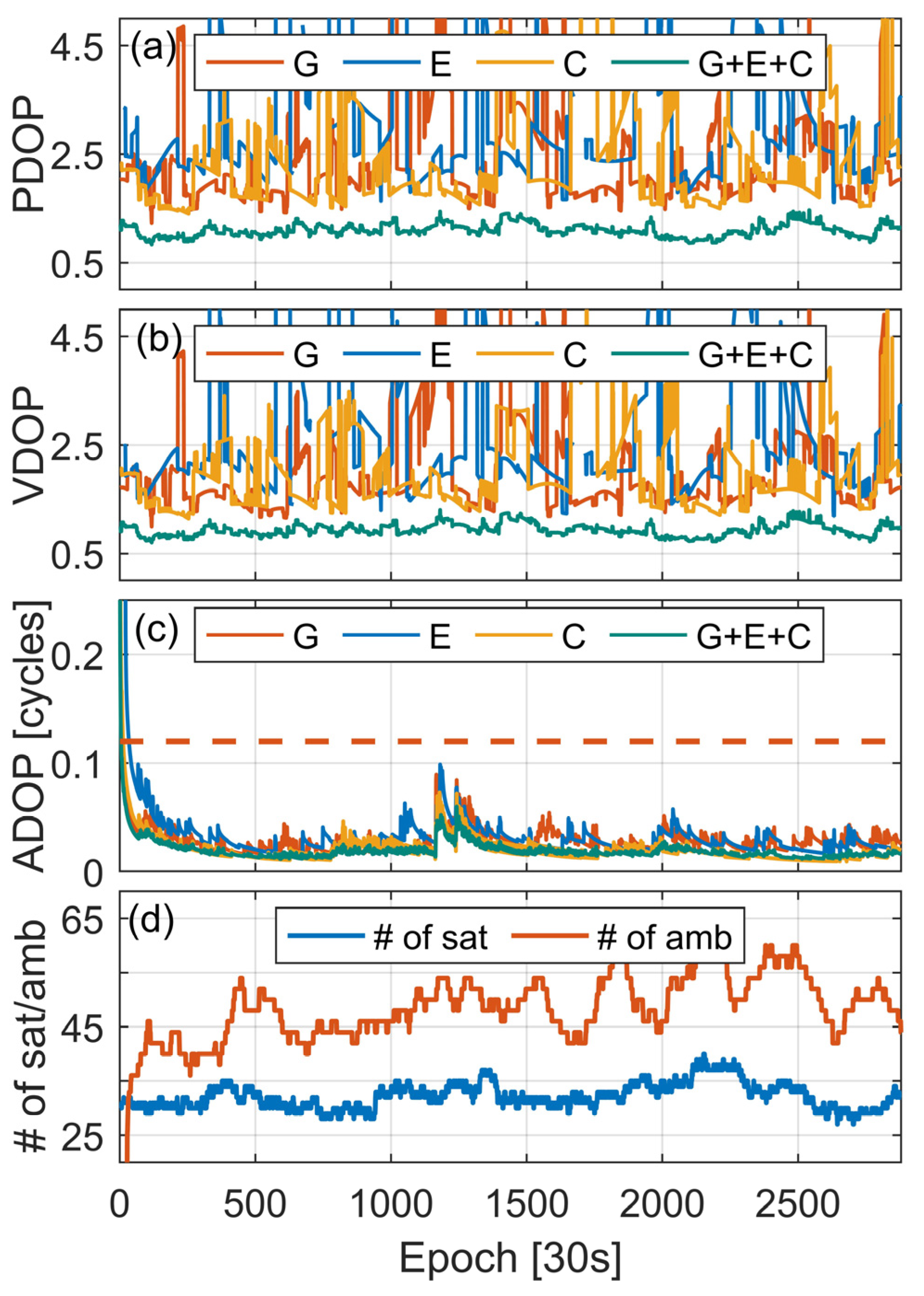
An adequate quantity of satellites contributes to the estimation of various correction terms, and a favorable satellite geometry accelerates convergence time, reducing the impact of multipath effects to some extent. PDOP and VDOP are crucial values for measuring the precision of satellite positioning and the geometric strength of observations. From Figure 3a,b, it can be seen that, in comparison to occasional significant fluctuations in the PDOP and VDOP of a single system, the PDOP and VDOP of the combined G+E+C system are more stable, consistently stabilizing below the value of 1. This indicates that the three systems combined can achieve a better distribution of satellites, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of positioning. Figure 3c plots the time series of ADOP. It can be observed that after ADOP gradually converges and falls below the threshold of 0.12 cycles, the convergence and fluctuation behaviors of ADOP for a single system and the three systems combined are similar, with the latter converging the fastest, followed by BDS, GPS, and GAL. The initial convergence speed may be related to the number of available satellites and the accuracy of the remaining parameters estimated by each system. The available number of satellites and the number of fixed ambiguities for the combined G+E+C system are presented in Figure 3d, with an average number of satellites of 32 and an average number of fixed ambiguities of 49, which can provide sufficient correction terms for VRS observation generation.
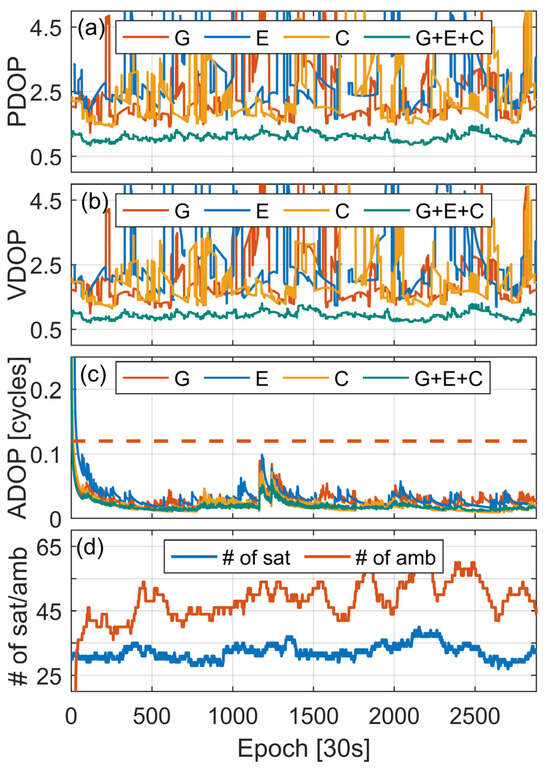
Figure 3.
DOP and # of satellites for BL06 on DOY 339, 2023. (a) PDOP, (b) VDOP, (c) ADOP; the threshold of 0.12 cycles is delineated by the presence of the orange dashed line. (d) The blue line represents the total # of G+E+C satellites, while the red line denotes the # of fixed ambiguities.
