Lunar High Alumina Basalts in Mare Imbrium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. LRO Diviner Products
2.2. Remote Sensing Identification of HA Basalts
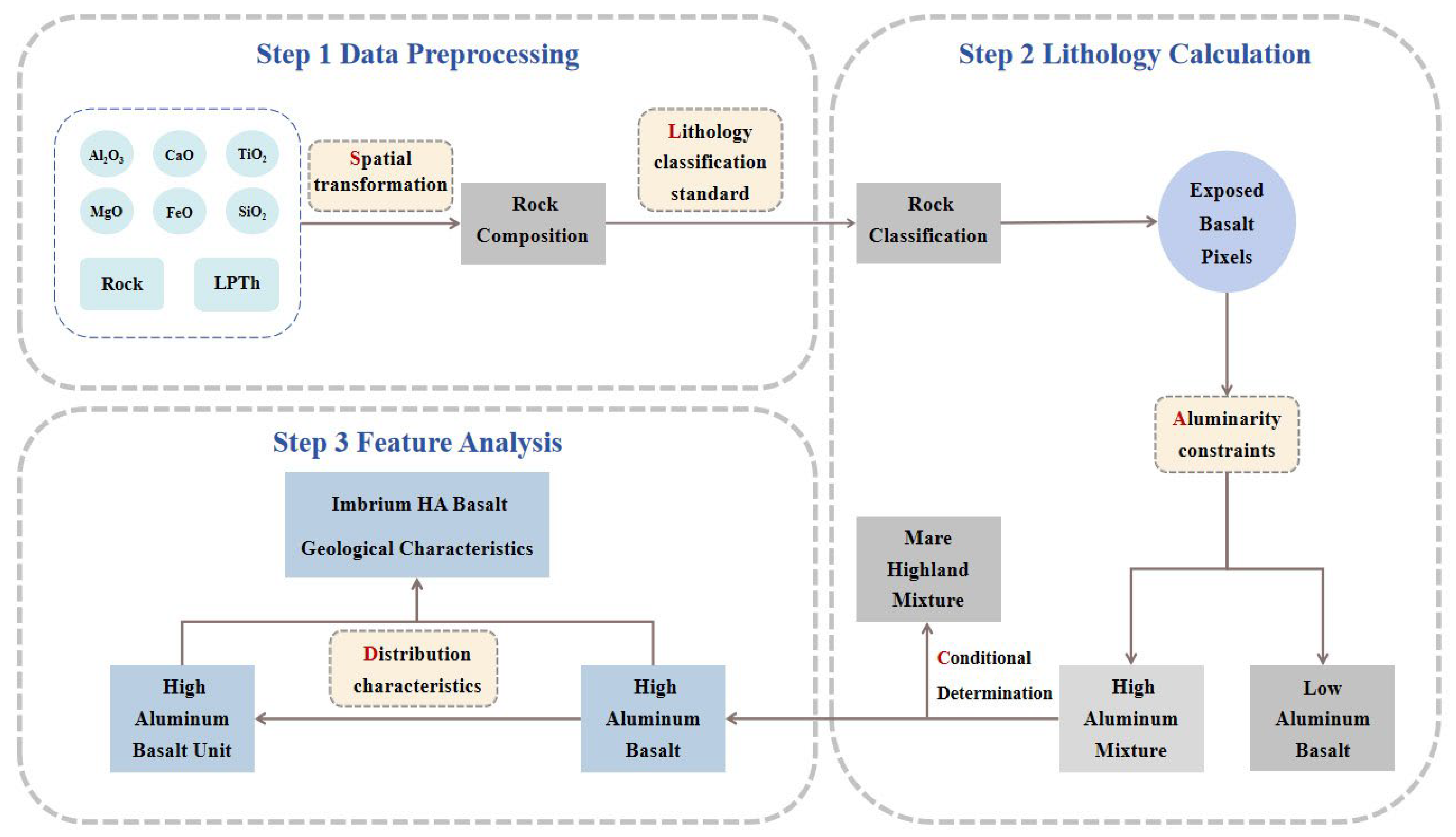
2.3. HA Basalt Pixels and Unit Characteristic Calculation
3. Results
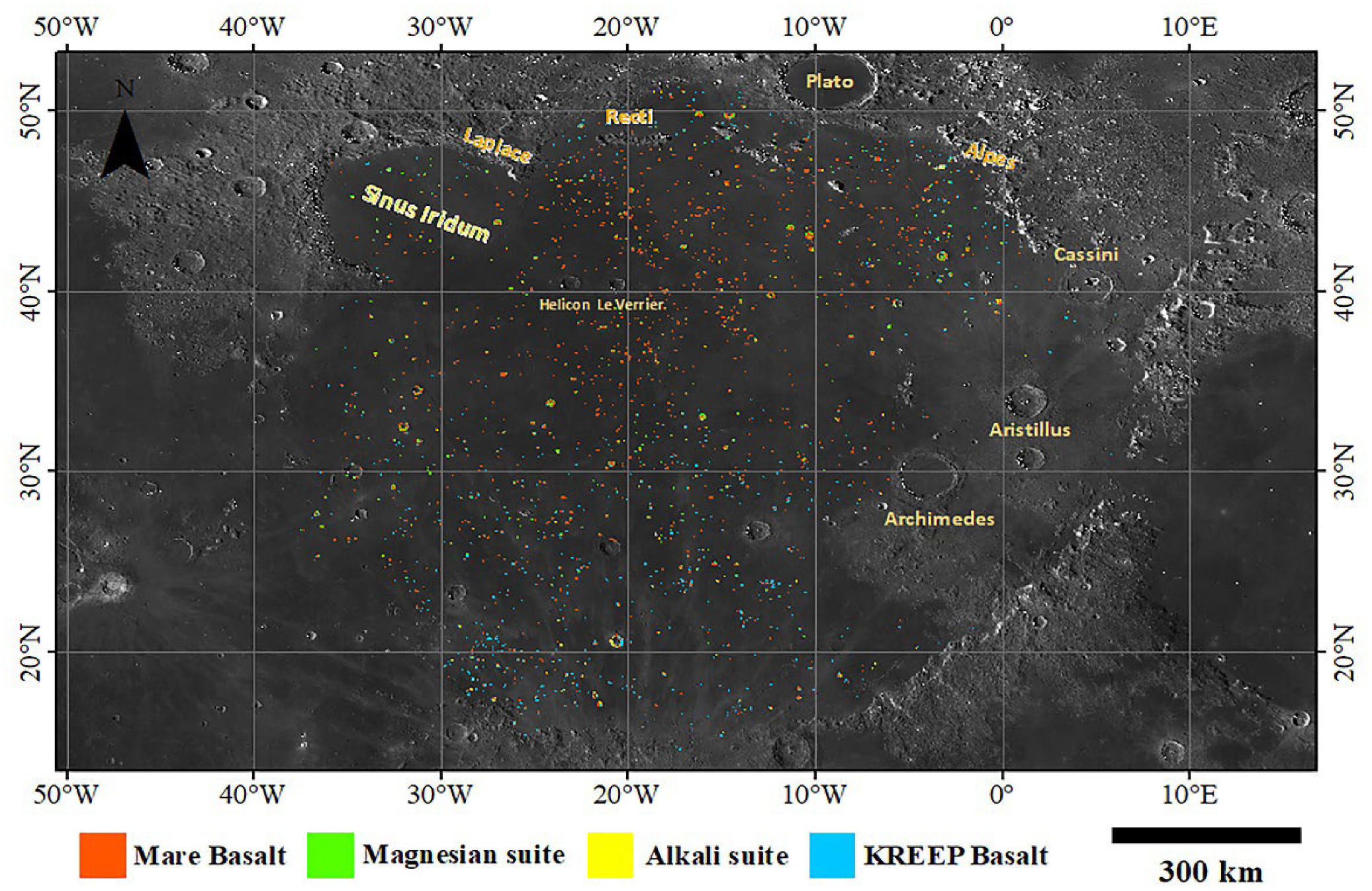
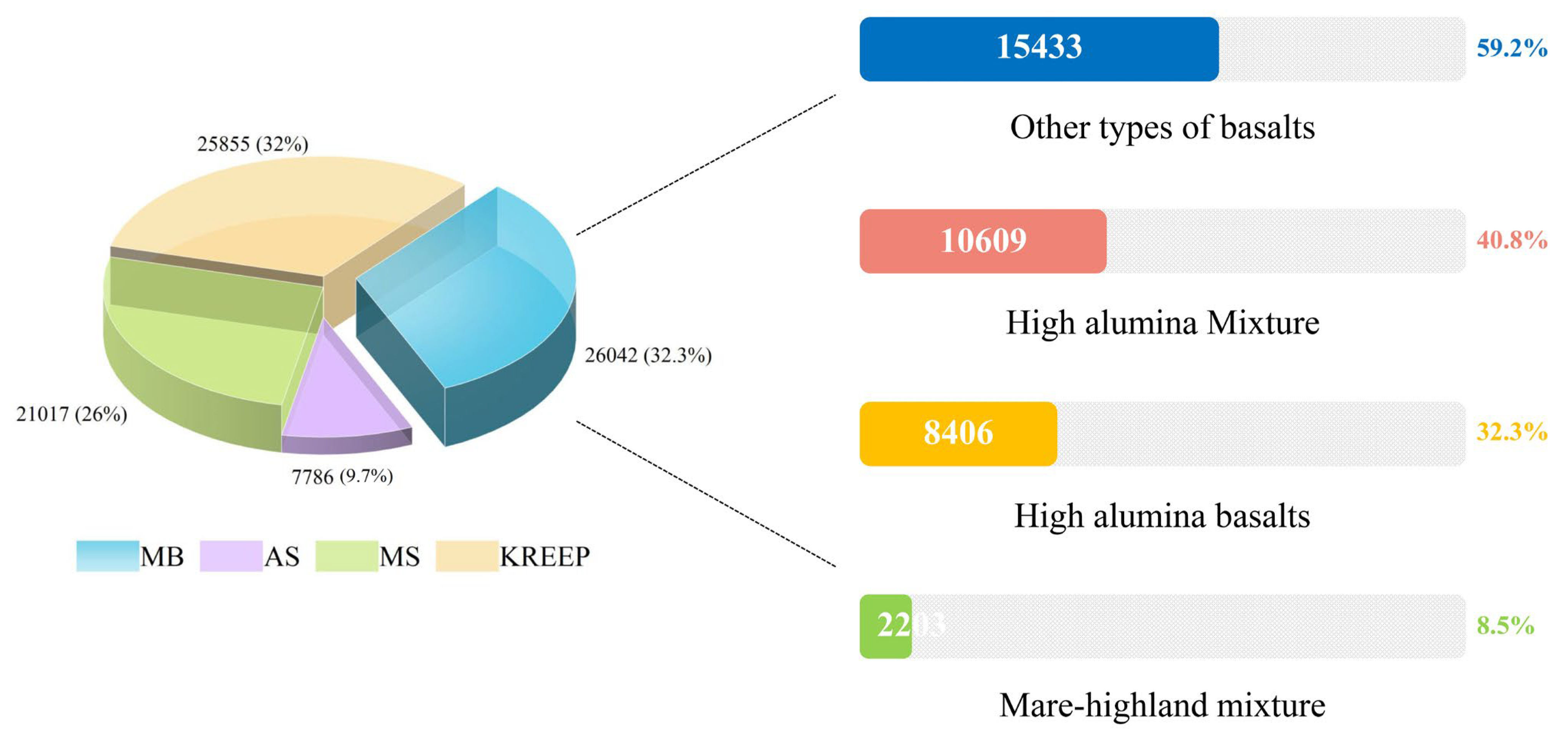
3.1. Lithology Classification
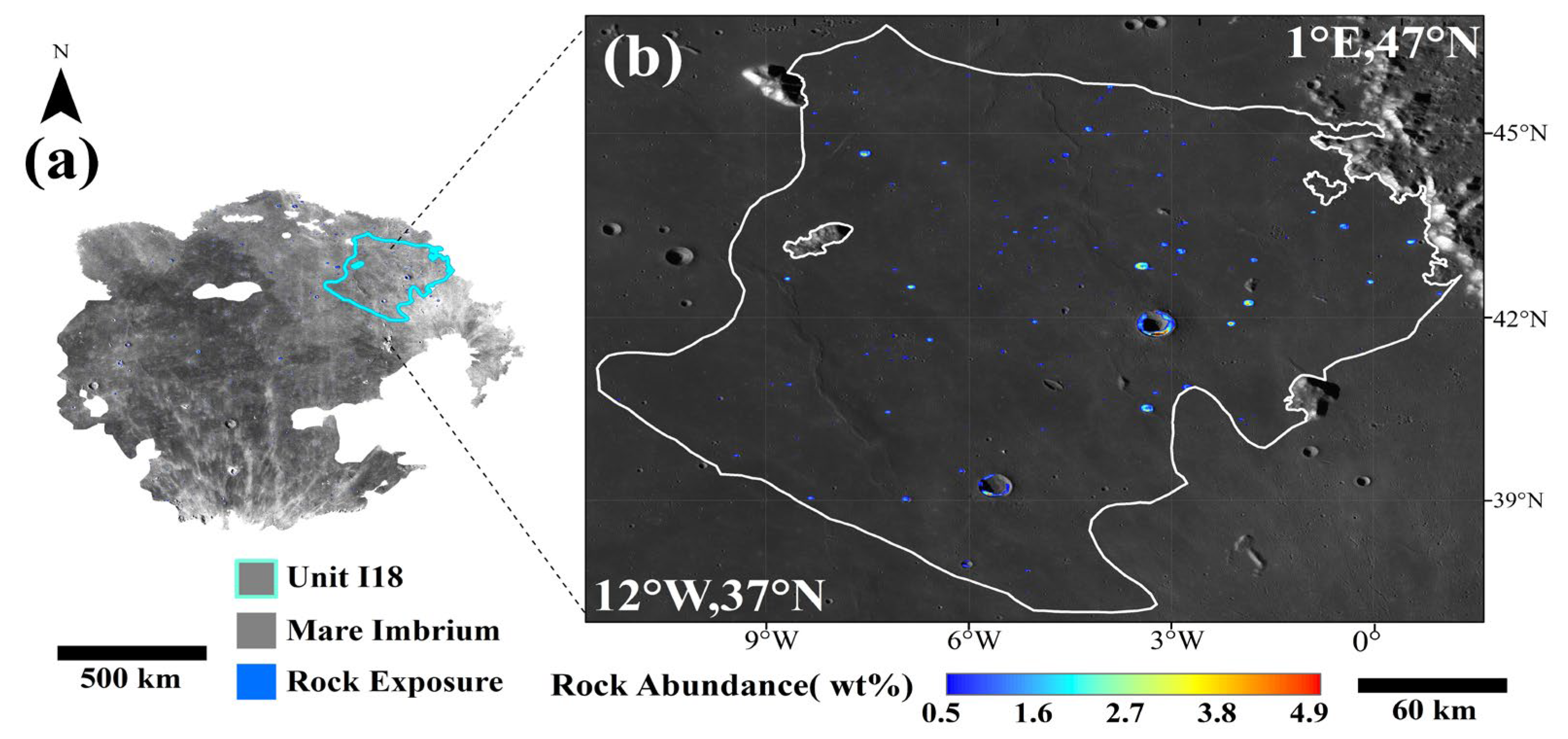
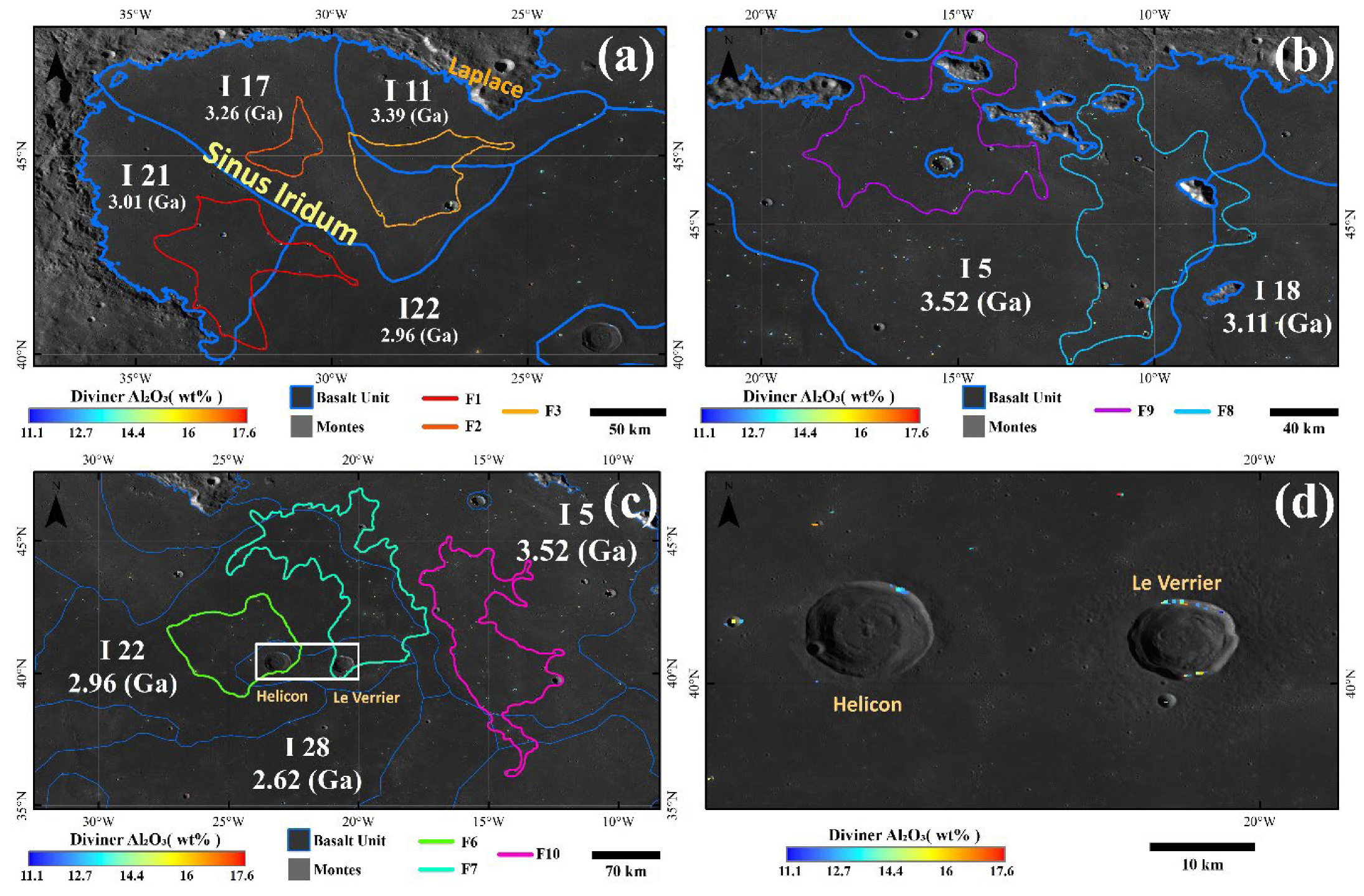
3.2. Mare Imbrium HA Basalt Units
3.3. HA Basalt Unit Distribution Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with the Results of Previous Studies
4.2. Mare Imbrium HA Basalt Layers
4.3. Morphological and Geological Characteristics of Imbrium HA Basalts
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Spectral interpretation of late-stage mare basalt mineralogy unveiled by Chang’E-5 samples. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.M.; Harish; Patel, D.; Solanki, P.M.; El-Maarry, M.R. Hybrid Volcanic Episodes within the Orientale Basin, Moon. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, J.W., III. Lunar volcanism in space and time. Rev. Geophys. 1976, 14, 265–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelms, D.E.; McCauley, J.F.; Trask, N.J. The Geologic History of the Moon; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; pp. 2330–7102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Hsu, W.; Guan, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Petrogenesis of the Northwest Africa 4898 high-Al mare basalt. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2016, 51, 1268–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.R.; Taylor, L.A.J.G.e.C.A. Petrogenesis of mare basalts: A record of lunar volcanism. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 2177–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, X.Z.; Chen, J.; Han, K.Y.; Shi, C.L.; Jin, M.; Liu, L.W.; Liu, X.B.; Deng, J.Y. Interpretation of Geological Features and Volcanic Activity in the Tsiolkovsky Region of the Moon. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, C.K.; Hess, P.C.; Wieczorek, M.A.; Pritchard, M.E.; Parmentier, E.M.; Borg, L.E.; Longhi, J.; Elkins-Tanton, L.T.; Neal, C.R.; Antonenko, I.; et al. Thermal and magmatic evolution of the moon. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 60, 365–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, J.W. Lava Flooding of Ancient Planetary Crusts-Geometry, Thickness, and Volumes of Flooded Lunar Impact Basins. Moon Planets 1982, 26, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerty, J.J.; Shearer, C.K.; Papike, J.J. Petrogenesis of the Apollo 14 high-alumina basalts: Implications from ion microprobe analyses. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 5831–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.Y.; Jolliff, B.L.; Neal, C.R. Distinguishing high-alumina mare basalts using clementine UVVIS and lunar prospector GRS data: Mare moscoviense and mare nectaris. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2008, 113, E01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.Y.; Jolliff, B.L.; Neal, C.R. Searching for high alumina mare basalts using Clementine UVVIS and Lunar Prospector GRS data: Mare Fecunditatis and Mare Imbrium. Icarus 2008, 198, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.R.; Taylor, L.A.; Lindstrom, M.M. Apollo 14 mare basalt petrogenesis-Assimilation of KREEP-like components by a fractionating magma. In Proceedings (A89-10851 01-91), Proceedings of the 18th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 16–20 March 1987; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 1988; pp. 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, C.; Taylor, L.; Schmitt, R.; Hughes, S.; Lindstrom, M. High alumina (HA) and very high potassium (VHK) basalt clasts from Apollo 14 breccias. II-Whole rock geochemistry-Further evidence for combined assimilation and fractional crystallization within the lunar crust. In Proceedings (A89-36486 15-91), Proceedings of the 19th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 14–18 March 1988; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 1989; pp. 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Finnila, A.; Hess, P.; Rutherford, J.o.G.R.P. Assimilation by lunar mare basalts: Melting of crustal material and dissolution of anorthite. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1994, 99, 14677–14690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, W. On high-alumina mare basalts. In Proceedings (A78-46603 21-91), Proceedings of the 6th Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 17–21 March 1975; Pergamon Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; Volume 1, pp. 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Papike, J.; Vaniman, D. The lunar mare basalt suite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1978, 5, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.; Neal, C.R.; Shih, C.-Y.; Nyquist, L.E. Petrogenetic association of the oldest lunar basalts: Combined Rb-Sr isotopic and trace element constraints. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 373, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.A.; Taylor, L.A.; Neal, C.R. A chemical model for generating the sources of mare basalts: Combined equilibrium and fractional crystallization of the lunar magmasphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 3809–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, P.H.; Kallemeyn, G.W.; Kyte, F.T. Siderophile element evidence indicates that Apollo 14 high-Al mare basalts are not impact melts. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 17–21 March 1997; p. 1501. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, H.; Oshrin, J.G.; Neal, C.R. Investigation into the petrogenesis of Apollo 14 high-Al basaltic melts through crystal stratigraphy of plagioclase. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 6439–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.; Banerdt, W.; Alkalai, L.; Team, L. Lunette: A two-lander Discovery-class geophysics mission to the Moon. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 7–11 March 2011; p. 2832. [Google Scholar]
- Nyquist, L.; Wooden, J.; Shih, C.-Y.; Wiesmann, H.; Bansal, B. Isotopic and REE studies of lunar basalt 12038: Implications for petrogenesis of aluminous mare basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1981, 55, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, R.A.; Korotev, R.L.; Haskin, L.A.; Jolliff, B.L.; Gillis, J.J. Petrography and geochemistry of five new Apollo 16 mare basalts and evidence for post-basin deposition of basaltic material at the site. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2006, 41, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, R.A.; McKay, G.A.; Weill, D.F. Microprobe studies of three Luna 16 basalt fragments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1972, 13, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, R.; McKay, G.; Smith, H.; Weill, D. Lunar polymict breccia 14321: A petrographic study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1975, 39, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.S.; Schmitt, R.; Nielsen, R.; Taylor, G.; Warner, R.; Keil, K. Petrogenesis of Luna 16 aluminous mare basalts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1979, 6, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, T.; Taylor, G.; Keil, K.; Schmitt, R.A.; Hughes, S.; Smith, M. Apollo 14 aluminous mare basalts and their possible relationship to KREEP. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1985, 90, C365–C374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.Y.; Jaiswal, B.; Hawke, B.R.; Oehman, T.; Giguere, T.A.; Johnson, K. The basalts of Mare Frigoris. J. Geophys. Res.Planets 2015, 120, 1646–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudis, P.D. The Geology of Multi-Ring Impact Basins; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hiesinger, H.; Jaumann, R.; Neukum, G.; Head, J.W., III. Ages of mare basalts on the lunar nearside. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2000, 105, 29239–29275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugiolacchi, R.; Guest, J.E. Compositional and temporal investigation of exposed lunar basalts in the Mare Imbrium region. Icarus 2008, 197, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.S. Major Elements Concentrations in Chang’E-3 Landing Site from Active Particle-Induced X-ray Spectrometer. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadermann, F.J.; Heusser, E.; Jessberger, E.K.; Lingner, S.; Stöffler, D. The case for a younger Imbrium basin: New 40Ar-39Ar ages of Apollo 14 rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotev, R.L. Compositional variation in Apollo 16 impact-melt breccias and inferences for the geology and bombardment history of the Central Highlands of the Moon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3931–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.; Norman, M.; Ryder, G.; Dalrymple, G.; Huard, J. Identifying impact events within the lunar cataclysm from 40Ar-39Ar ages of Apollo 16 impact melt rocks. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, League City, TX, USA, 15 March 2004; p. 1328. [Google Scholar]
- Nyquist, L.; Shih, C.; Reese, Y. Dating melt rock 63545 by Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd: Age of Imbrium; SPA dress rehearsal. In Proceedings of the 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 7–11 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L.; Liu, J.Z.; Ji, J.Z.; Guo, D.J.; Liu, J.W. Redefinition and geological significance of periods of basaltic magma filling in lunar Mare Imbrium. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yun-Zhao, W. Reflectance spectroscopy of the Moon and its application. Earth Sci. Front. 2014, 21, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudis, P.D.; Hawke, B.R.; Lucey, P.G. Materials and formation of the Imbrium basin. In Proceedings (A89-10851 01-91), NASA-Supported Research, Proceedings of the 18th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 16–20 March 1987; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 1988; pp. 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, B.; Lucey, P.; Gillis, J. Mapping iron in the lunar mare: An improved approach. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2005, 110, E2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.G.; Blewett, D.T.; Taylor, G.J.; Hawke, B.R. Imaging of lunar surface maturity. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2000, 105, 20377–20386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Li, B.Z.; Chen, S.B.; Lu, T.Q.; Lu, P.; Lu, Y.; Jin, Q. Global estimates of lunar surface chemistry derived from LRO diviner data. Icarus 2022, 371, 114697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeck, V.R. The role of ballistic erosion and sedimentation in lunar stratigraphy. Rev. Geophys. 1975, 13, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerty, J.J.; Shearer, C.K.; Vaniman, D.T. Heat-producing elements in the lunar mantle: Insights from ion microprobe analyses of lunar pyroclastic glasses. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3457–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Minton, D.A.; Hirabayashi, M.; Elliott, J.R.; Richardson, J.E.; Fassett, C.I.; Zellner, N.E.B. Heterogeneous impact transport on the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2017, 122, 1158–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, J.W.; Wilson, L. Generation, ascent and eruption of magma on the Moon: New insights into source depths, magma supply, intrusions and effusive/explosive eruptions (Part 2: Predicted emplacement processes and observations). Icarus 2017, 283, 176–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.G.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, A.A. The Provenance of Regolith at the Chang’e-5 Candidate Landing Region. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2020, 125, E6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhao, S.Y. New Insights into Lithology Distribution Across the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2017, 122, 2034–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.G.; Greenhagen, B.; Hanna, K.D.; Bowles, N.; Flom, A.; Paige, D.A. Christiansen Feature Map from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment: Improved Corrections and Derived Mineralogy. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2021, 126, E6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.P.; Paige, D.A.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Sefton-Nash, E. The global surface temperatures of the moon as measured by the diviner lunar radiometer experiment. Icarus 2017, 283, 300–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhagen, B.T.; Lucey, P.G.; Wyatt, M.B.; Glotch, T.D.; Allen, C.C.; Arnold, J.A.; Bandfield, J.L.; Bowles, N.E.; Hanna, K.L.D.; Hayne, P.O.; et al. Global Silicate Mineralogy of the Moon from the Diviner Lunar Radiometer. Science 2010, 329, 1507–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhagen, B.; Lucey, P.; Bandfield, J.; Hayne, P.; Williams, J.; Paige, D. The Diviner Lunar Radiometer compositional data products: Description and examples. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 7–11 March 2011; p. 2679. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.G.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Song, E.; Arnold, J.A.; Lemelin, M.; Hanna, K.D.; Bowles, N.E.; Glotch, T.D.; Paige, D.A. Space weathering effects in Diviner Lunar Radiometer multispectral infrared measurements of the lunar Christiansen Feature: Characteristics and mitigation. Icarus 2017, 283, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, L.M.; Hunt, G.R.; Salisbury, J.W. The use of mid-infrared spectroscopy in remote sensing of space targets. In Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy of Lunar and Terrestrial Minerals; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1975; pp. 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, K.L.D.