Early Detection of Rice Sheath Blight Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. Collection of Canopy Spectra
2.2.2. Measurement of LAI and the Chlorophyll Content
2.2.3. Survey of the Disease
2.3. Methodology
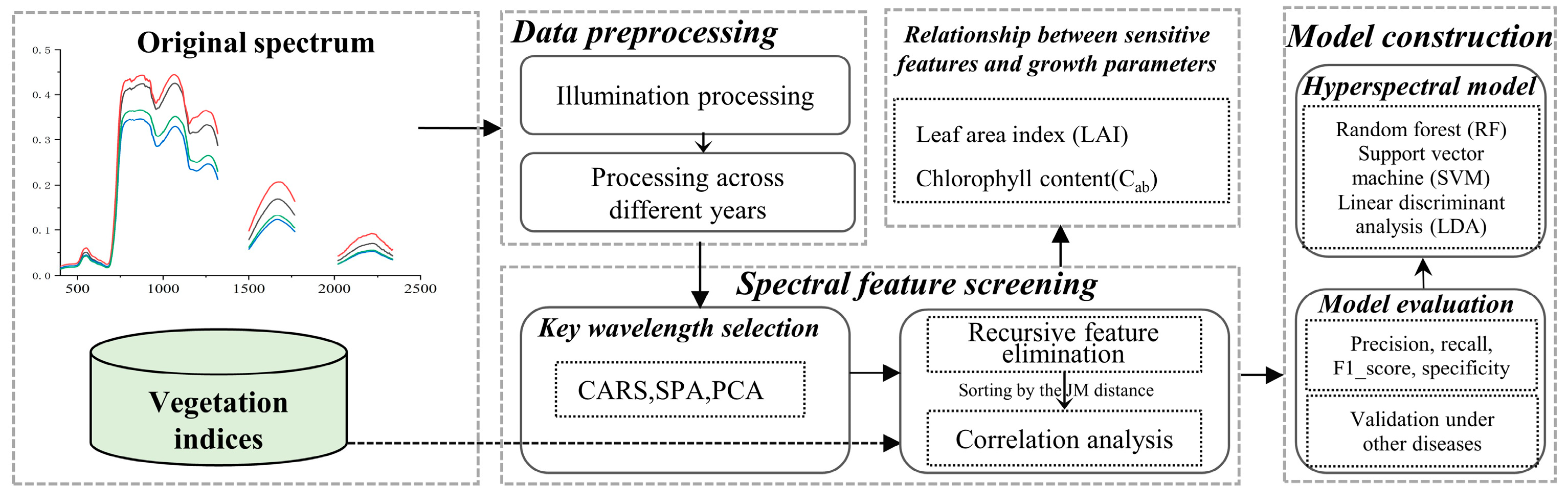
2.3.1. The Study Framework
2.3.2. Preprocessing of Original Spectral Data
2.3.3. Vegetation Indices Selected for Early Detection of Rice ShB
2.3.4. The Screening Strategy of Spectral Characteristics for the Early Detection of ShB
- Algorithms of the dimensionality reduction in wavebands;
- The set of wavelengths not selected is denoted as M;
- Then, compute the projection vectors of the remaining column vectors;
- Further optimal methods of key wavelengths and various vegetation indices.