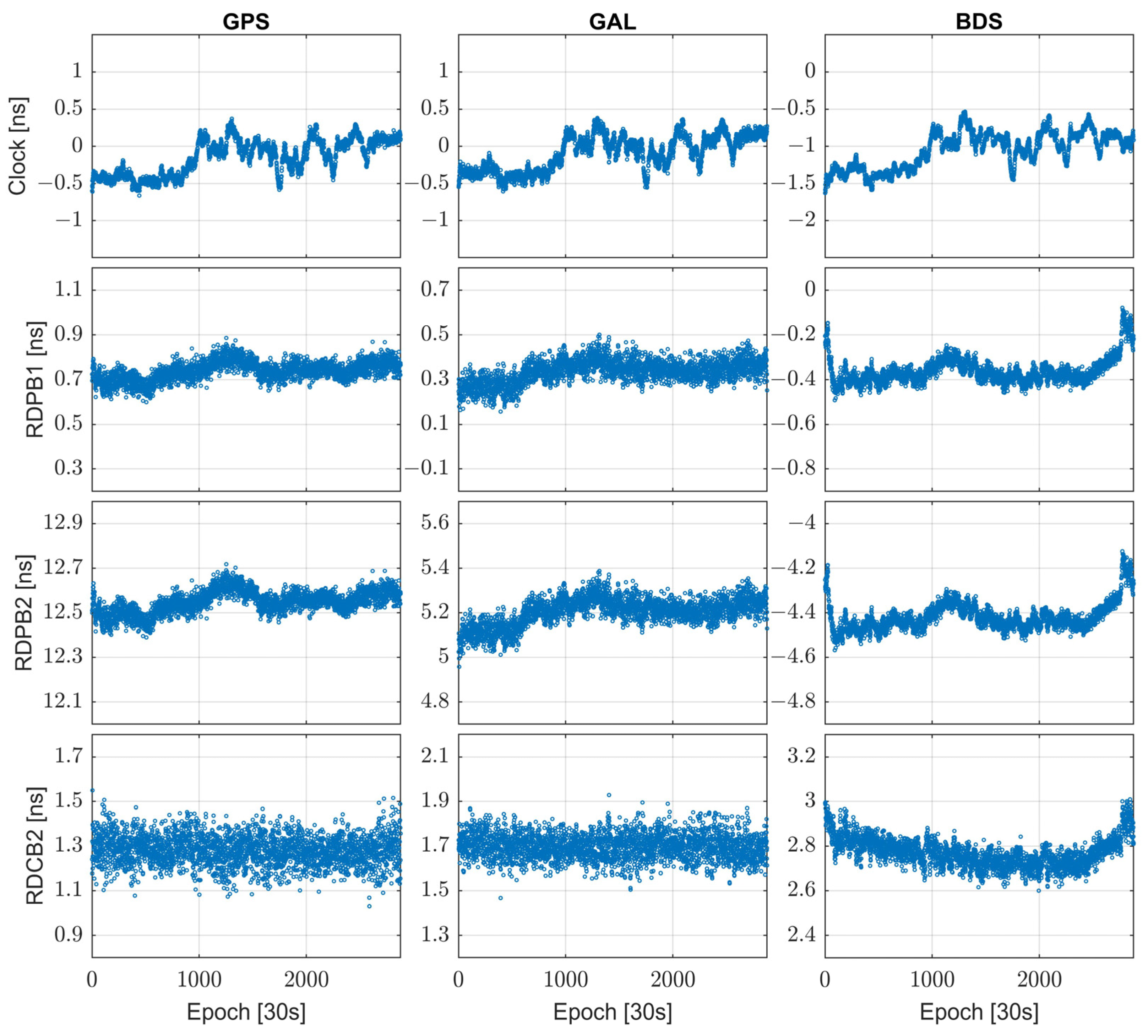
Differently from the DD observation model, which can eliminate all errors related to the satellites and receivers, the SD model requires the estimation of the between-receiver relative clock bias and the receiver code and phase biases (RDCB and RDPB). Figure 4 illustrates the biases parameters related to the receiver for baseline BL06 in each system. From the figure, it can be observed that the receiver clock bias for the three systems combined exhibits similar variations but does not show a clear regular pattern. In the experiment, we treat the RDPB and RDCB parameters as white noise for estimation. Rows 2–4 in Figure 4 depict the time series of phase bias (GPS L1 and L2, BDS B1I and B3I, GAL E1 and E5b) and code biases (GPS L2, BDS B3I, GAL E5b), respectively, with the code bias on the first frequency serving as the datum and not plotted. It can be seen from the figure that the RDPB and RDCB parameters change during the day, confirming reports from other studies [34]. Therefore, it is inappropriate to treat the RDCB and RDPB parameters as time-invariant, even though this could further enhance the model’s strength. Conversely, treating the two types of bias parameters as white noise for estimation reflects, to some extent, their temporal changes but weakens the model’s strength. This may lead to discontinuous and inconsistent ambiguity parameters, affecting the extraction of parameters such as ionospheric delay and tropospheric delay. Existing studies also indicate that receiver phase bias and code bias exhibit time-varying characteristics, and related experiments have demonstrated that the changes in the two types of biases may be closely related to environmental temperature [31,47,51]. In recent years, some researchers have proposed modeling RDCB and RDPB through the establishment of a random-walk model or a temperature-related model [32,51], achieving a certain degree of progress.
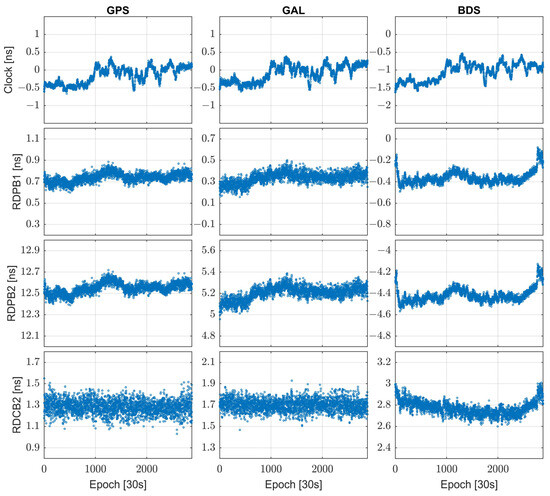
Figure 4.
Time series of differential clock bias, differential phase bias, and differential code bias between receivers for baseline BL06 on DOY 339, 2023. Columns represent GPS, Galileo, and BeiDou receiver bias terms, respectively, with mean and standard deviation values annotated in nanoseconds (ns).