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Patterson, W.R.; Pieters, C.M.; Mustard, J.F.; Bowles, N.E.; Paige, D.A.; Glotch, T.D.; Thompson, C. Effects of varying environmental conditions on emissivity spectra of bulk lunar soils: Application to Diviner thermal infrared observations of the Moon. Icarus 2017, 283, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.C.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Hanna, K.L.D.; Paige, D.A. Analysis of lunar pyroclastic deposit FeO abundances by LRO Diviner. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2012, 117, E3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, K.L.D.; Wyatt, M.B.; Thomas, I.R.; Bowles, N.E.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Maturilli, A.; Helbert, J.; Paige, D.A. Thermal infrared emissivity measurements under a simulated lunar environment: Application to the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2012, 117, E3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Li, B.; Lu, T.; Han, C.; Tian, P. Study on remote sensing identification and geological characteristics analysis of high alumina mare basalt in Mare Frigoris. Chin. J. Geophys. 2022, 65, 4628–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, J.R.; Chen, S.B.; Li, B.Z.; Han, C.H.; Tian, P. High alumina basalts identification and their feature analysis in Mare Fecunditatis. Icarus 2024, 407, 115464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandfield, J.L.; Ghent, R.R.; Vasavada, A.R.; Paige, D.A.; Lawrence, S.J.; Robinson, M.S. Lunar surface rock abundance and regolith fines temperatures derived from LRO Diviner Radiometer data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2011, 116, E3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Robinson, M.S.; Hapke, B.; Denevi, B.W.; Boyd, A.K. Resolved Hapke parameter maps of the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2014, 119, 1775–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, P.H.; Kallemeyn, G.W. Geochemical investigation of two lunar mare meteorites: Yamato-793169: And Asuka-881757. In Proceedings of the NIPR Symposium on Antarctic Meteorites, Tokyo, Japan, 31 May–2 June 1993; pp. 35–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Korotev, R.L.; Gillis, J.J.; Taylor, L.A.; Lawrence, D.; Campbell, B.A.; Elphic, R.; Feldman, B.; Hood, L.L.; Hunten, D. Understanding the lunar surface and space-Moon interactions. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 60, 83–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.A.; Jolliff, B.L.; Khan, A.; Pritchard, M.E.; Weiss, B.P.; Williams, J.G.; Hood, L.L.; Righter, K.; Neal, C.R.; Shearer, C.K.; et al. The constitution and structure of the lunar interior. In New Views of the Moon; Jolliff, B.L., Wieczorek, M.A., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 2006; Volume 60, p. 221. [Google Scholar]
