Polar Stratospheric Cloud Observations at Concordia Station by Remotely Controlled Lidar Observatory
Abstract
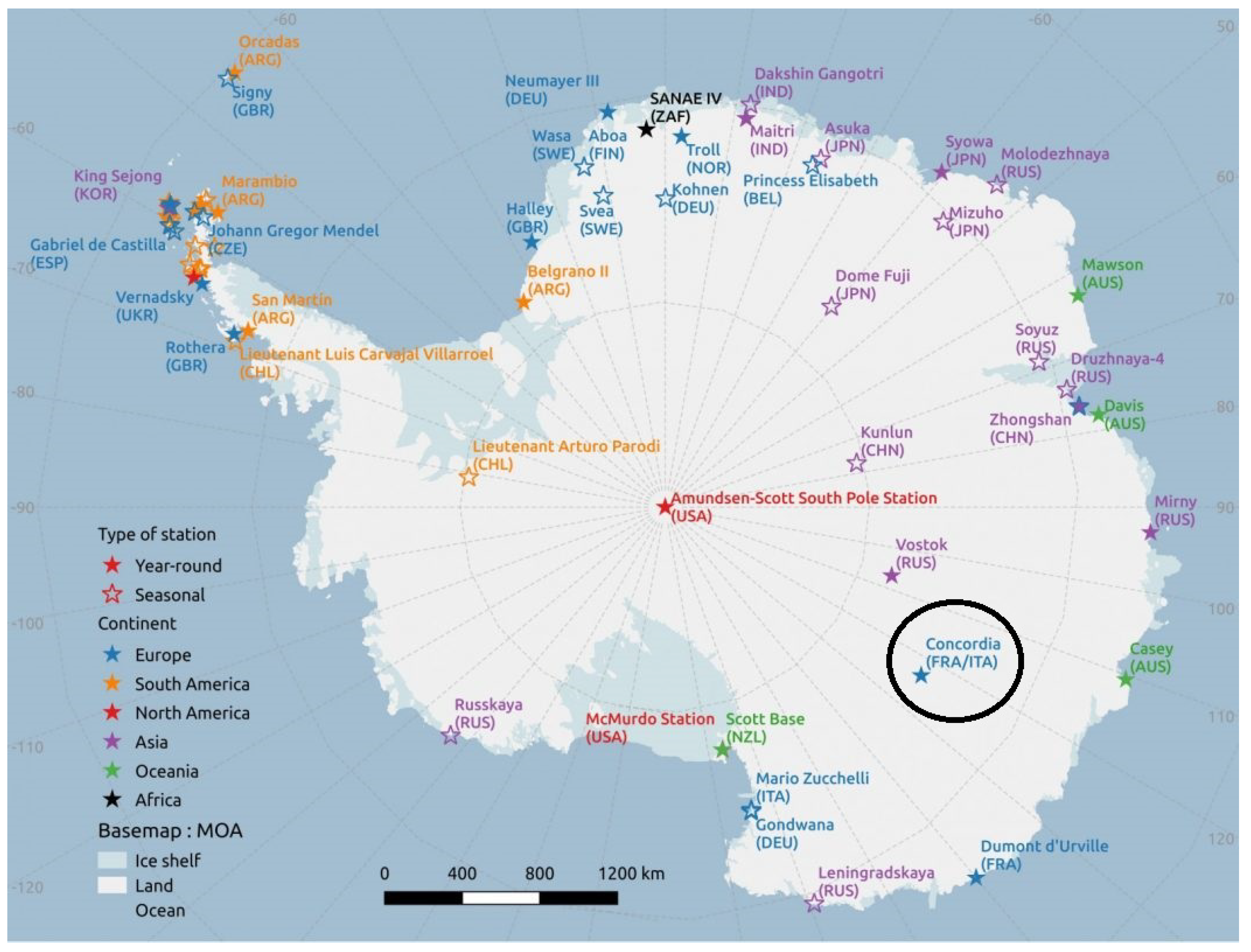
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
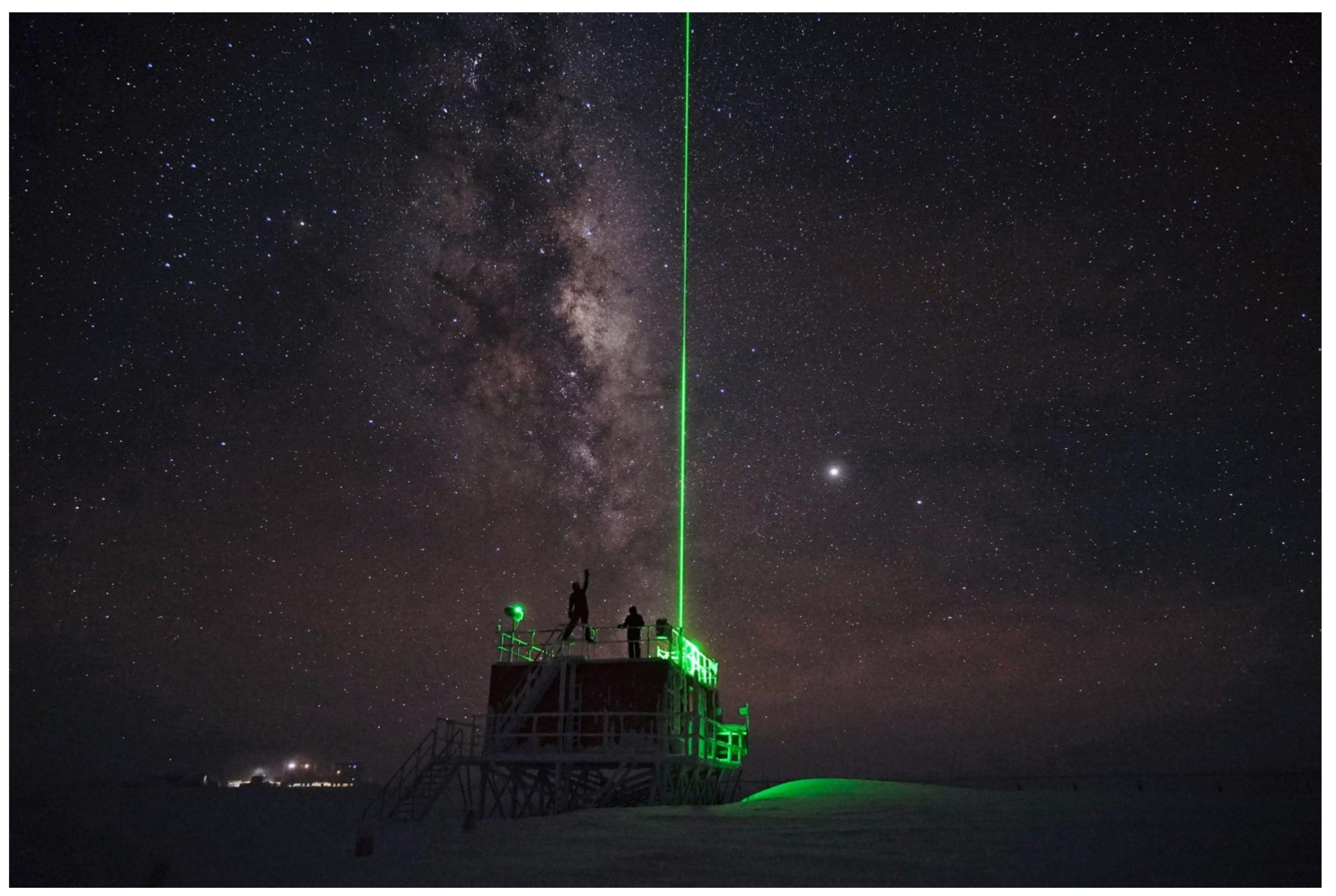
2.1. Description of the Remote-Controlled Lidar
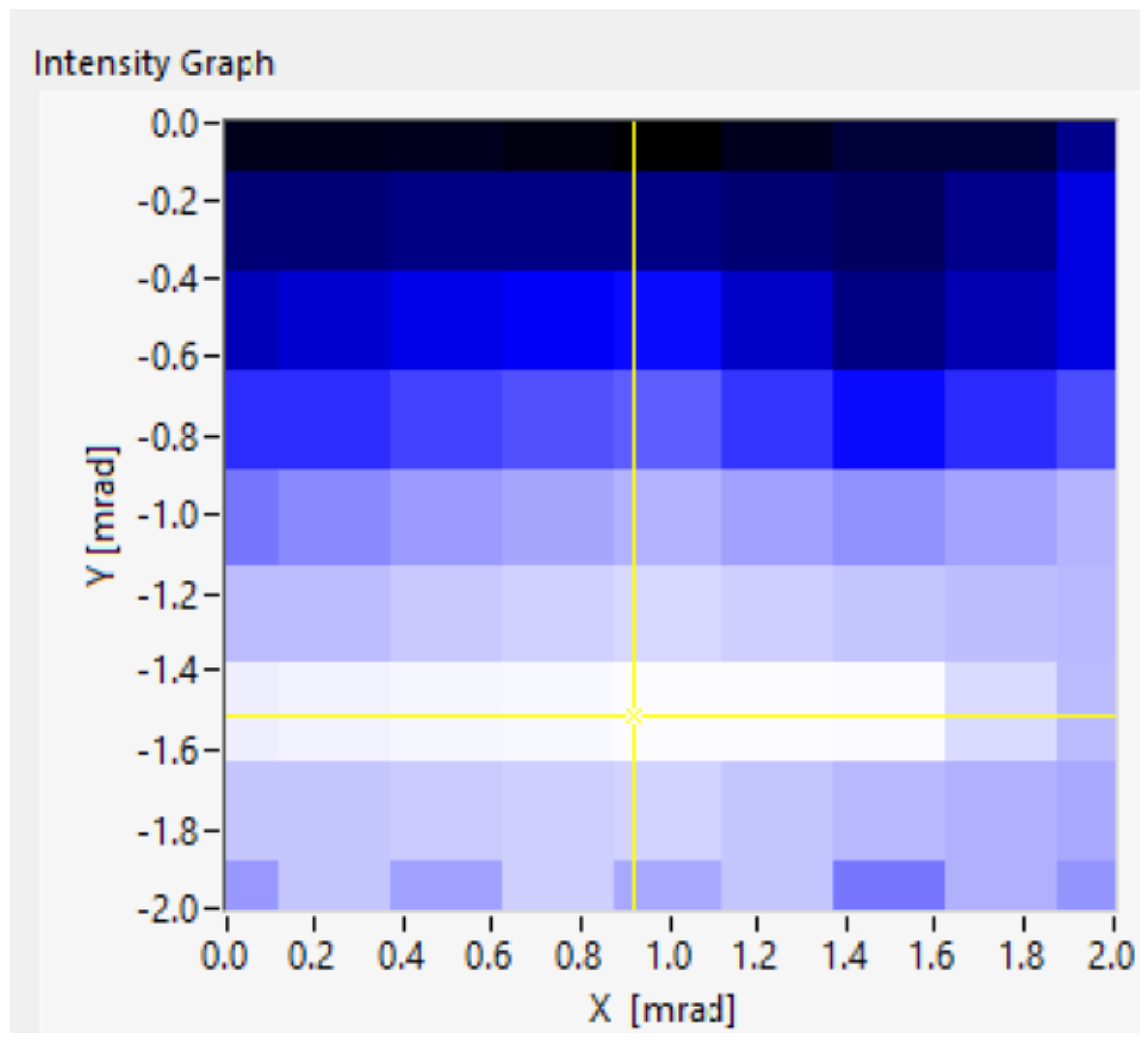
2.2. Description of the Measurement Methods
2.3. Preprocessing of the Raw Lidar Data
2.4. Detection and Classification of PSCs
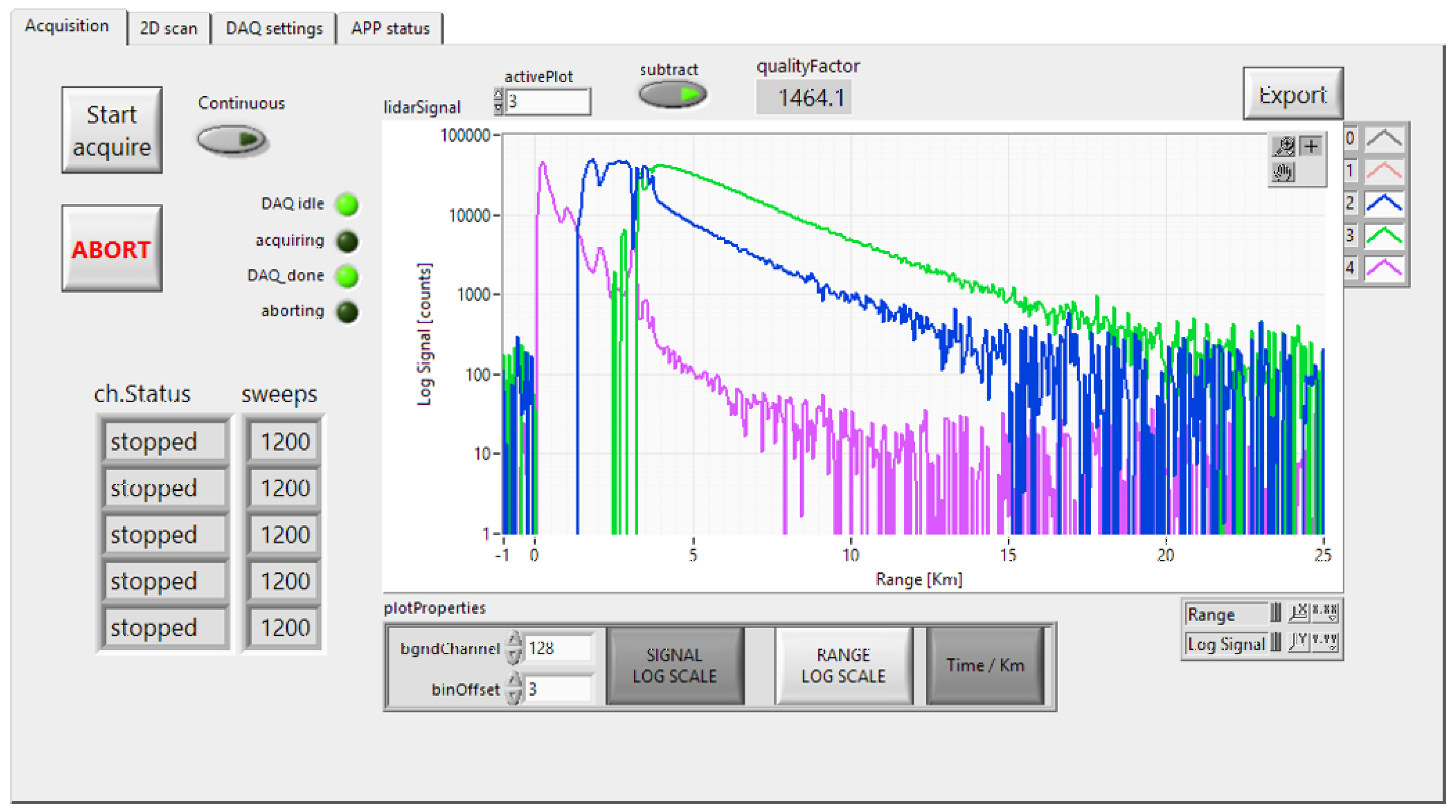
3. Results
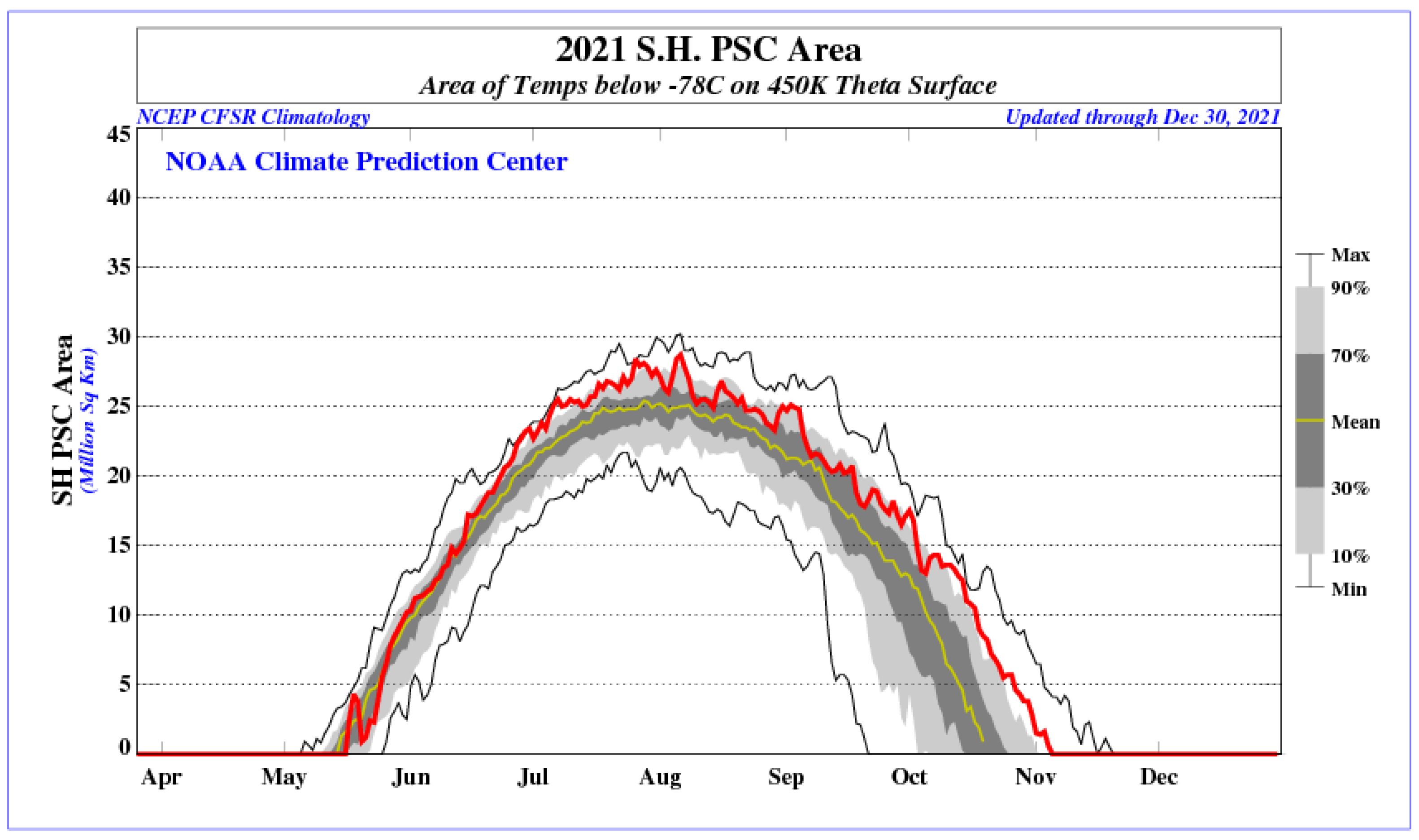
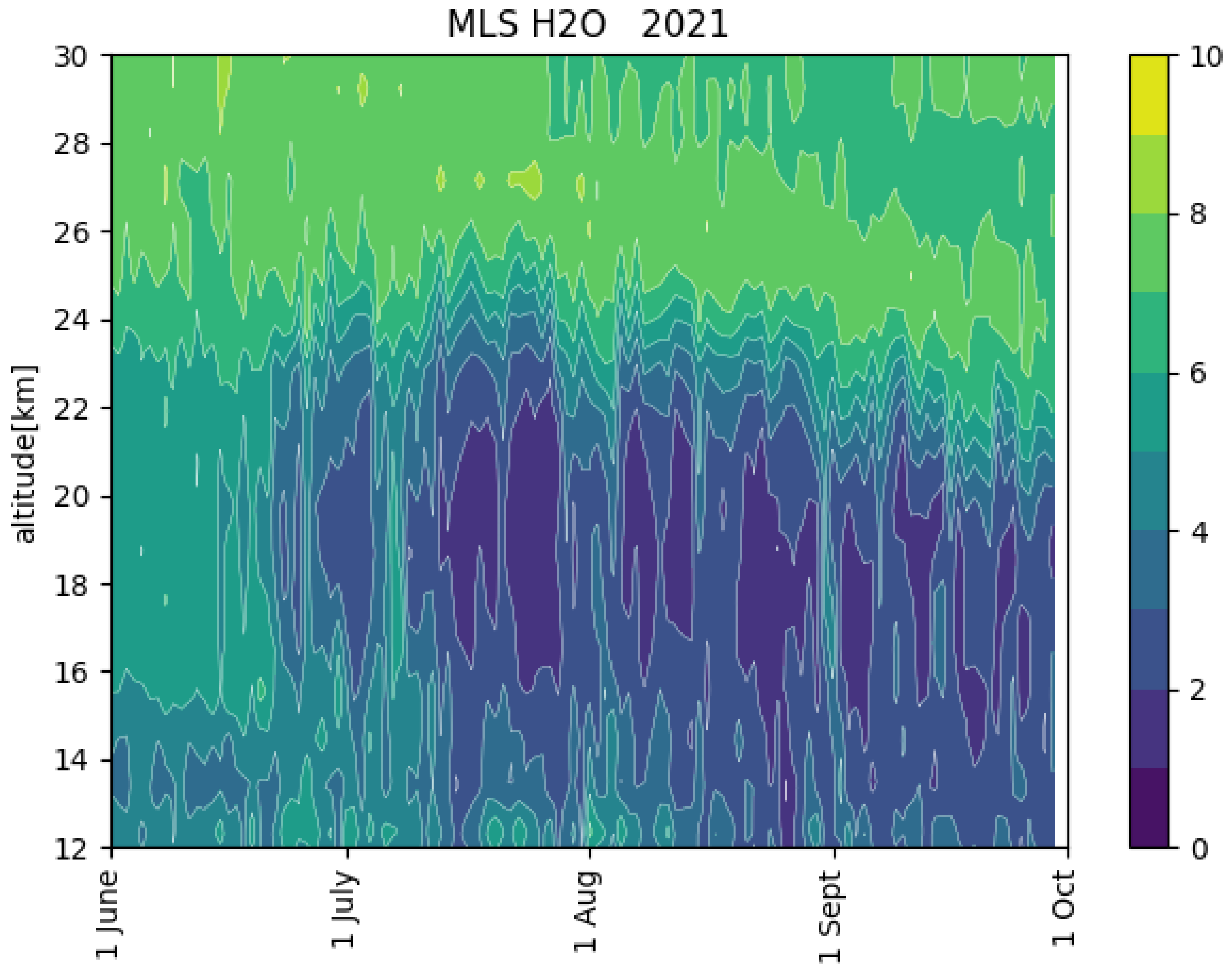
Ground-Based and CALIOP PSC Observations in 2021
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSC | Polar Stratospheric Cloud |
| LIDAR | LIght Detecting And Ranging |
| CALIOP | Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization |
| CALIPSO | Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation |
| NAT | Nitric Acid Trihydrate |
| STS | Supercooled Ternary Solution |
| MLS | Microwave Limb Sounder |
| PNRA | Programma Nazionale delle Ricerche in Antartide |
| NDACC | Network for the Detection of Stratospheric Change |
| NCEP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| ERA-5 | ECMWF ReAnalysis version 5 |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
References
- Sassen, K. The Polarization Lidar Technique for Cloud Research: A Review and Current Assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1991, 72, 1848–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, B.C. Observations of polar stratospheric clouds in the Arctic winter 1989 at 79 N. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, G.; Cacciani, M.; Di Girolamo, P.; Fua, D. Stratospheric clouds at South-Pole during 1988 1. Results of lidar observations and their relationship to temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 5939–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanutti, L.; Morandi, M.; Guasta, M.D.; Godin, S.; Megie, G.; Brechet, J.; Piquard, J. Polar stratospheric cloud observations over the Antarctic continent at Dumont d’Urville. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1991, 96, 12975–12987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tencé, F.; Jumelet, J.; Bouillon, M.; Cugnet, D.; Bekki, S.; Safieddine, S.; Keckhut, P.; Sarkissian, A. 14 years of lidar measurements of polar stratospheric clouds at the French Antarctic station Dumont d’Urville. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriani, A.; Massoli, P.; Di Donfrancesco, G.; Cairo, F.; Moriconi, M.; Snels, M. Climatology of polar stratospheric clouds based on lidar observations from 1993 to 2001 over McMurdo Station, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D24211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snels, M.; Scoccione, A.; Di Liberto, L.; Colao, F.; Pitts, M.; Poole, L.; Deshler, T.; Cairo, F.; Cagnazzo, C.; Fierli, F. Comparison of Antarctic polar stratospheric cloud observations by ground-based and spaceborne lidars and relevance for chemistry-climate Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snels, M.; Colao, F.; Cairo, F.; Shuli, I.; Scoccione, A.; De Muro, M.; Pitts, M.; Poole, L.; Di Liberto, L. Quasi-coincident observations of polar stratospheric clouds by ground-based lidar and CALIOP at Concordia (Dome