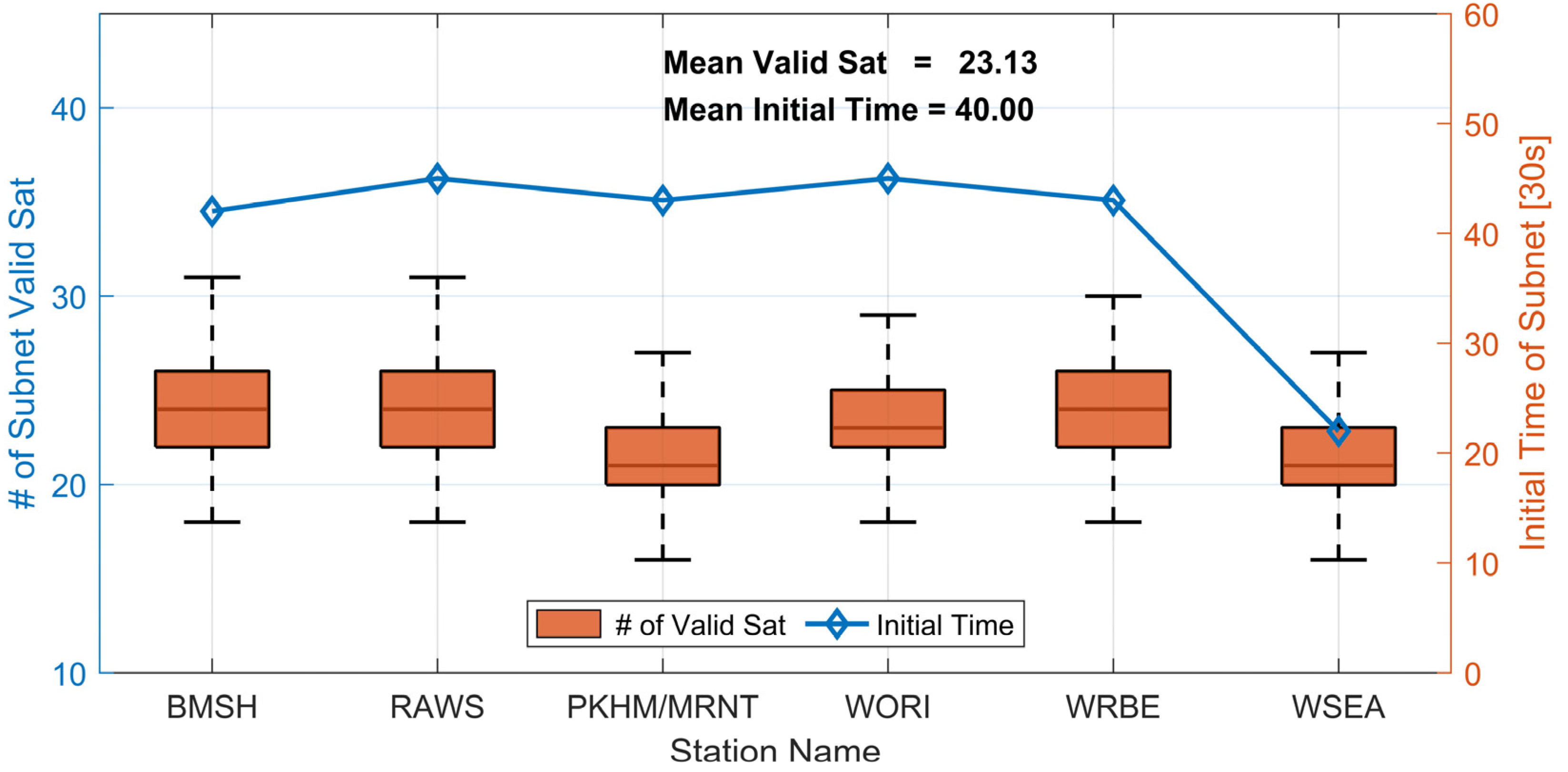
In contrast to the favorable observation conditions with open views at the reference station, network RTK technology users may be in “urban canyon” areas where observation conditions are less optimal. Therefore, the goal of the server side is to provide users with as many available satellite observations as possible. A sufficient number of available satellites is a crucial factor in achieving high-precision user positioning, especially in challenging urban environments. The initialization time of each subnet is another vital indicator for evaluating the server’s solution performance. Figure 5 illustrates the initialization time and average number of available satellites for seven subnets, each restarting every four hours. To simulate real-world user scenarios and ensure the accuracy and availability of the provided service, the conditions for a successful subnet initialization are as follows:
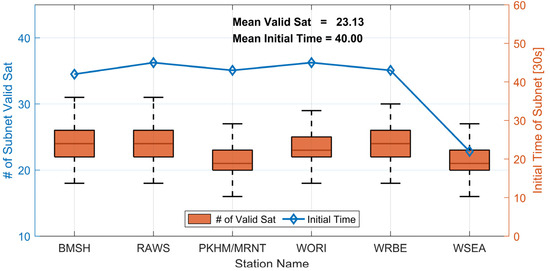
Figure 5.
Availability of satellites and initialization time on DOY 339, 2023. The orange boxplot depicts the quantity of satellites satisfying initialization conditions and with elevation above 20 degrees. The blue line denotes the average initialization time, conducted at four-hour intervals. The x-axis is annotated with the user station names representing their respective subnetworks.
- Float ambiguities pass bootstrapped success rate test with threshold greater than 99.99%;
- Ambiguities successfully fixed, and the integer DD ambiguity closure error is strictly zero for each subnet;
- The number of available satellites is greater than 15, and the VRS observations of the three systems are all available.
The available satellites are counted under the above successful initialization conditions, and just considering satellites with an elevation greater than 20°. In Figure 5, the orange boxplots illustrate the number of available satellites for each subnet, while the blue line represents the average initialization time. The graph reveals that the average number of available satellites reaches 23 (with an elevation greater than 20°) for each subnet. This ensures that the service fulfills the high-precision positioning requirements of users. The average initialization time is approximately 40 epochs. Moreover, combining analysis with Figure 2 and Table 3 allows us to infer that the subnet initialization time correlates with the baseline length. Longer baselines tend to result in extended initialization time.
3.3. User-End Test Results and Analysis
The previous subsection analyzed the solution process and performance on the server side. This subsection will focus on testing and analyzing user ionospheric interpolation accuracy and positioning performance in different positioning modes.
The primary focus of this paper is to present the network RTK solution method based on single-differenced observations. We chose the LIM interpolation method to compute ionospheric and tropospheric corrections for VRS.