- Prettyman, T. Lunar Prospector GRS Elemental Abundance Bundle; NASA Planetary Data System: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.S.; Brylow, S.; Tschimmel, M.e.; Humm, D.; Lawrence, S.; Thomas, P.; Denevi, B.W.; Bowman-Cisneros, E.; Zerr, J.; Ravine, M. Lunar reconnaissance orbiter camera (LROC) instrument overview. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 150, 81–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyerer, E.; Robinson, M.; Denevi, B.; Team, L.S. Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera global morphological map of the Moon. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 7–11 March 2011; p. 2387. [Google Scholar]
- Haruyama, J.; Hara, S.; Hioki, K.; Iwasaki, A.; Morota, T.; Ohtake, M.; Matsunaga, T.; Araki, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Ishihara, Y. Lunar global digital terrain model dataset produced from SELENE (Kaguya) terrain camera stereo observations. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 19–23 March 2012; p. 1200. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.E.; Zuber, M.T.; Jackson, G.B.; Cavanaugh, J.F.; Neumann, G.A.; Riris, H.; Sun, X.L.; Zellar, R.S.; Coltharp, C.; Connelly, J.; et al. The Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter Investigation on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 150, 209–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.K.; Mazarico, E.; Neumann, G.A.; Zuber, M.T.; Haruyama, J.; Smith, D.E. A new lunar digital elevation model from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter and SELENE Terrain Camera. Icarus 2016, 273, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastassiou, D.; Wasserburg, G. RbSr ages of igneous rocks from the Apollo 14 mission and the age of the Fra Mauro formation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1971, 12, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, R.K.; Lee-Hu, C.-N.; Wetherill, G.W. Equilibration and ages-Rb-Sr studies of breccias 14321 and 15265. In Proceedings (A75-39540 19-91), Proceedings of the 5th Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 18–22 March 1974; Pergamon Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1974; Volume 2, pp. 1477–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, R.; Lee-Hu, C.; Wetherill, G. More on Rb-Sr in lunar breccia 14321. In Proceedings (A78-46668 21-91), Proceedings of the 6th Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 17–21 March 1975; Pergamon Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; Volume 2, pp. 1501–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Dasch, E.; Shih, C.-Y.; Bansal, B.; Wiesmann, H.; Nyquist, L. Isotopic analysis of basaltic fragments from lunar breccia 14321: Chronology and petrogenesis of pre-Imbrium mare volcanism. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