2.3.5. Descriptions of ShB Identification Algorithms
2.3.6. Evaluation Metrics of Models
3. Results
3.1. Optimal Spectral Features for Early Detection of Rice ShB
3.1.1. Selection of Key Wavelengths
3.1.2. Further Screening of Key Wavelengths and Vegetation Indices
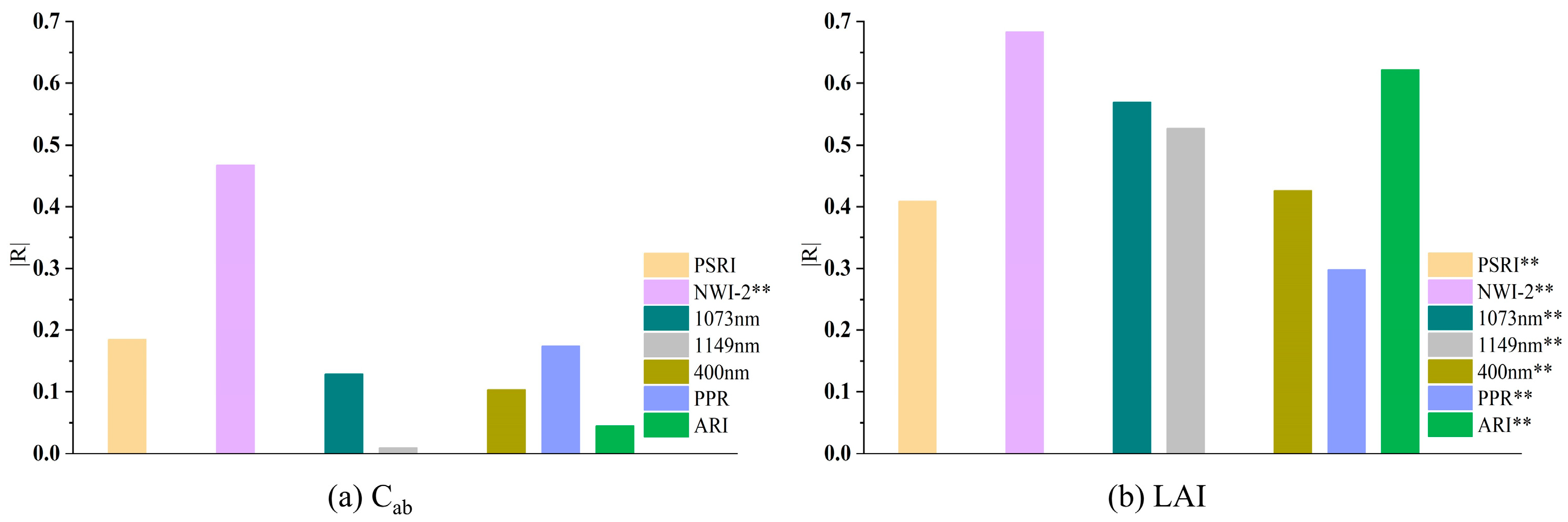
3.2. The Correlation Analysis of Optimal Spectral Features and Rice Growth Parameters
3.3. Detection Models Based on Hyperspectral Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The screening strategy of spectral features with two sequential parts was proposed, including the selection of a key wavelength set based on three different methods and further filtering of all features with key wavebands and vegetation indices through analysis of RF-RFE and CA. It was found that seven features are sensitive to early ShB through step-by-step optimization, namely, the reflectance at 400 nm, 1073 nm, and 1049 nm combined with NWI-2, PSRI, PPR, and ARI;
- Sheath blight can influence canopy chlorophyll and LAI changes in rice plants at the early stages of the disease. The spectral features selected have a significant correlation with LAI, especially the index NWI-2, which also exhibits a high association with the total chlorophyll content;
- The SVM model outperformed the RF and LDA models in early ShB identification and yielded different detective accuracies in a variety of rice. The simultaneous occurrence of several diseases/pests poses a limitation to assessing early ShB stress at the field scale.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Bao, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; He, H. Effect of heterocystous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria against rice sheath blight and the underlying mechanism. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 153, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Shu, B.S.; Sethuraman, V.; Zhong, G.H. Design, synthesis, fungicidal property and QSAR studies of novel β-carbolines containing urea, benzoylthiourea and benzoylurea for the control of rice sheath blight. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margani, R.; Hadiwiyono; Widadi, S. Utilizing Bacillus to inhibit the growth and infection by sheath blight pathogen, Rhizoctoniasolani in rice. In Proceedings of IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 012070. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Mazumdar, P.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Babu, S. Sheath blight of rice: A review and identification of priorities for future research. Planta 2019, 250, 1387–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Shah, F.; Yao, F.; Peng, S. Sheath blight reduces stem breaking resistance and increases lodging susceptibility of rice plants. Field Crops Res. 2012, 128, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, J. Sheath blight disease of paddy and their management. In Recent Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Plant Diseases; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Yuan, L.; Wang, J.H.; Luo, J.H.; Du, S.Z.; Huang, W.J. Research progress of crop diseases and pests monitoring based on remote sensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, V.K.; Pradhan, M.K. Rice plant disease classification using color features: A machine learning paradigm. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 103, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Lv, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Ni, H. Recognition of rice sheath blight based on a backpropagation neural network. Electronics 2021, 10, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, D.; Li, G. Image recognition of four rice leaf diseases based on deep learning and support vector machine. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 179, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, N.; Li, M. Recognition of Rice Sheath Blight Based on Image Procession. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2016, 38, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Nanehkaran, Y.A.; Li, D. Detection of rice plant diseases based on deep transfer learning. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3246–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, C.R.; Arko, P.S.; Ali, M.E.; Khan, M.A.I.; Apon, S.H.; Nowrin, F.; Wasif, A. Identification and recognition of rice diseases and pests using convolutional neural networks. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 194, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.L.; Jiang, K.L.; Yu, Z.X.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Y.D. Detection and Recognition of Rice Sheath Blight Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2020, 51, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Wang, T.; Hu, L. Rhizocotonia Solani Recognition Algorithm Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Chin J Rice Sci 2019, 33, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.T.; Yang, B.J.; Li, S.X.; Liao, F.B.; Liu, S.H.; Tang, J.; Yao, Q. Intelligent Forecasting Method of Rice Sheath Blight Based on Images. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Yan, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Wu, K. Diagnosing the symptoms of sheath blight disease on rice stalk with an in-situ hyperspectral imaging technique. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 209, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Guo, S.; Tan, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D. Identification of rice sheath blight through spectral responses using hyperspectral images. Sensors 2020, 20, 6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.-Y.; Lan, Y.-B.; Zhou, X.-G.; Chen, L.-P.; Murray, S.C.; Zhang, G.-Z. Research imagery and spectral characteristics of rice sheath blight using three portable sensors. In Proceedings of the 2015 ASABE Annual International Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26–29 July 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.W.; Yuan, J.; Ding, W.M.; Yang, H.B.; Shen, S.Q.; Cui, J.L. Identification of rice sheath blight based on hyperspectral imaging technique. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2018, 39, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Y.; Yang, H.B.; Li, Z.W. Early Detection and Identification of Rice Sheath Blight Disease Based on Hyperspectral Image and Chlorophyll Content. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.; Sharma, R.; Hunjan, M.S.; Sharma, V.K.; Thakur, S.; Chauhan, S. Physio-biochemical and histological alterations in response to sheath blight disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Phytopathol. 2022, 170, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Pan, X.; Zuo, S. Overexpression of OsOSM1 enhances resistance to rice sheath blight. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroppiana, D.; Boschetti, M.; Confalonieri, R.; Bocchi, S.; Brivio, P.A. Evaluation of LAI-2000 for leaf area index monitoring in paddy rice. Field Crops Res. 2006, 99, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, J.; Osterman, J.C.; Mitchell, J.L. Calibration of the Minolta SPAD-502 leaf chlorophyll meter. Photosynth. Res. 1995, 46, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NY/T 2720-2015; Rules for Evaluation of Rice for Resistance to Sheath Blight. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, P.; Zeng, F.; Wang, H. Hyperspectral detection of salted sea cucumber adulteration using different spectral preprocessing techniques and SVM method. Lwt 2021, 152, 112295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pu, R.; Huang, W.; Yuan, L.; Luo, J.; Wang, J. Using in-situ hyperspectral data for detecting and discriminating yellow rust disease from nutrient stresses. Field Crops Res. 2012, 134, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Huang, W.; Jing, Y.; Pignatti, S.; Laneve, G.; Dong, Y.; Ye, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, A.; Jiang, J. Identification of Fusarium head blight in winter wheat ears using continuous wavelet analysis. Sensors 2019, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Merzlyak, M.N.; Chivkunova, O.B. Optical properties and nondestructive estimation of anthocyanin content in plant leaves. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 74, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penuelas, J.; Baret, F.; Filella, I. Semi-empirical indices to assess carotenoids/chlorophyll a ratio from leaf spectral reflectance. Photosynthetica 1995, 31, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Tremblay, N.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Dextraze, L. Integrated narrow-band vegetation indices for prediction of crop chlorophyll content for application to precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughtry, C.S.; Walthall, C.; Kim, M.; De Colstoun, E.B.; McMurtrey Iii, J. Estimating corn leaf chlorophyll concentration from leaf and canopy reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G. Vegetation indices derived from high-resolution airborne videography for precision crop management. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2855–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Gamon, J.; Fredeen, A.; Merino, J.; Field, C. Reflectance indices associated with physiological changes in nitrogen-and water-limited sunflower leaves. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Merzlyak, M.N. Spectral reflectance changes associated with autumn senescence of Aesculus hippocastanum L. and Acer platanoides L. leaves. Spectral features and relation to chlorophyll estimation. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 143, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M. Evaluation of vegetation indices and a modified simple ratio for boreal applications. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 22, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamon, J.; Serrano, L.; Surfus, J. The photochemical reflectance index: An optical indicator of photosynthetic radiation use efficiency across species, functional types, and nutrient levels. Oecologia 1997, 112, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filella, I.; Serrano, L.; Serra, J.; Penuelas, J. Evaluating wheat nitrogen status with canopy reflectance indices and discriminant analysis. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamon, J.; Penuelas, J.; Field, C. A narrow-waveband spectral index that tracks diurnal changes in photosynthetic efficiency. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.D.; Balaguer, L.; Manrique, E.; Elvira, S.; Davison, A. A reappraisal of the use of DMSO for the extraction and determination of chlorophylls a and b in lichens and higher plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1992, 32, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merton, R. Monitoring community hysteresis using spectral shift analysis and the red-edge vegetation stress index. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 12–16 January 1998; JPL: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Merton, R.; Huntington, J. Early simulation results of the ARIES-1 satellite sensor for multi-temporal vegetation research derived from AVIRIS. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 9–11 February 1999; JPL: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Merzlyak, M.N.; Gitelson, A.A.; Chivkunova, O.B.; Rakitin, V.Y. Non-destructive optical detection of pigment changes during leaf senescence and fruit ripening. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 106, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broge, N.H.; Leblanc, E. Comparing prediction power and stability of broadband and hyperspectral vegetation indices for estimation of green leaf area index and canopy chlorophyll density. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V.; Smart, R. The influence of soil salinity, growth form, and leaf moisture on the spectral reflectance of Spartina alternifolia canopies. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1983, 49, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, A.; Bryant, R.; Baird, A. Detecting near-surface moisture stress in Sphagnum spp. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Biel, C.; Serrano, L.; Save, R. The reflectance at the 950–970 nm region as an indicator of plant water status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1887–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, M.; Reynolds, M.; Van Ginkel, M.; Klatt, A.; Raun, W.; Stone, M. Spectral reflectance to estimate genetic variation for in-season biomass, leaf chlorophyll, and canopy temperature in wheat. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Cao, D. Key wavelengths screening using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method for multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 648, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.F.C.; Gomes, A.A.; Araujo, M.C.U.; Galvão Filho, A.R.; Galvão, R.K.H. The successive projections algorithm. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 42, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Fowler, J.E. Hyperspectral image compression using JPEG2000 and principal component analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabboor, M.; Howell, S.; Shokr, M.; Yackel, J. The Jeffries–Matusita distance for the case of complex Wishart distribution as a separability criterion for fully polarimetric SAR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6859–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisner, D.A.; Schnyer, D.M. Support vector machine. In Machine Learning; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, P.; Pardalos, P.M.; Trafalis, T.B.; Xanthopoulos, P.; Pardalos, P.M.; Trafalis, T.B. Linear discriminant analysis. In Robust Data Mining; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, M.; Tiwari, A.; Sharma, N.; Chandra, P.; Bashyal, B.M.; Ellur, R.K.; Bhowmick, P.K.; Bollinedi, H.; Vinod, K.; Singh, A.K. Rhizoctonia solani Kühn pathophysiology: Status and prospects of sheath blight disease management in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 881116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Mubeen, M.; Iftikhar, Y.; Shakeel, Q.; Imran Arshad, H.M.; Carmen Zuñiga Romano, M.D.; Hussain, S. Rice Sheath Blight: A Comprehensive Review on the Disease and Recent Management Strategies. Sarhad J. Agric. 