Development of a Proof-of-Concept A-DInSAR-Based Monitoring Service for Land Subsidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Considering that the future of the A-DInSAR service is to provide continuously updated data, how can the TS datasets be used to detect subsidence hotspots and capture their dynamic behavior in time and space?
- -
- X-band A-DInSAR data are well-established for monitoring urbanized areas. These data will be produced in the forthcoming year as part of the IRIDE program. However, what is their suitability in the peri-urban areas that have a relevant diffusion in the Lombardy region and are poorly studied in the literature?
2. Test Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Methodology
3.1.1. A-DInSAR Data Processing
3.1.2. TS Analysis and Post-Processing
3.1.3. Reporting
4. Results
4.1. Hotspot of Land Subsidence in Turano Lodigiano
4.2. Driver of the Land Subsidence
4.2.1. Geological and Hydrogeological Control on the Land Subsidence
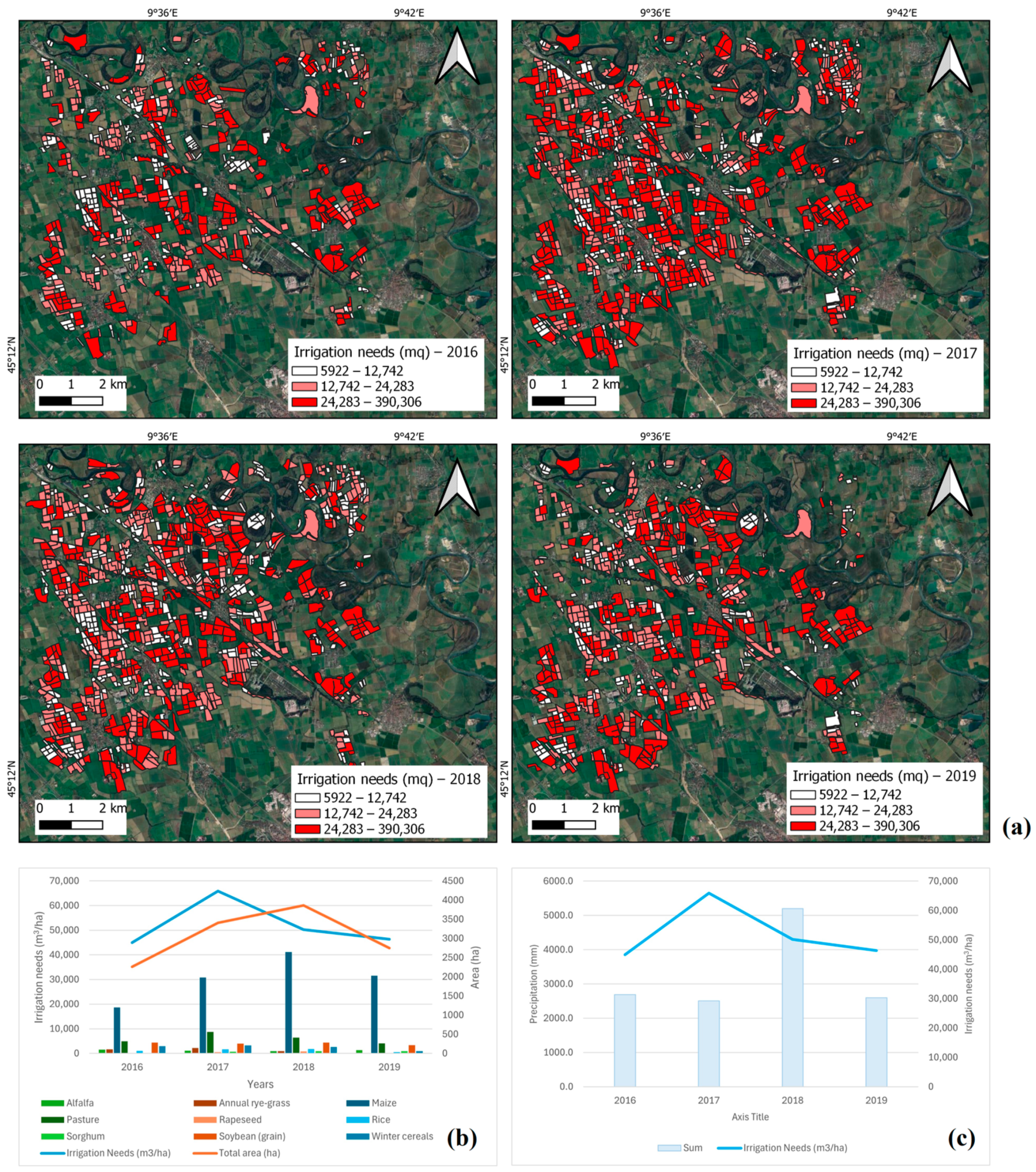
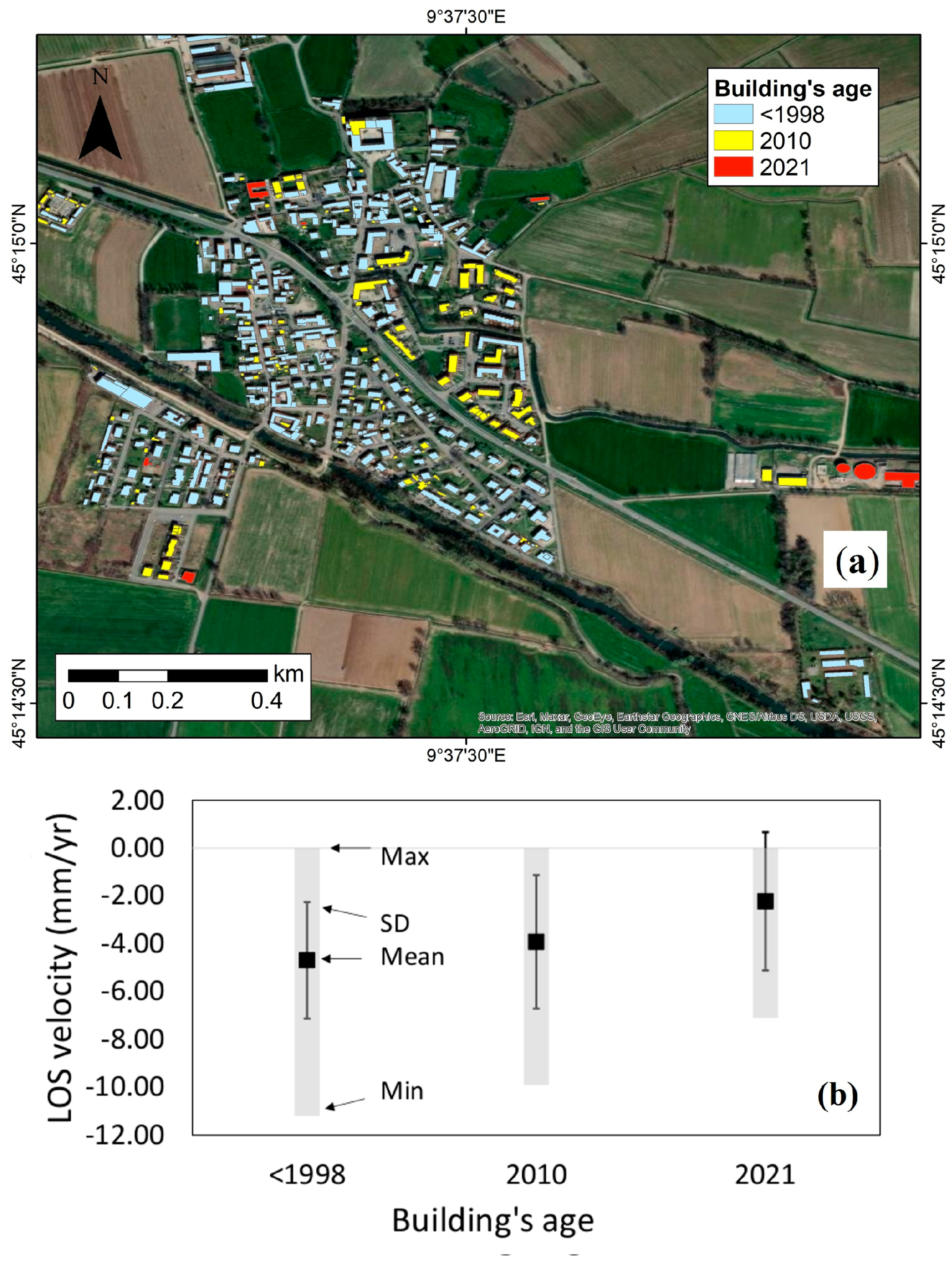
4.2.2. Impact of Urban Expansion on Land Subsidence
4.3. Confidence Degree of the Results and Suggested Actions
5. Discussions
5.1. Comparison of CSK with EGMS S1 Data
5.2. Land Subsidence and Hydraulic Risk
5.3. MapLombardy and IRIDE Future Services
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomás, R.; Romero, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturià, J.J.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; González, P.J.; Fernández, J.; et al. Radar Interferometry Techniques for the Study of Ground Subsidence Phenomena: A Review of Practical Issues through Cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Caleca, F.; Del Soldato, M.; Festa, D.; Confuorto, P.; Bianchini, S. Review of Satellite Radar Interferometry for Subsidence Analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 235, 104239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, C.A.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Uttini, A.; Giannico, C.; Meloni, F. Nationwide Deformation Monitoring with SqueeSAR® Using Sentinel-1 Data. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 382, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L.; Mróz, M.; Balasis-Levinsen, J.; Casagli, N.; Frei, M.; Oyen, A.; Moldestad, D.A.; Bateson, L.; Guerrieri, L.; et al. The Evolution of Wide-Area DInSAR: From Regional and National Services to the European Ground Motion Service. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Colombo, D.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Rucci, A. InSAR Data for Monitoring Land Subsidence: Time to Think Big. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Ferretti, A.; Minati, F.; Falco, S.; Trillo, F.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Malvarosa, F.; Mammone, C.; Vecchioli, F.; et al. Analysis of Surface Deformations over the Whole Italian Territory by Interferometric Processing of ERS, Envisat and COSMO-SkyMed Radar Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 250–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Falco, S.; Malvarosa, F.; Minati, F. A New Method for Identification and Analysis of Persistent Scatterers in Series of SAR Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008-2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; Volume 2, pp. II-449–II-452. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A New Algorithm for Processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Shanker, A.P.; Pascale, S.; Serio, C.; Sdao, F. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Based on COSMO-SkyMed Imagery. In Proceedings of the 33rd EARSeL Symposium Towards Horizon 2020, Matera, Italy, 3–6 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Home-Geoportale MASE-Geoportale. Available online: https://gn.mase.gov.it/portale (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- What Is InSAR?|NGU. Available online: https://www.ngu.no/en/geologisk-kartlegging/what-insar (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Dehls, J.F.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Lauknes, T.R.; Stødle, D.; Moldestad, D.A. INSAR.No: A National Insar Deformation Mapping/Monitoring Service in Norway—From Concept to Operations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 5461–5464. [Google Scholar]
- Bodenbewegungsdienst Deutschland. Available online: https://bodenbewegungsdienst.bgr.de/mapapps/resources/apps/bbd/index.html?lang=en (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Kalia, A.C.; Frei, M.; Lege, T. A Copernicus Downstream-Service for the Nationwide Monitoring of Surface Displacements in Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, P.; van der Marel, H.; van Leijen, F.; Samiei-Esfahany, S.; Klees, R.; Hanssen, R. InSAR Datum Connection Using GNSS-Augmented Radar Transponders. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodemdalingskaart 2.0. Available online: https://bodemdalingskaart.portal.skygeo.com/portal/bodemdalingskaart/u2/viewers/basic/ (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Levinsen, J.F. Approaching Target: A Service for Nationwide Deformation Monitoring in Denmark Using Sentinel-1; DTU: Delhi, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L. Satellite