An Improved Propagation Prediction Method of Low-Frequency Skywave Fusing Fine Channel Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Improvement
2.1. Method of ITU
2.2. Fine Channel Parameters and Method Improvement
2.2.1. Real-Time Reconstruction of Ionospheric Parameters
2.2.2. Refined Land–Sea Surface Electrical Characteristics
3. Analysis
3.1. Data Acquisition
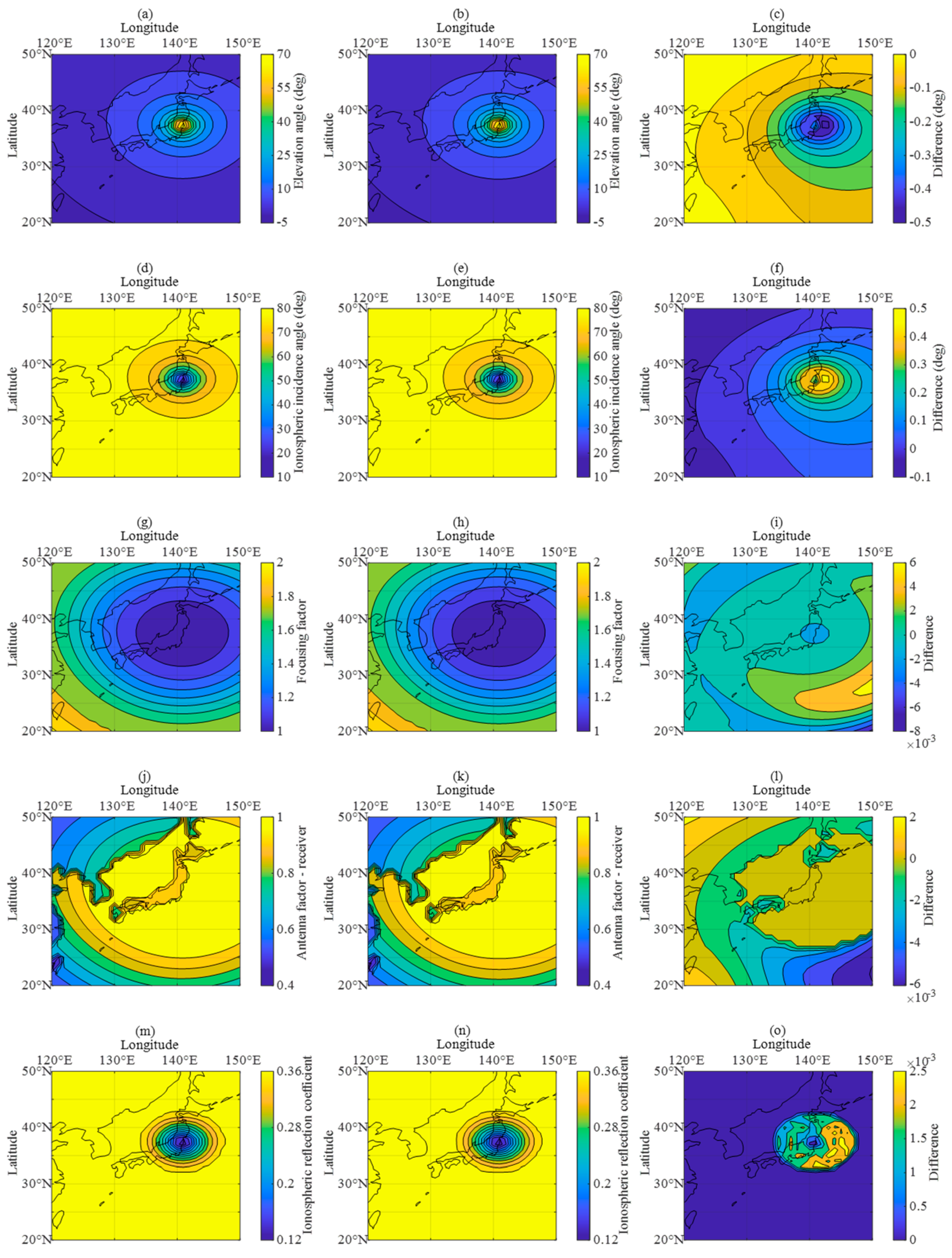
3.2. Analysis of Improved Method
- (1)
- For most links in the eastern part of the region, the elevation angle calculated via the PRO method is increased.