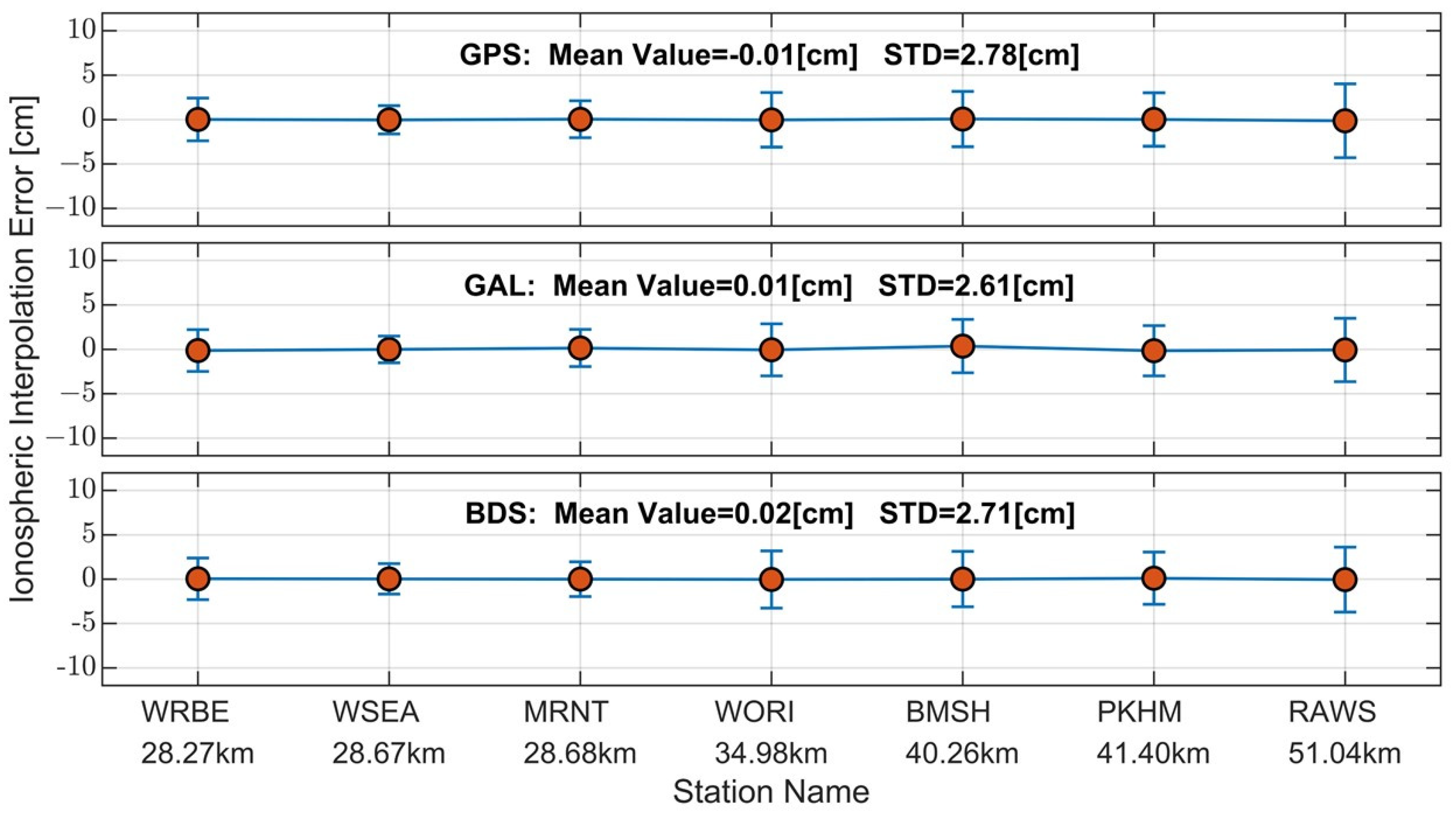
Table 5 provides statistics on ionospheric interpolation accuracy at different user stations, and Figure 6 illustrates the error bar of ionospheric interpolation for seven user stations. In the accuracy assessment process, utilizing the raw observations from the user station and its corresponding master reference station for RTK processing allows the calculation of ionospheric delay as a truth. From the figure and table, it can be observed that the mean values of ionospheric interpolation for GPS, Galileo, and BeiDou are close to 0. As the distance between the user station and the master reference station increases, the spatial correlation of ionospheric delay gradually decreases, and the corresponding STD increases. Relevant studies indicate that 5 cm is a critical threshold for ionospheric error. When it is less than 5 cm, the fixed rate of ambiguities can approach 100%, maintaining centimeter-level positioning accuracy [52]. In this test, the distance between the user station and the master reference station covers 20–50 km, with STD ranging from 1.50 to 4.16 cm, and a mean STD near 2.7 cm. When the user is 50 km away from the master reference station (user station RAWS), the corresponding results for the three systems indicate that centimeter-level positioning can be achieved within this baseline length range.

Table 5.
Ionospheric interpolation result of subnets.
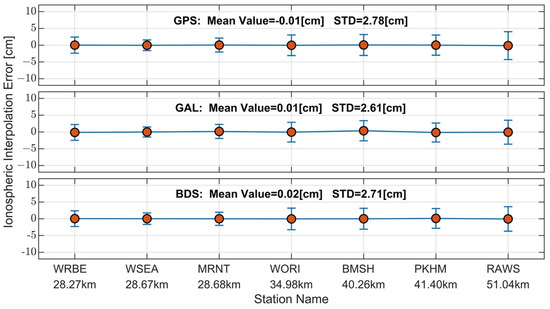
Figure 6.
Error bar of ionospheric interpolation errors at user stations on DOY 339, 2023: GPS (top row), GAL (middle row), and BDS (bottom row); the x-axis represents the names of user stations and their distances to the nearest master reference station.
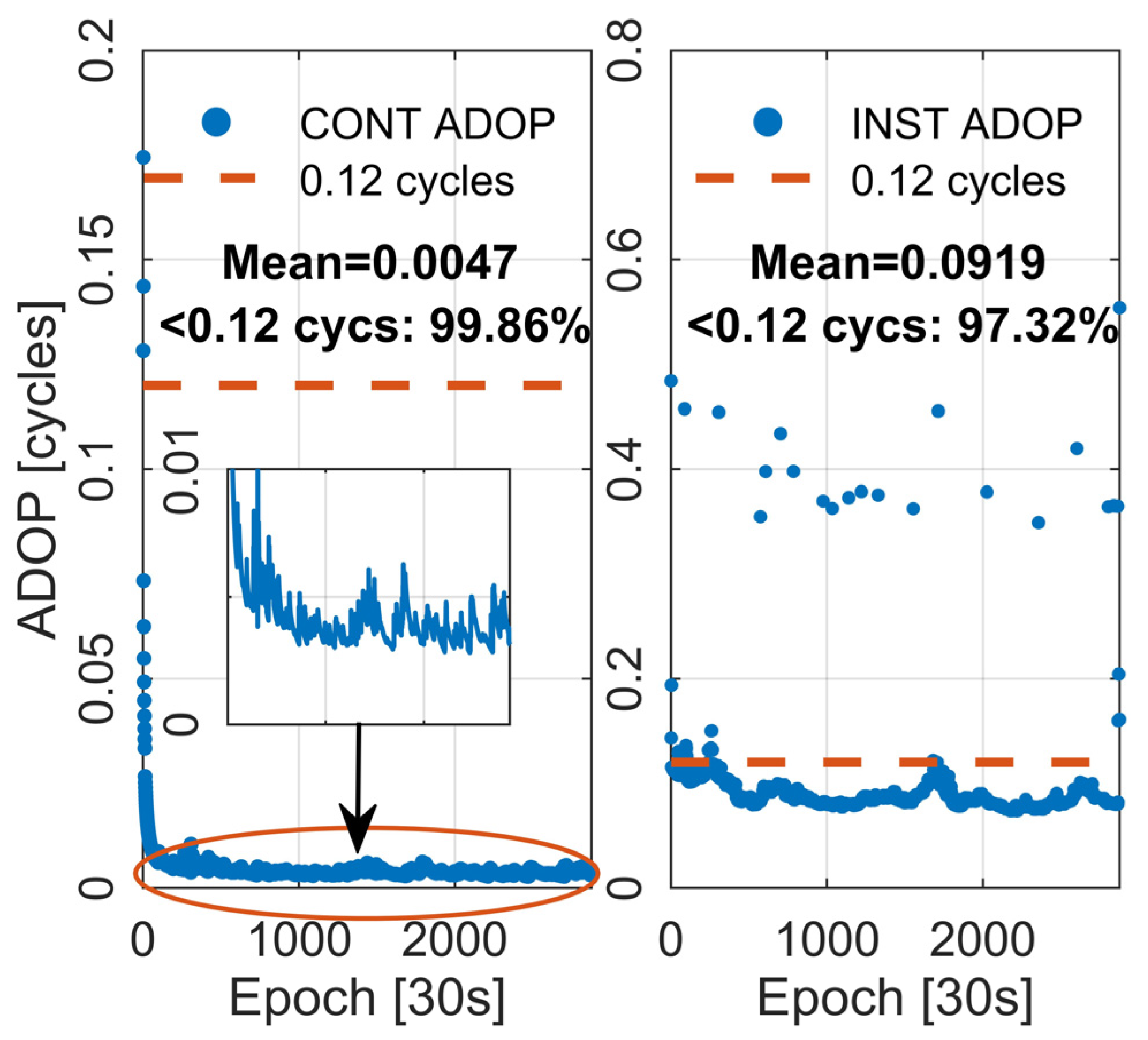
Short baseline RTK technology can achieve AR within seconds, providing high-precision positioning services by efficiently eliminating atmospheric errors. At this point, using the between-receiver SD model can eliminate the majority of atmospheric errors, especially ionospheric delays, making ambiguities less affected by system errors, thereby enhancing the geometric strength of ambiguity [53]. Ionospheric errors play a crucial role in ambiguity resolution, directly impacting AR and positioning