Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Based on Spectral Indices Combined with Water Removal Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To analyze the effect of moisture content on soil spectral reflectance and compare the ability of external parameter orthogonalization (EPO) and direct standardization (DS) to eliminate the effect of moisture in VNIR spectra.
- (2)
- To create a two-band spectral index and a three-band spectral index, investigate their correlation with soil organic matter content, and identify the most sensitive bands.
- (3)
- To construct an improved algorithm for combining SOM spectral indices with EPO and DS to overcome and eliminate the effect of soil moisture on the accuracy of SOM spectral monitoring in order to improve the accuracy of SOM detection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
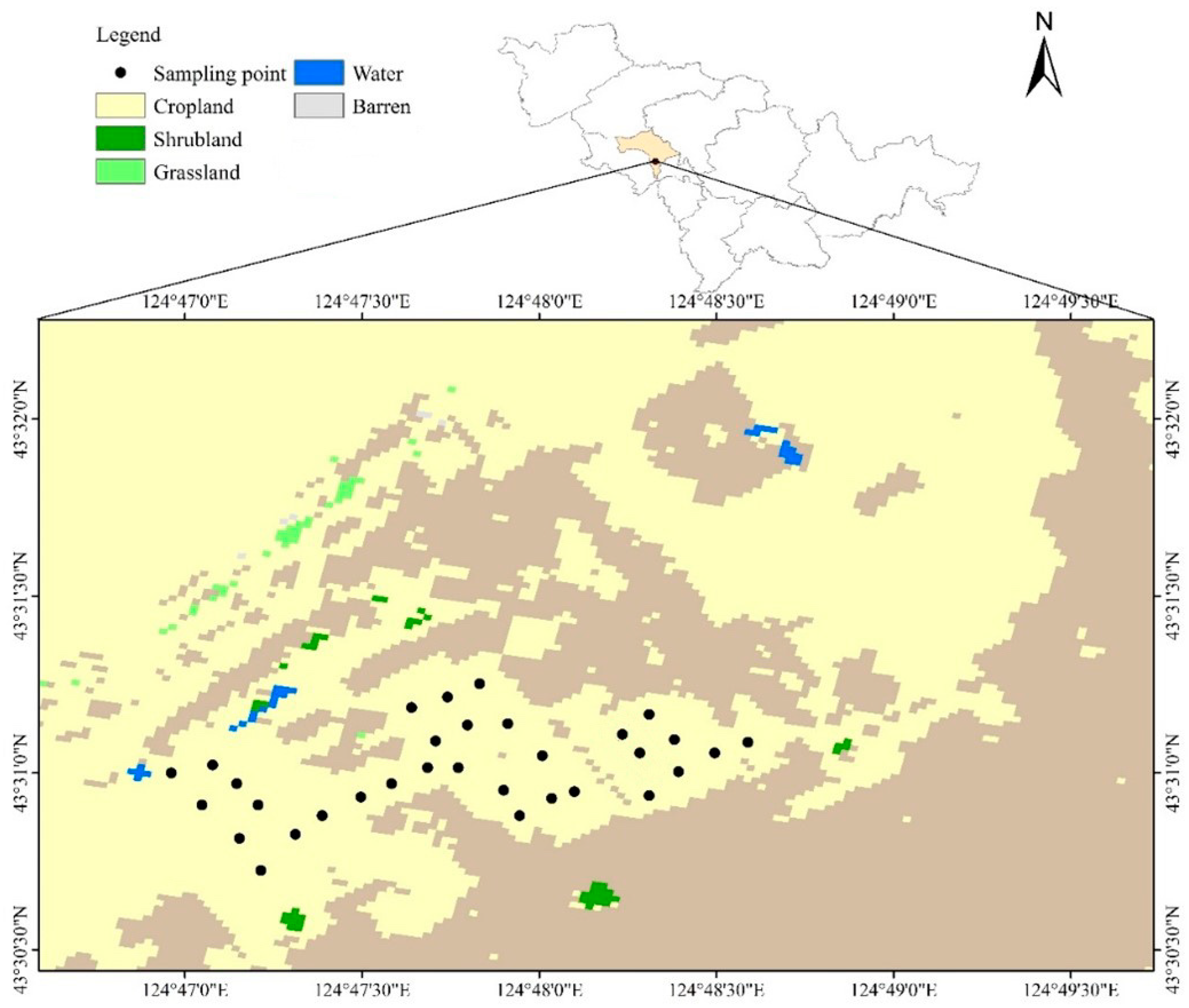
2.1.1. Study Area and Soil Data Collection
2.1.2. Soil Moisture Content Setting
2.1.3. Spectral Measurement
2.1.4. Data Preprocessing
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Spectral Index
2.2.2. External Parameter Orthogonalization (EPO)
- (1)
- Dry soil samples can be represented as (n × m), and the average spectrum of dry soil samples can be calculated as (1 × m).
- (2)
- Wet soil samples can be represented as (N × m), and the average spectrum of samples with different SMCs can be calculated as (h × m).
- (3)
- Calculate the difference between dry and wet soil samples as D (h × m).
- (4)
- Perform Principal Component Analysis on DTD to obtain the matrix V (m × m).
- (5)
- Define the dimension of EPO as g and calculate a subset Vs (m × g) of the V matrix.
- (6)
- Calculate Q = VsVs T.
- (7)
- Finally, calculate the projection matrix P using the formula P = I − Q, where I is an identity matrix.