2023, 39, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhai, W.; Zhu, L. Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling sheath blight resistance in two rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Badri, J.; Prakasam, V.; Bhadana, V.; Eswari, K.; Laha, G.; Priyanka, C.; Rajkumar, A.; Ram, T. Identification and agro-morphological characterization of rice genotypes resistant to sheath blight. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016, 45, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Cai, C.; Song, L.; Qiu, J.; Ma, C.; Wang, D.; Gu, X.; Yang, X.; Wei, W.; Tao, Y. Elevated CO2 and temperature under future climate change increase severity of rice sheath blight. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1115614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; TONG, Y.; Xu, J.; Pan, X. Defense response and physiological difference of rice cultivars with different sheath blight resistance levels to the toxins produced by Rhizoctonia solani. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2014, 28, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, K.A.; Karmakar, S.; Molla, J.; Bajaj, P.; Varshney, R.K.; Datta, S.K.; Datta, K. Understanding sheath blight resistance in rice: The road behind and the road ahead. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 895–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willocquet, L.; Noel, M.; Sackville Hamilton, R.; Savary, S. Susceptibility of rice to sheath blight: An assessment of the diversity of rice germplasm according to genetic groups and morphological traits. Euphytica 2012, 183, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Peng, S.; Buresh, R.J.; Zou, Y.; Castilla, N.P.; Mew, T.W.; Zhong, X. Rice varietal difference in sheath blight development and its association with yield loss at different levels of N fertilization. Field Crops Res. 2007, 102, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
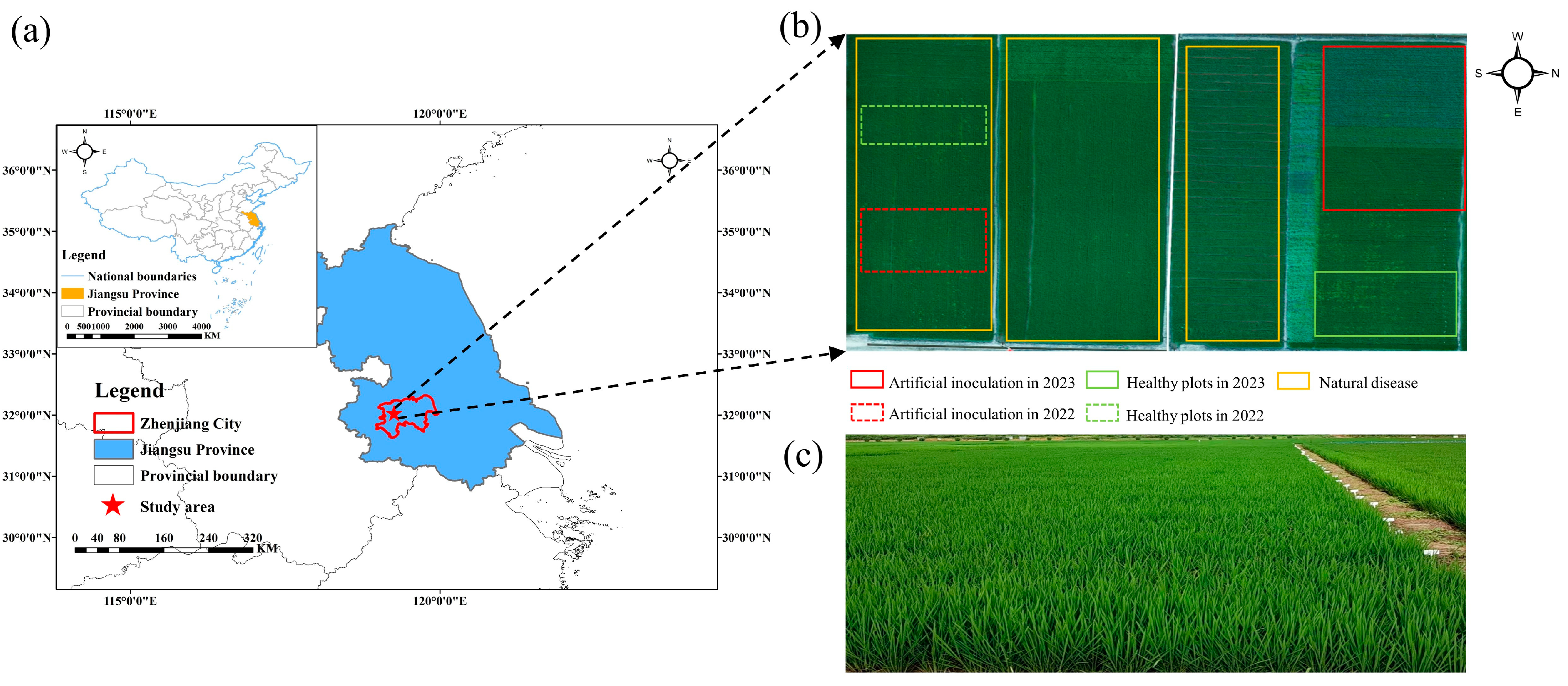





| Experiments | Varieties (Resistance) | Data Collection Time (Growth Period) | Sample Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment 1 | Wuyunjing24 (susceptibility) | 1 and 6 August 2022 (jointing stage) | 70 |
| Experiment 2 | Wuyunjing24 (susceptibility) | 24 July and 4 August 2023 (tillering stage) | 84 |
| Huruan1212 (moderateness) | |||
| Yongyou1245 (moderateness) |
| Disease Levels | Symptoms | Classes |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | There are no symptoms on the leaf sheaths and leaves of the plant. | Healthy |
| 1 | There are a few scattered lesions at the base of the plant. | Early-infected |
| 2 | The lesions extend to the inverted 5-leaf sheath or corresponding leaves (the sword leaf is the inverted leaf). | |
| 3 | The lesions extend to the inverted 4-leaf sheath or corresponding leaves. | |
| 4 | The lesions extend to the inverted 3-leaf sheaths or corresponding leaves. | |
| 5 | The lesions extend to the inverted 2-leaf sheaths or corresponding leaves. | |
| 6 | The lesions extend to less than half of the flag leaf sheath. | |
| 7 | The lesions extend to more than half of the flag leaf sheath. | |
| 8 | The sword leaves appear to have disease spots or become yellow due to loss of water. | |
| 9 | Part or all of the diseased stems and ears of rice die abnormally. |