- (2)
- For most links in the eastern part of the region, the ionospheric incidence angle calculated via the PRO method is reduced.
- (3)
- The ionospheric focusing factor and antenna factor are different between the two methods.
- (4)
- The ionospheric reflection coefficient slightly decreases around the transmitting point after correction.
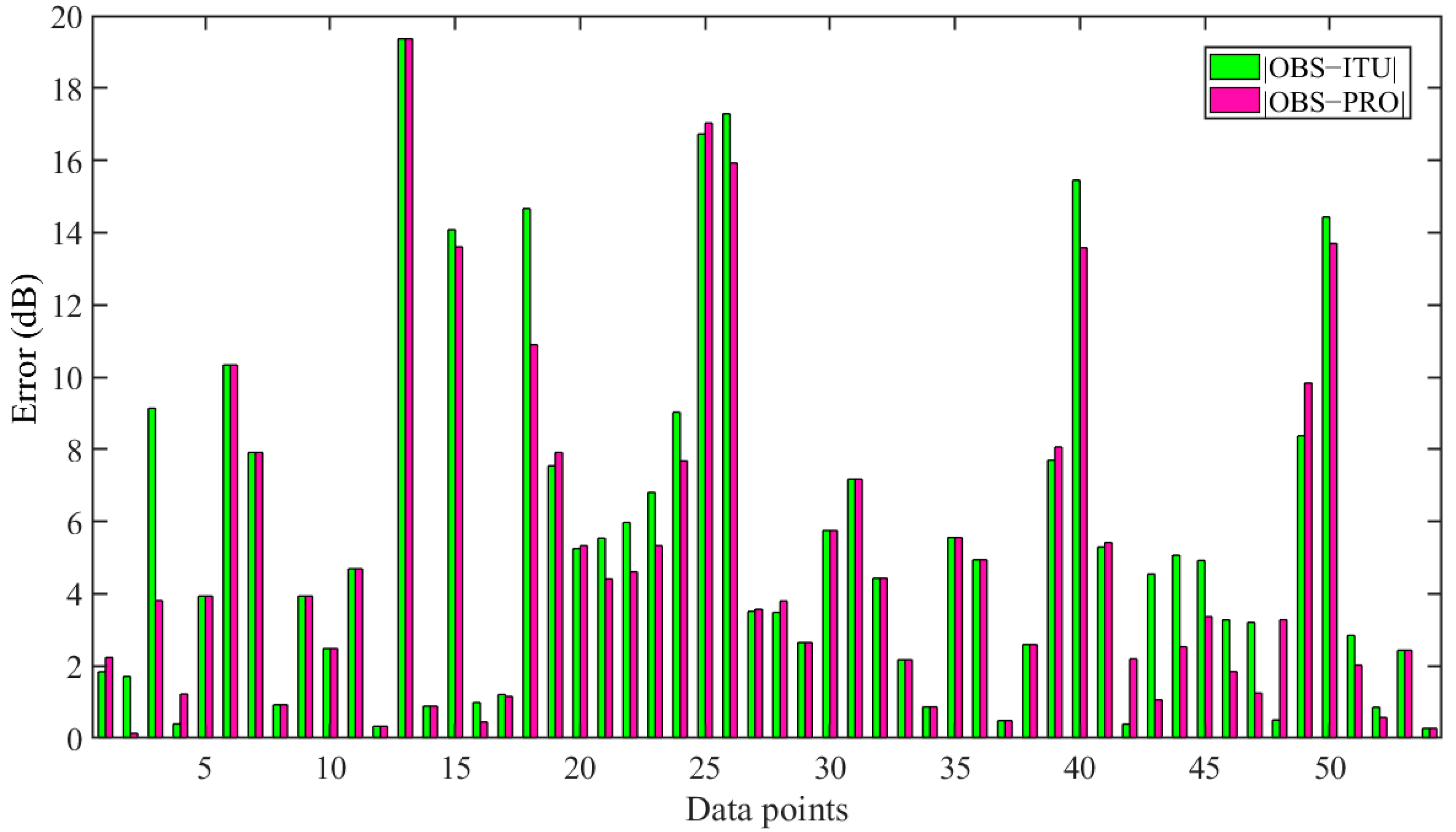
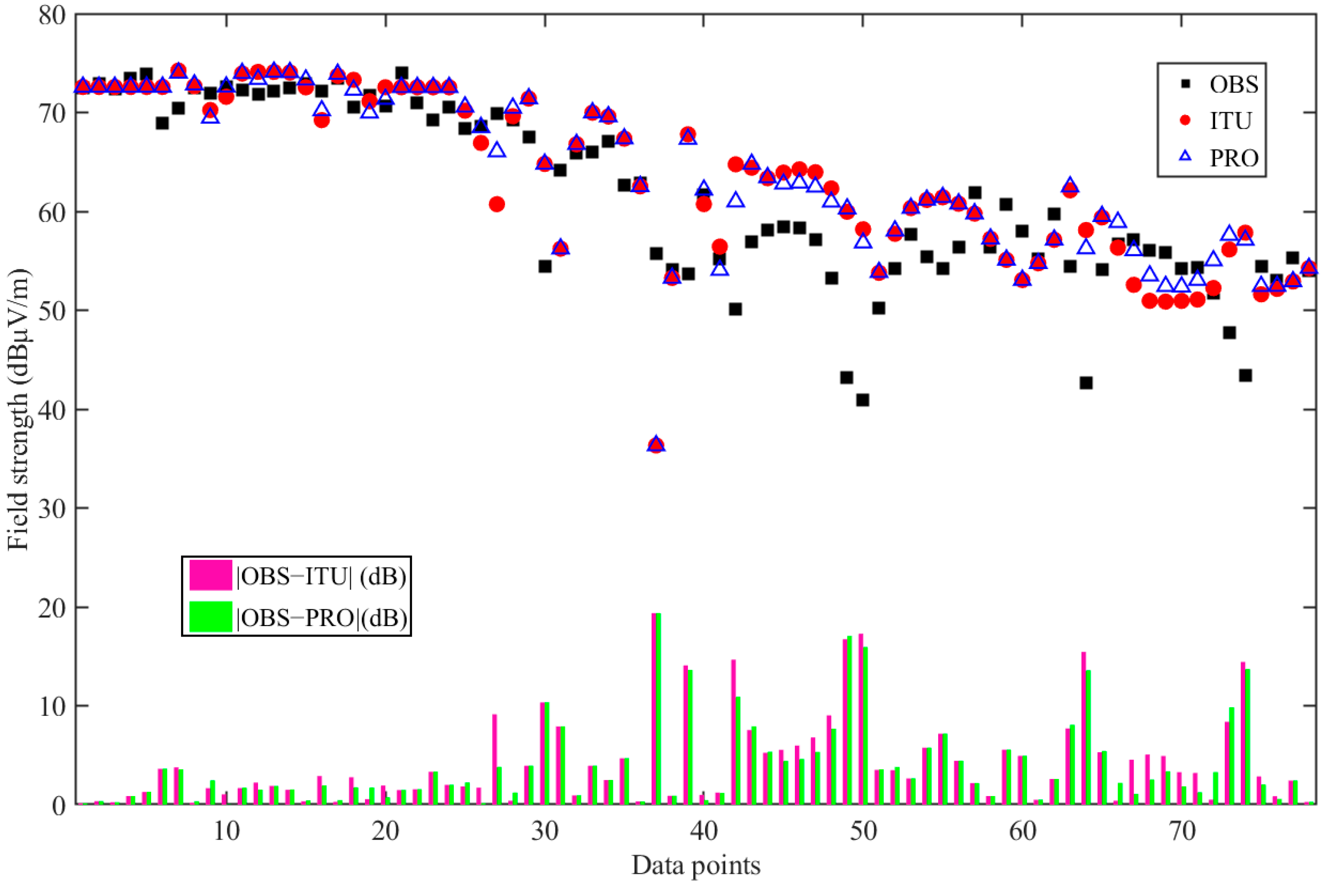
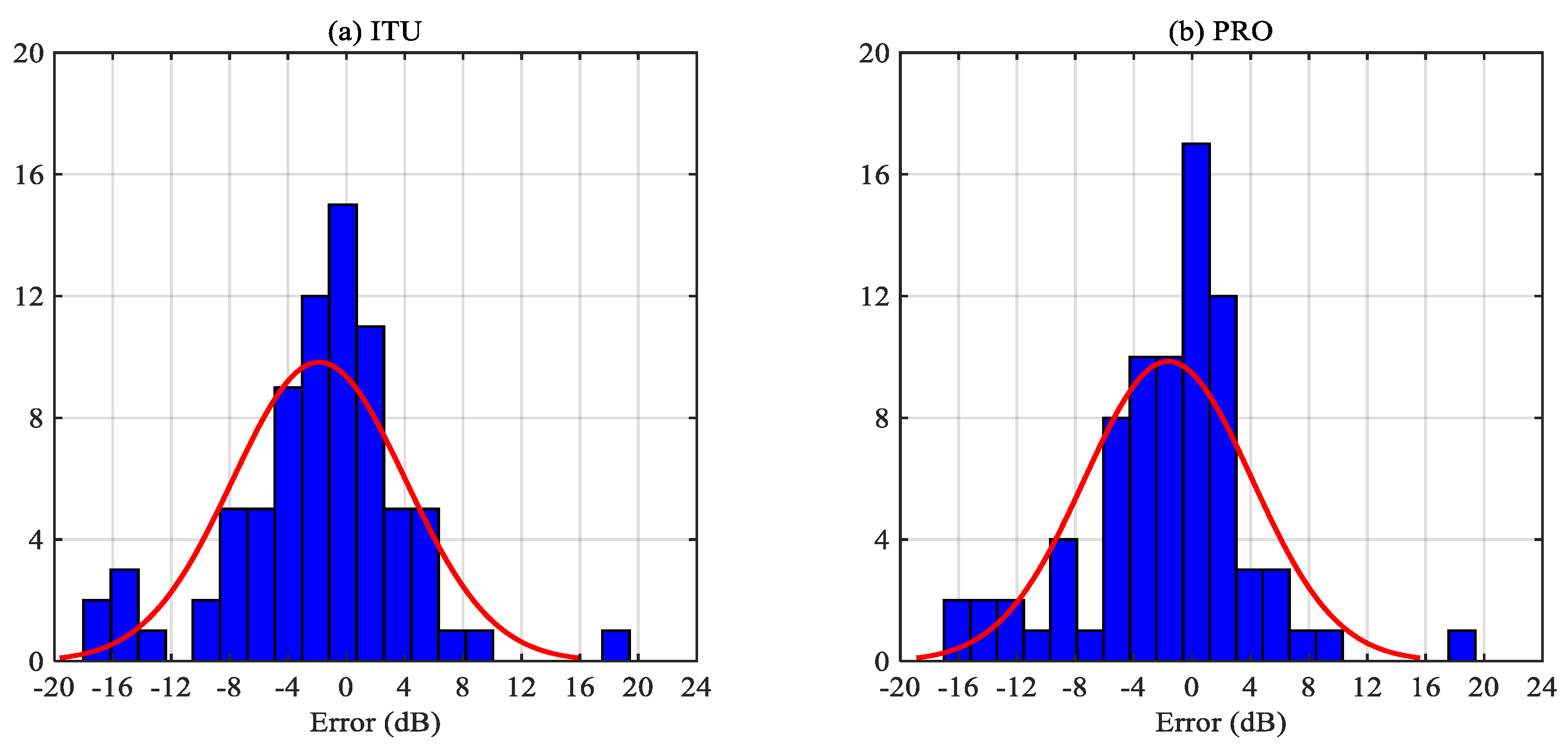
3.3. Analysis of Time Domain Characteristics
3.4. Analysis of Spatial Domain Characteristics
3.5. Comprehensive Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Telecommunication Union. ITU-R V.431, Nomenclature of the Frequency and Wavelength Bands Used in Telecommunications; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Appleton, E.V. The Propagation of Radio Waves over the Earth. Nature 1925, 115, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, H.G. Propagation of Wave-Packets Incident Obliquely upon a Stratified Doubly Refracting Ionosphere. Phil. Trans. R Soc. Lond. A 1938, 237, 411–451. [Google Scholar]
- Bracewell, R.; Budden, K.G.; Ratcliffe, J.; Straker, T.; Weekes, K. The ionospheric propagation of low- and very-low-frequency radio waves over distances less than 1000 km. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1951, 98, 221–236. [Google Scholar]
- Budden, K.G.; Chang, H. Radio Waves in the Ionosphere; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.C.H. An objective evaluation of available LF/MF sky-wave propagation models. Radio Sci. 1999, 34, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrington, E.M.; Jones, T.B. Propagation of low-frequency radio waves. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2000, 147, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Liang, Z. The effect of atmospheric refraction on the calculation of skywave propagation geometry parameters. J. Xidian Univ. 2002, 29, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wakai, N.; Kurihara, N.; Otsuka, A. Numerical Method for Calculating LF Sky-Wave, Ground-Wave and Their Resultant Wave Field Strengths. Electron. Lett. 2004, 40, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakai, N.; Kurihara, N.; Otsuka, A.; Imamura, K.; Takahashi, Y. Wintertime Survey of LF Field Strengths in Japan. Radio Sci. 2006, 41, 2005RS003344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.H. Seasonal Variation of LF/MF Sky-Wave Field Strengths. IEEE Trans. Broadcast 2008, 54, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeru, T.; Kuniyasu, I.; Hiroyuki, I.; Hideo, M.; Minoru, K.; Kenro, N. 2-9 Prediction method and proof measurement of LF standard frequency waves. J. Natl. Inst. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2010, 57, 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Lv, Y. Approximate solution for vertically polarized VLF/LF waves in lower ionosphere. In Proceedings of the ISAPE2012, Xi’an, China, 22–26 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Hobara, Y.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Schnoor, P.W. Effects of the major sudden stratospheric warming event of 2009 on the subionospheric very low frequency/low frequency radio signals. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 7555–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Mu, Z.; Xi, X.; He, L. LF Radio Wave Prediction at Short Ranges with High Propagation Angles Over Irregular Terrain. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchinov, V.; Pavlov, A.; Soloviev, B.; Bashkuev, Y.; Dembelov, M. The Seasonal Variations of LF-MF Electromagnetic Waves on Permafrost Radio Paths. In Proceedings of the 2019RWP, Kazan, Russia, 23–24 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Yan, J.; Mu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; He, L. Study on Time Delay Characteristics of Low Frequency One-hop Sky Waves in the Isotropic Ionosphere. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2020, 42, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Gasdia, F.; Marshall, R.A. A New Longwave Mode Propagator for the Earth–Ionosphere Waveguide. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 8675–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Hu, X.; He, L. Comparison of low frequency multi-hop sky wave delay estimation algorithms. Chin. J. Radio Sci. 2022, 37, 244–250. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xi, X. Analysis of low-frequency sky wave signal characteristics based on IRI ionospheric model. Chin. J. Radio Sci. 2022, 37, 898–904. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Pu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xi, X. An Improved Model for Loran-C One-Hop Sky Waves Propagation at Short-Range. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Telecommunication Union. ITU-R P.368-10: Ground-Wave Propagation Prediction Method for Frequencies between 10 kHz and 30 MHz; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- International Telecommunication Union. ITU-R P.1239-3: ITU-R Reference Ionospheric Characteristics; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W. Long