C, Antarctica) from 2014 to 2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snels, M.; Cairo, F.; Di Liberto, L.; Scoccione, A.; Bracaglia, M.; Deshler, T. Comparison of Coincident Optical Particle Counter and Lidar Measurements of Polar Stratospheric Clouds Above McMurdo (77.85°S, 166.67°E) from 1994 to 1999. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, F.; Deshler, T.; Di Liberto, L.; Scoccione, A.; Snels, M. A study of optical scattering modelling for mixed-phase polar stratospheric clouds. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Achtert, P.; Pitts, M.C. On the best locations for ground-based polar stratospheric cloud (PSC) observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liberto, L.; Cairo, F.; Fierli, F.; Di Donfrancesco, G.; Viterbini, M.; Deshler, T.; Snels, M. Observation of polar stratospheric clouds over McMurdo (77.85°S, 166.67°E) (2006–2010). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5528–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J. Lidar Inversion with Variable Backscatter/Extinction Ratios. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.A.; Vaughan, M.A. The Retrieval of Profiles of Particulate Extinction from Cloud-Aerosol Lidar Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) Data: Algorithm Description. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckmann, C.; Ritter, C. Properties of Polar Stratospheric Clouds over the European Arctic from Ground-Based Lidar. In Proceedings of the 30th International Laser Radar Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 26 June–1 July 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, G. Lidar estimation of stratospheric aerosol properties—Surface, volume, and extinction to backscatter ratio. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 11219–11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snels, M.; Cairo, F.; Colao, F.; Di Donfrancesco, G. Calibration method for depolarization lidar measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 5725–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, A.; Nakamura, T. Calculation of the calibration constant of polarization lidar and its dependency on atmospheric temperature. Opt. Express 2002, 10, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, F.; Donfrancesco, G.D.; Adriani, A.; Pulvirenti, L.; Fierli, F. Comparison of various linear depolarization parameters measured by lidar. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 4425–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitts, M.C.; Poole, L.R.; Gonzalez, R. Polar stratospheric cloud climatology based on CALIPSO spaceborne lidar measurements from 2006–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 2018, 10881–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabazadeh, A.; Toon, O.; Hamill, P. Freezing behaviour of stratospheric sulfate aerosols inferred from trajectory studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.; Knudsen, B.; Rosen, J.; Kjome, N.; Neuber, R.; Kyro, E. Temperature histories in liquid and solid polar stratospheric cloud formation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 23505–23517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toon, O.; Tabazadeh, A.; Browell, E.; Jordan, J. Analysis of lidar observations of Arctic polar stratospheric clouds during January 1989. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20589–20615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.; Mauersberger, K. Laboratory studies of the nitric acid trihydrate: Implications for the south polar stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M.; Koop, T. Review of the vapour pressures of ice and supercooled water for atmospheric applications. Quart. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 1539–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romps, D.M. Accurate Expressions for the Dewpoint and Frost Point Derived from the Rankine–Kirchhoff Approximations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 78, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritscher, I.; Pitts, M.C.; Poole, L.R.; Alexander, S.P.; Cairo, F.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Grooß, J.U.; Höpfner, M.; Lambert, A.; Luo, B.; et al. Polar Stratospheric Clouds: Satellite Observations, Processes, and Role in Ozone Depletion. Rev. Geophys. 2021, 59, e2020RG000702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, K.S.; Wirth, M.; Tsias, A.; Luo, B.P.; Dörnbrack, A.; Leutbecher, M.; Volkert, H.; Renger, W.; Bacmeister, J.T.; Peter, T. Particle microphysics and chemistry in remotely observed mountain polar stratospheric clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 5785–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, T.; Ng, H.P.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J. A New Optical Technique to Study Aerosol Phase Transitions: The Nucleation of Ice from H2SO4 Aerosols. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 8924–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, T.; Biermann, U.; Raber, W.; Luo, B.; Crutzen, P.; Peter, T. Do stratospheric droplets freeze above the ice frost point? Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, T.; Carslaw, K.S.; Peter, T. Thermodynamic stability and phase transitions of PSC particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, T. Microphysics and heterogeneous chemistry of polar stratospheric clouds. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1997, 48, 785–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, T.; Grooß, J.U. Polar Stratospheric Clouds and Sulfate Aerosol Particles: Microphysics, Denitrification and Heterogeneous Chemistry. In Stratospheric Ozone Depletion and Climate Change; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2012; pp. 108–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtius, J. Observations of meteoritic material and implications for aerosol nucleation in the winter Arctic lower stratosphere derived from in situ particle measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2005, 5, 5039–5080. [Google Scholar]
- Carslaw, K.; Luo, B.; Peter, T. An analytic expression for the composition of acqueous HNO3-H2SO4 stratospheric aerosols including gas-phase removal of HNO3. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 1877–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Vane, D.G.; Boain, R.J.; Mace, G.G.; Sassen, K.; Wang, Z.; Illingworth, A.J.; O’Connor, E.J.; Rossow, W.B.; Durden, S.L.; et al. The CloudSat mission and the A-Train: A new dimension of space-based observations of clouds and precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1771–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.; Winker, D.; Pelon, J.; Trepte, C.; Vane, D.; Yuhas, C.; L’Ecuyer, T.; Lebsock, M. CloudSat and CALIPSO within the A-Train: Ten Years of Actively Observing the Earth System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, M.C.; Poole, L.R.; Thomason, L.W. CALIPSO polar stratospheric cloud observations: Second-generation detection algorithm and composition discrimination. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7577–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, M.C.; Poole, L.R.; Dörnbrack, A.; Thomason, L.W. The 2009–2010 Arctic polar stratospheric cloud season: A CALIPSO perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2161–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, M.C.; Poole, L.R.; Lambert, A.; Thomason, L.W. An assessment of CALIOP polar stratospheric cloud composition classification. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2975–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtert, P.; Tesche, M. Assessing lidar-based classification schemes for polar stratospheric clouds based on 16 years of measurements at Esrange, Sweden. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1386–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, K.R.; Raphael, M.N.; Adusumilli, S.; Baiman, R.; Banwell, A.F.; Barreira, S.; Beadling, R.L.; Colwell, S.; Coy, L.; Datta, R.T.; et al. Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, S307–S340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

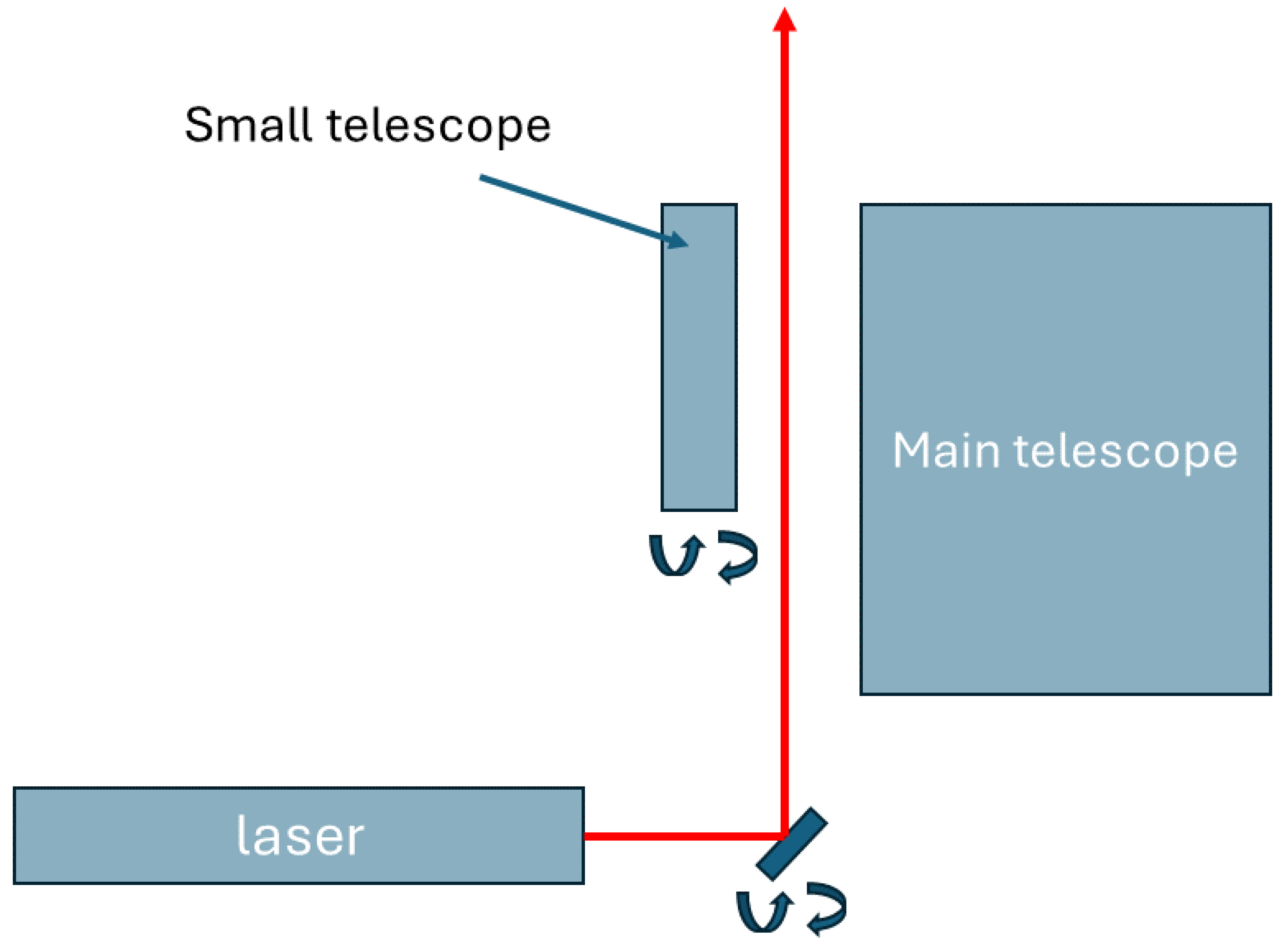
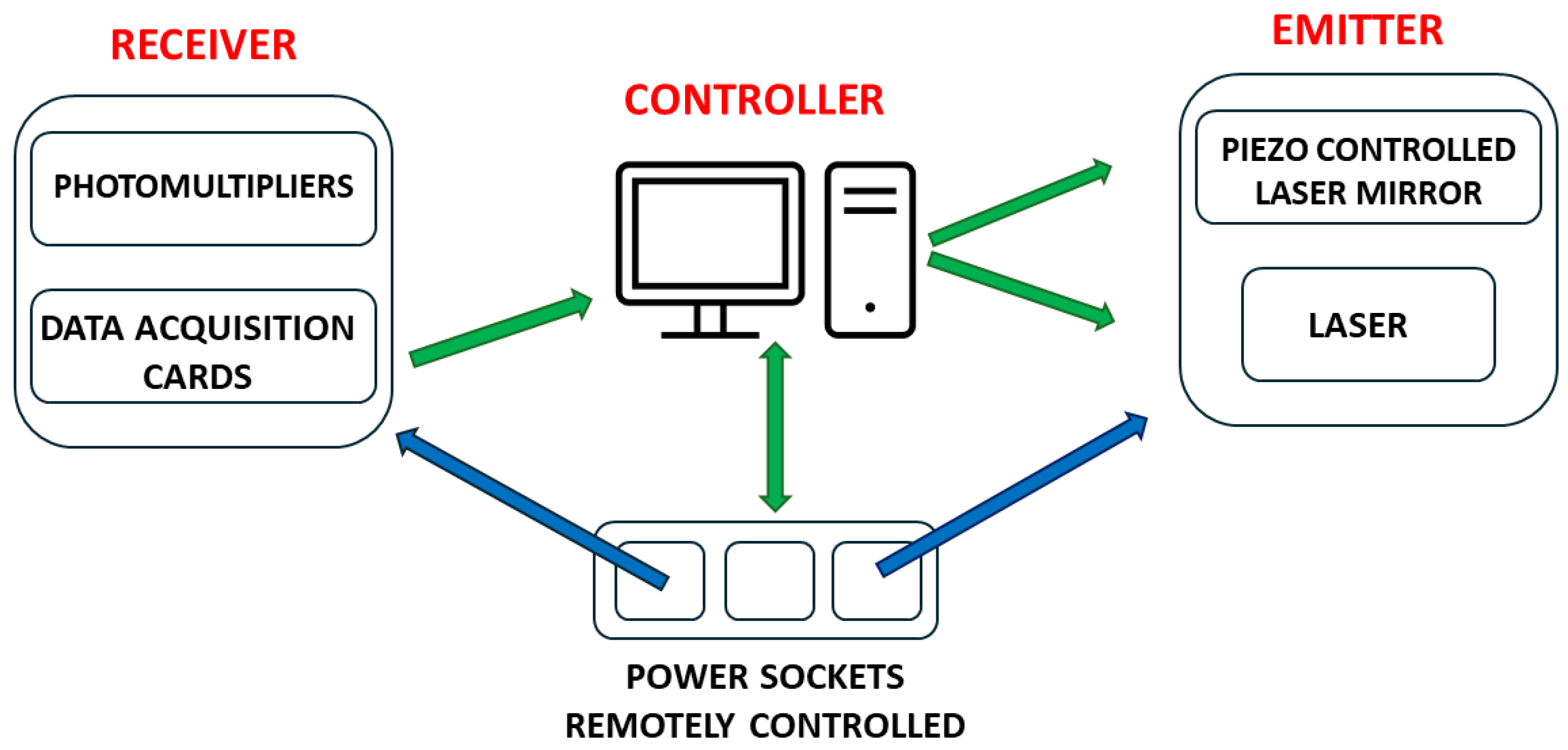