2.2.3. Direct Standardization (DS)
2.2.4. Model Construction Methods and Accuracy Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
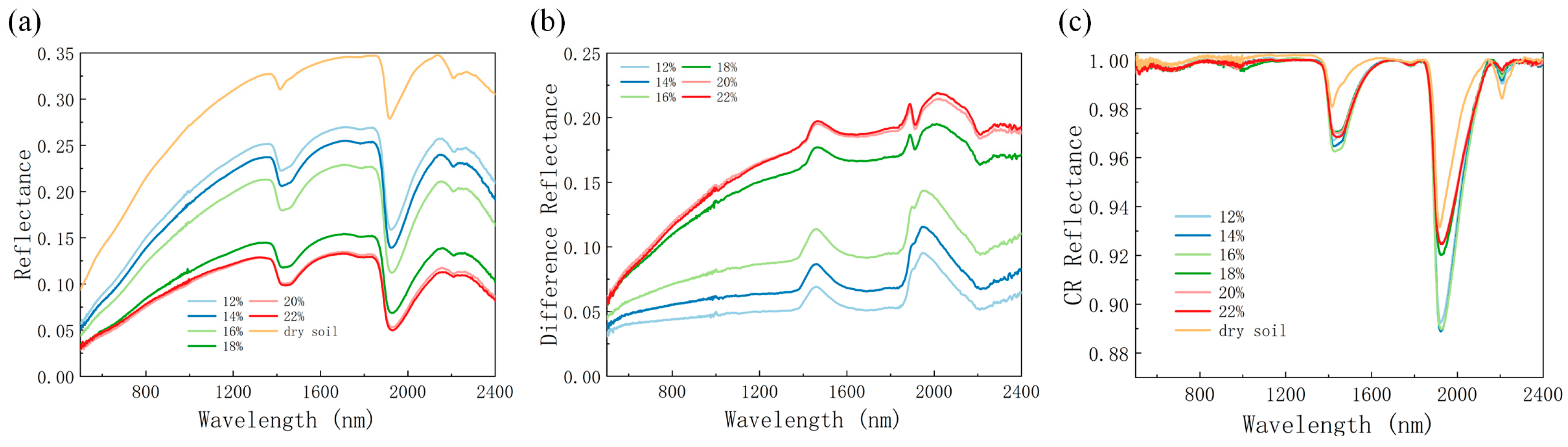
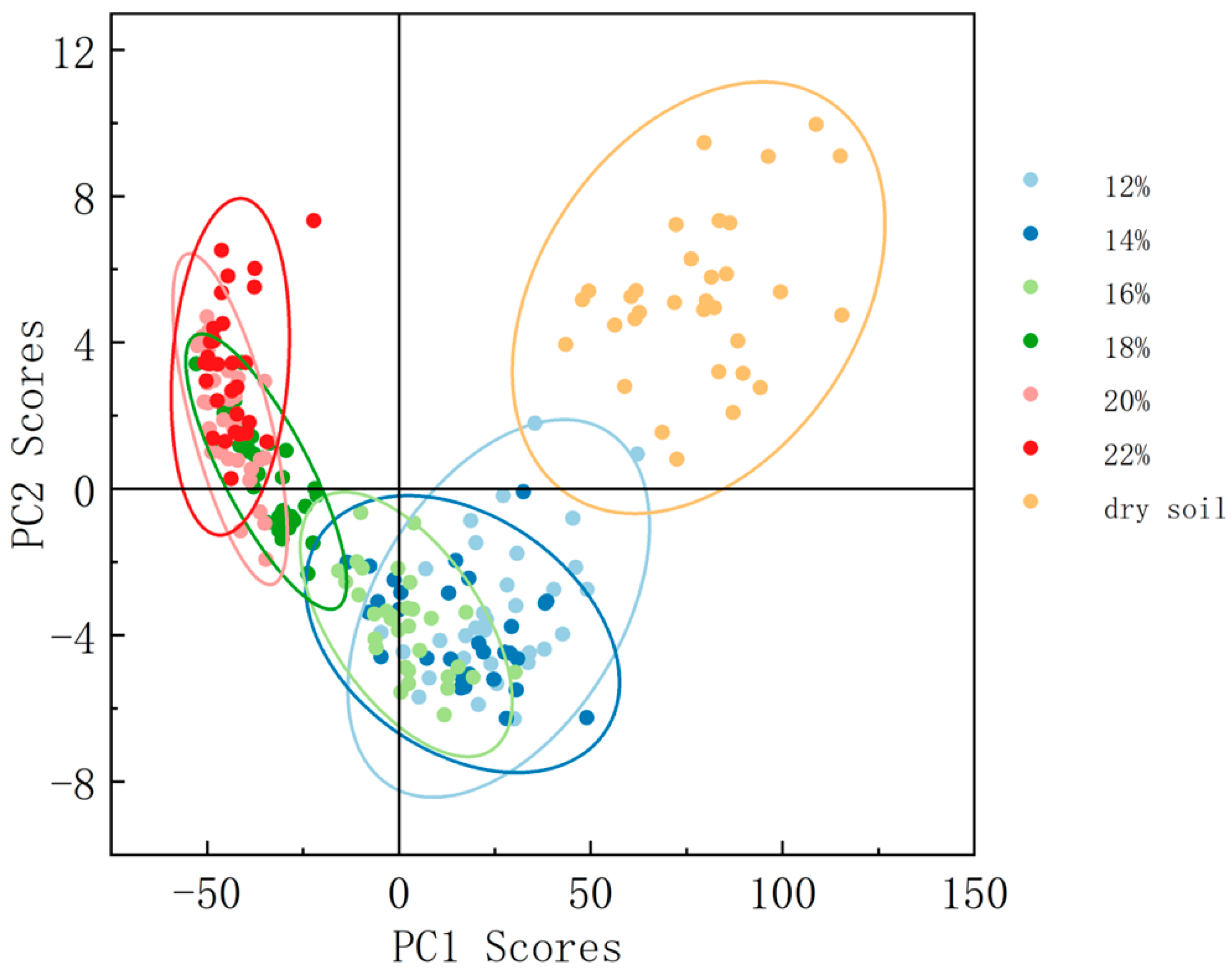
3.1. Effect of Soil Moisture Content on Soil Spectral Reflectance
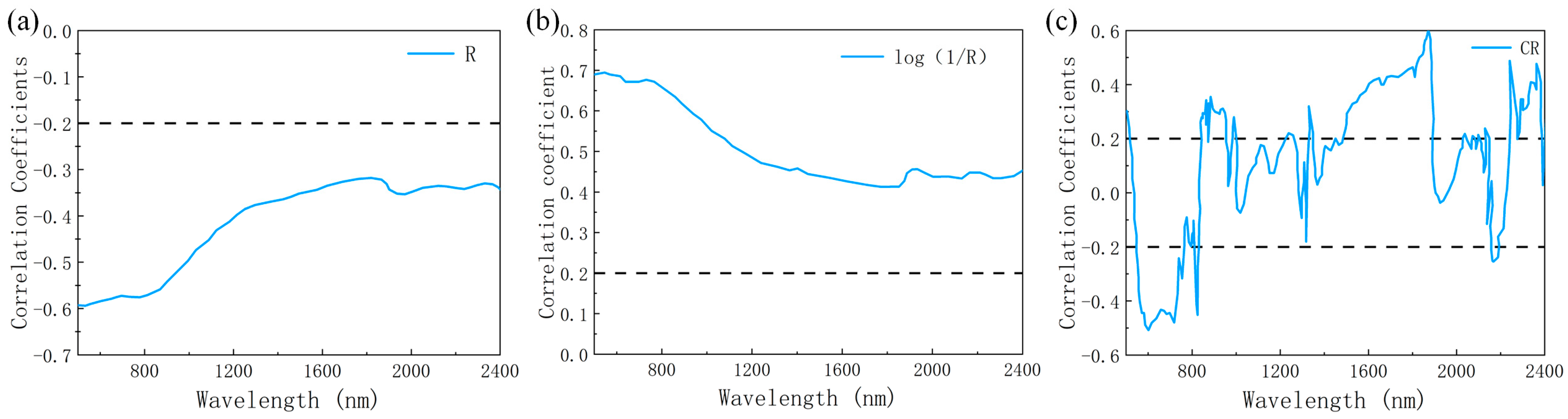
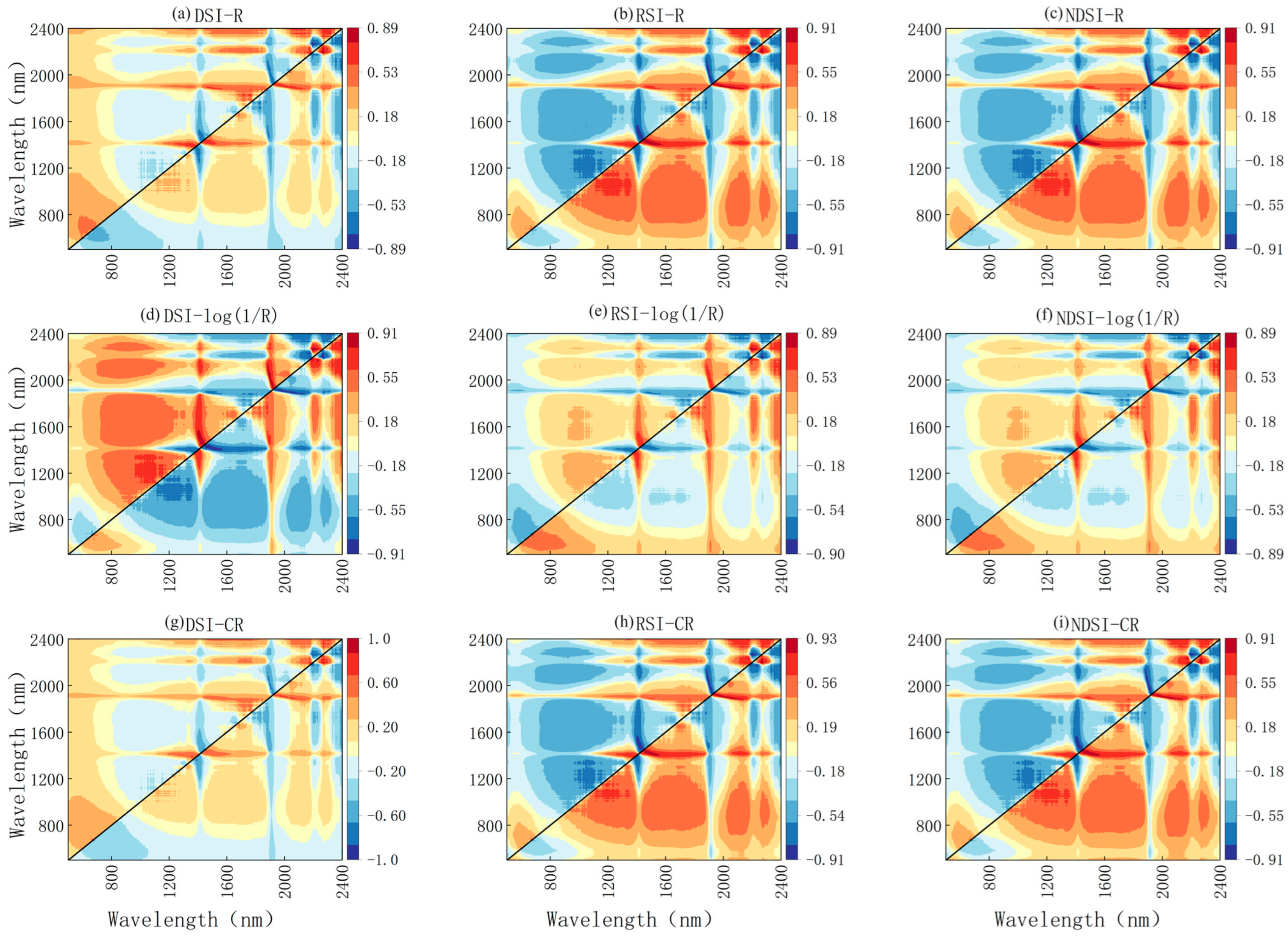
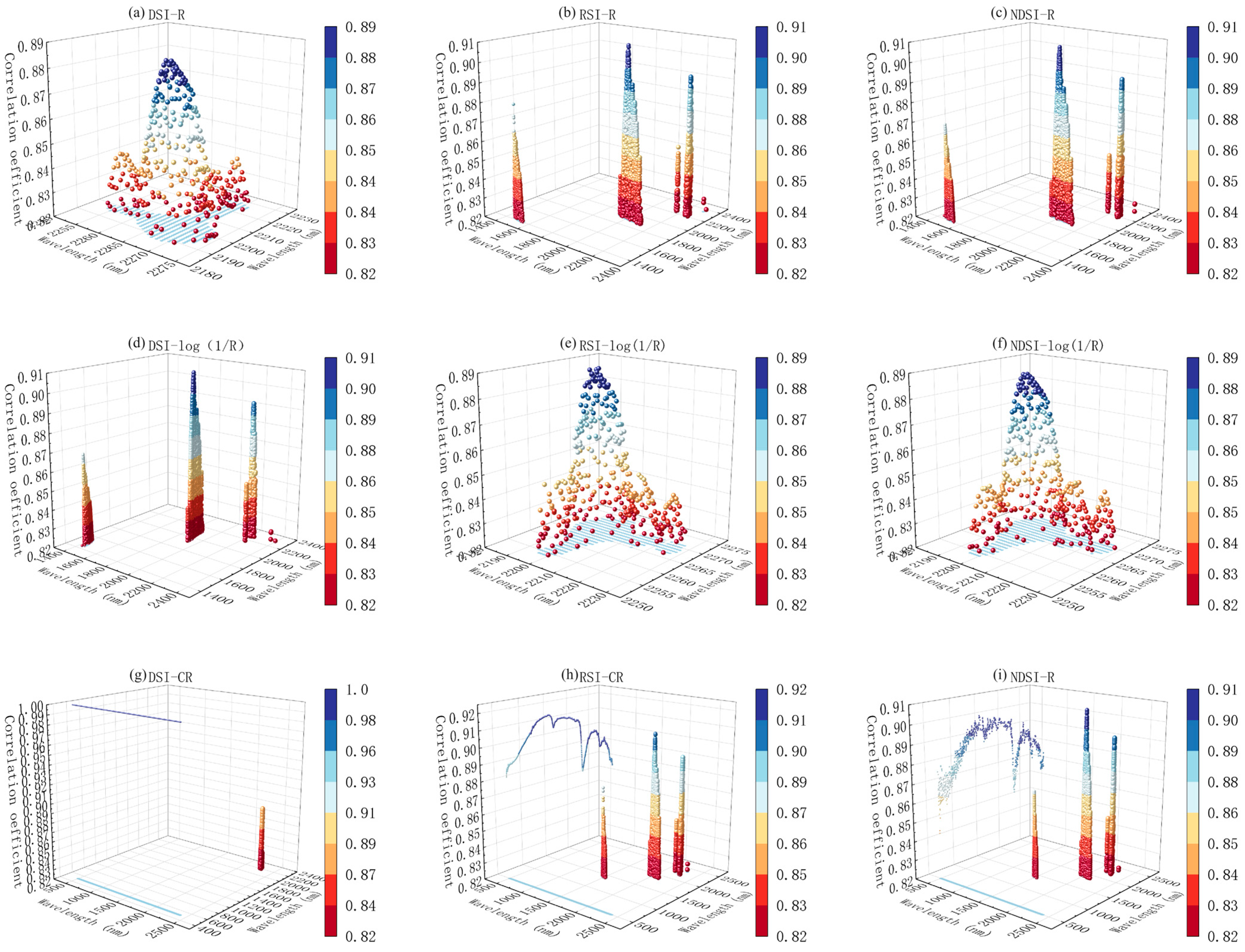
3.2. Construction of Spectral Index
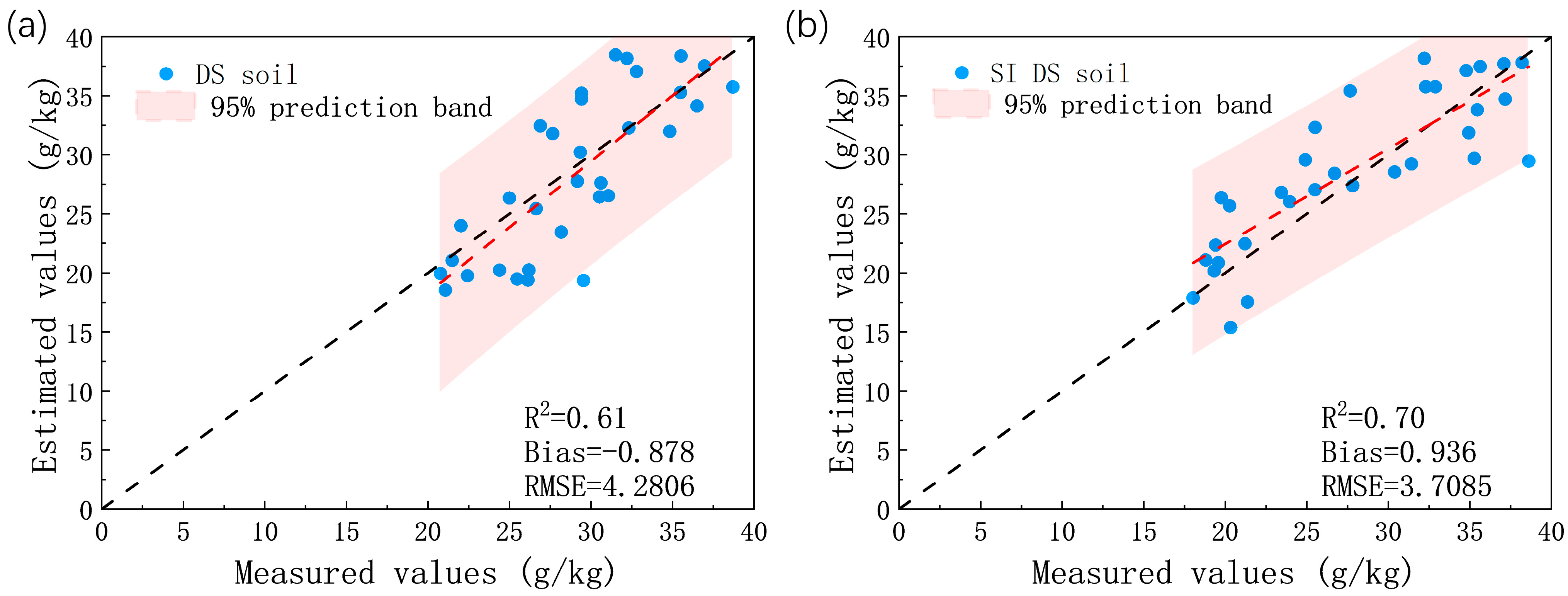
3.3. EPO-PLS and DS-PLS Prediction Results after Using Spectral Index
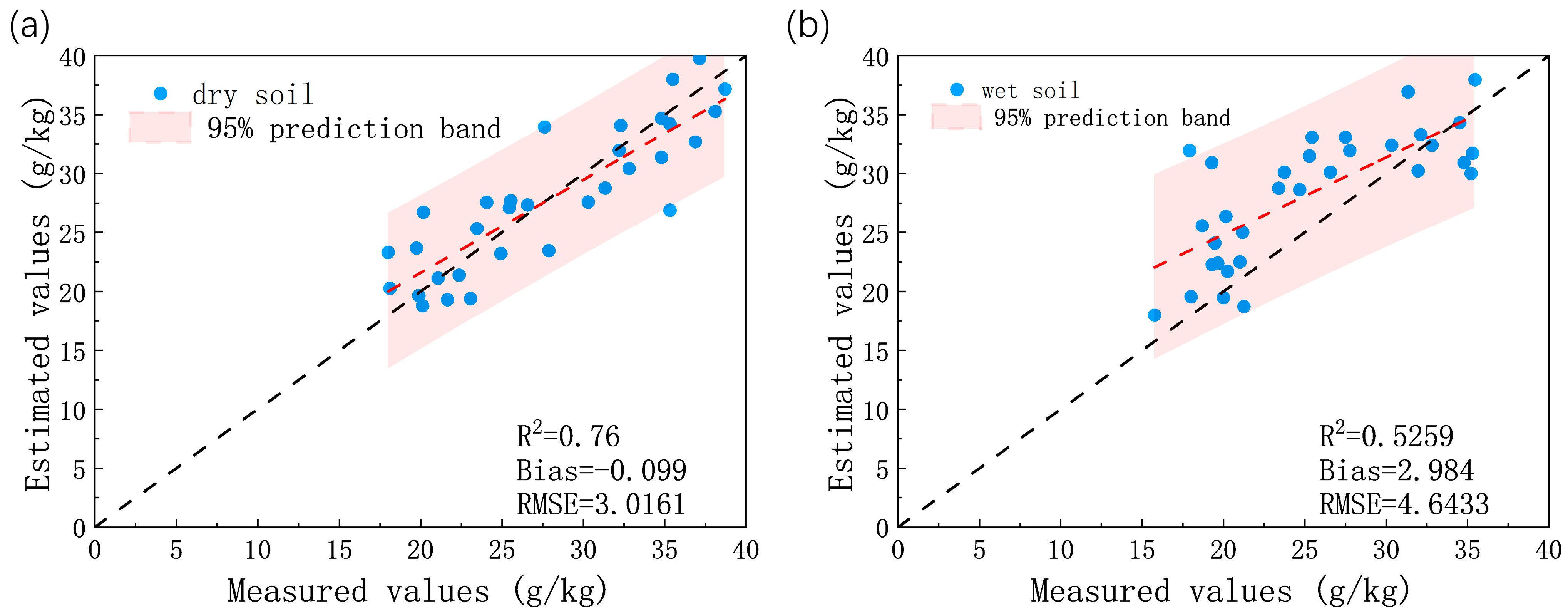
3.3.1. PLS Prediction of Wet Soil and Dry Soil
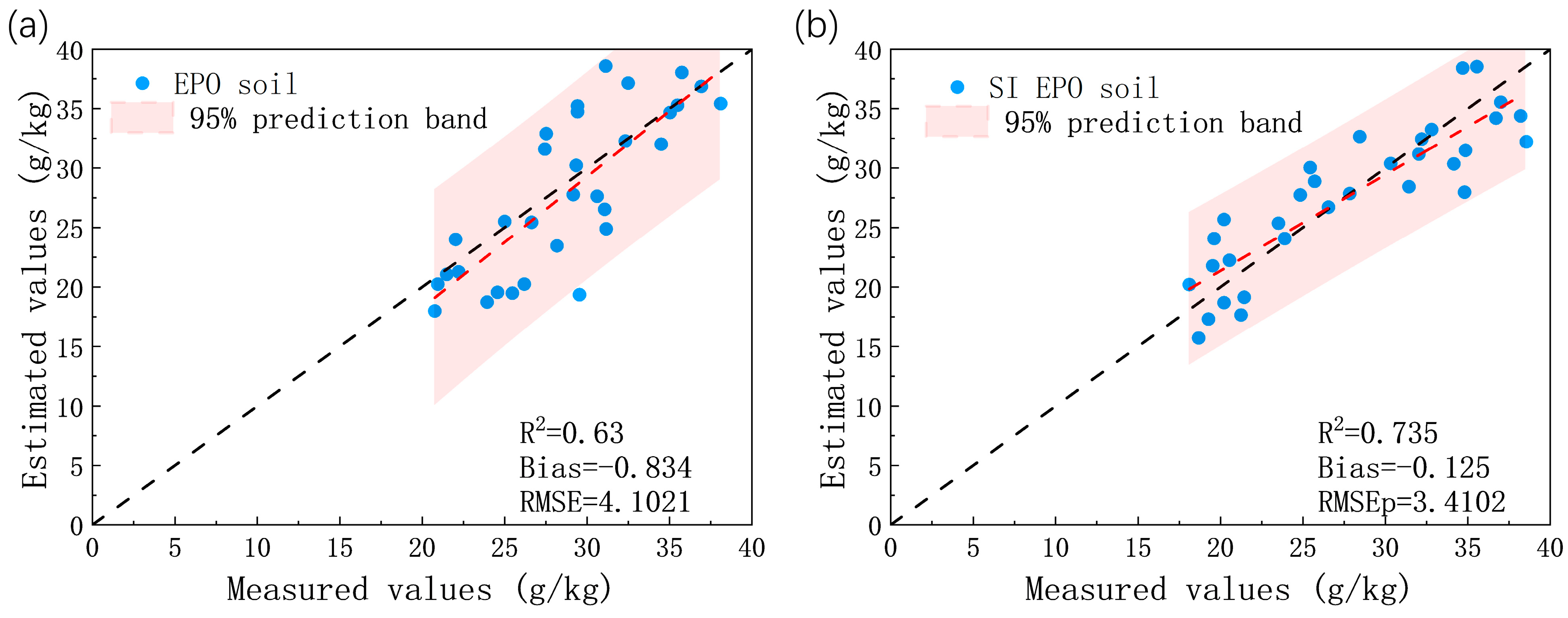
3.3.2. Model of Spectral Index Combined with EPO
3.3.3. Model of Spectral Index Combined with DS
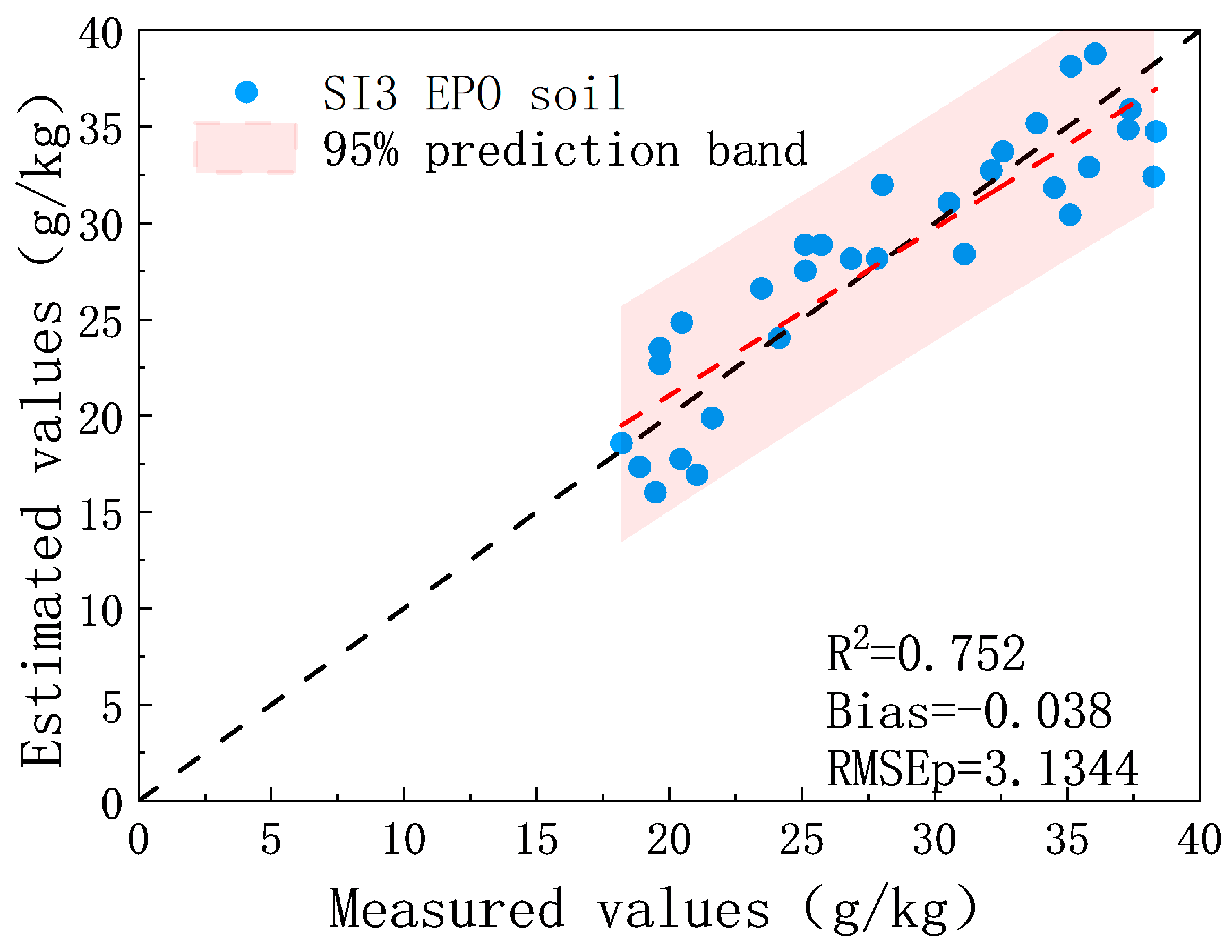
3.4. EPO-PLS Prediction Results after Using Three-Band Spectral Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of SMC on Spectrum
4.2. The Influence of the Spectral Index on the Correlation between Spectrum and SOM
4.3. The Model Advantage of Spectral Index Combined with Water Removal Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Lin, D.; Hou, M.; Li, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, Z. Transformation of soil organic matter subjected to environmental disturbance and preservation of organic matter bound to soil minerals: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yan, C.; Yuan, J.; Ding, N.; Chen, Z. Prediction of soil properties based on characteristic wavelengths with optimal spectral resolution by using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 293, 122452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaene, G.; Bartmiński, P.; Siłuch, M. In Situ VIS-NIR Spectroscopy for a Basic and Rapid Soil Investigation. Sensors 2023, 23, 5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Shen, Q.; Zhai, X.; Du, S.; Zhang, X. Impact of Environmental Factors on the Spatiotemporal Variability of