wave sky wave propagation. In LF VLF ELF Wave Propagation; UESTC Press: Chengdu, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Recommendation ITU-R P. 684-6: Prediction of Field Strength at Frequencies below about 150 kHz; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Stanisκawska, I.; Juchnikowski, G.; Cander, L. Kriging method for instantaneous mapping at low and equatorial latitudes. Adv. Space Res. 1996, 18, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukesh, R.; Soma, P.; Karthikeyan, V.; Sindhu, P. Prediction of ionospheric vertical total electron content from GPS data using ordinary kriging-based surrogate model. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, H.; Huang, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ma, J. Simplified Regional Prediction Model of Long-Term Trend for Critical Frequency of Ionospheric F2 Region over East Asia. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, F.J.; Garner, W.E. An Investigation of the Modal Interference of VLF Radio Waves. Radio Sci. 1967, 2, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



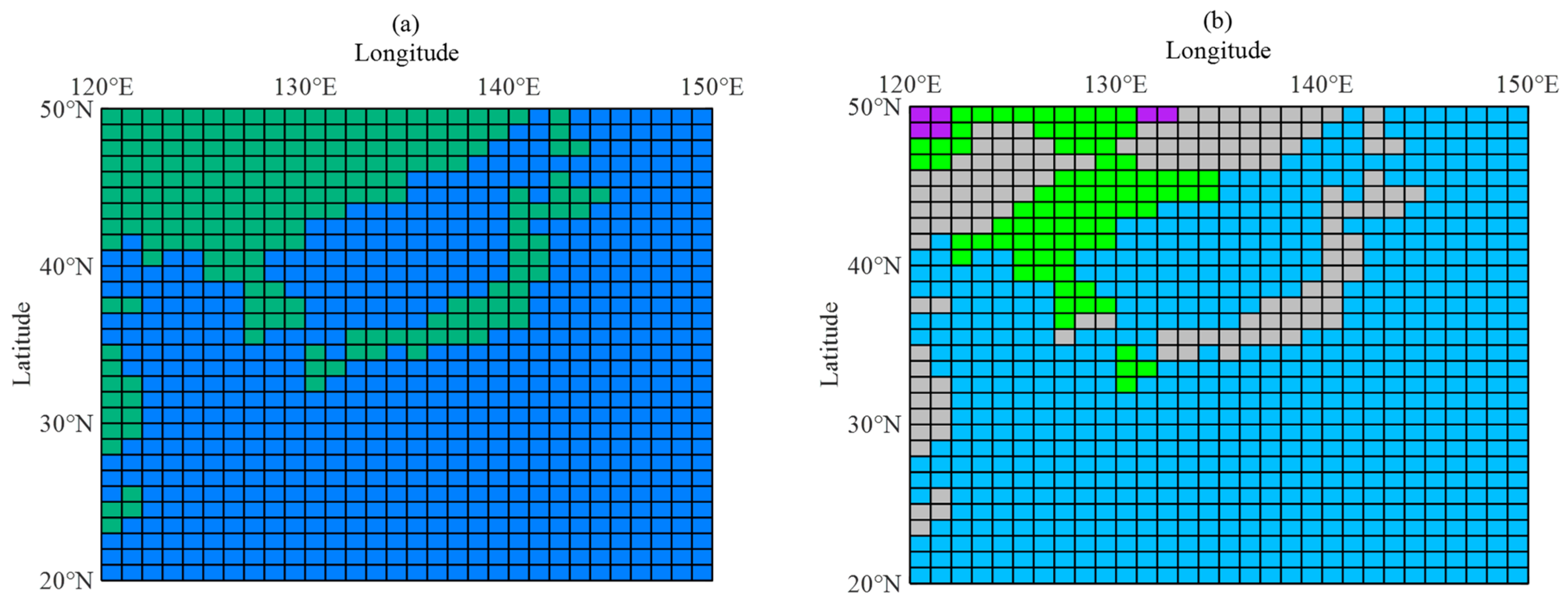






| Method | Before Refinement—(a) | After Refinement—(b) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Blue | Dark Green | Light Blue | Green | Grey | Purple |
| Permittivity, ε (F/m) | 80 | 15 | 70 | 30 | 15 | 3 |
| Conductivity, σ (S/m) | 5 | 0.002 | 5 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.0001 |
| Specific Information | |
|---|---|
| Transmitting Station | JJY |
| Place | Fukushima, JPN |
| Longitude | 140.8°E |
| Latitude | 37.4°N |
| Antenna type | Stayed monopole of umbrella type |
| Antenna height | 250 m |