| Laser energy per pulse | 180 mJ |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 10 Hz |
| Laser pulse duration | 9 ns |
| Laser divergence full angle | 1.5 mrad |
| Laser pointing stability | 100 μrad |
| Main telescope diameter | 355.6 mm |
| Main telescope focal length | 3910 mm |
| Main telescope field of view | 4 mrad |
| Small telescope diameter | 152.4 mm |
| Small telescope focal length | 1500 mm |
| Small telescope field of view | 2 mrad |
| FWHM interference filter @ 532 nm | 2 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Liberto, L.; Colao, F.; Serva, F.; Bracci, A.; Cairo, F.; Snels, M. Polar Stratospheric Cloud Observations at Concordia Station by Remotely Controlled Lidar Observatory. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122228
Di Liberto L, Colao F, Serva F, Bracci A, Cairo F, Snels M. Polar Stratospheric Cloud Observations at Concordia Station by Remotely Controlled Lidar Observatory. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(12):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122228
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Liberto, Luca, Francesco Colao, Federico Serva, Alessandro Bracci, Francesco Cairo, and Marcel Snels. 2024. "Polar Stratospheric Cloud Observations at Concordia Station by Remotely Controlled Lidar Observatory" Remote Sensing 16, no. 12: 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122228
APA StyleDi Liberto, L., Colao, F., Serva, F., Bracci, A., Cairo, F., & Snels, M. (2024). Polar Stratospheric Cloud Observations at Concordia Station by Remotely Controlled Lidar Observatory. Remote Sensing, 16(12), 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122228