Interferometry Data Interpretation and Exploitation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Ground Motion Service—Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/en/products/european-ground-motion-service (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Papoutsis, I.; Kontoes, C.; Alatza, S.; Apostolakis, A.; Loupasakis, C. InSAR Greece with Parallelized Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A National Ground Motion Service for Big Copernicus Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, Y. Nationwide Urban Ground Deformation Monitoring in Japan Using Sentinel-1 LiCSAR Products and LiCSBAS. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronczyk, L.; Zelenka-Hegyi, A.; Török, G.; Orbán, Z.; Defilippi, M.; Kovács, I.P.; Kovács, D.M.; Burai, P.; Pasquali, P. Nationwide, Operational Sentinel-1 Based InSAR Monitoring System in the Cloud for Strategic Water Facilities in Hungary. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martire, D.; Paci, M.; Confuorto, P.; Costabile, S.; Guastaferro, F.; Verta, A.; Calcaterra, D. A Nation-Wide System for Landslide Mapping and Risk Management in Italy: The Second Not-Ordinary Plan of Environmental Remote Sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 63, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Dollevoet, R.P.B.J.; Hanssen, R.F. Nationwide Railway Monitoring Using Satellite SAR Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, E.A.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Solano-Rojas, D.; Salazar-Tlaczani, L.; Gárcia-Venegas, J.; Marquez-Azúa, B.; Graham, S.; Villarnobo-Gonzalez, K.M. Country-Scale Assessment of Urban Areas, Population, and Households Exposed to Land Subsidence Using Sentinel-1 InSAR, and GPS Time Series. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 1577–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás, R.; Pagán, J.I.; Navarro, J.A.; Cano, M.; Pastor, J.L.; Riquelme, A.; Cuevas-González, M.; Crosetto, M.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; et al. Semi-Automatic Identification and Pre-Screening of Geological–Geotechnical Deformational Processes Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, D.; Bonano, M.; Casagli, N.; Confuorto, P.; De Luca, C.; Del Soldato, M.; Lanari, R.; Lu, P.; Manunta, M.; Manzo, M.; et al. Nation-Wide Mapping and Classification of Ground Deformation Phenomena through the Spatial Clustering of P-SBAS InSAR Measurements: Italy Case Study. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 189, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, E.; Dejana, M.; Bevilacqua, M. NOCTUA: Potenzialità Innovative per l’Osservazione Della Terra. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/NOCTUA%3A-potenzialit%C3%A0-innovative-per-l%27Osservazione-Giglio-Dejana/6ee3ededee4cfc4b3f5df8e52d2a996f8c5026e9 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Fissore, V.; Bovio, L.; Perotti, L.; Boccardo, P.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Towards a Digital Twin Prototype of Alpine Glaciers: Proposal for a Possible Theoretical Framework. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Eugeni, M.; Marzioli, P.; Pasquali, M.; Schiavon, E.; Nguyen Xuan, A.; Antonella, T.; Geraldini, S.; Piergentili, F.; Taramelli, A.; et al. A Model-Based Approach for the Preliminary Design of the SAR Upstream Element for the Italian IRIDE EO Constellation Based on Users’ Demand. CEAS Space J. 2024. Under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, E.; Taramelli, A.; Tornato, A.; Lee, C.M.; Luvall, J.C.; Schollaert Uz, S.; Townsend, P.A.; Cima, V.; Geraldini, S.; Nguyen Xuan, A.; et al. Maximizing Societal Benefit across Multiple Hyperspectral Earth Observation Missions: A User Needs Approach. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2023, 128, e2023JG007569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, E.; Sapio, S.; Schiavon, E.; Righini, M.; Monteleone, B.; Taramelli, A. Development of a Pre-Automatized Processing Chain for Agricultural Monitoring Using a Multi-Sensor and Multi-Temporal Approach. Land 2024, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, M.; Gatti, I.; Taramelli, A.; Arosio, M.; Valentini, E.; Sapio, S.; Schiavon, E. Integrated Flood Impact and Vulnerability Assessment Using a Multi-Sensor Earth Observation Mission with the Perspective of an Operational Service in Lombardy, Italy. Land 2024, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattivelli, V. The Governance of Peri-Urban Areas in Lombardy (IT): The Strengths and Weaknesses of the Regional Territorial Governance System: La Governance Delle Aree Periurbane in Lombardia (IT): I Punti Di Forza e Di Debolezza Del Sistema Di Governance Territoriale Regionale. Valori Valutazioni 2023, 33, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdikan, S.; Arıkan, M.; Sanli, F.B.; Cakir, Z. Monitoring of Coal Mining Subsidence in Peri-Urban Area of Zonguldak City (NW Turkey) with Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Using ALOS-PALSAR. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistiche Istat. Available online: http://dati.istat.it/Index.aspx (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Carcano, C.; Piccin, A.; Lombardia, R. (Eds.) Geologia degli acquiferi padani della Regione Lombardia: Relazione tecnica; S.EL.CA.: Firenze, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Home. Available online: https://www.geoportale.regione.lombardia.it/ (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Comune Di Turano Lodigiano. Available online: https://www.comune.turanolodigiano.lo.it/piano-gestione-territoriale.php (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Pagliara, P.; Basile, G.; Cara, P.; Corazza, A.; Duro, A.; Manfrè, B.; Onori, R.; Proietti, C.; Sansone, V. Integration of Earth Observation and Ground-Based HR Data in the Civil Protection Emergency Cycle: The Case of the DORIS Project. In Mathematics of Planet Earth; Pardo-Igúzquiza, E., Guardiola-Albert, C., Heredia, J., Moreno-Merino, L., Durán, J.J., Vargas-Guzmán, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Taramelli, A.; Di Matteo, L.; Ciavola, P.; Guadagnano, F.; Tolomei, C. Temporal Evolution of Patterns and Processes Related to Subsidence of the Coastal Area Surrounding the Bevano River Mouth (Northern Adriatic)—Italy. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2015, 108, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Pilla, G.; Meisina, C. Methodology for Detection and Interpretation of Ground Motion Areas with the A-DInSAR Time Series Analysis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldini, S.; Bruschi, A.; Bellotti, G.; Taramelli, A. User Needs Analysis for the Definition of Operational Coastal Services. Water 2021, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D.; Casagli, N. Semi-Automated Extraction of Deviation Indexes (DI) from Satellite Persistent Scatterers Time Series: Tests on Sedimentary Volcanism and Tectonically-Induced Motions. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2012, 19, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal Component Analysis: A Review and Recent Developments. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Bürgmann, R.; Shirzaei, M.; Fielding, E.J.; Baker, B. Predictability of Hydraulic Head Changes and Characterization of Aquifer-System and Fault Properties from InSAR-Derived Ground Deformation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 6572–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, D.; Novellino, A.; Hussain, E.; Bateson, L.; Casagli, N.; Confuorto, P.; Del Soldato, M.; Raspini, F. Unsupervised Detection of InSAR Time Series Patterns Based on PCA and K-Means Clustering. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Liang, C.; Wang, H. Coastal Subsidence Detection and Characterization Caused by Brine Mining over the Yellow River Delta Using Time Series InSAR and PCA. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigamonti, S.; Dattola, G.; Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B. A Multivariate Time Series Analysis of Ground Deformation Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-14091-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Strozzi, T. Natural versus Anthropogenic Subsidence of Venice. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taramelli, A.; Manzo, C.; Valentini, E.; Cornacchia, L. Coastal Subsidence: Causes, Mapping and Monitoring. In Natural Hazards; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 253–289. ISBN 978-1-138-05443-1. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional Land Subsidence Accompanying Groundwater Extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-García, G.; Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; López-Vinielles, J.; Rossi, M.; Mateos, R.M.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Lambert, J.; Teatini, P.; et al. Mapping the Global Threat of Land Subsidence. Science 2021, 371, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home|Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/home/en (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Running, S.; Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Moreno, A. MODIS/Terra Net Evapotranspiration Gap-Filled 8-Day L4 Global 500m SIN Grid V061; LP DAAC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Casa, R.; Rossi, M.; Sappa, G.; Trotta, A. Assessing Crop Water Demand by Remote Sensing and GIS for the Pontina Plain, Central Italy. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 1685–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payero, J.O.; Irmak, S. Daily Energy Fluxes, Evapotranspiration and Crop Coefficient of Soybean. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Climate Info Tool. Available online: https://aquastat.fao.org/climate-information-tool/ (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Meteo e Clima—ARPA Lombardia. Available online: https://www.arpalombardia.it/dati-e-indicatori/meteo-e-clima/ (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Istat.it—6° Censimento Agricoltura 2010. Available online: https://www.istat.it/it/censimenti-permanenti/censimenti-precedenti/agricoltura/agricoltura-2010 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Bozzano, F.; Esposito, C.; Mazzanti, P.; Patti, M.; Scancella, S. Imaging Multi-Age Construction Settlement Behaviour by Advanced SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bozzano, F.; Marra, F.; Wegmuller, U.; Cinti, F.R.