performance. Rapid AR can only be achieved with the accurate correction of ionospheric errors. ADOP was mentioned as a theoretical indicator reflecting AR performance. In this section, we evaluate the theoretical performance of AR using VRS observations corrected for atmospheric effects. Two different processing modes were employed in the experiment, ‘Instantaneous’ (INST) and ‘Continuous’ (CONT). INST mode refers to a single-epoch mode with no parameter transfer between epochs, while CONT mode only transfers float ambiguities and zenith tropospheric wet delays between epochs. Figure 7 depicts the ADOP of the user station WSEA. The left subplot is in CONT mode, while the right subplot is in INST mode. It is evident from the figure that in CONT mode, after ADOP convergence, it consistently maintains at a low level due to the transfer of float ambiguities between epochs, keeping the variance low. The mean of ADOP is 0.0047 cycles, with epochs below 0.12 cycles reaching 99.86%. Theoretically, this favors rapid AR. Under INST mode, where ambiguities are not transferred, the mean of ADOP is 0.0919 cycles, and epochs below 0.12 cycles still reach 97.32%. This indicates that VRS virtual observations generated by the server side showed high accuracy, providing favorable conditions for AR.
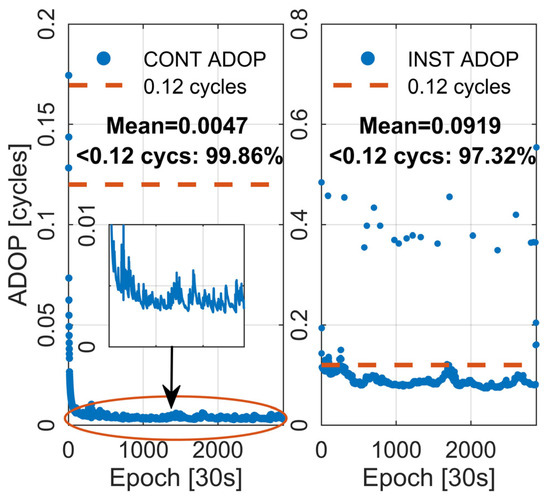
Figure 7.
The time series of ADOP at user station WSEA on DOY 339, 2023. The left panel depicts the “Continuous” mode, while the right panel illustrates the “Instantaneous” mode.
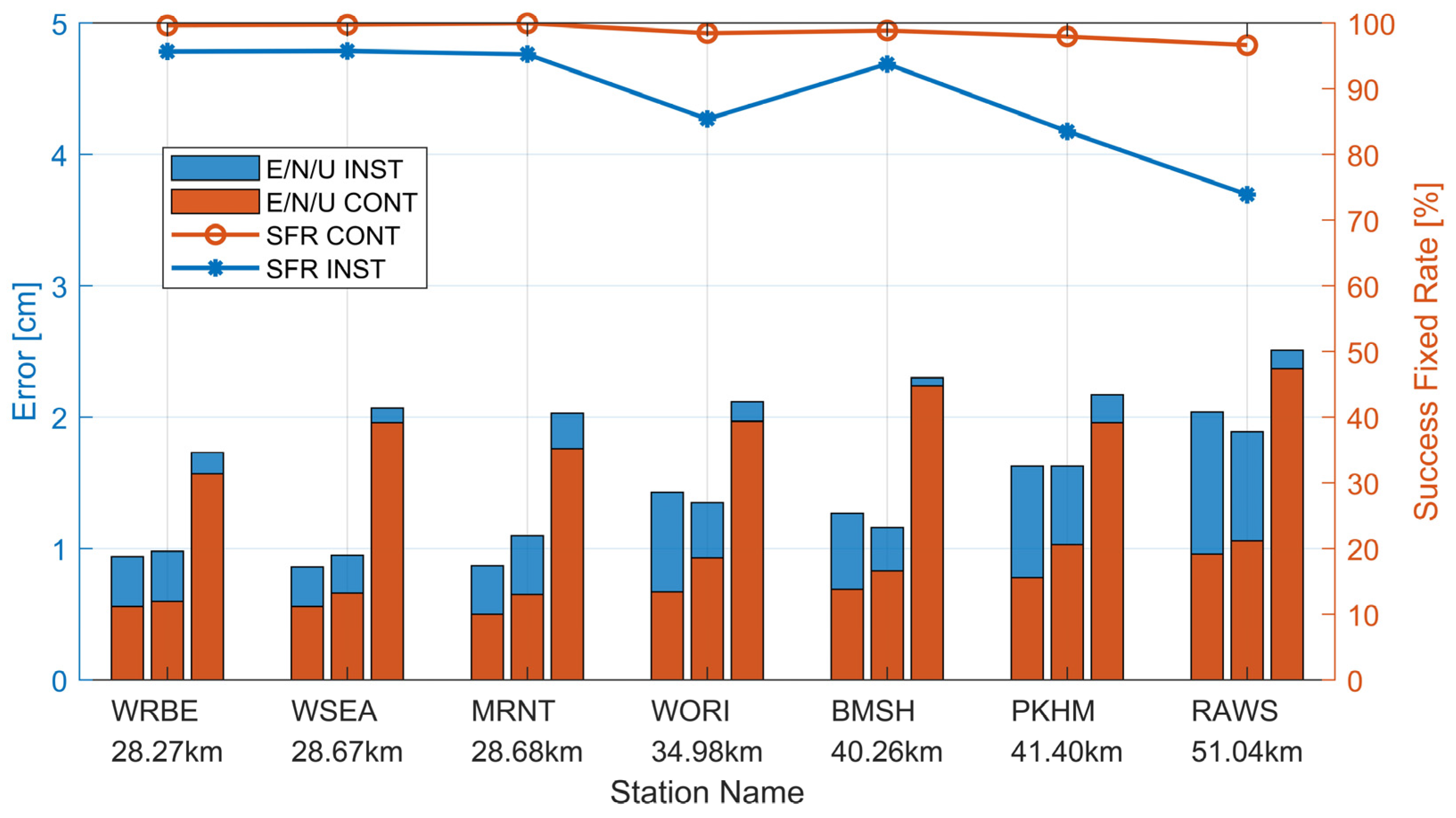
Although ADOP and bootstrapped success rate (BSSR) are widely used as theoretical indicators of GNSS AR performance, they cannot fully represent the actual performance of AR. To more accurately assess the performance of AR, it is necessary to use positional accuracy assessments and improvements in the time taken to fix ambiguities to verify the final performance of AR. During user positioning, two modes were used, ‘Instantaneous’ and ‘Continuous’, and the positioning accuracy of both modes was analyzed. Unlike reference station estimating, ionospheric and tropospheric delays are no longer estimated. Figure 8 and Table 6, respectively, illustrate the positioning results for seven user