Soil Organic Matter: A Case Study in a Typical Small Mollisol Watershed of Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Dou, S.; Lin, N.; Jiang, R.; Zhu, B. Estimation and Mapping of Soil Organic Matter Content Using a Stacking Ensemble Learning Model Based on Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Du, Q.; Du, P.; Pan, C. Estimation of the Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal in Agricultural Soils Using Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging and Random Forest. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 120987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.-X.; Wang, S.-R.; Ju, X.-P.; Li, Y. Soil Moisture Retrieval Model for Remote Sensing Using Reflected Hyperspectral Information. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Qi, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wei, H. Rapid Retrieval of Cadmium and Lead Content from Urban Greenbelt Zones Using Hyperspectral Characteristic Bands. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hong, Y.; Geng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Cao, J.; Nie, Y. Hyperspectral estimation of soil organic matter content based on partial least squares regression. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 103–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, D.; Guo, K. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Inversion and Monitoring of Organic Matter in Black Soil Based on Dynamic Fitness Inertia Weight Particle Swarm Optimization Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Tan, K.; Lai, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Semi-supervised DNN regression on airborne hyperspectral imagery for improved spatial soil properties prediction. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; Cen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N. Predicting cadmium concentration in soils using laboratory and field reflectance spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.; Minasny, B.; Jones, E.; McBratney, A. To spike or to localize? Strategies to improve the prediction of local soil properties using regional spectral library. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padarian, J.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A. Using deep learning to predict soil properties from regional spectral data. Geoderma Reg. 2019, 16, e00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Ma, G.; Ge, X.; Li, Z.; Han, L. Strategies for the efficient estimation of soil organic matter in salt-affected soils through Vis-NIR spectroscopy: Optimal band combination algorithm and spectral degradation. Geoderma 2021, 382, 114729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ding, J.; Zou, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W. Soil moisture retrival based on sentinel-1 imagery under sparse vegetation coverage. Sensors 2019, 19, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knadel, M.; Castaldi, F.; Barbetti, R.; Ben-Dor, E.; Gholizadeh, A.; Lorenzetti, R. Mathematical techniques to remove moisture effects from visible-near-infrared-shortwave-infrared soil spectra—Review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2023, 58, 629–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, C.; Lu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Tao, Y.; Pan, X. Evaluating the characteristics of soil Vis-NIR spectra after the removal of moisture effect using external parameter orthogonalization. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, X. Simultaneous estimation of multiple soil properties under moist conditions using fractional-order derivative of Vis-NIR spectra and deep learning. Geoderma 2023, 438, 116653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Water-absorption-trough dewatering machine for estimation of organic carbon in moist soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Luo, D.; Peng, J. Predicting soil organic carbon content using simulated insitu spectra and moisture correction algorithms in southern Xinjiang, China. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 37, e00783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B. Reducing the moisture effect and improving the prediction of soil organic matter with VIS-NIR spectroscopy in black soil area. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 5895–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Xu, D.; Zhao, X.; Shi, Z.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Z. Removing the moisture effect on predicting soil organic matter using vis-NIR spectroscopy with external parameter orthogonalization. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 37, e00797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudier, P.; Hedley, C.; Lobsey, C.; Rossel, R.V.; Leroux, C. Evaluation of two methods to eliminate the effect of water from soil vis-NIR spectra for predictions of organic carbon. Geoderma 2017, 296, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnaf, M.A.; Mouazen, A.M. Removal of external influences from on-line vis-NIR spectra for predicting soil organic carbon using machine learning. CATENA 2022, 211, 106015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H. Prediction of soil organic matter by VIS-NIR spectroscopy using normalized soil moisture index as a proxy of soil moisture. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Zhao, G.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, R.Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, J.C. Improvement of soil organic matter content prediction accuracy by removing the influence of soil moisture in hyperspectral estimation. J. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 91–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Yuan, J.; Yan, C.; Xu, J.; Ma, C.; Dai, H. Impact of Spectral Resolution and Signal-to-Noise Ratio in Vis-NIR Spectrometry on Soil Organic Matter Estimation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, J.