Fusion of Google Street View, LiDAR, and Orthophoto Classifications Using Ranking Classes Based on F1 Score for Building Land-Use Type Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. GSV Dataset
2.2. LiDAR Point Cloud, Orthophoto, and Building Footprint Dataset
2.3. ImageNet Data
2.4. Preprocessing
2.5. Deep-Learning Models Applied for Building Land-Use Type Classification
2.5.1. MobileNetV2
2.5.2. VGG Model
2.5.3. ResNet152
2.5.4. InceptionV3
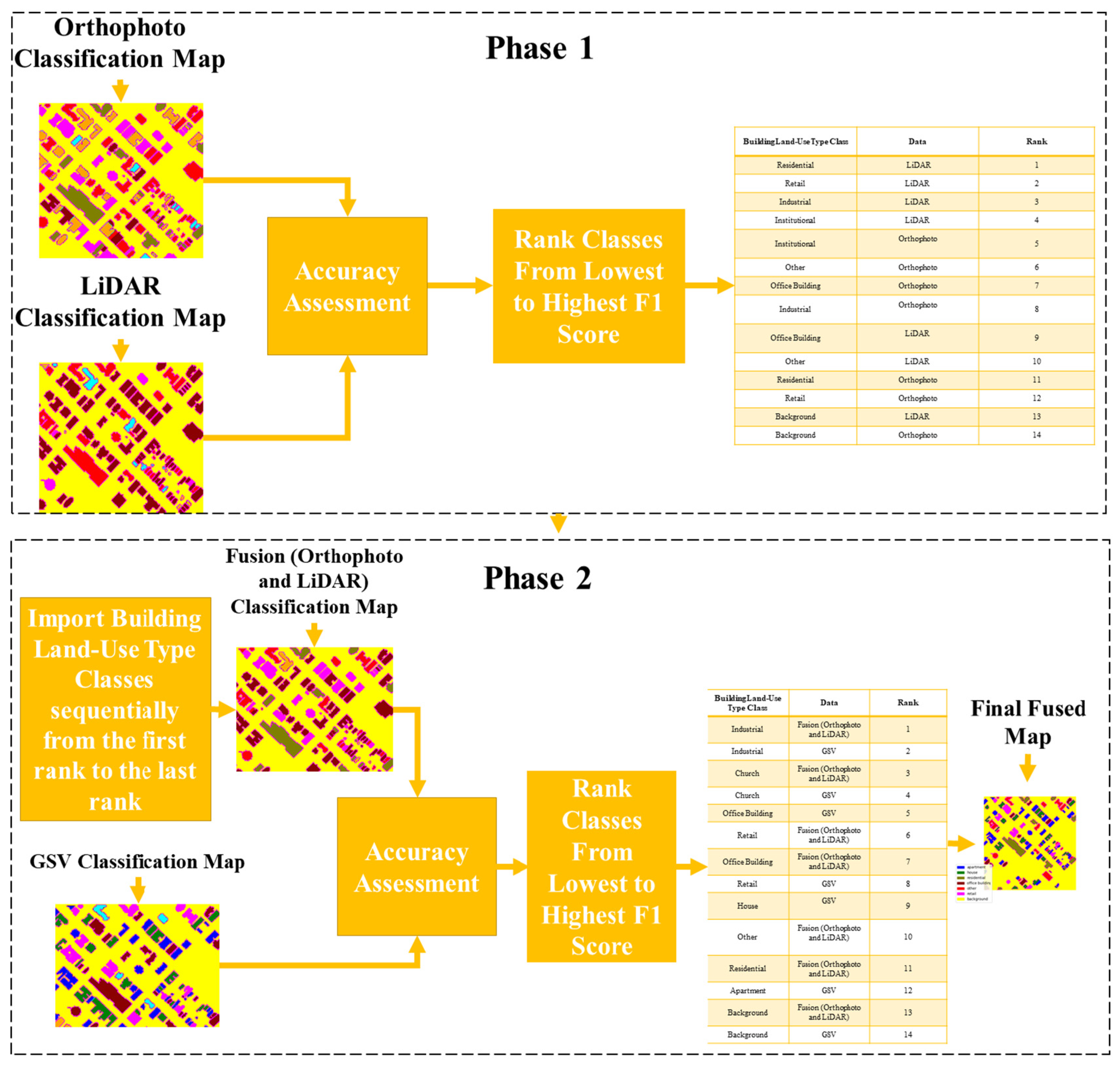
2.6. Fusion Methods
2.6.1. Ranking Classes Based on F1 Score
2.6.2. Fuzzy Fusion-Based on the Gompertz Function
2.7. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Experiments on Google Street View Images
Examining the Generalization Ability of DL Models Trained on GSV Images for the Greater Toronto Area
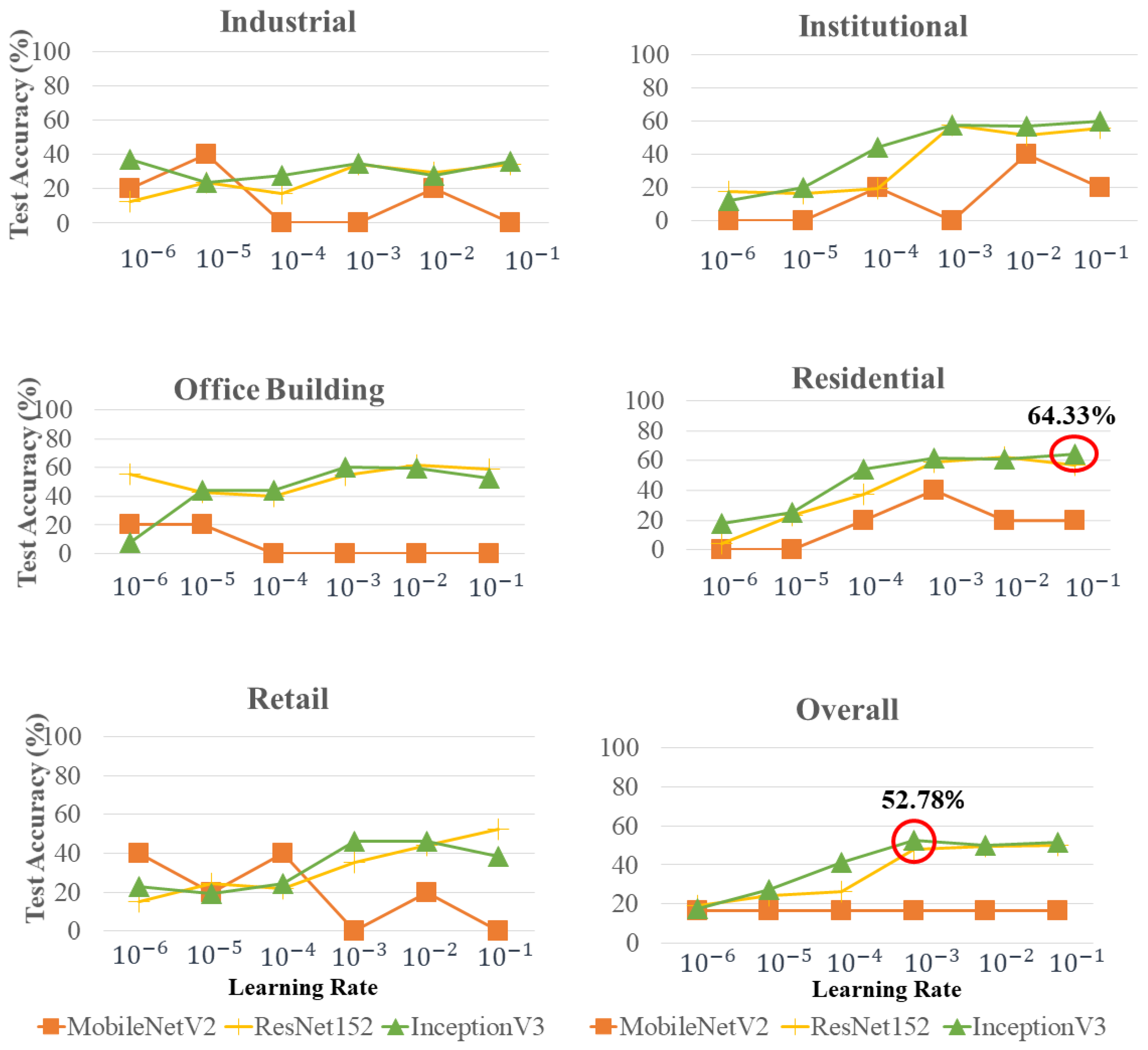
3.2. Experiments on LiDAR-Derived Features
3.2.1. Influence of DL Model and Learning Rate on Building Land-Use Type Detection Accuracies When Training Models from Scratch
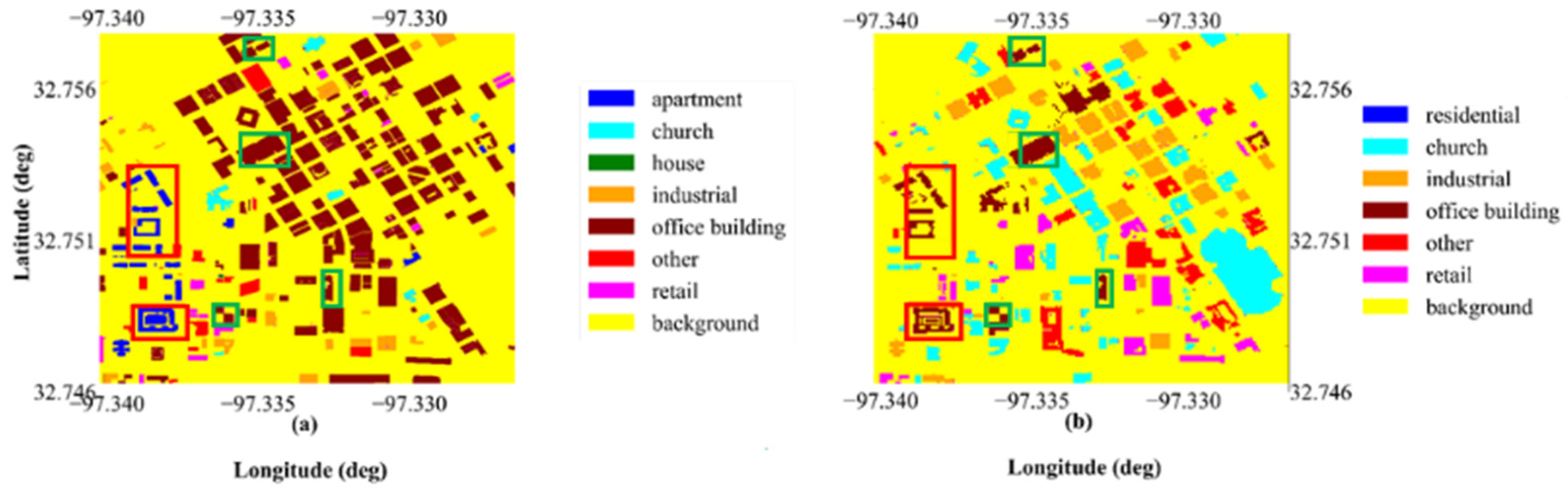
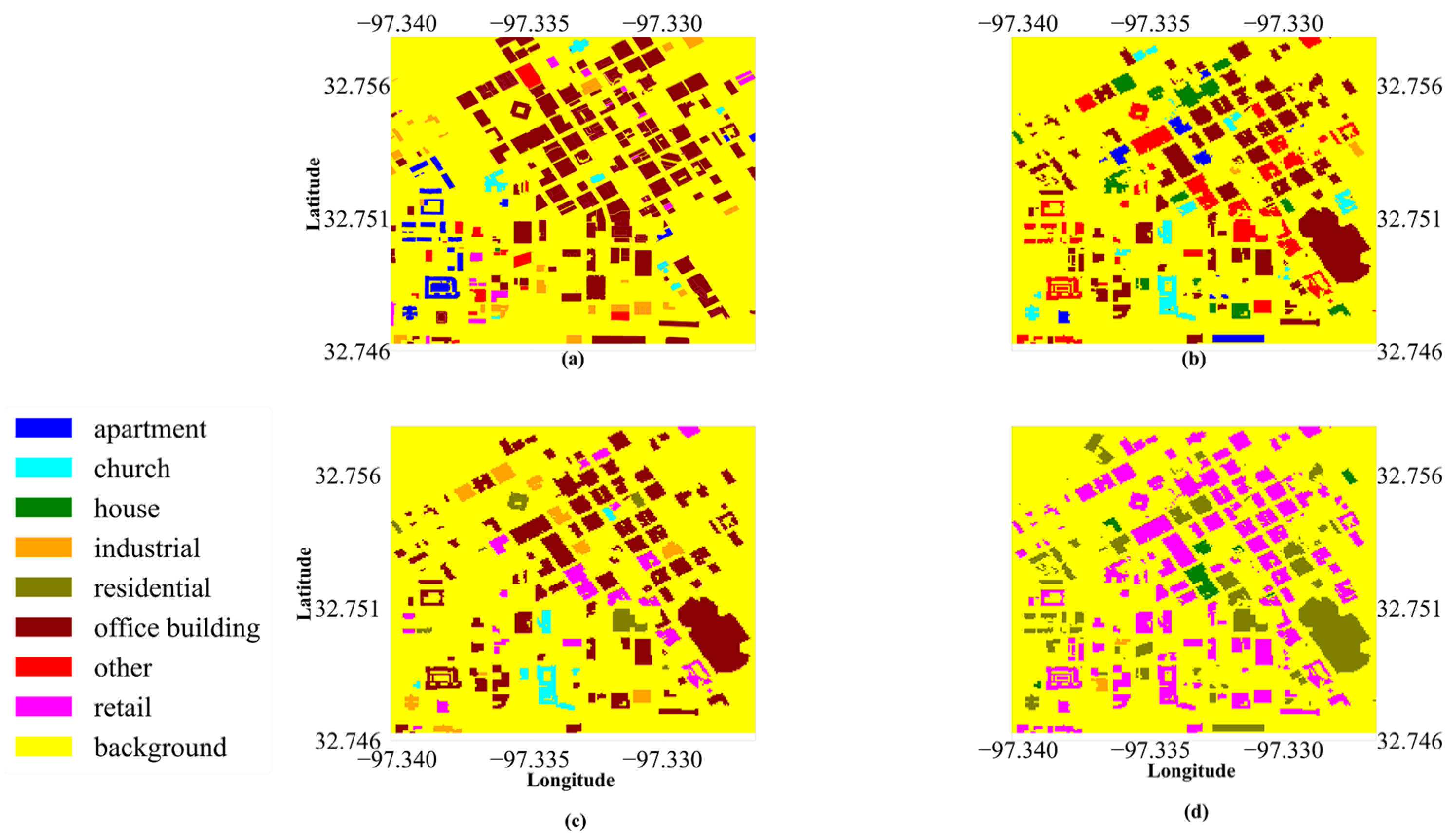
3.2.2. LiDAR Building Land-Use Type Classification Maps
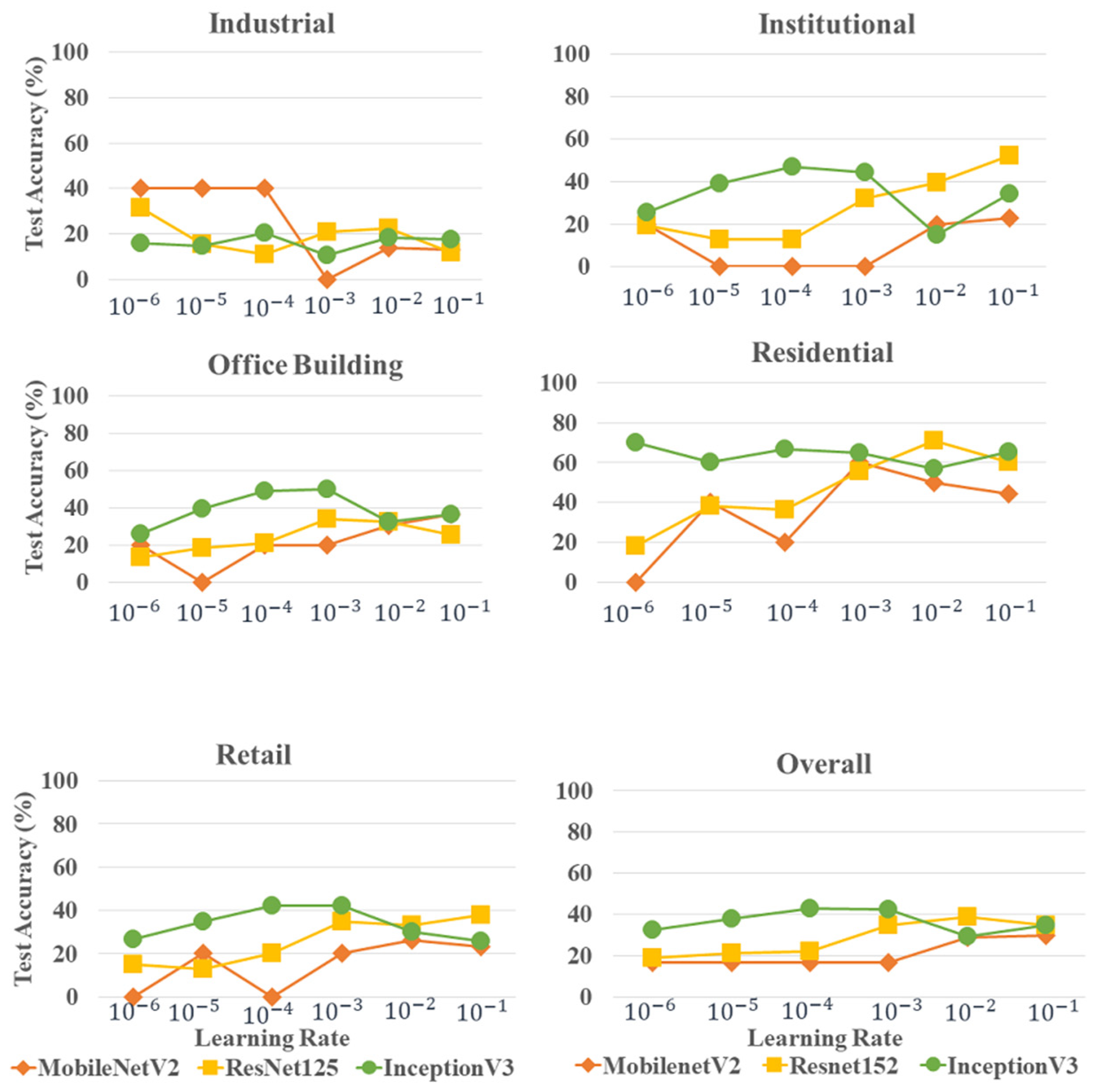
3.3. Experiments on Orthophoto Images
3.3.1. Influence of DL Model and Learning Rate on Building Land-Use Type Detection Accuracies When Training from Scratch
3.3.2. Influence of DL Model and Learning Rate on Building Land-Use Type Detection Accuracies When Using Transfer Learning
3.3.3. Orthophoto Building Land-Use Type Classification Maps
4. Discussion
4.1. Deep-Learning Models Training Time
4.2. Fusion of Orthophotos, LiDAR, and GSV