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M. Subsidence Induced by Urbanisation in the City of Rome Detected by Advanced InSAR Technique and Geotechnical Investigations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, R.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, F.; Meng, X. Detection of Land Subsidence Associated with Land Creation and Rapid Urbanization in the Chinese Loess Plateau Using Time Series InSAR: A Case Study of Lanzhou New District. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Bosino, A.; Meisina, C.; Novellino, A.; Bateson, L.; McCormack, H. A Methodology to Detect and Characterize Uplift Phenomena in Urban Areas Using Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, M.; Fontana, A.; Tessari, G.; Mulè, M. Subsidence Zonation Through Satellite Interferometry in Coastal Plain Environments of NE Italy: A Possible Tool for Geological and Geomorphological Mapping in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Imagery—Overview. Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=10df2279f9684e4a9f6a7f08febac2a9#! (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Available online: https://italia.indettaglio.it/ita/lombardia/turanolodigiano.html (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Navarro-Hernández, M.I.; Valdes-Abellan, J.; Tomás, R.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Ezquerro, P.; Bru, G.; Bonì, R.; Meisina, C.; Herrera, G. ValInSAR: A Systematic Approach for the Validation of Differential SAR Interferometry in Land Subsidence Areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 3650–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Sunar, F.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E. Time Series Analysis of InSAR Data: Methods and Trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Qin, X.; Liao, M. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of a Reclamation Settlement in the Shanghai Coastal Area with Time Series Analyses of X-, C-, and L-Band SAR Datasets. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D. A Refinement of Inverse Distance Weighted Interpolation. Geo-Processing 1985, 2, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Hernández, M.I.; Valdes-Abellan, J.; Tomás, R.; Tessitore, S.; Ezquerro, P.; Herrera, G. Analysing the Impact of Land Subsidence on the Flooding Risk: Evaluation Through InSAR and Modelling. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 4363–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Becerril, J.A.; Garzón, G.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Martínez-Díaz, J.J. Towards an Increase of Flash Flood Geomorphic Effects Due to Gravel Mining and Ground Subsidence in Nogalte Stream (Murcia, SE Spain). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2273–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carisi, F.; Domeneghetti, A.; Gaeta, M.G.; Castellarin, A. Is Anthropogenic Land Subsidence a Possible Driver of Riverine Flood-Hazard Dynamics? A Case Study in Ravenna, Italy. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 2440–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoni, U.; Tessari, U.; Corbau, C.; Tosatto, O.; Polo, P.; Teatini, P. Impact of Land Subsidence due to Residual Gas Production on Surficial Infrastructures: The Dosso Degli Angeli Field Study (Ravenna, Northern Italy). Eng. Geol. 2017, 229, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Guo, H.; Ma, P.; Tang, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, W.; Gao, S.; Lin, H. Sustainable Development of World Cultural Heritage Sites in China Estimated from Optical and SAR Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 298, 113838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

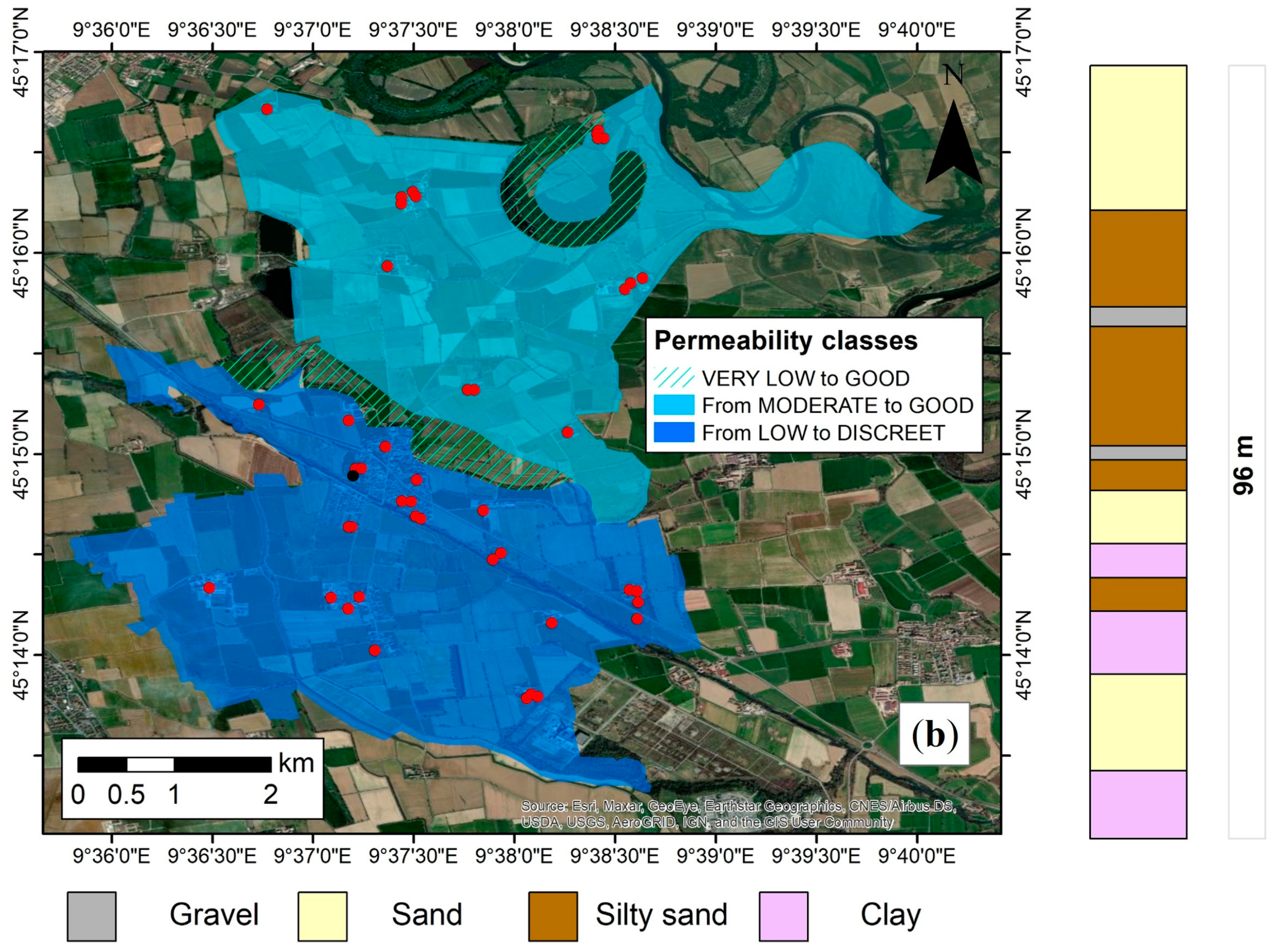


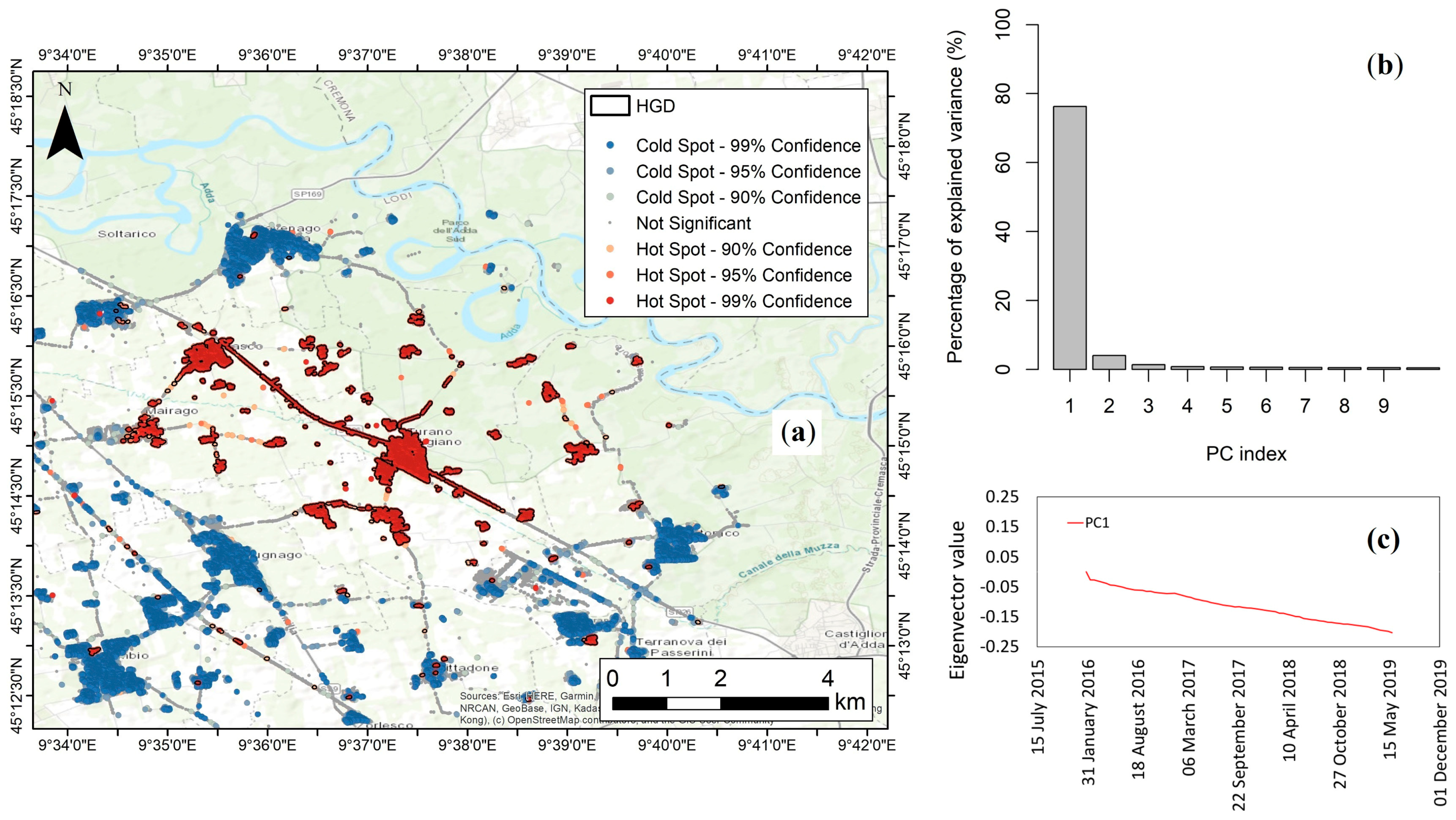
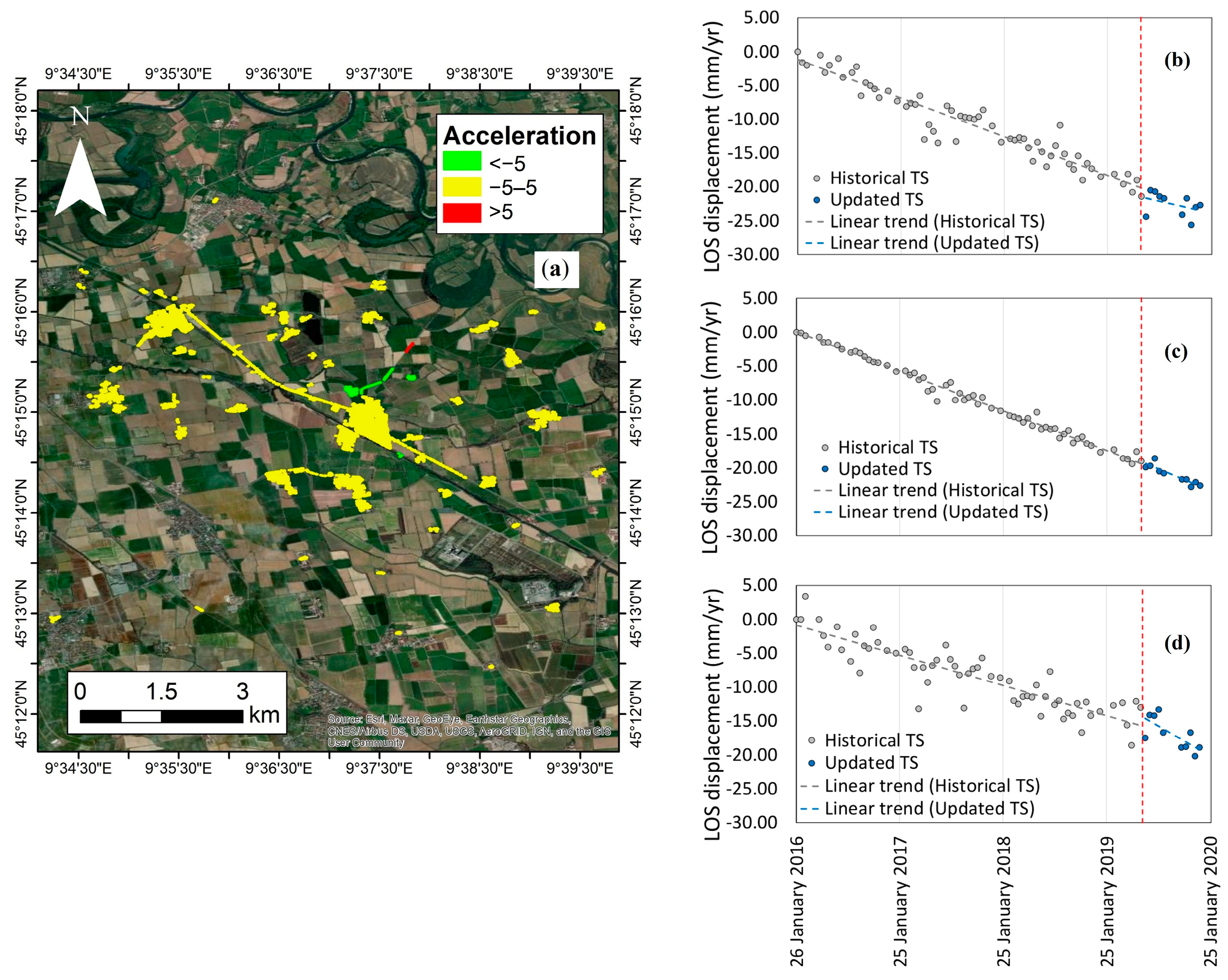
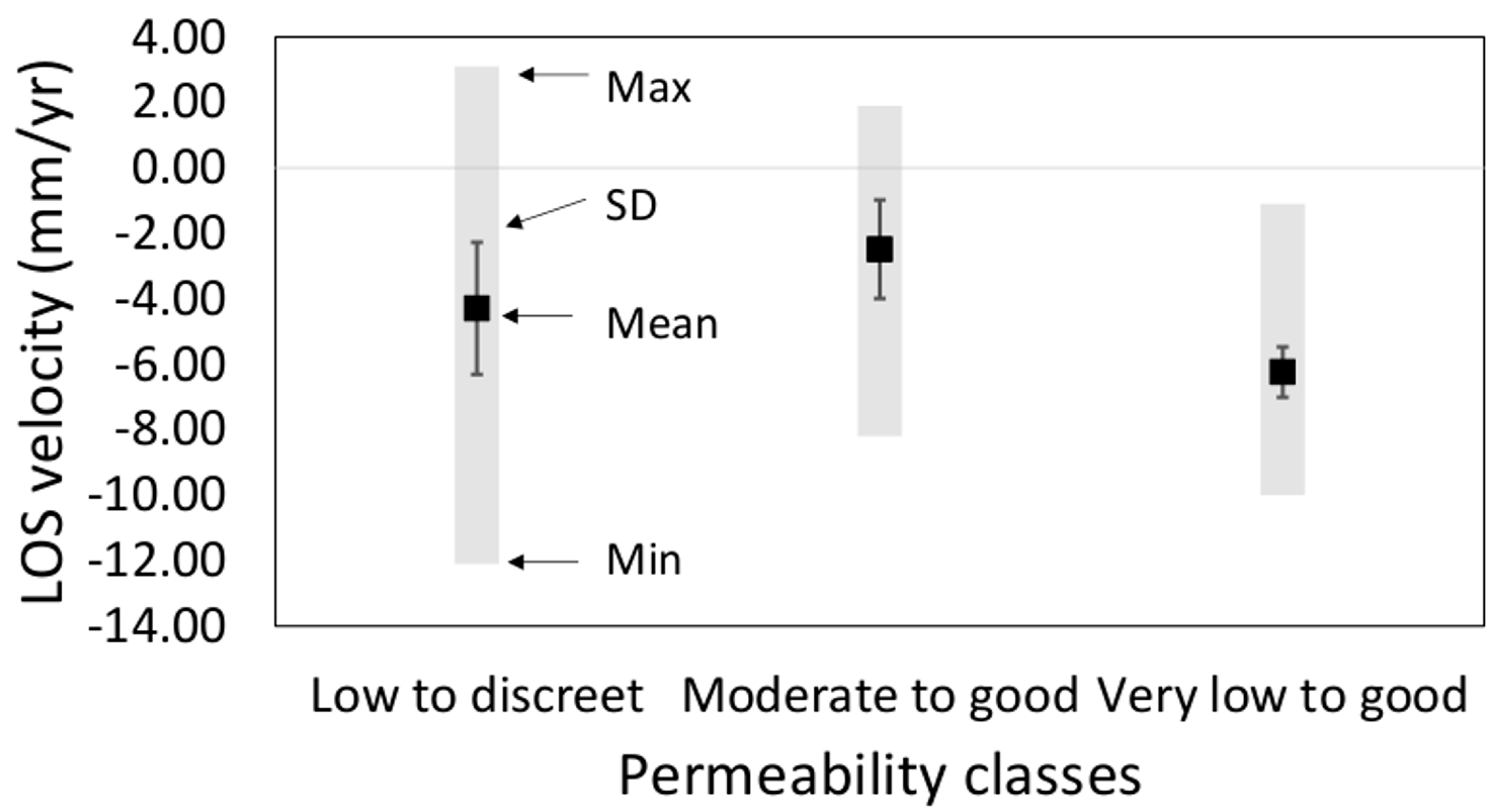




| Satellite | CSK |
| Wavelength | 3.12 cm |
| Acquisition geometry | Descending |
| Satellite track | 39 |
| Monitored period | 26 January 2016–20 December 2019 |
| Number of SAR images | 72 |
| Number of measurement points (MP) | 191,275 |
| Area | 229.2 sq km |
| MP density | 834.5 MP/sq km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Righini, M.; Bonì, R.; Sapio, S.; Gatti, I.; Salvadore, M.; Taramelli, A. Development of a Proof-of-Concept A-DInSAR-Based Monitoring Service for Land Subsidence. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111981
Righini M, Bonì R, Sapio S, Gatti I, Salvadore M, Taramelli A. Development of a Proof-of-Concept A-DInSAR-Based Monitoring Service for Land Subsidence. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(11):1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111981
Chicago/Turabian StyleRighini, Margherita, Roberta Bonì, Serena Sapio, Ignacio Gatti, Marco Salvadore, and Andrea Taramelli. 2024. "Development of a Proof-of-Concept A-DInSAR-Based Monitoring Service for Land Subsidence" Remote Sensing 16, no. 11: 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111981
APA StyleRighini, M., Bonì, R., Sapio, S., Gatti, I., Salvadore, M., & Taramelli, A. (2024). Development of a Proof-of-Concept A-DInSAR-Based Monitoring Service for Land Subsidence. Remote Sensing, 16(11), 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111981