-M.; Chauchard, F.; Bellon-Maurel, V. EPO-PLS external parameter orthogonalisation of PLS application to temperature-independent measurement of sugar content of intact fruits. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2003, 66, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Bellon-Maurel, V.; Roger, J.-M.; Gobrecht, A.; Ferrand, L.; Joalland, S. Removing the effect of soil moisture from NIR diffuse reflectance spectra for the prediction of soil organic carbon. Geoderma 2011, 167–168, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, C.; Peng, J. Minimize of moisture effects from laboratory simulations of in-situ Vis-NIR spectral for the prediction of soil salinity. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 137, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Shi, Z. Accounting for the effects of water and the environment on proximally sensed vis-NIR soil spectra and their calibrations. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, A.; Klyueva, V.; Romanenko, K.; Fomin, D. Micro- within macro: How micro-aggregation shapes the soil pore space and water-stability. Geoderma 2022, 415, 115771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Ding, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, K. Prediction of soil organic matter content based on characteristic band selection method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 273, 120949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C. Hyperspectral inversion of soil organic matter content in cultivated land based on wavelet transform. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, H. A dynamic normalized difference index for estimating soil organic matter concentration using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Tan, K.; Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, Z. A novel semi-empirical soil multi-factor radiative transfer model for soil organic matter estimation based on hyperspectral imagery. Geoderma 2023, 437, 116605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Tan, K.