| Index | Formulation | Related to | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anth reflectance index (ARI) | (R550)−1 − (R700)−1 | Pigment content and variation | [30] |
| Structure Intensive Pigment Index (SIPI) | (R800 − R445)/(R800 + R680) | [31] | |
| Transformed Chlorophyll Absorption in Reflectance Index (TCARI) | 3((R700 − R670) − 0.2(R700 − R550)(R700/R670)) | [32] | |
| Modified Chlorophyll Absorption in Reflectance Index (MCARI) | ((R700-R670) − 0.2(R700 − R550)(R700/R670)) | [33] | |
| Plant Pigment Ratio (PPR) | (R550 − R450)/(R550 + R450) | [34] | |
| Normalized Chlorophyll Pigment Ratio Index (NPCI) | (R680 − R430)/(R680 + R430) | [35] | |
| Red-Edge NDVI(RNDVI) | (R750 − R705)/(R750 + R705) | Crop growth | [36] |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | (R750 − R650)/(R750 + R650) | [34] | |
| Modified Simple Ratio (MSR) | (R750/R650 − 1)/(R750/R650 + 1)1/2 | [37] | |
| Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI) | (R570 − R531)/(R570 + R531) | Photosynthetic activity | [38] |
| Nitrogen Reflectance Index (NRI) | (R570 − R670)/(R570 + R670) | [39] | |
| physiological health reflectance index (PHRI) | (R550 − R531)/(R550 + R531) | [40] | |
| Normalized Pheophytization Index (NPQI) | (R415 − R435)/(R415+ R435) | Physiological variation | [41] |
| Red-Edge Vegetation Stress Index 1 (RVS1) | (R714 + R750)/2 − R733 | [42] | |
| Red-Edge Vegetation Stress Index 2 (RVS2) | (R651 + R750)/2 − R751 | [42] | |
| Red-edge vegetation stress index (RVSI) | (R712 + R752)/2 − R732 | [43] | |
| Plant Senescence Reflectance Index (PSRI) | (R680 − R500)/R750 | [44] | |
| Triangular Vegetation Index (TVI) | 0.5(120(R750 − R550) − 200(R670 − R550)) | [45] | |
| Normalized Difference Infrared Index (NDII) | (R819 − R1600)/(R819 + R1600) | Stress state | [46] |
| Moisture Stress Index (MSI) | Rmean(1550~1750)/Rmean(760~800) | [47] | |
| Water Index (WI) | R970/R900 | [48] | |
| Normalized water Index-2 (NWI-2) | (R970 − R850)/(R970 +R850) | [49] |
| Method | Variable Number | Wavelengths |
|---|---|---|
| CARS | 21 | 489, 506, 510, 514, 517, 518, 520, 994, 995, 996, 998, 999, 1073, 1093, 1292, 1299, 2025, 2053, 2054, 2304, 2324 |
| SPA | 22 | 400, 519, 736, 934, 992, 1149, 1576, 2021, 2025, 2033, 2044, 2053, 2075, 2295, 2299, 2305, 2312, 2317, 2321, 2325, 2330, 2336 |
| PCA | 10 | 671, 707, 741, 745, 1224, 1501, 1640, 1700, 2074, 2328 |
| Growth Factor | Items | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cab | Between | 165.083 | 1 | 165.083 | 4.436 | 0.037 * |
| Within | 5656.399 | 152 | 37.213 | |||
| Total | 5821.482 | 153 | ||||
| LAI | Between | 8.935 | 1 | 8.935 | 12.133 | 0.001 * |
| Within | 111.939 | 152 | 0.736 | |||
| Total | 120.874 | 153 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, F.; Li, B.; Zhou, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J. Early Detection of Rice Sheath Blight Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122047
Lin F, Li B, Zhou R, Chen H, Zhang J. Early Detection of Rice Sheath Blight Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(12):2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122047
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Fenfang, Baorui Li, Ruiyu Zhou, Hongzhou Chen, and Jingcheng Zhang. 2024. "Early Detection of Rice Sheath Blight Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 16, no. 12: 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122047
APA StyleLin, F., Li, B., Zhou, R., Chen, H., & Zhang, J. (2024). Early Detection of Rice Sheath Blight Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 16(12), 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122047