stations. In CONT mode, the average positioning accuracy in the E/N/U directions is 0.67/0.82/1.98 cm, respectively, with an average success fixed rate of 98.76%. In INST mode (single-epoch solution), the average positioning error in the E/N/U directions is 1.29/1.29/2.13 cm, respectively, with an average success fixed rate of 89.56%. From the Figure 9, it can be observed that using VRS observations generated by the server side enables centimeter-level high-precision positioning. When using CONT mode and the user is within 30 km of the master station, the horizontal accuracy is better than 1 cm and the vertical accuracy is better than 2 cm. When the user station is 30–50 km away from the master station, the horizontal accuracy is greater than 1.5 cm and the vertical accuracy is still greater than 2.5 cm. To more accurately evaluate the AR performance, this paper defines the AR success fixed rate as follows: passing ratio and BSSR tests, and errors in the E/N/U directions smaller than 10 cm. According to the results, the AR success fixed rate in CONT mode is higher than that in INST mode. The success fixed rate in INST mode reflects the single-epoch AR ability, directly indicating the accuracy of ionospheric and tropospheric interpolation and virtual observations. From the statistical results, the overall success fixed rate decreases as the distance from the master reference station increases. The success fixed rate for user station WORI is smaller than that for user station BMSH. The main reason is that its ionospheric interpolation accuracy is slightly lower than that of BMSH, indicating that ionospheric interpolation accuracy significantly affects positioning accuracy and AR success fixed rate.
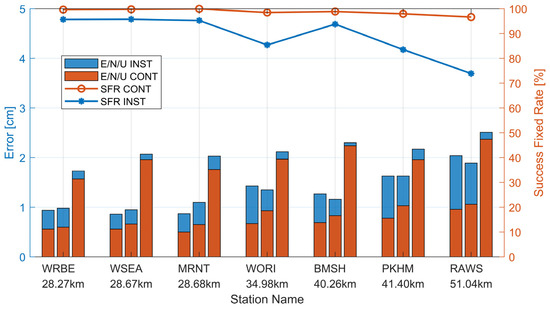
Figure 8.
Statistical analysis of user station positioning results on DOY 339, 2023. The red bar chart illustrates the positioning accuracy in “CONT” mode, while the blue bar chart represents the positioning accuracy in “INST” mode. The red line depicts the success fixed rate in “CONT” mode, whereas the blue line illustrates the success fixed rate in “INST” mode.

Table 6.
User station results overview.
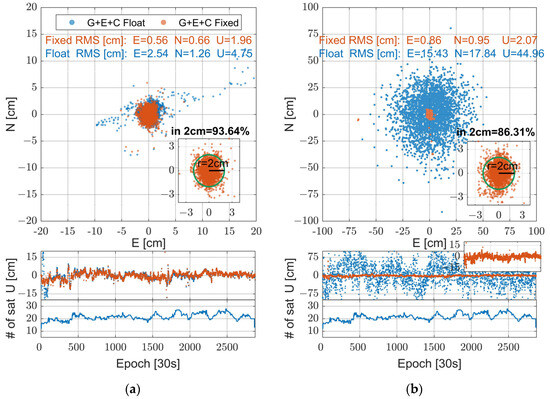
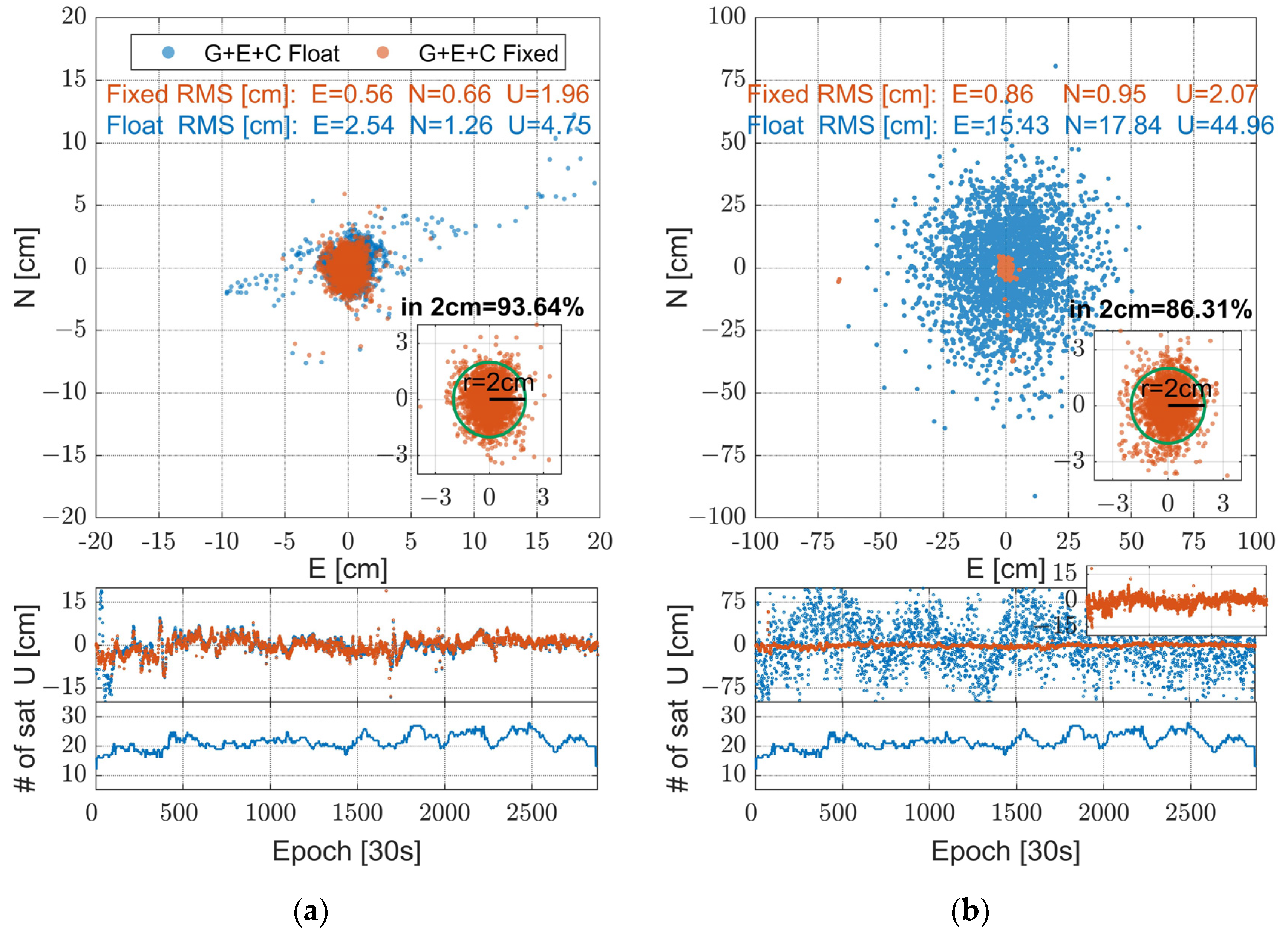
Figure 9.