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Zou, B. Prediction of soil organic matter by Kubelka-Munk based airborne hyperspectral moisture removal model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, J.; Ruan, Y. Effects of different spectral processing methods on soil organic matter prediction based on VNIR-SWIR spectroscopy in karst areas, Southwest China. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Gao, J.; Yu, B.; Yan, C.; Ma, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Estimation of soil organic matter content based on spectral indices constructed by improved Hapke model. Geoderma 2024, 443, 116823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

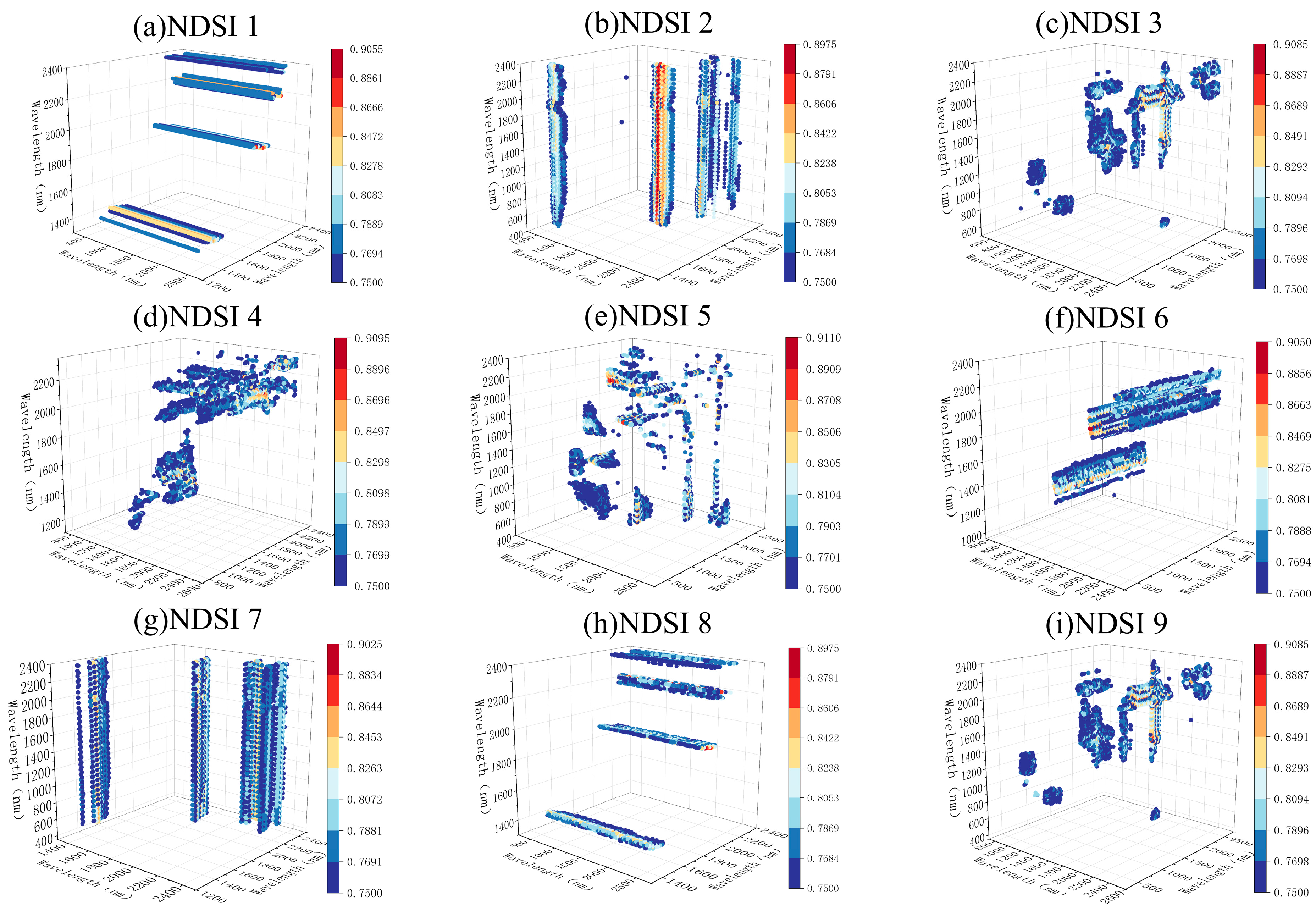
| Spectral Index | Formula |
|---|---|
| Difference spectral index | |
| Ratio spectral index | |
| SI2 Normalized difference spectral index | |
| SI3 Normalized difference spectral index |
| SMC | PC1 (%) | PC2 (%) | Accumulation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry soil | 98.73 | 0.76 | 99.49 |
| 12% | 97.90 | 1.35 | 99.25 |
| 14% | 99.05 | 0.58 | 99.63 |
| 16% | 98.27 | 1.03 | 99.29 |
| 18% | 97.40 | 1.52 | 98.92 |
| 20% | 95.34 | 3.11 | 98.45 |
| 22% | 90.53 | 8.04 | 98.57 |
| Spectral Transformation | Spectral Index | Maximum Correlation Band Combination | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | DSI | 2267 2197 | 0.8851 |
| RSI | 2004 1900 | 0.9094 | |
| NDSI | 2004 1900 | 0.9094 | |
| Log(1/R) | DSI | 1900 2003 | 0.9080 |
| RSI | 2198 2267 | 0.8890 | |
| NDSI | 2197 2266 | 0.8868 | |
| CR | DSI | 2267 2201 | 0.8868 |
| RSI | 2005 1901 | 0.9076 | |
| NDSI | 2005 1901 | 0.9069 |
| (nm) | (nm) | Correlation with Two Bands | (nm) | Correlation with Three Bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 2380 | 0.91 | 1900 | 0.91 |
| 2300 | 2380 | 0.76 | 2380 | 0.77 |