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Habashna, A. Building Type Classification from Street-View Imagery Using Convolutional Neural Networks; Statistics Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2022; Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/en/pub/18-001-x/18-001-x2021003-eng.pdf?st=A02HTs8U (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Belgiu, M.; Tomljenovic, I.; Lampoltshammer, T.J.; Blaschke, T.; Höfle, B. Ontology-based classification of building types detected from airborne laser scanning data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1347–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Im, J.; Rhee, J.; Hodgson, M. Building type classification using spatial and landscape attributes derived from LiDAR remote sensing data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 130, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, M.; Schmitt, A.; Taubenböck, H. Building types’ classification using shape-based features and linear discriminant functions. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Currit, N.; Wang, L.; Yang, X. Detect residential buildings from lidar and aerial photographs through object-oriented land-use classification. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lary, D.J.; Zewdie, G.K.; Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Levetin, E.; Allee, R.J.; Malakar, N.; Walker, A.; Mussa, H.; Mannino, A.; et al. Machine learning applications for earth observation. Earth Obs. Open Sci. Innov. 2018, 165, 165–180. [Google Scholar]
- Camps-Valls, G. Machine learning in remote sensing data processing. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Machine LEARNING for Signal Processing, Grenoble, France, 1–4 September 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, G.; Zhao, Z. Building Footprints Extraction from PolSAR Image Using Multi-Features and Edge Information. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Image and Data Fusion, Tengchong, China, 9–11 August 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, A.; Pradhan, B.; Gite, S.; Alamri, A. Building footprint extraction from high resolution aerial images using generative adversarial network (GAN) architecture. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 209517–209527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yao, L.; Qin, J.; Lu, N.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, C. Multi-scale attention integrated hierarchical networks for high-resolution building footprint extraction. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 109, 102768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, K.; Bodani, P.; Sharma, S.A. Automatic building footprint extraction from very high-resolution imagery using deep learning techniques. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Hu, H.; Xu, B.; Shang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q. SuperpixelGraph: Semi-automatic generation of building footprint through semantic-sensitive superpixel and neural graph networks. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 125, 103556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhou, J. Classification of urban building type from high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery using extended MRS and soft BP network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3515–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ren, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Schmitt, M.; Hänsch, R.; Sun, X.; Huang, H.; Mayer, H. Urban building classification (ubc)-a dataset for individual building detection and classification from satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1413–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Xu, N. Street view image classification based on convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 25–26 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1439–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Hanink, D.M.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Parcel-based urban land use classification in megacity using airborne LiDAR, high resolution orthoimagery, and Google Street View. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 64, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Körner, M.; Wang, Y.; Taubenböck, H.; Zhu, X.X. Building instance classification using street view images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laupheimer, D.; Tutzauer, P.; Haala, N.; Spicker, M. Neural networks for the classification of building use from street-view imagery. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 4, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, Q.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Z. Mixed land use measurement and mapping with street view images and spatial context-aware prompts via zero-shot multimodal learning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 125, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Lee, J.; Farkoushi, M.G.; Lee, E.; Sohn, H.-G. Automatic generation of land use maps using aerial orthoimages and building floor data with a Conv-Depth Block (CDB) ResU-Net architecture. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.J.; Wang, Y.; Werner, M.; Kang, J.; Zhu, X.X. Model fusion for building type classification from aerial and street view images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhu, J.; Tu, W.; Li, Q.; Cao, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, G. Integrating aerial and street view images for urban land use classification. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Canada. Census Profile, 2021 Census of Population. Profile Table. Available online: https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2021/dp-pd/prof/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&DGUIDlist=2021A00053519038&GENDERlist=1&STATISTIClist=1&HEADERlist=0 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Vaughan Economic Development. 