Error distribution in user station WSEA (east/north/up directions) on DOY 339, 2023. The left subfigure (a) illustrates the error distribution in “CONT” mode, while the right subfigure (b) depicts the error distribution in “INST” mode.
The error distribution characteristics under the two user positioning modes will now be further analyzed by taking WSEA as an example. In the error distribution depicted in Figure 9, it is evident that the most notable distinction between the two positioning modes lies in the error distribution of the float solution. Owing to the transmission of float ambiguities between epochs in CONT mode, its float positioning results are considerably better than the float positioning accuracy of INST mode, accompanied by an apparent process of position convergence. Additionally, when considering the proportion of horizontal positioning error within 2 cm, the percentages for the two modes are 93.64% and 86.31%, respectively, with CONT mode maintaining superiority over INST mode.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the utilization of the single-differenced ionosphere-weighted network RTK algorithm based on GPS, GAL, and BDS proposed in this paper enables rapid initialization on the server side and achieves fast centimeter-level positioning accuracy at the user end.
This paper has proposed a SD ionosphere-weighted network RTK function model based on GPS, GAL, and BDS. While ensuring the estimability of integer ambiguity, the model directly estimates the single-differenced ionospheric delay and tropospheric delay between stations, reducing the noise in DD observations. Benefiting from the direct estimation of atmospheric delay in SD form between receivers, there is no need to further determine the pivot satellite apart from selecting the initial datum satellite for ambiguities. This is beneficial for real-time filtering and virtual observation generating.
Firstly, the PDOP/VDOP/ADOP and the number of available satellites were statistically analyzed. The results suggest that utilizing multi-system observations ensures a uniform distribution of satellite geometry, enhancing the success fixed rate of AR. Subsequently, an analysis of the receiver biases for one of the baselines was conducted. Finally, we tested the initialization and solution status of each subnet. The statistical results indicate that each subnet has an average initialization time of 40 epochs and an average number of available satellites of 23 (with an elevation greater than 20 degrees), meeting users’ positioning requirements.
Two positioning modes, CONT and INST, were employed to assess the positioning accuracy of VRS users. The distance between the user station and the master station ranged from 20 to 50 km, aligning with practical application scenarios. In CONT mode, the average positioning accuracy in the E/N/U directions was 0.67/0.82/1.98 cm, respectively, with an average success fixed rate of 98.76%. In INST mode (single-epoch solution), the average positioning accuracy in the E/N/U directions was 1.29/1.29/2.13 cm, respectively, with an average success fixed rate of 89.56%. Moreover, the analysis of ionospheric interpolation accuracy indicates that ionospheric interpolation values are near to zero. The STD increases with the distance between the user and the master station, and ionospheric delay interpolation accuracy directly impacts the positioning accuracy and success fixed rate of users.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, and methodology, Y.M., Y.W., H.X., Y.Y. and X.C.; validation, Q.A. and X.C.; data curation, Y.Y. and Z.D.; formal analysis, Y.W. and X.C.; funding acquisition, Y.W., Y.Y. and Q.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the science and technology project of China Southern Power Grid Yunnan Power Grid Co., Ltd., (No. YNKJXM20220033). The open fund of state key laboratory of geodesy and earth’s dynamics innovation academy for precision measurement science and technology, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. SKLGED2024-3-3), and it was also supported by postdoctoral innovation research posts in Hubei Province (No. R22R6201).