| 2120 | 2360 | 0.72 | 2298 | 0.74 |
| 2260 | 2200 | 0.86 | 2270 | 0.89 |
| 2140 | 2200 | 0.74 | 2266 | 0.82 |
| 1360 | 1400 | 0.71 | 1509 | 0.88 |
| 1120 | 1100 | 0.71 | 1191 | 0.74 |
| 2140 | 1420 | 0.72 | 1485 | 0.80 |
| 1460 | 1440 | 0.85 | 1448 | 0.88 |
| 1540 | 1400 | 0.82 | 1342 | 0.85 |
| Number | a | b | c | d | e | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDSI 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| NDSI 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 0 |
| NDSI 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| NDSI 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| NDSI 5 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −1 |
| NDSI 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| NDSI 7 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| NDSI 8 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −1 |
| NDSI 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Yuan, J. Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Based on Spectral Indices Combined with Water Removal Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122065
Xu J, Liu Y, Yan C, Yuan J. Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Based on Spectral Indices Combined with Water Removal Algorithm. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(12):2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122065
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiawei, Yuteng Liu, Changxiang Yan, and Jing Yuan. 2024. "Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Based on Spectral Indices Combined with Water Removal Algorithm" Remote Sensing 16, no. 12: 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122065
APA StyleXu, J., Liu, Y., Yan, C., & Yuan, J. (2024). Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Based on Spectral Indices Combined with Water Removal Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 16(12), 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122065