2021 Census Insights and Findings—Population and Dwellings. Available online: https://vaughanbusiness.ca/insights/2021-census-insights-and-findings-population-and-dwellings/ (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Government of Canada. Focus on Geography Series, 2016 Census. Available online: https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/as-sa/fogs-spg/Facts-cd-eng.cfm?LANG=Eng&GK=CD&GC=3521&TOPIC=1 (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Government of Canada. Population and Dwelling Counts: Canada and Population Centres. Available online: https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2016/as-sa/fogs-spg/Facts-csd-eng.cfm?LANG=Eng&GK=CSD&GC=3520005&TOPIC=1 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- City of Fort Worth. Chapter 1 Population Trends. Available online: https://www.fortworthtexas.gov/files/assets/public/v/1/the-fwlab/documents/comprehensive-planning/pdf-adopted/01_populationtrends.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts, Fort Worth City, Texas; Texas. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/fortworthcitytexas (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F.F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Fan, L. Scene segmentation of remotely sensed images with data augmentation using U-net++. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Artificial Intelligence (ICCEAI), Shanghai, China, 27–29 August 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Karadal, C.H.; Kaya, M.C.; Tuncer, T.; Dogan, S.; Acharya, U.R. Automated classification of remote sensing images using multileveled MobileNetV2 and DWT techniques. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 185, 115659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Abhishek, K.; Singh, A.K.; Nerurkar, P.; Chandane, M.; Bhirud, S.; Patel, D.; Busnel, Y. Multilabel classification of remote sensed satellite imagery. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2021, 32, e3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yu, S.; Liu, S. An improved InceptionV3 network for obscured ship classification in remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 4738–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part I 13; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
















| Case Study | Source | Vertical Accuracy | Point Density | Flight Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTA | Scholars Geo Portal | 20.76 cm | 6234 feet | |
| Vancouver | Government of British Columbia | 78 cm | 8 points/ | 1850 m |
| Fort Worth | Texas Natural Resources Information System (TNRIS) | 21.2 cm | 2 points/ | 6000 feet |
| Data | Case Study | Source | Year | Bands | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orthophoto | GTA | Scholars Geo Portal | 2018 | R, G, B, and NIR | 20 cm |
| Vancouver | Vancouver Open Data Portal | 2015 | R, G, B | 7.5 cm | |
| Fort Worth | Texas Natural Resources Information System (TNRIS) | 2018–2019 | R, G, B, and NIR | 60 cm | |
| Building Footprint | GTA | Statistics Canada | 2019 | ||
| Vancouver | Vancouver Open Data Portal | 2015 | |||
| Fort Worth | City of Fort Worth |
| Feature | Statistics |
|---|---|
| FR * | Mean |
| Max | |
| Standard deviation | |
| LR ** | Mean |
| Max | |
| Standard deviation | |
| Intensity | Mean |
| Standard deviation | |
| Slope | Min |
| Mean | |
| Standard deviation | |
| Range | |
| nDSM | Variance |
| Data | DL Model | Optimizers | Initial Learning Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| GSV | MobilenetV2 | SGD | 10−1 |
| VGG16 | SGD | 10−3 | |
| Orthophoto | MobilenetV2 | SGD | 10−1 |
| ResNet152 | SGD | 10−2 | |
| InceptionV3 | Adam | 10−3 | |
| LiDAR | MobileNetV2 | SGD | 10−6 |
| ResNet152 | SGD | 10−3 | |
| InceptionV3 | Adam | 10−3 |