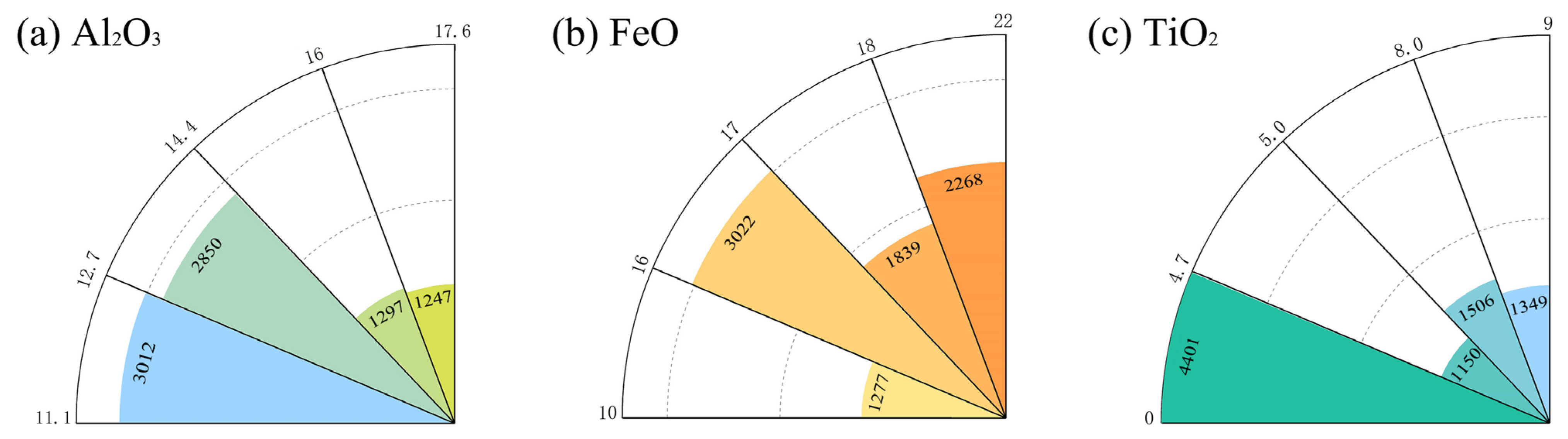

| Lithology | Classification Criteria |
|---|---|
| Magnesian Suite | Th/MgO ≤ 0.4495 and TiO2/MgO ≤ 0.03132 |
| Alkali Suite | (1) Th/MgO ≤ 0.4495 and TiO2/MgO > 0.03132 and FeO/CaO ≤ 1.2967 and Th/CaO > 0.09372 (2) Th/MgO > 0.4495 and TiO2/Al2O3 ≤ 0.68435 and Th/Al2O3 ≤ 1.32803 and MgO/CaO ≤ 0.575 (3) Th/MgO > 0.4495 and TiO2/Al2O3 ≤ 0.68435 and Th/Al2O3 > 1.32803 |
| KREEP basalt | Th/MgO > 0.4495 and TiO2/Al2O3 ≤ 0.68435 and Th/Al2O3 ≤ 1.32803 and MgO/CaO > 0.575 |
| Mare Basalt | (1) Th/MgO > 0.4495 and TiO2/Al2O3 > 0.68435 (2) Th/MgO ≤ 0.4495 and TiO2/MgO > 0.03132 and FeO/CaO > 1.2967 |
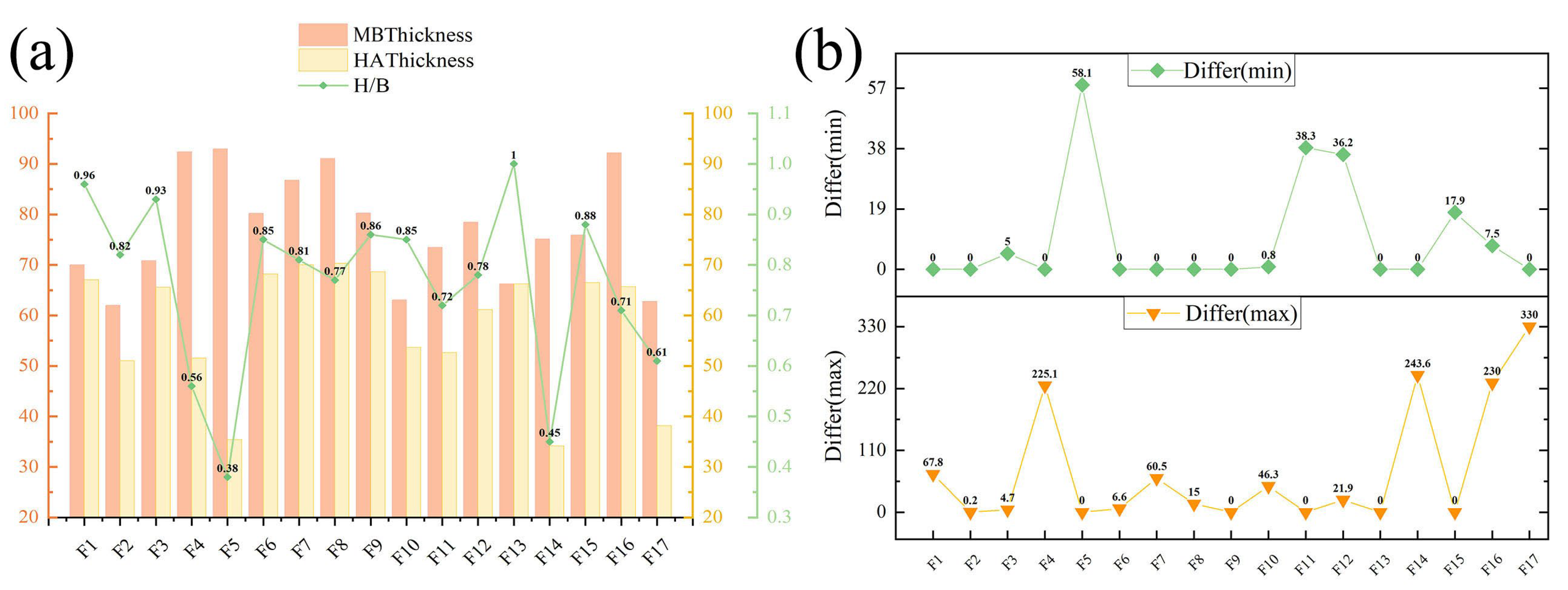
| Designation | HA | Al2O3 | TiO2 | FeO | Area (km2) | Max Depth (m) | Min Depth (m) | Thick Ness (m) | Volume (km3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 253 | 13.8 | 5.3 | 17.2 | 6900 | 582 | 1.6 | 67 | 462 |
| F2 | 63 | 13.1 | 4.8 | 17.1 | 1339 | 896 | 64.6 | 51 | 68 |
| F3 | 284 | 14.4 | 6.1 | 17.6 | 4781 | 576 | 6.5 | 66 | 313 |
| F4 | 177 | 13.2 | 5.9 | 18.2 | 5678 | 504 | 8.1 | 52 | 287 |
| F5 | 62 | 14.9 | 5.4 | 16.9 | 5651 | 588 | 58.6 | 35 | 200 |
| F6 | 315 | 14.3 | 5.9 | 17.4 | 12,193 | 716 | 1.7 | 68 | 799 |
| F7 | 1580 | 13.8 | 5.7 | 17.4 | 17,072 | 737 | 0.5 | 70 | 1219 |
| F8 | 1287 | 13.9 | 5.6 | 17.5 | 14,906 | 793 | 1.4 | 70 | 1048 |
| F9 | 982 | 13.7 | 5.1 | 16.9 | 12,939 | 708 | 0.9 | 69 | 888 |
| F10 | 1643 | 13.7 | 5.4 | 17.2 | 16,096 | 820 | 1.1 | 54 | 864 |
| F11 | 86 | 13.8 | 5.2 | 17.4 | 1842 | 482 | 41.8 | 53 | 97 |
| F12 | 111 | 13.6 | 4.9 | 16.5 | 1425 | 410 | 38.9 | 61 | 87 |
| F13 | 480 | 13.7 | 5.2 | 17.0 | 5256 | 767 | 2.0 | 66 | 300 |
| F14 | 125 | 13.7 | 6.8 | 19.3 | 2972 | 385 | 3.3 | 34 | 101 |
| F15 | 63 | 14.8 | 5.3 | 16.8 | 2498 | 615 | 31.9 | 66 | 166 |
| F16 | 29 | 13.7 | 4.7 | 16.8 | 2067 | 465 | 23.5 | 66 | 136 |
| F17 | 76 | 13.5 | 4.7 | 16.9 | 2751 | 291 | 6.1 | 38 | 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Ma, M.; Jiang, Y. Lunar High Alumina Basalts in Mare Imbrium. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112045
Chen J, Chen S, Ma M, Jiang Y. Lunar High Alumina Basalts in Mare Imbrium. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(11):2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112045
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jingran, Shengbo Chen, Ming Ma, and Yijun Jiang. 2024. "Lunar High Alumina Basalts in Mare Imbrium" Remote Sensing 16, no. 11: 2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112045
APA StyleChen, J., Chen, S., Ma, M., & Jiang, Y. (2024). Lunar High Alumina Basalts in Mare Imbrium. Remote Sensing, 16(11), 2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112045