| Transmitter power | 50 kW |
| Carrier frequency | 40 kHz |
| Radiation efficiency | 25% |
| Methods | ITU | PRO |
|---|---|---|
| Day | 1.93 dB | 1.70 dB |
| Night | 1.88 dB | |
| Distances | 200~800 km | 800~1400 km | 1400~2000 km |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITU | 7.48 dB | 9.57 dB | 5.85 dB |
| PRO | 7.42 dB | 7.65 dB | 5.99 dB |
| Methods | Kriging | Nearest | Linear |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improvement | 6.81% | 9.95% | 6.28% |
| Methods | Kriging | Nearest | Linear |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improvement | 3.69% | 0.20% | −0.82% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Duan, C.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, C. An Improved Propagation Prediction Method of Low-Frequency Skywave Fusing Fine Channel Parameters. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122241
Wang J, Duan C, Chen Y, Shi Y, Yang C. An Improved Propagation Prediction Method of Low-Frequency Skywave Fusing Fine Channel Parameters. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(12):2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122241
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Chengsong Duan, Yu Chen, Yafei Shi, and Cheng Yang. 2024. "An Improved Propagation Prediction Method of Low-Frequency Skywave Fusing Fine Channel Parameters" Remote Sensing 16, no. 12: 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122241
APA StyleWang, J., Duan, C., Chen, Y., Shi, Y., & Yang, C. (2024). An Improved Propagation Prediction Method of Low-Frequency Skywave Fusing Fine Channel Parameters. Remote Sensing, 16(12), 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122241