Data Availability Statement
GNSS observation data can be found at https://data.gnss.ga.gov.au/, accessed on 4 June 2024. GNSS broadcast ephemeris data can be found at https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/data/daily/ (accessed on 4 June 2024).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge AUSCORS (https://gnss.ga.gov.au/stream) for providing access to multi-GNSS data (accessed on 4 June 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Yi Ma, Yifan Wang, and Zelin Dai were employed by the company Yunnan Power Grid Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Dang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, J.; Xue, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Luo, Z.; et al. Research Progress of Geodesy in China (2019–2023). Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2023, 52, 1419. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Geng, J.; Chu, B. High-Precision Velocity Determination Using Mass-Market Android GNSS Measurements in the Case of Anomalous Clock Variations. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naciri, N.; Bisnath, S. RTK-Quality Positioning with Global Precise Point Positioning Corrections. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2023, 70, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Geng, J. Single-Frequency Multi-GNSS PPP-RTK for Smartphone Rapid Centimeter-Level Positioning. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 18, 21553–21561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Dai, C.; Mao, F.; Fang, W. Integration of Multi-GNSS PPP-RTK/INS/Vision with a Cascading Kalman Filter for Vehicle Navigation in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Du, S.; Wang, D. GNSS Techniques for Real-Time Monitoring of Landslides: A Review. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.; Odijk, D. A Novel Un-Differenced PPP-RTK Concept. J. Navig. 2011, 64, S180–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y. PPP-RTK Based on Undifferenced and Uncombined Observations: Theoretical and Practical Aspects. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Connecting Integer Ambiguities to Avoid Reinitialization and Keep VRS Seamless Switching for Virtual Grid-Based NRTK. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardanelli, G.; Maltese, A.; Pipitone, C.; Pisciotta, A.; Lo Brutto, M. NRTK, PPP or Static, That Is the Question. Testing Different Positioning Solutions for GNSS Survey. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, H.; Bezcioglu, M.; Yilmaz, M. Performance of Network RTK Correction Techniques (FKP, MAC and VRS) under Limited Sky View Condition. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2019, 4, 492496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L. Improved Ambiguity Resolution by Regional Differential Modelling of the Ionosphere. In Proceedings of the 8th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1995), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 12–15 September 1995; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninger, L. Real-Time Differential GPS Error Modelling in Regional Reference Station Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Positioning and Reference Frames; Brunner, F.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. The GPS/GLONASS Integrated CORS Network Atmosphere Modeling and RTK Algorithm Implementation; Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wübbena, G.; Bagge, A.; Seeber, G.; Böder, V.; Hankemeier, P. Reducing Distance Dependent Errors for Real−Time Precise DGPS Applications by Establishing Reference Station Networks; Institute of Navigation: Garbsen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, H.J.; Keenan, C.R.; Zebhause, B.E. Study of a Simplified Approach in Utilizing Information from Permanent Reference Station Arrays. In Proceedings of the 14th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 2001), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 11–14 September 2001; pp. 379–391. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; McLellan, J.F. Carrier Phase Based Regional Area Differential GPS for Decimeter-Level Positioning and Navigation. In Proceedings of the 10th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1997), Kansas City, MO, USA, 16–19 September 1997; pp. 1305–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y. Improving Ambiguity Resolution for a Regional Area DGPS System Using Multiple Days of Data. In Proceedings of the 11th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1998), Nashville, TN, USA, 15–18 September 1998; pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Cannon, M.E.; Melgard, T.E. Real-Time GPS Reference Network Carrier Phase Ambiguity Resolution. In Proceedings of the 1999 National Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–27 January 1999; pp. 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S. Carrier Phase-Based Long-Range GPS Kinematic Positioning. Ph.D. Thesis, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; LIU, J.; Shi, C.; Lou, Y. Three Steps Method to Determine Double Difference Ambiguities Resolution of Network RTK Reference Station. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2007, 32, 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.Z.; Liu, J.N.; Tang, W.M.; Gao, X.W. The Algorithm of Single-Epoch Integer Ambiguity Resolution between Long-Range Network RTK Base Stations. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2012, 41, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Meng, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Algorithms for Sparse Network-Based RTK GPS Positioning and Performance Assessment. J. Navig. 2013, 66, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, D. Analysis of Ionospheric Anomalies before the Tonga Volcanic Eruption on 15 January 2022. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y. Study on Theories and Methods of Correcting Ionospheric Delay and Monitoring Ionosphere Based on GPS; Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics Chinese Academy of Sciences: Wuhan, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Abbey, D.A.; Castleden, N.; Featherstone, W.E.; Earls, C.; Ovstedal, O.; Weihing, D. An Approach for Instantaneous Ambiguity Resolution for Medium- to Long-Range Multiple Reference Station Networks. GPS Solut. 2005, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Gao, W.; Yang, L. GNSS Ambiguity Resolution with Controllable Failure Rate for Long Baseline Network RTK. J. Geod. 2014, 88, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P. The Ionosphere-Weighted GPS Baseline Precision in Canonical Form. J. Geod. 1998, 72, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D. Weighting Ionospheric Correction to Improve Fast GPS Positioning Over Medium Distances. In Proceedings of the 13th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 2000), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–22 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y. Multi-GNSS RTK Positioning with Integer Ambiguity Resolution: From Double-Differenced to Single-Differenced. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2021, 17, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Zhang, B.; Odolinski, R.; Yuan, Y. On the Temperature Sensitivity of Multi-GNSS Intra- and Inter-System Biases and the Impact on RTK Positioning. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zha, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, B. LS-VCE Applied to Stochastic Modeling of GNSS Observation Noise and Process Noise. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y. Analysis of the Stochastic Characteristics of GPS/BDS/Galileo Multi-Frequency Observ-ables with Different Types of Receivers. J. Spat. Sci. 2021, 66, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Yuan, Y. On the Short-Term Temporal Variations of GNSS Receiver Differential Phase Biases. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Gan, C.; He, C.; Lyu, H.; Hernandez-Pajares, M.; Lou, Y.; Geng, J.; Zhao, Q. Quasi-4-Dimension Ionospheric Modeling and Its Application in PPP. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P. Combined GPS and BeiDou Instantaneous RTK Positioning. Navigation 2014, 61, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D. Combined GPS+ BDS for Short to Long Baseline RTK Positioning. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 045801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.; Odijk, D. First Combined COMPASS/BeiDou-2 and GPS Positioning Results in Australia. Part II: Single- and Multiple-Frequency Single-Baseline RTK Positioning. J. Spat. Sci. 2014, 59, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Low-Cost, 4-System, Precise GNSS Positioning: A GPS, Galileo, BDS and QZSS Ionosphere-Weighted RTK Analysis. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 125801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D. Fast Precise GPS Positioning in the Presence of Ionospheric Delays. Publ. Geod. 2002, 52. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/27348975_Fast_Precise_GPS_Positioning_in_the_Presence_of_Ionospheric_Delays (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Morton, Y.J.; van Diggelen, F.; Spilker, J.J., Jr.; Parkinson, B.W.; Lo, S.; Gao, G. Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century: Integrated Satellite Navigation, Sensor Systems, and Civil Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.; Odijk, D.; Zhang, B. PPP-RTK: Results of CORS Network-Based PPP with Integer Ambiguity Resolution. J. Aeronaut. Astronaut. Aviat. Ser. A 2010, 42, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y. Combined GPS+BDS Instantaneous Single- and Dual-Frequency RTK Positioning: Stochastic Modelling and Performance Assessment. J. Spat. Sci. 2021, 66, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Combined BeiDou-2 and BeiDou-3 Instantaneous RTK Positioning: Stochastic Modeling and Positioning Performance Assessment. J. Spat. Sci. 2020, 65, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Rizos, C. An Instantaneous Ambiguity Resolution Technique for Medium-Range GPS Kinematic Positioning. Navigation 2000, 47, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Bai, Q. A Modified Combined Bias Interpolation Method for GNSS Network RTK. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2007, 32, 1156–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; Hou, P. Ionosphere-Weighted Undifferenced and Uncombined PPP-RTK: Theoretical Models and Experimental Results. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A Canonical Theory for Short GPS Baselines. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. ADOP in Closed Form for a Hierarchy of Multi-Frequency Single-Baseline GNSS Models. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.; De Jonge, P.; Tiberius, C. The Volume of the GPS Ambiguity Search Space and Its Relevance for Integer Ambiguty Resolution. In Proceedings of the 9th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1996), Kansas City, MO, USA, 17–20 September 1996; Volume 9, pp. 889–898. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B. Ionosphere-Weighted Post-Processing Kinematic for Airborne Positioning with Refined Modeling of Receiver Phase Biases and Tropospheric Zenith Wet Delays. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. GNSS/SINS/Vision Multi-Sensors Integration for Precise Positioning and Orientation Determination. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Robustness of GNSS Integer Ambiguity Resolution in the Presence of Atmospheric Biases. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).