| Model | Number of Trained Layers | Average Training Accuracy (%) | Average Validation Accuracy (%) | Average Test Accuracy (%) | Training Time (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV2 | 154 (from scratch) | 89.26 | 72.78 | 93.87 | 22.07 |
| 150 | 89.63 | 72.17 | 94.28 | 32.37 | |
| 100 | 88.94 | 71.08 | 92.76 | 17.61 | |
| 50 | 87.03 | 71.02 | 93.03 | 25.45 | |
| 0 | 50.48 | 58.87 | 81.62 | 19.33 | |
| VGG16 | 13 (from scratch) | 72.66 | 71.27 | 92.15 | 23.96 |
| 10 | 72.94 | 71.06 | 92.86 | 29.33 | |
| 5 | 72.17 | 71.38 | 92.19 | 22.09 | |
| 0 | 44 | 54.15 | 74.61 | 22.06 |
| Class | Number of Images |
|---|---|
| Apartment | 149 |
| House | 465 |
| Industrial | 95 |
| Mixed r/c | 9 |
| Office building | 28 |
| Retail | 63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghasemian Sorboni, N.; Wang, J.; Najafi, M.R. Fusion of Google Street View, LiDAR, and Orthophoto Classifications Using Ranking Classes Based on F1 Score for Building Land-Use Type Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112011
Ghasemian Sorboni N, Wang J, Najafi MR. Fusion of Google Street View, LiDAR, and Orthophoto Classifications Using Ranking Classes Based on F1 Score for Building Land-Use Type Detection. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(11):2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112011
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhasemian Sorboni, Nafiseh, Jinfei Wang, and Mohammad Reza Najafi. 2024. "Fusion of Google Street View, LiDAR, and Orthophoto Classifications Using Ranking Classes Based on F1 Score for Building Land-Use Type Detection" Remote Sensing 16, no. 11: 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112011
APA StyleGhasemian Sorboni, N., Wang, J., & Najafi, M. R. (2024). Fusion of Google Street View, LiDAR, and Orthophoto Classifications Using Ranking Classes Based on F1 Score for Building Land-Use Type Detection. Remote Sensing, 16(11), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16112011







